

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 22-33.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020271
收稿日期:2020-06-15
修回日期:2020-07-15
出版日期:2021-07-20
发布日期:2021-06-03
通讯作者:
王自奎
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: wzk@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Gulnazar Ali, Hai-ning TAO, Zi-kui WANG( ), Yu-ying SHEN
), Yu-ying SHEN
Received:2020-06-15
Revised:2020-07-15
Online:2021-07-20
Published:2021-06-03
Contact:
Zi-kui WANG
摘要:
黄土高原地区降水较少且季节性分配不均,苜蓿连续种植所导致的深层土壤干燥化问题已经引起普遍关注,苜蓿与粮食作物轮作是恢复苜蓿草地土壤水分、提高粮草种植系统可持续性的有效方式。但是长期轮作对土壤水分环境和水分利用效率的影响仍然缺乏研究,农业生产系统模拟模型(APSIM)具有广泛的适应性,可准确模拟耕作管理对作物系统资源利用的影响。首先根据黄土旱塬区庆阳、长武、镇原3个试验区试验数据验证APSIM模型模拟苜蓿长期连作和苜蓿-小麦轮作系统深层土壤水分和苜蓿产量的可行性,然后设置历时38年的81组轮作情景,评估不同轮作模式对农田深层土壤水分、系统干物质产量、氮素吸收和水分利用效率的影响。结果表明:APSIM模型模拟苜蓿产量的精度较高,模拟结果的决定系数(R2)为0.65,均方误差(RMSE)和平均绝对误差(MAE)分别为0.23 t·hm-2和0.17 t·hm-2,归一化均方误差(NRMSE)为29.2%;模型能够精确模拟长期苜蓿连作和苜蓿轮作小麦农田0~1000 cm的土壤含水量,长期连作模拟结果的R2为0.73,RMSE、MAE及NRMSE分别为0.021 t·hm-2、0.017 t·hm-2和11.7%,轮作系统模拟结果的决定系数为0.83,RMSE、MAE及NRMSE分别为0.024 t·hm-2、0.018 t·hm-2和11.8%。情景模拟结果表明,随着苜蓿在系统中轮作年限的增加,0~1000 cm土壤剖面水分极度缺乏(含水量在0.10~0.15)的区域以400~600 cm土层为起点不断扩大,当苜蓿轮作年限大于12年时,所有轮作周期的处理土壤都出现了大范围水分缺乏。81个情景中12年苜蓿轮作14年小麦(L12W14)、L12W16和L8W16这3个处理的总产量最大;系统吸氮量随着苜蓿加入年限的增加而增加,小麦轮作年限大于10年以后系统吸氮量急剧下降;苜蓿轮作大于8年以后系统水分利用效率随着苜蓿年限的增加而降低。综合考虑土壤水分环境和水分利用效率,建议研究区苜蓿-小麦轮作系统中苜蓿轮作年限为4~6年,小麦轮作年限大于4年。研究结果可为黄土旱塬区苜蓿草地管理及草田轮作实践提供一定的参考。
古丽娜扎尔·艾力null, 陶海宁, 王自奎, 沈禹颖. 基于APSIM模型的黄土旱塬区苜蓿——小麦轮作系统深层土壤水分及水分利用效率研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 22-33.
Gulnazar Ali, Hai-ning TAO, Zi-kui WANG, Yu-ying SHEN. Evaluating the deep-horizon soil water content and water use efficiency in the alfalfa-wheat rotation system on the dryland of Loess Plateau using APSIM[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(7): 22-33.
试验地点 Experiment site | 试验类型 Experiment design | 试验年限 Experiment period | 主要获取的数据Main extracted data | 水分测定深度Soil water depth (cm) | 数据用途 Data application in this study | 数据来源 Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
甘肃庆阳 Qingyang, Gansu | 玉米-小麦-大豆轮作及苜蓿连作Zea mays-T. aestivum-Glycine max rotation and M. sativa continuous | 2001-2010 | 产量,土壤水分Biomass, soil water | 0~200 | 验证产量及土壤水分Test biomass and soil water | 杨轩[ Yang[ |
甘肃庆阳 Qingyang, Gansu | 苜蓿-小麦轮作M. sativa-T. aestivum rotation | 1997-2003 | 土壤水分 Soil water | 0~300 | 验证短期轮作土壤水分Test soil water for short-term rotation | Shen et al.[ |
甘肃镇原 Zhenyuan, Gansu | 苜蓿连作M. sativa continuous | 2006-2007 | 产量,土壤水分 Biomass, soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期连作产量及土壤水分Test biomass and soil water for long-term rotation | 万素梅[ Wan[ |
甘肃镇原 Zhenyuan, Gansu | 苜蓿-作物轮作M. sativa-crops rotation | 2005,2008 | 土壤水分 Soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期轮作土壤水分Test soil water for long-term rotation | 方新宇[ Fang[ |
陕西长武 Changwu, Shaanxi | 苜蓿连作M. sativa continuous | 1985-2001 | 产量,土壤水分 Biomass, soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期连作产量和土壤水分Test biomass and soil water for long-term rotation | Li et al.[ |
陕西长武 Changwu, Shaanxi | 苜蓿连作M. sativa continuous | 2007-2012 | 土壤水分 Soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期连作土壤水分Test soil water for long-term rotation | Cheng et al.[ |
表1 黄土旱塬区苜蓿连作及苜蓿-作物轮作试验信息
Table 1 Information about the continuous alfalfa and alfalfa-wheat rotation experiment
试验地点 Experiment site | 试验类型 Experiment design | 试验年限 Experiment period | 主要获取的数据Main extracted data | 水分测定深度Soil water depth (cm) | 数据用途 Data application in this study | 数据来源 Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
甘肃庆阳 Qingyang, Gansu | 玉米-小麦-大豆轮作及苜蓿连作Zea mays-T. aestivum-Glycine max rotation and M. sativa continuous | 2001-2010 | 产量,土壤水分Biomass, soil water | 0~200 | 验证产量及土壤水分Test biomass and soil water | 杨轩[ Yang[ |
甘肃庆阳 Qingyang, Gansu | 苜蓿-小麦轮作M. sativa-T. aestivum rotation | 1997-2003 | 土壤水分 Soil water | 0~300 | 验证短期轮作土壤水分Test soil water for short-term rotation | Shen et al.[ |
甘肃镇原 Zhenyuan, Gansu | 苜蓿连作M. sativa continuous | 2006-2007 | 产量,土壤水分 Biomass, soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期连作产量及土壤水分Test biomass and soil water for long-term rotation | 万素梅[ Wan[ |
甘肃镇原 Zhenyuan, Gansu | 苜蓿-作物轮作M. sativa-crops rotation | 2005,2008 | 土壤水分 Soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期轮作土壤水分Test soil water for long-term rotation | 方新宇[ Fang[ |
陕西长武 Changwu, Shaanxi | 苜蓿连作M. sativa continuous | 1985-2001 | 产量,土壤水分 Biomass, soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期连作产量和土壤水分Test biomass and soil water for long-term rotation | Li et al.[ |
陕西长武 Changwu, Shaanxi | 苜蓿连作M. sativa continuous | 2007-2012 | 土壤水分 Soil water | 0~1000 | 验证长期连作土壤水分Test soil water for long-term rotation | Cheng et al.[ |
苜蓿生长年限 Phase of alfalfa in rotation (years) | 轮作小麦年限 Phase of wheat in rotation (year) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | |
| 2 | L2W2 | L2W4 | L2W6 | L2W8 | L2W10 | L2W12 | L2W14 | L2W16 | L2W18 |
| 4 | L4W2 | L4W4 | L4W6 | L4W8 | L4W10 | L4W12 | L4W14 | L4W16 | L4W18 |
| 6 | L6W2 | L6W4 | L6W6 | L6W8 | L6W10 | L6W12 | L6W14 | L6W16 | L6W18 |
| 8 | L8W2 | L8W4 | L8W6 | L8W8 | L8W10 | L8W12 | L8W14 | L8W16 | L8W18 |
| 10 | L10W2 | L10W4 | L10W6 | L10W8 | L10W10 | L10W12 | L10W14 | L10W16 | L10W18 |
| 12 | L12W2 | L12W4 | L12W6 | L12W8 | L12W10 | L12W12 | L12W14 | L12W16 | L12W18 |
| 14 | L14W2 | L14W4 | L14W6 | L14W8 | L14W10 | L14W12 | L14W14 | L14W16 | L14W18 |
| 16 | L16W2 | L16W4 | L16W6 | L16W8 | L16W10 | L16W12 | L16W14 | L16W16 | L16W18 |
| 18 | L18W2 | L18W4 | L18W6 | L18W8 | L18W10 | L18W12 | L18W14 | L18W16 | L18W18 |
表2 苜蓿-小麦轮作系统轮作周期情景设置
Table 2 Scenarios of rotation phases in the alfalfa and wheat rotation systems
苜蓿生长年限 Phase of alfalfa in rotation (years) | 轮作小麦年限 Phase of wheat in rotation (year) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | |
| 2 | L2W2 | L2W4 | L2W6 | L2W8 | L2W10 | L2W12 | L2W14 | L2W16 | L2W18 |
| 4 | L4W2 | L4W4 | L4W6 | L4W8 | L4W10 | L4W12 | L4W14 | L4W16 | L4W18 |
| 6 | L6W2 | L6W4 | L6W6 | L6W8 | L6W10 | L6W12 | L6W14 | L6W16 | L6W18 |
| 8 | L8W2 | L8W4 | L8W6 | L8W8 | L8W10 | L8W12 | L8W14 | L8W16 | L8W18 |
| 10 | L10W2 | L10W4 | L10W6 | L10W8 | L10W10 | L10W12 | L10W14 | L10W16 | L10W18 |
| 12 | L12W2 | L12W4 | L12W6 | L12W8 | L12W10 | L12W12 | L12W14 | L12W16 | L12W18 |
| 14 | L14W2 | L14W4 | L14W6 | L14W8 | L14W10 | L14W12 | L14W14 | L14W16 | L14W18 |
| 16 | L16W2 | L16W4 | L16W6 | L16W8 | L16W10 | L16W12 | L16W14 | L16W16 | L16W18 |
| 18 | L18W2 | L18W4 | L18W6 | L18W8 | L18W10 | L18W12 | L18W14 | L18W16 | L18W18 |

图3 黄土旱塬区连作苜蓿地0~1000 cm土壤水分的实测值和APSIM模型模拟值的比较a: 镇原3龄苜蓿 3-year-old alfalfa at Zhenyuan; b: 镇原4龄苜蓿 4-year-old alfalfa at zhenyuan; c: 镇原6龄苜蓿 6-year-old alfalfa at zhenyuan; d: 镇原8龄苜蓿 8-year-old alfalfa at Zhenyuan; e: 镇原12龄苜蓿 12-year-old alfalfa at Zhenyuan; f: 镇原18龄苜蓿 18-year-old alfalfa at Zhenyuan; g: 镇原26龄苜蓿 26-year-old alfalfa at Zhenyuan; h: 长武2龄苜蓿 2-year-old alfalfa at Changwu; i:长武3龄苜蓿 3-year-old alfalfa at Changwu; j: 长武4龄苜蓿 4-year-old alfalfa at Changwu; k: 长武5龄苜蓿 5-year-old alfalfa at Changwu; l: 长武6龄苜蓿 6-year-old alfalfa at Changwu; m: 长武7龄苜蓿 7-year-old alfalfa at Changwu; n: 长武12龄苜蓿 12-year-old alfalfa at Changwu; o: 长武16龄苜蓿 16-year-old alfalfa at Changwu.
Fig.3 Measured and simulated soil water content in the 0-1000 cm soil layer in alfalfa field on the dryland of Loess Plateau

图4 黄土旱塬区连作苜蓿地0~1000 cm土壤水分的实测值和APSIM模型模拟值的比较
Fig.4 Measured and simulated soil water content in the 0-1000 cm soil layer in alfalfa field on the dryland of Loess Plateau
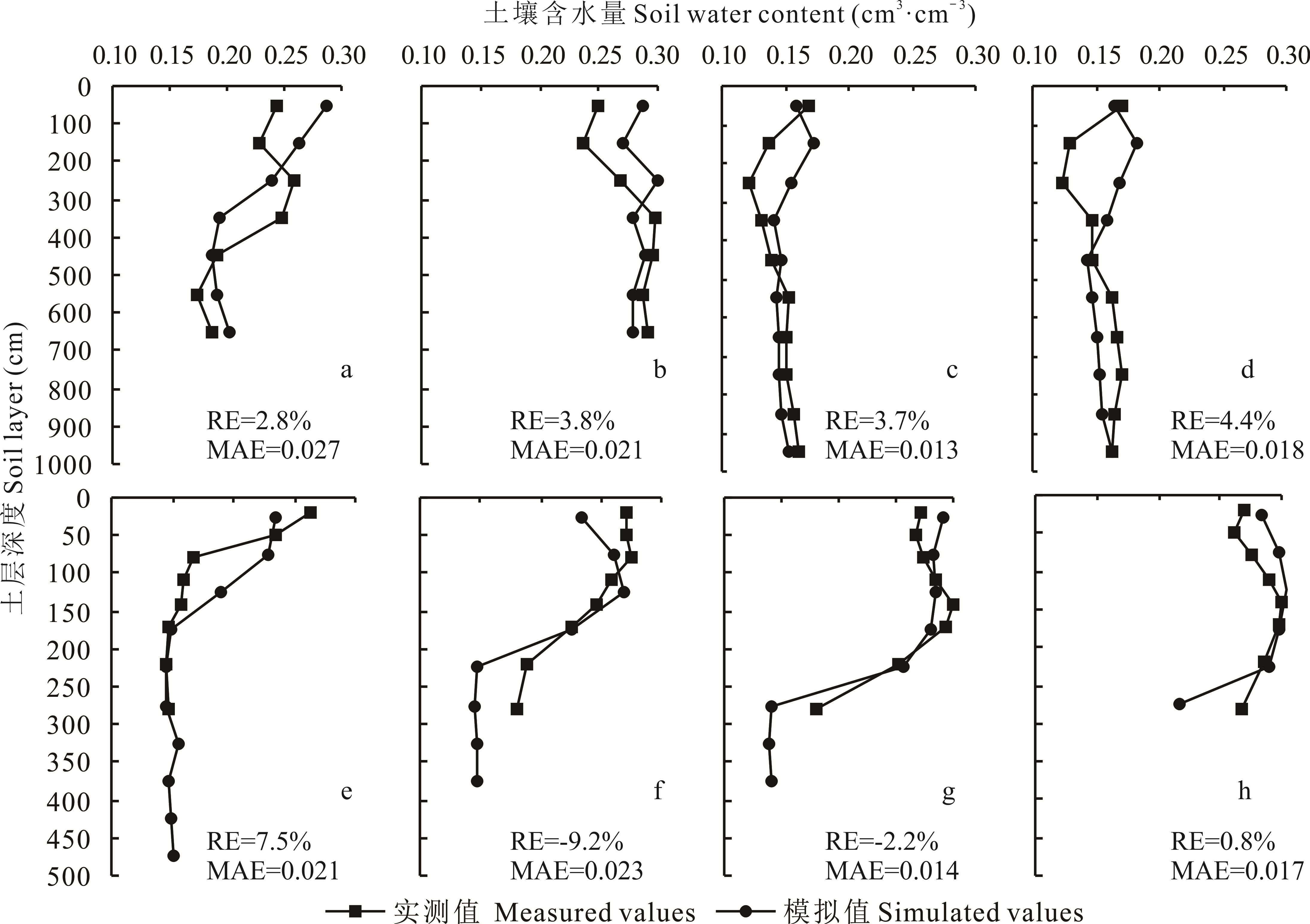
图5 黄土旱塬区苜蓿-作物轮作地0~1000 cm土壤水分的实测值和APSIM模型模拟值的比较a: 镇原8年苜蓿轮作3年作物8 years alfalfa rotated with 3 years annual crops at Zhenyuan; b: 镇原12年苜蓿轮作15年作物12 years alfalfa rotated with 15 years annual crops at Zhenyuan; c: 镇原13年苜蓿轮作4年作物13 years alfalfa rotated with 4 years annual crops at Zhenyuan; d: 镇原11年苜蓿轮作10年作物11 years alfalfa rotated with 10 years annual crops at Zhenyuan; e: 庆阳5年苜蓿轮作1年小麦5 years alfalfa rotated with 1 year wheat at Qingyang; f: 庆阳5年苜蓿后休闲1年5 years alfalfa with 1 year of fallow at Qingyang; g: 庆阳5年苜蓿轮作2年小麦5 years alfalfa rotated with 2 years of wheat at Qingyang; h: 庆阳5年苜蓿后休闲2年5 years alfalfa with 2 years of fallow at Qingyang.
Fig.5 Measured and simulated soil water content in the 0-1000 cm soil layer in alfalfa and grain crops rotation field on the dryland of Loess Plateau
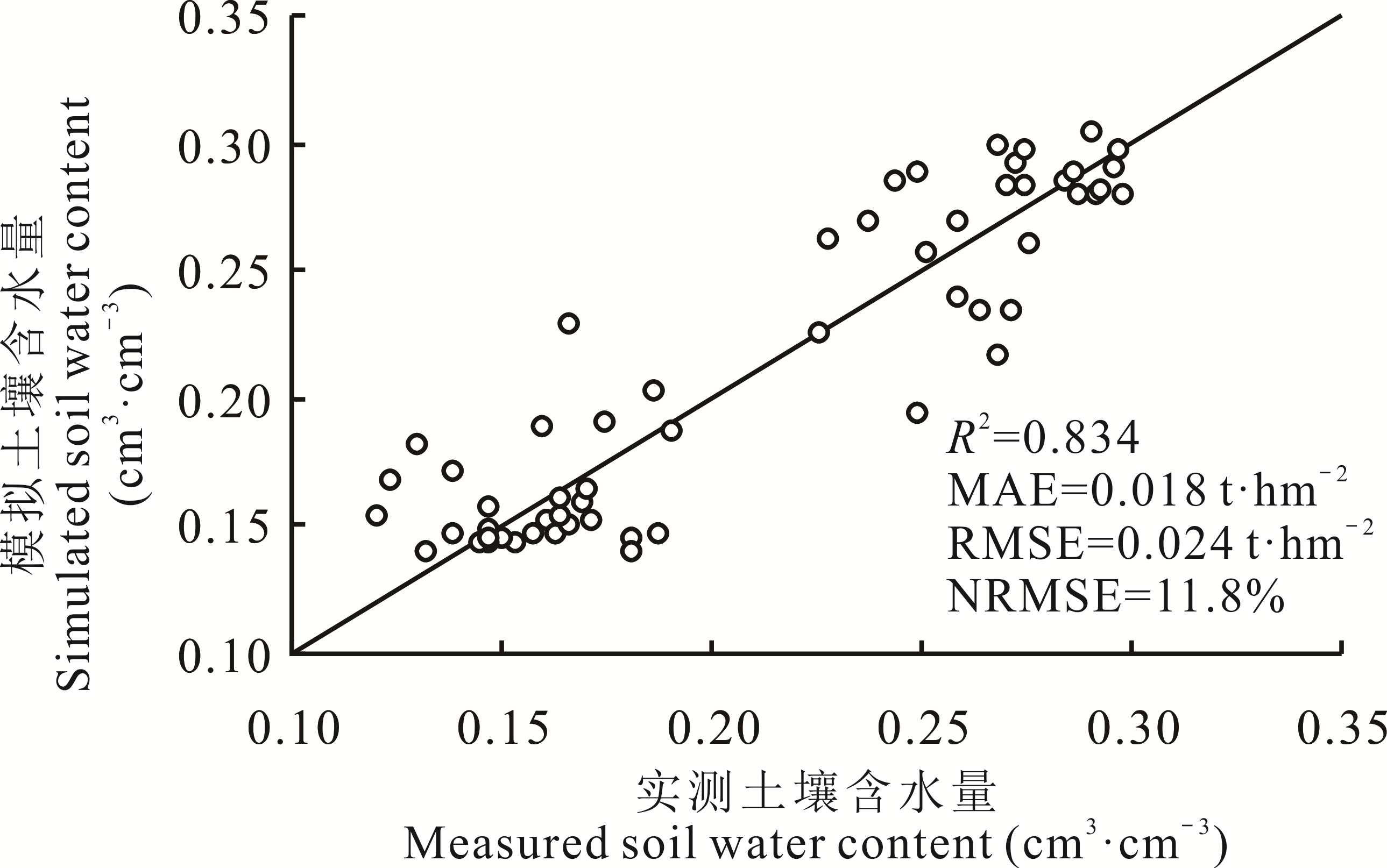
图6 黄土旱塬区苜蓿-小麦轮作地0~1000 mm土壤水分的实测值和APSIM模型模拟值的比较
Fig.6 Measured and simulated soil water content in the 0-1000 mm soil layer in alfalfa and grain crops rotation on the dryland of Loess Plateau
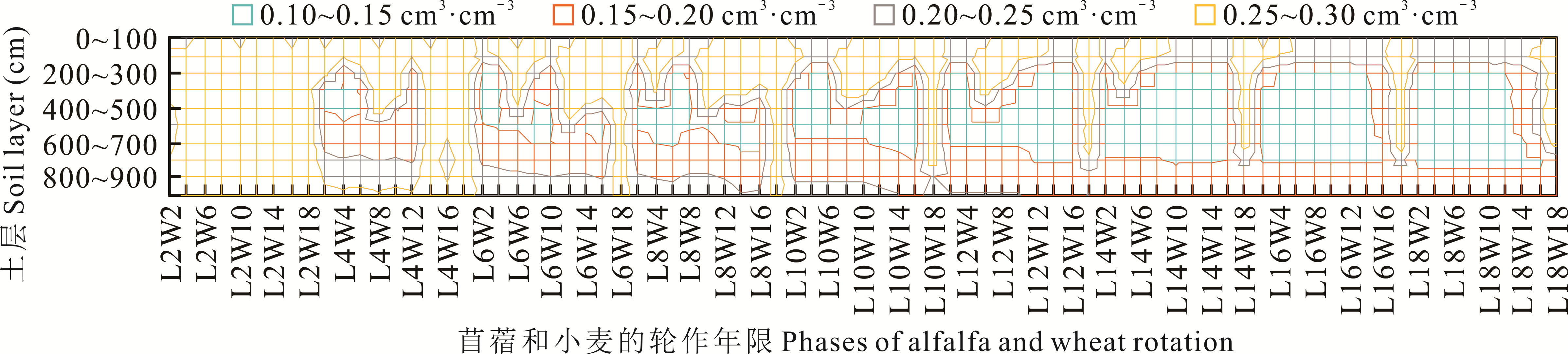
图7 黄土旱塬区不同苜蓿-小麦轮作周期下轮作38年后0~1000 cm剖面土壤水分的分布
Fig.7 Soil water content distribution in the 0-1000 cm soil layer in alfalfa-wheat rotation field with different rotation patterns on the dryland of Loess Plateau
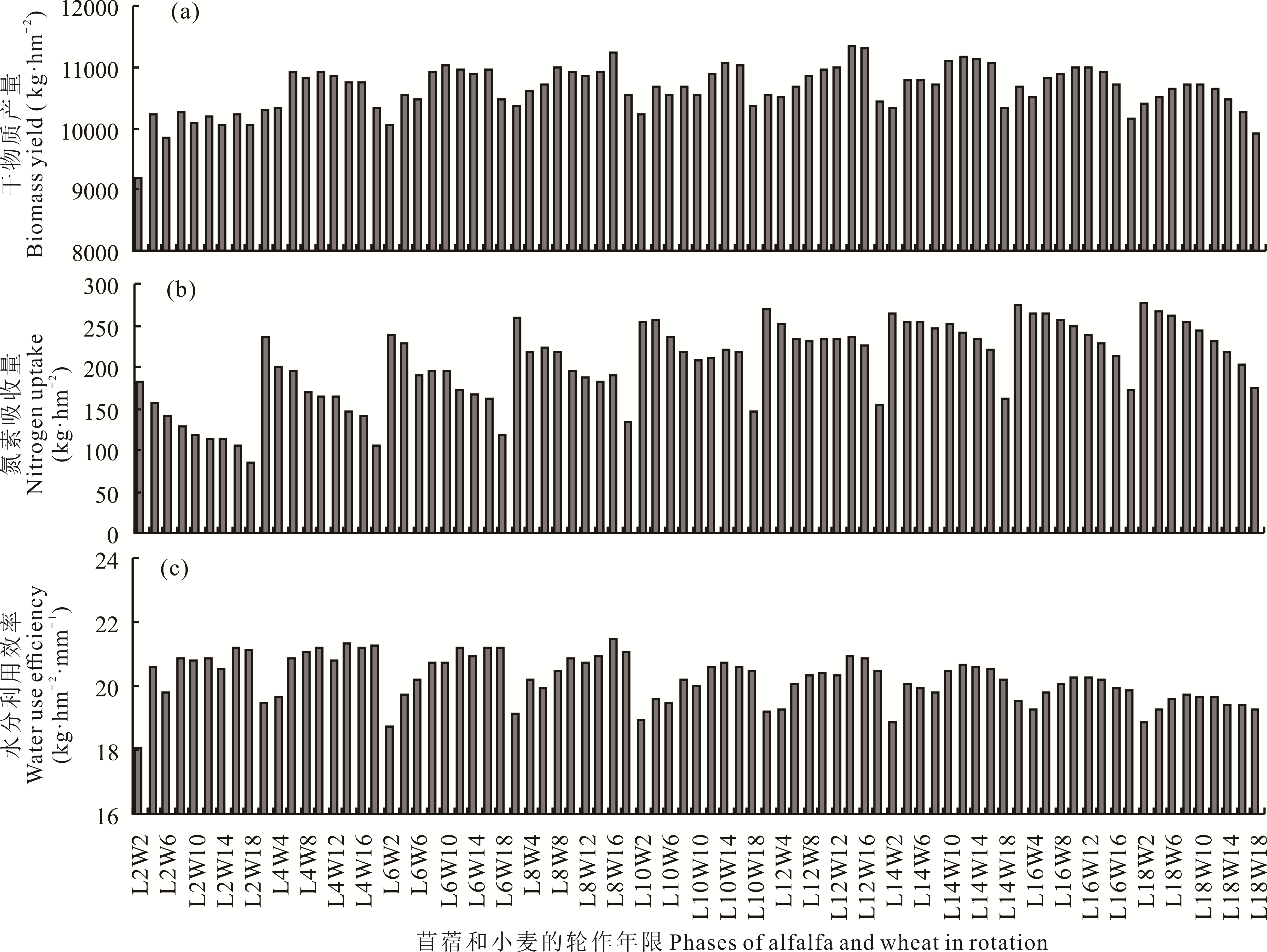
图8 黄土旱塬区不同苜蓿-小麦轮作周期处理38年平均干物质产量、氮素吸收量及水分利用效率
Fig.8 Biomass yield, nitrogen uptake and soil water content in alfalfa-wheat rotation field with different rotation patterns on the dryland of Loess Plateau
| 1 | Yang X, Li Z, Cui S, et al. Cropping system productivity and evapotranspiration in the semiarid Loess Plateau of China under future temperature and precipitation changes: An APSIM-based analysis of rotational vs. continuous systems. Agricultural Water Management, 2020, 229: 105959. |
| 2 | Fang X Y. Simulation of alfalfa-grain crop potation effects semi-humid areas of the loess plateau. Yangling: North West Agriculture and Forestry University, 2010. |
| 方新宇. 黄土高原半湿润区苜蓿—粮食作物轮作效应模拟研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2010. | |
| 3 | Jiang X J, Liu S, Zhang H. Effects of different management practices on vertical soil water flow patterns in the Loess Plateau. Soil and Tillage Research, 2017, 166: 33-42. |
| 4 | Wan S M. Study on alfalfa production performance and ifs ecological effects soil environment in the loess plateau. Yangling: North West Agriculture and Forestry University, 2008. |
| 万素梅. 黄土高原地区不同生长年限苜蓿生产性能及对土壤环境效应研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2008. | |
| 5 | Luo Z Z, Niu Y N, Li L L, et al. Response of soil physical properties to alfalfa growth years in the Western Loess Plateau. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(11): 1500-1507. |
| 罗珠珠, 牛伊宁, 李玲玲, 等. 黄土高原丘陵沟壑区土壤物理性质对苜蓿种植年限的响应. 中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(11): 1500-1507. | |
| 6 | Chen K. Dry soil layer formation and soil water recharging of alfalfa field on the Loess Plateau of Central Gansu. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2013. |
| 陈凯. 陇中黄土高原紫花苜蓿地土壤干层形成及其恢复效应研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2013. | |
| 7 | Wang M Y, Li J, Sun J, et al. Soil desiccation characteristics of alfalfa grasslands and soil water restoration effects in alfalfa-grain crop rotations on the semi-arid areas of the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(8): 4526-4534. |
| 王美艳, 李军, 孙剑, 等. 黄土高原半干旱区苜蓿草地土壤干燥化特征与粮草轮作土壤水分恢复效应. 生态学报, 2009, 29(8): 4526-4534. | |
| 8 | Li Y S. Productivity dynamic of alfalfa and its effects on water eco-environment. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2002(3): 404-411. |
| 李玉山. 苜蓿生产力动态及其水分生态环境效应. 土壤学报, 2002(3): 404-411. | |
| 9 | Shan L, Liu Z M, Xin Y Q, et al. A study on the grass and field crops potation in mountain region of southern Ningxia. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 1992(4): 60-68. |
| 山仑, 刘忠民, 辛业全, 等. 宁夏山区草田轮作研究——不同轮作方式的生产力及效益. 水土保持学报, 1992(4): 60-68. | |
| 10 | Wang X C, Li J, Fang X Y, et al. Restoration of soil water in alfalfa-grain crop rotation fields on semi-arid region. Transactions of the CSAE, 2011, 27(1): 81-88. |
| 王学春, 李军, 方新宇, 等. 半干旱区草粮轮作田土壤水分恢复效应.农业工程学报, 2011, 27(1): 81-88. | |
| 11 | Shen Y Y, Nan Z B, Gao C Y, et al. Spatial and temporal characteristics of soil water dynamics and crop yield response from a 4-year of lucerne and winter wheat rotation system in the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004(3): 640-647. |
| 沈禹颖, 南志标, 高崇岳, 等. 黄土高原苜蓿-冬小麦轮作系统土壤水分时空动态及产量响应. 生态学报, 2004(3): 640-647. | |
| 12 | Luo Y, Guo W. Development and problems of crop models. Transactions of the CSAE, 2008, 24(5): 307-312. |
| 13 | Shen Y Y, Nan Z B, Bill B, et al. Development of APSIM (agricultural production systems simulator) and its application. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(8): 1027-1032. |
| 沈禹颖, 南志标, Bill Bellotti, 等. APSIM 模型的发展与应用. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(8): 1027-1032. | |
| 14 | Yang X, Wang Z K, Cao Q, et al. Effects of precipitation and air temperature changes on yield of winter wheat, maize and lucerne in Eastern Gansu of China. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(9): 106-114. |
| 杨轩, 王自奎, 曹铨, 等. 陇东地区几种旱作作物产量对降水与气温变化的响应. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(9): 106-114. | |
| 15 | Yang X. Effects of climate change on yield, water use and soil nutrients of the crop production systems on the Loess Plateau. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019. |
| 杨轩. 气候变化对黄土高原作物生产系统产量、水分利用及土壤养分的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. | |
| 16 | Shen Y Y, Li L L, Chen W, et al. Soil water, soil nitrogen and productivity of lucerne-wheat sequences on deep silt loams in a summer dominant rainfall environment. Field Crops Research, 2009, 111: 97-108. |
| 17 | Li Y S, Huang M B. Pasture yield and soil water depletion of continuous growing alfalfa in the Loess Plateau of China. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2008, 124: 24-32. |
| 18 | Cheng L P, Liu W Z. Long term effects of farming system on soil water content and dry soil layer in deep loess profile of loess tableland in China. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2014, 13(6): 1382-1392. |
| 19 | Shen Y Y. Soil and crop composition dynamics of alfalfa-wheat rotation system on the Loess Plateau. Guangzhou: Sun Yat-sen University, 2004. |
| 沈禹颖. 黄土高原苜蓿-小麦轮作系统土壤与作物的组分动态. 广州: 中山大学, 2004. | |
| 20 | Chen W, Shen Y Y, Robertson M J, et al. Simulation analysis of Lucerne-wheat crop rotation on the Loess Plateau of Northern China. Field Crops Research, 2008, 108: 179-187. |
| 21 | Keating B A, Carberry P S, Hammer G L, et al. An overview of APSIM, a model designed for farming systems simulation. European Journal of Agronomy, 2003, 18(3): 267-288. |
| 22 | Wang L. Study on crop potential productivity and optimal irrigation technique in the north China plain by agricultural production system simulator. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 2007. |
| 王琳. APSIM模型应用于华北平原作物生产潜力和节水优化模式. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2007. | |
| 23 | Dai T, Wang J, He D, et al. Adaptability of APSIM model in Southwestern China: A case study of winter wheat in Chongqing City.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(4): 1237-1243. |
| 戴彤, 王靖, 赫迪, 等. APSIM模型在西南地区的适应性评价——以重庆冬小麦为例. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(4): 1237-1243. | |
| 24 | Yang X. Analysis of the production potential of winter wheat, maize and lucerne based on the APSIM model. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2013. |
| 杨轩. 基于APSIM模型的冬小麦、玉米和紫花苜蓿的生产潜力分析. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2013. | |
| 25 | Liu P S, Li J, Jia Z K, et al. Effect of different alfalfa-rotation patterns on soil nutrient dynamic. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 32(3): 81-85. |
| 刘沛松, 李军, 贾志宽, 等. 不同草田轮作模式对土壤养分动态的影响. 水土保持通报, 2012, 32(3): 81-85. | |
| 26 | Mao G L, Hu D Y, Xu X, et al. Effects of alfalfa post-harvest rotation on water use efficiency and crop yield in arid andy area. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 29(3): 219-224. |
| 毛桂莲, 虎德钰, 许兴, 等. 干旱风沙区苜蓿后茬不同轮作方式对水分利用效率和产量的影响. 水土保持学报, 2015, 29(3): 219-224. | |
| 27 | Fan J, Hao M D, Shao M A. Water consumption of deep soil layers and eco-environmental effects of agricultural ecosystem in the Loess Plateau. Transactions of the CSAE, 2004(1): 61-64. |
| 樊军, 郝明德, 邵明安. 黄土旱塬农业生态系统土壤深层水分消耗与水分生态环境效应. 农业工程学报, 2004(1): 61-64. | |
| 28 | Cheng J M, Wan H E, Wang J. Alfalfa growth and its relation with soil water status in loess hilly and gully region. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2005(3): 435-438. |
| 程积民, 万惠娥, 王静. 黄土丘陵区紫花苜蓿生长与土壤水分变化. 应用生态学报, 2005(3): 435-438. |
| [1] | 周倩倩, 张亚见, 张静, 殷涂童, 盛下放, 何琳燕. 产硫化氢细菌的筛选及阻控苜蓿吸收铅和改良土壤的作用[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 44-52. |
| [2] | 臧真凤, 白婕, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿形态和生理指标响应干旱胁迫的品种特异性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 73-81. |
| [3] | 谢展, 穆麟, 张志飞, 陈桂华, 刘洋, 高帅, 魏仲珊. 乳酸菌或有机酸盐与尿素复配添加对紫花苜蓿混合青贮的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 165-173. |
| [4] | 王吉祥, 宫焕宇, 屠祥建, 郭侲洐, 赵嘉楠, 沈健, 栗振义, 孙娟. 耐亚磷酸盐紫花苜蓿品种筛选及评价指标的鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 186-199. |
| [5] | 张小芳, 魏小红, 刘放, 朱雪妹. PEG胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗内源激素对NO的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 160-169. |
| [6] | 候怡谣, 李霄, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅, 郭长虹. 过量表达紫花苜蓿MsHB7基因对拟南芥耐旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 170-179. |
| [7] | 马欣, 罗珠珠, 张耀全, 刘家鹤, 牛伊宁, 蔡立群. 黄土高原雨养区不同种植年限紫花苜蓿土壤细菌群落特征与生态功能预测[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 54-67. |
| [8] | 沙栢平, 谢应忠, 高雪芹, 蔡伟, 伏兵哲. 地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿草产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 102-114. |
| [9] | 李振松, 万里强, 李硕, 李向林. 苜蓿根系构型及生理特性对干旱复水的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 189-196. |
| [10] | 吴勇, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 童长春. 河西荒漠灌区紫花苜蓿施肥效应及其基于数据包络分析法的经济效益研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 94-105. |
| [11] | 邢易梅, 蕫理, 战力峰, 才华, 杨圣秋, 孙娜. 混合接种摩西球囊霉和根瘤菌对紫花苜蓿耐碱能力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 136-145. |
| [12] | 覃凤飞, 李志华, 刘信宝, 渠晖, 平措卓玛, 洛松群措, 苏梦涵. 外源2,4表油菜素内酯对越夏期高温与弱光胁迫下紫花苜蓿生长和光合性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 146-160. |
| [13] | 童长春, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 于铁峰. 基于平衡施肥的紫花苜蓿光合特性及光合因子的产量效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 70-80. |
| [14] | 才璐, 王林林, 罗珠珠, 李玲玲, 牛伊宁, 蔡立群, 谢军红. 中国苜蓿产量及水分利用效率对种植年限响应的Meta分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 27-38. |
| [15] | 何国兴, 宋建超, 温雅洁, 刘彩婷, 祁娟. 不同根瘤菌肥对紫花苜蓿生产力及土壤肥力的综合影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 109-120. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||