

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 44-52.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020265
周倩倩( ), 张亚见, 张静, 殷涂童, 盛下放, 何琳燕(
), 张亚见, 张静, 殷涂童, 盛下放, 何琳燕( )
)
收稿日期:2020-06-08
修回日期:2020-07-06
出版日期:2021-07-20
发布日期:2021-06-03
通讯作者:
何琳燕
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: helyan0794@njau.edu.cn基金资助:
Qian-qian ZHOU( ), Ya-jian ZHANG, Jing ZHANG, Tu-tong YIN, Xia-fang SHENG, Lin-yan HE(
), Ya-jian ZHANG, Jing ZHANG, Tu-tong YIN, Xia-fang SHENG, Lin-yan HE( )
)
Received:2020-06-08
Revised:2020-07-06
Online:2021-07-20
Published:2021-06-03
Contact:
Lin-yan HE
摘要:
为了探究产硫化氢细菌阻控牧草吸收重金属、修复重金属污染土壤的作用,从生长在矿区污染地的苜蓿中分离纯化产硫化氢细菌,根据菌株生理特性、产硫化氢能力、铅镉抗性以及吸附铅能力筛选高效菌株,然后以某农田受污染土壤为供试土壤,采用田间小区试验,研究高效菌株对紫花苜蓿生长及阻控苜蓿吸收Pb的效果与机制。结果表明,从生长在矿区污染地的苜蓿中分离筛选到一株高产硫化氢细菌Sar15,其具有合成吲哚乙酸(IAA)、铁载体和脲酶的特性,在溶液条件下能显著降低Pb2+的浓度(60%)。经16S rDNA分析将菌株Sar15归属于彭氏变形菌。菌株Sar15能够在紫花苜蓿根部定殖。与不接菌对照相比,菌株Sar15能显著增加受污染农田中生长的苜蓿地上部和根部干重、显著降低其Pb含量。菌株Sar15使得苜蓿地上部和根部Pb含量分别降低43%和45%。并且该菌株能够提高紫花苜蓿根际土壤pH和酶活性,降低根际土壤有效态Pb含量,减轻Pb对紫花苜蓿的毒害。Sar15处理具有修复中度Pb污染土壤、保障牧草安全生产的潜力。
周倩倩, 张亚见, 张静, 殷涂童, 盛下放, 何琳燕. 产硫化氢细菌的筛选及阻控苜蓿吸收铅和改良土壤的作用[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 44-52.
Qian-qian ZHOU, Ya-jian ZHANG, Jing ZHANG, Tu-tong YIN, Xia-fang SHENG, Lin-yan HE. Isolation of a beneficial hydrogen sulfide-producing bacterial strain that reduces lead uptake by Medicago sativa and aids remediation of Pb-contaminated soil[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(7): 44-52.

图2 菌株对溶液中铅浓度的影响*表示与CK相比,在0.05水平有显著差异(P<0.05),**表示与CK相比,在0.01水平有极显著差异(P<0.01),***表示与CK相比,在0.001水平有极显著差异(P<0.001)。下同。* indicates that there is a significant difference at the 0.05 level (P<0.05) compared to CK, ** indicates that there is a very significant difference at the 0.01 level (P<0.01), *** indicates a very significant difference at 0.001 level compared to CK (P<0.001). The same below.
Fig.2 Effect of strains on the concentration of Pb in solution
| 菌株Strains | 吲哚乙酸IAA (mg·L-1) | 铁载体Siderophore | 脲酶Urease | Pb耐性Pb tolerance (mg·L-1) | Cd耐性Cd tolerance (mg·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mr2 | 65.9 | ++ | - | 300 | 20 |
| Mr3 | 4.1 | +++++ | + | 500 | 20 |
| Mr11 | 23.8 | +++ | - | 500 | 10 |
| Mr40 | 38.7 | +++++ | + | 400 | 30 |
| Sar15 | 15.8 | ++ | + | 800 | 50 |
表1 菌株的生理特性
Table 1 Physiological characteristics of the isolated strains
| 菌株Strains | 吲哚乙酸IAA (mg·L-1) | 铁载体Siderophore | 脲酶Urease | Pb耐性Pb tolerance (mg·L-1) | Cd耐性Cd tolerance (mg·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mr2 | 65.9 | ++ | - | 300 | 20 |
| Mr3 | 4.1 | +++++ | + | 500 | 20 |
| Mr11 | 23.8 | +++ | - | 500 | 10 |
| Mr40 | 38.7 | +++++ | + | 400 | 30 |
| Sar15 | 15.8 | ++ | + | 800 | 50 |
处理 Treatments | 干重 Dry weight (g·5 plant-1) | Pb含量 Pb content (mg·kg-1) | Pb 总量 Total Pb content (μg) | 转移系数 Translocation factor | 根富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部Shoot | 根部Root | 地上部Shoot | 根部Root | 地上部Shoot | 根部Root | |||
| 对照Control | 1.2±0.10 | 0.4±0.05 | 8.7±0.70 | 13.0±0.10 | 10.7±0.20 | 5.2±0.90 | 0.66 | 0.033 |
| 活菌Sar15 Live Sar15 | 1.5±0.03* | 0.5±0.08** | 4.9±0.02*** | 7.2±0.10*** | 7.3±0.30*** | 3.6±0.30*** | 0.68 | 0.018*** |
| 灭活菌Sar15 Inactivation Sar15 | 1.3±0.03 | 0.4±0.03 | 8.4±0.80 | 12.0±0.30 | 10.5±0.90 | 5.3±0.50 | 0.70 | 0.032 |
表2 Sar15对紫花苜蓿干重、Pb含量、总量、转移系数和富集系数的影响
Table 2 Effects of strain Sar15 on the dry weight, Pb content, total content, translocation factor and bioconcentration factor of M. sativa
处理 Treatments | 干重 Dry weight (g·5 plant-1) | Pb含量 Pb content (mg·kg-1) | Pb 总量 Total Pb content (μg) | 转移系数 Translocation factor | 根富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部Shoot | 根部Root | 地上部Shoot | 根部Root | 地上部Shoot | 根部Root | |||
| 对照Control | 1.2±0.10 | 0.4±0.05 | 8.7±0.70 | 13.0±0.10 | 10.7±0.20 | 5.2±0.90 | 0.66 | 0.033 |
| 活菌Sar15 Live Sar15 | 1.5±0.03* | 0.5±0.08** | 4.9±0.02*** | 7.2±0.10*** | 7.3±0.30*** | 3.6±0.30*** | 0.68 | 0.018*** |
| 灭活菌Sar15 Inactivation Sar15 | 1.3±0.03 | 0.4±0.03 | 8.4±0.80 | 12.0±0.30 | 10.5±0.90 | 5.3±0.50 | 0.70 | 0.032 |
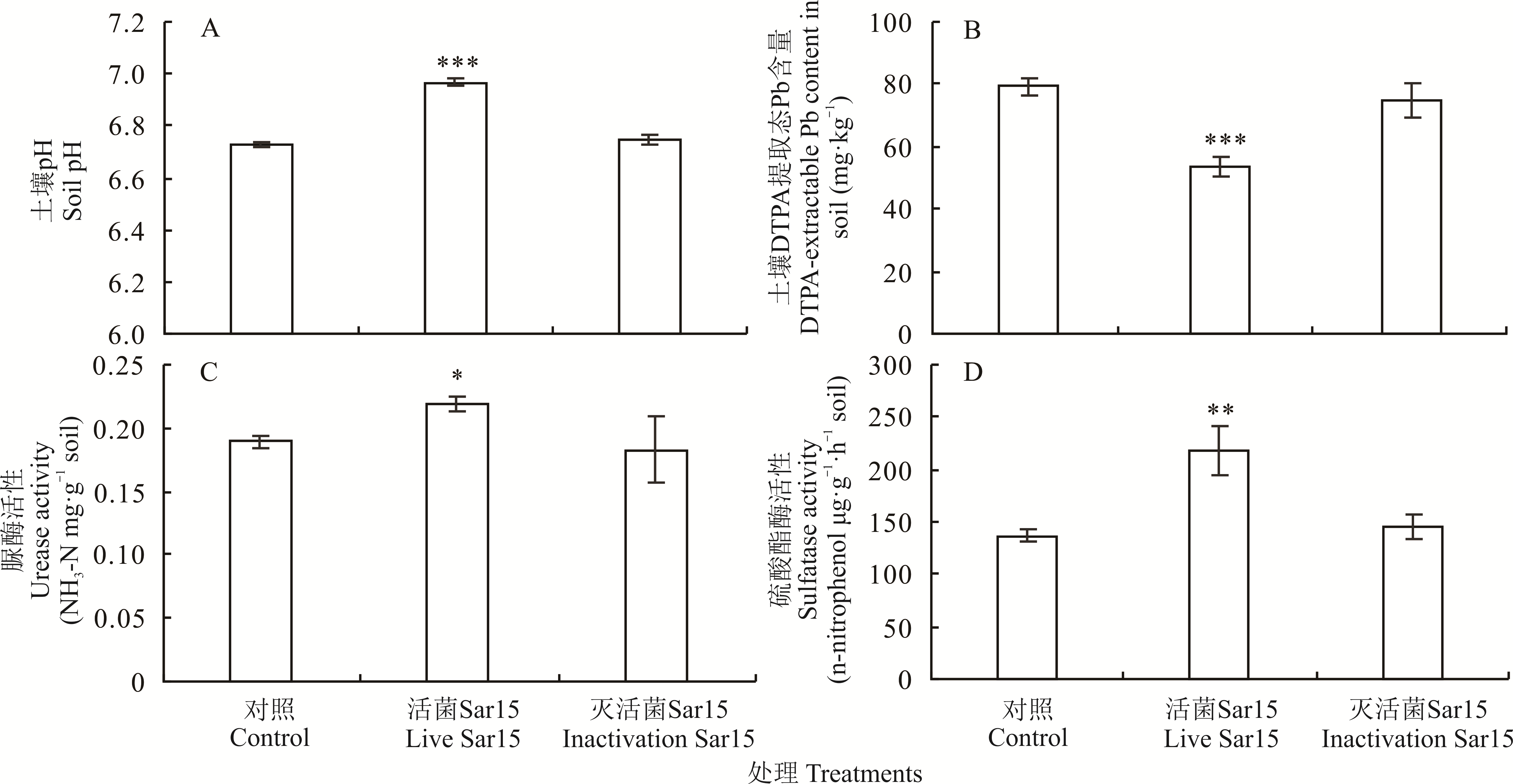
图3 菌株Sar15对苜蓿根际土壤pH、DTPA提取态铅含量、脲酶和硫酸酯酶活性的影响
Fig.3 Effects of strain Sar15 on pH, DTPA-extractable Pb content, urease and sulfatase activity in rhizosphere soil of M. sativa
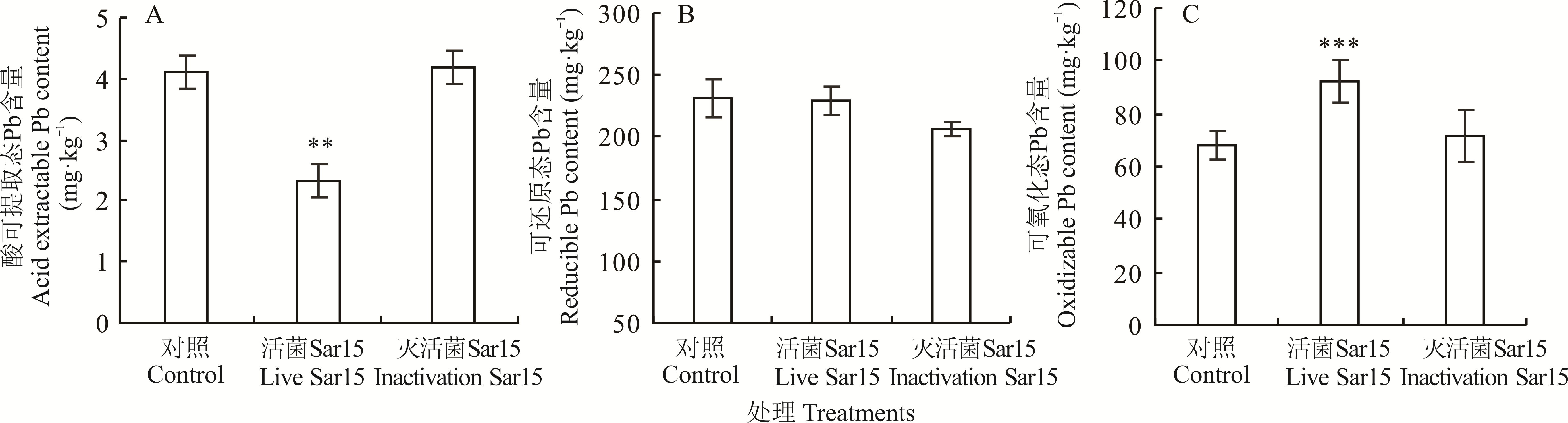
图4 菌株Sar15对苜蓿根际土壤酸可提取态Pb、可还原态Pb和可氧化态Pb含量的影响
Fig.4 Effects of strain Sar15 on the content of acid extractable Pb, reducible Pb and oxidizable Pb in M. sativa rhizosphere soil
| 1 | He G X, Song J C, Wen Y J, et al. Effects of different rhizobium fertilizers on alfalfa productivity and soil fertility. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(5): 109-120. |
| 何国兴, 宋建超, 温雅洁, 等. 不同根瘤菌肥对紫花苜蓿生产力及土壤肥力的综合影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 109-120. | |
| 2 | Zhang H, Kou J T, Shi S L. Physiological and biochemical responses of Medicago sativa seed to cobalt stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(9): 146-153. |
| 张虎, 寇江涛, 师尚礼. 紫花苜蓿种子萌发对钴胁迫的生理生化响应. 草业学报, 2015, 24(9): 146-153. | |
| 3 | Qiu L L, Fan X F, Xu S J, et al. The stress effect of heavy metal Pb on the growth and physiological and biochemical indexes of Medicago sativa seedlings. Gansu Science and Technology, 2013, 29(16): 148-151. |
| 邱丽莉, 范小峰, 许姝娟, 等. 重金属Pb对紫花苜蓿幼苗生长及生理生化指标的胁迫效应. 甘肃科技, 2013, 29(16): 148-151. | |
| 4 | Wei C Y, Chen T B. Hyperaccumulators and phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil: A review of studies in China and abroad. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2001, 21(7): 1196-1203. |
| 韦朝阳, 陈同斌. 重金属超富集植物及植物修复技术研究进展. 生态学报, 2001, 21(7): 1196-1203. | |
| 5 | Han H, Wang Q, He L Y, et al. Increased biomass and reduced rapeseed Cd accumulation of oilseed rape in the presence of Cd-immobilizing and polyamine-producing bacteria. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 353: 280-289. |
| 6 | Peng H, Zhang Y, Palmer L D, et al. Hydrogen sulfide and reactive sulfur species impact proteome S-sulfhydration and global virulence regulation in Staphylococcus aureus. ACS Infectious Diseases, 2017(3): 744-755. |
| 7 | Huang Z Z, He K, Song Z X, et al. Alleviation of heavy metal and silver nanoparticle toxicity and enhancement of their removal by hydrogen sulfide in Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Chemosphere, 2019, 224: 554-561. |
| 8 | Jin Z P, Pei Y X. Physiological implications of hydrogen sulfide in plants: Pleasant exploration behind its unpleasant odour. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2015, (2015-05-11). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/397502. |
| 9 | Zhang H, Hu L Y, Hu K D, et al. Hydrogen sulfide promotes wheat seed germination and alleviates oxidative damage against copper stress. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2009, 50(12): 1518-1529. |
| 10 | Lin Y T, Li M Y, Cui W T, et al. Haem oxygenase-1 is involved in hydrogen sulfide-induced cucumber adventitious root formation. Plant Growth Regulation, 2012, 31(4): 519-528. |
| 11 | Wang L, Wan R J, Shi Y H, et al. Hydrogen sulfide activates S-type anion channel via OST1 and Ca2+ modules. Molecular Plant, 2016, 9(3): 489-491. |
| 12 | Pei Y X. Gasotransmitter hydrogen sulfide in plants:Stinking to high heaven, but refreshing to fine life. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2016, 32(7): 721-733. |
| 裴雁曦. 植物中的气体信号分子硫化氢: 无香而立,其臭如兰. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2016, 32(7): 721-733. | |
| 13 | Cui W T, Chen H P, Zhu K K, et al. Cadmium-induced hydrogen sulfide synthesis is involved in cadmium tolerance in Medicago sativa by reestablishment of reduced (homo) glutathione and reactive oxygen species homeostases. PLoS One, 2014, 9(10): e109669. |
| 14 | Fang L C, Ju W L, Yang C L, et al. Application of signaling molecules in reducing metal accumulation in alfalfa and alleviating metal-induced phytotoxicity in Pb/Cd-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 182, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109459. |
| 15 | Shatalin K, Shatalina E, Mironov A, et al. H2S: A universal defense against antibiotics in bacteria. Science, 2011, 334: 986-990. |
| 16 | Jiang C Y, Sheng X F, Qian M. Isolation and characterization of a heavy metal-resistant Burkholderia sp. from heavy metal-contaminated paddy field soil and its potential in promoting plant growth and heavy metal accumulation in metal-polluted soil. Chemosphere, 2008, 72(2): 157-164. |
| 17 | Rajkumar M, Nagendran R, Lee K J. Influence of plant growth promoting bacteria and Cr6+ on the growth of Indian mustard. Chemosphere, 2006, 62(5): 741-748. |
| 18 | Ignatius R K P, Yen S C, Kwong S W, et al. Isolation and characterization of urease-producing bacteria from tropical peat. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 2018, 13: 168-175. |
| 19 | Li S J, Zhang T, Li J F, et al. Stabilization of Pb(II) accumulated in biomass through phosphate-pretreated pyrolysis at low temperatures. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 324: 464-471. |
| 20 | Qian F, Zhu X D, Liu Y C, et al. Influences of temperature and metal on subcritical hydrothermal liquefaction of hyperaccumulator: Implications for the recycling of hazardous hyperaccumulators. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(4): 2225-2234. |
| 21 | Guan S Y. Soil enzymes and their research methods. Beijing: Agricultural Press, 1986. |
| 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法. 北京: 农业出版社, 1986. | |
| 22 | Dai H, Jia G. Effects of Se on the growth, tolerance, and antioxidative systems of three alfalfa cultivars. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(17): 15196-15201. |
| 23 | Bonfranceschi B A, Flocco C G, Donati E R. Study of the heavy metal phytoextraction capacity of two forage species growing in an hydroponic environment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 165: 366-371. |
| 24 | Yun L, Larson S R, Jensen K B, et al. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) and candidate genes associated with trace element concentrations in perennial grasses grown on phytotoxic soil contaminated with heavy metals. Plant and Soil, 2015, 396: 277-296. |
| 25 | Ghada S, Mohamed I. Roles of hydrogen sulfide and cysteine in alleviation of nickel induced oxidative damages in wheat seedling. The Egyotian Journal of Experimental Biology, 2013, 9(1): 105-114. |
| 26 | Mostofa M G, Rahman A, Ansary M M U, et al. Hydrogen sulfide modulates cadmium-induced physiological and biochemical responses to alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 14078. |
| 27 | Fang H, Jing T, Liu Z, et al. Hydrogen sulfide interacts with calcium signaling to enhance the chromium tolerance in Setaria italica. Cell Calcium, 2014, 56: 472-481. |
| 28 | Amooaghaie R, Zangene-Madar F, Enteshari S. Role of two-sided crosstalk between NO and H2S on improvement of mineral homeostasis and antioxidative defense in Sesamum indicum under lead stress. Ecotoxicol Environment Safety, 2017, 139: 210-218. |
| 29 | Kaya C, Ashraf M, Akram N A. Hydrogen sulfide regulates the levels of key metabolites and antioxidant defense system to counteract oxidative stress in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants exposed to high zinc regime. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(13): 12612-12618. |
| 30 | Yan J, Xia L, Sheng X F, et al. Isolation of heavy metal-tolerant Sinorhizobium meliloti and the effect on copper uptake of alfalfa, Perennial ryegrass and Sorghum bicolor plants grown on copper-contaminated soil. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(2): 102-111. |
| 严警, 夏丽, 盛下放, 等. 耐重金属苜蓿中华根瘤菌的筛选及其与能源植物联合富集铜的特性. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 102-111. | |
| 31 | Singh V K, Singh A K, Singh P P, et al. Interaction of plant growth promoting bacteria with tomato under abiotic stress: A review. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2018, 267: 129-140. |
| 32 | Cao Q H, Pu S P, Xu W H, et al. Advances in research on morphology and bioavailability of heavy metals in rhizosphere. Guangzhou Environmental Sciences, 2006(3): 1-4. |
| 曹秋华, 普绍苹, 徐卫红, 等. 根际重金属形态与生物有效性研究进展. 广州环境科学, 2006(3): 1-4. | |
| 33 | Huai J S, Shen Y. Study on the quality control of soil heavy metal morphology. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2018, 45(12): 104-105. |
| 怀俊晟, 沈艳. 土壤重金属形态分析质量控制研究. 广东化工, 2018, 45(12): 104-105. | |
| 34 | Zhang Y L, Chen L J. Research advance in soil arylsulphatase. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2006(4): 792-798. |
| 张玉兰, 陈利军. 土壤芳基硫酸酯酶及其活性和农业措施影响. 土壤通报, 2006(4): 792-798. | |
| 35 | Treesubsuntorn C, Dhurakit P, Khaksar G, et al. Effect of microorganisms on reducing cadmium uptake and toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(26): 25690-25701. |
| [1] | 古丽娜扎尔·艾力null, 陶海宁, 王自奎, 沈禹颖. 基于APSIM模型的黄土旱塬区苜蓿——小麦轮作系统深层土壤水分及水分利用效率研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 22-33. |
| [2] | 臧真凤, 白婕, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿形态和生理指标响应干旱胁迫的品种特异性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 73-81. |
| [3] | 谢展, 穆麟, 张志飞, 陈桂华, 刘洋, 高帅, 魏仲珊. 乳酸菌或有机酸盐与尿素复配添加对紫花苜蓿混合青贮的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 165-173. |
| [4] | 王吉祥, 宫焕宇, 屠祥建, 郭侲洐, 赵嘉楠, 沈健, 栗振义, 孙娟. 耐亚磷酸盐紫花苜蓿品种筛选及评价指标的鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 186-199. |
| [5] | 张小芳, 魏小红, 刘放, 朱雪妹. PEG胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗内源激素对NO的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 160-169. |
| [6] | 候怡谣, 李霄, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅, 郭长虹. 过量表达紫花苜蓿MsHB7基因对拟南芥耐旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 170-179. |
| [7] | 马欣, 罗珠珠, 张耀全, 刘家鹤, 牛伊宁, 蔡立群. 黄土高原雨养区不同种植年限紫花苜蓿土壤细菌群落特征与生态功能预测[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 54-67. |
| [8] | 沙栢平, 谢应忠, 高雪芹, 蔡伟, 伏兵哲. 地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿草产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 102-114. |
| [9] | 李振松, 万里强, 李硕, 李向林. 苜蓿根系构型及生理特性对干旱复水的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 189-196. |
| [10] | 吴勇, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 童长春. 河西荒漠灌区紫花苜蓿施肥效应及其基于数据包络分析法的经济效益研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 94-105. |
| [11] | 邢易梅, 蕫理, 战力峰, 才华, 杨圣秋, 孙娜. 混合接种摩西球囊霉和根瘤菌对紫花苜蓿耐碱能力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 136-145. |
| [12] | 覃凤飞, 李志华, 刘信宝, 渠晖, 平措卓玛, 洛松群措, 苏梦涵. 外源2,4表油菜素内酯对越夏期高温与弱光胁迫下紫花苜蓿生长和光合性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 146-160. |
| [13] | 童长春, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 于铁峰. 基于平衡施肥的紫花苜蓿光合特性及光合因子的产量效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 70-80. |
| [14] | 何国兴, 宋建超, 温雅洁, 刘彩婷, 祁娟. 不同根瘤菌肥对紫花苜蓿生产力及土壤肥力的综合影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 109-120. |
| [15] | 于浩然, 格根图, 王志军, 贾玉山, 连植, 贾鹏飞. 甲酸添加剂及青贮时间对紫花苜蓿青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 89-95. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||