

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 53-61.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020252
收稿日期:2020-05-27
修回日期:2020-10-26
出版日期:2021-07-20
发布日期:2021-06-03
通讯作者:
蔡庆生
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: qscai@njau.edu.cn基金资助:
Hui-li WU( ), Wei TIAN, Yan-ling JI, Lai-qing LOU, Qing-sheng CAI(
), Wei TIAN, Yan-ling JI, Lai-qing LOU, Qing-sheng CAI( )
)
Received:2020-05-27
Revised:2020-10-26
Online:2021-07-20
Published:2021-06-03
Contact:
Qing-sheng CAI
摘要:
植物根际促生菌(PGPR)具有促进植物生长和提高重金属吸收的能力。因此,将PGPR作为土壤修复菌接种到具有较大生物量的植物根际,对提高植物修复效率具有重要意义。从镉污染地区的植物根际土壤中分离得到30株耐镉菌株,根据其分泌吲哚乙酸(IAA)、溶磷、产1-氨基环丙烷-1-羧酸(ACC)脱氨酶、铁载体及促生试验结果,选取2株具有PGPR特性的菌株接种到耐镉性不同的两种一年生黑麦草品种IdyⅡ和Wasehope中,测定它们对黑麦草生长和镉吸收积累的影响。当土壤镉含量为(19.5±0.42) mg·kg-1时,分别接种Pi01和Ma02,结果表明:镉处理下,接种2种菌株后两种一年生黑麦草的生物量和镉积累量均显著提高(P<0.05);叶绿素含量增加;光合作用增强;根际土壤镉有效态含量增加。因此,接种筛选出的2种PGPR能够促进黑麦草生长,增加其对镉的积累。
吴慧丽, 田薇, 纪燕玲, 娄来清, 蔡庆生. 促进镉吸收积累的植物根际促生菌的筛选及其对一年生黑麦草的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 53-61.
Hui-li WU, Wei TIAN, Yan-ling JI, Lai-qing LOU, Qing-sheng CAI. Screening for plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria that promote cadmium absorption and accumulation and their effects on annual ryegrass[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(7): 53-61.
菌株 Strains | IAAa Secreting IAA ability | 溶磷b Phosphate solubilization | ACC脱氨酶 ACC deaminase activity | 铁载体 Producing siderophores | 菌株 Strains | IAAa Secreting IAA ability | 溶磷b Phosphate solubilization | ACC脱氨酶 ACC deaminase activity | 铁载体 Producing siderophores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ts01 | - | - | - | + | Cc08 | - | - | + | - |
| Tm01 | - | ++++ | - | - | Pi06 | ++ | - | - | - |
| As12 | - | - | - | - | Pi11 | ++ | - | - | - |
| Ls01 | + | - | - | - | Pl01 | ++ | - | - | + |
| Ma04 | ++ | - | - | - | Ki02 | - | - | - | + |
| Pi01 | ++ | - | - | + | Mh02 | +++ | + | - | - |
| Ma02 | ++ | ++ | - | + | Fs01 | - | - | - | - |
| Pi03 | +++ | - | - | + | Af05 | - | + | + | - |
| Sp01 | - | + | - | + | As05 | ++ | ++++ | - | - |
| Cch02 | - | - | - | + | Ts02 | - | - | - | - |
| Fs03 | - | +++ | - | - | Ra07 | - | - | - | + |
| Ma11 | - | - | - | + | As16 | - | +++ | - | - |
| Ls03 | - | + | + | - | Pv02 | - | ++ | - | - |
| As13 | ++ | - | - | - | Cc09 | - | + | - | - |
| Ra12 | - | - | - | + | Cc11 | - | + | - | - |
表1 30株耐镉菌促生特性
Table 1 Characteristics of 30 cadmium tolerant strains
菌株 Strains | IAAa Secreting IAA ability | 溶磷b Phosphate solubilization | ACC脱氨酶 ACC deaminase activity | 铁载体 Producing siderophores | 菌株 Strains | IAAa Secreting IAA ability | 溶磷b Phosphate solubilization | ACC脱氨酶 ACC deaminase activity | 铁载体 Producing siderophores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ts01 | - | - | - | + | Cc08 | - | - | + | - |
| Tm01 | - | ++++ | - | - | Pi06 | ++ | - | - | - |
| As12 | - | - | - | - | Pi11 | ++ | - | - | - |
| Ls01 | + | - | - | - | Pl01 | ++ | - | - | + |
| Ma04 | ++ | - | - | - | Ki02 | - | - | - | + |
| Pi01 | ++ | - | - | + | Mh02 | +++ | + | - | - |
| Ma02 | ++ | ++ | - | + | Fs01 | - | - | - | - |
| Pi03 | +++ | - | - | + | Af05 | - | + | + | - |
| Sp01 | - | + | - | + | As05 | ++ | ++++ | - | - |
| Cch02 | - | - | - | + | Ts02 | - | - | - | - |
| Fs03 | - | +++ | - | - | Ra07 | - | - | - | + |
| Ma11 | - | - | - | + | As16 | - | +++ | - | - |
| Ls03 | - | + | + | - | Pv02 | - | ++ | - | - |
| As13 | ++ | - | - | - | Cc09 | - | + | - | - |
| Ra12 | - | - | - | + | Cc11 | - | + | - | - |
菌株编号 Strains code | 分泌IAAa Secreting IAA ability (μg·mL-1) | ACC脱氨酶活性 ACC deaminase activity | 溶磷能力b Phosphate solubilization | 产铁载体能力 Producing siderophores | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ma02 | 53.76±4.25 | - | 2.52±0.38 | 2.18±0.30 | 鹅肠菜根际土壤 Chickweed rhizosphere soil |
| Pi01 | 91.84±8.12 | - | - | 1.85±0.09 | 翅果菊根际土壤 Pterocarpus rhizosphere soil |
表2 供试菌株促生特性
Table 2 Promoting characteristics of tested strains
菌株编号 Strains code | 分泌IAAa Secreting IAA ability (μg·mL-1) | ACC脱氨酶活性 ACC deaminase activity | 溶磷能力b Phosphate solubilization | 产铁载体能力 Producing siderophores | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ma02 | 53.76±4.25 | - | 2.52±0.38 | 2.18±0.30 | 鹅肠菜根际土壤 Chickweed rhizosphere soil |
| Pi01 | 91.84±8.12 | - | - | 1.85±0.09 | 翅果菊根际土壤 Pterocarpus rhizosphere soil |
| 菌株Strains | 革兰氏染色Gram stain | 菌株形态特征Morphological characteristics of strains | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 形态Shape | 表面Surface | 边缘Edge | 颜色Color | 透明度Transparency | 隆起状况Uplift | ||
| Ma02 | - | 杆状Rod-shaped | 湿润Wet | 整齐Neat | 淡黄色Light yellow | 不透明Opaque | 凸起Raised |
| Pi01 | - | 杆状Rod-shaped | 湿润Wet | 整齐Neat | 淡黄色Light yellow | 不透明Opaque | 凸起Raised |
表3 菌株革兰氏染色结果
Table 3 Strains of gram stain results
| 菌株Strains | 革兰氏染色Gram stain | 菌株形态特征Morphological characteristics of strains | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 形态Shape | 表面Surface | 边缘Edge | 颜色Color | 透明度Transparency | 隆起状况Uplift | ||
| Ma02 | - | 杆状Rod-shaped | 湿润Wet | 整齐Neat | 淡黄色Light yellow | 不透明Opaque | 凸起Raised |
| Pi01 | - | 杆状Rod-shaped | 湿润Wet | 整齐Neat | 淡黄色Light yellow | 不透明Opaque | 凸起Raised |
菌株 Strains | GenBank登录号 Genbank accession number | 相似度 Similarity (%) | 鉴定结果 Identification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ma02 | MT436801 | 99.79 | Enterobacter sp. |
| Pi01 | MT436802 | 99.29 | Enterobacter sp. |
表4 菌株鉴定结果
Table 4 Strain identification results
菌株 Strains | GenBank登录号 Genbank accession number | 相似度 Similarity (%) | 鉴定结果 Identification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ma02 | MT436801 | 99.79 | Enterobacter sp. |
| Pi01 | MT436802 | 99.29 | Enterobacter sp. |
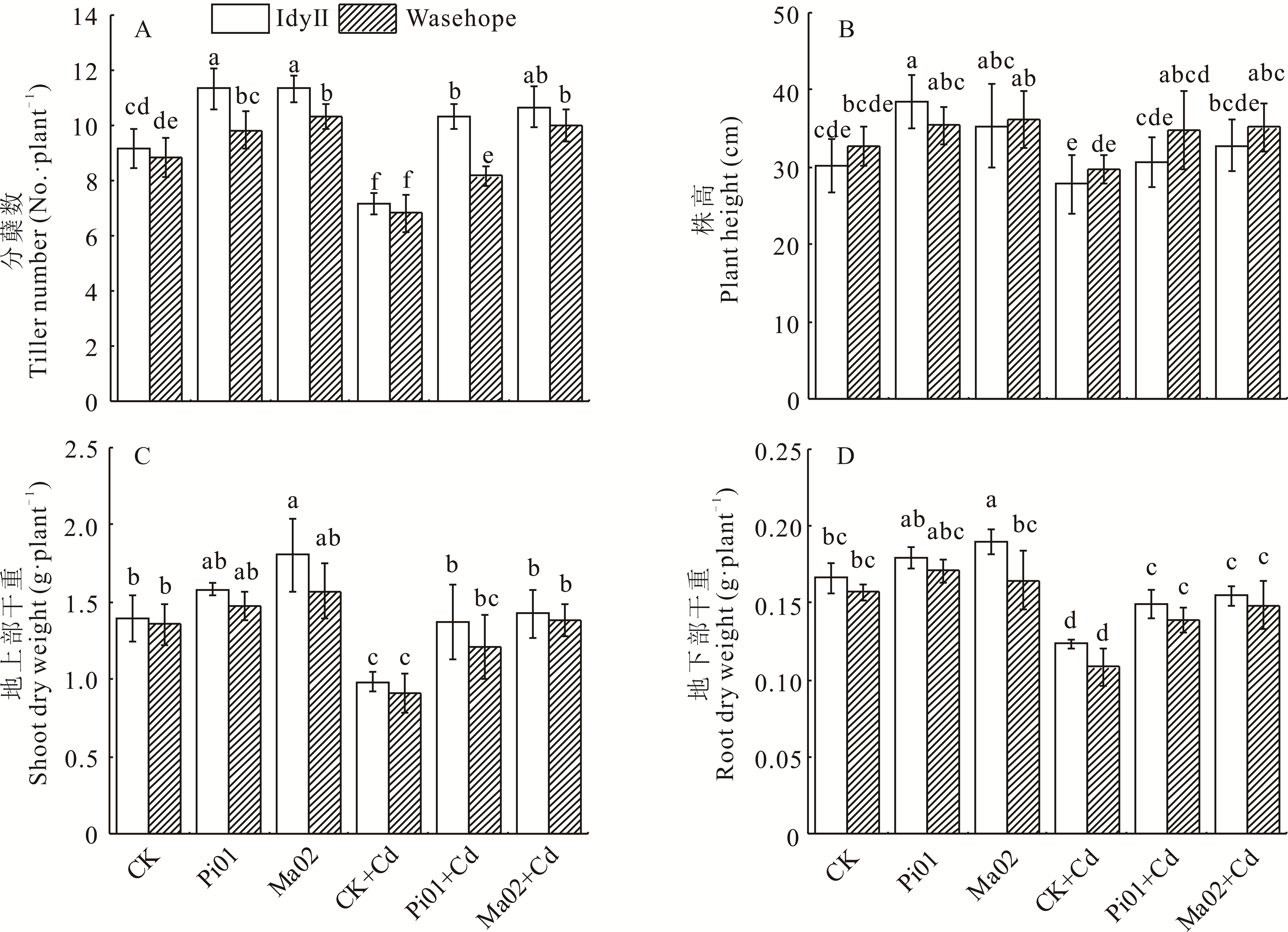
图1 不同处理对两种一年生黑麦草分蘖数、株高和干重的影响不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the P<0.05 level. The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of different treatments on the tiller number, plant height, and dry weight of two annual ryegrass species (mean±SD, n=3)

图2 不同处理对两种一年生黑麦草镉浓度、转运系数、镉积累量和镉积累总量的影响
Fig.2 Effects of different treatments on cadmium concentration, translocation factor, cadmium accumulation and cadmium accumulation of two annual ryegrass species (mean±SD, n=3)
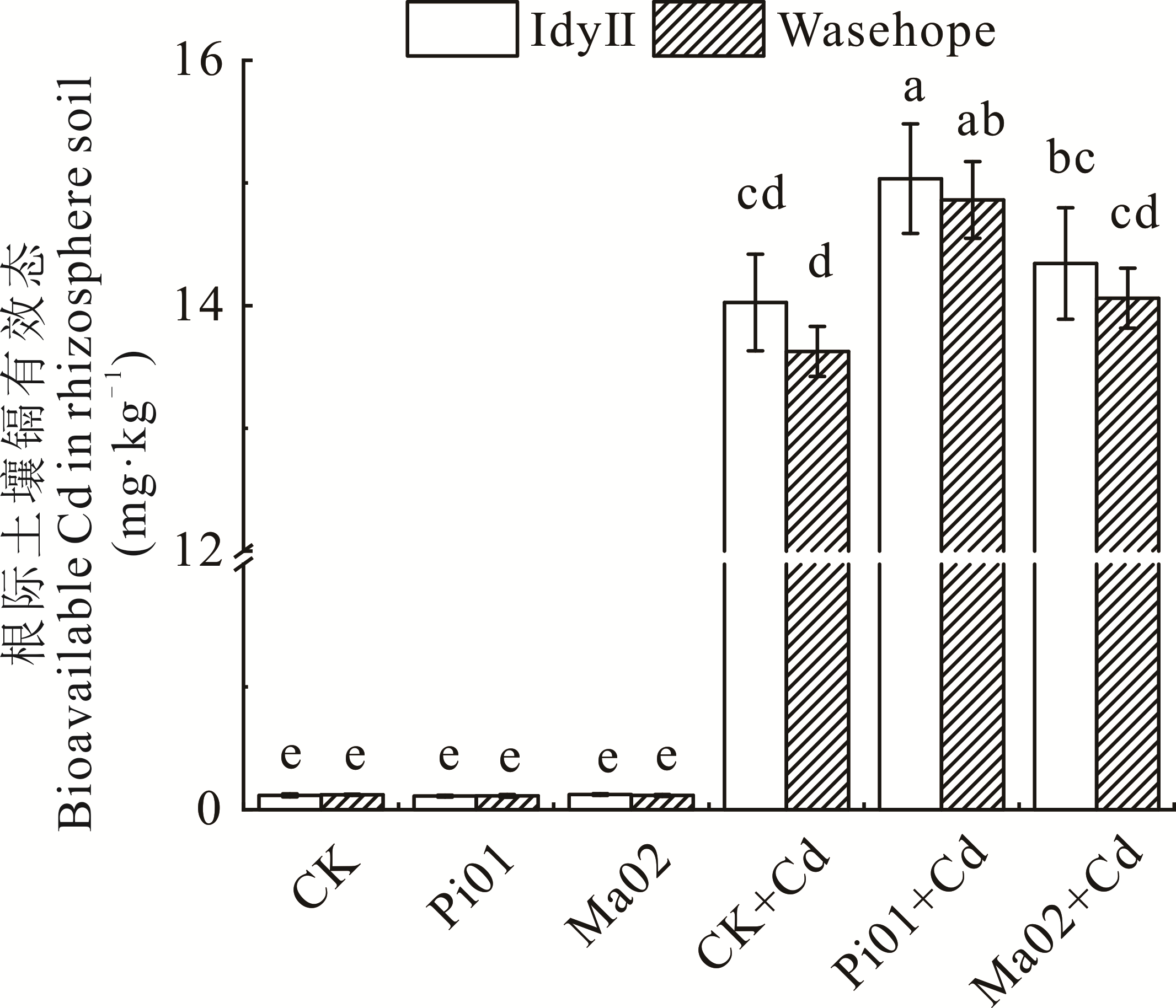
图5 不同处理对两种一年生黑麦草根际土壤镉有效态的影响
Fig.5 Effects of different treatments on the available cadmium in the rhizosphere soil of two annual ryegrass (mean±SD, n=3)
| 1 | Ministry of Environmental Protection, Ministry of Land and Resources. Report on the national general survey of soil contamination. Environmental Education, 2014(6): 8-10. |
| 环境保护部, 国土资源部. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报. 环境教育, 2014(6): 8-10. | |
| 2 | Cuypers A, Plusquin M, Remans T, et al. Cadmium stress: An oxidative challenge. Biometals, 2010, 23(5): 927-940. |
| 3 | Ding T, Luo J Y, Yang S H, et al. Recent research progress on natural medicines in treatment of cadmium toxicity. China Journal of Chinese Material Medica, 2018, 43(10): 2006-2013. |
| 丁通, 骆骄阳, 杨世海, 等. 天然药物防治镉中毒的现代研究进展. 中国中药杂志, 2018, 43(10): 2006-2013. | |
| 4 | Vetterlein D, Wesenberg D, Nathan P, et al. Pteris vittata-revisited: Uptake of as and its speciation, impact of P, role of phytochelatins and S. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(11): 3016-3024. |
| 5 | Hu P J, Li Z, Zhong D X, et al. Research progress on the phytoextraction of heavy metal contaminated soils in China. Plant Physiology Journal, 2014, 50(5): 577-584. |
| 胡鹏杰, 李柱, 钟道旭, 等. 我国土壤重金属污染植物吸取修复研究进展. 植物生理学报, 2014, 50(5): 577-584. | |
| 6 | Bashan Y, de-Bashan L E, Prabhu S R, et al. Advances in plant growth-promoting bacterial inoculant technology: Formulations and practical perspectives (1998-2013). Plant and Soil, 2014, 378(1/2): 1-33. |
| 7 | Pal A K, Sengupta C. Isolation of cadmium and lead tolerant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: Lysinibacillus varians and Pseudomonas putida from Indian agricultural soil. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 2019, 28(7): 601-629. |
| 8 | Himadri B B, Lipika N, Subhasis D, et al. Isolation of ACC deaminase producing PGPR from rice rhizosphere and evaluating their plant growth promoting activity under salt stress. Plant and Soil, 2013, 366(1/2): 93-105. |
| 9 | Izzeddine Z Z, Bilal R, Lakhdar K, et al. Algerian sahara PGPR confers maize root tolerance to salt and aluminum toxicity via ACC deaminase and IAA. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2019, 41(6): 1-10. |
| 10 | Barriuso J, Solano B R, Santamariac, et al. Effect of inoculation with putative plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria isolated from Pinus spp. on Pinus pinea growth, mycorrhization and rhizosphere microbial communities. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2008, 105(5): 1298-1309. |
| 11 | Yasuda M, Takenouchi Y, Nitta Y, et al. Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam) as a high-potential bio-ethanol resource. Bioenergy Research, 2015, 8: 1303-1309. |
| 12 | Liu C Y, Sun X Y, Zhu T C, et al. Comparison of production performance and screening of superior varieties of different ryegrasses. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(4): 39-48. |
| 刘春英, 孙学映, 朱体超, 等. 不同黑麦草品种生产性能比较与优势品种筛选. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 39-48. | |
| 13 | Zhang X, He S Y, Wu Q L. Remediation of Cd contaminated soil by ryegrass enhanced by EDTA and GA_3 and its detoxification mechanism. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 28(5): 280-285. |
| 张熹, 何闪英, 吴秋玲. EDTA与GA_3强化黑麦草修复Cd污染土壤及其解毒机制. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(5): 280-285. | |
| 14 | Hu Z Y, Wang Y F, Fang Z G, et al. Italian ryegrass-rice rotation system for biomass production and cadmium removal from contaminated paddy fields. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2020, 20(2): 874-882. |
| 15 | Ministry of Ecological Environment. Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land (trial implementation), GB 15618-2018. Beijing: Ministry of Ecological Environment, 2018. |
| 生态环境部. 土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行), GB 15618-2018. 北京: 生态环境部, 2018. | |
| 16 | Gordon S A, Weber R P. Colorimetric estimation of indoleacetic acid. Plant Physiology, 1951, 26(1): 192. |
| 17 | Huang J, Sheng X F, He L Y. Biodiversity of phosphate-dissolving and plant growth-promoting endophytic bacteria of two crops. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2015, 50(6): 710-716. |
| 黄静, 盛下放, 何琳燕. 具溶磷能力的植物内生促生细菌的分离筛选及其生物多样性. 微生物学报, 2015, 50(6): 710-716. | |
| 18 | Xia J J. Screening of plant growth-promoting endophytic bacteria and their effects on the accumulation of lead and cadmium from soil by rape. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2003. |
| 夏娟娟. 植物促生内生细菌的筛选及其强化油菜富集土壤铅镉重金属的研究. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2003. | |
| 19 | Kumar A, Singh R, Yadav A, et al. Isolation and characterization of bacterial endophytes of Curcuma longa L. 3 Biotech, 2016, 6(1): 1-8. |
| 20 | Fang Z G, Hu Z Y, Zhao H, et al. Screening for cadmium tolerance of 21 cultivars from Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam) during germination. Grassland Science, 2017, 63(1): 36-45. |
| 21 | Fang Z G. Screening for cadmium tolerance from Italian ryegrass cultivars and mechanism study of exogenous GSH alleviating effect cadmium toxicity. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 方志刚. 多花黑麦草耐镉品种的筛选及外源GSH缓解镉毒害机理的研究. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2018. | |
| 22 | Liu M, Liu F Z, Liu B F. Determination of available lead and cadmium in soil. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2007(Supple1): 300-302. |
| 刘铭, 刘凤枝, 刘保峰. 土壤中有效态铅和镉的测定. 农业环境科学学报, 2007(增刊1): 300-302. | |
| 23 | Gupta S, Pandey S. ACC deaminase producing bacteria with multifarious plant growth promoting traits alleviates salinity stress in french bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) plants. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019(10): 1506. |
| 24 | Huo W, Cai Q S. The advance of the enhancement of plant heavy metal resistance by plant growth-promote bacteria. Microbiology China, 2010, 37(9): 1374-1378. |
| 霍伟, 蔡庆生. 植物促生菌提高植物重金属耐受性研究进展. 微生物学通报, 2010, 37(9): 1374-1378. | |
| 25 | Akmak R. Screening of multi-trait rhizobacteria for improving the growth, enzyme activities, and nutrient uptake of tea (Camellia sinensis). Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2016, 47(13/14): 1680-1690. |
| 26 | Kamran M A, Syed J H, Eqani S A M A S, et al. Effect of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria inoculation on Cadmium (Cd) uptake by Eruca sativa. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(12): 9275-9283. |
| 27 | Khanna K, Jamwal V L, Gandhi S G,et al. Metal resistant PGPR lowered Cd uptake and expression of metal transporter genes with improved growth and photosynthetic pigments in Lycopersicon esculentum under metal toxicity. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(3): 17859-17879. |
| 28 | Ferchuchi N, Toukabri, Boularess M, et al. Isolation, identification and plant growth promotion ability of endophytic bacteria associated with lupine root nodule grown in Tunisian soil. Archives of Microbiology, 2019, 201(10): 1333-1349. |
| 29 | Wali M, Llugany M, Corrales L, et al. High salinity helps the halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum in defense against Cd toxicity by maintaining redox balance and photosynthesis. Planta, 2016, 244(2): 333-346. |
| 30 | Li X M, Song J L. Cadmium uptake and root morphological changes in Medicago sativa under cadmium stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(2): 178-186. |
| 李希铭, 宋佳龙. 镉胁迫对紫花苜蓿镉吸收特征及根系形态影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 178-186. | |
| 31 | Wang Q, Ma L Y, Zhou Q Y, et al. Inoculation of plant growth promoting bacteria from hyperaccumulator facilitated non-host root development and provided promising gents for elevated phytoremediation efficiency. Chemosphere, 2019(232): 243-253. |
| 32 | Itusha A, Osborne W J, VaithilingamM, et al. Enhanced uptake of Cd by biofilm forming Cd resistant plant growth promoting bacteria bioaugmented to the rhizosphere of Vetiveria zizanioides. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2019, 21(5): 487-495. |
| 33 | Asad S A, Masood R, Ahmad R, et al. Differential uptake of cadmium and chromium in Brassica oleracea in response to application of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 2018, 20(7): 1613-1622. |
| 34 | Han H, Wang Q, He L Y, et al. Increased biomass and reduced rapeseed Cd accumulation of oilseed rape in the presence of Cd-immobilizing and polyamine-producing bacteria. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 353: 280-289. |
| [1] | 肖逸, 杨忠富, 聂刚, 韩佳婷, 帅杨, 张新全. 12个多花黑麦草品种(系)在成都平原的生产性能和营养价值综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 174-185. |
| [2] | 漫静, 唐波, 邓波, 李佳欢, 何玉娟, 张佳良. 羊草根际促生菌的分离筛选及促生作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 59-71. |
| [3] | 周瀚洋, 孙鹏越, 尉欣荣, 周雨, 张智伟, 高金柱, 赵东豪, 罗艺岚, 呼天明, 付娟娟. 琥珀酸黄杆菌缓解遮阴对多年生黑麦草胁迫的效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 137-143. |
| [4] | 魏勇, 王晓瑜, 李应德, 段廷玉. AM真菌在白三叶-黑麦草体系中对抗逆信号的传导作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 138-146. |
| [5] | 申午艳, 冯政君, 秦文芳, 范远. 盐碱胁迫下黑麦草生长及离子微区分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 52-63. |
| [6] | 刘建新, 欧晓彬, 王金成, 刘瑞瑞, 贾海燕. 镉胁迫下裸燕麦幼苗对外源H2O2的生理响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 125-134. |
| [7] | 马碧花, 蔺伟虎, 高敏, 王兴迪, 田沛. 干旱胁迫下水杨酸和内生真菌对多年生黑麦草的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 135-144. |
| [8] | 王日明, 王志强, 向佐湘. γ-氨基丁酸对高温胁迫下黑麦草光合特性及碳水化合物代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 168-178. |
| [9] | 邓杰, 李芳, 段廷玉. 温室条件下AM真菌和禾草内生真菌对根腐离蠕孢侵染黑麦草的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 103-113. |
| [10] | 胡冰钰, 方志刚, 娄来清, 蔡庆生. 14份柳枝稷种质资源苗期耐镉性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 27-36. |
| [11] | 李继伟, 悦飞雪, 王艳芳, 张亚梅, 倪瑞景, 王发园, 付国占, 刘领. 施用生物炭和AM真菌对镉胁迫下玉米生长和生理生化指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 120-129. |
| [12] | 宋丹丹,何丙辉,罗松平,吴耀鹏. 黑麦草和生物炭对喀斯特地区黄壤养分影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 195-201. |
| [13] | 李金波, 李诗刚, 宋桂龙, 濮阳雪华, 薛博晗. 两种黑麦草砷吸收特征及其与茎叶营养元素积累的关系研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 79-87. |
| [14] | 辛建攀, 李文明, 祁茜, 田如男. 镉对梭鱼草叶片保护酶活性、光合及荧光特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 23-34. |
| [15] | 王学春, 王红妮, 黄晶, 杨国涛, 胡运高. 基于EPIC模型的四川丘陵区黑麦草生长过程及其土壤水分动态变化模拟[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 1-13. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||