

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 34-46.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021266
收稿日期:2021-07-05
修回日期:2021-09-13
出版日期:2022-03-20
发布日期:2022-01-15
通讯作者:
王长庭,吴鹏飞
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: wupf@swun.edu.cn,ctwang@swun.edu.cn基金资助:
Lei ZHOU( ), Xue WEI, Chang-ting WANG(
), Xue WEI, Chang-ting WANG( ), Peng-fei WU(
), Peng-fei WU( )
)
Received:2021-07-05
Revised:2021-09-13
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-01-15
Contact:
Chang-ting WANG,Peng-fei WU
摘要:
小型土壤节肢动物是草地生态系统的重要组成部分,并对环境变化具有高度敏感性。为了查明小型土壤节肢动物群落对高寒草地退化的响应及其在退化过程中的指示作用,在川西北地区选取了未退化、轻度退化、中度退化和重度退化的高寒草地,于2019和2020年的7月对小型土壤节肢动物群落进行调查。采集各样地0~20 cm的土样,用干漏斗法(Tullgren法)分离小型土壤节肢动物。结果为:1)小型土壤节肢动物群落组成结构和优势类群在不同退化阶段高寒草地间存在差异,群落密度、类群数和Shannon-Wiener多样性指数均随退化程度加重呈先增加后下降的趋势(P<0.01),而Simpson优势度指数则先下降后上升(P<0.01);2)不同类群的小型土壤节肢动物对退化的响应不同,随高寒草地退化程度的加重,螨类密度持续降低(P<0.01),而跳虫密度则呈先增加后下降的趋势(P<0.01),表明高寒草地退化对螨类具有持续抑制作用,而对跳虫则是先促进后抑制;3)土壤有机碳(SOC)、湿度、全氮(TN)、pH、碳氮比(C/N),以及植物的群落高度和物种数是影响小型土壤节肢动物群落密度及多样性的主要因子(P<0.001, 0.01或0.05),其中土壤容重、SOC、TN、C/N和pH对螨类数量有显著影响(P<0.001, 0.01或0.05),而各因子对跳虫均无显著影响(P>0.05)。研究表明,小型土壤节肢动物群落的组成结构、密度及多样性对高寒草地响应敏感,并受土壤等环境因子影响;而螨类密度在退化过程中持续下降,可以用作高寒草地退化的指示生物。
周磊, 魏雪, 王长庭, 吴鹏飞. 高寒草地小型土壤节肢动物群落特征及其对草地退化的指示作用[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 34-46.
Lei ZHOU, Xue WEI, Chang-ting WANG, Peng-fei WU. Differences in soil microarthropod community structure in alpine grasslands with differing degrees of degradation[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 34-46.
项目 Item | 环境变量 Environmental variables | 未退化 Non-degraded | 轻度退化 Lightly degraded | 中度退化 Moderately degraded | 重度退化 Severely degraded | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
植物群落 Plant communities | 植物种类数 Number of species | 13.74±1.27a | 12.89±0.77a | 13.78±0.66a | 6.70±0.54b | 14.88 | <0.01 |
| 盖度 Coverage (%) | 92.93±1.69a | 89.32±1.26b | 87.93±1.69b | 67.39±3.84c | 17.99 | <0.01 | |
| 高度 Height (cm) | 15.67±2.01a | 9.17±0.41a | 9.55±0.96a | 5.59±0.81b | 15.30 | <0.01 | |
| 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | 92.93±1.70a | 96.74±3.01a | 90.33±5.71a | 60.52±3.91b | 16.87 | <0.01 | |
土壤理化性质 Soil properties | pH | 5.87±0.04b | 5.99±0.06b | 6.12±0.08ab | 6.45±0.13a | 15.48 | <0.01 |
| 有机碳 Soil organic carbon (g·kg-1) | 75.39±11.07a | 59.95±2.57b | 69.20±5.79ab | 54.44±4.33b | 3.51 | <0.05 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 11.31±2.18ab | 10.13±1.07ab | 12.92±1.81a | 6.68±0.73b | 3.12 | <0.05 | |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 1.12±0.09a | 0.85±0.04bc | 0.91±0.04ab | 0.72±0.05c | 7.60 | <0.01 | |
| 碳氮比 C/N (%) | 9.00±0.56a | 8.65±0.57a | 7.83±0.59a | 11.38±1.69a | 1.36 | >0.05 | |
| 碳磷比 C/P (%) | 72.51±11.42a | 88.93±9.18a | 75.37±4.75a | 78.80±6.15a | 0.73 | >0.05 | |
| 氮磷比 N/P (%) | 10.90±2.11a | 13.82±1.55a | 13.52±1.63a | 9.63±1.30a | 1.28 | >0.05 | |
| 土壤含水量 Water content (%) | 0.48±0.03a | 0.46±0.02a | 0.40±0.02a | 0.39±0.03a | 1.86 | >0.05 | |
| 容重 Bulk density (g·cm | 0.76±0.05b | 0.86±0.02ab | 0.87±0.03ab | 0.97±0.05a | 3.52 | <0.05 |
表1 不同退化程度高寒草地的基本情况
Table 1 Characteristics of plant communities and soil properties in different degradation stages
项目 Item | 环境变量 Environmental variables | 未退化 Non-degraded | 轻度退化 Lightly degraded | 中度退化 Moderately degraded | 重度退化 Severely degraded | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
植物群落 Plant communities | 植物种类数 Number of species | 13.74±1.27a | 12.89±0.77a | 13.78±0.66a | 6.70±0.54b | 14.88 | <0.01 |
| 盖度 Coverage (%) | 92.93±1.69a | 89.32±1.26b | 87.93±1.69b | 67.39±3.84c | 17.99 | <0.01 | |
| 高度 Height (cm) | 15.67±2.01a | 9.17±0.41a | 9.55±0.96a | 5.59±0.81b | 15.30 | <0.01 | |
| 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | 92.93±1.70a | 96.74±3.01a | 90.33±5.71a | 60.52±3.91b | 16.87 | <0.01 | |
土壤理化性质 Soil properties | pH | 5.87±0.04b | 5.99±0.06b | 6.12±0.08ab | 6.45±0.13a | 15.48 | <0.01 |
| 有机碳 Soil organic carbon (g·kg-1) | 75.39±11.07a | 59.95±2.57b | 69.20±5.79ab | 54.44±4.33b | 3.51 | <0.05 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 11.31±2.18ab | 10.13±1.07ab | 12.92±1.81a | 6.68±0.73b | 3.12 | <0.05 | |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 1.12±0.09a | 0.85±0.04bc | 0.91±0.04ab | 0.72±0.05c | 7.60 | <0.01 | |
| 碳氮比 C/N (%) | 9.00±0.56a | 8.65±0.57a | 7.83±0.59a | 11.38±1.69a | 1.36 | >0.05 | |
| 碳磷比 C/P (%) | 72.51±11.42a | 88.93±9.18a | 75.37±4.75a | 78.80±6.15a | 0.73 | >0.05 | |
| 氮磷比 N/P (%) | 10.90±2.11a | 13.82±1.55a | 13.52±1.63a | 9.63±1.30a | 1.28 | >0.05 | |
| 土壤含水量 Water content (%) | 0.48±0.03a | 0.46±0.02a | 0.40±0.02a | 0.39±0.03a | 1.86 | >0.05 | |
| 容重 Bulk density (g·cm | 0.76±0.05b | 0.86±0.02ab | 0.87±0.03ab | 0.97±0.05a | 3.52 | <0.05 |
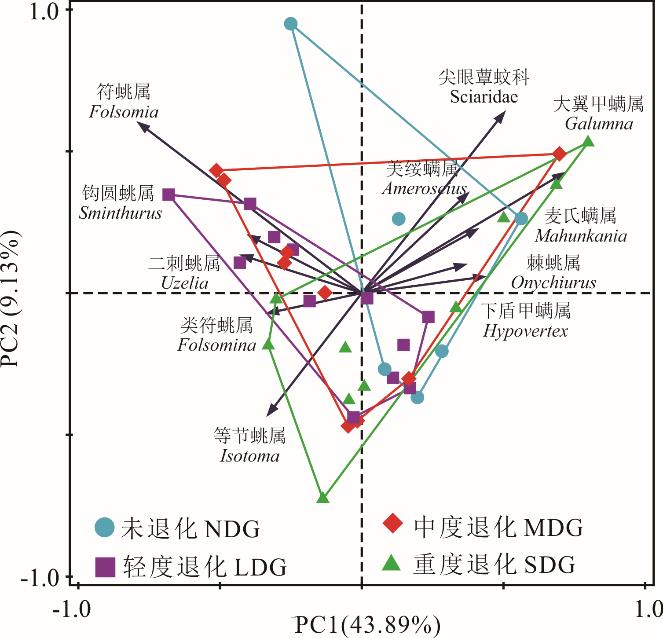
图2 不同退化程度草地间小型土壤动物群落结构差异NDG: 未退化草地Non-degraded grassland; LDG: 轻度退化草地Lightly degraded grassland; MDG: 中度退化草地Moderately degraded grassland; SDG: 重度退化草地Severely degraded grassland. 下同The same below.
Fig.2 Community structure of soil microarthropod in different degraded grasslands
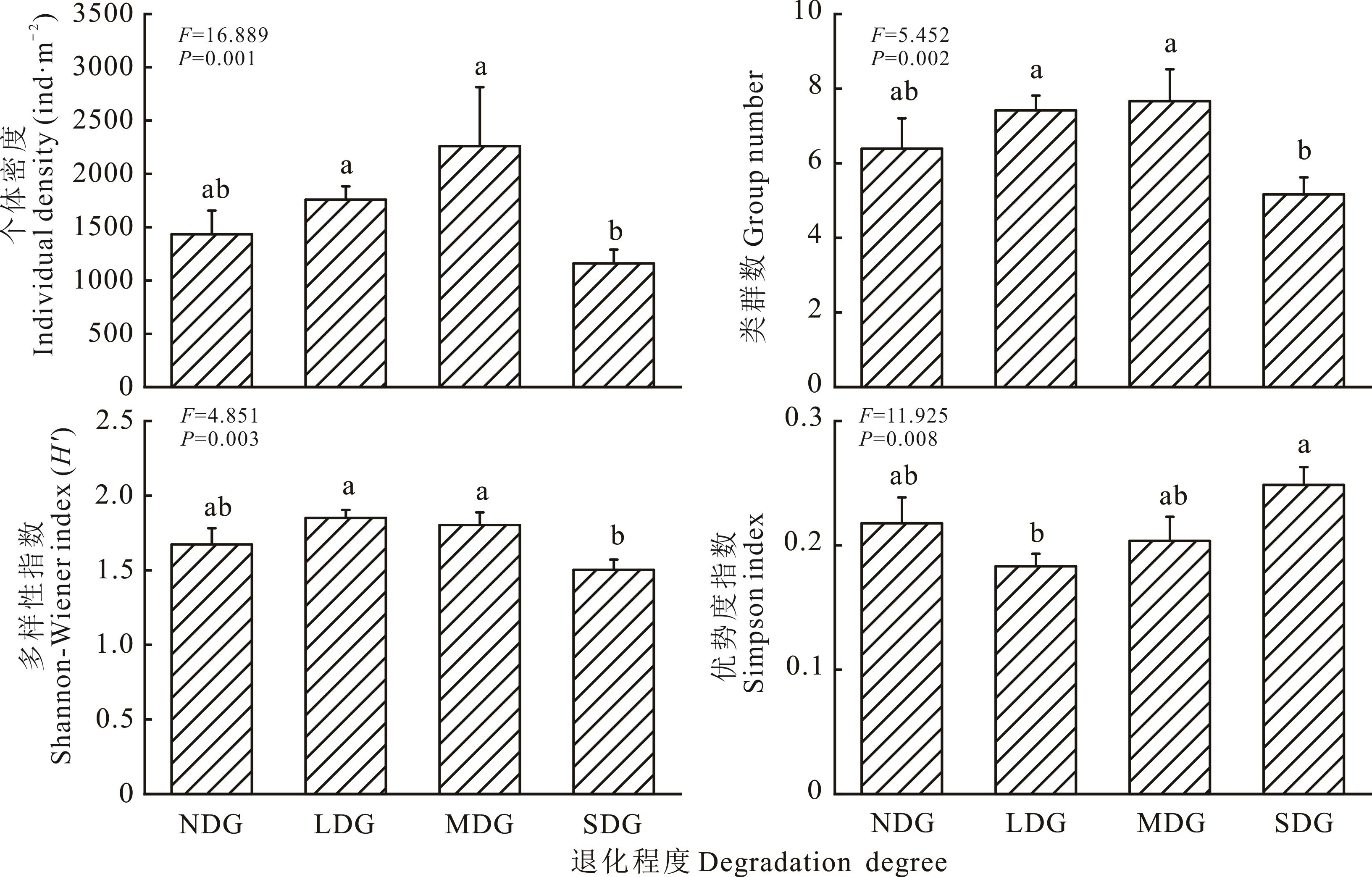
图3 不同退化程度草地间小型土壤节肢动物群落密度及多样性不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters mean significant differences(P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.3 Density and diversity index of soil microarthropod communities in different degraded grasslands (mean±SE)
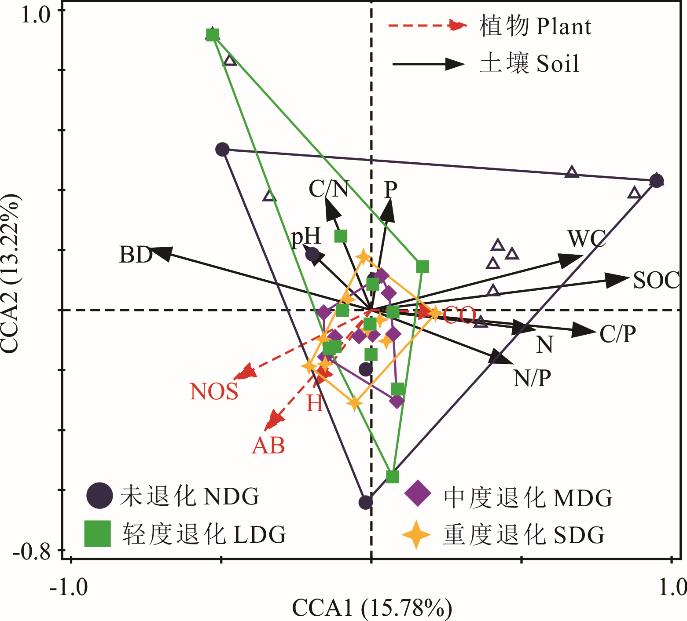
图5 小型土壤节肢动物群落与环境因子的典范对应分析BD:土壤容重Bulk density; WC:土壤含水量Water content; SOC:土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon; TN:全氮 Total nitrogen; TP:全磷 Total phosphorus; C/N:碳氮比 Ratio of C and N; C/P: 碳磷比 Ratio of C and P; N/P: 氮磷比 Ratio of N and P; NOS:植物物种数 Number of species; CO:盖度 Coverage; H: 高度 Height; AB: 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass. 下同The same below.
Fig.5 Canonical correspondence analysis on soil microarthropod communities and environment factors

图6 小型土壤节肢动物与土壤环境因子间的相关性分析*: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001; 螨类和跳虫为其个体密度指标The parameters for mites and collembola were the individual density; 图例颜色越深表示相关系数越大The color of the legend is darker, the correlation coefficient is greater.
Fig.6 Correlation analysis on the relationships between soil microarthropods and soil environmental factors
| 1 | Sampson A W. Plant succession in relation to range management. Ieice Transactions on Communications, 1919, 89(12): 3425-3427. |
| 2 | Ellison L. Influence of grazing on plant succession of rangelands. Botanical Review, 1960, 26(1): 1-78. |
| 3 | Rosiere R E. An evaluation of grazing intensity influences on California annual range. Rangeland Ecology & Management, 1987, 40(2): 160-165. |
| 4 | Li B. The rangeland degradation in north China and its preventive strategy. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1997, 30(6): 2-10. |
| 李博. 中国北方草地退化及其防治对策. 中国农业科学, 1997, 30(6): 2-10. | |
| 5 | Ren J Z. Research methods of pratacultural science. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1998. |
| 任继周. 草业科学研究方法. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1998. | |
| 6 | Cao Y H, Lin C C, Wang D L, et al. Spatial characteristics of vegetation rehabilitation in landscape boundary. Journal of Northeast Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2003, 35(2): 74-79. |
| 曹勇宏, 林长纯, 王德利, 等. 农田—草原景观界面中植被恢复的空间特征. 东北师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 35(2): 74-79. | |
| 7 | Sun X D, Dong Q M, Ma Y S. Research status of classification standard of degraded grassland in alpine meadow. Chinese Qinghai Journal of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 2008, 38(4): 54-55. |
| 孙小弟, 董全民, 马玉寿. 高寒草甸退化草地分级标准研究现状. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2008, 38(4): 54-55. | |
| 8 | Wang C T, Wang G X, Li X Z, et al. Effects of N addition on the plant and soil microbial community in alpine Kobresia tibetica meadow of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(2): 405-415. |
| 王长庭, 王根绪, 李香真, 等. 氮肥添加对高寒藏嵩草(Kobresia tibetica)沼泽化草甸和土壤微生物群落的影响. 生态学报, 2017, 37(2): 405-415. | |
| 9 | Duan Y F, Ren Z Y, Sun Y J. Time-lay effects of climate on water use efficiency in the Loess Plateau of northern Shaanxi. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(10): 258-269. |
| 段艺芳, 任志远, 孙艺杰. 陕北黄土高原植被生态系统水分利用效率气候时滞效应. 生态学报, 2020, 40(10): 258-269. | |
| 10 | Li S L, Chen Y J, Guan S Y, et al. Relationships between soil degradation and rangeland degradation. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2002, 16(1): 92-95. |
| 李绍良, 陈有君, 关世英, 等. 土壤退化与草地退化关系的研究. 干旱区资源与环境, 2002, 16(1): 92-95. | |
| 11 | Ma L, Xu M H, Zhai D T, et al. Response of alpine meadow vegetation-soil system to climate change: A review. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(6): 1708-1717. |
| 马丽, 徐满厚, 翟大彤, 等. 高寒草甸植被-土壤系统对气候变暖响应的研究进展. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(6): 1708-1717. | |
| 12 | Yang L M, Li J D. Division on degenerate successional stages of main grassland communities for grazing in the Songnen Plain of China. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 1996, 4(4): 281-287. |
| 杨利民, 李建东. 松嫩平原主要草地群落放牧退化演替阶段的划分. 草地学报, 1996, 4(4): 281-287. | |
| 13 | Hemerik L, Brussaard L. Diversity of soil macro-invertebrates in grasslands under restoration succession. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2002, 38(2): 145-150. |
| 14 | Doblas-Miranda E, Wardle D A, Peltzer D A, et al. Changes in the community structure and diversity of soil invertebrates across the Franz Josef Glacier chronosequence. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2008, 40(5): 1069-1081. |
| 15 | Neher D A, Weicht T R, Moorhead D L, et al. Elevated CO2 alters functional attributes of nematode communities in forest soils. Functional Ecology, 2004, 18(4): 584-591. |
| 16 | Wang C T, Long R J, Wang G X, et al. Relationship between plant communities, characters, soil physical and chemical properties, and soil microbiology in alpine meadows. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2010, 19(6): 25-34. |
| 王长庭, 龙瑞军, 王根绪, 等. 高寒草甸群落地表植被特征与土壤理化性状、土壤微生物之间的相关性研究. 草业学报, 2010, 19(6): 25-34. | |
| 17 | Tian Y B, Xiong M B, Song G Y. Restoration succession of wetland soils and their changes of water and nutrient in Ruoergai Plateau. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2005, 24(1): 21-25. |
| 田应兵, 熊明标, 宋光煜. 若尔盖高原湿地土壤的恢复演替及其水分与养分变化. 生态学杂志, 2005, 24(1): 21-25. | |
| 18 | Wu P F, Yang D X. Effect of habitat degradation on soil meso- and microfaunal communities in the Zoige alpine meadow, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(13): 3745-3757. |
| 吴鹏飞, 杨大星. 若尔盖高寒草甸退化对中小型土壤动物群落的影响. 生态学报, 2011, 31(13): 3745-3757. | |
| 19 | Gao Y M, Wu P F. Effects of alpine meadow degradation on soil insect diversity in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016(8): 2327-2336. |
| 高艳美, 吴鹏飞. 高寒草甸退化对土壤昆虫多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2016(8): 2327-2336. | |
| 20 | Wei X, Wu P F. Responses of soil insect communities to alpine wetland degradation on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2021, 103: 103276. |
| 21 | Wu P F, Zhang H Z, Wang Y. The response of soil macroinvertebrates to alpine meadow degradation in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Applied Soil Ecology, 2015, 90: 60-67. |
| 22 | Shao Z Z, Wu P F. Responses of epigeic microarthropods to alpine wetland degradation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(19): 36-47. |
| 邵珍珍, 吴鹏飞. 小型表栖节肢动物群落对高寒湿地退化的响应. 生态学报, 2019, 39(19): 36-47. | |
| 23 | Bongers T, Ferris H. Nematode community structure as a bioindicator in environmental monitoring. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 1999, 14(6): 224-228. |
| 24 | Gladys L M, Daniel I, France B, et al. Soil fauna abundance and diversity in a secondary semi-evergreen forest in Guadeloupe (Lesser Antilles): Influence of soil type and dominant tree species. Biology & Fertility of Soils, 2007, 44(2): 269-276. |
| 25 | Wu P F, Zhang H Z, Cui L W, et al. Impacts of alpine wetland degradation on the composition, diversity and trophic structure of soil nematodes on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 837. |
| 26 | Long W, Gao Y M, Wu P F. Effects of alpine meadow degradation on epigeic arthropod communities in Zoige. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(1): 128-138. |
| 龙伟, 高艳美, 吴鹏飞. 若尔盖高寒草甸退化对表栖节肢动物群落的影响. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(1): 128-138. | |
| 27 | Wu P F, Zhang H Z, Cui L W, et al. Response of soil macrofauna communities to degradation of alpine meadow. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2013, 50(4): 786-799. |
| 吴鹏飞, 张洪芝, 崔丽巍, 等. 大型土壤动物群落对高寒草甸退化的响应. 土壤学报, 2013, 50(4): 786-799. | |
| 28 | Yin W Y. Pictorical keys to soil animals of China. Beijing: Science Press, 1998. |
| 尹文英. 中国土壤动物检索图鉴. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998. | |
| 29 | Li H X, Sui J Z, Zhou S X, et al. Insect taxonomic retrieval. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1987. |
| 李鸿兴, 隋敬之, 周士秀, 等. 昆虫分类检索. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1987. | |
| 30 | Xin J L. Agricultural mites. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1988. |
| 忻介六. 农业螨类学. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1988. | |
| 31 | Lu R K. Soil argrochemistry analysis protocoes. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. | |
| 32 | Li Y C. Study on diversity of soil animal and population ecology of Chrysolina aeruginosa in Artemisia desertorum association habitats in desert grasslands of Ningxia. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2015. |
| 李岳诚. 宁夏荒漠草原沙蒿群丛生境土壤节肢动物多样性及沙蒿金叶甲种群生态学研究. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2015. | |
| 33 | Wang H X, Yin X Q, Zhou D W. Ecological study on small-middle size soil animals in a compound ecosystem of farmland, grassland and woodland in the grassland region of Songnen Plain. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(10): 1715-1718. |
| 王海霞, 殷秀琴, 周道玮. 松嫩草原区农牧林复合系统中小型土壤动物群落生态研究. 应用生态学报, 2003, 14(10): 1715-1718. | |
| 34 | Omar A, Gulbostan N, Abudurusul T, et al. Community characteristics of soil mesofauna in Kanas Natural Reserve, Xinjiang. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2014, 28(2): 68-73. |
| 吾玛尔·阿布力孜, 古丽布斯坦·努尔买买提, 阿布都肉苏力·吐孙, 等. 新疆喀纳斯国家自然保护区中小型土壤动物群落特征研究. 干旱区资源与环境, 2014, 28(2): 68-73. | |
| 35 | Fu G Q. Study on the relationships between dynamic of soil animals biodiversity and ecological factors of different halophilous habitat in the Leymus chinensis grassland of Jilin Province. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2007. |
| 付关强. 吉林省羊草草原不同盐碱生境土壤动物多样性动态与生态因子关系研究. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2007. | |
| 36 | De H S, Hong M, Zhao B, et al. Effect of simulated warming and N addition on soil mesofauna community in desert steppe of Inner Mongolia. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(6): 122-128. |
| 德海山, 红梅, 赵巴音那木拉, 等. 模拟增温、施氮对荒漠草原土壤中小型动物群落的影响. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(6): 122-128. | |
| 37 | Wenninger E J, Inouye R S. Insect community response to plant diversity and productivity in a sagebrush-steppe ecosystem. Journal of Arid Environments, 2008, 72(1): 24-33. |
| 38 | Huang X, Wen W Q, Zhang J, et al. Soil faunal diversity under typical alpine vegetations in West Sichuan. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2010, 21(1): 181-190. |
| 黄旭, 文维全, 张健, 等. 川西高山典型自然植被土壤动物多样性. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(1): 181-190. | |
| 39 | Wardle D A, Bardgett R D, Klironomos J N, et al. Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota. Science, 2004, 304(5677): 1629-1633. |
| 40 | Tyler G. Differences in abundance, species richness, and body size of ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) between beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) forests on Podzol and Cambisol. Forest Ecology & Management, 2008, 256(12): 2154-2159. |
| 41 | Viketoft M, Palmborg C, Sohlenius B, et al. Plant species effects on soil nematode communities in experimental grasslands. Applied Soil Ecology, 2005, 30(2): 90-103. |
| 42 | Li Y, Wu P F, Long W, et al. Effects of different forage species on soil arthropod communities on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(20): 368-379. |
| 李雨, 吴鹏飞, 龙伟, 等. 高寒地区种植不同种类牧草对土壤节肢动物群落的影响. 生态学报, 2019, 39(20): 368-379. | |
| 43 | Liu J L, Yin X Q, Qiu L L. Large-sized soil fauna and soil factors in Zuojia Nature Reserve. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2008, 45(1): 130-136. |
| 刘继亮, 殷秀琴, 邱丽丽. 左家自然保护区大型土壤动物与土壤因子关系研究. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(1): 130-136. | |
| 44 | Zhu X Y, Gao B J, Bi H M, et al. Community diversity of soil arthropods in forest-steppe ecotone. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007, 18(11): 179-184. |
| 朱新玉, 高宝嘉, 毕华铭, 等. 森林-草原交错带土壤节肢动物群落多样性. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(11): 179-184. | |
| 45 | Xiao N W, Liu X H, Ge F, et al. Research on soil faunal community composition and structure in the Gaoligong Mountains National Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(7): 3576-3584. |
| 肖能文, 刘向辉, 戈峰, 等. 高黎贡山自然保护区大型土壤动物群落特征. 生态学报, 2009, 29(7): 3576-3584. | |
| 46 | Zhou Y Z, Wu P F. Diversity and spatiotemporal distribution of soil microarthropod communities in forests on the eastern slope of Gongga Mountain. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(2): 586-599. |
| 周育臻, 吴鹏飞. 贡嘎山东坡森林小型土壤节肢动物群落多样性与时空分布. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(2): 586-599. | |
| 47 | Bao Y X, Cheng H Y, Ge B M, et al. Soil macrofauna community in different using type of soils. Journal of Zhejiang Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2007(2): 121-127. |
| 鲍毅新, 程宏毅, 葛宝明, 等. 不同土地利用方式下大型土壤动物群落对土壤理化性质的响应. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2007(2): 121-127. | |
| 48 | Setälä H, Marshall V G, Trofymow J A. Influence of micro- and macro-habitat factors on collembolan communities in Douglas-fir stumps during forest succession. Applied Soil Ecology, 1995, 2(4): 227-242. |
| 49 | Bray S R, Kitajima K, Mack M C. Temporal dynamics of microbial communities on decomposing leaf litter of 10 plant species in relation to decomposition rate. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2012, 44: 30-37. |
| 50 | Gu Y F, Yan B, Xiang Q J, et al. Degradation shaped bacterial and archaeal communities with predictable taxa and their association patterns in Zoige wetland at Tibet Plateau. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 3884. |
| 51 | Zhang A J, Zhang J, Li J J, et al. Characteristics of soil faunal community structure before and after the rotation period of Eucalyptus grandis plantations with various densities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(3): 64-77. |
| 张阿娟, 张健, 李金金, 等. 轮伐期前后不同密度巨桉(Eucalyptus grandis)人工林土壤动物群落结构特征. 生态学报, 2020, 40(3): 64-77. | |
| 52 | Shea K, Roxburgh S H, Rauschert E. Moving from pattern to process: Coexistence mechanisms under intermediate disturbance regimes. Ecology Letters, 2010, 7(6): 491-508. |
| 53 | Behan V M. Oribatid mite biodiversity in agroecosystems: Role for bioindication. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 1999, 74(1/2/3): 411-423. |
| 54 | Huang Y M, Yang W Q, Zhang J, et al. Response of soil faunal community to simulated understory plant loss in the subalpine coniferous plantation of western Sichuan. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(8): 2018-2025. |
| 黄玉梅, 杨万勤, 张健, 等. 川西亚高山针叶林土壤动物群落对模拟林下植物丧失的响应. 生态学报, 2010, 30(8): 2018-2025. | |
| 55 | Pazliya H, Omar A, Aliya S. Correlation between the diversity of soil mite communities and environmental factors in Tianshan Forest Park in Xinjiang, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(5): 159-172. |
| 排孜丽耶·合力力, 吾玛尔·阿布力孜, 阿丽亚·司地克. 新疆天山森林公园土壤螨类群落多样性与环境因子的相关性. 生态学报, 2019, 39(5): 159-172. | |
| 56 | Xue J, Wei X, He X J, et al. Effects of ant-hills on the community structure of soil microarthropods in an alpine meadow ecosystem. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(4): 1613-1624. |
| 薛娟, 魏雪, 何先进, 等. 高寒草甸生态系统蚁丘对小型土壤节肢动物群落的影响. 生态学报, 2021, 41(4): 1613-1624. | |
| 57 | Shao Y H, Zhang W X, Liu S J, et al. Diversity and function of soil fauna. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(20): 6614-6625. |
| 邵元虎, 张卫信, 刘胜杰, 等. 土壤动物多样性及其生态功能. 生态学报, 2015, 35(20): 6614-6625. | |
| 58 | Ma R, Zhao J M. Relationship between the grassland and soil conditions in the Eastern Qilian Mountains. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(2): 374-381. |
| 马瑞, 赵锦梅. 东祁连山河谷高寒草地植被群落特征及其与土壤性状的关系. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(2): 374-381. | |
| 59 | Viketoft M. Effects of six grassland plant species on soil nematodes: A glasshouse experiment. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2007, 40(4): 906-915. |
| 60 | Wu Y N. The ecological effects of elevated carbon dioxide concentrations on communities of meso- micro soil fauna and soil microbial in Honghe Nature Reserve. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2019. |
| 伍一宁. CO2浓度升高对洪河自然保护区中小型土壤动物及微生物群落生态影响研究. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2019. | |
| 61 | Xu S, Zhou L Z, Pan C Y, et al. Avoidance behaviour of earthworm (Eisenia andrei) to carbendazim polluted soil. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40(2): 810-812. |
| 徐甦, 周玲珠, 潘辰苑, 等. 蚯蚓对多菌灵污染土壤回避行为的研究. 安徽农业科学, 2012, 40(2): 810-812. | |
| 62 | Zheng C Y, Hu D X, Li W J. Effects of EM compost on soil mites community in farmland. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2002, 22(7): 1116-1121. |
| 郑长英, 胡敦孝, 李维炯. 施用EM堆肥对土壤螨群落结构的影响. 生态学报, 2002, 22(7): 1116-1121. | |
| 63 | Edwards P J, Coulson J M. Choice of earthworm species for laboratory tests//Greig-Smith P W, Becker H, Edwards P J, et al. Ecotoxicology of earthworms. Andover: Intercept Publishing, 1992: 36-43. |
| 64 | Wu D H, Yin W Y, Yang Z M. Difference in soil mite community characteristics among different vegetation restoration practices in the moderatly degraded pasture of Songnen grassland. Current Zoology, 2007, 53(4): 607-615. |
| 吴东辉, 尹文英, 杨振明. 松嫩草原中度退化草地不同植被恢复方式下土壤螨类群落特征的差异. 动物学报, 2007, 53(4): 607-615. |
| [1] | 孙彩彩, 董全民, 刘文亭, 冯斌, 时光, 刘玉祯, 俞旸, 张春平, 张小芳, 李彩弟, 杨增增, 杨晓霞. 放牧方式对青藏高原高寒草地土壤节肢动物群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 62-75. |
| [2] | 王斌, 李满有, 王欣盼, 董秀, 庞军宝, 兰剑. 深松浅旋对半干旱区退化紫花苜蓿人工草地改良效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 107-117. |
| [3] | 刘佳丽, 范建容, 张茜彧, 杨超, 徐富宝, 张晓雪, 梁博. 高寒草地生长季/非生长季植被盖度遥感反演[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 15-26. |
| [4] | 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 王宏生, 鲍根生. 内生真菌对高寒草地紫花针茅凋落物分解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 150-158. |
| [5] | 赵京东, 乌云娜, 宋彦涛. 短期围封对辽西北退化草地群落牧草品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 51-61. |
| [6] | 王传旗, 刘文辉, 张永超, 周青平. 野生老芒麦苗期耐旱性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 127-136. |
| [7] | 赵京东, 宋彦涛, 徐鑫磊, 乌云娜. 施氮和刈割对辽西北退化草地牧草产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 36-48. |
| [8] | 石明明, 王晓敏, 陈奇, 韩炳宏, 周秉荣, 肖建设, 肖宏斌. 高寒草地干湿生态系统土壤水分及入渗对降水的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 49-58. |
| [9] | 李聪聪, 周亚星, 谷强, 杨明新, 朱传鲁, 彭子原, 薛凯, 赵新全, 王艳芬, 纪宝明, 张静. 三江源区典型高寒草地丛枝菌根真菌多样性及构建机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 46-58. |
| [10] | 陈红, 马文明, 周青平, 杨智, 刘超文, 刘金秋, 杜中曼. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体稳定性及其铁铝氧化物分异的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 73-84. |
| [11] | 邱月, 吴鹏飞, 魏雪. 三种人工草地小型土壤节肢动物群落多样性动态及其差异[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 21-32. |
| [12] | 王婷, 张永超, 赵之重. 青藏高原退化高寒湿地植被群落结构和土壤养分变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 9-18. |
| [13] | 李元春, 葛静, 侯蒙京, 高宏元, 刘洁, 包旭莹, 殷建鹏, 高金龙, 冯琦胜, 梁天刚. 基于CCI-LC数据的甘南和川西北地区土地覆盖类型时空动态分布及草地面积变化驱动力研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 1-15. |
| [14] | 李成一, 李希来, 杨元武, 李宏林, 梁德飞. 氮添加对不同坡度退化高寒草甸土壤细菌多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 161-170. |
| [15] | 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 鲍根生, 王宏生. 狼毒防除对高寒草地群落植物养分重吸收的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 47-57. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||