

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 49-58.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020436
石明明1,2( ), 王晓敏1,3, 陈奇1,2, 韩炳宏4, 周秉荣1,2(
), 王晓敏1,3, 陈奇1,2, 韩炳宏4, 周秉荣1,2( ), 肖建设1,2, 肖宏斌1,2
), 肖建设1,2, 肖宏斌1,2
收稿日期:2020-09-28
修回日期:2020-12-17
出版日期:2021-11-11
发布日期:2021-11-11
通讯作者:
周秉荣
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: zbr0515@foxmail.com基金资助:
Ming-ming SHI1,2( ), Xiao-min WANG1,3, Qi CHEN1,2, Bing-hong HAN4, Bing-rong ZHOU1,2(
), Xiao-min WANG1,3, Qi CHEN1,2, Bing-hong HAN4, Bing-rong ZHOU1,2( ), Jian-she XIAO1,2, Hong-bin XIAO1,2
), Jian-she XIAO1,2, Hong-bin XIAO1,2
Received:2020-09-28
Revised:2020-12-17
Online:2021-11-11
Published:2021-11-11
Contact:
Bing-rong ZHOU
摘要:
为厘清高寒草地土壤水分动态对降水的响应,利用2015-2017年的降水和不同土层(5、10、20、30和40 cm)土壤水分连续观测数据,分析了高寒草原和沼泽草甸生长季土壤水分变化及入渗对降水事件的响应。结果表明:相比于草原,生长季沼泽草甸降水频次较高,小降水事件占比较大。草原和沼泽草甸土壤水分对降水事件的响应存在较大差异,小降水事件(≤5 mm)仅增加了草原5 cm土层土壤含水量,而对沼泽草甸0~40 cm土壤剖面各层土壤含水量均起到微弱的补充;草原5~10 mm的降水事件明显增加了10 cm土层土壤含水量,而>10 mm的降水事件才可明显补充10 cm以下土层土壤含水量;在沼泽草甸>5 mm的降水事件对40 cm土层土壤含水量的增加较上层(0~30 cm)明显。土壤水分增量不仅受降水事件大小和强度的显著影响(P<0.001),同时受降水前表层(0~10 cm)土壤含水量和降水期间气温的显著影响(P<0.05)。相比草原,沼泽草甸土壤中湿润锋运移较快;小降水事件发生时,沼泽草甸0~40 cm土壤剖面蓄水量增加较多;大降水事件发生时,沼泽草甸0~40 cm土壤剖面蓄水量增加较少。结果表明,草原大降水事件(>10 mm)占比较大的特征对于土壤剖面蓄水具有重要作用,沼泽草甸高频次降水和雨水渗透更快更深的特征,有利于土壤更频繁获取和有效地保持水分资源。该研究结果可为理解高寒草地区域尺度上复合生态系统土壤水分维持对降水格局的响应提供理论基础。
石明明, 王晓敏, 陈奇, 韩炳宏, 周秉荣, 肖建设, 肖宏斌. 高寒草地干湿生态系统土壤水分及入渗对降水的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 49-58.
Ming-ming SHI, Xiao-min WANG, Qi CHEN, Bing-hong HAN, Bing-rong ZHOU, Jian-she XIAO, Hong-bin XIAO. Responses of soil moisture to precipitation and infiltration in dry and wet alpine grassland ecosystems[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(12): 49-58.
站点 Site | 植被特征Vegetation properties | 土壤特征Soil properties (0~40 cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
盖度 Cover (%) | 高度 Height (cm) | 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | 土壤类型 Soil type | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | |
| 草原Grassland | 85 | 12 | 391.99 | 山地灰褐色土Montane grey drab soil | 1.31 |
| 沼泽草甸Swamp meadow | 90 | 20 | 586.71 | 泥炭土Peat soil | 0.65 |
表1 试验站基本信息
Table 1 General information of testing sites
站点 Site | 植被特征Vegetation properties | 土壤特征Soil properties (0~40 cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
盖度 Cover (%) | 高度 Height (cm) | 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | 土壤类型 Soil type | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | |
| 草原Grassland | 85 | 12 | 391.99 | 山地灰褐色土Montane grey drab soil | 1.31 |
| 沼泽草甸Swamp meadow | 90 | 20 | 586.71 | 泥炭土Peat soil | 0.65 |

图1 降水月均值变化与各量级降水情况不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different small letters indicate significant differences at the P<0.05 level, the same below.
Fig.1 Mean monthly precipitation and rainfall at various levels
土层 Soil layer | 草原(44次降水事件) Grassland (44 rainfall events) | 沼泽草甸(35次降水事件) Swamp meadow (35 rainfall events) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方程Equation | R2 | P | 方程Equation | R2 | P | |
| 0~10 cm | y=0.0043x1+0.0035x2-0.0018 | 0.75 | <0.001 | y=0.0003x1+0.0007x2+0.0032 | 0.26 | 0.017 |
| 10~40 cm | y=0.0010x1+0.0020x2-0.0013 | 0.63 | <0.001 | y=0.0007x1-0.0001x2+0.0028 | 0.38 | 0.001 |
表2 土壤水分增量与降水事件大小和降水强度的关系
Table 2 The relationship between the increase of soil moisture content and rainfall event size and rainfall intensity
土层 Soil layer | 草原(44次降水事件) Grassland (44 rainfall events) | 沼泽草甸(35次降水事件) Swamp meadow (35 rainfall events) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方程Equation | R2 | P | 方程Equation | R2 | P | |
| 0~10 cm | y=0.0043x1+0.0035x2-0.0018 | 0.75 | <0.001 | y=0.0003x1+0.0007x2+0.0032 | 0.26 | 0.017 |
| 10~40 cm | y=0.0010x1+0.0020x2-0.0013 | 0.63 | <0.001 | y=0.0007x1-0.0001x2+0.0028 | 0.38 | 0.001 |
站点 Site | 土层 Soil layer | 土壤含水量 Sil moisture content | 气温 Air temperature | 风速 Wind speed | 相对湿度 Relative humidity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
草原 Grassland | 0~10 cm | 0.179 | -0.129 | -0.073 | 0.260 |
| 10~40 cm | 0.479* | -0.389* | -0.022 | 0.014 | |
沼泽草甸 Swamp meadow | 0~10 cm | 0.411* | -0.208 | -0.047 | -0.103 |
| 10~40 cm | 0.501** | -0.277 | -0.194 | 0.021 |
表3 单位降水引起的土壤水分增量和降水前表层(0~10 cm)土壤含水量、气温、风速、相对湿度之间的相关性
Table 3 The correlation between the increase of soil moisture content induced by 1 mm rainfall and surface (0-10 cm) soil moisture content before rainfall events, air temperature, wind speed, relative humidity
站点 Site | 土层 Soil layer | 土壤含水量 Sil moisture content | 气温 Air temperature | 风速 Wind speed | 相对湿度 Relative humidity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
草原 Grassland | 0~10 cm | 0.179 | -0.129 | -0.073 | 0.260 |
| 10~40 cm | 0.479* | -0.389* | -0.022 | 0.014 | |
沼泽草甸 Swamp meadow | 0~10 cm | 0.411* | -0.208 | -0.047 | -0.103 |
| 10~40 cm | 0.501** | -0.277 | -0.194 | 0.021 |
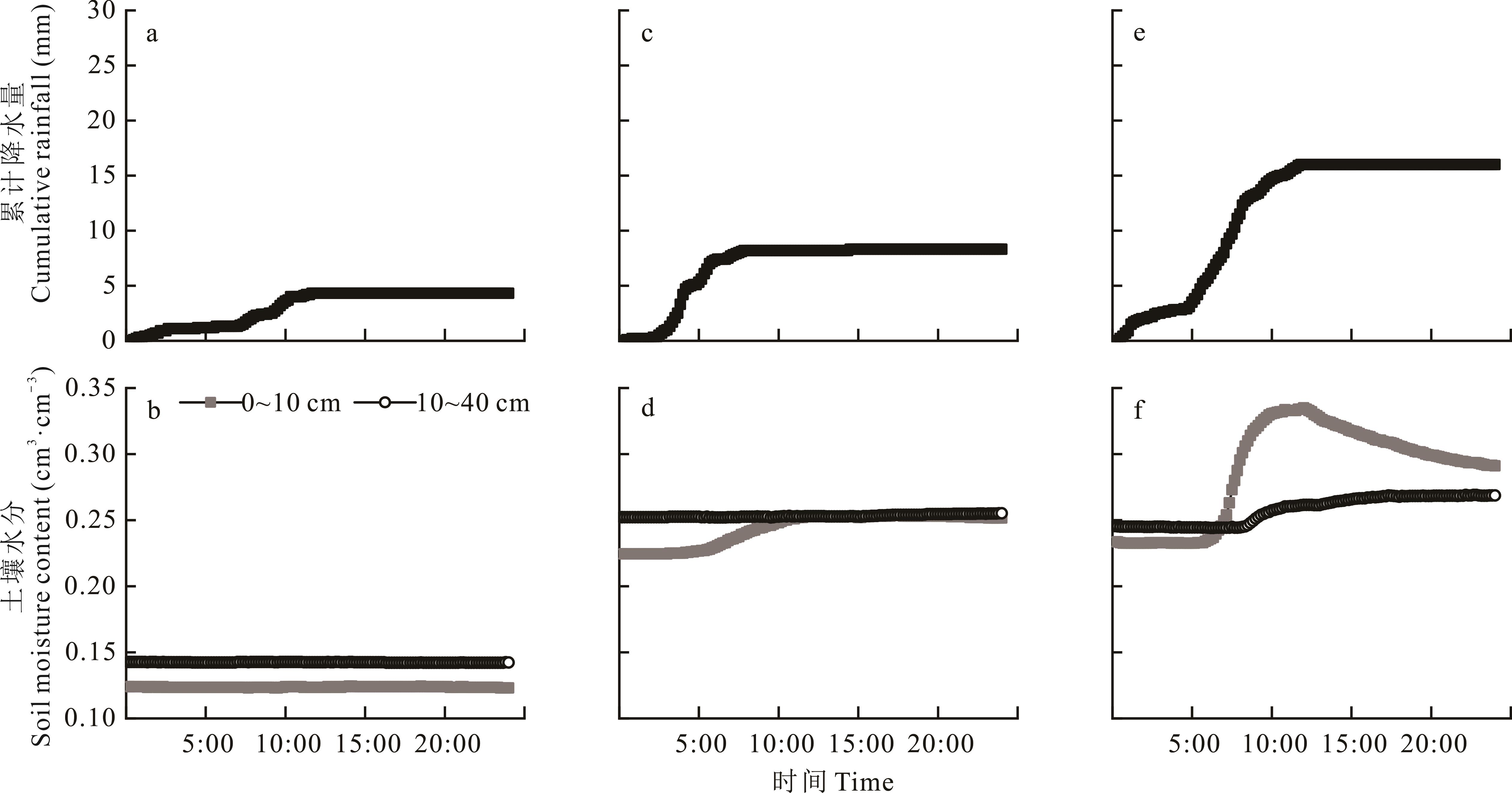
图3 草原入渗过程土壤剖面水分变化a与b、c与d和e与f分别为4.3、8.3和16.0 mm的降水事件及对应的土壤含水量变化。The changes of soil water content at soil profiles 0-10 cm and 10-40 cm during the individual rainfall events of 4.3 (a, b), 8.3 (c, d) and 16.0 mm (e, f), respectively.
Fig.3 The wetting front infiltration processes in the alpine grassland
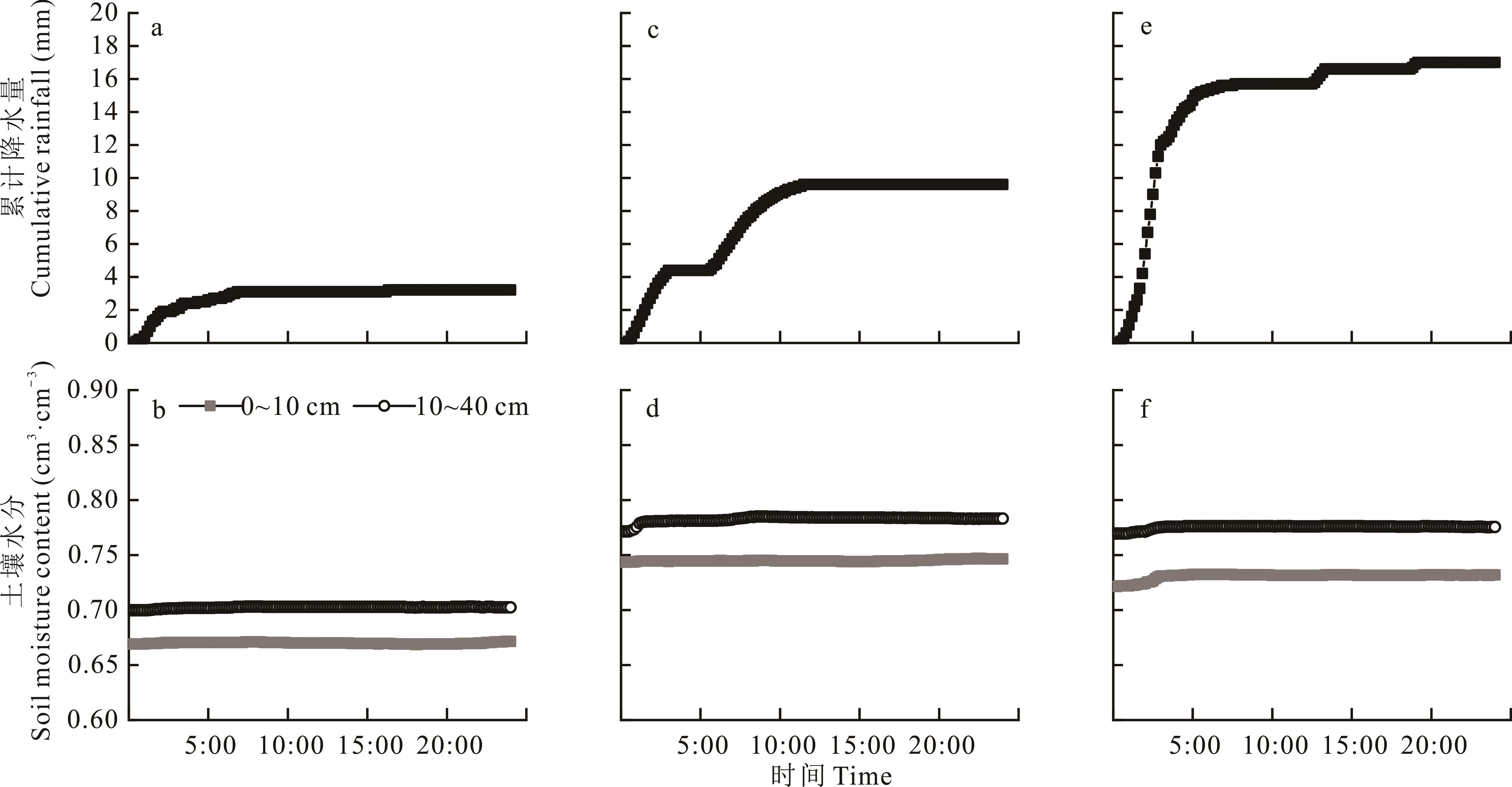
图4 沼泽草甸入渗过程土壤剖面水分变化a与b、c与d和e与f分别为3.2、9.6和17.0 mm的降水事件及对应的土壤含水量变化。The changes of soil water content at soil profiles 0-10 cm and 10-40 cm during the individual rainfall events of 3.2 (a, b), 9.6 (c, d) and 17.0 mm (e, f), respectively.
Fig.4 The wetting front infiltration processes in the alpine swamp meadow
| 1 | Oki T, Kanae S. Global hydrological cycles and world water resources. Science, 2006, 313: 1068-1072. |
| 2 | Seneviratne S I, Corti T, Davin E L, et al. Investigating soil moisture-climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth-Science Reviews, 2010, 99(3/4): 125-161. |
| 3 | Chen M L, Zhang B W, Ren T T, et al. Responses of soil moisture to precipitation pattern change in semiarid grasslands in Inner Mongolia, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2016, 40(7): 658-668. |
| 陈敏玲, 张兵伟, 任婷婷, 等. 内蒙古半干旱草原土壤水分对降水格局变化的响应. 植物生态学报, 2016, 40(7): 658-668. | |
| 4 | Wang H M, Hou Q, Feng X Y, et al. Effect of different magnitude rainfall process on soil moisture in typical grassland of Xilinhot of Inner Mongolia. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(6): 1010-1015. |
| 王海梅, 侯琼, 冯旭宇, 等. 自然降雨过程对典型草原土壤水分的影响研究——以锡林浩特为例. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(6): 1010-1015. | |
| 5 | Li X L, Wu B, Zhang J P, et al. Dynamics of shallow soil water content in Nitraria tangutorum nebkha and response to rainfall. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(15): 5701-5708. |
| 李新乐, 吴波, 张建平, 等. 白刺沙包浅层土壤水分动态及其对不同降雨量的响应. 生态学报, 2019, 39(15): 5701-5708. | |
| 6 | Wang S, Fu B J, Gao G Y, et al. Responses of soil moisture in different land cover types to rainfall events in a re-vegetation catchment area of the Loess Plateau, China. Catena, 2013, 101: 122-128. |
| 7 | Heisler-White J L, Knapp A K, Kelly E F. Increasing precipitation event size increases aboveground net primary productivity in a semi-arid grassland. Oecologia, 2008, 158(1): 129-140. |
| 8 | Heisler-White J L, Blair J M, Kelly E F, et al. Contingent productivity responses to more extreme rainfall regimes across a grassland biome. Global Change Biology, 2009, 15(12): 2894-2904. |
| 9 | Knapp A K, Fay P A, Blair J M, et al. Rainfall variability, carbon cycling, and plant species diversity in a mesic grassland. Science, 2002, 298: 2202-2205. |
| 10 | Feng X L, Shen H Y, Li W Z, et al. Spatiotemporal changes for extreme precipitation in the wet season over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and the surroundings during 1961-2017. Plateau Meteorology, 2020, 39(4): 694-705. |
| 冯晓莉, 申红艳, 李万志, 等. 1961-2017年青藏高原暖湿季节极端降水时空变化特征. 高原气象, 2020, 39(4): 694-705. | |
| 11 | Gao Y H, Lan C, Zhang Y X. Changes in moisture flux over the Tibetan Plateau during 1979-2011 and possible mechanisms. Journal of Climate, 2014, 27(5): 1876-1893. |
| 12 | Xu J W, Gao Y H, Peng B F, et al. Change characteristics of precipitation and its cause during 1979-2016 over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Plateau Meteorology, 2020, 39(2): 234-244. |
| 许建伟, 高艳红, 彭保发, 等. 1979-2016年青藏高原降水的变化特征及成因分析. 高原气象, 2020, 39(2): 234-244. | |
| 13 | Wang J Y, Chang X X, Ge S L, et al. Vertical distribution of the vegetation and water and heat conditions of Qilian Mountain (northern slope). Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2001, 16(S1): 1-3. |
| 王金叶, 常学向, 葛双兰, 等. 祁连山(北坡)水热状况与植被垂直分布. 西北林学院学报, 2001, 16(S1): 1-3. | |
| 14 | Xing Y, Jiang Q G, Li W Q, et al. Landscape spatial patterns changes of the wetland in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2009, 18(3): 1010-1015. |
| 邢宇, 姜琦刚, 李文庆, 等. 青藏高原湿地景观空间格局的变化. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(3): 1010-1015. | |
| 15 | Li H M, Li L, Xiao H B, et al. Influences of different grades precipitation on the drought release in alpine grassland. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(1): 10-21. |
| 李红梅, 李林, 肖宏斌, 等. 高寒草原不同量级降水对干旱解除的影响. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(1): 10-21. | |
| 16 | Wang G X, Li Y S, Wang Y B, et al. Typical alpine wetland system changes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in recent 40 years. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2007(5): 35-45. |
| 王根绪, 李元寿, 王一博, 等. 近40年来青藏高原典型高寒湿地系统的动态变化. 地理学报, 2007(5): 35-45. | |
| 17 | Li H L, Xu D H, Du G Z. Effect of change of plant community composition along degradation gradients on water conditions in an alpine swamp wetland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2012, 36(5): 403-410. |
| 李宏林, 徐当会, 杜国祯. 青藏高原高寒沼泽湿地在退化梯度上植物群落组成的改变对湿地水分状况的影响. 植物生态学报, 2012, 36(5): 403-410. | |
| 18 | He Z B, Zhao W Z, Liu H, et al. The response of soil moisture to rainfall event size in subalpine grassland and meadows in a semi-arid mountain range: A case study in Northwestern China’s Qilian Mountains. Journal of Hydrology, 2012, 420: 183-190. |
| 19 | Zhu X C, Shao M A, Zhu J T, et al. Temporal stability of surface soil moisture in alpine meadow ecosystem on Northern Tibetan Plateau. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(8): 212-218. |
| 朱绪超, 邵明安, 朱军涛, 等. 高寒草甸生态系统表层土壤水分时间稳定性研究. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(8): 212-218. | |
| 20 | Ma F L, Yang Y S, Wang J B, et al. Temporal heterogeneity and dominant factors of soil water content in the grassland in the Northern Qinghai Province. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(4): 178-183. |
| 马扶林, 杨永胜, 王军邦, 等. 青海北部草地水分时间异质性及主导因素. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(4): 178-183. | |
| 21 | Wang X P, Cui Y, Pan Y X, et al. Effects of rainfall characteristics on infiltration and redistribution patterns in revegetation-stabilized desert ecosystems. Journal of Hydrology, 2008, 358(1/2): 134-143. |
| 22 | Xiao Q L, Huang M B, Shao M A, et al. Infiltration and drainage processes of different textural soil moisture in middle reaches of Heihe River Basin. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(2): 124-131. |
| 肖庆礼, 黄明斌, 邵明安, 等. 黑河中游绿洲不同质地土壤水分的入渗与再分布. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(2): 124-131. | |
| 23 | Schwinning S, Sala O E. Hierarchy of responses to resource pulses in arid and semi-arid ecosystems. Oecologia, 2004, 141(2): 211-220. |
| 24 | Huxman T E, Snyder K A, Tissue D, et al. Precipitation pulses and carbon fluxes in semiarid and arid ecosystems. Oecologia, 2004, 141(2): 254-268. |
| 25 | Thomey M L, Collins S L, Vargas R, et al. Effect of precipitation variability on net primary production and soil respiration in a Chihuahuan desert grassland. Global Change Biology, 2011, 17(4): 1505-1515. |
| 26 | Li D F, Shao M A. Temporal stability of soil water storage in three landscapes in the middle reaches of the Heihe River, Northwestern China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 73: 3095-3107. |
| 27 | Lin S, Wang L, Li Y H, et al. Soil moisture characteristic of typical standing artificial forests in loess area of the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(18): 6610-6621. |
| 林莎, 王莉, 李远航, 等. 青藏高原东北缘黄土区典型立地人工林分土壤水分特性研究. 生态学报, 2019, 39(18): 6610-6621. | |
| 28 | Song A Y, Dong L S, Liu S R, et al. Soil infiltration characteristics and its influencing factors in different subalpine meadow communities. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 128(3): 45-49. |
| 宋爱云, 董林水, 刘世荣, 等. 不同亚高山草甸群落类型的土壤入渗特征及影响因素. 水土保持研究, 2018, 128(3): 45-49. | |
| 29 | Zou Y, Chen H S, Su Y R, et al. Study on ponded water infiltration and soil water redistribution in red soil. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2005, 19(3): 174-177. |
| 邹焱, 陈洪松, 苏以荣, 等. 红壤积水入渗及土壤水分再分布规律室内模拟试验研究. 水土保持学报, 2005, 19(3): 174-177. |
| [1] | 刘佳丽, 范建容, 张茜彧, 杨超, 徐富宝, 张晓雪, 梁博. 高寒草地生长季/非生长季植被盖度遥感反演[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 15-26. |
| [2] | 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 王宏生, 鲍根生. 内生真菌对高寒草地紫花针茅凋落物分解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 150-158. |
| [3] | 付刚, 王俊皓, 李少伟, 何萍. 藏北高寒草地牧草营养品质对放牧的响应机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 38-50. |
| [4] | 南志标, 王彦荣, 聂斌, 李春杰, 张卫国, 夏超. 春箭筈豌豆新品种“兰箭3号”选育与特性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 111-120. |
| [5] | 吴瑞, 刘文辉, 张永超, 秦燕, 魏小星, 刘敏洁. 青藏高原老芒麦落粒性及农艺性状相关性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 130-139. |
| [6] | 张茹, 李建平, 彭文栋, 王芳, 李志刚. 柠条枝条覆盖对宁夏荒漠草原土壤水热及补播牧草生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 58-67. |
| [7] | 韩福贵, 满多清, 郑庆钟, 赵艳丽, 张裕年, 肖斌, 付贵全, 杜娟. 青土湖典型湿地白刺灌丛沙堆群落物种多样性及土壤养分变化特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 36-45. |
| [8] | 李聪聪, 周亚星, 谷强, 杨明新, 朱传鲁, 彭子原, 薛凯, 赵新全, 王艳芬, 纪宝明, 张静. 三江源区典型高寒草地丛枝菌根真菌多样性及构建机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 46-58. |
| [9] | 陈红, 马文明, 周青平, 杨智, 刘超文, 刘金秋, 杜中曼. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体稳定性及其铁铝氧化物分异的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 73-84. |
| [10] | 马千虎, 张学梅, 王自奎, 杨惠敏. 基于APSIM模型的高寒地区燕麦灌溉制度优化[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 1-10. |
| [11] | 邱月, 吴鹏飞, 魏雪. 三种人工草地小型土壤节肢动物群落多样性动态及其差异[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 21-32. |
| [12] | 于露, 周玉蓉, 赵亚楠, 郭天斗, 孙忠超, 王红梅. 荒漠草原土壤种子库对灌丛引入和降水梯度的响应特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 41-50. |
| [13] | 高丽敏, 苏晶, 田倩, 沈益新. 施氮对不同水分条件下紫花苜蓿氮素吸收及根系固氮酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 130-136. |
| [14] | 杨阳, 田莉华, 田浩琦, 孙怀恩, 赵景学, 周青平. 增温对川西北高寒草甸草场植物凋落物分解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 35-46. |
| [15] | 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 鲍根生, 王宏生. 狼毒防除对高寒草地群落植物养分重吸收的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 47-57. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||