

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 168-178.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023012
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
徐宗昌1,5( ), 鲁雪莉1,5, 魏云冲2, 孟晨1,5, 张梦超1,3, 张缘杨1,5, 王萌2, 王菊英4, 张成省1,5, 李义强1,5(
), 鲁雪莉1,5, 魏云冲2, 孟晨1,5, 张梦超1,3, 张缘杨1,5, 王萌2, 王菊英4, 张成省1,5, 李义强1,5( )
)
收稿日期:2023-01-05
修回日期:2023-02-27
出版日期:2023-11-20
发布日期:2023-09-27
通讯作者:
李义强
作者简介:E-mail: liyiqiang@caas.cn基金资助:
Zong-chang XU1,5( ), Xue-li LU1,5, Yun-chong WEI2, Chen MENG1,5, Meng-chao ZHANG1,3, Yuan-yang ZHANG1,5, Meng WANG2, Ju-ying WANG4, Cheng-sheng ZHANG1,5, Yi-qiang LI1,5(
), Xue-li LU1,5, Yun-chong WEI2, Chen MENG1,5, Meng-chao ZHANG1,3, Yuan-yang ZHANG1,5, Meng WANG2, Ju-ying WANG4, Cheng-sheng ZHANG1,5, Yi-qiang LI1,5( )
)
Received:2023-01-05
Revised:2023-02-27
Online:2023-11-20
Published:2023-09-27
Contact:
Yi-qiang LI
摘要:
土壤盐渍化是制约中国农业生产的重要问题,通过对航天诱变的野大豆材料进行耐盐性评价,筛选高耐盐的野大豆材料对盐碱地的开发利用具有重要的意义。本研究对129份野大豆航天诱变SP1苗期材料用150 mmol·L-1浓度的NaCl进行盐胁迫处理,测定苗期株高、下胚轴长、下胚轴粗(茎粗)、叶绿素含量、单叶干鲜重以及叶面积等11个指标,采用主成分分析、耐盐性综合评价分析以及聚类分析等多元统计分析方法对野大豆突变材料进行苗期耐盐性评价。结果表明盐胁迫下野大豆突变材料农艺性状多态性丰富,变异系数范围为6.45%~51.78%,21 d株高、7 d株高和叶面积3个指标受盐胁迫影响较大,并且11个性状指标间存在着不同程度的相关性。以5个主成分综合指标为基础获得综合评价指标D值,根据D值筛选到高耐盐野大豆突变材料10份,耐盐材料53份,中间型材料63份以及3份不耐盐材料。生理指标检测发现过氧化物酶活性在野大豆诱变材料耐盐过程中发挥重要作用。鉴定出的耐盐材料为野大豆耐盐育种特别是栽培大豆的耐盐育种提供了优异种质资源。
徐宗昌, 鲁雪莉, 魏云冲, 孟晨, 张梦超, 张缘杨, 王萌, 王菊英, 张成省, 李义强. 航天诱变野大豆SP1群体苗期耐盐性鉴定与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 168-178.
Zong-chang XU, Xue-li LU, Yun-chong WEI, Chen MENG, Meng-chao ZHANG, Yuan-yang ZHANG, Meng WANG, Ju-ying WANG, Cheng-sheng ZHANG, Yi-qiang LI. Salt tolerance identification and evaluation of a population of wild soybean SP1 mutants at the seedling stage[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(11): 168-178.
| 指标Index | 最大值Maximum | 最小值Minimum | 极差Range | 平均值Mean | 标准差Standard deviation | 变异系数Variable coefficient (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7PH (cm) | 4.69 | 1.62 | 3.07 | 3.08 | 0.77 | 24.96 |
| 7HL (cm) | 3.55 | 1.30 | 2.25 | 2.17 | 0.48 | 22.35 |
| 7HD (cm) | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 11.09 |
| 21PH (cm) | 22.00 | 1.50 | 20.50 | 9.24 | 4.78 | 51.78 |
| 21HL (cm) | 3.53 | 1.40 | 2.13 | 2.31 | 0.52 | 22.55 |
| 21DD (cm) | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 18.19 |
| CCA (mg·L-1) | 9.13 | 6.83 | 2.30 | 8.45 | 0.55 | 6.45 |
| CCB (mg·L-1) | 5.74 | 3.89 | 1.85 | 4.60 | 0.52 | 11.20 |
| LA (cm2) | 548.12 | 203.73 | 344.39 | 332.53 | 79.92 | 24.03 |
| FWL (mg) | 102.32 | 68.25 | 34.07 | 85.00 | 12.46 | 14.66 |
| DWL (mg) | 17.09 | 12.49 | 4.60 | 14.81 | 1.66 | 11.24 |
表1 野大豆SP1群体盐胁迫下各性状变异统计
Table 1 Variation analysis of characters in SP1 population of wild soybean under salt stress
| 指标Index | 最大值Maximum | 最小值Minimum | 极差Range | 平均值Mean | 标准差Standard deviation | 变异系数Variable coefficient (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7PH (cm) | 4.69 | 1.62 | 3.07 | 3.08 | 0.77 | 24.96 |
| 7HL (cm) | 3.55 | 1.30 | 2.25 | 2.17 | 0.48 | 22.35 |
| 7HD (cm) | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 11.09 |
| 21PH (cm) | 22.00 | 1.50 | 20.50 | 9.24 | 4.78 | 51.78 |
| 21HL (cm) | 3.53 | 1.40 | 2.13 | 2.31 | 0.52 | 22.55 |
| 21DD (cm) | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 18.19 |
| CCA (mg·L-1) | 9.13 | 6.83 | 2.30 | 8.45 | 0.55 | 6.45 |
| CCB (mg·L-1) | 5.74 | 3.89 | 1.85 | 4.60 | 0.52 | 11.20 |
| LA (cm2) | 548.12 | 203.73 | 344.39 | 332.53 | 79.92 | 24.03 |
| FWL (mg) | 102.32 | 68.25 | 34.07 | 85.00 | 12.46 | 14.66 |
| DWL (mg) | 17.09 | 12.49 | 4.60 | 14.81 | 1.66 | 11.24 |
| 指标 Index | 7PH | 7HL | 7HD | 21PH | 21HL | 21DD | CCA | CCB | LA | FWL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7HL | 0.75** | |||||||||
| 7HD | -0.23 | -0.59* | ||||||||
| 21PH | 0.67* | -0.13 | -0.74** | |||||||
| 21HL | 0.41 | 0.54* | -0.11 | 0.54* | ||||||
| 21DD | 0.21 | 0.32 | 0.73** | -0.97** | -0.61* | |||||
| CCA | 0.12 | -0.12 | -0.48 | 0.11 | -0.16 | 0.21 | ||||
| CCB | -0.43 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.85** | 0.24 | 0.52* | 0.36 | |||
| LA | 0.76** | -0.31 | 0.36 | 0.55 | 0.79** | -0.19 | 0.26 | 0.52 | ||
| FWL | 0.53* | 0.86** | -0.11 | 0.41* | 0.15 | -0.74** | 0.72** | 0.32 | 0.87** | |
| DWL | 0.66* | 0.72** | -0.14 | 0.27 | 0.33 | -0.84** | 0.23 | -0.17 | 0.75** | 0.85** |
表2 野大豆SP1群体盐胁迫下各个指标相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of each index in SP1 population of wild soybean under salt stress
| 指标 Index | 7PH | 7HL | 7HD | 21PH | 21HL | 21DD | CCA | CCB | LA | FWL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7HL | 0.75** | |||||||||
| 7HD | -0.23 | -0.59* | ||||||||
| 21PH | 0.67* | -0.13 | -0.74** | |||||||
| 21HL | 0.41 | 0.54* | -0.11 | 0.54* | ||||||
| 21DD | 0.21 | 0.32 | 0.73** | -0.97** | -0.61* | |||||
| CCA | 0.12 | -0.12 | -0.48 | 0.11 | -0.16 | 0.21 | ||||
| CCB | -0.43 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.85** | 0.24 | 0.52* | 0.36 | |||
| LA | 0.76** | -0.31 | 0.36 | 0.55 | 0.79** | -0.19 | 0.26 | 0.52 | ||
| FWL | 0.53* | 0.86** | -0.11 | 0.41* | 0.15 | -0.74** | 0.72** | 0.32 | 0.87** | |
| DWL | 0.66* | 0.72** | -0.14 | 0.27 | 0.33 | -0.84** | 0.23 | -0.17 | 0.75** | 0.85** |
指标 Index | 主成分因子 Principal component factor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | |
| 7PH | 0.09 | -0.07 | 0.23 | 0.52 | 0.05 |
| 7HL | 0.28 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.39 | 0.13 |
| 7HD | -0.25 | 0.13 | 0.45 | -0.18 | -0.04 |
| 21PH | -0.34 | 0.19 | -0.01 | 0.34 | 0.24 |
| 21HL | 0.26 | -0.20 | 0.25 | -0.38 | 0.24 |
| 21DD | 0.34 | 0.05 | -0.37 | 0.04 | 0.13 |
| CCA | -0.14 | -0.24 | -0.38 | 0.14 | 0.29 |
| CCB | 0.08 | 0.40 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.33 |
| LA | -0.14 | 0.32 | -0.31 | -0.14 | -0.28 |
| FWL | 0.24 | 0.33 | -0.01 | -0.03 | -0.37 |
| DWL | 0.01 | -0.23 | 0.06 | 0.30 | -0.62 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 6.81 | 3.71 | 2.36 | 4.17 | 1.06 |
| 贡献率Contribution rate (%) | 36.49 | 15.56 | 12.36 | 16.67 | 10.64 |
| 累计贡献率Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 36.49 | 52.05 | 64.41 | 81.08 | 91.72 |
表3 前5个主成分的特征值及特征向量描述
Table 3 Eigen values and eigenvectors of the first five principal components
指标 Index | 主成分因子 Principal component factor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | |
| 7PH | 0.09 | -0.07 | 0.23 | 0.52 | 0.05 |
| 7HL | 0.28 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.39 | 0.13 |
| 7HD | -0.25 | 0.13 | 0.45 | -0.18 | -0.04 |
| 21PH | -0.34 | 0.19 | -0.01 | 0.34 | 0.24 |
| 21HL | 0.26 | -0.20 | 0.25 | -0.38 | 0.24 |
| 21DD | 0.34 | 0.05 | -0.37 | 0.04 | 0.13 |
| CCA | -0.14 | -0.24 | -0.38 | 0.14 | 0.29 |
| CCB | 0.08 | 0.40 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.33 |
| LA | -0.14 | 0.32 | -0.31 | -0.14 | -0.28 |
| FWL | 0.24 | 0.33 | -0.01 | -0.03 | -0.37 |
| DWL | 0.01 | -0.23 | 0.06 | 0.30 | -0.62 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 6.81 | 3.71 | 2.36 | 4.17 | 1.06 |
| 贡献率Contribution rate (%) | 36.49 | 15.56 | 12.36 | 16.67 | 10.64 |
| 累计贡献率Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 36.49 | 52.05 | 64.41 | 81.08 | 91.72 |
| 株系Strain | D值 D value | 排名Rank | 耐盐等级 Salt tolerance class | 聚类 Clustering | 株系Strain | D值 D value | 排名Rank | 耐盐等级 Salt tolerance class | 聚类 Clustering |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP1-1 | 0.6229 | 37 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-66 | 0.7135 | 17 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-2 | 0.5601 | 47 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-67 | 0.5843 | 42 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-3 | 0.3598 | 98 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-68 | 0.6676 | 25 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-4 | 0.3480 | 100 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-69 | 0.5255 | 55 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-5 | 0.4847 | 66 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-70 | 0.6432 | 32 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-6 | 0.3404 | 104 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-71 | 0.7192 | 14 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-7 | 0.3622 | 97 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-72 | 0.5888 | 41 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-8 | 0.3746 | 90 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-73 | 0.3633 | 96 | 中间型Intermediate type | IV |
| SP1-9 | 0.4559 | 79 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-74 | 0.2876 | 114 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-10 | 0.4577 | 78 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-75 | 0.4414 | 82 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-11 | 0.3847 | 89 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-76 | 0.6373 | 33 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | III |
| SP1-12 | 0.2757 | 119 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-77 | 0.3260 | 108 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-13 | 0.2772 | 118 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-78 | 0.5218 | 58 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-14 | 0.2626 | 120 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-79 | 0.5927 | 40 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-15 | 0.2822 | 117 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-80 | 0.5477 | 50 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-16 | 0.3421 | 101 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-81 | 0.5031 | 62 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-17 | 0.4758 | 71 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-82 | 0.3211 | 109 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-18 | 0.2948 | 113 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-83 | 0.4403 | 83 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-19 | 0.5093 | 61 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-84 | 0.3636 | 95 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-20 | 0.6152 | 38 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-85 | 0.4728 | 73 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-21 | 0.5510 | 48 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-86 | 0.3695 | 93 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-22 | 0.7257 | 13 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-87 | 0.3407 | 103 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-23 | 0.6890 | 23 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-88 | 0.5386 | 52 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | III |
| SP1-24 | 0.7327 | 12 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-89 | 0.4092 | 86 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-25 | 0.5336 | 53 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-90 | 0.4602 | 76 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-26 | 0.6592 | 28 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-91 | 0.2594 | 121 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-27 | 0.8893 | 3 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I | SP1-92 | 0.2975 | 112 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-28 | 0.7582 | 10 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I | SP1-93 | 0.4834 | 67 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-29 | 0.8920 | 2 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I | SP1-94 | 0.3310 | 106 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-30 | 0.2340 | 126 | 不耐盐Salt sensitivity | II | SP1-95 | 0.3685 | 94 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-31 | 0.1890 | 128 | 不耐盐Salt sensitivity | II | SP1-96 | 0.2555 | 122 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-32 | 0.3410 | 102 | 中间型Intermediate type | II | SP1-97 | 0.4901 | 63 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-33 | 0.8981 | 1 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | IV | SP1-98 | 0.4591 | 77 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-34 | 0.7777 | 8 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | IV | SP1-99 | 0.2975 | 111 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-35 | 0.5144 | 60 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-100 | 0.2532 | 124 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-36 | 0.6296 | 35 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-101 | 0.2539 | 123 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-37 | 0.5256 | 54 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-102 | 0.3993 | 88 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-38 | 0.4045 | 87 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-103 | 0.3206 | 110 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-39 | 0.6759 | 24 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-104 | 0.4745 | 72 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-40 | 0.2170 | 127 | 不耐盐Salt sensitivity | II | SP1-105 | 0.5699 | 45 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-41 | 0.3719 | 92 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-106 | 0.5790 | 43 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-42 | 0.4539 | 80 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-107 | 0.6973 | 20 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-43 | 0.4880 | 64 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-108 | 0.5983 | 39 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-44 | 0.4833 | 68 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-109 | 0.5161 | 59 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-45 | 0.2834 | 116 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-110 | 0.5161 | 59 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-46 | 0.4266 | 84 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-111 | 0.5494 | 49 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-47 | 0.4778 | 70 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-112 | 0.5241 | 57 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-48 | 0.4497 | 81 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-113 | 0.6659 | 26 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-49 | 0.3731 | 91 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-114 | 0.6961 | 21 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-50 | 0.3550 | 99 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-115 | 0.7685 | 9 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-51 | 0.3294 | 107 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-116 | 0.7913 | 6 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-52 | 0.4213 | 85 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-117 | 0.7041 | 19 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-53 | 0.2505 | 125 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-118 | 0.7786 | 7 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-54 | 0.4787 | 69 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-119 | 0.5248 | 56 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-55 | 0.4656 | 75 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-120 | 0.6519 | 30 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-56 | 0.8648 | 4 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I | SP1-121 | 0.6657 | 27 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-57 | 0.8087 | 5 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I | SP1-122 | 0.7180 | 15 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-58 | 0.5428 | 51 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-123 | 0.7078 | 18 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-59 | 0.6246 | 36 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-124 | 0.4724 | 74 | 中间型Intermediate type | IV |
| SP1-60 | 0.5680 | 46 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-125 | 0.3340 | 105 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-61 | 0.7451 | 11 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-126 | 0.2854 | 115 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-62 | 0.7144 | 16 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-127 | 0.5715 | 44 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-63 | 0.6555 | 29 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-128 | 0.6451 | 31 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-64 | 0.6307 | 34 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-129 | 0.4878 | 65 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-65 | 0.6923 | 22 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
表4 野大豆不同突变株系耐盐性综合评价D值及耐盐等级分类
Table 4 D-value and classification classes of salt tolerance of different mutants of wild soybean
| 株系Strain | D值 D value | 排名Rank | 耐盐等级 Salt tolerance class | 聚类 Clustering | 株系Strain | D值 D value | 排名Rank | 耐盐等级 Salt tolerance class | 聚类 Clustering |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP1-1 | 0.6229 | 37 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-66 | 0.7135 | 17 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-2 | 0.5601 | 47 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-67 | 0.5843 | 42 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-3 | 0.3598 | 98 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-68 | 0.6676 | 25 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-4 | 0.3480 | 100 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-69 | 0.5255 | 55 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-5 | 0.4847 | 66 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-70 | 0.6432 | 32 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-6 | 0.3404 | 104 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-71 | 0.7192 | 14 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-7 | 0.3622 | 97 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-72 | 0.5888 | 41 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-8 | 0.3746 | 90 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-73 | 0.3633 | 96 | 中间型Intermediate type | IV |
| SP1-9 | 0.4559 | 79 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-74 | 0.2876 | 114 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-10 | 0.4577 | 78 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-75 | 0.4414 | 82 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-11 | 0.3847 | 89 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-76 | 0.6373 | 33 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | III |
| SP1-12 | 0.2757 | 119 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-77 | 0.3260 | 108 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-13 | 0.2772 | 118 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-78 | 0.5218 | 58 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-14 | 0.2626 | 120 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-79 | 0.5927 | 40 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-15 | 0.2822 | 117 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-80 | 0.5477 | 50 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-16 | 0.3421 | 101 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-81 | 0.5031 | 62 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-17 | 0.4758 | 71 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-82 | 0.3211 | 109 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-18 | 0.2948 | 113 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-83 | 0.4403 | 83 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-19 | 0.5093 | 61 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-84 | 0.3636 | 95 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-20 | 0.6152 | 38 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-85 | 0.4728 | 73 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-21 | 0.5510 | 48 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-86 | 0.3695 | 93 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-22 | 0.7257 | 13 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-87 | 0.3407 | 103 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-23 | 0.6890 | 23 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-88 | 0.5386 | 52 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | III |
| SP1-24 | 0.7327 | 12 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-89 | 0.4092 | 86 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-25 | 0.5336 | 53 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-90 | 0.4602 | 76 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-26 | 0.6592 | 28 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-91 | 0.2594 | 121 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-27 | 0.8893 | 3 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I | SP1-92 | 0.2975 | 112 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-28 | 0.7582 | 10 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I | SP1-93 | 0.4834 | 67 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-29 | 0.8920 | 2 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I | SP1-94 | 0.3310 | 106 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-30 | 0.2340 | 126 | 不耐盐Salt sensitivity | II | SP1-95 | 0.3685 | 94 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-31 | 0.1890 | 128 | 不耐盐Salt sensitivity | II | SP1-96 | 0.2555 | 122 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-32 | 0.3410 | 102 | 中间型Intermediate type | II | SP1-97 | 0.4901 | 63 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-33 | 0.8981 | 1 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | IV | SP1-98 | 0.4591 | 77 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-34 | 0.7777 | 8 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | IV | SP1-99 | 0.2975 | 111 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-35 | 0.5144 | 60 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-100 | 0.2532 | 124 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-36 | 0.6296 | 35 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-101 | 0.2539 | 123 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-37 | 0.5256 | 54 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-102 | 0.3993 | 88 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-38 | 0.4045 | 87 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-103 | 0.3206 | 110 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-39 | 0.6759 | 24 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-104 | 0.4745 | 72 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-40 | 0.2170 | 127 | 不耐盐Salt sensitivity | II | SP1-105 | 0.5699 | 45 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-41 | 0.3719 | 92 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-106 | 0.5790 | 43 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-42 | 0.4539 | 80 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-107 | 0.6973 | 20 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-43 | 0.4880 | 64 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-108 | 0.5983 | 39 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-44 | 0.4833 | 68 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-109 | 0.5161 | 59 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-45 | 0.2834 | 116 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-110 | 0.5161 | 59 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-46 | 0.4266 | 84 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-111 | 0.5494 | 49 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-47 | 0.4778 | 70 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-112 | 0.5241 | 57 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-48 | 0.4497 | 81 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-113 | 0.6659 | 26 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-49 | 0.3731 | 91 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-114 | 0.6961 | 21 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-50 | 0.3550 | 99 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-115 | 0.7685 | 9 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-51 | 0.3294 | 107 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-116 | 0.7913 | 6 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-52 | 0.4213 | 85 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-117 | 0.7041 | 19 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-53 | 0.2505 | 125 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-118 | 0.7786 | 7 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I |
| SP1-54 | 0.4787 | 69 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-119 | 0.5248 | 56 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-55 | 0.4656 | 75 | 中间型Intermediate type | III | SP1-120 | 0.6519 | 30 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-56 | 0.8648 | 4 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I | SP1-121 | 0.6657 | 27 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-57 | 0.8087 | 5 | 高耐盐High salt tolerance | I | SP1-122 | 0.7180 | 15 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-58 | 0.5428 | 51 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-123 | 0.7078 | 18 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-59 | 0.6246 | 36 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-124 | 0.4724 | 74 | 中间型Intermediate type | IV |
| SP1-60 | 0.5680 | 46 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-125 | 0.3340 | 105 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-61 | 0.7451 | 11 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-126 | 0.2854 | 115 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-62 | 0.7144 | 16 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | I | SP1-127 | 0.5715 | 44 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-63 | 0.6555 | 29 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-128 | 0.6451 | 31 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |
| SP1-64 | 0.6307 | 34 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV | SP1-129 | 0.4878 | 65 | 中间型Intermediate type | III |
| SP1-65 | 0.6923 | 22 | 耐盐Salt tolerance | IV |

图1 129份野大豆材料D值聚类分析绿色标注为I类,D值为0.5093~0.8930,主要是耐盐和高耐盐材料The green line represented class I, and the D value was between 0.5093 to 0.8930, which were mainly salt tolerance and high salt tolerantce materials;黄色标注为II类,D值为0.1890~0.3410,主要是不耐盐材料The yellow line represented class II, and the D value was between 0.1890 to 0.3410, which were mainly salt sensitivity materials;红色标注为III类,D值为0.2505~0.6373,主要是中间型材料Class III was marked in red, with D values ranging from 0.2505 to 0.6373, which were mainly materials with intermediate type;蓝色标注为IV类,D值为0.3633~0.8981,主要是耐盐材料Blue was labeled as class IV, D value was between 0.3633 to 0.8981, which were mainly salt tolerance materials.
Fig.1 D-value cluster of 129 wild soybean materials
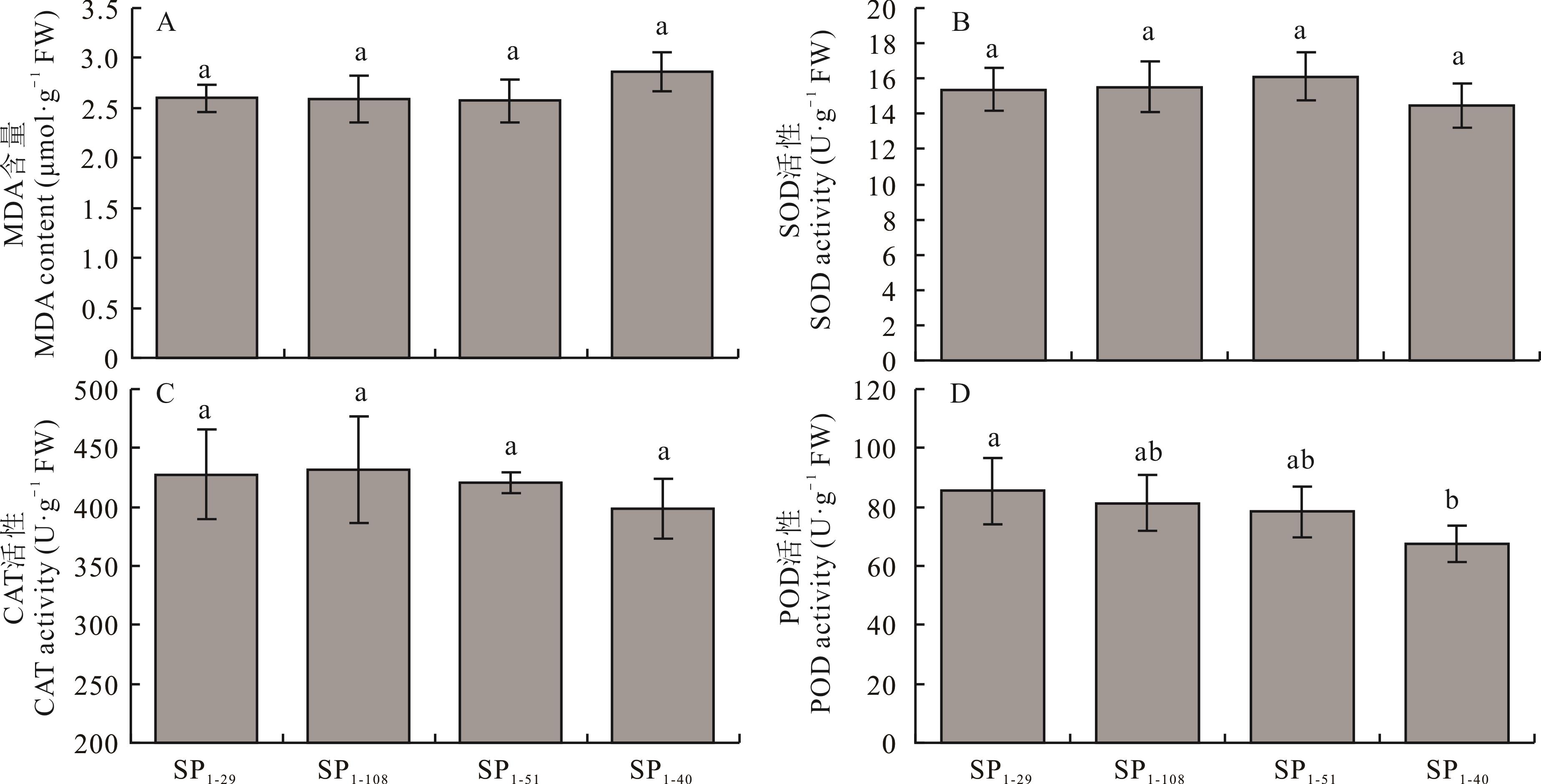
图2 代表性诱变个体生理指标测定不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平上差异显著。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05.
Fig.2 Physiological indexes of representative mutagenic individuals
| 1 | Munns R M, Tester M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2008, 59: 651-681. |
| 2 | Shahid S A, Zaman M, Heng L. Soil salinity: Historical perspectives and a world overview of the problem//Guideline for salinity assessment, mitigation and adaptation using nuclear and related techniques.Cham, Switzerland: Springer, 2018: 43-53. |
| 3 | Wang J L, Huang X J, Zhong T Y, et al. Review on sustainable utilization of salt-affected land. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2011, 66(5): 673-684. |
| 王佳丽, 黄贤金, 钟太洋, 等. 盐碱地可持续利用研究综述. 地理学报, 2011, 66(5): 673-684. | |
| 4 | Yang M F, Yao H J, Wu S N, et al. Application progress on spaceflight mutation breeding in our country. Northern Rice, 2014, 44(6): 78-80. |
| 杨明飞, 姚红军, 吴苏霓, 等. 我国航天诱变技术在育种上的应用进展. 北方水稻, 2014, 44(6): 78-80. | |
| 5 | Chen Z Q, Zhou D H, Guo T, et al. Development and prospect of plant space breeding. Satellite Application, 2021, 12: 19-24. |
| 陈志强, 周丹华, 郭涛, 等. 植物航天育种的发展及其展望. 卫星应用, 2021, 12: 19-24. | |
| 6 | Kostina L, Anikeeva I, Vaulina E. The influence of space flight factors on viability and mutability of plants. Advances in Space Research, 1984, 4(10): 65-70. |
| 7 | Yang H S, Chang G Z, Bao W S, et al. Morphological variation of space mutation in alfalfas. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(5): 222-228. |
| 杨红善, 常根柱, 包文生, 等. 紫花苜蓿航天诱变田间形态学变异研究. 草业学报, 2012, 21(5): 222-228. | |
| 8 | Yang H S, Wang Y R, Chang G Z, et al. A study on the space mutation of forages. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2015, 37(1): 104-110. |
| 杨红善, 王彦荣, 常根柱, 等. 牧草的航天诱变研究. 中国草地学报, 2015, 37(1): 104-110. | |
| 9 | Zhou M J, Shi F F, Kang M, et al. Research progress on the effects of space breeding technology on medicinal plants. Chinese Medicine Modern Distance Education of China, 2019, 17(20): 129-131. |
| 周孟焦, 史芳芳, 康明, 等. 航天育种技术对药用植物影响的研究进展. 中国中医药现代远程教育, 2019, 17(20): 129-131. | |
| 10 | Cui B B, Sun Y H, Li Y. Research progress on the space-flight mutation breeding of woody plant. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 27(12): 1853-1857. |
| 崔彬彬, 孙宇涵, 李云. 木本植物航天诱变育种研究进展. 核农学报, 2013, 27(12): 1853-1857. | |
| 11 | Li M L, Zheng L. A study on the major components and feeding value of Wuhe Glycine soja seed. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2011, 20(4): 137-142. |
| 李孟良, 郑琳. 五河野生大豆种子营养成分及饲用价值研究. 草业学报, 2011, 20(4): 137-142. | |
| 12 | Chen L L, Wang M J, He L J, et al. Report on breeding and product comparison of “S001 hybrid wild soybean”. Grassland and Prataculture, 2016, 28(3): 30-33. |
| 陈丽丽, 王明玖, 何丽君, 等. “S001草实兼用杂交野大豆”品种选育及品比试验研究报告. 草原与草业, 2016, 28(3): 30-33. | |
| 13 | Zheng W, Guo T, Wang Z X, et al. Research progress on the space-flight mutation breeding of soybean. Journal of Radiation Research and Radiation Process, 2015, 33(5): 1-9. |
| 郑伟, 郭泰, 王志新, 等. 大豆航天育种研究进展. 辐射研究与辐射工艺学报, 2015, 33(5): 1-9. | |
| 14 | Goulden C H. Problems in plant selection. Edinburgh: Proceeding of the Seventh Genetics Congress, 1939: 132-133. |
| 15 | Xue X D, Dong X Y, Duan Y X, et al. A comparison of salt resistance of three kinds of Zoysia at different salt concentrations. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(6): 315-320. |
| 薛秀栋, 董晓颖, 段艳欣, 等. 不同盐浓度下3种结缕草的耐盐性比较研究. 草业学报, 2013, 22(6): 315-320. | |
| 16 | Xia C Z, Zhang L H. Molecular marker technique in space mutation breeding. Letters in Biotechnology, 2006, 17(5): 814-816. |
| 夏承志, 张玲华. 空间诱变育种的分子标记技术. 生物技术通报, 2006, 17(5): 814-816. | |
| 17 | Wang R Z, Cheng C M, Hu S X, et al. Preliminary study on character variation of spring soybean carried by airship. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2001, 13(4): 62-64. |
| 王瑞珍, 程春明, 胡水秀, 等. 春大豆空间诱变性状变异研究初报. 江西农业学报, 2001, 13(4): 62-64. | |
| 18 | Deng H Q, Tang C M, Liu Z L, et al. Study on variation of main traits of upland cotton space mutation SP1-SP3. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(12): 64-74. |
| 邓惠清, 唐灿明, 刘正銮, 等. 陆地棉空间诱变SP1~SP3主要性状变异分析. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(12): 64-74. | |
| 19 | Liu X L, Ma Y S, Luan X Y, et al. Effect of space mutation on photosynthetic characteristics of soybean varieties. Soybean Science, 2011, 30(4): 606-608. |
| 刘鑫磊, 马岩松, 栾晓燕, 等. 航天诱变对大豆品种光合性状的影响. 大豆科学, 2011, 30(4): 606-608. | |
| 20 | Yu S X, Han F X, Sun J M, et al. Effect of induced mutation by space-flight on main agronomic traits and protein components in soybean. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 24(3): 453-459. |
| 于绍轩, 韩粉霞, 孙君明, 等. 空间环境对大豆主要农艺性状及蛋白品质的诱变效应. 核农学报, 2010, 24(3): 453-459. | |
| 21 | Hu L L, Wang S H, Wang L X, et al. Establishment of screening method for salt tolerant soybean at emergence stage and screening of tolerant germplasm. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(2): 367-379. |
| 胡亮亮, 王素华, 王丽侠, 等. 绿豆种质资源苗期耐盐性鉴定及耐盐种质筛选. 作物学报, 2022, 48(2): 367-379. | |
| 22 | Zhang Y M, Hu R F, Lin G Q. Screening of Glycine soja germplasm from Fujian Province for salt tolerance. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014, 30(27): 114-118. |
| 张玉梅, 胡润芳, 林国强. 福建省野生大豆耐盐种质的筛选. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30(27): 114-118. | |
| 23 | Shi L R. Comparison of anti-salinization of wild soybean in 3 different habitats. Journal of Hengshui University, 2020, 22(4): 22-26. |
| 时丽冉. 3种不同生境野大豆抗盐性比较. 衡水学院学报, 2020, 22(4): 22-26. | |
| 24 | Zhang Q, Tao M H, Li D, et al. Effects of saline-alkali stresses on seed germination of wild soybean. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2022, 43(4): 104-108. |
| 张旗, 陶梦慧, 李丹, 等. 盐碱胁迫对野生大豆种子萌发的影响. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2022, 43(4): 104-108. | |
| 25 | Zhao R H, Ding J N, Yu S P, et al. Effects of NaCl stress on physiological and chlorophyll fluorescence properties of wild soybean seedlings. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2022, 38(14): 23-29. |
| 赵如皓, 丁俊男, 于少鹏, 等. NaCl胁迫对野生大豆幼苗生理及叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(14): 23-29. | |
| 26 | Zhao L, Sun Y Y, Cao J F, et al. Screening and evaluation of salt tolerant Glycine soja germplasm in Baiyangdian. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021. [2023-02-27]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20210819.1812.017.html. |
| 赵琳, 孙永媛, 曹金锋, 等. 白洋淀耐盐性野生大豆(Glycine soja)种质筛选与评价. 分子植物育种, 2021. [2023-02-27]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20210819.1812.017.html. | |
| 27 | Kan G Z, Zhang W, Li Y K, et al. Association mapping of wild soybean (Glycine soja) seed germination under salt stress. Soybean Science, 2017, 36(5): 737-745. |
| 阚贵珍, 张威, 李亚凯, 等. 野生大豆芽期耐盐性状的关联分析. 大豆科学, 2017, 36(5): 737-745. | |
| 28 | Xiao G Z, Teng K, Li L J, et al. Antioxidant enzyme activity and gene expression in creeping bentgrass under salt stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(9): 74-82. |
| 肖国增, 滕珂, 李林洁, 等. 盐胁迫下匍匐翦股颖抗氧化酶活性及基因表达机制研究. 草业学报, 2016, 25(9): 74-82. |
| [1] | 康燕霞, 姜渊博, 齐广平, 银敏华, 马彦麟, 汪精海, 贾琼, 唐仲霞, 汪爱霞. 红豆草与无芒雀麦混播草地生产力提升的水分调控模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 115-128. |
| [2] | 冯华昊, 王涵, 周建祯, 张晗, 唐韬, 彭燕. 白三叶耐铝种质筛选及耐铝评价指标分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 100-111. |
| [3] | 曹玉莹, 苏雪萌, 周正朝, 郑群威, 岳佳辉. 黄土高原典型草本植物根-土复合体抗剪性能的空间差异性及其影响因素研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 94-105. |
| [4] | 朱丽丽, 张业猛, 李万才, 赵亚利, 李想, 陈志国. 39个我国不同生态区培育的青贮玉米品种在青海高原适应性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 68-78. |
| [5] | 王腾飞, 王斌, 邓建强, 李满有, 倪旺, 冯琴, 妥昀昀, 兰剑. 宁夏干旱区滴灌条件下拉巴豆不同播种量与甜高粱混播饲草生产性能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 30-40. |
| [6] | 李春艳, 王艳, 李欣瑞, 李英主, 李明峰, 陈丽丽, 雷雄, 闫利军, 游明鸿, 季晓菲, 张昌兵, 吴婍, 苟文龙, 李达旭, 鄢家俊, 白史且. 中国野生老芒麦形态多样性研究与种质利用潜力分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 67-79. |
| [7] | 王占军, 季波, 纪童, 蒋齐. 5种豆科牧草抗旱性研究与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 187-199. |
| [8] | 王珊珊, 谷海涛, 谢慧芳, 何绍冬, 甘长波, 卫小勇, 孔广超. 113份饲草型六倍体小黑麦种质饲草产量与品质性状的评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 192-202. |
| [9] | 李瑞强, 王玉祥, 孙玉兰, 张磊, 陈爱萍. 盐胁迫对5份无芒雀麦苗期生长和生理生化的影响及综合性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 99-111. |
| [10] | 沈吉成, 王蕾, 赵彩霞, 叶发慧, 吕士凯, 刘德梅, 刘瑞娟, 张怀刚, 陈文杰. 77份裸燕麦品种籽粒相关性状分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 156-167. |
| [11] | 陈子英, 常单娜, 韩梅, 李正鹏, 严清彪, 张久东, 周国朋, 孙小凤, 曹卫东. 47份箭筈豌豆品种(系)在青海作秋绿肥的能力评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 39-51. |
| [12] | 常利芳, 李欣, 郭慧娟, 乔麟轶, 张树伟, 陈芳, 畅志坚, 张晓军. 小偃麦衍生系表型遗传多样性分析及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 61-74. |
| [13] | 何海锋, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 许兴. 盐碱条件下施磷对柳枝稷生长发育及耐盐性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 64-74. |
| [14] | 吴廷美, 林慧龙, 范迪, 籍常婷, 赵玉婷, 魏靖琼. 冻原高山草地牧户家畜养殖规模影响因素分析——以青海省为例[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 117-126. |
| [15] | 王传旗, 刘文辉, 张永超, 周青平. 野生老芒麦苗期耐旱性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 127-136. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||