

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (4): 212-222.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024201
• 综合评述 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-06-03
修回日期:2024-08-22
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2025-02-19
通讯作者:
高英志
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: gaoyz108@nene.edu.cn基金资助:
Xue-xi MA1,2,3( ), Ying-zhi GAO1,4(
), Ying-zhi GAO1,4( )
)
Received:2024-06-03
Revised:2024-08-22
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-02-19
Contact:
Ying-zhi GAO
摘要:
草原灌丛化在全球干旱和半干旱地区广泛发生,逐渐成为生态学研究的焦点。本研究从灌丛化全球分布现状,灌丛化对降水、草地土壤水分、入渗、地表径流、蒸散发影响等方面综述了灌丛化对草地土壤水文过程影响的研究进展。灌丛化广泛发生在全球不同类型的生态系统中,且受到降水的显著影响。在干旱区增加降水抑制灌丛化发生,湿润区降水增加则促进灌丛化发生。灌丛化可以增加草地土壤水分入渗、减少地表径流量,改变草地生态系统蒸散发组分,降低水土流失的风险。未来应结合新技术和新方法,聚焦降水格局对灌丛化草地生态系统水文过程影响机理等方面的研究。本研究旨在为灌丛化草原科学合理管理提供理论支撑,以更好提升草原生态系统整体服务功能。
马学喜, 高英志. 灌丛化对草地土壤水文过程影响的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 212-222.
Xue-xi MA, Ying-zhi GAO. Impact of shrub encroachment on soil hydrological processes in grassland[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(4): 212-222.
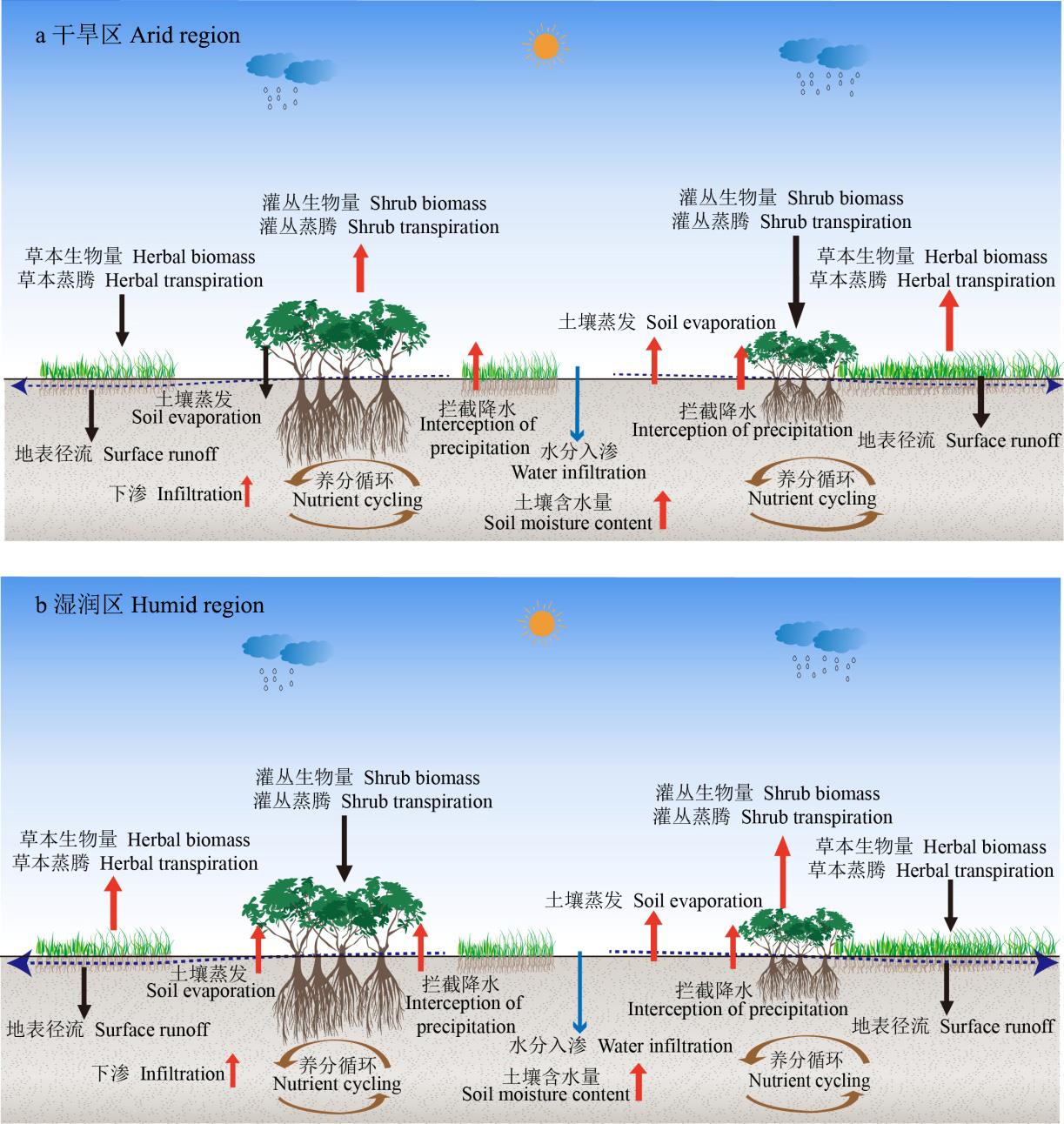
图2 灌丛化对草地生态系统水循环过程的影响红色箭头表示水循环过程相关指标增加,黑色箭头表示水循环过程相关指标减少The red arrows indicate that the water cycle process related index increases, and the black arrows indicate that the water cycle process related index decreases.
Fig. 2 The effect of shrub encroachment on water cycle processes in grassland ecosystem
| 1 | Eldridge D J, Bowker M A, Maestre F T, et al. Impacts of shrub encroachment on ecosystem structure and functioning: Towards a global synthesis. Ecology Letters, 2011, 14(7): 709-722. |
| 2 | Peng H Y, Li X Y, Tong S Y. Advance in shrub encroachment in arid and semiarid region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(2): 313-322. |
| 彭海英, 李小雁, 童绍玉. 干旱半干旱区草原灌丛化研究进展. 草业学报, 2014, 23(2): 313-322. | |
| 3 | Gaitán J J, Oliva G E, Bran D E, et al. Vegetation structure is as important as climate for explaining ecosystem function across Patagonian rangelands. Journal of Ecology, 2014, 102: 1419-1428. |
| 4 | Ding J Y, Eldridge D J. Woody encroachment: social-ecological impacts and sustainable management. Biological Reviews, 2024. DOI: 10.1111/brv.13104 . |
| 5 | Wang L, Du L T, Ma L L, et al. Effects of planted shrub encroachment on carbon storage of desert steppe ecosystem. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(1): 246-254. |
| 王乐, 杜灵通, 马龙龙, 等. 人工灌丛化对荒漠草原生态系统碳储量的影响. 生态学报, 2022, 42(1): 246-254. | |
| 6 | Yan B L, Lv S J, Wang Z W, et al. The advance of shrub encroachment in grassland and its impact on ecosystem. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(2): 95-101. |
| 闫宝龙, 吕世杰, 王忠武, 等. 草地灌丛化成因及其对生态系统的影响研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(2): 95-101. | |
| 7 | Peng H Y, Li X Y, Tong S Y. Effects of shrub (Caragana microphalla Lam.) encroachment on water redistribution and utilization in the typical steppe of Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(9): 2256-2265. |
| 彭海英, 李小雁, 童绍玉. 内蒙古典型草原灌丛化对水分再分配和利用的影响. 生态学报, 2014, 34(9): 2256-2265. | |
| 8 | Wang Y X, Chen X J, Lou S N, et al. Woody-plant encroachment in grasslands: a review of mechanisms and after effects. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(5): 219-227. |
| 王迎新, 陈先江, 娄珊宁, 等. 草原灌丛化入侵: 过程、机制和效应. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 219-227. | |
| 9 | Wilcox B P, Basant S, Olariu H, et al. Ecohydrological connectivity: A unifying framework for understanding how woody plantencroachment alters the water cycle in drylands. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2022, 10: 934535. |
| 10 | Smith M D, Wilkinsc K D, Holdrege M C, et al. Extreme drought impacts have been underestimated in grasslands and shrublands globally. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2024, 121(4): e2309881120. |
| 11 | Hu J, Cao Q H, Liu X L, et al. Research progress on the effect of the transition between shrub and grass vegetation on grassland ecosystem and its water-carbon processes. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(11): 4324-4333. |
| 胡健, 曹全恒, 刘小龙, 等. 草灌植被转变对草地生态系统及其水碳过程的影响研究进展. 生态学报, 2022, 42(11): 4324-4333. | |
| 12 | Ding J Y, Yin C C, Han Y, et al. Research progress and perspectives on the impact of shrub encroachment on ecosystem multifunctionality. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(20): 8257-8267. |
| 丁婧祎, 尹彩春, 韩逸, 等. 草原灌丛化对生态系统多功能性的影响. 生态学报, 2023, 43(20): 8257-8267. | |
| 13 | Ding J Y, Eldridge D J. Ecosystem service trade-offs resulting from woody plant removal vary with biome, encroachment stage and removal method. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 61(2): 236-248. |
| 14 | Deng Y H, Li X Y, Shi F Z, et al. Woody plant encroachment enhanced global vegetation greening and ecosystem water-use efficiency. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2021, 30(12): 2337-2353. |
| 15 | Stanton R A, Boone W W, Soto-Shoender J, et al. Shrub encroachment and vertebrate diversity: A global meta-analysis. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2018, 27: 368-379. |
| 16 | Khazieva E, Verburg P H, Pazur R. Grassland degradation by shrub encroachment: Mapping patterns and drivers of encroachment in Kyrgyzstan. Journal of Arid Environments, 2022, 207: 104849. |
| 17 | Peng H Y, Li X Y, Li G Y, et al. Shrub encroachment with increasing anthropogenic disturbance in the semiarid Inner Mongolian grasslands of China. Catena, 2013, 109: 39-48. |
| 18 | Brandt J S, Haynes M A, Kuemmerle T, et al. Regime shift on the roof of the world: Alpine meadows converting to shrublands in the southern Himalayas. Biological Conservation, 2013, 158(2): 116-127. |
| 19 | Venter Z S, Cramer M D, Hawkins H J. Drivers of woody plant encroachment over Africa. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 2272. |
| 20 | O’Connor T G, Puttick J R, Hoffman M T. Bush encroachment in southern Africa: changes and causes. African Journal of Range and Forage Science, 2014, 31(2): 67-88. |
| 21 | Knapp A K, Briggs J M, Collins S L, et al. Shrub encroachment in North American grasslands: shifts in growth form dominance rapidly alters control of ecosystem carbon inputs. Global Change Biology, 2008, 14(3): 615-623. |
| 22 | Chen D J, Mi P, Chu J, et al. Patterns and drivers of soil microbial communities along a precipitation gradient on the Mongolian Plateau. Landscape Ecology, 2014, 30: 1669-1682. |
| 23 | Zhang Y, Liu Y H, Teng L C, et al. Effects of woody proliferation on chemical structure and thermal stability of soil organic carbon in arid grasslands. Soils, 2022, 54(6): 1138-1148. |
| 张宇, 刘耘华, 滕俐闯, 等. 灌丛化对干旱区草地土壤有机碳化学结构和热稳定性的影响. 土壤, 2022, 54(6): 1138-1148. | |
| 24 | Zhou L H. Effects of shrub encroachment on community structure and soil carbon composition in northern grasslands in China. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy Sciences, 2018. |
| 周鲁宏. 灌丛化对中国北方草原群落结构和土壤碳组分的影响. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2018. | |
| 25 | Li H, Shen H, Chen L, et al. Effects of shrub encroachment on soil organic carbon in global grasslands. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 28974. |
| 26 | Acharya B S, Hao Y H, Ochsne T E, et al. Woody plant encroachment alters soil hydrological properties and reduces downward flux of water in tallgrass prairie. Plant and Soil, 2017, 414: 379-391. |
| 27 | Rivest D, Rolo V, López-Díaz L, et al. Shrub encroachment in Mediterranean silvopastoral systems: Retama sphaerocarpa and Cistus ladanifer induce contrasting effects on pasture and Quercus ilex production. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2011, 141(3/4): 447-454. |
| 28 | Chen J, Li C, Jia B, et al. Regulation of soil nitrogen cycling by shrubs in grasslands. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2024, 191: 109327. |
| 29 | Liu X L, Hu J, Zhou Q P, et al. Effects of typical shrub-encroached grassland on vegetation characteristics and soil nutrients in the Zoige Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(4): 901-908. |
| 刘小龙, 胡健, 周青平, 等. 若尔盖高原典型草地灌丛化对植被特征和土壤养分的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(4): 901-908. | |
| 30 | Knapp A, Smith L. Variation among biomes in temporal dynamics of aboveground primary production. Science, 2001, 291: 481-484. |
| 31 | Criado M G, Myers-Smith I H, Bjorkman A D, et al. Woody plant encroachment intensifies under climate change across tundra and savanna biomes. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2020, 29: 925-943. |
| 32 | Angassa A, Oba G. Relating long-term rainfall variability to cattle population dynamics in communal rangelands and a government ranch in southern Ethiopia. Agricultural Systems, 2007, 94(3): 715-725. |
| 33 | Briske D D, Fuhlendorf S D, Smeins F E. Vegetation dynamics on rangelands: a critique of the current paradigms. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 40(4): 601-614. |
| 34 | Sankaran M, Hanan N P, Scholes R J, et al. Determinants of woody cover in African savannas. Nature, 2005, 438(7069): 846-849. |
| 35 | Gao Q, Reynolds J F. Historical shrub-grass transitions in the northern Chihuahuan Desert: Modeling the effects of shifting rainfall seasonality and event size over a landscape gradient. Global Change Biology, 2003, 9(10): 1475-1493. |
| 36 | Brunsell N A, Van Vleck E S, Nosshi M, et al. Assessing the roles of fire frequency and precipitation in determining woody plant expansion in Central U.S. grasslands. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2017, 122(10): 2683-2698. |
| 37 | Good S P, Caylor K K. Climatogical determinants of woody cover in Africa. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(12): 4902-4907. |
| 38 | Heisler J L, Briggs J M, Knapp A K, et al. Direct and indirect effects of fire on shrub density and aboveground productivity in a mesic grassland. Ecology, 2004, 85(8): 2245-2257. |
| 39 | Zhu Y K, Shen H H, Akinyemi D S, et al. Increased precipitation attenuates shrub encroachment by facilitating herbaceous growth in a Mongolian grassland. Functional Ecology, 2022, 36: 2356-2366. |
| 40 | Kulmatiski A, Beard K. Woody plant encroachment facilitated by increased precipitation intensity. Nature Climate Change, 2013, 3: 833-837. |
| 41 | Liu J S, Xu X, Zhang Y, et al. Effect of rainfall interannual variability on the biomass and soil water distribution in a semiarid shrub community. Science China, Life Sciences, 2010, 40(2): 166-174. |
| 刘峻杉, 徐霞, 张勇, 等. 长期降雨波动对半干旱灌木群落生物量和土壤水分动态的效应. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2010, 40(2): 166-174. | |
| 42 | Brown J H, Valone T J, Curtin C G. Reorganization of an arid ecosystem in response to recent climate change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1997, 94(18): 9729-9733. |
| 43 | Honda E A, Duriganand G. Woody encroachment and its consequences on hydrological processes in the savannah. Philosophical Transactions of Royal Society B, 2016, 371: 20150313. |
| 44 | Schreiner-McGraw A P, Vivoni E R, Ajami H, et al. Woody plant encroachment has a larger impact than climate change on dryland water budgets. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 8112. |
| 45 | Wang L F. Simulation of the effects of precipitation and grazing on shrub encroachment in temperate grassland. Beijing: Beijing Normal University, 2021. |
| 王凌菲. 降水变化与放牧活动对典型草原灌木入侵进程影响的模拟研究. 北京: 北京师范大学, 2021. | |
| 46 | Zhu Y K. Effects of altered precipitation on plant growth and community structure in a shrub-encroached grassland. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy Sciences, 2020. |
| 朱言坤. 改变降水对灌丛化草原植物生长及群落结构的影响. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2020. | |
| 47 | Keen R M, Helliker B R, McCulloh K A, et al. Save or spend? Diverging water-use strategies of grasses and encroaching clonal shrubs. Journal of Ecology, 2024, 112(4): 870-885. |
| 48 | Caterina G L, Will R E, Turton D J, et al. Water use of Juniperus virginiana trees encroached into Mesic prairies in Oklahoma, USA. Ecohydrology, 2014, 7: 1124-1134. |
| 49 | Zou C B, Caterina G L, Will R E, et al. Canopy interception for a tallgrass prairie under Juniper encroachment. PLoS One, 2015, 10: e0141422. |
| 50 | Breshears D D, Whicker J J, Zou C B, et al. A conceptual framework for dryland aeolian sediment transport along the grassland-forest continuum: Effects of 30 woody plant canopy cover and disturbance. Geomorphology, 2009, 105: 28-38. |
| 51 | Zhao Y N, Wang H M, Li Z L, et al. Responses of spatial pattern and driving factors for soil water deficit of desert grassland-shrubland transition sites. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(4): 22-34. |
| 赵亚楠, 王红梅, 李志丽, 等. 荒漠草原灌丛转变过程土壤水分亏缺空间特征及影响因素. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 22-34. | |
| 52 | Liu Y F, Cui Z, Huang Z, et al. Shrub encroachment in alpine meadows increases the potential risk of surface soil salinization by redistributing soil water. Catena, 2022, 219: 106593. |
| 53 | Gao Z, Hu X, Li X Y. Changes in soil water retention and content during shrub encroachment process in Inner Mongolia, Northern China. Catena, 2021, 206: 105528. |
| 54 | Ma Y L, Liu Y F, López-Vicente M, et al. Divergent shift of normal alpine meadow towards shrub and degraded meadows reduces soil water retention and storage capacity. Journal of Hydrology, 2023, 625: 130109. |
| 55 | Liu Y F, Fang H, Shi J J, et al. Climate change-induced shrub encroachment changes soil hydraulic properties and inhibits herbaceous growth in alpine meadows. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2023, 340: 109629. |
| 56 | Li X, Zhang S Y, Peng H Y, et al. Soil water and temperature dynamics in shrub-encroached grasslands and climatic implications: Results from Inner Mongolia steppe ecosystem of north China. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2013, 171/172: 20-30. |
| 57 | Peng H Y, Tong S Y, Li X Y. Effects of thicketization of rangeland on soil and soil hydrological processes in Inner Mongolia. Journal of Natural Resources, 2017, 32(4): 642-653. |
| 彭海英, 童绍玉, 李小雁. 内蒙古典型草原土壤及其水文过程对灌丛化的响应. 自然资源学报, 2017, 32(4): 642-653. | |
| 58 | Yin X, Li D M, Li Y, et al. Effects of shrub encroachment on soil hydraulic properties in alpine meadow. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 36(5): 121-129. |
| 尹霞, 李冬梅, 李易, 等. 灌丛化对高寒草甸土壤水力性质的影响. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(5): 121-129. | |
| 59 | Li Q Y, Lai L M, Zhou J H, et al. Water use characteristics of main species in different shrub encroachment stages on Ordos Plateau. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(1): 89-96. |
| 李巧燕, 来利明, 周继华, 等. 鄂尔多斯高原草地灌丛化不同阶段主要植物水分利用特征. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(1): 89-96. | |
| 60 | Darrouzet-Nardi A, D'Antonio C M, Dawson T E. Depth of water acquisition by invading shrubs and resident herbs in a Sierra Nevada meadow. Plant and Soil, 2006, 285(1/2): 31-43. |
| 61 | Wang J, Fu B J, Lu N, et al. Seasonal variation in water uptake patterns of three plant species based on stable isotopes in the semi-arid Loess Plateau. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 609: 27-37. |
| 62 | Liu X, Zhuang Q L, Lai L M, et al. Soil water use sources and patterns in shrub encroachment in semiarid grasslands of Inner Mongolia. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2021, 308/309: 108579. |
| 63 | Ding J Y, Eldridge D J. The success of woody plant removal depends on encroachment stage and plant traits. Nature Plants, 2023, 9: 58-67. |
| 64 | Zou C B, Turton D J, Will R E, et al. Alteration of hydrological processes and streamflow with juniper (Juniperus virginiana) encroachment in a mesic grassland catchment. Hydrological Process, 2014, 28: 6173-6182. |
| 65 | Leite P A M, Wilcox B P, Kevin J M. Woody plant encroachment enhances soil infiltrability of a semiarid karst savanna. Environment Research Communication, 2020, 2(11): 115005. |
| 66 | Schlesinger W H, Reynolds J F, Cunningham G L, et al. Biological feedbacks in global desertification. Science, 1990, 247: 1043-1048. |
| 67 | Cui Z, Huang Z, Liu Y, et al. Natural compensation mechanism of soil water infiltration through decayed roots in semi-arid vegetation species. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 819: 151985. |
| 68 | Parizek B, Rostagno C M, Sottini R. Soil erosion as affected by shrub encroachment in northeastern Patagonia. Journal of Range Management, 2002, 55(1): 43-48. |
| 69 | Howard K S C, Eldridge D J, Soliveres S. Positive effects of shrubs on plant species diversity do not change along a gradient in grazing pressure in an arid shrubland. Basic and Applied Ecology, 2012, 13: 159-168. |
| 70 | Bhark E W, Small E E. Association between plant canopies and the spatial patterns of infiltration in shrubland and grassland of the Chihuahuan Desert, New Mexico. Ecosystems, 2003, 6(2): 185-196. |
| 71 | Eldridge D J, Wang L, Ruiz-Colmenero M. Shrub encroachment alters the spatial patterns of infiltration. Ecohydrology, 2015, 8(1): 83-93. |
| 72 | Zhang S Y, Zhang Z H, He B, et al. Interactions between shrub encroachment and water infiltration on the hillslope of a typical steppe. Ecohydrology, 2023, 16: e2489. |
| 73 | Leung A, Boldrin D, Liang T, et al. Plant age effects on soil infiltration rate during early plant establishment. Geotechnique, 2018, 68: 646-652. |
| 74 | Leite P A M, Schmidt L M, Rempe D M, et al. Woody plant encroachment modifies carbonate bedrock: field evidence for enhanced weathering and permeability. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13: 15431. |
| 75 | Hu X, Li Z C, Li X Y, et al. Influence of shrub encroachment on CT-measured soil macropore characteristics in the Inner Mongolia grassland of northern China. Soil and Tillage Research, 2015, 150: 1-9. |
| 76 | Wilcox B P. Shrub control and streamflow on rangelands: a process-based viewpoint. Journal of Range Management, 2002, 55: 318-326. |
| 77 | Qiao L, Zou C B, Stebler E, et al. Woody plant encroachment reduces annual runoff and shifts runoff mechanisms in the tallgrass prairie, USA. Water Resources Research, 2017, 53: 4838-4849. |
| 78 | Peng H Y. Spatial pattern of shrub patches and its ecohydrological mechanism at the typical steppe in Inner Mongolia. Beijing: Beijing Normal University, 2012. |
| 彭海英. 内蒙古典型草原小叶锦鸡儿灌丛空间分布格局及其生态水文机理. 北京: 北京师范大学, 2012. | |
| 79 | Li X J, Gao Y P. Effects of shrub encroachment in desert grassland on runoff and the induced nitrogen loss in southeast fringe of Tengger Desert. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(24): 7828-7835. |
| 李小军, 高永平. 腾格里沙漠东南缘沙质草地灌丛化对地表径流及氮流失的影响. 生态学报, 2012, 32(24): 7828-7835. | |
| 80 | Shen X J, Liu Y W, Liu B H, et al. Effect of shrub encroachment on land surface temperature in semi-arid areas of temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2022, 320: 108943. |
| 81 | Wang J, Xiao X, Zhang Y, et al. Enhanced gross primary production and evapotranspiration in juniper-encroached grasslands. Global Change Biology, 2018, 24: 5655-5667. |
| 82 | Wang P, Li X Y, Wang L, et al. Divergent evapotranspiration partition dynamics between shrubs and grasses in a shrub-encroached steppe ecosystem. New Phytologist, 2018, 219: 1325-1337. |
| 83 | Wang Q D, Yang W X, Huang J Y, et al. Shrub encroachment effect on the evapotranspiration and its component-A numerical simulation study of a shrub encroachment grassland in Nei Mongol, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2017, 41(3): 348-358. |
| 王芑丹, 杨温馨, 黄洁钰, 等. 灌丛化的蒸散耗水效应数值模拟研究—以内蒙古灌丛化草原为例. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(3): 348-358. | |
| 84 | Dan Y, Du L T, Wang L, et al. Effects of planted shrub encroachment on evapotranspiration and its components in desert steppe: a case study in Yanchi county, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(16): 5638-5648. |
| 丹杨, 杜灵通, 王乐, 等. 荒漠草原人工灌丛化对蒸散发及其组分的影响-以盐池县为例. 生态学报, 2020, 40(16): 5638-5648. | |
| 85 | Newman B D, Breshears D D, Gard M O. Evapotranspiration partitioning in a semiarid woodland: ecohydrologic heterogeneity and connectivity of vegetation patches. Vadose Zone Journal, 2010, 9(3): 561-572. |
| [1] | 贺世龙, 叶贺, 李静, 张雅玲, 德海山, 红梅. 不同时限氮沉降和降水变化对荒漠草原中小型土壤节肢动物群落结构与多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 140-154. |
| [2] | 赵亚楠, 王红梅, 李志丽, 张振杰, 陈彦硕, 苏荣霞. 荒漠草原灌丛转变过程土壤水分亏缺空间特征及影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 22-34. |
| [3] | 赵娅如, 曹雲翔, 杨成参, 史锋厚, 付红祥, 初磊. 人工降雨条件下高速公路植被边坡模型水文效应测试[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 24-33. |
| [4] | 张东, 侯晨, 马文明, 王长庭, 邓增卓玛, 张婷. 高寒草地不同灌丛化梯度下土壤酶活性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 79-92. |
| [5] | 李雪敏, 李同宁, 吴芝雨, 武振国. 多情景模拟下内蒙古草地生态系统服务价值时空演变[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 14-27. |
| [6] | 杨瑞杰, 何淑勤, 周树峰, 杨晶月, 金钰宪, 郑子成. 杂交粱草生长期土壤抗冲性变化特征及其根系调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 149-159. |
| [7] | 江奥, 敬路淮, 泽让东科, 田黎明. 放牧影响草地凋落物分解研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 208-220. |
| [8] | 李江文, 裴婧宏, 韩国栋, 何邦印, 李彩. 基于植物功能性状分析异常降水对不同载畜率下荒漠草原功能群多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 212-222. |
| [9] | 吴旭东, 蒋齐, 王占军, 季波, 任小玢. 降水对荒漠草原地上生物量稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 30-39. |
| [10] | 米扬, 郭蓉, 王媛, 王占军, 蒋齐, 俞鸿千, 马琨. 宁夏荒漠草原土壤细菌与真菌群落对降水变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 81-92. |
| [11] | 许政勇, 孙斌, 张王菲, 李毅夫, 闫紫钰, 岳巍, 滕思翰. 基于优化三角形植被指数(TVI)的灌丛化草原植被地上生物量遥感估测方法研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 1-14. |
| [12] | 陆姣云, 张鹤山, 田宏, 熊军波, 刘洋. 氮沉降影响草地生态系统土壤氮循环过程的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 221-234. |
| [13] | 张晓宁, 李晓丹, 年丽丽, 杨莹博, 刘学录. 基于文献计量的草地生态系统水源涵养功能研究现状[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 35-49. |
| [14] | 郭志霞, 刘任涛, 赵文智. 荒漠灌丛和土壤动物关系及对降水变化的响应研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 206-216. |
| [15] | 王春雯, 赵芳, 张晨, 解李娜, 马成仓. 小叶锦鸡儿灌丛对草地土壤固氮微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 28-40. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||