

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (9): 134-146.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024403
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-10-17
修回日期:2024-12-05
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-07-02
通讯作者:
王波
作者简介:E-mail: wangbo@xjau.edu.cn基金资助:
Yuan-yuan LIU( ), Xu WANG, Qi WEI, Li-juan CHE, Meng YUAN, Bo WANG(
), Xu WANG, Qi WEI, Li-juan CHE, Meng YUAN, Bo WANG( )
)
Received:2024-10-17
Revised:2024-12-05
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-07-02
Contact:
Bo WANG
摘要:
先前的研究表明,梭梭幼苗在生长过程中通过胁迫锻炼而获得高温、干旱等胁迫耐受性,并且14-3-3蛋白基因HaFT-9的表达受到高温和干旱胁迫的诱导,提示HaFT-9可能参与高温与干旱胁迫信号的交叉调控。为此,本研究探讨了HaFT-9在高温与干旱胁迫交叉调控作用中的功能。通过对梭梭幼苗进行高温胁迫锻炼后,再施加干旱胁迫,发现高温胁迫锻炼显著促进了HaFT-9在次级干旱胁迫下的表达。进一步的试验表明,经过高温胁迫锻炼与次级干旱胁迫处理,HaFT-9过表达的拟南芥株系表现出比野生型更高的存活率和更低的细胞死亡率。在次级干旱胁迫条件下,HaFT-9过表达株系中P5CS1、P5CS2、CAT2、CHLI1、HSP21、HsfA2及BI-1等抗逆相关基因的表达水平均显著升高。同时,过表达株系中的过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性、脯氨酸和叶绿素含量也显著增加,丙二醛(MDA)含量则显著降低,而且过表达株系的二氨基联苯胺(DAB)与硝基氮蓝四唑(NBT)染色较浅。综上所述,HaFT-9的过表达显著增强了拟南芥对次级干旱胁迫的适应性,表明HaFT-9在高温与干旱胁迫信号交叉响应中发挥了关键的调控作用。本研究为深入理解梭梭幼苗的耐逆分子机制提供了理论依据,并为保护其种质资源提供了参考。
刘媛媛, 王旭, 魏琪, 车丽娟, 袁梦, 王波. 梭梭14-3-3蛋白HaFT-9在高温-干旱胁迫信号交叉调控中的功能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 134-146.
Yuan-yuan LIU, Xu WANG, Qi WEI, Li-juan CHE, Meng YUAN, Bo WANG. The role of HaFT-9, a 14-3-3 protein from Haloxylon ammodendron, in the cross regulation of high temperature and drought stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(9): 134-146.
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物Forward primer (5′→3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Ha18SrRNA | CTCTGCCCGTTGCTCTGATGAT | CCTTGGATGTGGTAGCCGTTTC |
| HaFT-9 | TACTTTGGGTGAAGAGTCCTACA | TTTGATCCTGCATGTCTGATGT |
| P5CS1 | GATACGGATATGGCAAAGCG | CCAAGTCCAAATCGGAAACC |
| P5CS2 | GTTAAGCGTATCGTCGTCAAGGTT | CCTAAACGTCCAAGAGCCAATCT |
| CAT2 | ACATTCGTTGACCCTTTTCAC | GGCCACACACGATAACAAC |
| CDS1 | CTGCATCTCTACTGGACCTC | CCACATCCAACTCTCGAGC |
| CHLI1 | TGTTGATGGGTTGAGAGGAG | AACGGTTGCAACATCATCTG |
| DREB2a | CAACAGCAGGATTCGCTATCTG | ACATCGTCGCCATTTAGGTCA |
| HSP21 | TGGACGTCTCTCCTTTCGGATTGT | TGCACGAATCTCTGACACTCCACT |
| HsfA2 | GAGATTTTCCGGCGTGATTT | ACATCGGACCTGAAAGAGAG |
| BI-1 | ACATTCGTTGACCCTTTTCAC | GGCCACACACGATAACAAC |
| At18SrRNA | AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG | CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA |
表1 本研究所用引物
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物Forward primer (5′→3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Ha18SrRNA | CTCTGCCCGTTGCTCTGATGAT | CCTTGGATGTGGTAGCCGTTTC |
| HaFT-9 | TACTTTGGGTGAAGAGTCCTACA | TTTGATCCTGCATGTCTGATGT |
| P5CS1 | GATACGGATATGGCAAAGCG | CCAAGTCCAAATCGGAAACC |
| P5CS2 | GTTAAGCGTATCGTCGTCAAGGTT | CCTAAACGTCCAAGAGCCAATCT |
| CAT2 | ACATTCGTTGACCCTTTTCAC | GGCCACACACGATAACAAC |
| CDS1 | CTGCATCTCTACTGGACCTC | CCACATCCAACTCTCGAGC |
| CHLI1 | TGTTGATGGGTTGAGAGGAG | AACGGTTGCAACATCATCTG |
| DREB2a | CAACAGCAGGATTCGCTATCTG | ACATCGTCGCCATTTAGGTCA |
| HSP21 | TGGACGTCTCTCCTTTCGGATTGT | TGCACGAATCTCTGACACTCCACT |
| HsfA2 | GAGATTTTCCGGCGTGATTT | ACATCGGACCTGAAAGAGAG |
| BI-1 | ACATTCGTTGACCCTTTTCAC | GGCCACACACGATAACAAC |
| At18SrRNA | AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG | CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA |

图1 HaFT-9基因在高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理下的表达A:梭梭幼苗的高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理,分为CK、H、D、HD组,每个红框表示取样点;B:HaFT-9在高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理下的表达量;不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平上差异显著。A: The heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment for H. ammodendron seedlings, divided into CK, H, D and HD group, and each red box indicates a sampling point; B: Expression level of HaFT-9 under the heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment; Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05level. 下同The same below.
Fig.1 The expression of the HaFT-9 gene under the heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment

图2 高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理对拟南芥生长的影响A:拟南芥幼苗的高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理,分为CK、H、D、HD组,每个红框表示取样点;B:拟南芥成株的高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理,分为CK、H、D、HD组,每个红框表示取样点;C:拟南芥幼苗的生长表型;D:拟南芥成株的生长表型;WT为野生型拟南芥,9-4和9-37为HaFT-9过表达株系。A: The heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment for Arabidopsis seedlings, divided into group CK, H, D and HD, and each red box indicates a sampling point; B: The heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment for mature Arabidopsis, divided into CK, H, D and HD group, and each red box indicates a sampling point; C: Growth phenotype of Arabidopsis seedlings; D: Growth phenotype of mature Arabidopsis; WT refers to the wild-type Arabidopsis, while 9-4 and 9-37 are the HaFT-9 overexpression lines. 下同The same below.
Fig.2 The effects of the heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment on the growth of Arabidopsis
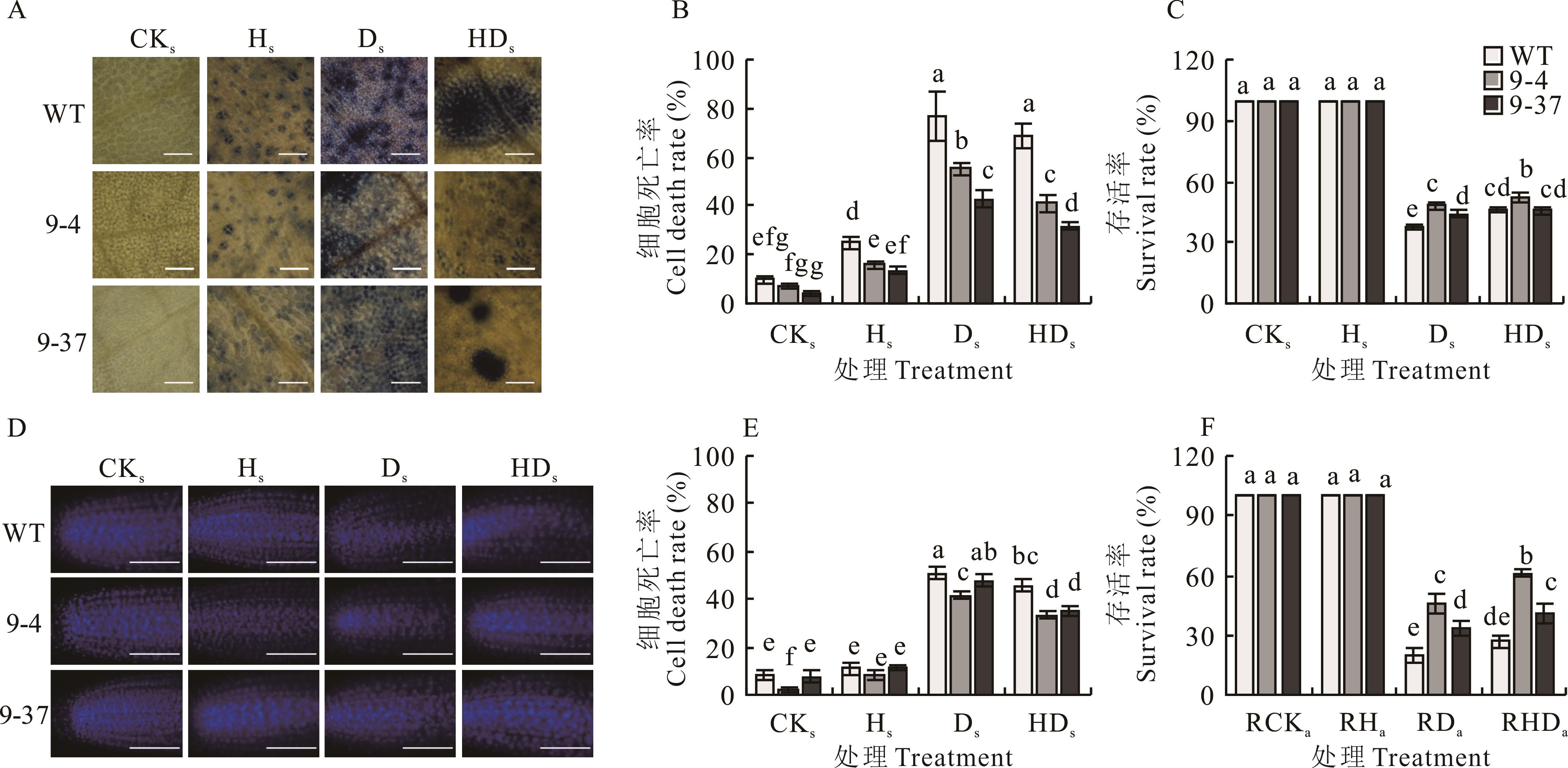
图3 高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理对拟南芥存活率及细胞死亡率的影响A:拟南芥幼苗台盼蓝染色(叶片,标尺=50 μm);B:拟南芥幼苗台盼蓝染色后叶片的细胞死亡率;C:拟南芥幼苗的存活率;D:拟南芥幼苗DAPI染色(根尖,标尺=50 μm);E:拟南芥幼苗DAPI染色后的根尖细胞死亡率;F:拟南芥成株的存活率。A: Trypan blue staining in Arabidopsis seedlings (leaf, bar=50 μm); B: Cell death rate of leaves in Arabidopsis seedlings after Trypan blue staining; C: Survival rate of Arabidopsis seedlings; D: DAPI staining in Arabidopsis seedlings(root tip, bar=50 μm); E: Cell death rate in the root tips of Arabidopsis seedlings after DAPI staining; F: Survival rate of mature Arabidopsis.
Fig.3 The effects of the heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment on the survival rate and cell death rate in Arabidopsis
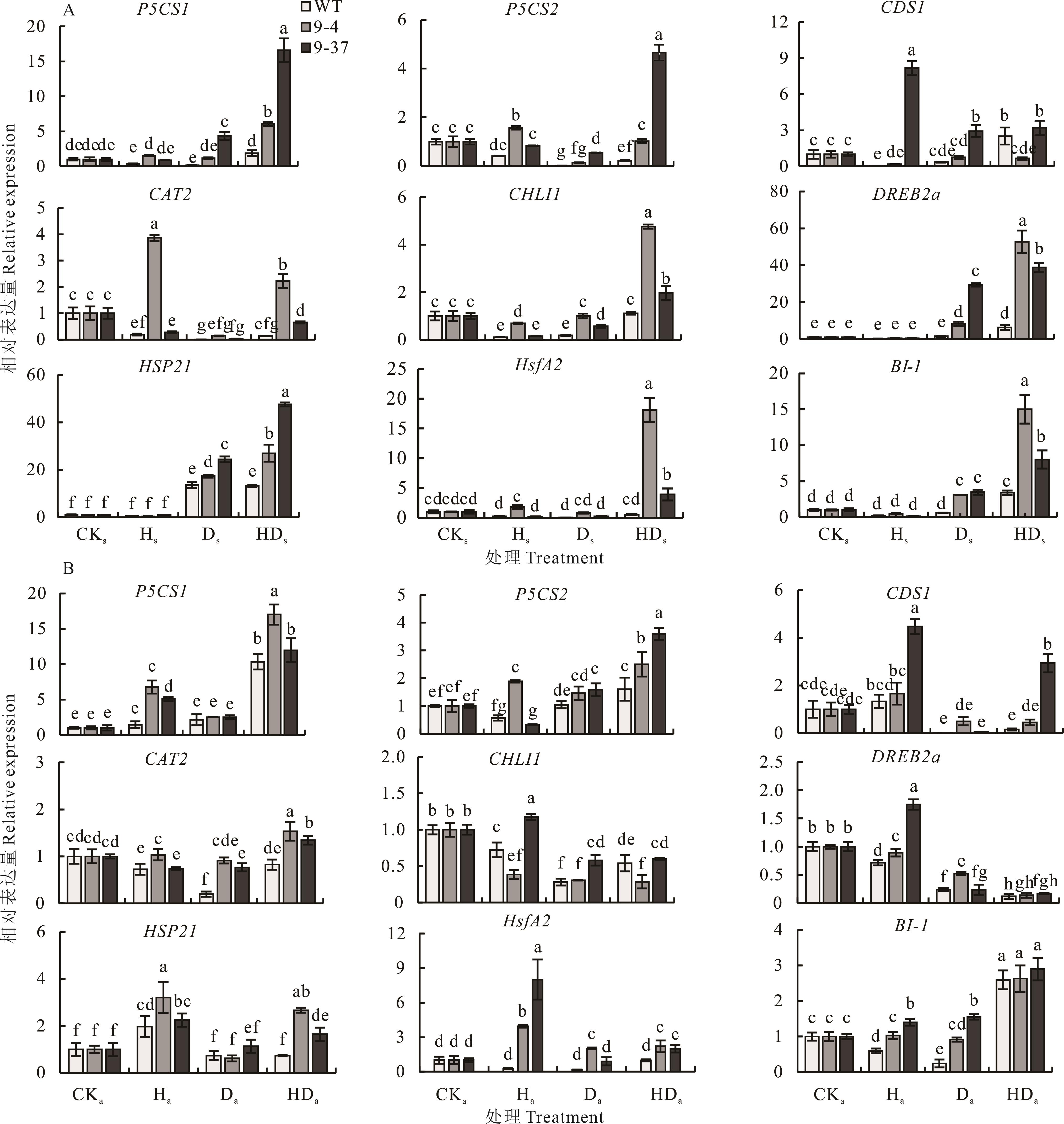
图4 拟南芥在高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理下的相关基因表达A:拟南芥幼苗在高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理下的相关基因表达;B:拟南芥成株在高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理下的相关基因表达。A: The expression of related genes in Arabidopsis seedlings under the heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment; B: The expression of related genes in mature Arabidopsis under the heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment.
Fig.4 The expression of relevant genes under the heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment in Arabidopsis

图5 高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理下拟南芥的二氨基联苯胺(DAB)与硝基氮蓝四唑(NBT)染色A、B:分别为拟南芥幼苗在高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理下的二氨基联苯胺(DAB)和硝基氮蓝四唑(NBT)染色(标尺=100 μm);C、D:分别为拟南芥成株在高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理下的二氨基联苯胺(DAB)和硝基氮蓝四唑(NBT)染色(标尺=2.5 mm)。A, B: Diaminobenzidine (DAB) and nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) staining of Arabidopsis seedlings under the heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment, respectively (Bar=100 μm); C, D: Diaminobenzidine (DAB) and nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) staining of mature Arabidopsis under the heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment, respectively (Bar=2.5 mm).
Fig.5 Diaminobenzidine (DAB) and nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) staining of Arabidopsis under the heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment
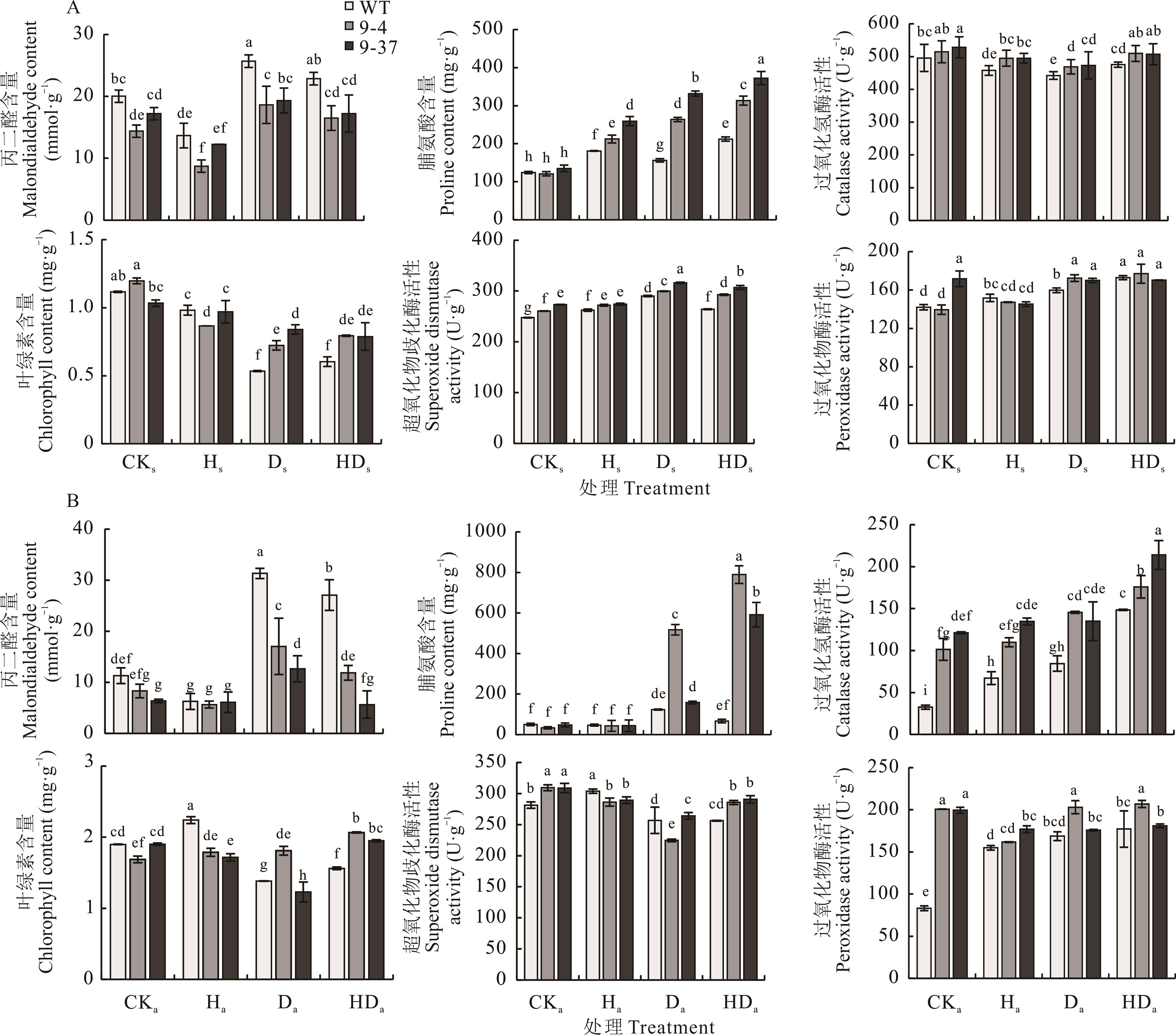
图6 高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理下拟南芥的抗氧化酶活性、脯氨酸和叶绿素含量A:高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理下拟南芥幼苗的抗氧化酶活性、脯氨酸和叶绿素含量;B:高温胁迫锻炼-次级干旱胁迫处理下拟南芥成株的抗氧化酶活性、脯氨酸和叶绿素含量。A: Antioxidant enzyme activity, proline content, and chlorophyll content under the heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment in Arabidopsis seedlings; B: Antioxidant enzyme activity, proline content, and chlorophyll content under the heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment in mature Arabidopsis.
Fig.6 Antioxidant enzyme activity, proline content, and chlorophyll content under the heat stress priming-the secondary drought stress treatment in Arabidopsis
| [1] | Paul A L, Denison F C, Schultz E R, et al. 14-3-3 phosphoprotein interaction networks-does isoform diversity present functional interaction specification? Frontiers in Plant Science, 2012, 3: 190. |
| [2] | Li X D, Wu J H, Sun F, et al. Enhanced tolerance of Arabidopsis over expressing Fa14-3-3C from tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea) to low-nitrogen stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(9): 104-112. |
| 李小冬, 吴佳海, 孙方, 等. 过量表达Fa14-3-3C促进拟南芥对低氮胁迫耐受性的研究. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 104-112. | |
| [3] | Zhou H P, Lin H X, Chen S, et al. Inhibition of the Arabidopsis salt overly sensitive pathway by 14-3-3 proteins. Plant Cell, 2014, 26(3): 1166-1182. |
| [4] | Hilker M, Schmülling T. Stress priming, memory, and signalling in plants. Plant Cell and Environment, 2019, 42(3): 753-761. |
| [5] | Liang X H, Ai F F, Zhong T X, et al. Cross adaptation under drought and low temperature stress in perennial ryegrass. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(1): 163-170. |
| 梁小红, 艾非凡, 钟天秀, 等. 多年生黑麦草对干旱-低温交叉适应的生理响应. 草业学报, 2016, 25(1): 163-170. | |
| [6] | Liu H P, Able A J, Able J A. Priming crops for the future: rewiring stress memory. Trends in Plant Science, 2022, 27(7): 699-716. |
| [7] | Gallusci P, Agius D R, Moschou P N, et al. Deep inside the epigenetic memories of stressed plants. Trends in Plant Science, 2023, 28(2): 142-153. |
| [8] | Lu Y, Lei J Q, Zeng F J, et al. Effects of salt treatments on the growth and ecophysiological characteristics of Haloxylon ammodendron. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(3): 152-159. |
| 鲁艳, 雷加强, 曾凡江, 等. NaCl处理对梭梭生长及生理生态特征的影响. 草业学报, 2014, 23(3): 152-159. | |
| [9] | Ma H, Zhang H, Ma L, et al. None-watering and tube-protecting planting technique for Haloxylon ammodendron under desert and its extension. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2014, 44(3): 248-256. |
| 麻浩, 张桦, 马林, 等. 无灌溉管件防护梭梭荒漠造林新技术及其示范推广. 中国科学(生命科学), 2014, 44(3): 248-256. | |
| [10] | Pan R, Ren W J, Liu S S, et al. Ectopic over-expression of HaFT-1, a 14-3-3 protein from Haloxylon ammodendron, enhances acquired thermotolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Molecular Biology, 2023, 112(4/5): 261-277. |
| [11] | Cao Y H, Ren W, Gao H J, et al. HaASR2 from Haloxylon ammodendron confers drought and salt tolerance in plants. Plant Science, 2023, 328: 111572. |
| [12] | Wang J. Expression patterns and functional analysis of 14-3-3 genes related to stress resistance of Haloxylon ammodendron. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 王娇. 与抗逆相关的梭梭14-3-3蛋白基因的表达模式和功能分析. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2017. | |
| [13] | Liu S S, Wang B, Zong X F, et al. Cloning and characterization analysis of HaFT-9 gene in 14-3-3 protein in Haloxylon ammodendron. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(6): 1083-1094. |
| 刘栓栓, 王波, 宗兴风, 等. 梭梭14-3-3蛋白基因HaFT-9的克隆及特性分析. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(6): 1083-1094. | |
| [14] | Wei Q. Functional analysis of heat stress memory key genes HaHsfA2a and HaFT-9 under abiotic stress in Haloxylon ammodendron. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2023. |
| 魏琪. 梭梭高温胁迫记忆关键基因HaHsfA2a与HaFT-9在非生物胁迫下的功能分析. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2023. | |
| [15] | Montero-Barrientos M, Hermosa R, Cardoza R E, et al. Transgenic expression of the Trichoderma harzianum hsp70 gene increases Arabidopsis resistance to heat and other abiotic stresses. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2010, 167(8): 659-665. |
| [16] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| [17] | Xu M, Liu J, Ayiguli A. Comparative methods on chlorophyll extraction in plant physiology experiment teaching. Experiment Science and Technology, 2018, 16(4): 129-133. |
| 徐敏, 刘君, 阿衣古力·阿布都瓦依提. 植物生理实验教学中叶绿素提取方法比较. 实验科学与技术, 2018, 16(4): 129-133. | |
| [18] | Li W Y, Chen Y F, He H, et al. Effects of high temperature exercise on growth and physiological and biochemical characters of Taxus wallichiana var. mairei under drought stress. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 55(9): 57-63. |
| 李文杨, 陈亚飞, 何辉, 等. 高温锻炼对干旱胁迫下南方红豆杉生长和生理生化指标的影响. 山东农业科学, 2023, 55(9): 57-63. | |
| [19] | Fan Z H, Zhu Y Q, Kuang W, et al. The 14-3-3 protein GRF8 modulates salt stress tolerance in apple via the WRKY18-SOS pathway. Plant Physiology, 2024, 194(3): 1906-1922. |
| [20] | Ren Y R, Yang Y Y, Zhang R, et al. MdGRF11, an apple 14-3-3 protein, acts as a positive regulator of drought and salt tolerance. Plant Science, 2019, 288: 110219. |
| [21] | Sirichandra C, Davanture M, Turk B E, et al. The Arabidopsis ABA-activated kinase OST1 phosphorylates the bZIP transcription factor ABF3 and creates a 14-3-3 binding site involved in its turnover. PLoS One, 2010, 5(11): e13935. |
| [22] | Jiang W, Tong T, Li W, et al. Molecular evolution of plant 14-3-3 proteins and function of Hv14-3-3A in stomatal regulation and drought tolerance. Plant Cell Physiology, 2023, 63(12): 1857-1872. |
| [23] | Wiese A J, Steinbachová L, Timofejeva L, et al. Arabidopsis bZIP18 and bZIP52 accumulate in nuclei following heat stress where they regulate the expression of a similar set of genes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(2): 530. |
| [24] | Liu J Z, Feng L L, Gu X T, et al. An H3K27me3 demethylase-HSFA2 regulatory loop orchestrates transgenerational thermomemory in Arabidopsis. Cell Research, 2019, 29(5): 379-390. |
| [25] | Kim J M, To T K, Seki M. An epigenetic integrator: new insights into genome regulation, environmental stress responses and developmental controls by histone deacetylase 6. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2012, 53(5): 794-800. |
| [26] | Liu M Y, Guo L Z, Yue Y S, et al. Physiological and antioxidant enzyme gene expression differences between female and male Buchloe dactyloides plants under drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(10): 93-103. |
| 刘牧野, 郭丽珠, 岳跃森, 等. 干旱胁迫下不同性别野牛草生理及抗氧化酶基因表达差异. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 93-103. | |
| [27] | Zhang J, Cheng K, Wang Y C. Analysis of the calcium-dependent protein kinase RtCDPK16 response to abiotic stress in Reaumuria trigyna. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(2): 97-109. |
| 张洁, 程凯, 王迎春. 长叶红砂钙依赖蛋白激酶RtCDPK16的非生物胁迫应答分析. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 97-109. | |
| [28] | Liu J P, Sun X J, Liao W C, et al. Involvement of OsGF14b adaptation in the drought resistance of rice plants. Rice, 2019, 12(1): 82. |
| [29] | Lukaszewicz M, Matysiak-Kata I, Aksamit A, et al. 14-3-3 protein regulation of the antioxidant capacity of transgenic potato tubers. Plant Science, 2002, 163(1): 125-130. |
| [30] | Wang L Y, Tian Y C, Shi W, et al. The miR396-GRFs module mediates the prevention of photo-oxidative damage by brassinosteroids during seedling de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2020, 32(8): 2525-2542. |
| [31] | Liu X, Challabathula D K, Quan W L, et al. Transcriptional and metabolic changes in the desiccation tolerant plant Craterostigma plantagineum during recurrent exposures to dehydration. Planta, 2019, 249(4): 1017-1035. |
| [1] | 雍嘉仪, 马霜, 马风华, 赵小娜, 张译尹, 胡海英. 干旱及复水对河北木蓝生物量分配与渗透调节特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 158-170. |
| [2] | 李慧玲, 朱永兴, 陈檬, 刘姝, 王娇, 刘奕清, 张雪梅, 马慧慧. 干旱胁迫与复水对菊芋幼苗的生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 171-184. |
| [3] | 温小月, 赵颖, 王宝强, 王贤, 朱晓林, 王义真, 魏小红. 外源NO调控干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿AP2/ERFs基因的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 154-167. |
| [4] | 曾燕霞, 陈志龙, 尚继红, 沙晓弟, 吴娟, 陈彩锦. 太空诱变对PEG-6000模拟干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿材料苗期生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 59-69. |
| [5] | 王小风, 马步东, 黄海霞, 罗永忠, 齐建伟, 邓卓. 干旱胁迫及复水对裸果木幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 93-103. |
| [6] | 王宝, 谢占玲, 郭璟, 唐永鹏, 孟清, 彭清青, 杨家宝, 董德誉, 徐鸿雁, 高太侦, 张凡, 段迎珠. 真菌发酵液浸种燕麦对其抗旱性及根际真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 126-139. |
| [7] | 张婷婷, 刘宇乐, 陈红, 许凌欣, 陈祥伟, 王恩姮, 严俊鑫. 不同外源物质对盐、碱及干旱胁迫下草木樨种子萌发、幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 122-132. |
| [8] | 魏娜, 敬文茂, 许尔文, 王荣新, 赵晶忠, 马雪娥, 张吉宇, 刘文献. 白花草木樨MaERF058基因耐旱功能验证[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 159-169. |
| [9] | 曾露婧, 王国华. 干旱及复水对荒漠绿洲过渡带一年生草本植物生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 41-57. |
| [10] | 尹仲毅, 马黎华, 李兆磊, 冯桦, 蒋先军. 高温条件对不同耕作模式紫色水稻土水、热、盐的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 80-91. |
| [11] | 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 李雯. 基于转录组测序的狗牙根抗旱根系关键代谢途径分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 186-198. |
| [12] | 李妍, 马富龙, 韩路, 王海珍. 美国‘WL’系列不同秋眠级苜蓿品种在南疆的生产性能与适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 139-149. |
| [13] | 邢静, 范文强, 王佳妮, 石凤翎. 干旱胁迫下 2个扁蓿豆品种根际细菌多样性及土壤灭菌对其生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 147-159. |
| [14] | 王雨欣, 陶佳丽, 朱慧森, 许涛, 张逸飞, 岑慧芳. 异源表达偏关苜蓿miR397-5p增强烟草干旱胁迫耐受能力[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 123-134. |
| [15] | 刘立靖, 吴静, 李纯斌, 常秀红. 2001-2020年黄土高原植被生长季干旱的时空分布[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 28-36. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||