

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (10): 85-94.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024460
收稿日期:2024-11-20
修回日期:2025-01-16
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-07-11
通讯作者:
张凡凡,孙国君
作者简介:sungj2010@sina.com基金资助:
Qing-yuan DENG( ), Dong-qing FU, Rong-zheng HUANG, Fan-fan ZHANG(
), Dong-qing FU, Rong-zheng HUANG, Fan-fan ZHANG( ), Guo-jun SUN(
), Guo-jun SUN( )
)
Received:2024-11-20
Revised:2025-01-16
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-07-11
Contact:
Fan-fan ZHANG,Guo-jun SUN
摘要:
本研究旨在明确松针精油对构树青贮品质及有氧稳定性的影响,为构树青贮加工利用提供理论支撑。试验采用单因素设计,分为4组,试验组分别在每kg构树青贮中添加160(Ⅰ组)、320(Ⅱ组)和480 mg(Ⅲ组)松针精油,并设置自然发酵组作为对照组(CK组)。在青贮的第3、7、15、30和60天取样,分析其营养成分、发酵品质及微生物数量,并取60 d样品分析其有氧稳定性。结果表明:青贮3 d,Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ组可溶性碳水化合物(WSC)含量、乳酸(LA)和乙酸(AA)浓度显著高于CK组(P<0.05),pH、氨态氮/总氮(NH3-N/TN)、丙酸(PA)浓度和霉菌数量显著低于CK组(P<0.05),Ⅱ和Ⅲ组乳酸菌和酵母菌数量与CK组间差异显著(P<0.05)。青贮7 d,Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ组乳酸、乙酸浓度和乳酸菌数量显著高于CK组(P<0.05),pH、NH3-N/TN、丙酸浓度、酵母菌和霉菌数量显著低于CK组(P<0.05),Ⅱ和Ⅲ组干物质(DM)和WSC含量显著高于CK组(P<0.05)。青贮15 d,Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ组粗蛋白(CP)、WSC含量、乳酸、乙酸浓度和乳酸菌数量显著高于CK组(P<0.05),pH、NH3-N/TN、丙酸浓度、酵母菌和霉菌数量显著低于CK组(P<0.05)。青贮30 d,Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ组WSC含量、乳酸、乙酸浓度和乳酸菌数量显著高于CK组(P<0.05),pH、NH3-N/TN、丙酸浓度、酵母菌数量显著低于CK组(P<0.05)。青贮60 d,Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ组CP、WSC含量、乳酸、乙酸浓度和乳酸菌数量显著高于CK组(P<0.05),pH、NH3-N/TN、丙酸浓度和酵母菌数量显著低于CK组(P<0.05),Ⅱ和Ⅲ组的有氧稳定性显著高于CK和Ⅰ组(P<0.05)。综上所述,松针精油可以减少构树青贮中CP和WSC损失,提高乳酸、乙酸浓度和乳酸菌数量,降低pH,抑制霉菌繁殖;同时能显著提高构树青贮的有氧稳定性。以480 mg·kg-1添加量改善效果为最佳。
邓清源, 付东青, 黄嵘峥, 张凡凡, 孙国君. 松针精油对构树青贮品质及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 85-94.
Qing-yuan DENG, Dong-qing FU, Rong-zheng HUANG, Fan-fan ZHANG, Guo-jun SUN. Effects of pine needle essential oil on the quality and aerobic stability of Broussonetia papyrifera silage[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(10): 85-94.
干物质 Dry matter (%FW) | 粗蛋白 Crude protein (%DM) | 可溶性碳水化合物 Water soluble carbohydrates (%DM) | 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber (%DM) | 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber (%DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 32.91±0.19 | 21.48±0.14 | 8.80±0.19 | 45.69±1.71 | 27.11±0.88 |
表1 构树原料的营养成分
Table 1 Nutritional composition of the raw materials for B. papyrifera
干物质 Dry matter (%FW) | 粗蛋白 Crude protein (%DM) | 可溶性碳水化合物 Water soluble carbohydrates (%DM) | 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber (%DM) | 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber (%DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 32.91±0.19 | 21.48±0.14 | 8.80±0.19 | 45.69±1.71 | 27.11±0.88 |
项目 Items | 处理 Treatments | 时间 Time | SEM | P值 P-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 7 d | 15 d | 30 d | 60 d | ||||
干物质 Dry matter (%FW) | CK | 31.94aA | 31.00bB | 29.98bC | 29.58bC | 29.44bC | 0.26 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 32.12aA | 31.31abB | 30.50abC | 29.81bD | 29.57abD | 0.27 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 32.35aA | 31.59aB | 30.44abC | 30.02abC | 29.91abC | 0.27 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 32.52aA | 31.72aB | 30.89aC | 30.35aD | 30.27aD | 0.24 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.14 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.11 | - | - | |
粗蛋白 Crude protein (%DM) | CK | 21.05aA | 20.23bB | 19.38cC | 18.58cD | 18.06cE | 0.29 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 20.99aA | 20.48abB | 19.96bC | 18.94bcD | 18.58bD | 0.25 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 21.17aA | 20.65abB | 20.20abC | 19.35abD | 18.96aD | 0.22 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 21.23aA | 20.88aB | 20.49aC | 19.45aD | 19.22aD | 0.22 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.14 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | 0.04 | 0.06 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber (%DM) | CK | 46.08aA | 46.62aA | 46.79aA | 46.75aA | 46.85aA | 0.28 | 0.94 |
| Ⅰ | 45.86aA | 46.39aA | 46.51aA | 46.53aA | 46.56aA | 0.30 | 0.96 | |
| Ⅱ | 45.72aA | 46.18aA | 46.37aA | 46.45aA | 46.43aA | 0.35 | 0.98 | |
| Ⅲ | 45.76aA | 46.12aA | 46.22aA | 46.26aA | 46.32aA | 0.37 | 0.99 | |
| SEM | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.32 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.96 | - | - | |
酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber (%DM) | CK | 27.87aA | 28.72aA | 28.82aA | 28.88aA | 28.86aA | 0.30 | 0.85 |
| Ⅰ | 27.71aA | 28.54aA | 28.70aA | 28.77aA | 28.81aA | 0.30 | 0.81 | |
| Ⅱ | 27.62aA | 28.67aA | 28.73aA | 28.84aA | 28.93aA | 0.32 | 0.74 | |
| Ⅲ | 27.65aA | 28.67aA | 28.78aA | 28.78aA | 28.80aA | 0.28 | 0.70 | |
| SEM | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.29 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | - | - | |
可溶性碳水化合物 Water soluble carbohydrates (%DM) | CK | 7.07cA | 5.10cB | 3.77cC | 3.01cD | 2.86cD | 0.42 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 7.49bA | 5.38bcB | 4.21bC | 3.53bD | 3.27bD | 0.41 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 7.73abA | 5.65abB | 4.35abC | 3.86aD | 3.64aD | 0.41 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 7.95aA | 5.87aB | 4.57aC | 4.09aD | 3.87aD | 0.40 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.12 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
表2 松针精油对构树青贮营养成分的影响
Table 2 Effects of pine needle essential oil on nutrient contents of B. papyrifera silage
项目 Items | 处理 Treatments | 时间 Time | SEM | P值 P-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 7 d | 15 d | 30 d | 60 d | ||||
干物质 Dry matter (%FW) | CK | 31.94aA | 31.00bB | 29.98bC | 29.58bC | 29.44bC | 0.26 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 32.12aA | 31.31abB | 30.50abC | 29.81bD | 29.57abD | 0.27 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 32.35aA | 31.59aB | 30.44abC | 30.02abC | 29.91abC | 0.27 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 32.52aA | 31.72aB | 30.89aC | 30.35aD | 30.27aD | 0.24 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.14 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.11 | - | - | |
粗蛋白 Crude protein (%DM) | CK | 21.05aA | 20.23bB | 19.38cC | 18.58cD | 18.06cE | 0.29 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 20.99aA | 20.48abB | 19.96bC | 18.94bcD | 18.58bD | 0.25 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 21.17aA | 20.65abB | 20.20abC | 19.35abD | 18.96aD | 0.22 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 21.23aA | 20.88aB | 20.49aC | 19.45aD | 19.22aD | 0.22 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.14 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | 0.04 | 0.06 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber (%DM) | CK | 46.08aA | 46.62aA | 46.79aA | 46.75aA | 46.85aA | 0.28 | 0.94 |
| Ⅰ | 45.86aA | 46.39aA | 46.51aA | 46.53aA | 46.56aA | 0.30 | 0.96 | |
| Ⅱ | 45.72aA | 46.18aA | 46.37aA | 46.45aA | 46.43aA | 0.35 | 0.98 | |
| Ⅲ | 45.76aA | 46.12aA | 46.22aA | 46.26aA | 46.32aA | 0.37 | 0.99 | |
| SEM | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.32 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.96 | - | - | |
酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber (%DM) | CK | 27.87aA | 28.72aA | 28.82aA | 28.88aA | 28.86aA | 0.30 | 0.85 |
| Ⅰ | 27.71aA | 28.54aA | 28.70aA | 28.77aA | 28.81aA | 0.30 | 0.81 | |
| Ⅱ | 27.62aA | 28.67aA | 28.73aA | 28.84aA | 28.93aA | 0.32 | 0.74 | |
| Ⅲ | 27.65aA | 28.67aA | 28.78aA | 28.78aA | 28.80aA | 0.28 | 0.70 | |
| SEM | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.29 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | - | - | |
可溶性碳水化合物 Water soluble carbohydrates (%DM) | CK | 7.07cA | 5.10cB | 3.77cC | 3.01cD | 2.86cD | 0.42 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 7.49bA | 5.38bcB | 4.21bC | 3.53bD | 3.27bD | 0.41 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 7.73abA | 5.65abB | 4.35abC | 3.86aD | 3.64aD | 0.41 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 7.95aA | 5.87aB | 4.57aC | 4.09aD | 3.87aD | 0.40 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.12 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
项目 Items | 处理 Treatments | 时间 Time | SEM | P值 P-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 7 d | 15 d | 30 d | 60 d | ||||
pH值 pH-value | CK | 6.75aA | 6.37aB | 5.98aC | 5.62aD | 5.45aD | 0.13 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 6.55bA | 6.04bB | 5.55bC | 5.28bD | 5.15bD | 0.14 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 6.43bcA | 5.98bB | 5.36cC | 5.02cD | 4.90cD | 0.15 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 6.38cA | 5.76cB | 5.19cC | 4.87cD | 4.72dD | 0.17 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.08 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
氨态氮/总氮 Ammonia-N/total-N (%) | CK | 2.59aE | 3.24aD | 3.68aC | 3.97aB | 4.28aA | 0.16 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 2.28bD | 2.66bC | 2.98bB | 3.24bA | 3.45bA | 0.11 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 1.95cE | 2.35cD | 2.62cC | 2.92cB | 3.19cA | 0.12 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 1.72dD | 2.08dC | 2.36dB | 2.54dA | 2.70dA | 0.10 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.17 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
乳酸 Lactic acid (%DM) | CK | 2.28cE | 2.81cD | 3.15dC | 3.52dB | 3.69dA | 0.14 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 2.77bD | 3.34bC | 3.71cB | 4.17cA | 4.25cA | 0.15 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 2.91bD | 3.86aC | 4.23bB | 4.71bA | 4.91bA | 0.19 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 3.27aD | 4.07aC | 4.62aB | 5.14aA | 5.21aA | 0.20 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.18 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
乙酸 Acetic acid (%DM) | CK | 0.43dE | 0.69dD | 0.97cC | 1.19cB | 1.27dA | 0.08 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 0.56cE | 0.84cD | 1.18bC | 1.33bB | 1.46cA | 0.09 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 0.64bE | 1.12bD | 1.54aC | 1.71aB | 1.82bA | 0.12 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 0.71aE | 1.27aD | 1.51aC | 1.80aB | 1.96aA | 0.12 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.11 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.30 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
丙酸 Propionic acid (%DM) | CK | 0.11aD | 0.14aC | 0.16aC | 0.19aB | 0.23aA | 0.01 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 0.07bC | 0.11bB | 0.13bB | 0.16bA | 0.18bA | 0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 0.07bcD | 0.10bC | 0.12bcB | 0.14bcA | 0.16bA | 0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 0.05cD | 0.08bC | 0.10cC | 0.12cB | 0.13cA | 0.01 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
表3 松针精油对构树青贮发酵品质的影响
Table 3 Effects of pine needle essential oil on fermentation quality of B. papyrifera silage
项目 Items | 处理 Treatments | 时间 Time | SEM | P值 P-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 7 d | 15 d | 30 d | 60 d | ||||
pH值 pH-value | CK | 6.75aA | 6.37aB | 5.98aC | 5.62aD | 5.45aD | 0.13 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 6.55bA | 6.04bB | 5.55bC | 5.28bD | 5.15bD | 0.14 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 6.43bcA | 5.98bB | 5.36cC | 5.02cD | 4.90cD | 0.15 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 6.38cA | 5.76cB | 5.19cC | 4.87cD | 4.72dD | 0.17 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.08 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
氨态氮/总氮 Ammonia-N/total-N (%) | CK | 2.59aE | 3.24aD | 3.68aC | 3.97aB | 4.28aA | 0.16 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 2.28bD | 2.66bC | 2.98bB | 3.24bA | 3.45bA | 0.11 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 1.95cE | 2.35cD | 2.62cC | 2.92cB | 3.19cA | 0.12 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 1.72dD | 2.08dC | 2.36dB | 2.54dA | 2.70dA | 0.10 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.17 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
乳酸 Lactic acid (%DM) | CK | 2.28cE | 2.81cD | 3.15dC | 3.52dB | 3.69dA | 0.14 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 2.77bD | 3.34bC | 3.71cB | 4.17cA | 4.25cA | 0.15 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 2.91bD | 3.86aC | 4.23bB | 4.71bA | 4.91bA | 0.19 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 3.27aD | 4.07aC | 4.62aB | 5.14aA | 5.21aA | 0.20 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.18 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
乙酸 Acetic acid (%DM) | CK | 0.43dE | 0.69dD | 0.97cC | 1.19cB | 1.27dA | 0.08 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 0.56cE | 0.84cD | 1.18bC | 1.33bB | 1.46cA | 0.09 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 0.64bE | 1.12bD | 1.54aC | 1.71aB | 1.82bA | 0.12 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 0.71aE | 1.27aD | 1.51aC | 1.80aB | 1.96aA | 0.12 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.11 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.30 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
丙酸 Propionic acid (%DM) | CK | 0.11aD | 0.14aC | 0.16aC | 0.19aB | 0.23aA | 0.01 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 0.07bC | 0.11bB | 0.13bB | 0.16bA | 0.18bA | 0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 0.07bcD | 0.10bC | 0.12bcB | 0.14bcA | 0.16bA | 0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 0.05cD | 0.08bC | 0.10cC | 0.12cB | 0.13cA | 0.01 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
项目 Items | 处理 Treatments | 时间 Time | SEM | P值 P-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 7 d | 15 d | 30 d | 60 d | ||||
乳酸菌 Lactic acid bacteria | CK | 6.22bD | 6.85dA | 6.75dA | 6.59cB | 6.40cC | 0.25 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 6.38bD | 7.25cA | 7.07cAB | 6.97bB | 6.68bC | 0.33 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 6.68aC | 7.49bA | 7.26bB | 7.20aB | 6.84bC | 0.32 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 6.79aC | 7.82aA | 7.66aA | 7.37aB | 7.23aB | 0.38 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.10 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
酵母菌 Yeast | CK | 5.81aA | 5.40aB | 5.11aC | 4.75aD | 4.23aE | 0.15 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 5.60aA | 4.89bB | 4.65bC | 4.36bD | 3.93bE | 0.15 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 5.15bA | 4.64bcB | 4.40cC | 3.92cD | 3.40cE | 0.16 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 5.18bA | 4.55cB | 4.34cB | 3.82cC | 3.40cD | 0.17 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.11 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
霉菌 Mold | CK | 4.99aA | 4.02aB | 3.18aC | 2.52aD | <2.00 | - | - |
| Ⅰ | 4.73bA | 3.63bB | 2.84bC | <2.00 | <2.00 | - | - | |
| Ⅱ | 4.23cA | 3.40cB | 2.64bC | <2.00 | <2.00 | - | - | |
| Ⅲ | 4.16cA | 3.40cB | 2.63bC | <2.00 | <2.00 | - | - | |
| SEM | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.08 | - | - | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | - | - | |
好氧细菌 Aerobic bacteria | CK | 8.22aA | 7.73aB | 7.30aC | 6.81aD | 6.21aE | 0.19 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 8.07abA | 7.62abB | 7.17abC | 6.73aD | 6.08aE | 0.19 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 7.95bA | 7.46bcB | 7.04bcC | 6.48bD | 5.92bE | 0.19 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 7.98bA | 7.36cB | 6.97cC | 6.37bD | 5.89bE | 0.20 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.04 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | 0.08 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
表4 松针精油对构树青贮中微生物数量的影响
Table 4 Effects of pine needle essential oil on the microbial population of B. papyrifera silage (lg cfu·g-1 FW)
项目 Items | 处理 Treatments | 时间 Time | SEM | P值 P-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 7 d | 15 d | 30 d | 60 d | ||||
乳酸菌 Lactic acid bacteria | CK | 6.22bD | 6.85dA | 6.75dA | 6.59cB | 6.40cC | 0.25 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 6.38bD | 7.25cA | 7.07cAB | 6.97bB | 6.68bC | 0.33 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 6.68aC | 7.49bA | 7.26bB | 7.20aB | 6.84bC | 0.32 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 6.79aC | 7.82aA | 7.66aA | 7.37aB | 7.23aB | 0.38 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.10 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
酵母菌 Yeast | CK | 5.81aA | 5.40aB | 5.11aC | 4.75aD | 4.23aE | 0.15 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 5.60aA | 4.89bB | 4.65bC | 4.36bD | 3.93bE | 0.15 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 5.15bA | 4.64bcB | 4.40cC | 3.92cD | 3.40cE | 0.16 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 5.18bA | 4.55cB | 4.34cB | 3.82cC | 3.40cD | 0.17 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.11 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
霉菌 Mold | CK | 4.99aA | 4.02aB | 3.18aC | 2.52aD | <2.00 | - | - |
| Ⅰ | 4.73bA | 3.63bB | 2.84bC | <2.00 | <2.00 | - | - | |
| Ⅱ | 4.23cA | 3.40cB | 2.64bC | <2.00 | <2.00 | - | - | |
| Ⅲ | 4.16cA | 3.40cB | 2.63bC | <2.00 | <2.00 | - | - | |
| SEM | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.08 | - | - | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | - | - | |
好氧细菌 Aerobic bacteria | CK | 8.22aA | 7.73aB | 7.30aC | 6.81aD | 6.21aE | 0.19 | <0.01 |
| Ⅰ | 8.07abA | 7.62abB | 7.17abC | 6.73aD | 6.08aE | 0.19 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅱ | 7.95bA | 7.46bcB | 7.04bcC | 6.48bD | 5.92bE | 0.19 | <0.01 | |
| Ⅲ | 7.98bA | 7.36cB | 6.97cC | 6.37bD | 5.89bE | 0.20 | <0.01 | |
| SEM | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.04 | - | - | |
| P值 P-value | 0.08 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | - | - | |
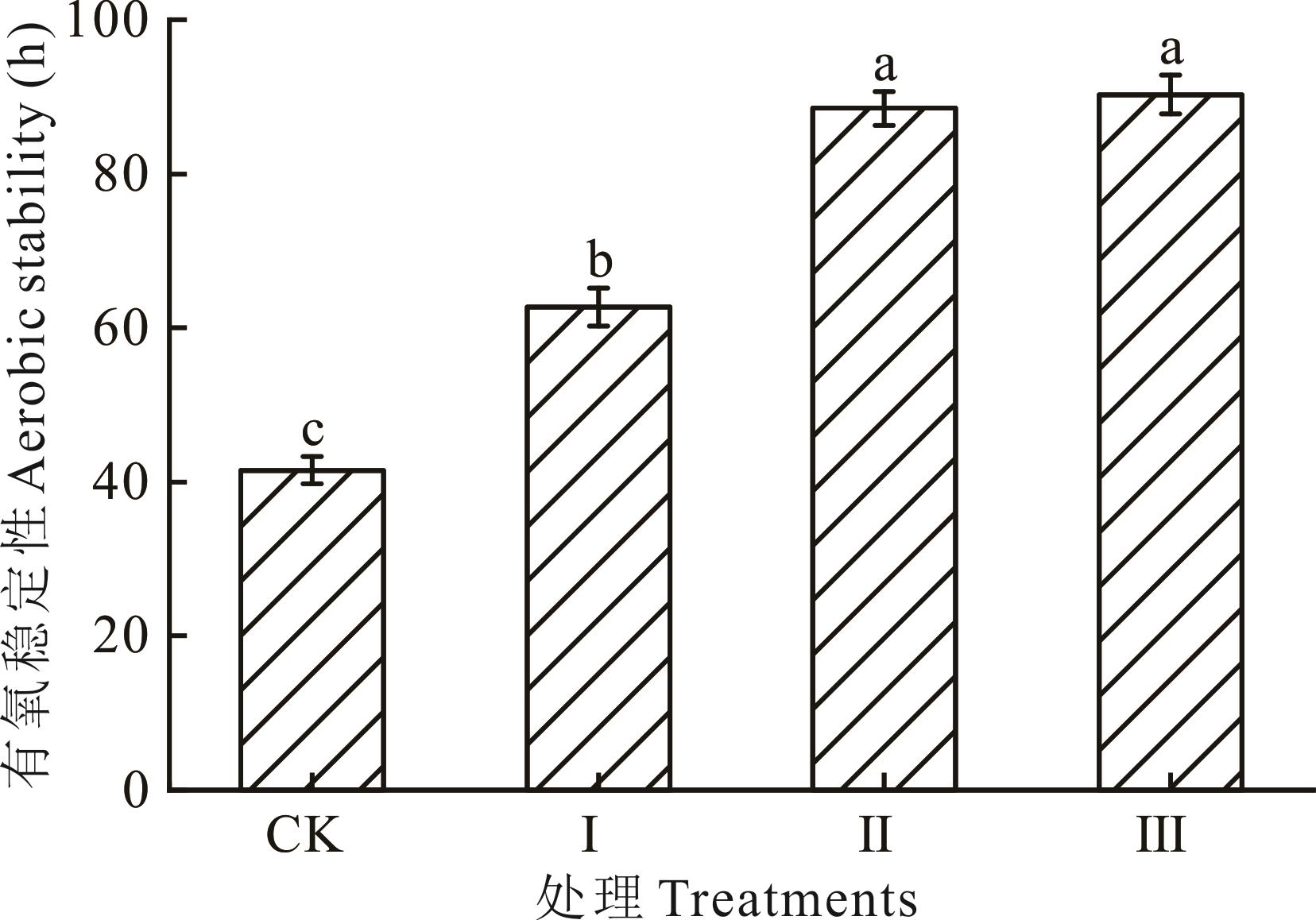
图 1 不同处理构树青贮的有氧稳定性不同小写字母表示处理之间差异显著(P<0.05);CK组每kg添加0 mg松针精油,Ⅰ组每kg添加160 mg松针精油,Ⅱ组每kg添加320 mg松针精油,Ⅲ组每kg添加480 mg松针精油。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among the treatments (P<0.05). The group CK added 0 mg of pine needle essential oil per kilogram, group Ⅰ added 160 mg of pine needle essential oil per kilogram, group Ⅱ added 320 mg of pine needle essential oil per kilogram, and group Ⅲ added 480 mg of pine needle essential oil per kilogram.
Fig. 1 Aerobic stability of B. papyrifera silage under different treatments
| [1] | Gong B, Tan L, Hou K, et al. Effects of hybrid Broussonetia papyrifera silage on growth performance, nutrient apparent digestibility and rumen fermentation parameters of fattening dairy bulls. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35(6): 3771-3779. |
| 宫斌, 檀论, 侯坤, 等. 杂交构树青贮对奶公牛生长性能、营养物质表观消化率和瘤胃发酵参数的影响. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(6): 3771-3779. | |
| [2] | Si B W, Tao H, Zhang X L, et al. Effect of Broussonetia papyrifera L. (paper mulberry) silage on dry matter intake, milk composition, antioxidant capacity and milk fatty acid profile in dairy cows. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2018, 31(8): 1259-1266. |
| [3] | Zhang S W, Wang X P, Zhang Z H, et al. Effects of Broussonetia papyrifera silage on growth performance, serum biochemical indexes and meat quality of Dorper×Hu crossbred sheep. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 89-99. |
| 张生伟, 王小平, 张展海, 等. 青贮杂交构树对杜湖杂交肉羊生长性能、血清生化指标和肉品质的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 89-99. | |
| [4] | Zhang F F, Guo X Y, Wang X Z. Production, processing, and cultivation techniques of Broussonetia papyrifera. Yanbian: Yanbian University Press, 2022. |
| 张凡凡, 郭新勇, 王旭哲. 构树的生产加工与栽培技术. 延边: 延边大学出版社, 2022. | |
| [5] | Wu C R, Dai S, Liang L F, et al. Effects of different additives on fermentation quality and protein degradation of Broussonetia papyrifera silage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(10): 169-179. |
| 吴长荣, 代胜, 梁龙飞, 等. 不同添加剂对构树青贮饲料发酵品质和蛋白质降解的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 169-179. | |
| [6] | Zhang Y L, Yang H J, Li C C, et al. Effects of different lactic acid bacteria treatments on nutritional quality, fermentation characteristics and aerobic stability of hybrid Broussonetia papyrifera silage. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35(4): 2702-2710. |
| 张玉琳, 杨寒珺, 李超程, 等. 不同乳酸菌处理对杂交构树青贮营养品质、发酵特性和有氧稳定性的影响. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(4): 2702-2710. | |
| [7] | Wang Y Z, Zhao Y Q, Wang D, et al. Progress in the study of antibacterial mechanism of plant essential oils from the perspective of multiomics. Food Science, 2024, 45(17): 348-356. |
| 王亚哲, 赵永强, 王迪, 等. 多组学视角下植物精油抑菌机理的研究进展. 食品科学, 2024, 45(17): 348-356. | |
| [8] | Sharma A, Rajendran S, Srivastava A, et al. Antifungal activities of selected essential oils against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici 1322, with emphasis on Syzygium aromaticum essential oil. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2017, 123(3): 308-313. |
| [9] | Gutierrez J, Rodriguez G, Barry-Ryan C, et al. Efficacy of plant essential oils against foodborne pathogens and spoilage bacteria associated with ready-to-eat vegetables: antimicrobial and sensory screening. Journal of Food Protection, 2008, 71(9): 1846-1854. |
| [10] | Zuo X, Wang C, Chen X Y, et al. Effects of eucalyptus oil and rosemary oil on silage quality of stylo. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(2): 89-97. |
| 邹璇, 王成, 陈晓阳, 等. 桉叶油和迷迭香油对柱花草青贮品质的影响. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(2): 89-97. | |
| [11] | Chen Y L, Li M Y, Long J H, et al. The effect of Amomum villosum essential oil on the quality of Broussonetia papyrifera silage. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2023, 59(6): 254-258. |
| 陈玉连, 李茂雅, 龙见华, 等. 砂仁精油对构树青贮品质的影响. 中国畜牧杂志, 2023, 59(6): 254-258. | |
| [12] | Hodjatpanah-Montazeri A, Mesgaran M D, Vakili A. Effect of essential oils of various plants as microbial modifier to alter corn silage fermentation and in vitro methane production. Iranian Journal of Applied Animal Science, 2016, 2(6): 269-276. |
| [13] | Saab A M, Gambari R, Sacchetti G, et al. Phytochemical and pharmacological properties of essential oils from Cedrus species. Natural Product Research, 2018, 32(12): 1415-1427. |
| [14] | Sun J Z. Study on the effect of pine needle essential oil on the quality and microorganisms of alfalfa silage. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2021. |
| 孙建政. 松针精油对苜蓿青贮品质及微生物的影响研究. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2021. | |
| [15] | Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of moisture in feedstuffs, GB/T 6435-2014. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2014. |
| 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 饲料中水分的测定, GB/T 6435-2014. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014. | |
| [16] | Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of crude protein in feeds-Kjeldahl method, GB/T 6432-2018. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2018. |
| 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 饲料中粗蛋白的测定—凯氏定氮法, GB/T 6432-2018. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. | |
| [17] | Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of neutral detergent fiber (NDF) in feeds, GB/T 20806-2022. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2022. |
| 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 饲料中中性洗涤纤维(NDF)的测定, GB/T 20806-2022. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2022. | |
| [18] | Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of acid detergent fiber (ADF) in feeds, NY/T 1459-2022. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2022. |
| 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 饲料中酸性洗涤纤维的测定, NY/T 1459-2022. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2022. | |
| [19] | Zhao J, Yin X J, Wang S R, et al. Effects of storage time on the fermentation quality, bacterial community composition, and functional profile of sweet sorghum silage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(8): 164-175. |
| 赵杰, 尹雪敬, 王思然, 等. 贮藏时间对甜高粱青贮发酵品质、微生物群落组成和功能的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 164-175. | |
| [20] | Fu D Q, Jia C Y, Zhang L, et al. Agronomic traits and fermentation quality of maize silage harvested at different grain-development stages in irrigated drought areas of southern Xinjiang. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 111-125. |
| 付东青, 贾春英, 张力, 等. 南疆干旱灌溉区青贮玉米农艺性状和发酵品质动态分析及评价. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 111-125. | |
| [21] | Xu Q F, Yu Z, Han J G, et al. Determining organic acid in alfalfa silage by HPLO. Grassland and Turf, 2007(2): 63-65. |
| 许庆方, 玉柱, 韩建国, 等. 高效液相色谱法测定紫花苜蓿青贮中的有机酸. 草原与草坪, 2007(2): 63-65. | |
| [22] | Sun Y C, Chai Y X, Hou G Q, et al. Fermentation quality and in vitro rumen gas production of corn straw wheat straw mixed with whole conformation tree. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(10): 3297-3304. |
| 孙颖超, 柴雨昕, 侯国庆, 等. 2种秸秆与全株构树混贮发酵品质及瘤胃体外产气特性. 草地学报, 2024, 32(10): 3297-3304. | |
| [23] | Guo X, Wu S, Zheng M Y, et al. Effects of addition of Neolamarckia cadamba leaves and chitosan oligosaccharides on fermentation quality and aerobic stability of sugarcane top silage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(6): 202-210. |
| 郭香, 吴硕, 郑明扬, 等. 添加黄梁木叶和壳寡糖对甘蔗梢青贮饲料发酵品质及有氧稳定性的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 202-210. | |
| [24] | Besharati M, Palangi V, Niazifar M, et al. Effect of adding flaxseed essential oil in alfalfa ensiling process on ruminal fermentation kinetics. KSU Journal of Agricultural Nature, 2023, 26(2): 450-458. |
| [25] | Sun J Z, Wang X N, Sun G J, et al. Effect of pine needle essential oil on the main microorganisms in silage. Feed Industry, 2020, 41(18): 36-41. |
| 孙建政, 王晓娜, 孙国君, 等. 松针精油对青贮饲料中主要微生物的影响. 饲料工业, 2020, 41(18): 36-41. | |
| [26] | Cardozo P W, Calsamiglia S, Ferret A, et al. Effects of natural plant extracts on ruminal protein degradation and fermentation profiles in continuous culture. Journal of Animal Science, 2004, 82(11): 3230-3236. |
| [27] | Akinci Y, Soycan-Önenc S. The effect of cumin essential oil on the fermentation quality, aerobic stability, and in vitro digestibility of vetch-oat silages. Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture, Ege University, 2021, 58(2): 217-228. |
| [28] | Chaves A V, Baah J, Wang Y, et al. Effects of cinnamon leaf, oregano and sweet orange essential oils on fermentation and aerobic stability of barley silage. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2012, 92(4): 906-915. |
| [29] | Li M, Fan X, Cheng Q, et al. Effect of Amomum villosum essential oil as an additive on the chemical composition, fermentation quality, and bacterial community of paper mulberry silage. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13(2): 1-10. |
| [30] | Besharati M, Palangi V, Niazifar M. Comparison study of flaxseed, cinnamon and lemon seed essential oils additives on quality and fermentation characteristics of lucerne silage. Acta Agriculturae Slovenica, 2020, 115(2): 455-462. |
| [31] | Liu X, He Y L, Hu Y Y, et al. Primary antibacterial activity and mechanism of 3-carene against the Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2019, 40(3): 601-608. |
| 刘雪, 何英兰, 胡月英, 等. 3-蒈烯对铜绿假单胞菌的抑菌活性及机理初探. 热带作物学报, 2019, 40(3): 601-608. | |
| [32] | He J R, Liu X, Chen W X, et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of (-)-β-pinene against Salmonella. Food Science, 2019, 40(1): 44-49. |
| 何静如, 刘雪, 陈文学, 等. (-)-β-蒎烯对沙门氏菌的抑菌机制. 食品科学, 2019, 40(1): 44-49. | |
| [33] | Turan A, Soycan-Önenc S. Effect of cumin essential oil usage on fermentation quality, aerobic stability and in vitro digetibility of alfalfa silage. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2018, 31(8): 1252-1258. |
| [34] | Li W, Yang M Y, Li S X. Effects of plant essential oil on fermentation quality, microbial quantity and feeding value of alfalfa. China Feed, 2021(16): 50-53. |
| 李伟, 杨敏一, 李舒心. 植物精油对苜蓿草发酵品质、微生物数量及饲用价值的影响. 中国饲料, 2021(16): 50-53. | |
| [35] | Cantoia J R, Capucho E, Garcia T M, et al. Lemongrass essential oil in sugarcane silage: fermentative profile, losses, chemical composition, and aerobic stability. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2020(260): 114371. |
| [36] | Soycan-Önenç S, Koc F, Coşkuntuna L, et al. The effect of oregano and cinnamon essential oils on fermentation quality and aerobic stability of field pea silages. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2015, 28(9): 1281-1287. |
| [37] | Yang D, Wu S, Chen D D, et al. Determination of the active components of essential oil in Neolamarckia cadamba and its effect on the aerobic stabilization of whole plant corn silage. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(9): 2860-2867. |
| 杨丹, 吴硕, 陈丹丹, 等. 黄梁木精油活性成分测定及其对全株玉米青贮有氧稳定的影响. 草地学报, 2023, 31(9): 2860-2867. |
| [1] | 吴娟燕, 田静, 郭香, 黄莉莹, 张建国. 籽实青贮的研究与利用进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 211-220. |
| [2] | 王思然, 丁成龙, 田吉鹏, 程云辉, 许能祥, 张文洁, 王欣, 刘蓓一. 乳酸菌和抗真菌添加剂对湿啤酒糟全混合日粮青贮发酵品质、体外消化率及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 213-226. |
| [3] | 毛开, 许艺, 王学梅, 柴欢, 黄帅, 王坚, 郇树乾, 玉柱, 王目森. 植物乳植杆菌与糖蜜对花生秧青贮饲料发酵品质、生物胺含量及细菌群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 146-158. |
| [4] | 王思然, 刘蓓一, 田吉鹏, 程云辉, 许能祥, 张文洁, 王欣, 丁成龙. 复合乳酸菌添加剂对低温环境下意大利黑麦草青贮发酵品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 159-170. |
| [5] | 梁宇成, 张晓雯, 邵涛, 王文博, 原现军. 乳酸菌对全株玉米青贮发酵品质和霉菌毒素含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 123-133. |
| [6] | 郭田心, 阮诗诗, 郭香, 詹佳琦, 梁秋雨, 陈晓阳, 周玮, 张庆. 不同复合菌酶添加对中药渣青贮饲料的营养价值及发酵品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 194-202. |
| [7] | 张睿, 韩重阳, 蔡家邦, 汪阳, 黄琳凯, 张新全, 聂刚. 6个苇状羊茅(型)品种在成都平原区的生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 138-148. |
| [8] | 李文龙, 李峰, 张仲鹃, 王殿清, 王欢, 靳慧卿, 特木热, 胡志玲, 陶雅. 鄂尔多斯高原北部一年两季燕麦种植模式生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 159-168. |
| [9] | 赵杰, 尹雪敬, 王思然, 董志浩, 李君风, 贾玉山, 邵涛. 贮藏时间对甜高粱青贮发酵品质、微生物群落组成和功能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 164-175. |
| [10] | 凌文卿, 张磊, 李珏, 冯启贤, 李妍, 周燚, 刘一佳, 阳伏林, 周晶. 布氏乳杆菌和不同糖类联用对紫花苜蓿青贮营养成分、发酵品质、瘤胃降解率及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 122-134. |
| [11] | 党浩千, 覃娟清, 郭宇康, 张富, 王迎港, 刘庆华. 不同添加剂发酵笋壳对湖羊生产性能及瘤胃发酵的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 135-148. |
| [12] | 梁梦琪, 武齐丰, 邵涛, 吴艾丽, 刘秦华. 添加剂对多花黑麦草青贮发酵品质、α-生育酚和β-胡萝卜素含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 180-189. |
| [13] | 徐远志, 刘新平, 王立龙, 胡鸿姣, 何玉惠, 张铜会, 景家琪. 华北驼绒藜青贮加工及营养价值评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 150-159. |
| [14] | 覃娟清, 党浩千, 金华云, 郭宇康, 张富, 刘庆华. 不同添加剂处理笋壳对其发酵品质及湖羊瘤胃微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 155-167. |
| [15] | 付东青, 贾春英, 张力, 张凡凡, 马春晖. 南疆干旱灌溉区青贮玉米农艺性状和发酵品质动态分析及评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 111-125. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||