

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 28-39.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025084
刘冬娅1( ), 杨燕1, 刘静1, 王博1, 李志刚1,2(
), 杨燕1, 刘静1, 王博1, 李志刚1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-12
修回日期:2025-04-29
出版日期:2026-02-20
发布日期:2025-12-24
通讯作者:
李志刚
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: lizg001@sina.com基金资助:
Dong-ya LIU1( ), Yan YANG1, Jing LIU1, Bo WANG1, Zhi-gang LI1,2(
), Yan YANG1, Jing LIU1, Bo WANG1, Zhi-gang LI1,2( )
)
Received:2025-03-12
Revised:2025-04-29
Online:2026-02-20
Published:2025-12-24
Contact:
Zhi-gang LI
摘要:
放牧家畜的粪便归还在草地土壤养分循环和物理性质改善等方面具有重要作用,但短期家畜粪便归还对荒漠草地土壤质量的影响仍缺乏关注。本研究以宁夏盐池荒漠草地为对象,模拟不同放牧强度下的羊粪蓄积量,探究了4种不同水平的羊粪蓄积量(MN:0 kg·hm-2 ;ML:4000 kg·hm-2 ;MM:8000 kg·hm-2 ;MH:16000 kg·hm-2)对土壤质量的影响。结果表明:1)羊粪归还2年后,土壤温度随着羊粪蓄积量的增加而升高,但土壤平均温度仅MH显著高于MN、ML和MM(P<0.05);土壤平均含水量也仅MH显著高于ML和MM(P<0.05)。2)随着羊粪蓄积量的增加,pH值呈降低趋势,但土壤胞外酶活性呈增加趋势。3)羊粪归还促进了土壤大团聚体的形成,而降低了微团聚体的数量,说明土壤团聚体稳定性随着羊粪蓄积量的增加而增强。4)与MN相比,ML、MM和MH显著增加了土壤质量指数(P<0.05);相关性分析和结构方程模型进一步表明,羊粪归还改善了土壤水热状况,激发了土壤碳氮循环相关酶活性,从而增加了土壤养分的输入及大团聚体的数量,并最终改善了土壤质量。总之,低、中和高羊粪归还量均能够有效改善土壤质量状况,可为退化草地土壤的恢复提供理论依据和实践参考。
刘冬娅, 杨燕, 刘静, 王博, 李志刚. 短期羊粪归还对荒漠草地土壤质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 28-39.
Dong-ya LIU, Yan YANG, Jing LIU, Bo WANG, Zhi-gang LI. Effects of short-term sheep manure return on soil quality of desert steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(2): 28-39.
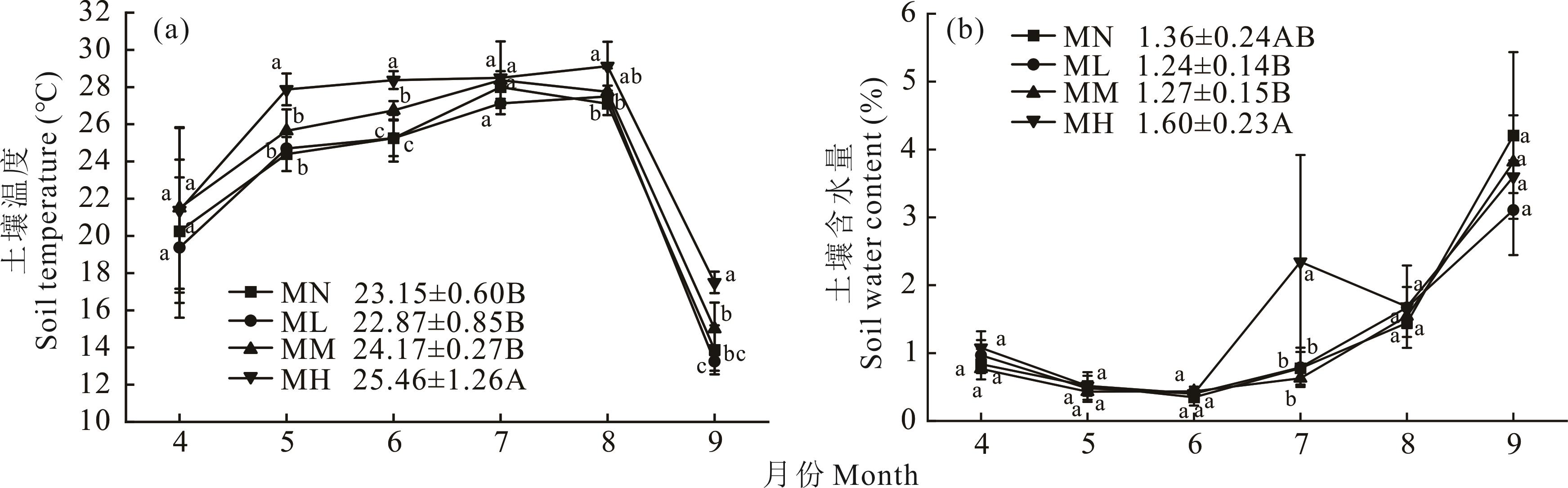
图1 不同羊粪蓄积量对土壤温度和土壤含水量的影响不同的大写字母代表4-9月份土壤温度和土壤含水量的平均值在不同羊粪蓄积量间存在显著差异(P<0.05),不同小写字母代表同一月份土壤温度和土壤含水量在不同羊粪蓄积量下存在显著差异(P<0.05)。MN:无羊粪蓄积。ML:低羊粪蓄积量。MM:中羊粪蓄积量。MH:高羊粪蓄积量。下同。Different uppercase letters represent significant differences in the average soil temperature and soil moisture content from April to September among different sheep manure accumulation amounts (P<0.05), while different lowercase letters represent significant differences in soil temperature and soil moisture content for the same month under different sheep manure accumulation amounts (P<0.05). MN: No sheep manure accumulation. ML: Low sheep manure accumulation. MM: Medium sheep manure accumulation. MH: High sheep manure accumulation. The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of different sheep manure volumes on soil temperature and soil water content

图2 不同羊粪蓄积量对土壤胞外酶活性的影响不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.2 Effects of different sheep manure volumes on soil extracellular enzymes activity

图4 不同羊粪蓄积量对土壤团聚体的影响MWD:平均重量直径。GMD:几何平均直径。MWD: Mean weight diameter; GMD: Geometric mean diameter.
Fig.4 Effects of different sheep manure volumes on soil aggregates
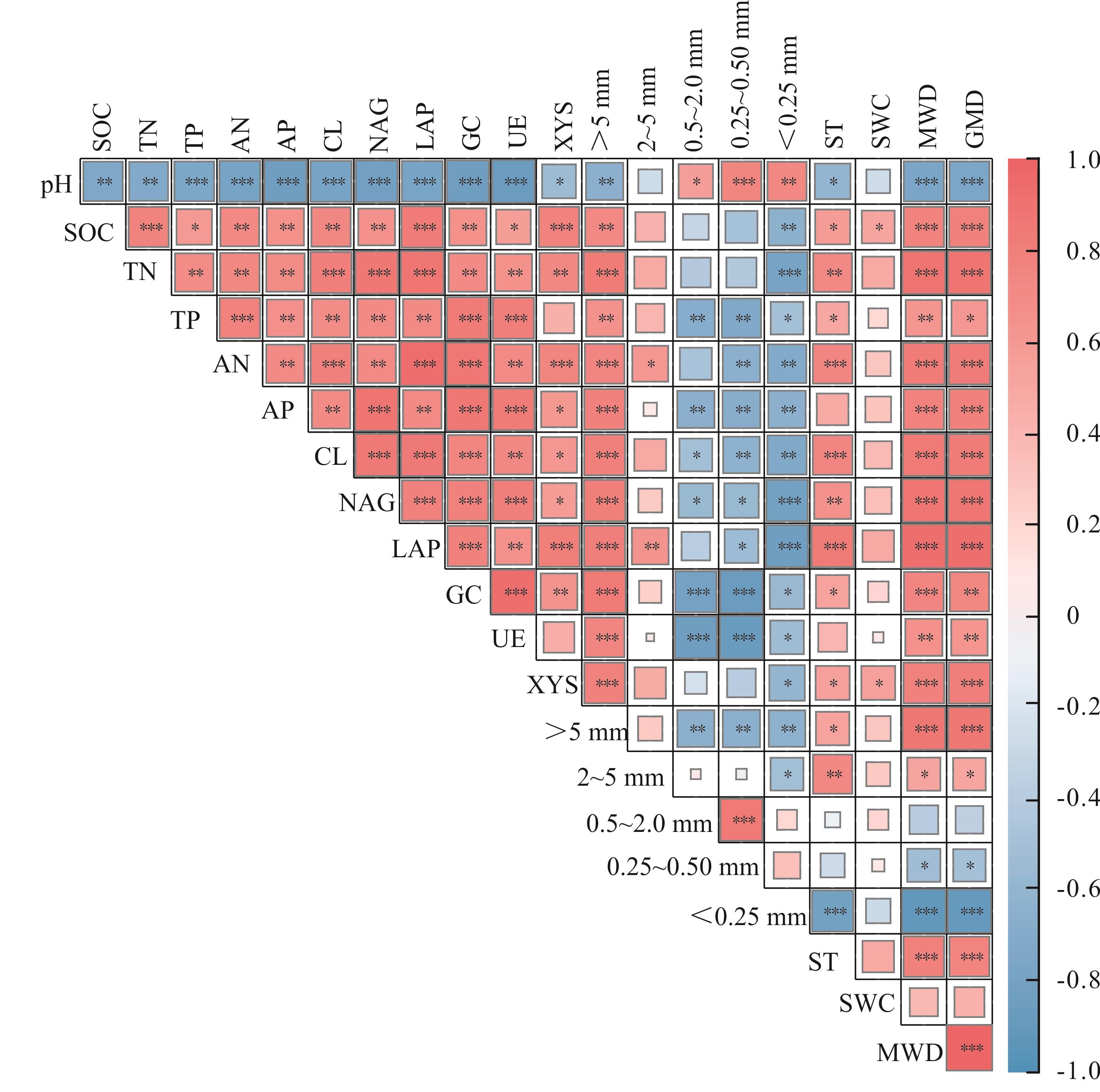
图5 土壤理化性质间的皮尔森相关性分析蓝色代表负相关,粉色代表正相关,*表示P<0.05, **表示P<0.01, ***表示P<0.001。 SOC:土壤有机碳;TN:土壤全氮;TP:土壤全磷; AN:土壤碱解氮;AP:土壤速效磷;CL:纤维素酶;NAG:β-1, 4-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶; LAP:亮氨酸氨基肽酶;GC:β-1, 4-葡萄糖苷酶;UE:脲酶;XYS:β-1, 4-木糖苷酶;ST:土壤温度;SWC:土壤含水量;MWD:平均重量直径;GMD:几何平均直径。下同。Blue represents negative correlation, pink represents positive correlation. * indicates P<0.05; ** indicates P<0.01; *** indicates P<0.001. SOC: Soil organic carbon; TN: Soil total nitrogen; TP: Soil total phosphorus; AN: Soil alkali-hydrolysable nitrogen; AP: Soil available phosphorus; CL: Cellulase; NAG: β-1, 4-N-acetylglucosaminidase; LAP: Leucine aminopeptidase; GC: β-1,4-glucosidase; UE: Urease; XYS: β-1,4-xylosidase; ST: Soil temperature; SWC: Soil water content; MWD: Mean weight diameter; GMD: Geometric mean diameter. The same below.
Fig.5 Pearson correlation analysis between soil physicochemical properties
土壤指标 Soil indicators | 主成分分析Principal component analysis | 公因子方差 Common factors variance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | ||
| 土壤pH Soil pH | -0.468 | -0.803 | 0.864 |
| 有机碳 Organic carbon | 0.783 | 0.386 | 0.761 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.770 | 0.495 | 0.839 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | 0.322 | 0.824 | 0.782 |
| 碱解氮 Soil alkali-hydrolysable nitrogen | 0.676 | 0.602 | 0.820 |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.469 | 0.769 | 0.811 |
| 纤维素酶 Cellulase | 0.653 | 0.614 | 0.804 |
| β-1,4-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶 β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminidase | 0.571 | 0.721 | 0.846 |
| 亮氨酸氨基肽酶 Leucine aminopeptidase | 0.839 | 0.486 | 0.939 |
| β-1,4-葡萄糖苷酶 β-1,4-glucosidase | 0.438 | 0.846 | 0.908 |
| 脲酶 Urease | 0.256 | 0.935 | 0.941 |
| β-1,4-木糖苷酶 β-1,4-xylosidase | 0.896 | 0.188 | 0.839 |
| 平均重量直径 Mean weight diameter | 0.842 | 0.476 | 0.936 |
| 几何平均直径 Geometric mean diameter | 0.858 | 0.453 | 0.942 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 10.900 | 1.132 | |
| 解释度 Explain of the degree (%) | 77.856 | 8.087 | |
| 累计解释度 Cumulative explanatory degree (%) | 72.671 | 85.943 | |
| 权重 Weighing value | 0.529 | 0.471 | |
表1 土壤指标主成分分析结果及公因子方差
Table 1 The results of principal component analysis of soil indicators and the variance of common factors
土壤指标 Soil indicators | 主成分分析Principal component analysis | 公因子方差 Common factors variance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | ||
| 土壤pH Soil pH | -0.468 | -0.803 | 0.864 |
| 有机碳 Organic carbon | 0.783 | 0.386 | 0.761 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.770 | 0.495 | 0.839 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | 0.322 | 0.824 | 0.782 |
| 碱解氮 Soil alkali-hydrolysable nitrogen | 0.676 | 0.602 | 0.820 |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.469 | 0.769 | 0.811 |
| 纤维素酶 Cellulase | 0.653 | 0.614 | 0.804 |
| β-1,4-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶 β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminidase | 0.571 | 0.721 | 0.846 |
| 亮氨酸氨基肽酶 Leucine aminopeptidase | 0.839 | 0.486 | 0.939 |
| β-1,4-葡萄糖苷酶 β-1,4-glucosidase | 0.438 | 0.846 | 0.908 |
| 脲酶 Urease | 0.256 | 0.935 | 0.941 |
| β-1,4-木糖苷酶 β-1,4-xylosidase | 0.896 | 0.188 | 0.839 |
| 平均重量直径 Mean weight diameter | 0.842 | 0.476 | 0.936 |
| 几何平均直径 Geometric mean diameter | 0.858 | 0.453 | 0.942 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 10.900 | 1.132 | |
| 解释度 Explain of the degree (%) | 77.856 | 8.087 | |
| 累计解释度 Cumulative explanatory degree (%) | 72.671 | 85.943 | |
| 权重 Weighing value | 0.529 | 0.471 | |
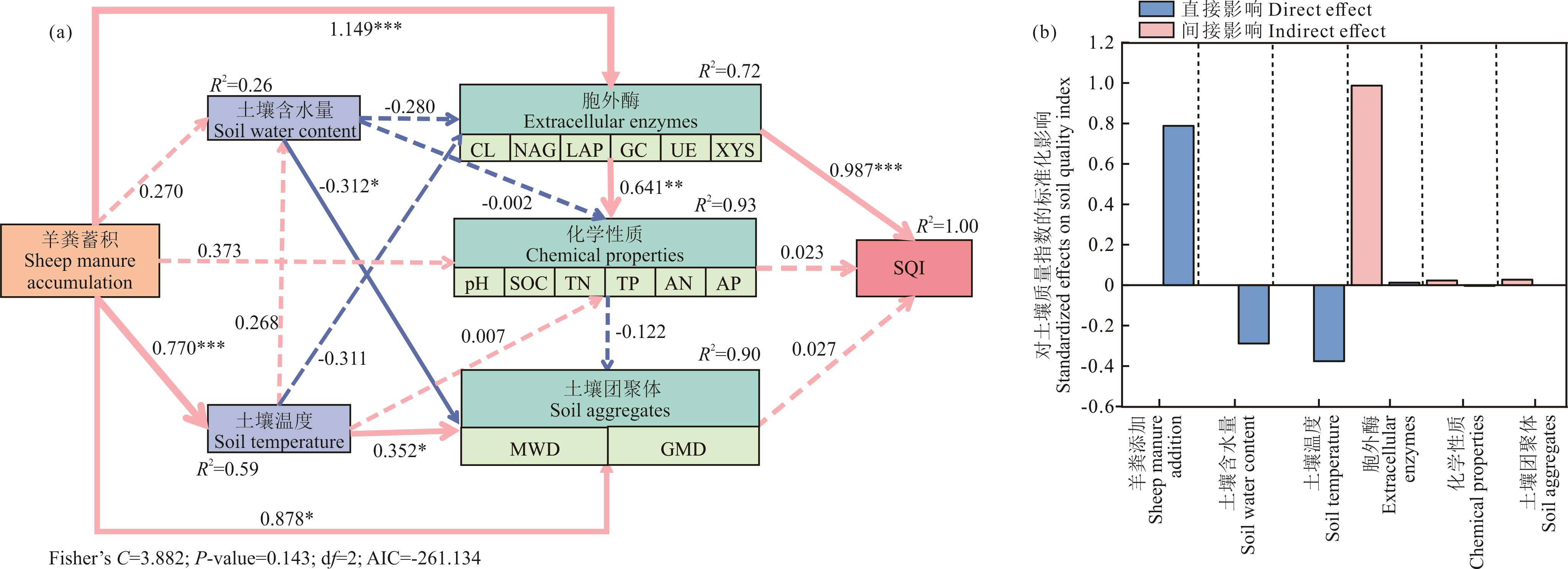
图7 羊粪归还对土壤质量指数影响的结构方程模型实线粉色和蓝色分别代表正相关和负相关,虚线代表相关性不显著(P>0.05),箭头的粗细与标准化路径系数的路径强度呈正比。粉色和蓝色柱子分别代表结构方程模型中每个变量的直接效应和间接效应。SQI:土壤质量指数;Fisher’s C:费希尔C统计量;P-value:概率值;df:自由度;AIC:赤池信息准则。Solid pink and blue lines represent positive and negative correlations, respectively, while dashed lines indicate non-significant correlations (P>0.05), the thickness of the arrows is proportional to the strength of the standardized path coefficients. The pink and blue bars represent the direct and indirect effects of each variable in the structural equation model (SEM), respectively. SQI: Soil quality index; Fisher’s C: Fisher’s C-statistic; P-value: Probability-value; df: Degrees of freedom; AIC: Akaike information criterion.
Fig.7 Structural equation model of the impact of sheep manure return on soil quality index
| [1] | Kang L, Han X G, Zhang Z B, et al. Grassland ecosystems in China: review of current knowledge and research advancement. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 2007, 362(1482): 997-1008. |
| [2] | Liu G X, Zhang Y J, Hovstad K A, et al. Competition of Leymus chinensis and Bromus inermis in response to gap size and neighbouring root exclusion. Grass & Forage Science, 2014, 69(3): 479-487. |
| [3] | Gang C C, Zhou W, Chen Y Z, et al. Quantitative assessment of the contributions of climate change and human activities on global grassland degradation. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 72(11): 4273-4282. |
| [4] | Schuman G E, Janzen H H, Herrick J E. Soil carbon dynamics and potential carbon sequestration by rangelands. Environmental Pollution, 2002, 116(3): 391-396. |
| [5] | Du Z Y, Cai Y J, Wang X D, et al. Research progress on grazing livestock dung decomposition and its influence on the dynamics of grassland soil nutrients. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(13): 4627-4637. |
| 杜子银, 蔡延江, 王小丹, 等. 放牧牲畜粪便降解及其对草地土壤养分动态的影响研究进展. 生态学报, 2019, 39(13): 4627-4637. | |
| [6] | Cai Y J, Akiyama H. Effects of inhibitors and biochar on nitrous oxide emissions, nitrate leaching, and plant nitrogen uptake from urine patches of grazing animals on grasslands: a meta-analysis. Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, 2017, 63(4): 405-414. |
| [7] | Frost C J, Hunter M D. Insect canopy herbivory and frass deposition affect soil nutrient dynamics and export in oak mesocosms. Ecology, 2004, 85(12): 3335-3347. |
| [8] | Veldhuis M P, Gommers M I, Olff H. Spatial redistribution of nutrients by large herbivores and dung beetles in a savanna ecosystem. Journal of Ecology, 2017, 106(1): 422-433. |
| [9] | An H, Li G Q. Effects of grazing on plant biomass and soil nutrient in desert steppe. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2013, 19(3): 705-712. |
| 安慧, 李国旗. 放牧对荒漠草原植物生物量及土壤养分的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(3): 705-712. | |
| [10] | Zhang R, Li J P, Peng W D, et al. Effects of mulching with caragana (Caragana intermedia) branches on soil moisture content and temperature and reseeded forage biomass in desertified grassland in Ningxia Province, China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(4): 58-67. |
| 张茹, 李建平, 彭文栋, 等. 柠条枝条覆盖对宁夏荒漠草原土壤水热及补播牧草生物量的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 58-67. | |
| [11] | Nan W L, Xie Y Z, Peng W D, et al. Restoration effects of reseeding and enclosure on vegetation of different degraded desert steppes. Pratacultural Science, 2024, 41(5): 1068-1077. |
| 南万璐, 谢应忠, 彭文栋, 等. 补播与围封对不同退化程度荒漠草地植被的恢复效果. 草业科学, 2024, 41(5): 1068-1077. | |
| [12] | Su J Q, Li X R, Yang H T, et al. Effects of fertilization on population density and biomass of herbaceous plants in desert steppe. Journal of Desert Research, 2013, 33(3): 696-702. |
| 苏洁琼, 李新荣, 杨昊天, 等. 施肥对荒漠化草原草本植物种群密度和生物量的影响. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(3): 696-702. | |
| [13] | Min X X, Ma Y S, Li S X, et al. Effects of sheep manure on productivity and nutrition of soil for Poa pratensis cv.Qinghai pasture. Pratacultural Science, 2014, 31(6): 1039-1044. |
| 闵星星, 马玉寿, 李世雄, 等. 羊粪对青海草地早熟禾草地生产力和土壤养分的影响. 草业科学, 2014, 31(6): 1039-1044. | |
| [14] | Zhang Y G, Yang S, Fu M M, et al. Sheep manure application increases soil exchangeable base cations in a semi-arid steppe of Inner Mongolia. Journal of Arid Land, 2015, 7(3): 361-369. |
| [15] | Kooch Y, Ghorbanzadeh N, Haghverdi K, et al. Soil quality cannot be improved after thirty years of land use change from forest to rangeland. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 856: 159132. |
| [16] | Ma J, Zhou Y, Lu Q, et al. Soil properties and quality evaluation of desert steppe under different management measures in arid windy and sandy areas. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2024, 40(24): 106-116. |
| 马菁, 周瑶, 陆琪, 等. 不同管理方式下干旱风沙区荒漠草原土壤性状变化及质量评价. 农业工程学报, 2024, 40(24): 106-116. | |
| [17] | Wan R P, Luo D Y, Liu J Y, et al. Superior improvement on soil quality by Pennisetum sinese vegetation restoration in the dry-hot valley region, SW China. The Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 878: 163185. |
| [18] | Li Z G, Xie Y Z. Improving desertified soil properties by incorporating and mulching tree branch in Ningxia Province. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(10): 174-181. |
| 李志刚, 谢应忠. 翻埋与覆盖林木枝条改善宁夏沙化土壤性质. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(10): 174-181. | |
| [19] | Wang X, Song N P, Yang X G, et al. Effects of sheep dung return on surface soil organic carbon and total nitrogen contents in deserted grassland. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 33(5): 6-10. |
| 王兴, 宋乃平, 杨新国, 等. 羊粪归还对荒漠草原表层土壤碳氮的影响. 水土保持通报, 2013, 33(5): 6-10. | |
| [20] | Zhao Q L, Sun M, Lin W, et al. Effects of sowing modes on soil water dynamics and grain protein formation in dryland wheat. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(11): 3977-3987. |
| 赵庆玲, 孙敏, 林文, 等. 播种方式对旱地小麦土壤水分变化和籽粒蛋白质形成的影响. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(11): 3977-3987. | |
| [21] | Liu G S. Soil physical and chemical analysis and description of soil profiles. Beijing: Standard Press of China, 1996. |
| 刘光崧. 土壤理化分析与剖面描述. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1996. | |
| [22] | Tisdall J M, Oades J M. Organic matter and water-stable aggregates in soils. Journal of Soil Science, 1982, 33(2): 141-163. |
| [23] | Bao S D. Soil agrochemistry analysis (the third edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| [24] | Liu J. The effects of Caragana korshinskii branches cover on the surficial sheep manure decomposition and associated with the regulation on soil-vegetation in a desert steppe. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2023. |
| 刘静. 柠条枝条覆盖对荒漠草地地表羊粪分解的影响及土壤-植被的调控. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2023. | |
| [25] | Ma X K, Xie Y P, Wang J, et al. Screening method of cellulase-producing fungi based on chromogenic enzyme reaction. Journal of Shenzhen University Science and Engineering, 2023, 40(4): 407-414. |
| 马学坤, 谢燕萍, 王娟, 等. 基于酶反应显色的产纤维素酶真菌筛选方法. 深圳大学学报(理工版), 2023, 40(4): 407-414. | |
| [26] | Saiya-Cork K R, Sinsabaugh R L, Zak D R. The effects of long term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2002, 34(9): 1309-1315. |
| [27] | Yao W R, Ding X L. Determination of β-glucosidase in cellulase system by pNPG method. Microbiology China, 1998, 25(3): 982-983. |
| 姚卫蓉, 丁霄霖. pNPG法测定纤维素酶系中β-葡萄糖苷酶. 微生物学通报, 1998, 25(3): 982-983. | |
| [28] | Huang S Y. The mechanism study of soil leucine aminopeptidase affected by cadmium contamination. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2023. |
| 黄舜禹. 土壤亮氨酸氨基肽酶对镉污染响应机制研究. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2023. | |
| [29] | Guan S Y. Soil enzyme and its research methods. Beijing: Agriculture Press, 1986. |
| 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法. 北京: 农业出版社, 1986. | |
| [30] | Schmitt S, Tsai P, Bell J, et al. Assessing the complex sponge microbiota: core, variable and species-specific bacterial communities in marine sponges. The ISME Journal, 2012, 6(3): 564-576. |
| [31] | Lu Q, Ma H B, Zhou Y, et al. Restoration of soil quality of degraded grassland can be accelerated by reseeding in an arid area of Northwest China. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1101295. |
| [32] | Zhou Y, Ma H B, Xie Y Z, et al. Assessment of soil quality indexes for different land use types in typical steppe in the loess hilly area, China. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 118: 106743. |
| [33] | Raiesi F. A minimum data set and soil quality index to quantify the effect of land use conversion on soil quality and degradation in native rangelands of upland arid and semiarid regions. Ecological Indicators, 2017, 75: 307-320. |
| [34] | Nabiollahi K, Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi R, Kerry R, et al. Assessment of soil quality indices for salt-affected agricultural land in Kurdistan Province, Iran. Ecological Indicators, 2017, 83: 482-494. |
| [35] | Wang M M, Ren C H, Huang Y F, et al. Research progress on the effects of sheep manure on soil properties and plant growth. Acta Ecologiae Animalis Domastici, 2024, 45(1): 1-8. |
| 王明明, 任春环, 黄桠锋, 等. 羊粪对土壤性状及植物生长影响的研究进展. 家畜生态学报, 2024, 45(1): 1-8. | |
| [36] | Liu W J, Jiang F Z, Qi K B, et al. Effects of different fertilization and sowing amounts on vegetation restoration and soil quality in alpine mining areas and comprehensive evaluation. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(5): 27-39. |
| 刘文谨, 蒋福祯, 祁凯斌, 等. 不同施肥量和播种量对高寒矿区植被恢复和土壤质量的影响及综合评价. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 27-39. | |
| [37] | Yang Y P, Yin J, Zhu Y H, et al. Effects of water and nitrogen regulation on potato yield and soil quality in the arid region of central Ningxia. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2024, 55(9): 358-370, 458. |
| 杨莹攀, 尹娟, 朱银浩, 等. 水氮调控对宁夏中部旱区马铃薯产量与土壤质量的影响. 农业机械学报, 2024, 55(9): 358-370, 458. | |
| [38] | Shukla G, Varma A. Soil enzymology. Germany: Springer Berlin Heidelberg Press, 2011. |
| [39] | An X T, Yu Z Y, Hu S B, et al. Effects of different fertilization combinations on soil physicochemical properties and enzyme activities in alpine mining area. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2025, 33(3): 984-991. |
| 安晓婷, 于中阳, 胡生斌, 等. 不同施肥组合对高寒矿区土壤理化性质及酶活性的影响. 草地学报, 2025, 33(3): 984-991. | |
| [40] | Mo S W, Yu W, Liang L X, et al. Organic fertilizer types and application methods on tea yield, quality and soil health. Journal of Guizhou Tea, 2024(5): 5-8. |
| 莫尚威, 余威, 梁林霞, 等. 有机肥料种类和施用方式对茶叶产量与品质及土壤健康的影响. 贵茶, 2024(5): 5-8. | |
| [41] | Wei X X, Xiong J F, Li T, et al. Effects of different organic amendments on soil organic carbon and its labile fractions in the paddy soil of a double rice cropping system. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(7): 2373-2380. |
| 魏夏新, 熊俊芬, 李涛, 等.有机物料还田对双季稻田土壤有机碳及其活性组分的影响. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(7): 2373-2380. | |
| [42] | Chen Y Q, Sui P, Yan L L, et al. Effects of different organic wastes incorporation on soil organic carbon and its fraction under wheat-maize cropping system in North China plain. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(S2): 94-102. |
| 陈源泉, 隋鹏, 严玲玲, 等. 有机物料还田对华北小麦玉米两熟农田土壤有机碳及其组分的影响. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(S2): 94-102. | |
| [43] | Chen G J. Effects of wild animal feces on soil organic carbon decomposition, formation and stabilization. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2024. |
| 陈广娇. 野生动物粪便对土壤有机碳分解、形成和稳定的影响. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2024. | |
| [44] | Cui H. Transformation and regulation of phosphorus fractions during livestock manure composting. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022. |
| 崔虎. 畜禽粪便堆肥过程中磷形态的转化与调控. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2022. | |
| [45] | Malik A A, Jeremy P, Buckeridge K M, et al. Land use driven change in soil pH affects microbial carbon cycling processes. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-10. |
| [46] | Angst G, Mueller K E, Kögel-Knabner I, et al. Aggregation controls the stability of lignin and lipids in clay-sized particulate and mineral associated organic matter. Biogeochemistry, 2017, 132(3): 307-324. |
| [47] | Zhu Y H, Merbold L, Leitner S, et al. The effects of climate on decomposition of cattle, sheep and goat manure in Kenyan tropical pastures. Plant and Soil, 2020, 451(1/2): 325-343. |
| [48] | Rabbi S M F, Warren C R, Swarbrick B, et al. Microbial decomposition of organic matter and wetting-drying promotes aggregation in artificial soil but porosity increases only in wet-dry condition. Geoderma, 2024, 447: 116924. |
| [49] | Jia P J, Liu Y M, Liu Y M, et al. Effects of understory vegetation on the growth and soil quality of young Phoebe zhennan forest. Journal of Forest and Environment, 2025, 45(1): 53-61. |
| 贾朋聚, 刘亚敏, 刘玉民, 等. 林下植被对桢楠幼林生长和土壤质量的影响. 森林与环境学报, 2025, 45(1): 53-61. |
| [1] | 康佳惠, 郑敏娜, 龚瑞杰, 韩志顺, 陈燕妮, 梁秀芝. 氮磷添加对一年生人工草地土壤微生物-胞外酶生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 13-24. |
| [2] | 邓文辉, 宋珂辰, 张浩, 管思雨, 雍嘉仪, 谢铁娜, 胡海英. 降水变化对荒漠草原植物群落主要物种气孔形态和光合生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 65-78. |
| [3] | 张邦彦, 谢小伟, 张朝辉, 武晋民, 王彬, 许兴. 有机-无机改良物料对盐碱地土壤质量及湖南稷子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 15-29. |
| [4] | 邓文辉, 宋珂辰, 张浩, 管思雨, 雍嘉仪, 胡海英. 降水变化条件下荒漠草原优势植物根际微生物群落结构和多样性特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 12-26. |
| [5] | 刘文谨, 蒋福祯, 祁凯斌, 宋明丹, 李正鹏. 不同施肥量和播种量对高寒矿区植被恢复和土壤质量的影响及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 27-39. |
| [6] | 蒋鹏, 李磊, 解昊郡, 徐得甲, 王锐, 虎强, 孙权. 净化沼液滴灌对砂壤土质量、青贮玉米生产力的影响及安全消纳容量分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 64-81. |
| [7] | 刘淑琪, 崔东, 刘文新, 杨海军, 杨延成, 江智诚, 闫江超, 刘江慧. 短期氮、水添加和刈割对苦豆子型退化草地植物群落特征与土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 41-55. |
| [8] | 马利利, 蒋福祯, 马玉寿, 祁凯斌, 贾顺斌, 李正鹏. 粒径配比、施肥量以及播量耦合对矿区煤矸石基质的改良效果[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 71-84. |
| [9] | 贾蕴欢, 胡雯颖, 邓健, 赵雪, 陈子玥, 王亚楠, 李江文, 张晓曦. 氮添加对黄土丘陵区草地土壤微生物养分限制特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 221-232. |
| [10] | 骆欣怡, 邱开阳, 金涛, 鲍平安, 黄业芸, 何毅, 谢应忠. 碳、氮、钾添加对荒漠草原凋落物分解特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 41-53. |
| [11] | 马蓉, 李俊瑶, 岳平, 马旭君, 白珍, 庄玲, 白敬, 赵学勇, 王少昆. 降水变化下荒漠草原优势植物功能性状对生物量分配的调节机制[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(11): 31-39. |
| [12] | 卢小倩, 陈金露, 杨卫君, 郭青云, 王单丽, 赵红梅. 氮肥减量配施腐植酸对北疆滴灌玉米田土壤真菌群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 120-131. |
| [13] | 闫玉龙, 杜学军, 王元月, 刘建立, 丁银贵, 魏源送. 脱硫石膏与粉煤灰配施对盐碱土改良效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 30-40. |
| [14] | 鲍平安, 文志林, 王炎, 陈彦虎, 季波, 王占军, 吴旭东, 蒋齐. 不同牧草补播模式对荒漠草原植物群落结构及土壤特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 62-73. |
| [15] | 赵文军, 梁婷, 王剑松, 刘魁, 冯瑜, 王正旭, 徐梓荷, 朱云聪, 孙蒙猛, 李湘伟, 付利波, 尹梅, 周国朋, 陈华, 曹卫东. 种植翻压光叶紫花苕配合氮肥减施提高烤烟产量和土壤质量[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 74-84. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||