

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (10): 74-84.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024453
赵文军1,2( ), 梁婷3(
), 梁婷3( ), 王剑松1, 刘魁1, 冯瑜4, 王正旭1, 徐梓荷1, 朱云聪1, 孙蒙猛1, 李湘伟1, 付利波5, 尹梅5, 周国朋6, 陈华5(
), 王剑松1, 刘魁1, 冯瑜4, 王正旭1, 徐梓荷1, 朱云聪1, 孙蒙猛1, 李湘伟1, 付利波5, 尹梅5, 周国朋6, 陈华5( ), 曹卫东3(
), 曹卫东3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-19
修回日期:2024-12-16
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-07-11
通讯作者:
陈华,曹卫东
作者简介:caoweidong@caas.cn基金资助:
Wen-jun ZHAO1,2( ), Ting LIANG3(
), Ting LIANG3( ), Jian-song WANG1, Kui LIU1, Yu FENG4, Zheng-xu WANG1, Zi-he XU1, Yun-cong ZHU1, Meng-meng SUN1, Xiang-wei LI1, Li-bo FU5, Mei YIN5, Guo-peng ZHOU6, Hua CHEN5(
), Jian-song WANG1, Kui LIU1, Yu FENG4, Zheng-xu WANG1, Zi-he XU1, Yun-cong ZHU1, Meng-meng SUN1, Xiang-wei LI1, Li-bo FU5, Mei YIN5, Guo-peng ZHOU6, Hua CHEN5( ), Wei-dong CAO3(
), Wei-dong CAO3( )
)
Received:2024-11-19
Revised:2024-12-16
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-07-11
Contact:
Hua CHEN,Wei-dong CAO
摘要:
探讨云南烟区绿肥翻压量配合氮肥减施的效应,以期为烤烟生产的节肥增效提供理论依据和技术途径。基于2017年开始的田间试验,于2022年研究了翻压不同量光叶紫花苕配合减氮15%及30%对烤烟产量和土壤质量的影响。相比冬闲-烤烟常规施肥(F100),22500~30000 kg·hm-2光叶紫花苕翻压量配合减施常规量氮肥15%和30%,烤烟产量提升了4.85%~9.94%(P<0.05)。翻压光叶紫花苕配合减施氮肥改善了土壤养分性状,其中,光叶紫花苕翻压30000 kg·hm-2配合减氮30%处理土壤有机质和可溶性有机氮含量最高,相比F100处理分别提高了28.2%和242.6%(P<0.05)。光叶紫花苕翻压22500和30000 kg·hm-2配合减氮30%处理土壤质量指数相比F100分别提高了49.1%和72.9%(P<0.05)。不同施氮水平下,土壤碳、氮、磷相关水解酶活性随着绿肥翻压量的增加而增加。偏最小二乘路径分析(PLS-PM)和随机森林分析表明,烤烟产量主要受土壤有机质及酶活性的影响。因此,种植翻压绿肥后合理减施氮肥能够提高烤烟产量和土壤质量,其中翻压光叶紫花苕22500~30000 kg·hm-2减施氮肥30%效果突出。
赵文军, 梁婷, 王剑松, 刘魁, 冯瑜, 王正旭, 徐梓荷, 朱云聪, 孙蒙猛, 李湘伟, 付利波, 尹梅, 周国朋, 陈华, 曹卫东. 种植翻压光叶紫花苕配合氮肥减施提高烤烟产量和土壤质量[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 74-84.
Wen-jun ZHAO, Ting LIANG, Jian-song WANG, Kui LIU, Yu FENG, Zheng-xu WANG, Zi-he XU, Yun-cong ZHU, Meng-meng SUN, Xiang-wei LI, Li-bo FU, Mei YIN, Guo-peng ZHOU, Hua CHEN, Wei-dong CAO. Planting and incorporation of smooth vetch together with reduced nitrogen fertilizer application enhances tobacco yield and soil quality[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(10): 74-84.
| pH | 有机质 Soil organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolysable nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.10 | 22.1 | 0.90 | 76.1 | 145.0 | 30.7 |
表1 土壤基础理化性状
Table 1 Soil basic physical and chemical properties
| pH | 有机质 Soil organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolysable nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.10 | 22.1 | 0.90 | 76.1 | 145.0 | 30.7 |
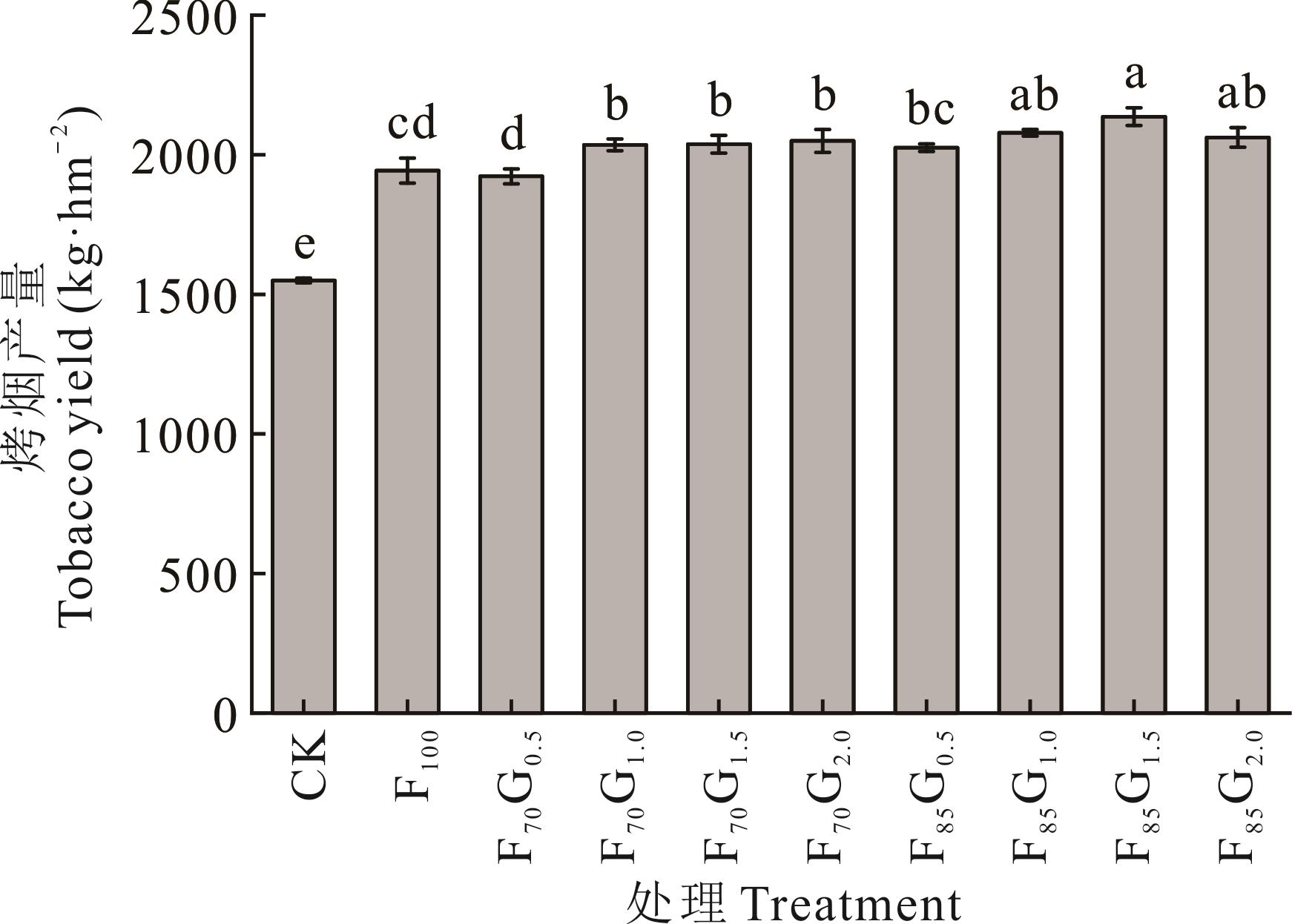
图1 不同施肥处理烤烟产量CK:冬闲不施氮肥;F100:冬闲+常规施用氮肥;F70G0.5:70%氮肥+绿肥7500 kg·hm-2;F70G1.0:70%氮肥+绿肥15000 kg·hm-2;F70G1.5:70%氮肥+绿肥22500 kg·hm-2;F70G2.0:70%氮肥+绿肥30000 kg·hm-2;F85G0.5:85%氮肥+绿肥7500 kg·hm-2;F85G1.0:85%氮肥+绿肥15000 kg·hm-2;F85G1.5:85%氮肥+绿肥22500 kg·hm-2;F85G2.0:85%氮肥+绿肥30000 kg·hm-2。不同小写字母表示不同处理间存在显著差异(P<0.05)。下同。CK: No nitrogen fertilizer in winter fallow; F100: Winter fallow with conventional application of nitrogen fertilizer; F70G0.5: 70% nitrogen fertilizer with green manure 7500 kg·ha-1; F70G1.0: 70% nitrogen fertilizer with green manure 15000 kg·ha-1; F70G1.5: 70% nitrogen fertilizer with green manure 22500 kg·ha-1; F70G2.0: 70% nitrogen fertilizer with green manure 30000 kg·ha-1; F85G0.5: 85% nitrogen fertilizer with green manure 7500 kg·ha-1; F85G1.0: 85% nitrogen fertilizer with green manure 15000 kg·ha-1; F85G1.5: 85% nitrogen fertilizer with green manure 22500 kg·ha-1; F85G2.0: 85% nitrogen fertilizer with green manure 30000 kg·ha-1. Different lowercase letters indicated significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Tobacco yield in different treatments
处理 Treatment | pH | 有机质 Soil organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 可溶性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon (mg·kg-1) | 可溶性有机氮 Dissolved organic nitrogen (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.16±0.10ab | 26.0±1.45cd | 1.66±0.04b | 6.22±0.17d | 55±5.63f | 42.3±0.66b | 380±30.0d | 83±7.54b | 77±39.4d |
| F100 | 6.26±0.03a | 25.5±1.40d | 2.06±0.03a | 7.66±0.48d | 66±13.60ef | 43.3±2.08b | 412±6.0cd | 81±4.51b | 76±19.4d |
| F70G0.5 | 6.00±0.09bc | 28.6±1.43bcd | 2.10±0.04a | 8.62±1.39d | 121±7.04bcd | 44.6±4.65ab | 653±81.9ab | 112±9.33a | 185±12.2bc |
| F70G1.0 | 6.03±0.01bc | 28.9±0.58abcd | 2.06±0.12a | 14.50±1.00c | 140±15.60bc | 45.9±2.94ab | 583±18.6abc | 103±3.02a | 191±20.3bc |
| F70G1.5 | 5.95±0.08c | 29.2±1.52abcd | 2.09±0.15a | 18.40±1.02b | 101±12.50cde | 47.7±3.26ab | 625±60.6ab | 111±4.58a | 221±18.0ab |
| F70G2.0 | 5.95±0.07c | 32.7±1.43a | 2.17±0.11a | 22.60±2.73a | 104±18.70cde | 50.1±1.31ab | 660±48.1ab | 113±14.00a | 259±13.4a |
| F85G0.5 | 6.12±0.03abc | 29.5±0.81abc | 2.13±0.07a | 7.50±0.05d | 90±5.26def | 42.2±2.83b | 478±91.4bcd | 103±5.84a | 136±13.4cd |
| F85G1.0 | 5.99±0.05bc | 30.6±1.17ab | 2.01±0.04a | 6.55±0.33d | 143±21.30bc | 45.9±6.35ab | 503±58.6abcd | 112±6.78a | 228±18.5ab |
| F85G1.5 | 6.01±0.03bc | 31.8±1.63ab | 1.90±0.19ab | 14.10±1.40c | 151±13.50b | 46.5±0.95ab | 590±115.0abc | 116±3.00a | 209±20.7ab |
| F85G2.0 | 6.01±0.09bc | 32.4±1.33ab | 1.99±0.06a | 6.93±0.61d | 250±22.40a | 52.9±1.10a | 678±81.9a | 117±3.37a | 242±19.0ab |
表2 不同施肥处理下土壤养分性状
Table 2 Soil nutrients in different treatments
处理 Treatment | pH | 有机质 Soil organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 可溶性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon (mg·kg-1) | 可溶性有机氮 Dissolved organic nitrogen (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.16±0.10ab | 26.0±1.45cd | 1.66±0.04b | 6.22±0.17d | 55±5.63f | 42.3±0.66b | 380±30.0d | 83±7.54b | 77±39.4d |
| F100 | 6.26±0.03a | 25.5±1.40d | 2.06±0.03a | 7.66±0.48d | 66±13.60ef | 43.3±2.08b | 412±6.0cd | 81±4.51b | 76±19.4d |
| F70G0.5 | 6.00±0.09bc | 28.6±1.43bcd | 2.10±0.04a | 8.62±1.39d | 121±7.04bcd | 44.6±4.65ab | 653±81.9ab | 112±9.33a | 185±12.2bc |
| F70G1.0 | 6.03±0.01bc | 28.9±0.58abcd | 2.06±0.12a | 14.50±1.00c | 140±15.60bc | 45.9±2.94ab | 583±18.6abc | 103±3.02a | 191±20.3bc |
| F70G1.5 | 5.95±0.08c | 29.2±1.52abcd | 2.09±0.15a | 18.40±1.02b | 101±12.50cde | 47.7±3.26ab | 625±60.6ab | 111±4.58a | 221±18.0ab |
| F70G2.0 | 5.95±0.07c | 32.7±1.43a | 2.17±0.11a | 22.60±2.73a | 104±18.70cde | 50.1±1.31ab | 660±48.1ab | 113±14.00a | 259±13.4a |
| F85G0.5 | 6.12±0.03abc | 29.5±0.81abc | 2.13±0.07a | 7.50±0.05d | 90±5.26def | 42.2±2.83b | 478±91.4bcd | 103±5.84a | 136±13.4cd |
| F85G1.0 | 5.99±0.05bc | 30.6±1.17ab | 2.01±0.04a | 6.55±0.33d | 143±21.30bc | 45.9±6.35ab | 503±58.6abcd | 112±6.78a | 228±18.5ab |
| F85G1.5 | 6.01±0.03bc | 31.8±1.63ab | 1.90±0.19ab | 14.10±1.40c | 151±13.50b | 46.5±0.95ab | 590±115.0abc | 116±3.00a | 209±20.7ab |
| F85G2.0 | 6.01±0.09bc | 32.4±1.33ab | 1.99±0.06a | 6.93±0.61d | 250±22.40a | 52.9±1.10a | 678±81.9a | 117±3.37a | 242±19.0ab |

图2 土壤养分性状及土壤质量指数pH:土壤pH值;NO3--N:硝态氮;NH4+-N:铵态氮;DON:可溶性有机氮;DOC:可溶性有机碳;AK:速效钾;AP:有效磷;TN:总氮;SOM:土壤有机质。下同。pH:Soil pH value;NO3--N: Nitrate nitrogen;NH4+-N: Ammonium nitrogen;DON: Dissolved organic nitrogen;DOC: Dissolved organic carbon;AK: Available potassium;AP: Available phosphorus;TN: Total nitrogen;SOM: Soil organic matter. The same below.
Fig.2 Soil nutrients and soil quality index
处理 Treatment | 碳转化相关酶 Carbon-related enzyme activities | 氮转化相关酶 Nitrogen-related enzyme activities | 磷转化相关酶 Phosphorus-related enzyme activities | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
β-葡萄糖苷酶 β-glucosidase | β-纤维二糖苷酶 β-cellobiosidase | β-木糖苷酶 β-xylosidase | α-葡萄糖苷酶 α-glucosidases | 乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶Acetylglucosaminidase | 亮氨酸氨基 肽酶Leucine aminopeptidase | 碱性磷酸酶 Alkaline phosphatase | |
| CK | 26.5±1.72bc | 1.62±0.16c | 2.51±0.27d | 0.96±0.07f | 7.6±0.25e | 514±9.57d | 509±20.3f |
| F100 | 28.1±0.86b | 1.82±0.24bc | 2.62±0.41d | 1.42±0.22ef | 10.6±0.74cd | 568±8.24cd | 606±11.4cde |
| F70G0.5 | 24.2±1.33bc | 1.75±0.11bc | 3.39±0.13d | 1.52±0.11e | 7.9±0.31e | 534±8.33d | 534±11.6ef |
| F70G1.0 | 28.7±1.64b | 2.19±0.07abc | 4.84±0.44c | 1.87±0.04de | 9.2±0.30de | 564±4.32cd | 580±9.9def |
| F70G1.5 | 36.6±2.50a | 2.24±0.14abc | 6.86±0.15b | 2.31±0.02cd | 11.6±0.90bc | 616±7.99bc | 645±39.4cd |
| F70G2.0 | 40.8±3.91a | 2.72±0.07a | 8.66±0.47a | 2.71±0.13bc | 15.7±1.05a | 680±20.40b | 835±30.4a |
| F85G0.5 | 20.9±3.23c | 1.94±0.06bc | 3.41±0.46d | 1.99±0.02d | 7.9±0.91e | 520±0.88d | 630±36.0cd |
| F85G1.0 | 29.8±0.52b | 2.33±0.17ab | 5.86±0.26bc | 2.22±0.04d | 12.5±0.49bc | 579±28.60cd | 666±4.4c |
| F85G1.5 | 30.1±0.74b | 2.72±0.52a | 5.95±0.56b | 2.91±0.18b | 12.8±0.31b | 655±17.90b | 675±13.5bc |
| F85G2.0 | 36.5±0.98a | 2.74±0.13a | 8.52±0.13a | 3.52±0.37a | 16.8±0.79a | 762±64.50a | 756±54.8ab |
表3 不同施肥处理土壤水解酶活性
Table 3 Hydrolase enzyme activities in soils under different treatments (nmol·h-1·g-1)
处理 Treatment | 碳转化相关酶 Carbon-related enzyme activities | 氮转化相关酶 Nitrogen-related enzyme activities | 磷转化相关酶 Phosphorus-related enzyme activities | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
β-葡萄糖苷酶 β-glucosidase | β-纤维二糖苷酶 β-cellobiosidase | β-木糖苷酶 β-xylosidase | α-葡萄糖苷酶 α-glucosidases | 乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶Acetylglucosaminidase | 亮氨酸氨基 肽酶Leucine aminopeptidase | 碱性磷酸酶 Alkaline phosphatase | |
| CK | 26.5±1.72bc | 1.62±0.16c | 2.51±0.27d | 0.96±0.07f | 7.6±0.25e | 514±9.57d | 509±20.3f |
| F100 | 28.1±0.86b | 1.82±0.24bc | 2.62±0.41d | 1.42±0.22ef | 10.6±0.74cd | 568±8.24cd | 606±11.4cde |
| F70G0.5 | 24.2±1.33bc | 1.75±0.11bc | 3.39±0.13d | 1.52±0.11e | 7.9±0.31e | 534±8.33d | 534±11.6ef |
| F70G1.0 | 28.7±1.64b | 2.19±0.07abc | 4.84±0.44c | 1.87±0.04de | 9.2±0.30de | 564±4.32cd | 580±9.9def |
| F70G1.5 | 36.6±2.50a | 2.24±0.14abc | 6.86±0.15b | 2.31±0.02cd | 11.6±0.90bc | 616±7.99bc | 645±39.4cd |
| F70G2.0 | 40.8±3.91a | 2.72±0.07a | 8.66±0.47a | 2.71±0.13bc | 15.7±1.05a | 680±20.40b | 835±30.4a |
| F85G0.5 | 20.9±3.23c | 1.94±0.06bc | 3.41±0.46d | 1.99±0.02d | 7.9±0.91e | 520±0.88d | 630±36.0cd |
| F85G1.0 | 29.8±0.52b | 2.33±0.17ab | 5.86±0.26bc | 2.22±0.04d | 12.5±0.49bc | 579±28.60cd | 666±4.4c |
| F85G1.5 | 30.1±0.74b | 2.72±0.52a | 5.95±0.56b | 2.91±0.18b | 12.8±0.31b | 655±17.90b | 675±13.5bc |
| F85G2.0 | 36.5±0.98a | 2.74±0.13a | 8.52±0.13a | 3.52±0.37a | 16.8±0.79a | 762±64.50a | 756±54.8ab |
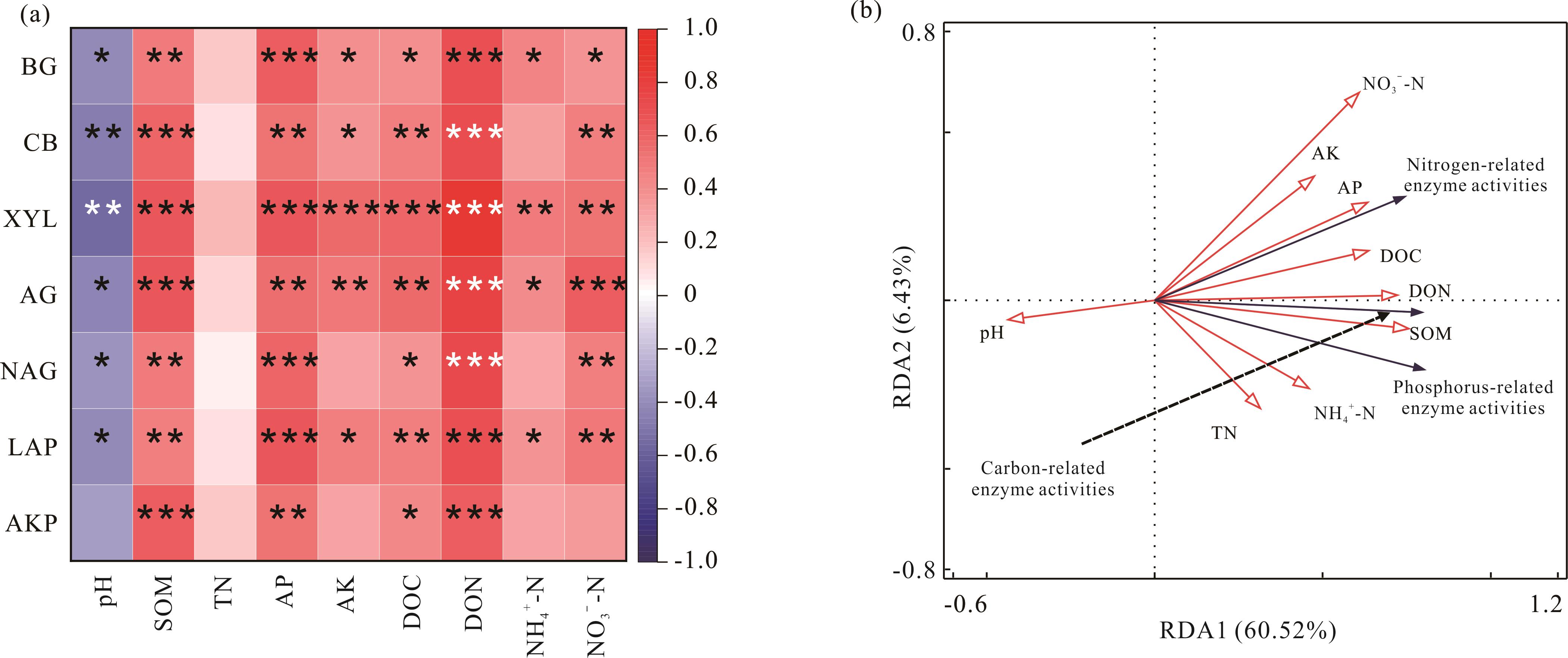
图3 相关性和冗余分析BG:β-葡萄糖苷酶;CB:β-纤维二糖苷酶;XYL:β-木糖苷酶;AG:α-葡萄糖苷酶;NAG:乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶;LAP:亮氨酸氨基肽酶;AKP:碱性磷酸酶。Nitrogen-related enzyme activities:氮转化相关酶活性;Carbon-related enzyme activities:碳转化相关酶活性;Phosphorus-related enzyme activities:磷转化相关酶活性。*表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01,***表示P<0.001。下同。BG: β-glucosidase; CB: β-cellobiosidase;XYL: β-xylosidase; AG: α-glucosidase; NAG: Acetylglucosaminidase; LAP: Leucine aminopeptidase; AKP: Alkaline phosphatase. *: P<0.05,**: P<0.01,***: P<0.001. The same below.
Fig.3 The correlation and redundancy analysis (RDA)
处理 Treatment | 有机质 Soil organic matter | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | pH | 可溶性有机氮 Dissolved organic nitrogen | 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | 速效钾 Available potassium | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 可溶性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon | 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 解释率Explains rate | 34.6 | 16.1 | 3.8 | 5.1 | 4.5 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 贡献率Contribution rate | 51.7 | 24.0 | 5.7 | 7.7 | 6.7 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| 显著性Significance | ** | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
表4 冗余分析参数
Table 4 Redundancy analysis parameters (%)
处理 Treatment | 有机质 Soil organic matter | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | pH | 可溶性有机氮 Dissolved organic nitrogen | 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | 速效钾 Available potassium | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 可溶性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon | 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 解释率Explains rate | 34.6 | 16.1 | 3.8 | 5.1 | 4.5 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 贡献率Contribution rate | 51.7 | 24.0 | 5.7 | 7.7 | 6.7 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| 显著性Significance | ** | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
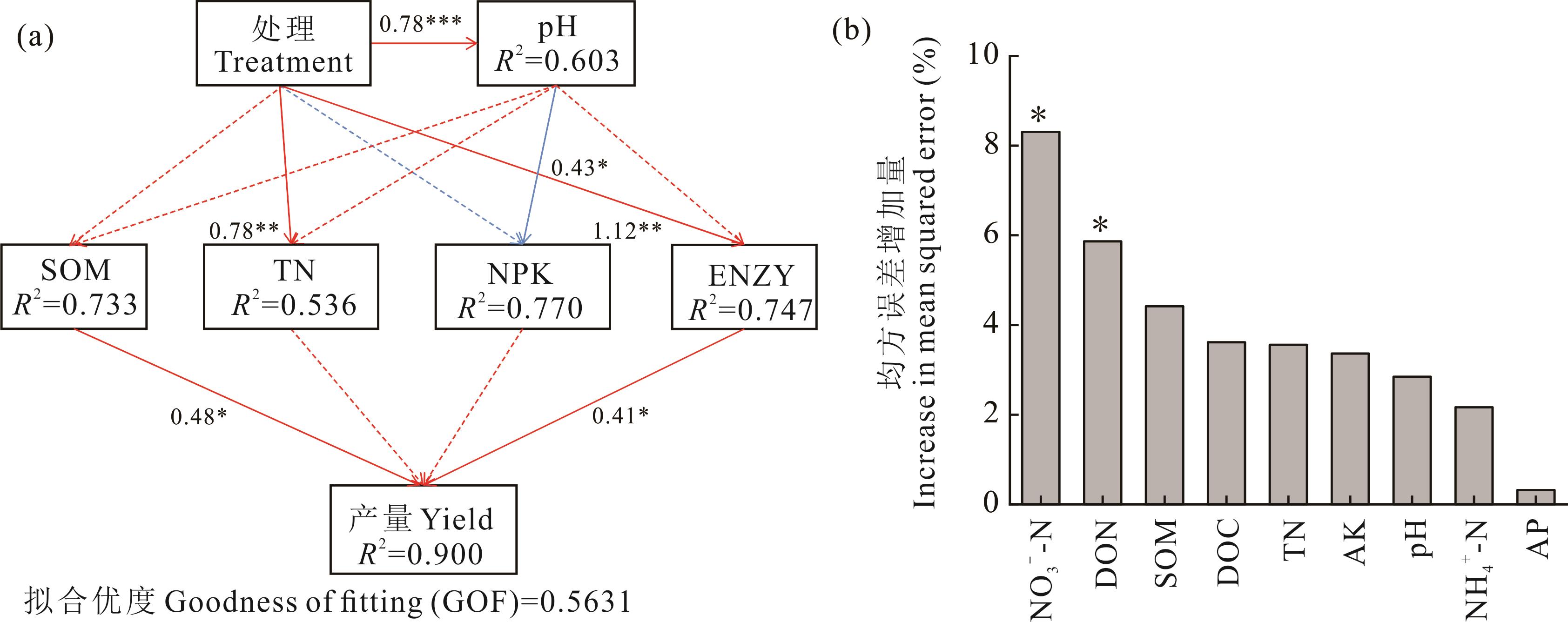
图4 偏最小二乘路径和随机森林模型NPK表示无机氮、有效磷和速效钾,因子载荷值分别为0.813、0.478和0.794,ENZY表示土壤BG、CB、XYL、AG、NAG、LAP和AKP活性,因子载荷值分别为0.752、0.780、0.824、0.946、0.912、0.907和0.886。NPK represents inorganic nitrogen, available phosphorus, and available potassium, with factor loadings of 0.813, 0.478, and 0.794, respectively. ENZY represents soil enzyme activities of BG, CB, XYL, AG, NAG, LAP, and AKP, with factor loadings of 0.752, 0.780, 0.824, 0.946, 0.912, 0.907, and 0.886, respectively.
Fig.4 The partial least squares path model and random forest model
| [1] | Liu G S. Tobacco cultivation (the second edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2016. |
| 刘国顺. 烟草栽培学(第2版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2016. | |
| [2] | Xie X Q, Li X W, Zhu Y C, et al. Research progresses and consideration on flue-cured tobacco planting regionalization in China. Soils, 2020, 52(6): 1105-1112. |
| 谢新乔, 李湘伟, 朱云聪, 等. 我国不同尺度烤烟种植区划与思考. 土壤, 2020, 52(6): 1105-1112. | |
| [3] | Liu Q L, Chen F, Zhang Y G, et al. Nitrogen uptake of flue-cured tobacco in typical types of soil in southwest China. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(3): 486-493. |
| 刘青丽, 陈阜, 张云贵, 等. 我国西南烟区典型植烟土壤烤烟氮素的吸收规律. 作物学报, 2013, 39(3): 486-493. | |
| [4] | Wang Y Q. Effects of long-term cultivation and fertilization on tobacco-grown soil productivity and nutrients. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2021. |
| 王亚麒. 长期种植施肥模式对烟地生产力和养分状况的影响. 重庆: 西南大学, 2021. | |
| [5] | Ning S Q, Jiang R, Li Z M, et al. Effects of three kinds of green manure on the yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco, soil nutrients and enzyme activities. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2024(4): 128-135. |
| 宁诗琪, 蒋如, 李治模, 等. 三种绿肥对烤烟产质量及土壤养分和酶活性的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2024(4): 128-135. | |
| [6] | Zhang J G, Shen G M, Zhang J Q, et al. Advance in continuous cropping problems of tobacco. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2011, 32(3): 95-99. |
| 张继光, 申国明, 张久权, 等. 烟草连作障碍研究进展. 中国烟草科学, 2011, 32(3): 95-99. | |
| [7] | Cao W D, Gao S J. Chinese green manure development strategy by 2025. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2023, 44(12): 1-9. |
| 曹卫东, 高嵩涓. 到2025年中国绿肥发展策略. 中国农业资源与区划, 2023, 44(12): 1-9. | |
| [8] | Gao S J, Zhou G P, Cao W D. Effects of milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus) as winter green manure on rice yield and rate of fertilizer application in rice paddies in south China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(12): 2115-2126. |
| 高嵩涓, 周国朋, 曹卫东. 南方稻田紫云英作冬绿肥的增产节肥效应与机制. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(12): 2115-2126. | |
| [9] | Xia R, Dong W J, Ma E D, et al. Effects of different green manure application on soil physical and chemical properties, yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco in continuous cropping field. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(7): 165-170. |
| 夏融, 童文杰, 马二登, 等. 绿肥掩青对连作烟田土壤性质及烤烟产质量的影响. 安徽农业科学, 2023, 51(7): 165-170. | |
| [10] | Garland G, Edlinger A, Banerjee S K, et al. Crop cover is more important than rotational diversity for soil multifunctionality and cereal yields in European cropping systems. Nature Food, 2021, 2(1): 28-37. |
| [11] | Huang P N, Qin D Z, Long H Y, et al. Effects of green manure-tobacco-paddy rice crop rotation to leaf tobacco yield quality and latter-stubble late rice yield. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(1): 103-108. |
| 黄平娜, 秦道珠, 龙怀玉, 等. 绿肥-烟-稻轮作与烟叶产量品质及后茬晚稻产量效应. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(1): 103-108. | |
| [12] | Feng Y, Chen H, Fu L B, et al. Utilizing green manure to increase tobacco quality and soil fertility in the erosion area of Fuxian Lake in Yunnan Province. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(11): 2083-2094. |
| 冯瑜, 陈华, 付利波, 等. 利用绿肥提高云南抚仙湖径流区烟田土壤养分和烤烟品质. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(11): 2083-2094. | |
| [13] | Liang H, Fu L B, Chen H, et al. Green manuring facilitates bacterial community dispersal across different compartments of subsequent tobacco. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2023, 22(4): 1199-1215. |
| [14] | Liang H, Li S, Zhou G P, et al. Targeted regulation of the microbiome by green manuring to promote tobacco growth. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2023, 60(1): 69-85. |
| [15] | Kong W, Chu L Z, Lu J W, et al. The influence on growth and development of flue-cured tobacco by different application times of Vicia villosa var. glabresens. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(1): 150-154. |
| 孔伟, 储刘专, 鲁剑巍, 等. 光叶紫花苕子不同翻压期对烤烟生长发育的影响. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(1): 150-154. | |
| [16] | Si G H, Wu W H, Mei D H, et al. Effect of different burying amount of Vicia villosa on yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2011, 32(S1): 82-86. |
| 佀国涵, 吴文昊, 梅东海, 等. 不同光叶紫花苕子翻压量对烤烟产量和品质的影响. 中国烟草科学, 2011, 32(S1): 82-86. | |
| [17] | Bao S D. Soil agriculture and chemistry analysis (the third edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| [18] | Zhao W J, Liu R, Wang Z X, et al. Effects of rotation with a green manure crop on soil quality and microbial nutrient limitation in a tobacco field in Yunnan. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(10): 147-158. |
| 赵文军, 刘蕊, 王正旭, 等. 烤烟-绿肥轮作对云南烟田土壤质量与微生物养分限制的影响. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 147-158. | |
| [19] | Kuzyakov Y, Gunina A, Zamanian K, et al. New approaches for evaluation of soil health, sensitivity and resistance to degradation. Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering, 2020, 7(3): 56-62. |
| [20] | Wang H, Zhou G P, Chang D N, et al. Nitrogen reduction effects in double rice by planting and returning Chinese milk vetch to the field in Northern Hunan Province. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(1): 33-44. |
| 王慧, 周国朋, 常单娜, 等. 湘北双季稻区种植翻压紫云英的氮肥减施效应. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(1): 33-44. | |
| [21] | Chen J R, Qin W J, Wang S X, et al. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer combined with Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) incorporation on rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency in double-rice cropping system. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(6): 280-287. |
| 陈静蕊, 秦文婧, 王少先, 等. 化肥减量配合紫云英还田对双季稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(6): 280-287. | |
| [22] | Zhang L, Xu C X, Liu J, et al. Effects of green manure on yield and nitrogen utilization of double rice under reduced 20% chemical fertilizer input in Jiangxi Province. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(5): 845-856. |
| 张磊, 徐昌旭, 刘佳, 等. 减施20%化肥下绿肥翻压量对江西双季稻产量及氮素利用的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(5): 845-856. | |
| [23] | Cao W D, Zhou G P, Gao S J. Effects and mechanisms of green manure on endogenous improving soil health. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2024, 30(7): 1274-1283. |
| 曹卫东, 周国朋, 高嵩涓. 绿肥内源驱动土壤健康的作用与机制. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2024, 30(7): 1274-1283. | |
| [24] | Chu J D, Yan H F, Wang S S, et al. Effects of reduced fertilization and biochar application on nitrogen leaching from tobacco-growing soils. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2022, 43(4): 40-47. |
| 褚继登, 闫慧峰, 王树声, 等. 化肥减量配施生物炭对植烟土壤氮素淋失的影响. 中国烟草科学, 2022, 43(4): 40-47. | |
| [25] | Yang L, Bai J, Liu J, et al. Green manuring effect on changes of soil nitrogen fractions, maize growth, and nutrient uptake. Agronomy, 2018, 8(11): 261. |
| [26] | Zhou G P, Chang D N, Gao S J, et al. Co-incorporating leguminous green manure and rice straw drives the synergistic release of carbon and nitrogen, increases hydrolase activities, and changes the composition of main microbial groups. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2021, 57(4): 547-561. |
| [27] | Zu W J. Effects of green manures by different tillage methods on soil properties and growth of flue-cured tobacco. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2020. |
| 祖韦军. 不同绿肥品种及耕作方式对土壤特性和烤烟生长的影响. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2020. | |
| [28] | Liu H, Ma Z H, Liu W F, et al. Effects of different tillage practices with organic fertilizers on rhizosphere soil microbial communities of maize in saline-alkali soils. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2025, 33(1): 25-39. |
| 刘昊, 麻仲花, 刘威帆, 等. 不同耕作方式配施有机肥对盐碱地玉米根际土壤微生物群落的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2025, 33(1): 25-39. | |
| [29] | Ye X F, Yang C, Li Z, et al. Effects of green manure in corporation on soil enzyme activities and fertility in tobacco-planting soils. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2013, 19(2): 445-454. |
| 叶协锋, 杨超, 李正, 等. 绿肥对植烟土壤酶活性及土壤肥力的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(2): 445-454. | |
| [30] | Luo Y, Lu B L, Zhou G P, et al. Effects of returning the root of green manure on reducing N application in maize within their intercropping system in Hexi oasis irrigation area. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(12): 2125-2135. |
| 罗跃, 卢秉林, 周国朋, 等. 河西绿洲灌区玉米间作绿肥根茬还田的氮肥减施效应. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(12): 2125-2135. | |
| [31] | Zhao W J, Yang J Z, Yin M, et al. Effects of combined application of green manure with reduced nitrogen fertilizer on yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 189-196. |
| 赵文军, 杨继周, 尹梅, 等. 绿肥模式下减量施氮对烤烟产量与品质的影响. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(4): 189-196. | |
| [32] | Zhou G, Gao S, Chang D, et al. Using milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) to promote rice straw decomposition by regulating enzyme activity and bacterial community. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 319: 124215. |
| [33] | Nevins C J, Lacey C, Armstrong S. The synchrony of cover crop decomposition, enzyme activity, and nitrogen availability in a corn agroecosystem in the Midwest United States. Soil and Tillage Research, 2020, 197: 104518. |
| [34] | Elfstrand S, Båth B, Mårtensson A. Influence of various forms of green manure amendment on soil microbial community composition, enzyme activity and nutrient levels in leek. Applied Soil Ecology, 2007, 36(1): 70-82. |
| [35] | Ye X, Liu H, Li Z, et al. Effects of green manure continuous application on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2014, 37(4): 498-508. |
| [36] | Zhou G P. The synergistic effects and mechanism of co-incorporating Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) and rice (Oryza sativa L.) straw. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020. |
| 周国朋. 紫云英-稻草共同还田的协同效应及机制. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2020. |
| [1] | 张邦彦, 谢小伟, 张朝辉, 武晋民, 王彬, 许兴. 有机-无机改良物料对盐碱地土壤质量及湖南稷子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 15-29. |
| [2] | 毛海龙, 邰继承, 杨恒山, 张玉芹, 张瑞富, 王真真. 带型配置对青贮玉米-大豆复合种植体冠层特性、产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 30-42. |
| [3] | 张译尹, 王斌, 王腾飞, 兰剑, 胡海英. 苜蓿种子田间作小黑麦对饲草产量、水分利用及苜蓿种子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 43-53. |
| [4] | 樊文娟, 宋建超, 张小娟, 盛宇航, 史金涛, 张龙骥, 鱼小军. 氮磷配施对甘肃省武威灌区扁蓿豆种子产量和质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 54-65. |
| [5] | 汤珊珊, 胡敏. 禾本科植物根际土壤酶活性和细菌群落结构差异[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 99-108. |
| [6] | 蒋学乾, 杨青川, 康俊梅. 紫花苜蓿在干旱胁迫下的产量损失与抗旱性遗传研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 219-234. |
| [7] | 姜沛沛, 郭锦花, 肖慧淑, 彭彦珉, 张军, 田文仲, 吕军杰, 吴金芝, 王贺正, 付国占, 黄明, 李友军. 轮耕模式对旱地玉-麦两熟体系作物产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 181-192. |
| [8] | 刘启林, 王小军, 王金兰, 刘文辉, 马巧玲, 李建辉, 张生原, 曹文侠, 李文. 氮磷配施对高寒区老芒麦饲草产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 193-202. |
| [9] | 秦文利, 张静, 肖广敏, 崔素倩, 叶建勋, 智健飞, 张立锋, 谢楠, 冯伟, 刘振宇, 潘璇, 代云霞, 刘忠宽. 绿肥部分替代化肥氮对土壤物理性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 27-45. |
| [10] | 刘耀博, 裴渌, 刘琛琢, 李晓霞, 邹博坤. 基于Meta分析中国老芒麦种子产量和产量组分对施肥的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 85-98. |
| [11] | 冯雅琪, 陈嘉慧, 张静妮, 隋超, 陈基伟, 刘志鹏, 周强, 刘文献. 基于重测序紫花苜蓿高蛋白、高产关联InDel分子标记开发[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 137-149. |
| [12] | 王腾飞, 马霞, 刘金龙, 王斌, 张译尹, 李佳旺, 马江萍, 王小兵, 兰剑. 引黄灌区复种饲用燕麦种植模式产量、品质及经济效益分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 27-37. |
| [13] | 蒋鹏, 李磊, 解昊郡, 徐得甲, 王锐, 虎强, 孙权. 净化沼液滴灌对砂壤土质量、青贮玉米生产力的影响及安全消纳容量分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 64-81. |
| [14] | 刘蕊, 常单娜, 周国朋, 高嵩涓, 柴强, 曹卫东. 农田氧化亚氮减排技术及其与绿肥协同应用分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 196-210. |
| [15] | 欧翔, 连海, 陈荣强, 邱静芸, 吴丽娟, 操贤洪, 张强, 雷小文. 不同施肥处理种植王草后对稀土尾矿土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 94-108. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||