

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (11): 31-39.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024489
马蓉1,2( ), 李俊瑶1,3, 岳平1, 马旭君1, 白珍4, 庄玲4, 白敬5, 赵学勇1, 王少昆1(
), 李俊瑶1,3, 岳平1, 马旭君1, 白珍4, 庄玲4, 白敬5, 赵学勇1, 王少昆1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-12
修回日期:2025-02-17
出版日期:2025-11-20
发布日期:2025-10-09
通讯作者:
王少昆
作者简介:E-mail: wangsk@lzb.ac.cn基金资助:
Rong MA1,2( ), Jun-yao LI1,3, Ping YUE1, Xu-jun MA1, Zhen BAI4, Ling ZHUANG4, Jing BAI5, Xue-yong ZHAO1, Shao-kun WANG1(
), Jun-yao LI1,3, Ping YUE1, Xu-jun MA1, Zhen BAI4, Ling ZHUANG4, Jing BAI5, Xue-yong ZHAO1, Shao-kun WANG1( )
)
Received:2024-12-12
Revised:2025-02-17
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-10-09
Contact:
Shao-kun WANG
摘要:
植物功能性状是决定植物生长和生存的关键特征,其在植物生物量分配中的作用对植物的环境适应性具有重要意义。通过控制试验研究降水变化对乌拉特荒漠草原优势植物沙生针茅和碱韭功能性状及生物量分配的影响,系统测定了不同降水处理下(减少50%降水、自然降水、增加50%降水)沙生针茅和碱韭的根系功能性状(比根长、根组织密度和比根面积)、叶片功能性状(比叶面积、叶干物质含量和叶组织密度)、地上生物量、地下生物量及根冠比。结果显示:1)碱韭的比叶面积随着降水减少显著增大,而沙生针茅的根、叶功能性状对降水变化的响应不显著。2)在减少50%降水时,碱韭地上生物量显著减少,地下生物量未发生显著变化,但根冠比显著高于自然降水;而在增加50%降水时,碱韭的地上地下生物量均无显著变化。在不同降水条件下,沙生针茅地上、地下生物量及根冠比均无显著变化。3)降水变化通过调节土壤电导率间接影响沙生针茅的生物量分配,通过调节比叶面积间接影响碱韭的生物量分配。研究结果为荒漠草原典型植物在降水变化下的生物量分配调节机制提供了理论依据。
马蓉, 李俊瑶, 岳平, 马旭君, 白珍, 庄玲, 白敬, 赵学勇, 王少昆. 降水变化下荒漠草原优势植物功能性状对生物量分配的调节机制[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(11): 31-39.
Rong MA, Jun-yao LI, Ping YUE, Xu-jun MA, Zhen BAI, Ling ZHUANG, Jing BAI, Xue-yong ZHAO, Shao-kun WANG. Regulatory mechanisms of biomass allocation governed by functional traits of dominant plants in desert steppe under precipitation changes[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(11): 31-39.
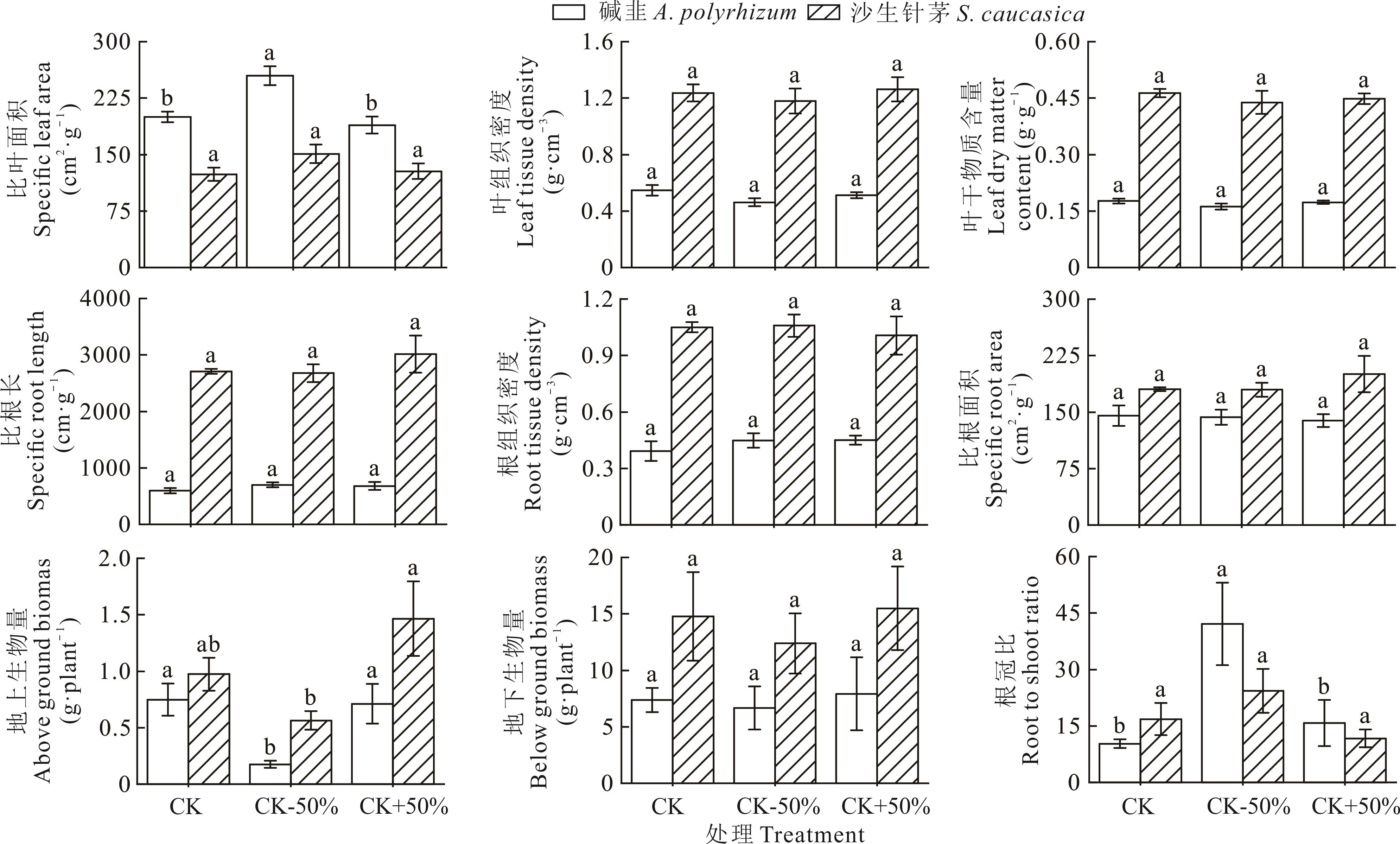
图1 降水变化对沙生针茅、碱韭地上地下功能性状及生物量的影响不同小写字母表示同一植物在不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments for the plant (P<0.05).
Fig.1 Effects of precipitation changes on aboveground and belowground functional traits and biomass of S. caucasica and A. polyrhizum
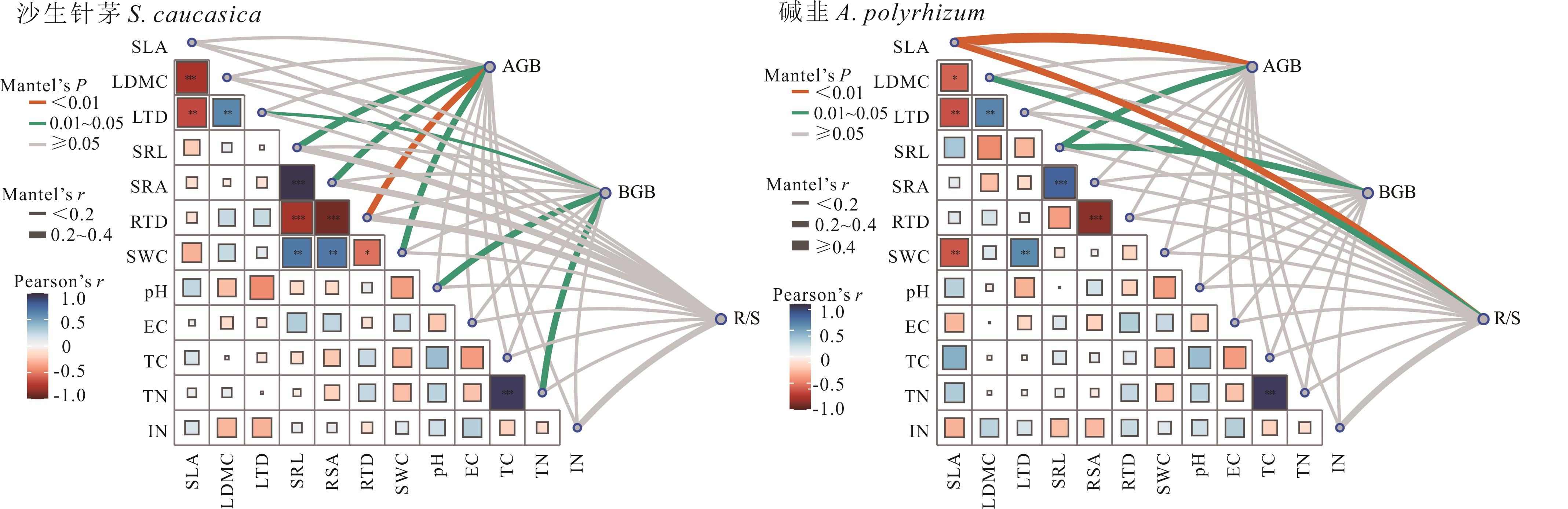
图2 沙生针茅、碱韭生物量与功能性状和土壤因子的Mantel检验SLA: 比叶面积Specific leaf area; LDMC: 叶干物质含量Leaf dry matter content; LTD: 叶组织密度Leaf tissue density; SRL: 比根长Specific root length; SRA: 比根面积Specific root area; RTD: 根组织密度Root tissue density; SWC: 土壤含水量Soil water content; EC: 电导率Electrical conductivity; TC: 全碳Total carbon; TN: 全氮Total nitrogen; IN: 无机氮Inorganic nitrogen; AGB: 地上生物量Aboveground biomass; BGB: 地下生物量Belowground biomass; R/S: 根冠比Root to shoot ratio. 下同The same below. 图右上侧连线表示AGB、BGB、R/S与影响因素间Mantel检验后的相关性及其显著性,线条粗细表示相关性强弱,线条颜色表示显著性程度。图左下侧色块表示影响因素间Pearson相关性,色块大小表示相关系数绝对值大小。The lines on the top-right side of the figure represent the correlations and significance levels between AGB, BGB, RT, and the influencing factors after the Mantel test. The line thickness indicates the strength of the correlation, while the line color represents the degree of significance. The color blocks on the bottom-left side of the figure indicate the Pearson correlations between the influencing factors, with the block size reflecting the absolute value of the correlation coefficient.
Fig.2 The Mantel test for the biomass, functional traits, and soil factors of S. caucasica and A. polyrhizum
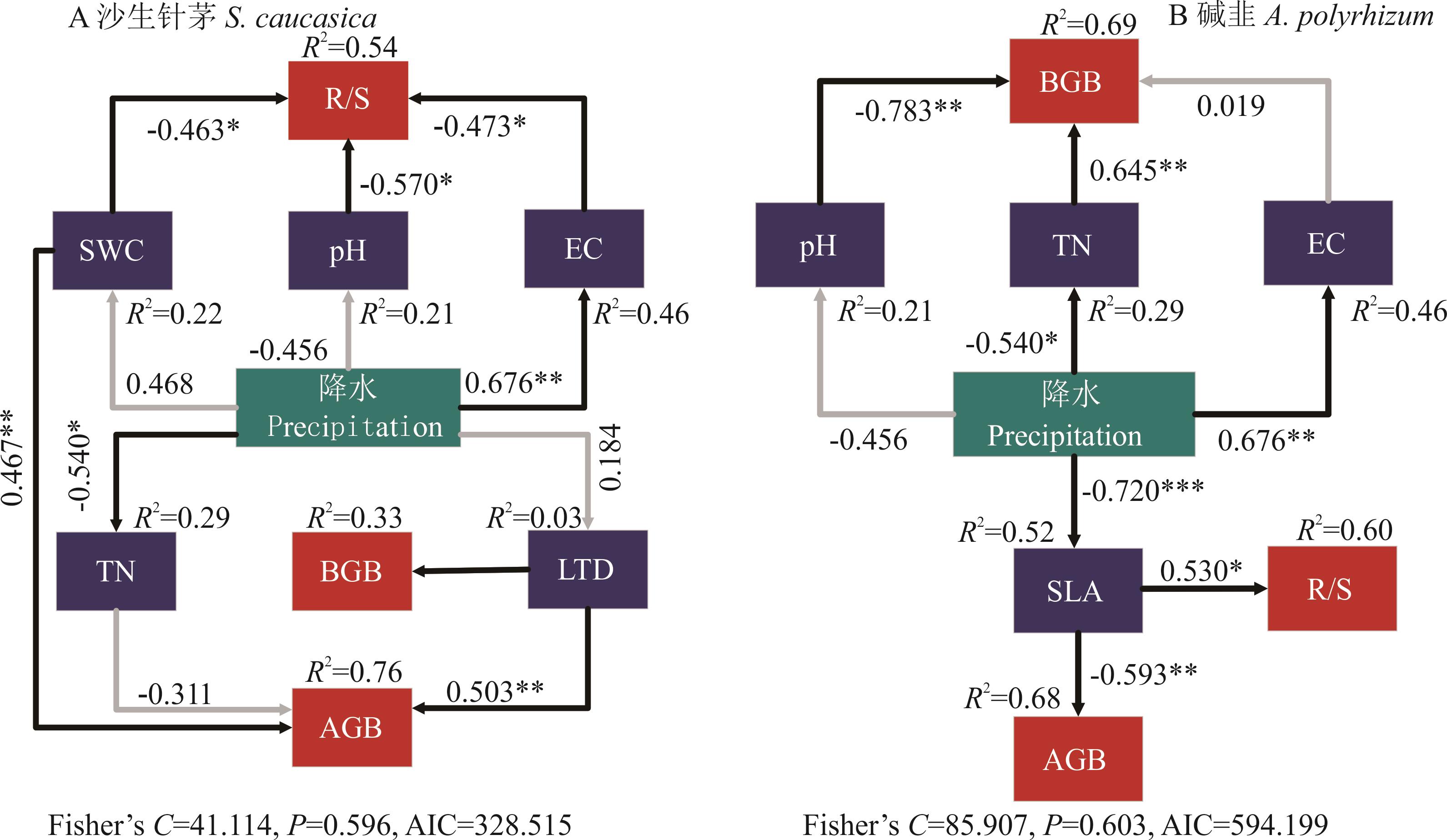
图3 降水变化下沙生针茅、碱韭植物性状与土壤因子对生物量分配的直接和间接影响的结构方程模型AIC: 赤池信息准则Akaike information criterion. 单头箭头表示路径。黑色箭头表示显著效应,灰色箭头表示无显著效应。箭头处的数字为标准化路径系数(*: P<0.05, **: P<0.01, ***: P<0.001),反映了关系的效应大小。模型中每个响应变量旁的R2为各变量的解释比例。Single-headed arrows indicate pathways. Black arrows indicate significant effects and gray arrows indicate no significant effects. The numbers at the arrows are standardized path coefficients (*: P<0.05, **: P<0.01, ***: P<0.001), which reflect the effect size of the relationship. The proportion of variance (R2) appears alongside each response variables in the model.
Fig.3 Structural equation models of direct and indirect effects of plant traits and soil factors on biomass allocation of S. caucasica and A. polyrhizum under precipitation variation
| [1] | The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate change 2021: The physical science basis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021. |
| [2] | Kim J B, So J M, Bae D H. Global warming impacts on severe drought characteristics in Asia Monsoon Region. Water, 2020, 12(5): 1360-1381. |
| [3] | Isbell F, Craven D, Connolly J, et al. Biodiversity increases the resistance of ecosystem productivity to climate extremes. Nature, 2015, 526(7574): 574-577. |
| [4] | Lyu X M, Wang Y H, Zhou G S, et al. Interactive effects of changing precipitation and elevated temperatures on plant biomass and its allocation of Stipa breviflora. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(3): 752-760. |
| 吕晓敏, 王玉辉, 周广胜, 等. 温度与降水协同作用对短花针茅生物量及其分配的影响. 生态学报, 2015, 35(3): 752-760. | |
| [5] | Liu X J, Ma K P. Plant functional traits-concepts, applocations and future directions. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 2015, 45(4): 325-339. |
| 刘晓娟, 马克平. 植物功能性状研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2015, 45(4): 325-339. | |
| [6] | Meng T T, Ni J, Wang G H. Plant functional traits, environmental and ecosystem functioning. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2007, 31(1): 150-165. |
| 孟婷婷, 倪健, 王国宏. 植物功能性状与环境和生态系统功能. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(1): 150-165. | |
| [7] | Reich P B. The world-wide ‘fast-slow’ plant economic spectrum: A traits manifesto. Journal of Ecology, 2014, 102(2): 275-301. |
| [8] | Li C B, Zheng Z, Peng Y F, et al. Precipitation and nitrogen addition enhance biomass allocation to aboveground in an alpine steppe. Ecology and Evolution, 2019, 9(21): 12193-12201. |
| [9] | Jin H R, Fan C K, Zhu H Y, et al. Responses of plant biomass allocation to changed precipitation timing in a semi-arid steppe. Plant and Soil, 2024, DOI: 10.1007/s11104-024-06928-9. |
| [10] | Li R, Shan L S, Xie T T, et al. Variation in the leaf functional traits of typical desert shrubs under precipitation gradient. Arid Zone Research, 2023, 40(3): 425-435. |
| 李瑞, 单立山, 解婷婷, 等. 典型荒漠灌木叶片功能性状特征随降水梯度的变化研究. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(3): 425-435. | |
| [11] | Sun L, Wang Y, Li Y, et al. Non-linear response of leaf functional traits to precipitation in alpine grassland, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(2): 756-767. |
| 孙乐, 王毅, 李洋, 等. 青藏高原高寒草地群落叶片功能性状对降水的非线性响应. 生态学报, 2023, 43(2): 756-767. | |
| [12] | Zhao Y H, Gong X W, Ning Q R, et al. Plasticity and coordination of branch and leaf traits in Ulmus pumila along a precipitation gradient. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(2): 324-332. |
| 赵宇航, 龚雪伟, 宁秋蕊, 等. 沿降水梯度白榆的枝叶性状可塑性与协同变异. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(2): 324-332. | |
| [13] | Xia L, Ji H, Zhang J Y, et al. Effects of different precipitation on root and leaf functional traits of plants in Inner Mongolia temperate steppe. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2022, 42(12): 2112-2122. |
| 夏蕾, 吉卉, 张家铱, 等. 降水差异对内蒙古温带草原植物根系和叶片功能性状的影响. 西北植物学报, 2022, 42(12): 2112-2122. | |
| [14] | Ryalls J M W, Moore B D, Johnson S N, et al. Root responses to domestication, precipitation and silicification: Weeping meadow grass simplifies and alters toughness. Plant and Soil, 2018, 427(1): 291-304. |
| [15] | Isaac M E, Martin A R, Rapidel B, et al. Intraspecific trait variation and coordination: Root and leaf economics spectra in coffee across environmental gradients. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8(2): 1196-1209. |
| [16] | Li H B, Liu B T, Mccormack M L, et al. Diverse belowground resource strategies underlie plant species coexistence and spatial distribution in three grasslands along a precipitation gradient. New Phytologist, 2017, 216(4): 1140-1150. |
| [17] | Zhou M, Wang J, Bai W, et al. The response of root traits to precipitation changes of herbaceous species in temperate grasslands. Functional Ecology, 2019, 33(10): 2030-2041. |
| [18] | Li X Y, Zuo X A, Yue P, et al. Drought of early time in growing season decreases community aboveground biomass, but increases belowground biomass in a desert steppe. BMC Ecology and Evolution, 2021, 21(1): 106-119. |
| [19] | Zuo X A, Zhang J, Lv P, et al. Plant functional diversity mediates the effects of vegetation and soil properties on community level plant nitrogen use in the restoration of semiarid sandy grassland. Ecological Indicators, 2016, 64: 272-280. |
| [20] | Du Z Y, An H, Wang B, et al. Effects of nutrient addition and precipitation manipulation on plant species diversity and biomass of in a desert grassland. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(4): 1100-1110. |
| 杜忠毓, 安慧, 王波, 等. 养分添加和降水变化对荒漠草原植物群落物种多样性和生物量的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(4): 1100-1110. | |
| [21] | Long M, Wu H H, Smith D M, et al. Nitrogen deposition promotes phosphorus uptake of plants in a semi-arid temperate grassland. Plant and Soil, 2016, 408(1/2): 475-484. |
| [22] | Guo X X, Yue P, Li X Y, et al. Effects of precipitation on above-ground biomass of Peganum harmala in desert steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 164-172. |
| 郭新新, 岳平, 李香云, 等. 降水量对荒漠草原骆驼蓬(Peganum harmala)地上生物量的影响. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 164-172. | |
| [23] | Guo X X, Zuo X A, Yue P, et al. Responses of leaf morphological traits of three dominant plants to water and nitrogen in desert steppe of Inner Mongolia. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 137-144. |
| 郭新新, 左小安, 岳平, 等. 内蒙古荒漠草原沙生针茅(Stipa glareosa)、碱韭(Allium polyrhizum)和骆驼蓬(Peganum harmala)叶形态性状对土壤水氮耦合的响应. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 137-144. | |
| [24] | Wang S K, Zhao X Y, Jia K F, et al. Soil bacterial diversity and its vertical distribution in Stipa klemenzii community of Urad desert steppe. Journal of Desert Research, 2016, 36(6): 1564-1570. |
| 王少昆, 赵学勇, 贾昆峰, 等. 乌拉特荒漠草原小针茅(Stipa klemenzii)群落土壤细菌多样性及垂直分布特征. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(6): 1564-1570. | |
| [25] | Bao P A, Qiu K Y, Huang Y Y, et al. Leaf functional trait characteristics and plasticity of desert steppe plants under nitrogen and phosphorus addition. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(3): 97-106. |
| 鲍平安, 邱开阳, 黄业芸, 等.荒漠草原植物在氮磷添加下叶功能性状特征及其可塑性. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 97-106. | |
| [26] | Liu Y, Zhong Q L, Xu Z B, et al. Relationship between fine root functional traits and rhizosphere microenvironment of Machilus pauhoi at different sizes. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2024, 48(6): 744-759. |
| 刘瑶, 钟全林, 徐朝斌, 等. 不同大小刨花楠细根功能性状与根际微环境关系.植物生态学报, 2024, 48(6): 744-759. | |
| [27] | Jing M H, Jia X T, Zhang Y L, et al. Effects of long-term nitrogen addition on community aboveground and belowground biomass and their ratio in a typical steppe of Inner Mongolia. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(10): 3185-3193. |
| 景明慧, 贾晓彤, 张运龙, 等. 长期氮添加对内蒙古典型草原植物地上、地下生物量及根冠比的影响. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(10): 3185-3193. | |
| [28] | Reynolds S. The gravimetric method of soil moisture determination Part IA study of equipment, and methodological problems. Journal of Hydrology, 1970, 11(3): 258-273. |
| [29] | Huang C B, Zeng F J, Lei J Q. Growth and functional trait responses of Alhagi sparsifolia seedlings to water and nitrogen addition. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(12): 150-160. |
| 黄彩变, 曾凡江, 雷加强. 骆驼刺幼苗生长和功能性状对不同水氮添加的响应. 草业学报, 2016, 25(12): 150-160. | |
| [30] | Luong J C, Holl K D, Loik M E. Leaf traits and phylogeny explain plant survival and community dynamics in response to extreme drought in a restored coastal grassland. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 58(8): 1670-1680. |
| [31] | Shi Y, Wen Z M, Gong S H. Comparisons of relationships between leaf and fine root traits in hilly area of the Loess Plateau, Yanhe River basin, Shaanxi Province, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(22): 6805-6814. |
| 施宇, 温仲明, 龚时慧. 黄土丘陵区植物叶片与细根功能性状关系及其变化. 生态学报, 2011, 31(22): 6805-6814. | |
| [32] | Wright I J, Reich P B, Westoby M. Strategy shifts in leaf physiology, structure and nutrient content between species of high- and low-rainfall and high- and low-nutrient habitats. Functional Ecology, 2001, 15(4): 423-434. |
| [33] | Weemstra M, Mommer L, Visser E J W, et al. Towards a multidimensional root trait framework: A tree root review. The New Phytologist, 2016, 211(4): 1159-1169. |
| [34] | Eapen D, Barroso M L, Ponce G, et al. Hydrotropism: Root growth responses to water. Trends in Plant Science, 2005, 10(1): 44-50. |
| [35] | Sun Y, He M Z, Wang L. Effects of precipitation control on plant diversity and biomass in a desert region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(7): 2425-2433. |
| 孙岩, 何明珠, 王立. 降水控制对荒漠植物群落物种多样性和生物量的影响. 生态学报, 2018, 38(7): 2425-2433. | |
| [36] | Lu W T, Chong P F, Tian Y L, et al. Effects of simulated precipitation changes and nitrogen deposition on biomass allocation patterns of Reaumuria soongarica and Salsola passerina seedlings under different growth modes. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(11): 2144-2154. |
| 陆文涛, 种培芳, 田艳丽, 等. 模拟氮沉降及降水作用下红砂和珍珠猪毛菜幼苗生物量的分配模式. 草业科学, 2021, 38(11): 2144-2154. | |
| [37] | Yan W. Biomass allocation pattern and its influcing factors across typical terrestrial ecosystems in China. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2017. |
| 颜韦. 中国典型陆地生态系统的生物量分配及其影响因素分析. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2017. | |
| [38] | Kou L, Wu Z M, Yang X D, et al. Responses of root system architecture to water stress at multiple levels: A Meta-analysis of trials under controlled conditions. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13(1): 1085409. |
| [39] | Wang X, Chen X, Xu J, et al. Precipitation dominates the allocation strategy of above- and belowground biomass in plants on macro scales. Plants, 2023, 12(15): 2843-2855. |
| [40] | Fan R, Lyu S, Ding Y, et al. Interactive effects of soil water, nutrients and clonal fragmentation on root growth of xerophilic plant Stipa breviflora. Agriculture, 2022, 12(12): 2112-2124. |
| [41] | Justin M V, Kekoa C N, Marco C M. Functional traits and drought strategy predict leaf thermal tolerance. Conservation Physiology, 2023, 11(1): 85-100. |
| [1] | 雍嘉仪, 马霜, 马风华, 赵小娜, 张译尹, 胡海英. 干旱及复水对河北木蓝生物量分配与渗透调节特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 158-170. |
| [2] | 邓文辉, 宋珂辰, 张浩, 管思雨, 雍嘉仪, 胡海英. 降水变化条件下荒漠草原优势植物根际微生物群落结构和多样性特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 12-26. |
| [3] | 骆欣怡, 邱开阳, 金涛, 鲍平安, 黄业芸, 何毅, 谢应忠. 碳、氮、钾添加对荒漠草原凋落物分解特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 41-53. |
| [4] | 鲍平安, 文志林, 王炎, 陈彦虎, 季波, 王占军, 吴旭东, 蒋齐. 不同牧草补播模式对荒漠草原植物群落结构及土壤特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 62-73. |
| [5] | 张振豪, 贾子玉, 李鑫宇, 程云湘. 荒漠草原混牧牛羊的放牧行为特征[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 226-237. |
| [6] | 贺世龙, 叶贺, 李静, 张雅玲, 德海山, 红梅. 不同时限氮沉降和降水变化对荒漠草原中小型土壤节肢动物群落结构与多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 140-154. |
| [7] | 曹颖, 聂明鹤, 沈艳, 胡艳, 马登宝, 李东, 候腾思, 方鹏, 王学琴. 宁夏干旱风沙区荒漠草原不同退化阶段植被土壤变化特征及其相关性[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 1-14. |
| [8] | 候腾思, 沈艳, 马红彬, 方鹏, 曹颖. 柠条平茬对荒漠草原土壤水分特征及水量平衡的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 15-24. |
| [9] | 佘洁, 沈爱红, 石云, 赵娜, 张风红, 何洪源, 吴涛, 李红霞, 马益婷, 朱晓雯. 基于无人机遥感影像和面向对象技术的荒漠草原植被分类[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 1-14. |
| [10] | 姜海鑫, 周瑶, 胡科, 丁占胜, 马红彬. 不同放牧时间对荒漠草原土壤颗粒组成及分形维数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 17-28. |
| [11] | 赵亚楠, 王红梅, 李志丽, 张振杰, 陈彦硕, 苏荣霞. 荒漠草原灌丛转变过程土壤水分亏缺空间特征及影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 22-34. |
| [12] | 李俊瑶, 蒋星驰, 胡晋瑜, 魏栋光, 赵学勇, 王少昆. 生物有机肥施加对荒漠草原植被-土壤-微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 34-45. |
| [13] | 鲍平安, 邱开阳, 黄业芸, 王思瑶, 崔璐瑶, 骆欣怡, 杨云涛, 谢应忠. 荒漠草原植物在氮磷添加下叶功能性状特征及其可塑性[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 97-106. |
| [14] | 鲍平安, 季波, 孙果, 张娜, 吴旭东, 何建龙, 王占军, 田英. 光伏电站建设对植物群落与土壤特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 23-33. |
| [15] | 常怡然, 史佳梅, 许冬梅, 康如龙, 马媛. 荒漠草原不同自然种群蒙古冰草生物量和养分权衡特征[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 186-197. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||