

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 83-94.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025091
任浩奇1( ), 李彤1(
), 李彤1( ), 杨荣2(
), 杨荣2( ), 王鸿4, 赵明新4, 刘学周5, 宋淑钧2,3, 孙开2,3, 薛俊武6
), 王鸿4, 赵明新4, 刘学周5, 宋淑钧2,3, 孙开2,3, 薛俊武6
收稿日期:2025-03-20
修回日期:2025-05-21
出版日期:2026-02-20
发布日期:2025-12-24
通讯作者:
李彤,杨荣
作者简介:yangrong@lzb.ac.cn基金资助:
Hao-qi REN1( ), Tong LI1(
), Tong LI1( ), Rong YANG2(
), Rong YANG2( ), Hong WANG4, Ming-xin ZHAO4, Xue-zhou LIU5, Shu-jun SONG2,3, Kai SUN2,3, Jun-wu XUE6
), Hong WANG4, Ming-xin ZHAO4, Xue-zhou LIU5, Shu-jun SONG2,3, Kai SUN2,3, Jun-wu XUE6
Received:2025-03-20
Revised:2025-05-21
Online:2026-02-20
Published:2025-12-24
Contact:
Tong LI,Rong YANG
摘要:
为明确旱区果园生草栽培模式的实施效应,揭示生草与清耕果园土壤养分指标差异的影响因素。以陇东地区12县(区)45组生草-清耕果园为研究对象,系统分析土壤表层有机质(SOM)、全氮(TN)、全碳(TC)、全磷(TP)、碱解氮(AN)和pH的差异性特征,并探讨气候条件、土壤类型及生草管理措施的调控效应。结果表明:1)与清耕相比,生草使SOM、TN、TC、AN和pH分别增加26.7%、7.1%、10.4%、18.2%和2.5%,TP降低8.3%;频率统计结果显示,生草较清耕SOM、TN、TC、TP、AN和pH明显增加的样点分别占比44.4%、35.6%、53.3%、26.7%、37.8%和73.3%。2)年降水量与SOM、TC、AN、pH变化率呈显著正相关(P<0.05),且年降水量超过400 mm时,土壤SOM、TC变化率大于0;年均气温的高低对TP和pH的变化率无显著影响,与SOM和AN的变化率呈显著正相关(P<0.05);3)生草年限与TN、TP、AN、SOM、TC变化率呈显著正相关(P<0.05),pH与生草年限的负线性关系未达到显著水平;SOM、TN、TC、AN、TP变化率均随生草年限增加而增加,其中TP的增速最快,达8.2 g·kg-1·a-1;生草4年以上的果园SOM、TN含量均高于清耕。4)人工生草TP变化率(-18.3%)显著低于自然生草(4.9%),pH值相反;黑垆土TC变化率比黄壤土提高25.7%,TP降低27.6%(P<0.05)。研究结果可为陇东地区果园生草技术的优化与推广提供科学依据,指导果农根据当地气候条件和土壤类型,合理选择生草类型和管理措施,以提高果园土壤肥力,促进果园生态系统的可持续发展。
任浩奇, 李彤, 杨荣, 王鸿, 赵明新, 刘学周, 宋淑钧, 孙开, 薛俊武. 生草对陇东果园土壤肥力影响的区域评估[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 83-94.
Hao-qi REN, Tong LI, Rong YANG, Hong WANG, Ming-xin ZHAO, Xue-zhou LIU, Shu-jun SONG, Kai SUN, Jun-wu XUE. Effects of herbage ground cover on orchard soil fertility enhancement in the Longdong Region of Gansu Province[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(2): 83-94.

图1 研究区域和取样点分布基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2022)1873号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS(2022)1873 of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig.1 Study area and sampling sites
| 指标Indicators | 分组Categories |
|---|---|
| 果园类型 Orchard types | 苹果M. pumila (88.9%)、樱桃Cerasus pseudocerasus (6.7%)、花椒Zanthoxylum bungeanum (4.4%) |
| 果树生长年限 Fruit tree growth ages | 5~10 (42.2%)、10~15 (37.8%)、15~20 (20.0%) |
| 生草类型 Grassing types | 豆科Fabaceae (15.6%)、禾本科Graminae (8.9%)、十字花科Brassicales (6.7%)、自然生草Self-sown grass (68.9%) |
| 生草年限 Grassing ages | 2 (6.7%)、3 (15.6%)、4 (6.7%)、5 (8.9%)、6 (15.6%)、7 (13.3%)、8 (13.3%)、9 (8.9%) |
表1 研究样点的果园类型、生草管理及年限分布
Table 1 Distribution of orchard types, grassing management, and grassing ages in the study
| 指标Indicators | 分组Categories |
|---|---|
| 果园类型 Orchard types | 苹果M. pumila (88.9%)、樱桃Cerasus pseudocerasus (6.7%)、花椒Zanthoxylum bungeanum (4.4%) |
| 果树生长年限 Fruit tree growth ages | 5~10 (42.2%)、10~15 (37.8%)、15~20 (20.0%) |
| 生草类型 Grassing types | 豆科Fabaceae (15.6%)、禾本科Graminae (8.9%)、十字花科Brassicales (6.7%)、自然生草Self-sown grass (68.9%) |
| 生草年限 Grassing ages | 2 (6.7%)、3 (15.6%)、4 (6.7%)、5 (8.9%)、6 (15.6%)、7 (13.3%)、8 (13.3%)、9 (8.9%) |
| 指标Indicators | 最小值Minimum | 最大值Maximum | 均值Average | 标准差Standard deviation | t值t value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | a | 4.0 | 19.4 | 12.0 | 3.3 | -2.7** |
| b | 5.8 | 49.1 | 15.2 | 8.0 | ||
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | a | 0.6 | 3.3 | 1.4 | 0.5 | -0.5 |
| b | 0.8 | 3.9 | 1.5 | 0.6 | ||
全碳 Total carbon (g·kg-1) | a | 15.9 | 34.0 | 22.2 | 3.8 | -3.0** |
| b | 17.8 | 49.5 | 24.5 | 5.7 | ||
全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | a | 1.4 | 5.4 | 2.4 | 0.8 | 1.5 |
| b | 1.5 | 4.6 | 2.2 | 0.7 | ||
碱解氮 Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | a | 37.3 | 217.5 | 89.1 | 33.4 | -1.1 |
| b | 27.3 | 429.8 | 105.3 | 69.8 | ||
| pH | a | 7.6 | 8.7 | 8.1 | 0.3 | -3.8*** |
| b | 7.8 | 8.7 | 8.3 | 0.2 | ||
表2 土壤养分含量的描述性统计及t检验结果
Table 2 Descriptive statistics of the indexes of soil nutrient contents and t-test result
| 指标Indicators | 最小值Minimum | 最大值Maximum | 均值Average | 标准差Standard deviation | t值t value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | a | 4.0 | 19.4 | 12.0 | 3.3 | -2.7** |
| b | 5.8 | 49.1 | 15.2 | 8.0 | ||
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | a | 0.6 | 3.3 | 1.4 | 0.5 | -0.5 |
| b | 0.8 | 3.9 | 1.5 | 0.6 | ||
全碳 Total carbon (g·kg-1) | a | 15.9 | 34.0 | 22.2 | 3.8 | -3.0** |
| b | 17.8 | 49.5 | 24.5 | 5.7 | ||
全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | a | 1.4 | 5.4 | 2.4 | 0.8 | 1.5 |
| b | 1.5 | 4.6 | 2.2 | 0.7 | ||
碱解氮 Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | a | 37.3 | 217.5 | 89.1 | 33.4 | -1.1 |
| b | 27.3 | 429.8 | 105.3 | 69.8 | ||
| pH | a | 7.6 | 8.7 | 8.1 | 0.3 | -3.8*** |
| b | 7.8 | 8.7 | 8.3 | 0.2 | ||
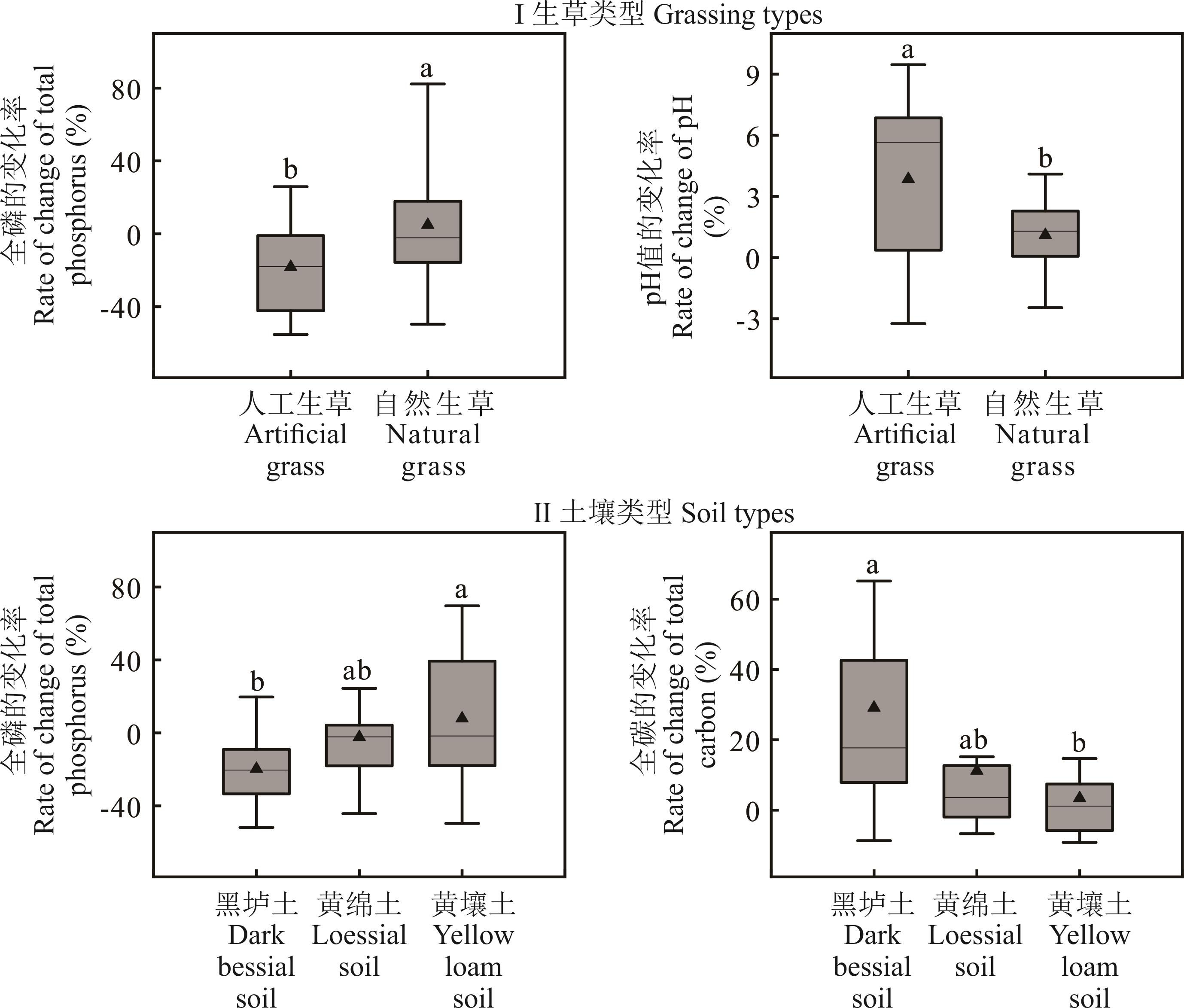
图6 不同生草类型、土壤类型的养分变化率特征不同字母表示不同组之间差异显著。The different letters mean significant differences among different groups.
Fig.6 Characterization of nutrient rates of change in different grassing types and soil types
| [1] | Kong X B, Chen W G, Dang Y X. Current situation, challenges and transformation of cultivated land protection in China. Journal of Social Science of Hunan Normal University, 2023, 52(5): 31-41. |
| 孔祥斌, 陈文广, 党昱譞. 中国耕地保护现状、挑战与转型. 湖南师范大学社会科学学报, 2023, 52(5): 31-41. | |
| [2] | Hao Z W, Ji L. Present situation and prospect of the study on interplanting grass in orchard in China. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(3): 486-490. |
| 郝紫微, 季兰. 我国果园生草研究现状与展望. 山西农业科学, 2017, 45(3): 486-490. | |
| [3] | Hu P, Gao X D, Zhao X N, et al. Effects of grassing on orchard ecosystem services: a global meta-analysis. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30(8): 1238-1248. |
| 呼盼, 高晓东, 赵西宁, 等. 生草对果园生态系统服务功能的影响: 全球数据整合分析研究. 中国生态农业学报, 2022, 30(8): 1238-1248. | |
| [4] | Cao W D. Green fertilizer germplasm resource description specifications and data standards. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2007: 1-3. |
| 曹卫东. 绿肥种质资源描述规范和数据标准. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2007: 1-3. | |
| [5] | Ma S K, Wang C M, Zhao C L, et al. Screening of water-saving and sink-enhancing plant species in arid and semi-arid regions of Northwest China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2024, 46(8): 122-131. |
| 马沈轲, 王春梅, 赵春林, 等. 西北干旱半干旱地区节水增汇植物种类筛选. 北京林业大学学报, 2024, 46(8): 122-131. | |
| [6] | Couëdel A, Alletto L, Tribouillois H, et al. Cover crop crucifer-legume mixtures provide effective nitrate catch crop and nitrogen green manure ecosystem services. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2018, 254(2): 50-59. |
| [7] | Li H K. Eco-environmental effect and integrated technical system of green cover in apple orchard in Weibei dryland farming areas. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2008. |
| 李会科. 渭北旱地苹果园生草的生态环境效应及综合技术体系构建. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2008. | |
| [8] | Chen J, Zhang Q, Yang M Y, et al. Effects of growing grass on microclimate environment and apple leaves in apple orchard. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(12): 158-167. |
| 陈俊, 张琦, 杨梦宇, 等. 生草对苹果园小气候环境及苹果叶片的影响. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(12): 158-167. | |
| [9] | Bhaskar V, Westbrook A S, Bellinder R R, et al. Integrated management of living mulches for weed control: A review. Weed Technology, 2021, 35(5): 856-868. |
| [10] | Cheng B, Zhao R F, Hua X Z, et al. Effects of interrow grass on soil nutrients, organic carbon components and enzyme activities in walnut orchard. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021(6): 57-64. |
| 程滨, 赵瑞芬, 滑小赞, 等. 行间生草对核桃园土壤养分、有机碳组分及酶活性影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(6): 57-64. | |
| [11] | Li H K, Zhang G J, Zhao Z Y, et al. Effects of interplanting of herbage on soil nutrient of non-irrigated apple orchard in the Loess Plateau. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2007, 34(2): 477-480. |
| 李会科, 张广军, 赵政阳, 等. 黄土高原旱地苹果园生草对土壤养分的影响. 园艺学报, 2007, 34(2): 477-480. | |
| [12] | Zhang F, Ma Z H, Li W F, et al. Effects of grass types on soil nutrition and fruit quality of apple orchards in dryland area. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2024, 59(1): 135-143. |
| 张帆, 马宗桓, 李文芳, 等. 生草类型对旱作区苹果园土壤营养及果实品质的影响. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2024, 59(1): 135-143. | |
| [13] | National Bureau of Statistics of China. Statistical yearbook of China. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2024. |
| 国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2024. | |
| [14] | Zhu X Z, Zhang J T. Improving the method of plotless sampling for forest community. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2008, 30(1): 137-140. |
| 朱珣之, 张金屯. 森林群落无样地取样方法的改进. 北京林业大学学报, 2008, 30(1): 137-140. | |
| [15] | Lu R K. Analytical methods for soil and agro-chemistry. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. | |
| [16] | Yan T Y. Variation characteristics of soil aggregates and aggregate carbon in orchards covered with living mulching. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2019. |
| 闫涛宇. 果园生草覆盖土壤团聚体和团聚体碳的变化特征. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2019. | |
| [17] | Liu Y P, Mao Y F, Hu Y L, et al. Effects of grass planting in apple orchard on soil microbial diversity, enzyme activities and carbon components. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(10): 1792-1805. |
| 刘业萍, 毛云飞, 胡艳丽, 等. 苹果园生草对土壤微生物多样性、酶活性及碳组分的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(10): 1792-1805. | |
| [18] | Cheng Z Z, Fan X P, Xia Y, et al. Combined effects of living mulch and fertilizer reduction on nitrogen and phosphorus runoff loss in a citrus orchard. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2023, 40(6): 1358-1367. |
| 程子珍, 范先鹏, 夏颖, 等. 生草覆盖及配合化肥减量对柑橘园地表径流氮磷流失的影响. 农业资源与环境学报, 2023, 40(6): 1358-1367. | |
| [19] | Qian J F, Wu J S, Huang J Q. Effects of sod-cultural practices on soil nutrients and microbial diversity in the Carya cathayensis forest. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(15): 4324-4332. |
| 钱进芳, 吴家森, 黄坚钦. 生草栽培对山核桃林地土壤养分及微生物多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2014, 34(15): 4324-4332. | |
| [20] | Huang Q Q. The study on the variation characteristics and bioavailability of soil phosphorus forms in apple orchard. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2021. |
| 黄倩倩. 果园生草土壤磷形态变化特征及其生物有效性的研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021. | |
| [21] | Ye G K, E S Z, Chen Z Y, et al. The forms and classification methods of phosphorus in soil: research progress. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(1): 96-102. |
| 冶赓康, 俄胜哲, 陈政宇, 等. 土壤中磷的存在形态及分级方法研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(1): 96-102. | |
| [22] | Yang L, Mao Y F, Hu Y L, et al. Effects of orchard grass on soil fertility and apple tree nutrition. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(2): 325-337. |
| 杨露, 毛云飞, 胡艳丽, 等. 生草改善果园土壤肥力和苹果树体营养的效果. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(2): 325-337. | |
| [23] | Wang Y, Chen C, Ma L N, et al. Inter-row grass: effects on soil nutrients and pH value of kiwifruit orchards in Northern Qinling Mountains. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 35(15): 59-65. |
| 王依, 陈成, 马拦妮, 等. 行间生草对秦岭北麓猕猴桃园土壤养分、pH值的影响. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(15): 59-65. | |
| [24] | Wang Q H, Wang J D, Li S, et al. Experiments to simulate the salinisation process of loess under a dynamic water cycle. Environmental Research, 2025, 268: 120739. |
| [25] | Yue X F, Zhang T H, Li Y Q. Effects of rainfall regime during the growing season on the annual plant communities in semiarid sandy land, northeast China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2023, 43: e02456. |
| [26] | Ju X, Yue Z R, Zhao S Y, et al. Response of soil pH to precipitation alterations across Chinese grassland: A Meta-analysis. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2025, 33(1): 262-272. |
| 居新, 岳卓然, 赵守逸, 等. 中国草地土壤pH值对降雨变化的响应——Meta分析. 草地学报, 2025, 33(1): 262-272. | |
| [27] | Zheng C H, Wang R S, Zhou X, et al. Effects of mulch and irrigation regimes on water distribution and root competition in an apple-soybean intercropping system in Loess Plateau, China. Agricultural Water Management, 2021, 246: 106656. |
| [28] | Gu S, Dupas R, Casquin A, et al. Hydrological conditions influence the prediction of soil phosphorus indices on phosphorus leaching in hydromorphic soils. Science of the Total Environment, 2025, 967: 178856. |
| [29] | Xu C, Dao C J, Zhao P C, et al. Effects of rainfall intensity on soil nitrogen and phosphorus leaching characteristics in different planting patterns. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2024, 43(7): 1568-1579. |
| 徐翠, 刀承娇, 赵鹏程, 等. 不同生草模式下降雨强度对土壤氮磷淋溶特性的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2024, 43(7): 1568-1579. | |
| [30] | Song B, Li Y S, Yu Z H, et al. Changes in enzyme activity, structure and growth strategies of the rhizosphere microbiome influenced by elevated temperature and CO2. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 954: 176522. |
| [31] | Li P, Xiao X X, Yao Y, et al. Site-specific apparent optimum air temperature for vegetation photosynthesis across the globe. Scientific Data, 2024, 11(1): 758. |
| [32] | Fu X Q, Liu J E, Huang W X. Effects of natural grass on soil microbiology, nutrient and fruit quality of Nanfeng tangerine yard. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2015, 42(8): 1551-1558. |
| 付学琴, 刘琚珥, 黄文新. 南丰蜜橘园自然生草对土壤微生物和养分及果实品质的影响. 园艺学报, 2015, 42(8): 1551-1558. | |
| [33] | Tian J, Liang C Y, Lu X, et al. Mechanism of root exudates regulating plant responses to phosphorus deficiency. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2019, 40(5): 175-185. |
| 田江, 梁翠月, 陆星, 等. 根系分泌物调控植物适应低磷胁迫的机制. 华南农业大学学报, 2019, 40(5): 175-185. | |
| [34] | Ma Y, Zhang D G. Regulation mechanisms of rhizosphere nutrient cycling processes in grassland: A review. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(11): 172-182. |
| 马源, 张德罡. 草地根际过程对养分循环调控机制研究进展. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 172-182. | |
| [35] | Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences. China soil database. Nanjing: Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2024. |
| 中国科学院南京土壤研究所. 中国土壤数据库. 南京: 中国科学院南京土壤研究所, 2024. | |
| [36] | Guo Z, Lu Y J. Influencing factors of content of organic carbon in cultivated soils of yellow soil and suggested countermeasures. Hans Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 9(6): 432-437. |
| 郭振, 卢垟杰. 黄壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究进展及提升对策. 农业科学, 2019, 9(6): 432-437. | |
| [37] | Xia L. Study on yellow soil adsorption and desorption characters of fluorine and phosphate in mountain regions of western Sichuan. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2010. |
| 夏丽. 氟、磷在川西山地黄壤中的吸附-解吸特征研究. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2010. | |
| [38] | Wang Q, Chen Y H, Zhang N Y, et al. Phosphorus adsorption and desorption characteristics as affected by long-term phosphorus application in black soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(9): 1569-1581. |
| 王琼, 陈延华, 张乃于, 等. 长期施磷黑土中磷的吸附-解吸特征及其影响因素. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(9): 1569-1581. |
| [1] | 王静, 李旭东, 韩天虎, 牛得草, 白春利, 郭丁. 高寒草甸不同草地微斑块土壤团聚体分布及其与有机碳矿化的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 15-27. |
| [2] | 宋一欣, 李明源, 麦日艳古·亚生, 王继莲. 新疆高寒草地3种植物根际土壤真菌群落结构及功能多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 167-178. |
| [3] | 刘冬娅, 杨燕, 刘静, 王博, 李志刚. 短期羊粪归还对荒漠草地土壤质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 28-39. |
| [4] | 魏孔涛, 张春平, 俞旸, 张正社, 周泽, 张雪, 王鑫鑫, 岳思玉, 曹铨, 董全民. 环青海湖共和盆地不同燕麦品种的产量、营养价值及对土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 107-118. |
| [5] | 康佳惠, 郑敏娜, 龚瑞杰, 韩志顺, 陈燕妮, 梁秀芝. 氮磷添加对一年生人工草地土壤微生物-胞外酶生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 13-24. |
| [6] | 张颖, 贺善睦, 何傲蕾, 李昌宁, 姚拓. 微生物菌剂与有机钙蛋白配施对紫花苜蓿生长和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 25-39. |
| [7] | 罗叙, 马慧, 韩翠, 赵雅欣, 赵莹, 谢应忠, 李建平. 地上净初级生产力对植物物种丰富度的响应及影响因子分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 26-37. |
| [8] | 冉健民, 宋小艳, 王丹, 王长庭. 退化高寒草甸土壤有机碳组分变化与增汇潜力研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 38-52. |
| [9] | 陈俊玲, 王莎莎, 叶菁, 林怡, 王义祥. 长期不同果园生草覆盖下土壤碳矿化及其温度敏感性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 53-64. |
| [10] | 马红钰, 周小国, 王宝, 宋渝川, 艾克热木·阿不拉提江null, 蒋邵丽, 闵九洲, 赵红梅, 程军回. 准噶尔荒漠梭梭和柽柳根际土壤微生物功能基因丰度变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 109-122. |
| [11] | 彭浩, 董宝珠, 马利娟, 于晓东, 张艺帆, 李晓芳. 内蒙古典型草原和荒漠草原土壤固碳微生物组成及其固碳途径差异分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 123-131. |
| [12] | 张琨, 乔建霞, 李金升, 王育鹏, 刘克思. 不同修复材料对退化高寒草地土壤理化性质及微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 132-148. |
| [13] | 张邦彦, 谢小伟, 张朝辉, 武晋民, 王彬, 许兴. 有机-无机改良物料对盐碱地土壤质量及湖南稷子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 15-29. |
| [14] | 卢天一, 艾艳梅, 汪洋, 那萌, 徐尚起, 周际海. 镉污染土壤中水稻的镉富集特征和生长响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 66-78. |
| [15] | 汤珊珊, 胡敏. 禾本科植物根际土壤酶活性和细菌群落结构差异[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 99-108. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||