

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 68-82.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025081
张继元1( ), 安海全2, 潘靖一1, 刘畅1, 龙思思1, 赵丽丽1(
), 安海全2, 潘靖一1, 刘畅1, 龙思思1, 赵丽丽1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-11
修回日期:2025-04-29
出版日期:2026-02-20
发布日期:2025-12-24
通讯作者:
赵丽丽
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: zhaolili_0508@163.com基金资助:
Ji-yuan ZHANG1( ), Hai-quan AN2, Jing-yi PAN1, Chang LIU1, Si-si LONG1, Li-li ZHAO1(
), Hai-quan AN2, Jing-yi PAN1, Chang LIU1, Si-si LONG1, Li-li ZHAO1( )
)
Received:2025-03-11
Revised:2025-04-29
Online:2026-02-20
Published:2025-12-24
Contact:
Li-li ZHAO
摘要:
以皇冠、角斗士、PANGO、巨能801、WL525、维多利亚、迪特7个紫花苜蓿品种种子为试验材料,采用浓度为15%的聚乙二醇-6000(PEG-6000)溶液模拟干旱胁迫14 d,实验室内分析了种子萌发、幼苗生长和生理生化指标对干旱胁迫的响应与变化。结果表明:干旱胁迫条件下,除PANGO外其余6个紫花苜蓿种子的发芽指数和活力指数均显著下降(P<0.05);皇冠和WL525幼苗的干重、苗长和根长显著增加(P<0.05);巨能801、维多利亚和角斗士幼苗的相对含水量均显著增加(P<0.05);除角斗士外其余6个品种的过氧化物酶(POD)活性均显著上升,除维多利亚外,其余6个品种的丙二醛(MDA)含量均显著上升;皇冠、迪特和巨能801的超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性均显著上升;角斗士的脯氨酸(Pro)和可溶性糖(SS)含量显著升高(P<0.05)。基于种子萌发、幼苗生长和生理生化等17个指标,利用主成分分析法结合隶属函数法综合评价,得出7个紫花苜蓿品种种子萌发与幼苗生长期的抗旱性由强到弱的排序为:巨能801>角斗士>WL525>维多利亚>PANGO>迪特>皇冠;基于系统聚类分析划分出:1)强抗旱品种为‘巨能801’;2)中抗旱品种为‘角斗士’、‘WL525’和‘维多利亚’;3)弱抗旱品种为‘PANGO’、‘迪特’和‘皇冠’。
张继元, 安海全, 潘靖一, 刘畅, 龙思思, 赵丽丽. 7个紫花苜蓿品种种子萌发及幼苗生长的抗旱性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 68-82.
Ji-yuan ZHANG, Hai-quan AN, Jing-yi PAN, Chang LIU, Si-si LONG, Li-li ZHAO. Drought resistance evaluation of seed germination and seedling growth of seven alfalfa cultivars[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(2): 68-82.
品种 Cultivars | 千粒重Thousand seeds weight (g) | 来源 Source | 原产地 Place of origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 皇冠Phabulous | 2.32 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 美国America |
| 角斗士Gladiator | 2.25 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 意大利Italy |
| PANGO | 2.25 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 美国America |
| 巨能801 Magnum 801 | 2.10 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 美国America |
| WL525 | 2.54 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 美国America |
| 维多利亚Victoria | 2.19 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 加拿大Canada |
| 迪特Dieter | 2.18 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 意大利Italy |
表1 供试紫花苜蓿品种
Table 1 Alfalfa cultivars tested
品种 Cultivars | 千粒重Thousand seeds weight (g) | 来源 Source | 原产地 Place of origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 皇冠Phabulous | 2.32 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 美国America |
| 角斗士Gladiator | 2.25 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 意大利Italy |
| PANGO | 2.25 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 美国America |
| 巨能801 Magnum 801 | 2.10 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 美国America |
| WL525 | 2.54 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 美国America |
| 维多利亚Victoria | 2.19 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 加拿大Canada |
| 迪特Dieter | 2.18 | 贵州众智恒生态科技有限公司Guizhou Zhongzhiheng Ecological Technology Co., Ltd | 意大利Italy |

图1 干旱胁迫对7个紫花苜蓿品种种子萌发的影响不同小写字母表示同一处理不同品种之间差异显著(P<0.05),不同大写字母表示同一品种不同处理之间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different cultivars of the same treatment (P<0.05), and different uppercase letters indicate significant difference between different treatments of the same cultivars (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Effects of drought stress on seed germination of seven alfalfa cultivars
品种 Cultivars | PEG-6000浓度 PEG-6000 concentration (%) | 干重 Dry weight (g·plant-1) | 鲜重 Fresh weight (g·plant-1) | 相对含水量 Relative water content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
皇冠 Phabulous | 0 | 0.0015±0.0001Bab | 0.0284±0.0022Aa | 94.72±0.0022Ab |
| 15 | 0.0017±0.0001Ab | 0.0242±0.0011Bbc | 92.88±0.0040Bc | |
角斗士 Gladiator | 0 | 0.0017±0.0003Aa | 0.0219±0.0036Bc | 92.26±0.0013Bd |
| 15 | 0.0017±0.0001Ab | 0.0297±0.0014Aa | 94.23±0.0017Ab | |
| PANGO | 0 | 0.0011±0.0001Bb | 0.0278±0.0030Aab | 95.68±0.0060Aa |
| 15 | 0.0022±0.0001Aa | 0.0232±0.0022Bc | 90.34±0.0085Be | |
巨能801 Magnum 801 | 0 | 0.0015±0.0001Aab | 0.0230±0.0021Ac | 93.38±0.0033Bc |
| 15 | 0.0012±0.0004Ac | 0.0272±0.0044Aab | 95.56±0.0091Aa | |
| WL525 | 0 | 0.0011±0.0002Bb | 0.0272±0.0021Aab | 95.64±0.0107Aa |
| 15 | 0.0019±0.0001Aab | 0.0225±0.0026Bc | 91.33±0.0126Bde | |
维多利亚 Victoria | 0 | 0.0016±0.0002Aa | 0.0238±0.0022Abc | 93.23±0.0060Bc |
| 15 | 0.0010±0.0000Bc | 0.0255±0.0010Abc | 95.86±0.0019Aa | |
迪特 Dieter | 0 | 0.0014±0.0002Aab | 0.0273±0.0019Aab | 94.54±0.0059Ab |
| 15 | 0.0013±0.0003Ac | 0.0164±0.0008Bd | 92.09±0.0143Bcd |
表2 干旱胁迫对7个紫花苜蓿品种幼苗生物量和相对含水量的影响
Table 2 Effects of drought stress on seedling biomass and relative water content of seven alfalfa cultivars
品种 Cultivars | PEG-6000浓度 PEG-6000 concentration (%) | 干重 Dry weight (g·plant-1) | 鲜重 Fresh weight (g·plant-1) | 相对含水量 Relative water content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
皇冠 Phabulous | 0 | 0.0015±0.0001Bab | 0.0284±0.0022Aa | 94.72±0.0022Ab |
| 15 | 0.0017±0.0001Ab | 0.0242±0.0011Bbc | 92.88±0.0040Bc | |
角斗士 Gladiator | 0 | 0.0017±0.0003Aa | 0.0219±0.0036Bc | 92.26±0.0013Bd |
| 15 | 0.0017±0.0001Ab | 0.0297±0.0014Aa | 94.23±0.0017Ab | |
| PANGO | 0 | 0.0011±0.0001Bb | 0.0278±0.0030Aab | 95.68±0.0060Aa |
| 15 | 0.0022±0.0001Aa | 0.0232±0.0022Bc | 90.34±0.0085Be | |
巨能801 Magnum 801 | 0 | 0.0015±0.0001Aab | 0.0230±0.0021Ac | 93.38±0.0033Bc |
| 15 | 0.0012±0.0004Ac | 0.0272±0.0044Aab | 95.56±0.0091Aa | |
| WL525 | 0 | 0.0011±0.0002Bb | 0.0272±0.0021Aab | 95.64±0.0107Aa |
| 15 | 0.0019±0.0001Aab | 0.0225±0.0026Bc | 91.33±0.0126Bde | |
维多利亚 Victoria | 0 | 0.0016±0.0002Aa | 0.0238±0.0022Abc | 93.23±0.0060Bc |
| 15 | 0.0010±0.0000Bc | 0.0255±0.0010Abc | 95.86±0.0019Aa | |
迪特 Dieter | 0 | 0.0014±0.0002Aab | 0.0273±0.0019Aab | 94.54±0.0059Ab |
| 15 | 0.0013±0.0003Ac | 0.0164±0.0008Bd | 92.09±0.0143Bcd |
品种 Cultivars | PEG-6000浓度 PEG-6000 concentration (%) | 苗长 Seedling length (mm) | 芽长 Bud length (mm) | 根长 Root length (mm) | 芽根比 Bud root ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
皇冠 Phabulous | 0 | 28.74±3.20Bc | 18.37±2.07Aa | 10.37±1.63Bd | 1.79±0.28Aa |
| 15 | 46.33±4.12Aa | 15.04±1.22Bb | 31.28±3.30Aa | 0.48±0.04Bc | |
角斗士 Gladiator | 0 | 31.96±6.13Abc | 16.82±1.80Aa | 15.14±4.41Abcd | 1.15±0.23Abcd |
| 15 | 34.38±5.79Abc | 14.95±0.84Ab | 19.43±6.56Ab | 0.89±0.48Abc | |
| PANGO | 0 | 34.77±2.26Aabc | 18.70±1.24Aa | 16.07±2.74Abcd | 1.19±0.23Abc |
| 15 | 25.75±5.72Bd | 8.51±1.90Bc | 17.24±3.86Abc | 0.49±0.02Bc | |
巨能801 Magnum 801 | 0 | 35.35±7.50Aabc | 16.00±1.69Aa | 19.35±6.02Aabc | 0.86±0.19Bcde |
| 15 | 30.71±1.95Acd | 18.10±1.64Aab | 12.60±2.44Ac | 1.49±0.38Aa | |
| WL525 | 0 | 30.26±1.58Bc | 16.62±1.32Aa | 13.64±2.11Bcd | 1.24±0.26Ab |
| 15 | 37.67±3.54Ab | 18.81±5.10Aa | 18.85±3.65Abc | 1.05±0.43Aab | |
维多利亚 Victoria | 0 | 38.31±4.87Aab | 17.03±1.75Ba | 21.28±4.78Aab | 0.83±0.19Bde |
| 15 | 37.90±3.50Ab | 20.56±0.38Aa | 17.33±3.52Abc | 1.22±0.25Aab | |
迪特 Dieter | 0 | 40.71±4.99Aa | 17.47±1.78Aa | 23.23±4.37Aa | 0.77±0.17Be |
| 15 | 36.47±2.68Abc | 18.65±0.88Aa | 17.81±2.54Abc | 1.06±0.15Aab |
表3 干旱胁迫对7个紫花苜蓿品种幼苗生长的影响
Table 3 Effects of drought stress on seedling growth of seven alfalfa cultivars
品种 Cultivars | PEG-6000浓度 PEG-6000 concentration (%) | 苗长 Seedling length (mm) | 芽长 Bud length (mm) | 根长 Root length (mm) | 芽根比 Bud root ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
皇冠 Phabulous | 0 | 28.74±3.20Bc | 18.37±2.07Aa | 10.37±1.63Bd | 1.79±0.28Aa |
| 15 | 46.33±4.12Aa | 15.04±1.22Bb | 31.28±3.30Aa | 0.48±0.04Bc | |
角斗士 Gladiator | 0 | 31.96±6.13Abc | 16.82±1.80Aa | 15.14±4.41Abcd | 1.15±0.23Abcd |
| 15 | 34.38±5.79Abc | 14.95±0.84Ab | 19.43±6.56Ab | 0.89±0.48Abc | |
| PANGO | 0 | 34.77±2.26Aabc | 18.70±1.24Aa | 16.07±2.74Abcd | 1.19±0.23Abc |
| 15 | 25.75±5.72Bd | 8.51±1.90Bc | 17.24±3.86Abc | 0.49±0.02Bc | |
巨能801 Magnum 801 | 0 | 35.35±7.50Aabc | 16.00±1.69Aa | 19.35±6.02Aabc | 0.86±0.19Bcde |
| 15 | 30.71±1.95Acd | 18.10±1.64Aab | 12.60±2.44Ac | 1.49±0.38Aa | |
| WL525 | 0 | 30.26±1.58Bc | 16.62±1.32Aa | 13.64±2.11Bcd | 1.24±0.26Ab |
| 15 | 37.67±3.54Ab | 18.81±5.10Aa | 18.85±3.65Abc | 1.05±0.43Aab | |
维多利亚 Victoria | 0 | 38.31±4.87Aab | 17.03±1.75Ba | 21.28±4.78Aab | 0.83±0.19Bde |
| 15 | 37.90±3.50Ab | 20.56±0.38Aa | 17.33±3.52Abc | 1.22±0.25Aab | |
迪特 Dieter | 0 | 40.71±4.99Aa | 17.47±1.78Aa | 23.23±4.37Aa | 0.77±0.17Be |
| 15 | 36.47±2.68Abc | 18.65±0.88Aa | 17.81±2.54Abc | 1.06±0.15Aab |
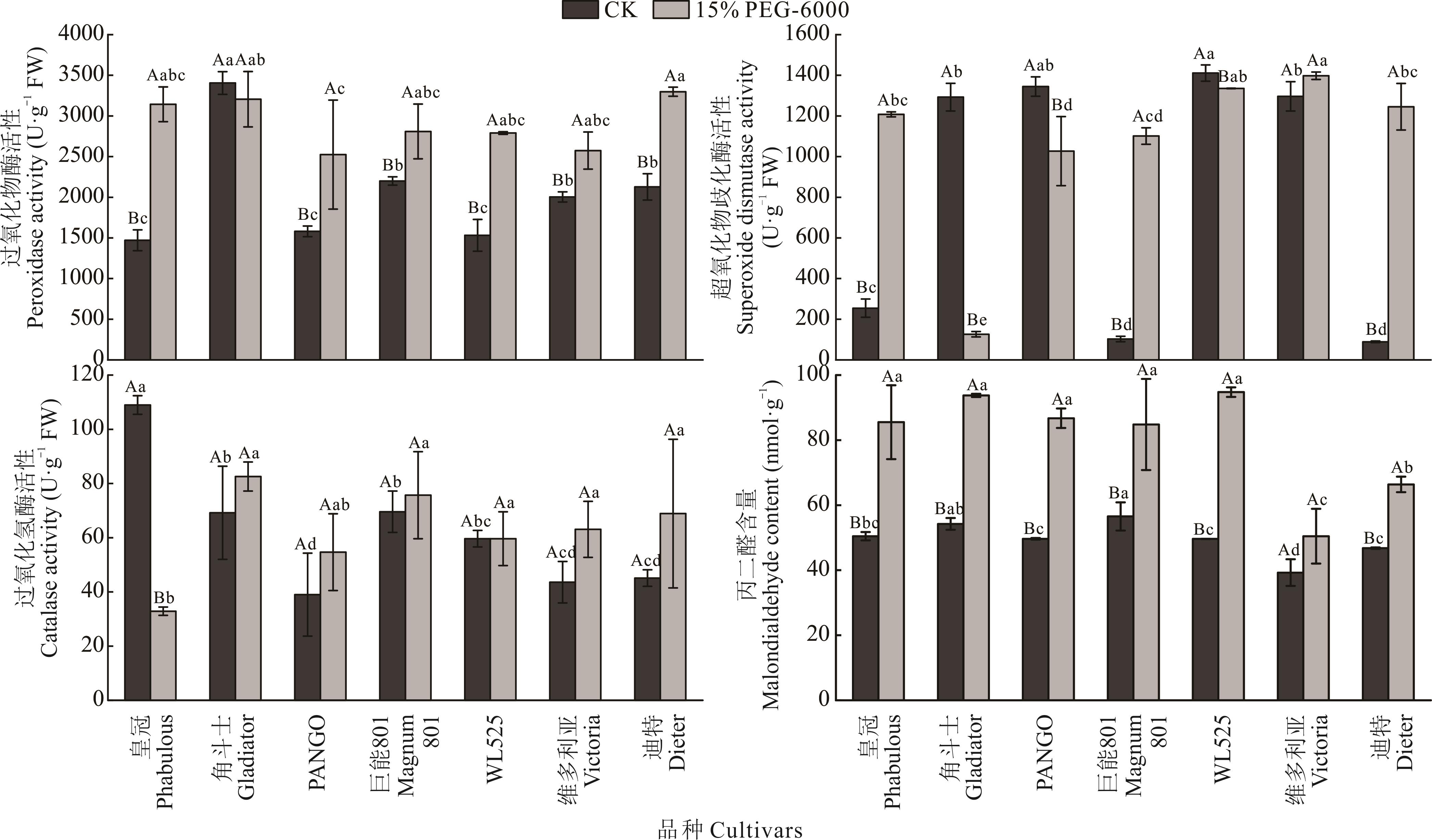
图2 干旱胁迫对7个紫花苜蓿品种抗氧化酶活性和丙二醛含量的影响
Fig. 2 Effects of drought stress on antioxidant enzymes activity and malondialdehyde content of seven alfalfa cultivars
| 项目 Item | PC 1 | PC 2 | PC 3 | PC 4 | PC 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 发芽率Germination rate | 0.3652 | 0.1368 | 0.0529 | 0.0467 | 0.0586 |
| X2 发芽势Germination potential | 0.3210 | 0.0467 | 0.0848 | 0.3509 | 0.0437 |
| X3 发芽指数Germination index | 0.3546 | 0.1194 | 0.0780 | 0.1903 | 0.0571 |
| X4 活力指数Vitality index | 0.3623 | 0.0553 | 0.1358 | 0.0530 | 0.1770 |
| X5 干重Dry weight | 0.2628 | 0.3338 | 0.1266 | 0.1266 | 0.1628 |
| X6 鲜重Fresh weight | 0.1794 | 0.0350 | 0.3092 | 0.4302 | 0.3595 |
| X7 相对含水量Relative water content | 0.1712 | 0.4238 | 0.1137 | 0.1909 | 0.0863 |
| X8 苗长Seedling length | 0.0671 | 0.4335 | 0.2217 | 0.1878 | 0.0738 |
| X9 芽长Bud length | 0.2116 | 0.2089 | 0.3784 | 0.0678 | 0.2957 |
| X10 根长Root length | 0.2206 | 0.3782 | 0.0130 | 0.1789 | 0.1084 |
| X11 芽根比Bud root ratio | 0.3043 | 0.0915 | 0.2717 | 0.0553 | 0.3173 |
| X12 过氧化物酶活性Peroxidase activity | 0.2073 | 0.0589 | 0.0865 | 0.5371 | 0.1533 |
| X13 超氧化物歧化酶活性Superoxide dismutase activity | 0.1160 | 0.2880 | 0.3690 | 0.1704 | 0.3086 |
| X14 过氧化氢酶活性Catalase activity | 0.1521 | 0.3481 | 0.0467 | 0.3652 | 0.0905 |
| X15 丙二醛含量Malondialdehyde content | 0.0092 | 0.0310 | 0.5448 | 0.0762 | 0.2911 |
| X16 脯氨酸含量Proline content | 0.2596 | 0.0969 | 0.3492 | 0.1770 | 0.2753 |
| X17 可溶性糖含量Soluble sugar content | 0.1960 | 0.2620 | 0.1006 | 0.1874 | 0.5515 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 6.806 | 3.797 | 2.953 | 1.861 | 1.123 |
| 贡献率Contribution rate (%) | 40.037 | 22.334 | 17.368 | 10.945 | 6.604 |
| 累积贡献率Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 40.037 | 62.371 | 79.740 | 90.685 | 97.289 |
| 权重 Weight | 0.412 | 0.230 | 0.179 | 0.113 | 0.068 |
表4 干旱胁迫下7个紫花苜蓿品种各项指标的主成分分析
Table 4 Principal component analysis of indicators of seven alfalfa cultivars under drought stress
| 项目 Item | PC 1 | PC 2 | PC 3 | PC 4 | PC 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 发芽率Germination rate | 0.3652 | 0.1368 | 0.0529 | 0.0467 | 0.0586 |
| X2 发芽势Germination potential | 0.3210 | 0.0467 | 0.0848 | 0.3509 | 0.0437 |
| X3 发芽指数Germination index | 0.3546 | 0.1194 | 0.0780 | 0.1903 | 0.0571 |
| X4 活力指数Vitality index | 0.3623 | 0.0553 | 0.1358 | 0.0530 | 0.1770 |
| X5 干重Dry weight | 0.2628 | 0.3338 | 0.1266 | 0.1266 | 0.1628 |
| X6 鲜重Fresh weight | 0.1794 | 0.0350 | 0.3092 | 0.4302 | 0.3595 |
| X7 相对含水量Relative water content | 0.1712 | 0.4238 | 0.1137 | 0.1909 | 0.0863 |
| X8 苗长Seedling length | 0.0671 | 0.4335 | 0.2217 | 0.1878 | 0.0738 |
| X9 芽长Bud length | 0.2116 | 0.2089 | 0.3784 | 0.0678 | 0.2957 |
| X10 根长Root length | 0.2206 | 0.3782 | 0.0130 | 0.1789 | 0.1084 |
| X11 芽根比Bud root ratio | 0.3043 | 0.0915 | 0.2717 | 0.0553 | 0.3173 |
| X12 过氧化物酶活性Peroxidase activity | 0.2073 | 0.0589 | 0.0865 | 0.5371 | 0.1533 |
| X13 超氧化物歧化酶活性Superoxide dismutase activity | 0.1160 | 0.2880 | 0.3690 | 0.1704 | 0.3086 |
| X14 过氧化氢酶活性Catalase activity | 0.1521 | 0.3481 | 0.0467 | 0.3652 | 0.0905 |
| X15 丙二醛含量Malondialdehyde content | 0.0092 | 0.0310 | 0.5448 | 0.0762 | 0.2911 |
| X16 脯氨酸含量Proline content | 0.2596 | 0.0969 | 0.3492 | 0.1770 | 0.2753 |
| X17 可溶性糖含量Soluble sugar content | 0.1960 | 0.2620 | 0.1006 | 0.1874 | 0.5515 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 6.806 | 3.797 | 2.953 | 1.861 | 1.123 |
| 贡献率Contribution rate (%) | 40.037 | 22.334 | 17.368 | 10.945 | 6.604 |
| 累积贡献率Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 40.037 | 62.371 | 79.740 | 90.685 | 97.289 |
| 权重 Weight | 0.412 | 0.230 | 0.179 | 0.113 | 0.068 |
品种 Cultivars | 隶属函数值Subordinate function values μ(Xj ) | 综合评价值 Comprehensive evaluation (D) | 排序 Sort | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC 1 | PC 2 | PC 3 | PC 4 | PC 5 | |||
| 皇冠Phabulous | 0.0000 | 0.1856 | 0.5822 | 0.4526 | 0.5167 | 0.2332 | 7 |
| 角斗士Gladiator | 0.2607 | 0.8494 | 1.0000 | 0.9071 | 0.8180 | 0.6399 | 2 |
| PANGO | 0.2695 | 0.6646 | 0.5640 | 0.0000 | 0.2457 | 0.3815 | 5 |
| 巨能801 Magnum 801 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.4875 | 0.4970 | 0.3074 | 0.8063 | 1 |
| WL525 | 0.9295 | 0.0000 | 0.8548 | 0.7233 | 0.1753 | 0.6296 | 3 |
| 维多利亚Victoria | 0.7198 | 0.3426 | 0.0000 | 0.5532 | 1.0000 | 0.5059 | 4 |
| 迪特Dieter | 0.1790 | 0.6234 | 0.0699 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3426 | 6 |
表5 干旱胁迫下7个紫花苜蓿品种的隶属函数值及综合评价值
Table 5 Subordinate function values and comprehensive evaluation values of seven alfalfa cultivars under drought stress
品种 Cultivars | 隶属函数值Subordinate function values μ(Xj ) | 综合评价值 Comprehensive evaluation (D) | 排序 Sort | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC 1 | PC 2 | PC 3 | PC 4 | PC 5 | |||
| 皇冠Phabulous | 0.0000 | 0.1856 | 0.5822 | 0.4526 | 0.5167 | 0.2332 | 7 |
| 角斗士Gladiator | 0.2607 | 0.8494 | 1.0000 | 0.9071 | 0.8180 | 0.6399 | 2 |
| PANGO | 0.2695 | 0.6646 | 0.5640 | 0.0000 | 0.2457 | 0.3815 | 5 |
| 巨能801 Magnum 801 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.4875 | 0.4970 | 0.3074 | 0.8063 | 1 |
| WL525 | 0.9295 | 0.0000 | 0.8548 | 0.7233 | 0.1753 | 0.6296 | 3 |
| 维多利亚Victoria | 0.7198 | 0.3426 | 0.0000 | 0.5532 | 1.0000 | 0.5059 | 4 |
| 迪特Dieter | 0.1790 | 0.6234 | 0.0699 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3426 | 6 |
| [1] | Mi J Z, Zhang L Y, Tian L, et al. Responses of seedling growth, yield of foxtail millet [Setaria italic( L.) Beauv.] and soil moisture to humic acid applications with different durations in dryland area. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(8): 2441-2449. |
| 米俊珍, 张兰英, 田露, 等. 旱作区谷子苗期生长、产量与土壤水分对不同施用年限腐殖酸的响应. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(8): 2441-2449. | |
| [2] | Kogan F, Adamenko T, Guo W. Global and regional drought dynamics in the climate warming era. Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 4(4): 364-372. |
| [3] | Wu M, Liu X B, Ding L R, et al. Effects of silicon on germination and physiological characteristics of alfalfa under drought stress simulated by PEG. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2017, 25(6): 1258-1264. |
| 吴淼, 刘信宝, 丁立人, 等. PEG模拟干旱胁迫下硅对紫花苜蓿萌发及生理特性的影响. 草地学报, 2017, 25(6): 1258-1264. | |
| [4] | Zou C H, Xie X Y, Zhou Z F. Future prospects in utilization of photo-taking unmanned aerial vehicle in low altitude of RS system in plateau mountain area of Guizhou. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2011, 29(2): 24-28. |
| 邹长慧, 谢晓尧, 周忠发. 无人机低空航拍遥感系统在贵州高原山区的应用前景探讨. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 29(2): 24-28. | |
| [5] | Zhang Z H. Exploring the way of controlling rocky desertification and developing ecological animal husbandry in Guizhou Province. Pratacultural Science, 2006, 23(8): 63-67. |
| 张自和. 贵州治理石漠化发展生态畜牧业探索之路. 草业科学, 2006, 23(8): 63-67. | |
| [6] | Wu X P, Zhou Z F, Zhu M, et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics of drought in different geomorphic types in typical karst cluster areas. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 30(1): 336-347. |
| 吴小飘, 周忠发, 朱孟, 等. 典型喀斯特聚集区不同地貌类型干旱时空特征. 水土保持研究, 2023, 30(1): 336-347. | |
| [7] | Li S M, Xie G D. Spatial and temporal heterogeneity of water conservation service for meadow ecosystem. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2015, 37(2): 88-93. |
| 李士美, 谢高地. 草甸生态系统水源涵养服务功能的时空异质性. 中国草地学报, 2015, 37(2): 88-93. | |
| [8] | Zhao Y, Wu M, Ye X X, et al. Growth and chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics parameters of Alchornea trewioides under drought and re-watering in karst areas. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2023, 43(9): 1537-1546. |
| 赵英, 吴敏, 叶晓霞, 等. 干旱与复水对喀斯特地区红背山麻杆生长及叶绿素荧光动力学参数的影响. 西北植物学报, 2023, 43(9): 1537-1546. | |
| [9] | Liu S X, Wang H W, Qin F. Genetic dissection of drought resistance for trait improvement in crops. The Crop Journal, 2023, 11(4): 975-985. |
| [10] | Maiti R, Rajkumar D, Vidyasagar P. Screening of rice varieties for drought resistance at seedling stage. Research on Crops, 2012, 13(3): 790-794. |
| [11] | Cui W N, Meng J J, Zhang W X, et al. Effect of gibberellin on seed germination and seedling growth of five species of forage seeds. Pratacultural Science, 2024, 41(1): 89-98. |
| 崔文宁, 孟静静, 张文香, 等. GA3处理对盐胁迫下5种牧草种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 草业科学, 2024, 41(1): 89-98. | |
| [12] | Soufan W, Okla M K, Salamatullah A, et al. Seasonal variation in yield, nutritive value, and antioxidant capacity of leaves of alfalfa plants grown in arid climate of Saudi Arabia. Chilean Journal of Agricultural Research, 2021, 81(2): 182-190. |
| [13] | Liu Z, Lan J, Li W, et al. Reseeding improved soil and plant characteristics of degraded alfalfa(Medicago sativa) grassland in loess hilly plateau region, China. Ecological Engineering, 2023, 190(1): 106933. |
| [14] | Wang J, Liu X J, Hao F, et al. Study on nitrogen utilization characteristics of alfalfa with different nitrogen efficiency in different growth periods. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(11): 2461-2469. |
| 王静, 刘晓静, 郝凤, 等. 不同氮效率紫花苜蓿各生育期氮利用特征研究. 草地学报, 2021, 29(11): 2461-2469. | |
| [15] | Chen Y C, Li X, Cai Y D, et al. Effects of dry-farming alfalfa on fungal communities in high altitude sandy areas of Xinjiang. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(5): 77-87. |
| 陈永成, 李肖, 蔡宜东, 等. 旱作紫花苜蓿对新疆高海拔沙区真菌群落的影响. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(5): 77-87. | |
| [16] | Tong C C, Liu X J, Lin F, et al. Yield effect of optimisation of photosynthetic characteristics of alfalfa through balanced fertilization. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 70-80. |
| 童长春, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 等. 基于平衡施肥的紫花苜蓿光合特性及光合因子的产量效应研究. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 70-80. | |
| [17] | Zhang X L, Liu X J, Qi M X, et al. Alfalfa seeding root characteristics under complex saline-alkali stress. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21(3): 340-346. |
| 张晓磊, 刘晓静, 齐敏兴, 等. 混合盐碱对紫花苜蓿苗期根系特征的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(3): 340-346. | |
| [18] | Chen Y X, Ma Q L, Ma D M, et al. Evaluation of the drought resistance of 66 alfalfa clones at the seedling stage. Pratacultural Science, 2024, 41(4): 908-918. |
| 陈云鑫, 马巧利, 麻冬梅, 等. 66个紫花苜蓿品种无性系苗期抗旱性评价. 草业科学, 2024, 41(4): 908-918. | |
| [19] | Xu H, He L, Song M Q, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the production performance of eight alfalfa varieties in the arid area of Qaidam. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2024, 42(2): 33-40. |
| 徐航, 何霖, 宋美琪, 等. 8个紫花苜蓿品种在柴达木旱区的生产性能综合评价. 干旱地区农业研究, 2024, 42(2): 33-40. | |
| [20] | Ruan Q, Bai X M, Wang Y Z, et al. Regulation of endogenous hormone and miRNA in leaves of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seedlings under drought stress by endogenous nitric oxide. BMC Genomics, 2024, 25(1): 2-19. |
| [21] | Xu M Z, Xu Z P, Liu Y R, et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals the vital role of aba plays in drought tolerance of the ABA-insensitive alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Agronomy, 2024, 14(3): 406. |
| [22] | Han Z S, Zheng M N, Liang X Z, et al. Effects of drought stress on morphological and physiological characteristics of different alfalfa cultivars. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 42(3): 37-43. |
| 韩志顺, 郑敏娜, 梁秀芝, 等. 干旱胁迫对不同紫花苜蓿品种形态特征和生理特性的影响. 中国草地学报, 2020, 42(3): 37-43. | |
| [23] | Yang Y, Liu Y C, Zhou M C, et al. Studies on the changes of seed contents in Rosa spinosissima under low temperature sand storage. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2023, 38(S1): 253-260. |
| 杨宇, 刘雨晨, 周美春, 等. 低温沙藏下密刺蔷薇种子内含物变化研究. 华北农学报, 2023, 38(S1): 253-260. | |
| [24] | El Harfi M, Hanine H, Rizki H, et al. Effect of drought and salt stresses on germination and early seedling growth of different color-seeds of sesame (Sesamum indicum). International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 2016, 18(6): 1088-1094. |
| [25] | Li W R, Zhang S Q, Shan L. Seeds germination characteristics and drought-tolerance of alfalfa and sorghum seedling under water stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(6): 3066-3074. |
| 李文娆, 张岁岐, 山仑. 水分胁迫下紫花苜蓿和高粱种子萌发特性及幼苗耐旱性. 生态学报, 2009, 29(6): 3066-3074. | |
| [26] | Shan X D, Zhang R, Maiwulidai K, et al. Effect of gibberellin soaking on seed germination of perennial ryegrass under polyethylene glycol simulated drought conditions. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(9): 2304-2311. |
| 单旭东, 张睿, 麦吾丽代·卡哈尔, 等. 赤霉素浸种对PEG模拟干旱条件下多年生黑麦草种子萌发的影响. 草业科学, 2019, 36(9): 2304-2311. | |
| [27] | Gao Z H, Li X Y, Lan J, et al. Comparison and evaluation of seed germination indexes of different forage-type oat cultivars under PEG-6000 stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(5): 1210-1218. |
| 高志昊, 李雪颖, 兰剑, 等. 干旱胁迫条件下不同饲用燕麦品种种子萌发指标比较与评价. 草地学报, 2022, 30(5): 1210-1218. | |
| [28] | Tian H, Zhang H S, Xiong J B, et al. Variability in drought resistance during seed germination among 34 Pennisetum alopecuroides gerplasms. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2024, 46(4): 11-24. |
| 田宏, 张鹤山, 熊军波, 等. 34份狼尾草萌发期抗旱性综合评价. 中国草地学报, 2024, 46(4): 11-24. | |
| [29] | Qu X H, Zhao L L, Wang P C, et al. Drought resistance of six Paspalum wettsteinii materials during germination period. Seed, 2017, 36(4): 24-27. |
| 屈兴红, 赵丽丽, 王普昶, 等. 6个宽叶雀稗材料种子萌发期抗旱性研究. 种子, 2017, 36(4): 24-27. | |
| [30] | Cheng B, Hu S R, Gao Y, et al. Drought resistance of 5 alfalfa species at germination period under PEG simulated drought stress. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(1): 53-59. |
| 程波, 胡生荣, 高永, 等. PEG模拟干旱胁迫下5种紫花苜蓿萌发期抗旱性的评估. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(1): 53-59. | |
| [31] | Fu B Z, Lan J, Li X W, et al. Effects of PEG-6000 drought stress on seed germination of 16 varieties of alfalfa. Seed, 2012, 31(4): 10-14. |
| 伏兵哲, 兰剑, 李小伟, 等. PEG-6000干旱胁迫对16个苜蓿品种种子萌发的影响. 种子, 2012, 31(4): 10-14. | |
| [32] | Yuan Z H, Wang C T, Li S P, et al. Effects of different plant hormones or PEG seed soaking on maize resistance to drought stress. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 2014, 94(8): 1491-1499. |
| [33] | Xu X, He B, Tan C Y, et al. Observation on seed germination microstructure of wild Glycine max in Guizhou under drought stress. Seed, 2025, 44(1): 170-177. |
| 徐熙, 何兵, 谭春燕, 等. 干旱胁迫下贵州野生大豆种子萌发微结构观察. 种子, 2025, 44(1): 170-177. | |
| [34] | Meng Q L, Guan Z B, Feng B L, et al. Principal component analysis and fuzzy clustering on drought-tolerance related traits of foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2009, 42(8): 2667-2675. |
| 孟庆立, 关周博, 冯佰利, 等. 谷子抗旱相关性状的主成分与模糊聚类分析. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(8): 2667-2675. | |
| [35] | Wu Y H, Liu W H, Liu K Q, et al. Effects of drought stress on leaf senescence and the active oxygen scavenging system of oat seedlings. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 75-86. |
| 吴雨涵, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 等. 干旱胁迫对燕麦幼苗叶片光合特性及活性氧清除系统的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 75-86. | |
| [36] | Geravandi M, Farshadfar E, Kahrizi D. Evaluation of some physiological traits as indicators of drought tolerance in bread wheat genotypes. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 2011, 58(1): 69-75. |
| [37] | Hou R H, Du K, Huang W Y, et al. Evaluation on drought resistance of 10 wild Medicago ruthenica L. materials from different provenances at germination period. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(2): 489-494. |
| 侯瑞虹, 杜柯, 黄伟业, 等. 10份不同种源野生花苜蓿材料种子萌发期抗旱性评价. 草地学报, 2024, 32(2): 489-494. | |
| [38] | Zhou J Y, Zhao W W, Yang Y, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of two different Pennisetum species during seed germination and seedling growth stages. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(8): 50-59. |
| 周洁仪, 赵文武, 杨杨, 等. 2种狼尾草属牧草萌发期和苗期抗旱性综合评价. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(8): 50-59. | |
| [39] | Wang J Y, Xu W N, Su Y, et al. Characterization and comparison of drought resistance of five alfalfa varieties during germination period under PEG-6000 simulated drought stress. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2023, 44(2): 81-91. |
| 王江银, 徐婉宁, 苏洋, 等. PEG-6000模拟干旱胁迫下5份苜蓿材料萌发期抗旱性鉴定与比较. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2023, 44(2): 81-91. | |
| [40] | Duan P C, Wang Y T, Yang D Y, et al. Improvement of degraded soil on tunnel construction waste slag dumps and its microbial community effect. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2025, 15(2): 651-662. |
| 段鹏昌, 王奕婷, 杨东阳, 等. 隧洞施工弃渣场退化土壤的改良及其微生物群落效应. 环境工程技术学报, 2025, 15(2): 651-662. | |
| [41] | Zhang M, Ye L, Li S P, et al. Effects of drought stress on the growth biomass and C, N, and P stoichiometric characteristics of Fraxinus malacophylla seedlings. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2024, 42(2): 397-404. |
| 张梅, 叶澜, 李树萍, 等. 干旱胁迫对白枪杆幼苗生长生物量及C、N、P化学计量特征的影响. 四川农业大学学报, 2024, 42(2): 397-404. | |
| [42] | Chaves M M, Oliveira M M. Mechanisms underlying plant resilience to water deficits: prospects for water-saving agriculture. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2004, 55(407): 2365-2384. |
| [43] | He A Y, Dean J M, Lodhi I J. Peroxisomes as cellular adaptors to metabolic and environmental stress. Trends in Cell Biology, 2021, 31(8): 656-670. |
| [44] | Shao Y J, Shan L. Advances in the studies on drought tolerance mechanism of plants. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2006, 14(4): 16-20. |
| 邵艳军, 山仑. 植物耐旱机制研究进展. 中国生态农业学报, 2006, 14(4): 16-20. | |
| [45] | Han D L, Wang Y R. Adaptability of Medicago sativa under water stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2005, 14(6): 7-13. |
| 韩德梁, 王彦荣. 紫花苜蓿对干旱胁迫适应性的研究进展. 草业学报, 2005, 14(6): 7-13. | |
| [46] | Shi X Y, Wang Y X, Jiang X, et al. Effects of nitric oxide on photosynthesis and physiological characteristics of apple rootstocks under water stress. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2017, 35(4): 249-254. |
| 石晓昀, 王延秀, 姜霄, 等. 一氧化氮对水分胁迫下苹果砧木新疆野苹果光合与生理特性的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2017, 35(4): 249-254. | |
| [47] | Zhou L Y, Liu S H, Qin H M, et al. A study on relationship between leaf epicuticular wax coverage and drought resistance of five alfalfa varieties. Pratacultural Science, 2013, 30(4): 596-601. |
| 周玲艳, 刘胜洪, 秦华明, 等. 5个苜蓿品种叶片表面蜡质覆盖与抗旱性的关系. 草业科学, 2013, 30(4): 596-601. | |
| [48] | Liao Y, Peng Y G, Chen G Z. Research advances in plant salt-tolerance mechanism. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(5): 2077-2089. |
| 廖岩, 彭友贵, 陈桂珠. 植物耐盐性机理研究进展. 生态学报, 2007, 27(5): 2077-2089. | |
| [49] | Hao J F, Zhang Y X, Zhu A M, et al. Evaluation of drought resistance of 15 alfalfa species at germination period under PEG-6000 simulated drought stress. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 589(1): 90-95. |
| 郝俊峰, 张玉霞, 朱爱民, 等. PEG-6000干旱胁迫下15个苜蓿品种种子萌发抗旱性评价. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2020, 589(1): 90-95. | |
| [50] | Wang Y, Cai W, Lan J, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of twelve alfalfa varieties. Grassland and Turf, 2018, 38(2): 80-88. |
| 王焱, 蔡伟, 兰剑, 等. 12个苜蓿品种抗旱性综合评价. 草原与草坪, 2018, 38(2): 80-88. | |
| [51] | Shi Y H, Wan L Q, Liu J N, et al. Analysis of the principal components and the subordinate function of Lolium perenne drought resistance. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2010, 18(5): 669-672. |
| 石永红, 万里强, 刘建宁, 等. 多年生黑麦草抗旱性主成分及隶属函数分析. 草地学报, 2010, 18(5): 669-672. | |
| [52] | Tan J Q, Zhang X H, Li S Y, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of 7 Phleum pratense forage germplasm materials during seed germination. Grassland and Turf, 2024, 44(2): 226-236. |
| 檀嘉琦, 张鲜花, 李思媛, 等. 7份梯牧草种质材料的种子萌发期抗旱性综合评价. 草原与草坪, 2024, 44(2): 226-236. | |
| [53] | Wang M, Li L, Jia R, et al. Evaluation of physiological characteristics and cold resistance of 10 alfalfa varieties under low temperature stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(6): 76-88. |
| 王敏, 李莉, 贾蓉, 等. 10种紫花苜蓿在低温胁迫下的生理特性及耐寒性评价. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 76-88. | |
| [54] | Xiong X, Gui W Y, Liu M H, et al. Evaluation of salt tolerance in different alfalfa varieties under uniform and non-uniform salt stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(9): 67-76. |
| 熊雪, 桂维阳, 刘沫含, 等. 不同紫花苜蓿品种在均匀与不均匀盐胁迫下的耐盐性评价. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 67-76. | |
| [55] | Yu L, Wang Y R, Garnett T, et al. A study on physiological responses of varieties of Medicago sativa and their relationship with the drought resistance capacity under drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2006, 15(3): 75-85. |
| 余玲, 王彦荣, Garnett T, 等. 紫花苜蓿不同品种对干旱胁迫的生理响应. 草业学报, 2006, 15(3): 75-85. | |
| [56] | Yang X Q, Ren W B, Bai Z A, et al. Drought resistance evaluation of 14 alfalfa varieties during seed germination. Grassland and Turf, 2025, 45(1): 205-211. |
| 杨学清, 任卫波, 白卓安, 等. 14份紫花苜蓿种子萌发期抗旱性评价. 草原与草坪, 2025, 45(1): 205-211. |
| [1] | 陈丽娟, 高荣, 王建喜, 马晖玲. 紫花苜蓿与红豆草在不同生长时期缩合单宁合成差异的比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 221-236. |
| [2] | 李瑒琨, 本转林, 张筠钰, 杨惠敏. 不同气候和土壤条件下施肥类型影响紫花苜蓿种子产量的整合分析[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 54-67. |
| [3] | 祁浩乐, 王思宁, 李晓霞, 石凤翎. 野牛草种质耐盐性综合评价及评价模型的初步构建[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 119-129. |
| [4] | 张颖, 贺善睦, 何傲蕾, 李昌宁, 姚拓. 微生物菌剂与有机钙蛋白配施对紫花苜蓿生长和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 25-39. |
| [5] | 俞鸿千, 马雪鹏, 曾翰国, 单晓艳, 李曼莉, 王占军. 地下滴灌时期和水量对紫花苜蓿种子生产的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 53-64. |
| [6] | 邹苇鹏, 刘怡, 翟佳兴, 周思懿, 宫祉祎, 岑慧芳, 朱慧森, 许涛. 紫花苜蓿MsNAC053基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 121-133. |
| [7] | 鲜燃, 邓雨, 付秋月, 蒋晶霞, 陶佳丽, 许涛, 朱慧森, 岑慧芳. 紫花苜蓿MsMYB86基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 162-172. |
| [8] | 刘沂欣, 隋晓青, 王鑫尧, 郎梦卿, 孙凌子寅, 吉尔尔格. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿的缓解作用[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 206-214. |
| [9] | 陈宁, 包凤轩, 赵辉祥, 王楠, 姜汝玉, 李国良, 刘香萍, 曲善民, 杨伟光. 寒冷区苏打盐碱生境下紫花苜蓿越冬期根颈的生理特性[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 78-86. |
| [10] | 李文秀, 姚拓, 李昌宁, 贾倩民, 何傲蕾, 周杨. “凹凸棒-有机基质”菌肥载体最佳配比的筛选及对紫花苜蓿的促生效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 88-98. |
| [11] | 白小红, 陈文燕, 李琴, 王奕璇, 张雪, 王磊, 曲文杰, 朱林. 不同种源乌拉尔甘草种子萌发及幼苗生长比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 196-209. |
| [12] | 蒋学乾, 杨青川, 康俊梅. 紫花苜蓿在干旱胁迫下的产量损失与抗旱性遗传研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 219-234. |
| [13] | 温小月, 赵颖, 王宝强, 王贤, 朱晓林, 王义真, 魏小红. 外源NO调控干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿AP2/ERFs基因的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 154-167. |
| [14] | 张英豪, 刘楚波, 周坤, 郭家存, 刘世鹏, 孙娈姿. 果草系统中枣树对不同方位紫花苜蓿和鸭茅生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 203-212. |
| [15] | 崔灿, 王梦琦, 赵琬璐, 刘新颖, 鉴晶晶, 严俊鑫. 胺鲜酯浸种对NaCl胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 46-58. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||