

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (8): 99-108.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024358
收稿日期:2024-09-23
修回日期:2024-11-06
出版日期:2025-08-20
发布日期:2025-06-16
通讯作者:
胡敏
作者简介:E-mail: humin@cczu.edu.cn基金资助:Received:2024-09-23
Revised:2024-11-06
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-06-16
Contact:
Min HU
摘要:
本研究旨在探讨不同禾草对土壤微生态环境的影响。选择百喜草、黑麦草、高羊茅和苏丹草4种禾草,通过盆栽种植试验,结合化学分析和高通量测序技术,研究禾草根际土壤酶活性、细菌群落组成及多样性,并分析其与土壤理化性质的相关性。结果表明:土壤可溶性有机碳(DOC)、铵态氮(NH4+-N)、硝态氮(NO3--N)和速效磷(AP)含量在不同禾草根际土中存在显著差异。与CK处理比,4种禾草处理均提高了根际土壤β-1,4-葡萄糖苷酶(βG)、纤维二糖水解酶(CBH)、β-1,4-木糖苷酶(βX)、β-1,4-N-乙酰葡糖氨糖苷酶(NAG)和碱性磷酸酶(ALP)活性。苏丹草处理中βG、CBH、βX和NAG活性最高;ALP活性在高羊茅处理中(33.21 nmol·g-1·h-1)最高。Pearson相关性分析显示,根际土壤βG、NAG活性与土壤有机碳(SOC)显著正相关,与NO3--N显著负相关,ALP活性与土壤有机碳和可溶性有机碳呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。黑麦草根际土壤Chao1指数最高,且Shannon指数显著高于其他处理(P<0.05)。变形菌门、酸杆菌门和放线菌门是4种禾草根际土壤细菌的优势菌门。冗余分析(RDA)结果表明,土壤速效磷主导根际土壤细菌群落组成的变化。总之,禾草能显著提高根际土壤的酶活性和养分含量,并优化根际土壤细菌群落结构,从而改善土壤微生态环境,这为土壤改良提供了科学依据。其中黑麦草可以促进土壤养分的循环与有效利用,显著增加细菌群落多样性,对于改善环境的效果最好,具有一定的推广价值。
汤珊珊, 胡敏. 禾本科植物根际土壤酶活性和细菌群落结构差异[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 99-108.
Shan-shan TANG, Min HU. Differences in enzyme activity and bacterial community structure in rhizosphere soil of four grass species[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(8): 99-108.
| 处理Treatment | pH | SOC (g·kg-1) | DOC (mg·kg-1) | NO3--N (mg·kg-1) | NH4+-N (mg·kg-1) | AP (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 7.94±0.03a | 5.99±0.03a | 153.04±2.91c | 4.56±0.38a | 3.85±0.07b | 15.87±0.20b |
| 百喜草P. notatum | 7.97±0.05a | 6.07±0.08a | 166.32±5.22b | 1.65±0.19c | 4.16±0.23a | 15.29±0.34c |
| 黑麦草L. perenne | 7.91±0.06a | 6.00±0.21a | 179.53±11.21a | 3.62±0.95b | 4.00±0.09ab | 16.46±0.15a |
| 高羊茅F. arundinacea | 7.89±0.14a | 6.13±0.14a | 187.97±7.02a | 2.38±0.18c | 4.13±0.02a | 16.49±0.46a |
| 苏丹草S. sudanense | 7.94±0.07a | 6.19±0.05a | 166.25±5.04b | 1.76±0.19c | 3.86±0.06b | 15.25±0.34c |
表1 不同禾草根际土壤理化性质差异
Table 1 Differences in physical and chemical properties of rhizosphere soil of different grasses
| 处理Treatment | pH | SOC (g·kg-1) | DOC (mg·kg-1) | NO3--N (mg·kg-1) | NH4+-N (mg·kg-1) | AP (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 7.94±0.03a | 5.99±0.03a | 153.04±2.91c | 4.56±0.38a | 3.85±0.07b | 15.87±0.20b |
| 百喜草P. notatum | 7.97±0.05a | 6.07±0.08a | 166.32±5.22b | 1.65±0.19c | 4.16±0.23a | 15.29±0.34c |
| 黑麦草L. perenne | 7.91±0.06a | 6.00±0.21a | 179.53±11.21a | 3.62±0.95b | 4.00±0.09ab | 16.46±0.15a |
| 高羊茅F. arundinacea | 7.89±0.14a | 6.13±0.14a | 187.97±7.02a | 2.38±0.18c | 4.13±0.02a | 16.49±0.46a |
| 苏丹草S. sudanense | 7.94±0.07a | 6.19±0.05a | 166.25±5.04b | 1.76±0.19c | 3.86±0.06b | 15.25±0.34c |
| 处理Treatment | βG | CBH | βX | NAG | ALP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 32.41±3.14c | 5.00±0.86c | 6.19±0.47b | 4.53±0.52c | 20.95±0.53c |
| 百喜草P. notatum | 40.29±5.87bc | 5.53±0.32c | 6.38±1.29b | 6.35±0.65b | 24.16±1.70bc |
| 黑麦草L. perenne | 48.42±7.17ab | 5.55±1.80c | 7.23±1.59b | 4.74±0.37c | 26.26±0.66b |
| 高羊茅F. arundinacea | 49.44±6.92ab | 8.88±1.72b | 10.48±1.58a | 6.36±0.84b | 33.21±3.56a |
| 苏丹草S. sudanense | 57.97±5.12a | 13.00±1.82a | 11.58±0.93a | 11.68±1.13a | 31.90±1.68a |
表2 不同禾草根际土壤酶活性的差异
Table 2 Differences of enzyme activities in rhizosphere soil of different grasses (nmol·g-1·h-1)
| 处理Treatment | βG | CBH | βX | NAG | ALP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 32.41±3.14c | 5.00±0.86c | 6.19±0.47b | 4.53±0.52c | 20.95±0.53c |
| 百喜草P. notatum | 40.29±5.87bc | 5.53±0.32c | 6.38±1.29b | 6.35±0.65b | 24.16±1.70bc |
| 黑麦草L. perenne | 48.42±7.17ab | 5.55±1.80c | 7.23±1.59b | 4.74±0.37c | 26.26±0.66b |
| 高羊茅F. arundinacea | 49.44±6.92ab | 8.88±1.72b | 10.48±1.58a | 6.36±0.84b | 33.21±3.56a |
| 苏丹草S. sudanense | 57.97±5.12a | 13.00±1.82a | 11.58±0.93a | 11.68±1.13a | 31.90±1.68a |
| 项目Item | pH | SOC | DOC | NO3--N | NH4+-N | AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| βG | -0.451 | 0.529* | 0.445 | -0.536* | -0.048 | 0.038 |
| CBH | 0.001 | 0.320 | 0.256 | -0.470 | -0.208 | -0.199 |
| βX | 0.116 | 0.314 | 0.417 | -0.385 | -0.058 | 0.024 |
| NAG | 0.021 | 0.546* | 0.001 | -0.634* | -0.153 | -0.512 |
| ALP | 0.014 | 0.519* | 0.594* | -0.511 | 0.123 | 0.091 |
表3 不同禾草根际土壤酶活性与土壤理化性质的相关性
Table 3 Correlation between enzyme activity and physical and chemical properties in rhizosphere soil of different grasses
| 项目Item | pH | SOC | DOC | NO3--N | NH4+-N | AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| βG | -0.451 | 0.529* | 0.445 | -0.536* | -0.048 | 0.038 |
| CBH | 0.001 | 0.320 | 0.256 | -0.470 | -0.208 | -0.199 |
| βX | 0.116 | 0.314 | 0.417 | -0.385 | -0.058 | 0.024 |
| NAG | 0.021 | 0.546* | 0.001 | -0.634* | -0.153 | -0.512 |
| ALP | 0.014 | 0.519* | 0.594* | -0.511 | 0.123 | 0.091 |
处理 Treatment | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | 覆盖度 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5250±140a | 7.12±0.05b | 0.98±0.000a |
| 百喜草P. notatum | 5353±112a | 7.11±0.05b | 0.98±0.000a |
| 黑麦草L. perenne | 5470±143a | 7.21±0.02a | 0.98±0.000a |
| 高羊茅F. arundinacea | 4918±171b | 7.04±0.04b | 0.98±0.000a |
| 苏丹草S. sudanense | 5205±34a | 6.90±0.02c | 0.98±0.000a |
表4 不同禾草对根际土壤细菌Alpha多样性指数的影响
Table 4 Effects of different grasses on the Alpha diversity index of rhizosphere soil bacteria
处理 Treatment | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | 覆盖度 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5250±140a | 7.12±0.05b | 0.98±0.000a |
| 百喜草P. notatum | 5353±112a | 7.11±0.05b | 0.98±0.000a |
| 黑麦草L. perenne | 5470±143a | 7.21±0.02a | 0.98±0.000a |
| 高羊茅F. arundinacea | 4918±171b | 7.04±0.04b | 0.98±0.000a |
| 苏丹草S. sudanense | 5205±34a | 6.90±0.02c | 0.98±0.000a |
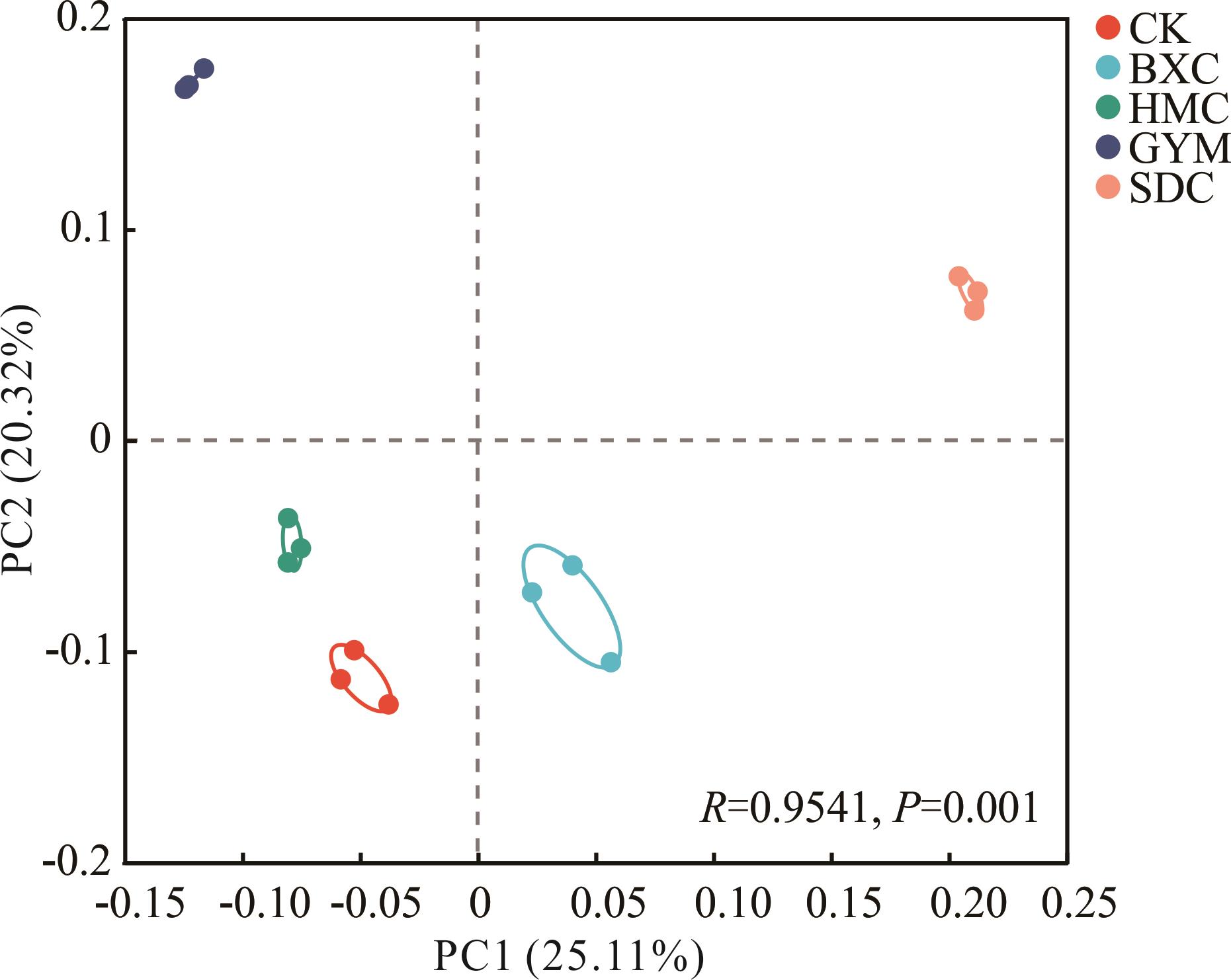
图1 土壤细菌群落结构主坐标分析CK: 空白对照Blank control; BXC: 百喜草P. notatum; HMC: 黑麦草L. perenne; GYM: 高羊茅F. arundinacea; SDC:苏丹草S. sudanense;下同The same below.
Fig.1 Principal co-ordinates analysis of soil bacterial community structure
| 项目Item | pH | SOC | DOC | NO3--N | NH4+-N | AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 0.456 | -0.378 | -0.275 | 0.238 | -0.025 | -0.231 |
| Shannon指数 Shannon index | 0.016 | -0.593* | 0.071 | 0.533* | 0.298 | 0.457 |
表5 细菌Alpha多样性指数与土壤理化性质的Pearson相关性分析
Table 5 Correlation analysis between bacterial Alpha diversity index and soil physical and chemical properties
| 项目Item | pH | SOC | DOC | NO3--N | NH4+-N | AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 0.456 | -0.378 | -0.275 | 0.238 | -0.025 | -0.231 |
| Shannon指数 Shannon index | 0.016 | -0.593* | 0.071 | 0.533* | 0.298 | 0.457 |
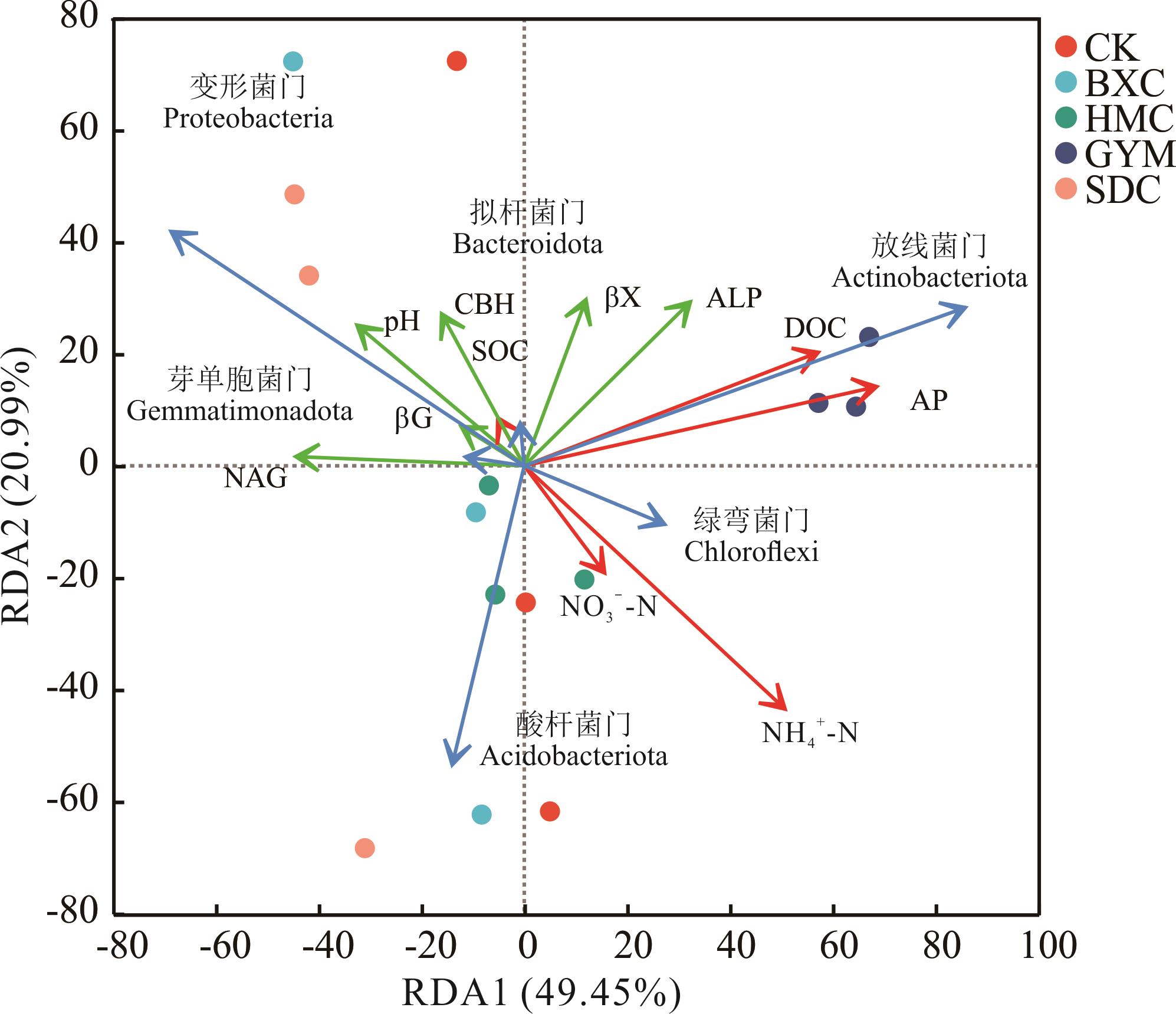
图3 细菌群落组成与土壤理化性质、酶活性的冗余分析图中蓝色、绿色和红色箭头分别表示门水平细菌、土壤酶活性以及土壤理化性质The blue arrow,green arrow and red arrow in the figure represent the phylum level bacteria,soil enzyme activity and soil physical and chemical properties, respectively.
Fig.3 Redundancy analysis of bacterial community composition, soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activity
| 1 | Aqeel M, Ran J Z, Hu W G, et al. Plant-soil-microbe interactions in maintaining ecosystem stability and coordinated turnover under changing environmental conditions. Chemosphere, 2023, 318: 137924. |
| 2 | Mueller C W, Baumert V, Carminati A, et al. From rhizosphere to detritusphere-Soil structure formation driven by plant roots and the interactions with soil biota. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2024, 193: 109396. |
| 3 | Borowik A, Wyszkowska J, Kucharski J. Impact of various grass species on soil bacteriobiome. Diversity, 2020, 12(6): 212. |
| 4 | Stefanowicz A M, Kapusta P, Stanek M, et al. Herbaceous plant species and their combinations positively affect soil microorganisms and processes and modify soil physicochemical properties in a mesocosm experiment. Forest Ecology and Management, 2023, 532: 120826. |
| 5 | Xiao L, Ma Y Y, Yuwen P Y, et al. Mixed grass species differ in rhizosphere microbial community structure and function response to drought compared to monocultures. Rhizosphere, 2022, 24: 100615. |
| 6 | Berendsen R L, Pieterse C M J, Bakker P A H M. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends in Plant Science, 2012, 17(8): 478-486. |
| 7 | Zhou J, Liu C Y, Shi L L, et al. Rhizosphere influence on microbial functions: consequence for temperature sensitivity of soil organic matter decomposition at early stage of plant growth. Plant and Soil, 2024, 494(1): 95-109. |
| 8 | Mencel J, Mocek-Płóciniak A, Kryszak A. Soil microbial community and enzymatic activity of grasslands under different use practices: A review. Agronomy, 2022, 12(5): 1136. |
| 9 | Bardgett R D, Bullock J M, Lavorel S, et al. Combatting global grassland degradation. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2021, 2(10): 720-735. |
| 10 | Chang J F, Ciais P, Gasser T, et al. Climate warming from managed grasslands cancels the cooling effect of carbon sinks in sparsely grazed and natural grasslands. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 118. |
| 11 | Bardgett R D. Linking aboveground-belowground ecology: a short historical perspective. Aboveground-Belowground Community Ecology, 2018, 234: 1-17. |
| 12 | Ma Y, Zhang D G. Regulation mechanisms of rhizosphere nutrient cycling processes in grassland: A review. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(11): 172-182. |
| 马源, 张德罡. 草地根际过程对养分循环调控机制研究进展. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 172-182. | |
| 13 | Wang Z, Jin K, Ding Y, et al. The mechanism of plants-soil microbial feedback in grassland succession. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(1): 95-103. |
| 王珍, 金轲, 丁勇, 等. 植物-土壤微生物反馈在草地演替过程中的作用机制. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(1): 95-103. | |
| 14 | Rumpel C, Crème A, Ngo P T, et al. The impact of grassland management on biogeochemical cycles involving carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2015, 15(2): 353-371. |
| 15 | Gong X W, Feng Y, Dang K, et al. Linkages of microbial community structure and root exudates: Evidence from microbial nitrogen limitation in soils of crop families. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 881: 163536. |
| 16 | Qi J J, Fu D Q, Wang X Z, et al. The effect of alfalfa cultivation on improving physicochemical properties soil microorganisms community structure of grey desert soil. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 13747. |
| 17 | Haney R L, Kiniry J R, Johnson M V V. Soil microbial activity under different grass species: Underground impacts of biofuel cropping. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2010, 139(4): 754-758. |
| 18 | Jian T K, Xia Y, He R P, et al. The influence of planting Carex praeclara and Leymus secalinus on soil properties and microbial community in a Zoige desertified alpine grassland. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2022, 34: e02002. |
| 19 | Tomazelli D, Peron R A D, Mendes S D C, et al. Plant diversity and root traits shape rhizosphere microbial communities in natural grasslands and cultivated pastures. Rhizosphere, 2024, 29: 100864. |
| 20 | Tomaskin J, Tomaskinova J. Evaluation of assortment of ornamental grasses and their environmental importance in the urban landscape. Journal of Environmental Protection and Ecology, 2020, 21(5): 1673-1682. |
| 21 | Sun D Y, Li J Z, Gong Y B. Effects of planting density of Poaceae species on slope community characteristics and artificial soil nutrients in high-altitude areas. Sustainability, 2023, 15(10): 8321. |
| 22 | Zhao Y F, Mao W, Pang L X, et al. Influence of Phragmites communis and Zizania aquatica on rhizosphere soil enzyme activity and bacterial community structure in a surface flow constructed wetland treating secondary domestic effluent in China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(21): 26141-26152. |
| 23 | Wang P, Wang Y, Wu Q S. Effects of soil tillage and planting grass on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal propagules and soil properties in citrus orchards in southeast China. Soil & Tillage Research, 2016, 155: 54-61. |
| 24 | Bao S D. Soil agrochemical analysis (the third edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 25 | Saiya-Cork K R, Sinsabaugh R L, Zak D R. The effects of long term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2002, 34(9): 1309-1315. |
| 26 | Magoč T, Salzberg S L. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(21): 2957-2963. |
| 27 | Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y, et al. Fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics, 2018, 34(17): i884-i890. |
| 28 | Edgar R C. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(10): 996-998. |
| 29 | Lan Y M, Wang Q, Cole J R, et al. Using the RDP classifier to predict taxonomic novelty and reduce the search space for finding novel organisms. PLoS One, 2012, 7(3): e32491. |
| 30 | Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, et al. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 41(D1): D590-D596. |
| 31 | Song Q, Song X S, Deng X, et al. Effects of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria microbial inoculants on the growth, rhizosphere soil properties, and bacterial community of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica annual seedlings. Scandinavian Journal of Forest Research, 2020, 36(4): 249-262. |
| 32 | Caporaso J G, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods, 2010, 7(5): 335-336. |
| 33 | Smith D J, Duston S, Barney J N, et al. Dissolved organic carbon characteristics are associated with changes in soil microbiome under different plant species. Applied Soil Ecology, 2024, 196: 105313. |
| 34 | Khalid M, Soleman N, Jones D L. Grassland plants affect dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen dynamics in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2007, 39(1): 378-381. |
| 35 | Chen X L, Chen H Y H, Chang S X. Meta-analysis shows that plant mixtures increase soil phosphorus availability and plant productivity in diverse ecosystems. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2022, 6(8): 1112-1121. |
| 36 | Luo L, Meng H, Gu J D. Microbial extracellular enzymes in biogeochemical cycling of ecosystems. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 197: 539-549. |
| 37 | Delgado-Baquerizo M, Maestre F T, Reich P B, et al. Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(1): 10541. |
| 38 | Daunoras J, Kačergius A, Gudiukaitė R. Role of soil microbiota enzymes in soil health and activity changes depending on climate change and the type of soil ecosystem. Biology, 2024, 13(2): 85. |
| 39 | Sinsabaugh R L, Lauber C L, Weintraub M N, et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecology Letters, 2008, 11(11): 1252-1264. |
| 40 | Yang F, Tian J, Fang H J, et al. Spatial heterogeneity of microbial community and enzyme activities in a broad-leaved Korean pine mixed forest. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2018, 88: 65-72. |
| 41 | Zheng Z M. Changes in soil physicochemical and biological properties of grassland in different years of enclosure on the Loess Plateau. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2019. |
| 郑周敏. 黄土高原不同封育年限草地土壤理化和生物学性质变化. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2019. | |
| 42 | Zhang C, Liu G B, Xue S, et al. Changes in rhizospheric microbial community structure and function during the natural recovery of abandoned cropland on the Loess Plateau, China. Ecological Engineering, 2015, 75: 161-171. |
| 43 | Ladygina N, Hedlund K. Plant species influence microbial diversity and carbon allocation in the rhizosphere. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2010, 42(2): 162-168. |
| 44 | Saleh D, Jarry J, Rani M, et al. Diversity, distribution and multi-functional attributes of bacterial communities associated with the rhizosphere and endosphere of timothy (Phleum pratense L.). Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2019, 127(3): 794-811. |
| 45 | Zhang H R, Fu G. Responses of plant, soil bacterial and fungal communities to grazing vary with pasture seasons and grassland types, northern Tibet. Land Degradation & Development, 2021, 32(4): 1821-1832. |
| 46 | Li Q M, Li S J, Wang X L, et al. Influences of changing carbon inputs on soil microbial carbon metabolism in natural secondary forest in Yimeng mountainous area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(10): 4110-4119. |
| 李秋梅, 黎胜杰, 王欣丽, 等. 改变碳输入对沂蒙山区典型次生林土壤微生物碳源代谢功能的影响. 生态学报, 2021, 41(10): 4110-4119. | |
| 47 | Das R, Bharadwaj P, Thakur D. Insights into the functional role of Actinomycetia in promoting plant growth and biocontrol in tea (Camellia sinensis) plants. Archives of Microbiology, 2024, 206(2): 65. |
| 48 | Chen H S, Liu S P, Liang G Q, et al. Effects of three cropping patterns on bacterial community structure and diversity in rhizosphere of broccoli. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 35(6): 1457-1465. |
| 陈海生, 刘守平, 梁国钱, 等. 3种西兰花种植方式对根际土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响研究. 核农学报, 2021, 35(6): 1457-1465. | |
| 49 | Li M, Zhang K R, Yan Z Q, et al. Soil water content shapes microbial community along gradients of wetland degradation on the Tibetan Plateau. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13: 824267. |
| 50 | Ma X W, Ren B H, Yu J X, et al. Changes in grassland soil types lead to different characteristics of bacterial and fungal communities in Northwest Liaoning, China. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2023, 14: 1205574. |
| 51 | Shu X Y, Hu Y F, Liu W J, et al. Linking between soil properties, bacterial communities, enzyme activities, and soil organic carbon mineralization under ecological restoration in an alpine degraded grassland. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2023, 14: 1131836. |
| 52 | Philippot L, Chenu C, Kappler A, et al. The interplay between microbial communities and soil properties. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2024, 22(4): 226-239. |
| 53 | Wang L X, Pang X Y, Li N, et al. Effects of vegetation type, fine and coarse roots on soil microbial communities and enzyme activities in eastern Tibetan Plateau. Catena, 2020, 194: 104694. |
| 54 | Gong B, He Y, Luo Z B, et al. Response of rhizosphere soil physicochemical properties and microbial community structure to continuous cultivation of tobacco. Annals of Microbiology, 2024, 74(1): 4. |
| 55 | Li L S, Wang Z Y, Bai H H, et al. Structure and diversity of bacterial communities in rhizosphere soil of four plant species in Mu Us Sandy Land. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2024, 38(2): 142-149. |
| 李林山, 王梓瑜, 白慧慧, 等. 毛乌素沙地4种不同植物根际土壤细菌群落结构和多样性特征. 干旱区资源与环境, 2024, 38(2): 142-149. |
| [1] | 马红钰, 周小国, 王宝, 宋渝川, 艾克热木·阿不拉提江null, 蒋邵丽, 闵九洲, 赵红梅, 程军回. 准噶尔荒漠梭梭和柽柳根际土壤微生物功能基因丰度变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 109-122. |
| [2] | 王颖, 李明源, 麦日艳古·亚生null, 王继莲. 新疆托木尔峰不同植物根际土壤真菌群落结构比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 83-94. |
| [3] | 欧翔, 连海, 陈荣强, 邱静芸, 吴丽娟, 操贤洪, 张强, 雷小文. 不同施肥处理种植王草后对稀土尾矿土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 94-108. |
| [4] | 姚佳妮, 刘爽, 张钧杰, 胡明珠, 代金霞. 宁夏荒漠草原典型灌丛根际土壤酶活性及微生物代谢多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 1-14. |
| [5] | 李思媛, 孙宗玖, 于冰洁, 周晨烨, 周磊, 郑丽, 刘慧霞, 冶华薇. 封育对伊犁绢蒿荒漠草地土壤碳氮磷、酶活性及其化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 25-40. |
| [6] | 何升然, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 汪雪, 王静. 紫花苜蓿/甜高粱间作对根际土壤特性及微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 92-105. |
| [7] | 黄琳曦, 陈倩, 张先言, 闫顺, 杨云, 辛培尧, 汪琼. 两种乔木凋落叶浸提液处理对地毯草土壤酶活性及其化学计量比的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 35-46. |
| [8] | 马源, 王晓丽, 马玉寿, 张德罡. 高寒草甸退化程度对优势物种根际土壤真菌群落和生态网络的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 125-137. |
| [9] | 张东, 侯晨, 马文明, 王长庭, 邓增卓玛, 张婷. 高寒草地不同灌丛化梯度下土壤酶活性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 79-92. |
| [10] | 马嵩科, 霍克, 张冬霞, 张静, 张俊豪, 柴雪茹, 王贺正. 玉米秸秆还田配施氮肥对豫西旱地小麦土壤酶活性和氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 120-133. |
| [11] | 王志婷, 刘廷玺, 童新, 段利民, 李东方, 刘小勇. 半干旱草甸草地不同处理下植被特征与土壤酶活性的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 41-55. |
| [12] | 许代香, 杨建峰, 苏杭, 翟建荣, 綦才, 赵龙刚, 郭彦军. 间作模式下作物根际土壤代谢物对微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 65-80. |
| [13] | 李春杰, 郎鸣晓, 陈振江, 陈泰祥, 刘静, 金媛媛, 魏学凯. Epichloë内生真菌对禾草种子萌发影响研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 192-206. |
| [14] | 张辉辉, 师尚礼, 武蓓, 李自立, 李小龙. 苜蓿与3种多年生禾草混播效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 159-170. |
| [15] | 马文明, 刘超文, 周青平, 邓增卓玛, 唐思洪, 迪力亚尔·莫合塔尔null, 侯晨. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体生态化学计量学及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 57-68. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
