

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (4): 42-53.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025269
李梦棋1( ), 董全民1,2, 孙彩彩1, 吕卫东1, 许蔚1, 刘玉祯1,2, 刘文亭1,2, 杨晓霞1,2(
), 董全民1,2, 孙彩彩1, 吕卫东1, 许蔚1, 刘玉祯1,2, 刘文亭1,2, 杨晓霞1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-07-01
修回日期:2025-08-28
出版日期:2026-04-20
发布日期:2026-02-07
通讯作者:
杨晓霞
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: xxyang@qhu.edu.cn基金资助:
Meng-qi LI1( ), Quan-min DONG1,2, Cai-cai SUN1, Wei-dong LYU1, Wei XU1, Yu-zhen LIU1,2, Wen-ting LIU1,2, Xiao-xia YANG1,2(
), Quan-min DONG1,2, Cai-cai SUN1, Wei-dong LYU1, Wei XU1, Yu-zhen LIU1,2, Wen-ting LIU1,2, Xiao-xia YANG1,2( )
)
Received:2025-07-01
Revised:2025-08-28
Online:2026-04-20
Published:2026-02-07
Contact:
Xiao-xia YANG
摘要:
牦牛和藏羊是青藏高原的主要放牧家畜,其粪便分解会对高寒草地生态系统产生直接影响,而目前关于两种粪便对土壤养分影响的作用机制和差异尚不清楚。本研究采用尼龙网袋法监测相同干重的新鲜牦牛和藏羊粪便的养分释放动态,并使用同心圆分层取样法研究粪便分解释放的养分在土壤垂直方向(粪下)和水平方向(粪周)的迁移特征和富集特征。结果表明:1)新鲜的牦牛和藏羊粪便中全碳、全氮、全磷含量分别为333.39和311.41 g·kg-1,22.25和15.51 g·kg-1,6.95和7.47 g·kg-1。2)经过45 d的自然分解后,牦牛和藏羊粪便的干物质、全碳、全氮、全磷含量分别损失了28.58%和12.82%,23.68%和17.85%,9.35%和15.54%,22.45%和30.21%。3)分解45 d后,牦牛和藏羊粪便处理下土壤全碳含量达到峰值,藏羊粪便处理粪周土壤全磷含量略高于牦牛,而牦牛粪下与粪周的全氮含量高于藏羊粪便处理。4)分解45 d时,藏羊粪下全碳富集率显著高于牦牛粪便,但两种粪便粪下和粪周土壤全氮富集率无显著差异。综上,新鲜牦牛粪便中全碳、全氮含量高于藏羊粪便,且牦牛粪便分解更快、氮释放更强,藏羊粪便则更利于土壤碳的持续富集,两者均能促进磷的积累,且养分在垂直方向的迁移优于水平方向。
李梦棋, 董全民, 孙彩彩, 吕卫东, 许蔚, 刘玉祯, 刘文亭, 杨晓霞. 环青海湖地区牦牛和藏羊粪便夏季分解对土壤养分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(4): 42-53.
Meng-qi LI, Quan-min DONG, Cai-cai SUN, Wei-dong LYU, Wei XU, Yu-zhen LIU, Wen-ting LIU, Xiao-xia YANG. Effects of summer decomposition of yak and Xizang sheep dung on soil nutrients in the Peri-Qinghai Lake Region[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(4): 42-53.
项目 Item | 全碳含量Total carbon content (g·kg-1) | 全氮含量Total nitrogen content (g·kg-1) | 全磷含量Total phosphorus content (g·kg-1) | 干基含水率Dry basis moisture content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 牦牛粪Yak dung | 333.39±2.74A | 22.25±0.63A | 6.95±0.10B | 387.71 |
| 藏羊粪Xizang sheep dung | 311.41±1.93B | 15.51±0.53B | 7.47±0.15A | 173.75 |
| 0~10 cm土壤深度Soil depth | 39.55±0.82a | 2.11±0.04a | 0.60±0.01a | |
| 10~20 cm土壤深度Soil depth | 35.31±0.82b | 1.53±0.05b | 0.54±0.01b | |
| 20~30 cm土壤深度Soil depth | 33.93±0.51b | 0.92±0.07c | 0.44±0.01c |
表1 牦牛和藏羊粪便以及土壤养分含量的初始值
Table 1 Initial values of nutrient content in yak and Xizang sheep dung and soil
项目 Item | 全碳含量Total carbon content (g·kg-1) | 全氮含量Total nitrogen content (g·kg-1) | 全磷含量Total phosphorus content (g·kg-1) | 干基含水率Dry basis moisture content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 牦牛粪Yak dung | 333.39±2.74A | 22.25±0.63A | 6.95±0.10B | 387.71 |
| 藏羊粪Xizang sheep dung | 311.41±1.93B | 15.51±0.53B | 7.47±0.15A | 173.75 |
| 0~10 cm土壤深度Soil depth | 39.55±0.82a | 2.11±0.04a | 0.60±0.01a | |
| 10~20 cm土壤深度Soil depth | 35.31±0.82b | 1.53±0.05b | 0.54±0.01b | |
| 20~30 cm土壤深度Soil depth | 33.93±0.51b | 0.92±0.07c | 0.44±0.01c |
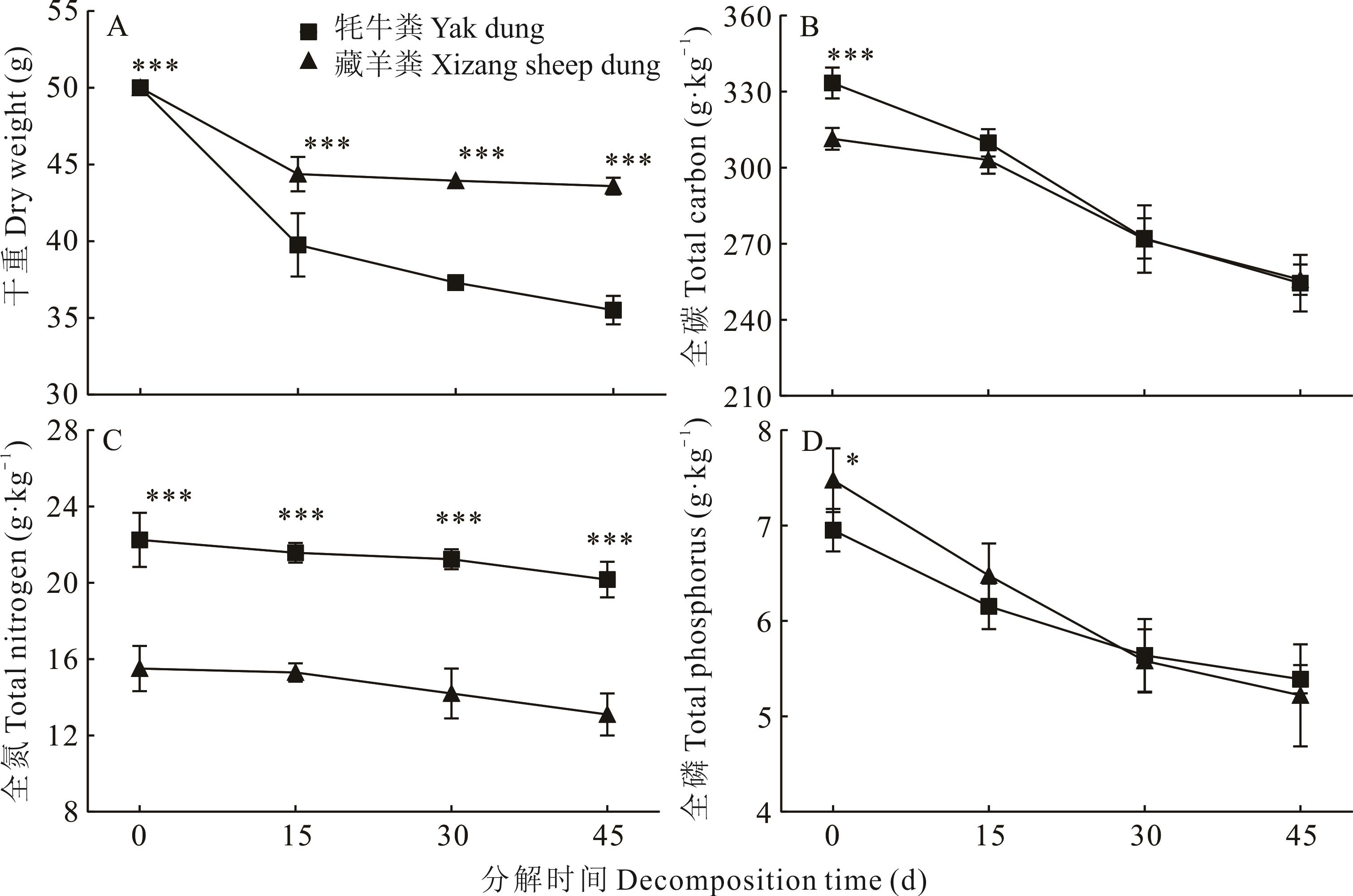
图2 不同分解时间下牦牛和藏羊粪便的养分变化*: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001; 下同The same below.
Fig.2 Nutrient variations in two fecal types under different decomposition periods

图3 不同处理土壤养分在不同分解时间不同土层的差异性特征YD: 牦牛粪便Yak dung; SD: 藏羊粪便Xizang sheep dung; CK: 无粪便处理No dung application; 不同小写字母表示同一处理下不同土层之间差异显著(P<0.05) Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different soil layers under the same treatment (at the 0.05 level); 图A、B、C和图D、E、F分别表示垂直方向(粪下)和水平方向(粪周)的养分变化Panels A, B, C and D, E, F represent nutrient changes in the vertical direction (beneath the dung) and horizontal direction (dung periphery), respectively; 下同The same below.
Fig.3 Response of soil nutrients to treatment, decomposition time, and soil depth
| [1] | Zhang Y J, Zhu J T, Shen R N, et al. Research progress on the effects of grazing on grassland ecosystem. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2020, 44(5): 553-564. |
| 张扬建, 朱军涛, 沈若楠, 等. 放牧对草地生态系统影响的研究进展. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(5): 553-564. | |
| [2] | Dong S K, Shang Z H, Gao J X, et al. Enhancing sustainability of grassland ecosystems through ecological restoration and grazing management in an era of climate change on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment, 2019, 287(C): 106684. |
| [3] | Willott J S, Miller J A, Incoll D L, et al. The contribution of rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus L.) to soil fertility in semi-arid spain. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2000, 31(5): 379-384. |
| [4] | Gao Z Y, Wang H Y, Zhang Y F. Soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometric characteristics and driving factors: a review. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2025, 42(3): 645-656. |
| 高子滢, 王海燕, 张亦凡. 土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征及其驱动因素. 浙江农林大学学报, 2025, 42(3): 645-656. | |
| [5] | Jiang S C, Zhou D W. The impact of cattle dung deposition on grasslands in the Songnen Grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2006, 15(4): 30-35. |
| 姜世成, 周道玮. 牛粪堆积对草地影响的研究. 草业学报, 2006, 15(4): 30-35. | |
| [6] | Wang C H, Xing X R, Han X G. Advances in study of factors affecting soil N mineralization in grassland ecosystems. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2004, 15(11): 2184-2188. |
| 王常慧, 邢雪荣, 韩兴国. 草地生态系统中土壤氮素矿化影响因素的研究进展. 应用生态学报, 2004, 15(11): 2184-2188. | |
| [7] | Liu X M, Chen H Y, Zheng R, et al. Decomposition of sheep and cattle dung in a steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2011, 17(6): 791-796. |
| 刘新民, 陈海燕, 峥嵘, 等. 内蒙古典型草原羊粪和牛粪的分解特征. 应用与环境生物学报, 2011, 17(6): 791-796. | |
| [8] | Liu X M. Assemblage characteristics of dung beetles in livestock dung in Inner Mongolian typical steppe. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2011, 30(1): 24-29. |
| 刘新民. 内蒙古典型草原家畜粪中的粪金龟子群落特征. 生态学杂志, 2011, 30(1): 24-29. | |
| [9] | Zhang Z Y, Zhang S T. Effects of yak dung deposition on soil enzyme activities in an alpine meadow in the Tibetan Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(5): 803-811. |
| 张志阳, 张世挺. 牦牛粪沉积对青藏高原高寒草甸土壤酶活性的影响. 草业科学, 2021, 38(5): 803-811. | |
| [10] | Zhao Y, Li S Y, Dong B W, et al. Effects of fresh sheep manure addition on vegetation and soil characteristics of moderately saline-alkali degraded Leymus chinensis grassland. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(9): 57-65. |
| 赵宇, 李思宇, 董博文, 等. 鲜羊粪添加对中度盐碱退化羊草草地植被及土壤特征的影响. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(9): 57-65. | |
| [11] | Sun P F. Research progress on the impacts of yak dung deposition from grazing on grassland-based animal husbandry. China Animal Industry, 2021, 7(2): 57. |
| 孙鹏飞. 放牧牦牛粪对草地畜牧业影响研究进展. 中国畜牧业, 2021, 7(2): 57. | |
| [12] | Wang J L, Cao W X, Li W. Response of foraging preference of Tibetan sheep to forage plants in different topographies on Qilian Mountains. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(16): 7213-7225. |
| 王金兰, 曹文侠, 李文. 祁连山不同地形饲用植物对藏羊偏食性的影响. 生态学报, 2024, 44(16): 7213-7225. | |
| [13] | Illius A W, Gordon I J. The allometry of food intake in grazing ruminants. Journal of Animal Ecology, 1987, 56(3): 989-999. |
| [14] | Du Z Y, Cai Y J, Wang X D, et al. Temporal variation of yak and Tibetan sheep dung nutrients from an alpine steppe in northern Tibet, China. Mountain Research, 2014, 32(4): 423-430. |
| 杜子银, 蔡延江, 王小丹, 等. 牦牛和藏绵羊粪便降解过程中的养分动态变化. 山地学报, 2014, 32(4): 423-430. | |
| [15] | Cao J M, Guo Y Y, Li N N, et al. Effects of dung beetles on characteristics of nutrient changes in cattle and horse feces and soil in Seirphidium semidesert. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(2): 75-81, 114. |
| 曹佳敏, 郭亚亚, 李娜娜, 等. 绢蒿荒漠粪甲虫对牛粪、马粪分解及粪下土壤养分的影响. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(2): 75-81, 114. | |
| [16] | Huang C, Yan P, Liang C N. Current status and development directions of the yak breeding industry in China. Chinese Livestock and Poultry Breeding, 2023, 19(7): 121-127. |
| 黄纯, 阎萍, 梁春年. 中国牦牛种业现状与发展方向. 中国畜禽种业, 2023, 19(7): 121-127. | |
| [17] | Lyu W D, Dong Q M, Sun C C, et al. Effects of yak and Tibetan sheep grazing on the nitrogen pool of plant communities of alpine grasslands in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(5): 1420-1428. |
| 吕卫东, 董全民, 孙彩彩, 等. 牦牛和藏羊放牧对青藏高原高寒草地植物群落氮库的影响. 草地学报, 2024, 32(5): 1420-1428. | |
| [18] | Sun C C, An H T, Dong Q M, et al. Responses of soil microbial activity to grazing intensity in alpine grasslands of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2024, 44(9): 2930-2937. |
| 孙彩彩, 安海涛, 董全民, 等. 青藏高原高寒草地土壤微生物活性对放牧强度的响应. 生态学杂志, 2024, 44(9): 2930-2937. | |
| [19] | Du Z Y, Wang X D, Hong J T, et al. Effects of seasonal freeze-thaw cycles and livestock excreta returning on soil physical properties, and nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in alpine grassland. Mountain Research, 2022, 40(1): 29-42. |
| 杜子银, 王小丹, 洪江涛, 等. 冻融及牲畜排泄物作用下的高寒草地土壤物理特性和氮磷变化. 山地学报, 2022, 40(1): 29-42. | |
| [20] | Shen Y L. Study on optical measurement method of leaf moisture content of lettuce. Zhengzhou: Hebei Agricultural University, 2019. |
| 申艳路. 生菜叶片含水率光学测量方法研究. 郑州: 河北农业大学, 2019. | |
| [21] | Ren X, Chu G X, Song R Q, et al. The characteristics of “fertile island” on Haloxylon ammodendron at an oasis-desert ecotone in the south edge of Junggar Basin. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2010, 41(1): 100-104. |
| 任雪, 褚贵新, 宋日权, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘绿洲——荒漠过渡带梭梭“肥岛”效应特征. 土壤通报, 2010, 41(1): 100-104. | |
| [22] | Wan J X, Wang X F, Yang T J, et al. Livestock manure type affects microbial community composition and assembly during composting. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 621126. |
| [23] | Wu X W, Li G Y, Sun S C. Effect of rainfall regimes on the decomposition rate of yak dung in an alpine meadow of northwest Sichuan Province, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(23): 28-36. |
| 吴新卫, 李国勇, 孙书存. 降水量对川西北高寒草甸牦牛粪分解速率的影响. 生态学报, 2011, 31(23): 28-36. | |
| [24] | Williams P H, Haynes R J. Effect of sheep, deer and cattle dung on herbage production and soil nutrient content. Grass and Forage Science, 1995, 50(3): 263-271. |
| [25] | Wachendorf C, Lampe C, Taube F, et al. Nitrous oxide emissions and dynamics of soil nitrogen under 15^N‐labeled cow urine and dung patches on a sandy grassland soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2008, 171(2): 171-180. |
| [26] | Ran X L, Deng Y, Sai N G, et al. Hotspots and future trends of phosphorus recycling from livestock manure: A bibliometric review. The Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 892: 164346. |
| [27] | Kong Y Y, Yu Y W, Hou F J. Interspecific associations in plant communities under yak dung depositions in an alpine meadow. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(3): 44-52. |
| 孔杨云, 于应文, 侯扶江. 牦牛粪沉积下高寒草甸植物群落种间关联研究. 草业学报, 2017, 26(3): 44-52. | |
| [28] | Nargiza G L, Xiao Y X, Song B Y, et al. Effects of “fertile island” effects of desert plants on spatial distribution of soil nutrients. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(6): 868-880. |
| 阿力甫那尔格孜, 肖钰鑫, 宋泊沂, 等. 荒漠植物“肥岛”效应对土壤养分空间分布的影响. 植物研究, 2023, 43(6): 868-880. | |
| [29] | MacDiarmid B N, Watkin B R. The cattle dung patch. 2. Effect of a dung patch on chemical status of soil, and ammonia nitrogen losses from patch. Journal of the British Grassland Society, 1972, 27(1): 43-48. |
| [30] | Sager M. Trace and nutrient elements in manure, dung and compost samples in Austria. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2006, 39(6): 1383-1390. |
| [31] | Aarons R S, O'Connor R C, Gourley P J C. Dung decomposition in temperate dairy pastures. I. Changes in soil chemical properties. Soil Research, 2004, 42(1): 107-114. |
| [32] | Finzi A, Mattachini G, Lovarelli D, et al. Technical, economic, and environmental assessment of a collective integrated treatment system for energy recovery and nutrient removal from livestock manure. Sustainability, 2020, 12(7): 2756. |
| [1] | 宋一欣, 李明源, 麦日艳古·亚生, 王继莲. 新疆高寒草地3种植物根际土壤真菌群落结构及功能多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 167-178. |
| [2] | 刘冬娅, 杨燕, 刘静, 王博, 李志刚. 短期羊粪归还对荒漠草地土壤质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 28-39. |
| [3] | 冯斌, 杨晓霞, 刘玉祯, 刘文亭, 吕卫东, 张艳芬, 董全民. 不同放牧方式对高寒草地物种多样性、生态位与种间联结性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 1-14. |
| [4] | 张琨, 乔建霞, 李金升, 王育鹏, 刘克思. 不同修复材料对退化高寒草地土壤理化性质及微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 132-148. |
| [5] | 朱炳淑, 樊江文, 张海燕, 黄麟, 田海静, 王林, 王守兴, 杨明新, 郭炎明. 三江源国家公园黄河源园区高寒草地健康评价[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 13-27. |
| [6] | 罗顺华, 刘新宇, 孟宝平, 陈璇黎, 胡仁杰, 于红妍, 王贤颖, 张勃, 秦彧. 祁连山国家公园高寒草地功能群多样性与生产力研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 14-26. |
| [7] | 刘文谨, 蒋福祯, 祁凯斌, 宋明丹, 李正鹏. 不同施肥量和播种量对高寒矿区植被恢复和土壤质量的影响及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 27-39. |
| [8] | 刘淑琪, 崔东, 刘文新, 杨海军, 杨延成, 江智诚, 闫江超, 刘江慧. 短期氮、水添加和刈割对苦豆子型退化草地植物群落特征与土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 41-55. |
| [9] | 马利利, 蒋福祯, 马玉寿, 祁凯斌, 贾顺斌, 李正鹏. 粒径配比、施肥量以及播量耦合对矿区煤矸石基质的改良效果[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 71-84. |
| [10] | 贺聪, 马永才, 字洪标. 不同围封年限对高寒草地植物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(11): 17-30. |
| [11] | 卢小倩, 陈金露, 杨卫君, 郭青云, 王单丽, 赵红梅. 氮肥减量配施腐植酸对北疆滴灌玉米田土壤真菌群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 120-131. |
| [12] | 闫玉龙, 杜学军, 王元月, 刘建立, 丁银贵, 魏源送. 脱硫石膏与粉煤灰配施对盐碱土改良效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 30-40. |
| [13] | 靳生伟, 韩银仓, 孙永刚, 丁维芹, 刘亚倩, 祁增源, 周建强. 冷季不同饲养方式对牦牛生长性能及血液生理生化指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 215-225. |
| [14] | 杨得玉, 黄文植, 冯宇哲, 薛斌, 张晓卫, 崔占鸿. 暖季补饲矿物质盐砖对放牧牦牛生长性能、瘤胃发酵、血液和被毛矿物质含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 105-118. |
| [15] | 徐玲玲, 牛犇, 张宪洲, 何永涛, 石培礼, 宗宁, 武建双, 王向涛. 藏北两个临近不同高寒草地碳通量对气候条件的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 1-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||