
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 30-44.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022298
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yan-shuo CHEN( ), Yan-ping MA, Hong-mei WANG(
), Yan-ping MA, Hong-mei WANG( ), Ya-nan ZHAO, Zhi-li LI, Zhen-jie ZHANG
), Ya-nan ZHAO, Zhi-li LI, Zhen-jie ZHANG
Received:2022-07-25
Revised:2022-09-07
Online:2023-06-20
Published:2023-04-21
Contact:
Hong-mei WANG
Yan-shuo CHEN, Yan-ping MA, Hong-mei WANG, Ya-nan ZHAO, Zhi-li LI, Zhen-jie ZHANG. Carbon source utilization by soil bacteria at different lengths of time after introducing shrubs to the desert steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(6): 30-44.
样地类型 Sample type | 样地概况 Sample situation | 草本生物量 Grass biomass (g·m-2) | 柠条生物量 Shrub biomass (g·m-2) | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 优势植物 Dominant plant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EG | 2003年封育 Enclosed in 2003 | 102.62 | 0 | 107°14′ E 37°53′ N | 蒙古冰草 A. mongolicum,猪毛蒿 A. scoparia,白草 Pennisetum centrasiaticum,虫实 Corispermum hyssopifolium,赖草 Aneurolepidium dasystachys |
| SY6 | 2014年种植 Planted in 2014 | 149.15 | 795.23 | 107°21′ E 37°50′ N | 猪毛蒿 A. scoparia,柠条锦鸡儿 C. korshinskii,白草P. centrasiaticum,蒙古冰草 A. mongolicum |
| SY15 | 2005年种植 Planted in 2005 | 60.03 | 1243.68 | 107°20′ E 37°51′ N | 短花针茅 S. breviflora,牛枝子 L. potaninii,柠条锦鸡儿 C. korshinskii,猪毛蒿 A. scoparia |
| SY25 | 1995年种植 Planted in 1995 | 99.49 | 1199.97 | 107°17′ E 37°51′ N | 牛枝子 L. potaninii,柠条锦鸡儿 C. korshinskii,猪毛蒿A. scoparia |
Table 1 General situation of the study sites
样地类型 Sample type | 样地概况 Sample situation | 草本生物量 Grass biomass (g·m-2) | 柠条生物量 Shrub biomass (g·m-2) | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 优势植物 Dominant plant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EG | 2003年封育 Enclosed in 2003 | 102.62 | 0 | 107°14′ E 37°53′ N | 蒙古冰草 A. mongolicum,猪毛蒿 A. scoparia,白草 Pennisetum centrasiaticum,虫实 Corispermum hyssopifolium,赖草 Aneurolepidium dasystachys |
| SY6 | 2014年种植 Planted in 2014 | 149.15 | 795.23 | 107°21′ E 37°50′ N | 猪毛蒿 A. scoparia,柠条锦鸡儿 C. korshinskii,白草P. centrasiaticum,蒙古冰草 A. mongolicum |
| SY15 | 2005年种植 Planted in 2005 | 60.03 | 1243.68 | 107°20′ E 37°51′ N | 短花针茅 S. breviflora,牛枝子 L. potaninii,柠条锦鸡儿 C. korshinskii,猪毛蒿 A. scoparia |
| SY25 | 1995年种植 Planted in 1995 | 99.49 | 1199.97 | 107°17′ E 37°51′ N | 牛枝子 L. potaninii,柠条锦鸡儿 C. korshinskii,猪毛蒿A. scoparia |
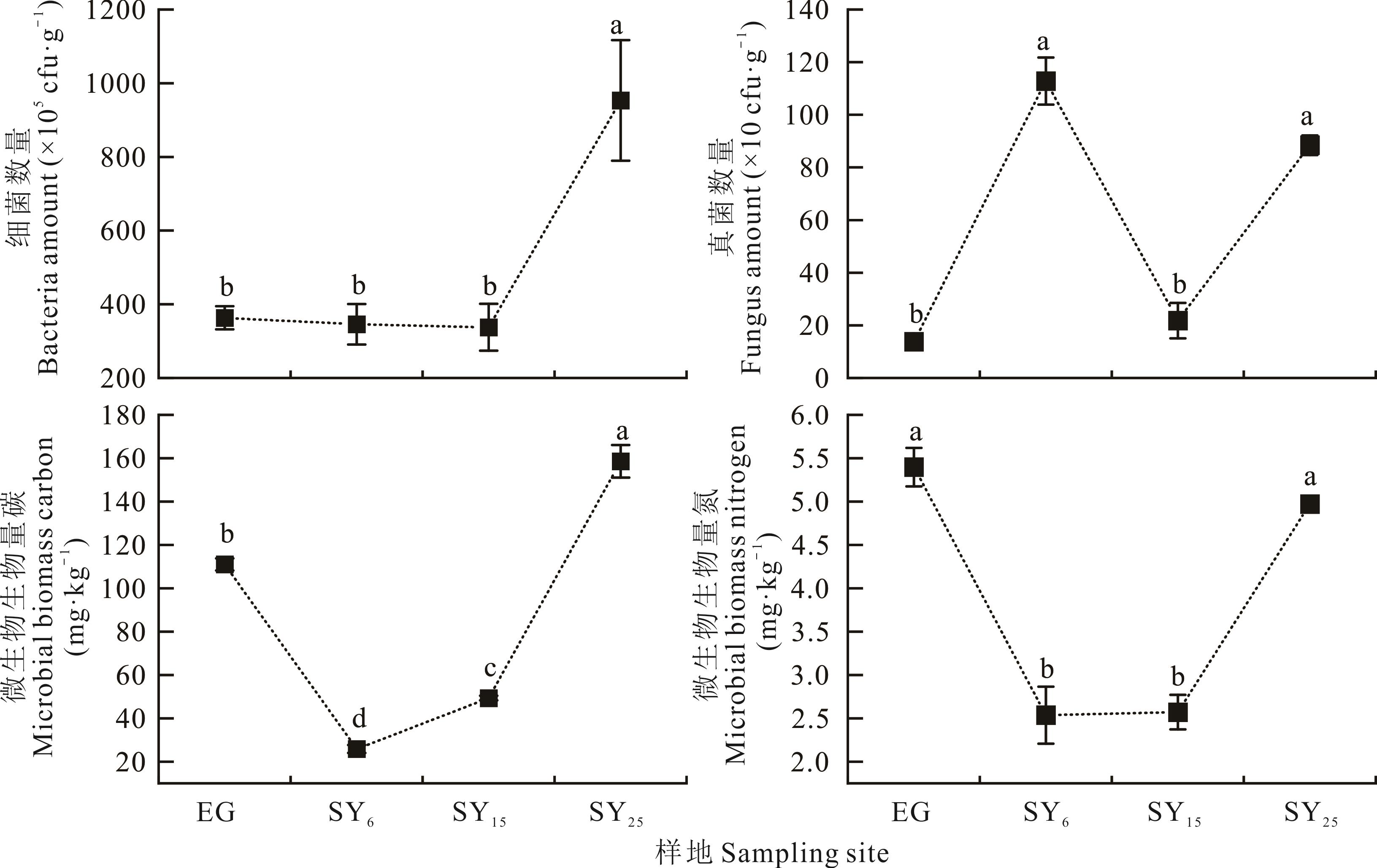
Fig.3 Variation characteristics of soil bacteria amount, fungus amount, microbial biomass carbon and microbial biomass nitrogen during the process of shrub introduction
样地 Plot | Shannon-Wiener丰富度指数 Richness index | Shannon均匀度指数 Evenness index | Simpson优势度指数 Dominance index | McIntosh指数 Index | 平均颜色变化率 AWCD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EG | 2.326±0.038d | 0.726±0.017c | 0.728±0.018c | 2.042±0.014d | 0.254±0.002d |
| SY6 | 2.648±0.004c | 0.804±0.005b | 0.905±0.002ab | 5.124±0.013a | 0.725±0.002a |
| SY15 | 2.745±0.030b | 0.852±0.005a | 0.889±0.007b | 3.672±0.020b | 0.526±0.003b |
| SY25 | 2.913±0.006a | 0.877±0.001a | 0.933±0.000a | 3.371±0.009c | 0.479±0.001c |
Table 2 Diversity index in soil bacteria community during the process of shrub introduction
样地 Plot | Shannon-Wiener丰富度指数 Richness index | Shannon均匀度指数 Evenness index | Simpson优势度指数 Dominance index | McIntosh指数 Index | 平均颜色变化率 AWCD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EG | 2.326±0.038d | 0.726±0.017c | 0.728±0.018c | 2.042±0.014d | 0.254±0.002d |
| SY6 | 2.648±0.004c | 0.804±0.005b | 0.905±0.002ab | 5.124±0.013a | 0.725±0.002a |
| SY15 | 2.745±0.030b | 0.852±0.005a | 0.889±0.007b | 3.672±0.020b | 0.526±0.003b |
| SY25 | 2.913±0.006a | 0.877±0.001a | 0.933±0.000a | 3.371±0.009c | 0.479±0.001c |
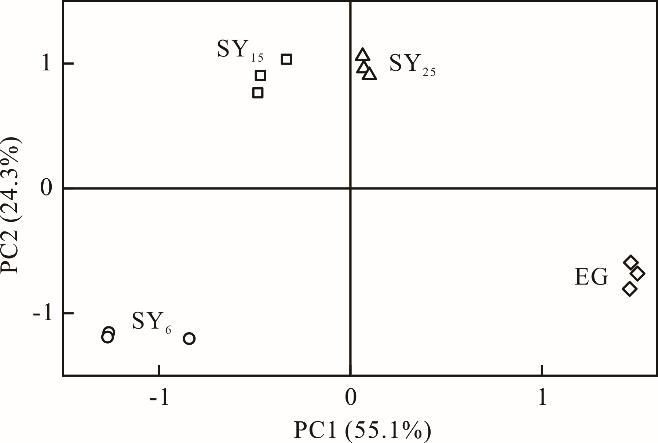
Fig.9 Principal component analysis of average utilization data of carbon substrate groups at 96 h in Biolog ECO by soil microbial community during the process of shrub introduction
主成分 Principal component | 碳源种类 Carbon source guild | 底物 Substrates | 载荷数 Number of load | 主成分 Principal component | 碳源种类 Carbon source guild | 底物 Substrates | 载荷数 Number of load |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 糖类Sugar | β-甲基-D-葡萄糖苷β-methyl-D-glucoside | 0.767 | PC1 | 聚合物类Polymers | 吐温40 Tween 40 | 0.880 |
| I-赤藻糖醇I-erythritol | 0.951 | 其他类Others | 丙酮酸甲酯Pyruvic acid methyl ester | 0.822 | |||
| D-甘露醇D-mannitol | 0.941 | D,L-α-甘油D,L-α-glycerol phosphate | 0.739 | ||||
| N-乙酰基-D-葡萄胺N-acetyl-D-glucosamine | 0.646 | PC2 | 糖类Sugar | D-木糖D-xylose | -0.861 | ||
| D-纤维二糖D-cellobiose | 0.934 | N-乙酰基-D-葡萄胺N-acetyl-D-glucosamine | -0.696 | ||||
| 葡萄糖-1-磷酸盐Glucose-1-phosphate | 0.968 | 羧酸类Carboxylic acids | D-半乳糖酸γ内酯D-galactonic acid γ-lactone | -0.852 | |||
| 羧酸类Carboxylic acids | D-半乳糖醛酸D-galacturonic acid | 0.822 | 2-羟苯甲酸2-Hydroxy benzoic acid | 0.931 | |||
| 4-羟基苯甲酸4-hydroxy benzoic acid | 0.918 | γ-羟基丁酸γ-hydroxybutyric acid | 0.635 | ||||
| D-苹果酸D-malic acid | 0.966 | D-氨基葡萄糖酸D-glucosaminic acid | -0.781 | ||||
| 氨基酸类Amino acids | L-精氨酸L-arginine | 0.918 | 聚合物类Polymers | 吐温80 Tween 80 | 0.640 | ||
| L-天冬酰胺酸L-asparagine | 0.983 | α-环状糊精α-cyclodextrin | 0.808 | ||||
| L-苯基丙氨酸L-phenylalanine | 0.827 | 肝糖Glycogen | 0.930 | ||||
| L-丝氨酸L-serine | 0.880 | PC3 | 糖类Sugar | β-甲基-D-葡萄糖苷 β-methyl-D-glucoside | 0.634 | ||
| L-苏氨酸L-threonine | 0.882 | α-D-乳糖α-D-lactose | -0.837 | ||||
| 甘氨酰-L-谷氨酸Glycyl-L-glutamic acid | -0.708 | 羧酸类Carboxylic acids | 衣康酸Itaconic acid | 0.745 | |||
| 胺类Amines | 苯乙基胺Phenylethylamine | 0.922 | α-丁酮酸α-ketobutyric acid | -0.884 | |||
| 腐胺Putrescine | 0.955 |
Table 3 Correlations between carbon substrate utilization in Biolog ECO and the principal components (PC1, PC2 and PC3)
主成分 Principal component | 碳源种类 Carbon source guild | 底物 Substrates | 载荷数 Number of load | 主成分 Principal component | 碳源种类 Carbon source guild | 底物 Substrates | 载荷数 Number of load |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 糖类Sugar | β-甲基-D-葡萄糖苷β-methyl-D-glucoside | 0.767 | PC1 | 聚合物类Polymers | 吐温40 Tween 40 | 0.880 |
| I-赤藻糖醇I-erythritol | 0.951 | 其他类Others | 丙酮酸甲酯Pyruvic acid methyl ester | 0.822 | |||
| D-甘露醇D-mannitol | 0.941 | D,L-α-甘油D,L-α-glycerol phosphate | 0.739 | ||||
| N-乙酰基-D-葡萄胺N-acetyl-D-glucosamine | 0.646 | PC2 | 糖类Sugar | D-木糖D-xylose | -0.861 | ||
| D-纤维二糖D-cellobiose | 0.934 | N-乙酰基-D-葡萄胺N-acetyl-D-glucosamine | -0.696 | ||||
| 葡萄糖-1-磷酸盐Glucose-1-phosphate | 0.968 | 羧酸类Carboxylic acids | D-半乳糖酸γ内酯D-galactonic acid γ-lactone | -0.852 | |||
| 羧酸类Carboxylic acids | D-半乳糖醛酸D-galacturonic acid | 0.822 | 2-羟苯甲酸2-Hydroxy benzoic acid | 0.931 | |||
| 4-羟基苯甲酸4-hydroxy benzoic acid | 0.918 | γ-羟基丁酸γ-hydroxybutyric acid | 0.635 | ||||
| D-苹果酸D-malic acid | 0.966 | D-氨基葡萄糖酸D-glucosaminic acid | -0.781 | ||||
| 氨基酸类Amino acids | L-精氨酸L-arginine | 0.918 | 聚合物类Polymers | 吐温80 Tween 80 | 0.640 | ||
| L-天冬酰胺酸L-asparagine | 0.983 | α-环状糊精α-cyclodextrin | 0.808 | ||||
| L-苯基丙氨酸L-phenylalanine | 0.827 | 肝糖Glycogen | 0.930 | ||||
| L-丝氨酸L-serine | 0.880 | PC3 | 糖类Sugar | β-甲基-D-葡萄糖苷 β-methyl-D-glucoside | 0.634 | ||
| L-苏氨酸L-threonine | 0.882 | α-D-乳糖α-D-lactose | -0.837 | ||||
| 甘氨酰-L-谷氨酸Glycyl-L-glutamic acid | -0.708 | 羧酸类Carboxylic acids | 衣康酸Itaconic acid | 0.745 | |||
| 胺类Amines | 苯乙基胺Phenylethylamine | 0.922 | α-丁酮酸α-ketobutyric acid | -0.884 | |||
| 腐胺Putrescine | 0.955 |
指标 Indication | Shannon-Wiener 丰富度指数 Richness index | Shannon 均匀度指数 Evenness index | Simpson 优势度指数 Dominance index | McIntosh 指数 Index | 平均颜色变化率 AWCD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全碳Total carbon | 0.767** | 0.725** | 0.756** | 0.476 | 0.511 |
| 全氮Total nitrogen | 0.691* | 0.682* | 0.663* | 0.290 | 0.316 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus | 0.460 | 0.427 | 0.676* | 0.793** | 0.789** |
| 有机碳Soil organic carbon | 0.301 | 0.263 | 0.203 | -0.047 | -0.026 |
| 微生物生物量碳Microbial biomass carbon | 0.171 | 0.134 | -0.101 | -0.651* | -0.632* |
| 微生物生物量氮Microbial biomass nitrogen | -0.264 | -0.298 | -0.489 | -0.795** | -0.802** |
| 细菌Bacteria | 0.592* | 0.531 | 0.416 | -0.102 | -0.074 |
| 真菌Fungi | 0.404 | 0.281 | 0.541 | 0.606* | 0.598* |
| 过氧化氢酶Catalase | 0.606* | 0.688* | 0.452 | -0.073 | -0.027 |
| 脲酶Urease | -0.225 | -0.174 | -0.350 | -0.537 | -0.530 |
| 蔗糖酶Invertase | 0.429 | 0.500 | 0.289 | -0.075 | -0.023 |
| 碱性磷酸酶Alkaline phosphatase | -0.334 | -0.291 | -0.184 | 0.210 | 0.197 |
Table 4 Correlation coefficients between soil microbial communities and soil biochemical indicators during the process of shrub introduction
指标 Indication | Shannon-Wiener 丰富度指数 Richness index | Shannon 均匀度指数 Evenness index | Simpson 优势度指数 Dominance index | McIntosh 指数 Index | 平均颜色变化率 AWCD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全碳Total carbon | 0.767** | 0.725** | 0.756** | 0.476 | 0.511 |
| 全氮Total nitrogen | 0.691* | 0.682* | 0.663* | 0.290 | 0.316 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus | 0.460 | 0.427 | 0.676* | 0.793** | 0.789** |
| 有机碳Soil organic carbon | 0.301 | 0.263 | 0.203 | -0.047 | -0.026 |
| 微生物生物量碳Microbial biomass carbon | 0.171 | 0.134 | -0.101 | -0.651* | -0.632* |
| 微生物生物量氮Microbial biomass nitrogen | -0.264 | -0.298 | -0.489 | -0.795** | -0.802** |
| 细菌Bacteria | 0.592* | 0.531 | 0.416 | -0.102 | -0.074 |
| 真菌Fungi | 0.404 | 0.281 | 0.541 | 0.606* | 0.598* |
| 过氧化氢酶Catalase | 0.606* | 0.688* | 0.452 | -0.073 | -0.027 |
| 脲酶Urease | -0.225 | -0.174 | -0.350 | -0.537 | -0.530 |
| 蔗糖酶Invertase | 0.429 | 0.500 | 0.289 | -0.075 | -0.023 |
| 碱性磷酸酶Alkaline phosphatase | -0.334 | -0.291 | -0.184 | 0.210 | 0.197 |
| 1 | Mazei Y A, Lebedeva N V, Taskaeva A A, et al. What role does human activity play in microbial biogeography: The revealing case of testate amoebae in the soils of Pyramiden, Svalbard. Pedobiologia, 2018, 67: 10-15. |
| 2 | Ingram L J, Stahl P D, Schuman G E, et al. Grazing impacts on soil carbon and microbial communities in a mixed-grass ecosystem. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2008, 72(4): 939-948. |
| 3 | Turpin-Jelfs T, Michaelides K, Biederman J A, et al. Soil nitrogen response to shrub encroachment in a degrading semi-arid grassland. Biogeosciences, 2019, 16(2): 369-381. |
| 4 | Ding L, Shang Y, Zhang W, et al. Disentangling the effects of driving forces on soil bacterial and fungal communities under shrub encroachment on the Guizhou Plateau of China. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 709: 136207. |
| 5 | Zhao Y N, Du Y Y, Ma Y P, et al. Soil organic carbon dynamics and the prediction of their spatial changes in response to anthropogenically introduced shrub encroachment in desert steppe of the Eastern Ningxia, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(6): 1927-1935. |
| 赵亚楠, 杜艳艳, 马彦平, 等. 宁夏东部荒漠草原灌丛引入过程中土壤有机碳变化及其空间格局预测. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(6): 1927-1935. | |
| 6 | Moore T E, Jones C S, Chong C, et al. Impact of rainfall seasonality on intraspecific trait variation in a shrub from a Mediterranean climate. Functional Ecology, 2020, 34(4): 865-876. |
| 7 | Batten K M, Scow K M, Davies K F, et al. Two invasive plants alter soil microbial community composition in serpentine grasslands. Biological Invasions, 2006, 8(2): 217-230. |
| 8 | Hawkes C V, Wren I F, Herman D J, et al. Plant invasion alters nitrogen cycling by modifying the soil nitrifying community. Ecology Letters, 2005, 8(9): 976-985. |
| 9 | Dassonville N, Vanderhoeven S, Vanparys V, et al. Impacts of alien invasive plants on soil nutrients are correlated with initial site conditions in NW Europe. Oecologia, 2008, 157(1): 131-140. |
| 10 | Chen D, Mi J, Chu P, et al. Patterns and drivers of soil microbial communities along a precipitation gradient on the Mongolian Plateau. Landscape Ecology, 2014, 30(9): 1669-1682. |
| 11 | Hu X, Li X Y, Zhao Y, et al. Changes in soil microbial community during shrub encroachment process in the Inner Mongolia grassland of northern China. Catena, 2021, 202(1): 105230. |
| 12 | Li H, Zhang J, Hu H, et al. Shift in soil microbial communities with shrub encroachment in Inner Mongolia grasslands, China. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2017, 79: 40-47. |
| 13 | Gao X, Zhao X, Li H, et al. Exotic shrub species (Caragana korshinskii) is more resistant to extreme natural drought than native species (Artemisia gmelinii) in a semiarid revegetated ecosystem. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2018, 263: 207-216. |
| 14 | Zhao Y N, Yu L, Zhou Y R, et al. Soil moisture dynamics and deficit of desert grassland with anthropogenic introduced shrub encroachment in the eastern Ningxia, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(4): 1305-1315. |
| 赵亚楠, 于露, 周玉蓉, 等. 宁夏东部荒漠草原灌丛引入对土壤水分动态及亏缺的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(4): 1305-1315. | |
| 15 | Yannarell A C, Menning S E, Beck A M. Influence of shrub encroachment on the soil microbial community composition of remnant hill prairies. Microbial Ecology, 2014, 67(4): 897-906. |
| 16 | Zhou L H, Li H, Shen H H, et al. Shrub-encroachment induced alterations in input chemistry and soil microbial community affect topsoil organic carbon in an Inner Mongolian grassland. Biogeochemistry, 2017, 136(3): 311-324. |
| 17 | Zhong Z K, Li W J, Lu X Q, et al. Adaptive pathways of soil microorganisms to stoichiometric imbalances regulate microbial respiration following afforestation in the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2020, 151: 108048. |
| 18 | Zheng H F, Chen Y M, Liu Y, et al. Effects of litter quality diminish and effects of vegetation type develop during litter decomposition of two shrub species in an alpine treeline ecotone. Ecosystems, 2020, 24(4): 197-210. |
| 19 | Courtney A C, Timothy R F, Thomas W B, et al. Grassland to woodland transitions: Dynamic response of microbial community structure and carbon use patterns. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2016, 121(6): 1675-1688. |
| 20 | Zheng Q Q, Du L T, Gong F, et al. Landscape characteristics of Caragana intermedia plantation based on GF-1 remote sensing image in Yanchi. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Sciences), 2019, 39(1): 152-159. |
| 郑琪琪, 杜灵通, 宫菲, 等. 基于GF-1遥感影像的宁夏盐池柠条人工林景观特征研究. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2019, 39(1): 152-159. | |
| 21 | Bao S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 22 | Guan S Y. Soil enzymes and its research. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1986. |
| 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法 . 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1986. | |
| 23 | Lu R K. Soil agricultural chemical analysis method. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. | |
| 24 | Liu Z F, Liu G H, Fu B J, et al. Dynamics of soil microbial biomass C, N along restoration chronosequences in Pine plantations. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(3): 1011-1018. |
| 刘占锋, 刘国华, 傅伯杰, 等. 人工油松林(Pinus tabulaeformis)恢复过程中土壤微生物生物量C、N的变化特征. 生态学报, 2007, 27(3): 1011-1018. | |
| 25 | Xu G H. Soil microbiological analysis methods manual. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1986. |
| 许光辉. 土壤微生物分析方法手册. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1986. | |
| 26 | Zhang M L, Chang H L, Ma M. Comparison of functional diversity of rhizosphere soil microorganisms between the exotic plant Xanthium italicum and its native partner Xanthium sibiricum by the Biolog method. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(10):179-187. |
| 张明莉, 常宏磊, 马淼. 基于Biolog技术的外来种意大利苍耳与本地种苍耳根际土壤微生物功能多样性的比较. 草业学报, 2017, 26(10): 179-187. | |
| 27 | Eldridge D J, Bowker M A, Maestre F T, et al. Impacts of shrub encroachment on ecosystem structure and functioning: Towards a global synthesis. Ecology Letters, 2011, 14(7): 709-722. |
| 28 | Ehrenfeld J G. Effects of exotic plant invasions on soil nutrient cycling processes. Ecosystems, 2003, 6(6): 503-523. |
| 29 | Li H, Shen H H, Zhou L H, et al. Shrub encroachment increases soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in temperate grasslands in China. Land Degradation & Development, 2019, 30(7): 756-767. |
| 30 | Pellegrini E, Boscutti F, Alberti G, et al. Stand age, degree of encroachment and soil characteristics modulate changes of C and N cycles in dry grassland soils invaded by the N2-fixing shrub Amorpha fruticose. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 792: 148295. |
| 31 | McCulley R L, Archer S R, Boutton T W, et al. Soil respiration and nutrient cycling in wooded communities developing in grassland. Ecology, 2004, 85(10): 2804-2817. |
| 32 | Gao X L, Li X G, Zhao L, et al. Regulation of soil phosphorus cycling in grasslands by shrubs. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2019, 133: 1-11. |
| 33 | Gao X L, Li X G, Zhao L, et al. Shrubs magnify soil phosphorus depletion in Tibetan meadows: Conclusions from C∶N∶P stoichiometry and deep soil profiles. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 785: 147320. |
| 34 | Bragazza L, Bardgett R D, Mitchell E A D, et al. Linking soil microbial communities to vascular plant abundance along a climate gradient. New Phytologist, 2015, 205(3): 1175-1182. |
| 35 | Hu Y, Xiang D, Veresoglou S D, et al. Soil organic carbon and soil structure are driving microbial abundance and community composition across the arid and semi-arid grasslands in northern China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 77: 51-57. |
| 36 | Jin Y T, Li X F, Cai Y, et al. Effects of straw returning with chemical fertilizer on soil enzyme activities and microbial community structure in rice-rape rotation. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(8): 3985-3996. |
| 靳玉婷, 李先藩, 蔡影, 等. 秸秆还田配施化肥对稻-油轮作土壤酶活性及微生物群落结构的影响. 环境科学, 2021, 42(8): 3985-3996. | |
| 37 | Sun Z C, Zhou Y R, Zhao Y N, et al. Responses of soil microbial mineralization to the anthropogenic introduced shrub encroachment and water gradients in the desert steppe. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(4): 1537-1550. |
| 孙忠超, 周玉蓉, 赵亚楠, 等. 荒漠草原土壤微生物矿化对灌丛引入过程及水分的响应. 生态学报, 2021, 41(4): 1537-1550. | |
| 38 | Sharma S K, Ramesh A, Sharma M P, et al. Microbial community structure and diversity as indicators for evaluating soil quality. Biodiversity, Biofuels, Agroforestry and Conservation Agriculture, 2010, 5: 317-358. |
| 39 | Garland J L, Mills A L. Classification and characterization of heterotrophic microbial communities on the basis of patterns of community-level sole-carbon-source utilization. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1991, 57(8): 2351-2359. |
| 40 | Mazía N, Moyano J, Perez L, et al. The sign and magnitude of tree-grass interaction along a global environmental gradient. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2016, 25(12): 1510-1519. |
| 41 | Xie L N, Santiago S, Eric A, et al. Woody species have stronger facilitative effects on soil biota than on plants along an aridity gradient. Journal of Vegetation Science, 2021, 32(3): e13034. |
| 42 | Yang J F, Zhang T R, Zhang R Q, et al. Long-term cover cropping seasonally affects soil microbial carbon metabolism in an apple orchard. Bioengineered, 2019, 10(1): 207-217. |
| 43 | Banning N C, Lalor B M, Cookson W R, et al. Analysis of soil microbial community level physiological profiles in native and post-mining rehabilitation forest: Which substrates discriminate? Applied Soil Ecology, 2012, 56: 27-34. |
| 44 | Graham M H, Haynes R J. Organic matter status and the size, activity and metabolic diversity of the soil microflora as indicators of the success of rehabilitation of mined sand dunes. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2004, 39(6): 429-437. |
| 45 | Zhang H F, Li G, Song X L, et al. Changes in soil microbial functional diversity under different vegetation restoration patterns for Hulunbeier Sandy Land. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(1): 38-44. |
| 46 | Sun Y H, Yang Z H, Zhao J J, et al. Functional diversity of microbial communities in cludge-amended soils. Physics Procedia, 2012, 33: 726-731. |
| 47 | Gong C J, Xu J, Fang Z G, et al. Carbon metabolic characteristics of airborne microbes in Hangzhou. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(2): 753-758. |
| 龚婵娟, 许晶, 方治国, 等. 杭州市空气微生物群落碳代谢特征研究. 环境科学, 2014, 35(2): 753-758. | |
| 48 | Sun H F, Li X L, Jin L Q, et al. Change over time in soil microbial diversity of artificial grassland in the Yellow River source zone. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(2): 46-58. |
| 孙华方, 李希来, 金立群, 等. 黄河源人工草地土壤微生物多样性对建植年限的响应. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 46-58. | |
| 49 | Kim J W, Rehmann L, Ray M B. Development of microalgal bioassay based on the community level physiological profiling (CLPP). Algal Research, 2017, 25: 47-53. |
| 50 | Wu L K, Lin X M, Lin W X. Advances and perspective in research on plant-soil-microbe interactions mediated by root exudates. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(3): 298-310. |
| 51 | Zhang T Y, Wu Y H, Zhuang L L, et al. Screening heterotrophic microalgal strains by using the Biolog method for biofuel production from organic wastewater. Algal Research, 2014, 6: 175-179. |
| 52 | Li H, Li X M, Yao Q Z, et al. Biolog-ECO analysis of rhizosphere soil microbial community characteristics of five different plants in two different grasslands. Microbiology China, 2020, 47(9): 2947-2958. |
| 李慧, 李雪梦, 姚庆智, 等. 基于Biolog-ECO方法的两种不同草原中5种不同植物根际土壤微生物群落特征. 微生物学通报, 2020, 47(9): 2947-2958. | |
| 53 | Wang R, Zhu K, Li G, et al. Metabolic characteristics of responses of soil fungi to land-use changes in the hilly regions of northeast China. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(9): 1925-1932. |
| 王蕊, 朱珂, 李刚, 等.东北丘陵区林地、耕地和草地土壤真菌群落代谢特征. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(9): 1925-1932. | |
| 54 | Zhao W, Yin Y L, Li S X, et al. Effects of vegetation reconstruction on vegetation and microbial community characteristics of black soil beach grassland. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2020, 29(1): 71-80. |
| 赵文, 尹亚丽, 李世雄, 等. 植被重建对黑土滩草地植被及微生物群落特征的影响. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(1): 71-80. | |
| 55 | Wang Y, Zhang C, Zhang G N, et al. Carbon input manipulations affecting microbial carbon metabolism in temperate forest soils-A comparative study between broadleaf and coniferous plantations. Geoderma, 2019, 355: 113914. |
| 56 | Li J, Cooper J M, Lin Z, et al. Soil microbial community structure and function are significantly affected by long-term organic and mineral fertilization regimes in the North China Plain. Applied Soil Ecology, 2015, 96: 75-87. |
| 57 | Diego N C, Romina A V, Emiliano J M, et al. Soil microbial functionality in response to the inclusion of cover crop mixtures in agricultural systems. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research, 2016, 14(2): e0304. |
| 58 | Wu D, Chi Q, Sui X, et al. Metabolic diversity and seasonal variation of soil microbial communities in natural forested wetlands. Journal of Forestry Research, 2021, 32(6): 2619-2631. |
| [1] | Mei-hui LI, Yu-hua LI, Xin-hui YAN, Hang-hang TUO, Meng-ru YANG, Zi-lin WANG, Wei LI. Characteristics of plant diversity and aboveground productivity and their relationship driven by subshrub expansion [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(5): 27-39. |
| [2] | Yu-xia HU, Ji-rui GONG, Chen-chen ZHU, Jia-yu SHI, Zi-he ZHANG, Liang-yuan SONG, Wei-yuan ZHANG. Spatial distribution of ecosystem services in the desert steppe, Inner Mongolia based on ecosystem service bundles [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(4): 1-14. |
| [3] | Wei-ling NIU, Hui CHEN, Hui-xin HOU, Chen-rui GUO, Jiao-lin MA, Jian-shuang WU. Ten-year livestock exclusion did not affect water and nitrogen use efficiency of alpine desert-steppe plants in Northwest Tibet [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 35-48. |
| [4] | Wan-long LIU, Dong-mei XU, Jia-mei SHI, Ai-yun XU. Plant cluster structure and leaf functional characters of Agropyron mongolicum populations in different plant species associations [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 72-80. |
| [5] | Wen-zhang GUO, Chang-qing JING, Xiao-jin DENG, Chen CHEN, Wei-kang ZHAO, Zhi-xiong HOU, Gong-xin WANG. Variations in carbon flux and factors influencing it on the northern slopes of the Tianshan Mountains [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(5): 1-12. |
| [6] | Ling JIN, Ying LU, Hong-bin MA, Ying-zhong XIE, Yan SHEN. Numerical classification and ordination of the desert steppe plant community in Etuokeqianqi, Inner Mongolia [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(4): 12-21. |
| [7] | Fang-fang NI, Shi-jie LV, Zhi-qiang QU, Lu BAI, Biao MENG, Bo-han ZHANG, Zhi-guo LI. Effects of vegetation characteristics of desert steppe in the non-growing season on near-surface dust flux under different stocking rates [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 26-33. |
| [8] | Yan-ming CHENG, Hong-bin MA, Jing MA, Zi-yuan MA, Jin-di LIU, Yao ZHOU, Wen-dong PENG. Effects of different grazing patterns on soil carbon and nitrogen storage and sequestration in desert steppee [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 18-27. |
| [9] | Zhi-xia GUO, Ren-tao LIU, Wen-zhi ZHAO. The relationships between desert shrubs and soil fauna and their responses to precipitation changes in arid regions: A review [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 206-216. |
| [10] | Lin CHEN, Gao-lu CHEN, Nai-ping SONG, Xue-bin LI, Hong-yun WAN, Wen-qiang HE. Response of photosynthetic characteristics and water use efficiency of Artemisia scoparia to rainfall changes in Eastern Ningxia desert steppe [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 87-98. |
| [11] | Wen-ming MA, Chao-wen LIU, Qing-ping ZHOU, Zhuo-ma DENGzeng, Si-hong TANG, Diliyaer·mohetaer, Chen HOU. Effects of shrub encroachment on soil aggregate ecological stoichiometry and enzyme activity in alpine grassland [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 57-68. |
| [12] | Feng ZHANG, Jia-wei SUN, Yu SUN, Jia-hua ZHENG, Ji-rong QIAO, Meng-li ZHAO. Effects of different stocking rates on interspecific relationships among dominant species and their spatial distribution characteristics in the Stipa breviflora desert steppe [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(8): 1-11. |
| [13] | Xu-dong WU, Qi JIANG, Xiao-bin REN, Hong-qian YU, Zhan-jun WANG, Jian-long HE, Bo JI, Jian-min DU. Effects of precipitation on carbon, nitrogen and microbial characteristics of biological soil crusts in a desert steppe of Northern China [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(7): 34-43. |
| [14] | Xiao-e LIU, Shi-ping SU, Yi LI. Soil physical and chemical properties under four typical shrubs found on the Northern and Southern Mountains of Lanzhou City, Northwest China [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(6): 28-39. |
| [15] | Ying MA, Zhi-hao XU, Qiao-hong ZENG, Jian-long MENG, Ya-hu HU, Jie-qiong SU. Impact of nitrogen addition on stoichiometric characteristics of herbaceous species in desert steppe [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(6): 64-72. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||