
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (7): 68-83.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023335
Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhen-huan ZHANG1,2( ), Li-rong YAO1,3, Jun-cheng WANG1,3, Er-jing SI1,3, Hong ZHANG1,3, Ke YANG1,3, Xiao-le MA1,3, Ya-xiong MENG1,3, Hua-jun WANG1,3, Bao-chun LI1,2(
), Li-rong YAO1,3, Jun-cheng WANG1,3, Er-jing SI1,3, Hong ZHANG1,3, Ke YANG1,3, Xiao-le MA1,3, Ya-xiong MENG1,3, Hua-jun WANG1,3, Bao-chun LI1,2( )
)
Received:2023-09-14
Revised:2023-11-03
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-04-08
Contact:
Bao-chun LI
Zhen-huan ZHANG, Li-rong YAO, Jun-cheng WANG, Er-jing SI, Hong ZHANG, Ke YANG, Xiao-le MA, Ya-xiong MENG, Hua-jun WANG, Bao-chun LI. Identification of AKR gene family members in Halogeton glomeratus and salt tolerance analysis of the root salt stress response gene HgAKR42639[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(7): 68-83.
| 引物名称Name of primers | 引物序列Sequences of primers (5’→3’) | 用途Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| HgAKR42639-F | AGGAAGCACATCGTTGAGGG | 实时荧光定量PCR Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR |
| HgAKR42639-R | TTCATTGCCCGGACAGTCTC | |
| HgActin-F | TGTTCTCAGTGGTGGTACAA | 盐生草内参基因引物 Reference gene primers in H. glomeratus |
| HgActin-R | GTGCCACCACCTTAATCTTC | |
| AtActin-F | ACCCAAAGGCCAACAGAGAG | 拟南芥内参基因引物 Reference gene primers in A. thaliana |
| AtActin-R | CACGTCCAGCAAGGTCAAGA |
Table 1 Real-time fluorescence quantitative primers
| 引物名称Name of primers | 引物序列Sequences of primers (5’→3’) | 用途Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| HgAKR42639-F | AGGAAGCACATCGTTGAGGG | 实时荧光定量PCR Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR |
| HgAKR42639-R | TTCATTGCCCGGACAGTCTC | |
| HgActin-F | TGTTCTCAGTGGTGGTACAA | 盐生草内参基因引物 Reference gene primers in H. glomeratus |
| HgActin-R | GTGCCACCACCTTAATCTTC | |
| AtActin-F | ACCCAAAGGCCAACAGAGAG | 拟南芥内参基因引物 Reference gene primers in A. thaliana |
| AtActin-R | CACGTCCAGCAAGGTCAAGA |
| 序号Number | 名称Name | 基因登录号Gene accession ID | 序号Number | 名称Name | 基因登录号Gene accession ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HgAKR01 | Hg02G012880.1 | 13 | HgAKR13 | Hg16G006890.1 |
| 2 | HgAKR02 | Hg02G012940.1 | 14 | HgAKR14 | Hg16G006900.1 |
| 3 | HgAKR03 | Hg03G002550.1 | 15 | HgAKR15 | Hg16G006910.1 |
| 4 | HgAKR04 | Hg07G000220.1 | 16 | HgAKR16 | Hg171G001710.2 |
| 5 | HgAKR05 | Hg09G006350.1 | 17 | HgAKR17 | Hg214G001090.1 |
| 6 | HgAKR06 | Hg09G010750.1 | 18 | HgAKR18 | Hg238G000730.2 |
| 7 | HgAKR07 | Hg09G010800.1 | 19 | HgAKR19 | Hg248G001020.1 |
| 8 | HgAKR08 | Hg102G000790.1 | 20 | HgAKR20 | Hg30G002300.1 |
| 9 | HgAKR09 | Hg15G004360.1 | 21 | HgAKR21 | Hg465G000090.1 |
| 10 | HgAKR10 | Hg16G006840.1 | 22 | HgAKR22 | Hg53G002170.1 |
| 11 | HgAKR11 | Hg16G006850.1 | 23 | HgAKR42639 | Hg02G042639.1 |
| 12 | HgAKR12 | Hg16G006870.1 |
Table 2 Basic information of AKR gene family in H. glomeratus
| 序号Number | 名称Name | 基因登录号Gene accession ID | 序号Number | 名称Name | 基因登录号Gene accession ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HgAKR01 | Hg02G012880.1 | 13 | HgAKR13 | Hg16G006890.1 |
| 2 | HgAKR02 | Hg02G012940.1 | 14 | HgAKR14 | Hg16G006900.1 |
| 3 | HgAKR03 | Hg03G002550.1 | 15 | HgAKR15 | Hg16G006910.1 |
| 4 | HgAKR04 | Hg07G000220.1 | 16 | HgAKR16 | Hg171G001710.2 |
| 5 | HgAKR05 | Hg09G006350.1 | 17 | HgAKR17 | Hg214G001090.1 |
| 6 | HgAKR06 | Hg09G010750.1 | 18 | HgAKR18 | Hg238G000730.2 |
| 7 | HgAKR07 | Hg09G010800.1 | 19 | HgAKR19 | Hg248G001020.1 |
| 8 | HgAKR08 | Hg102G000790.1 | 20 | HgAKR20 | Hg30G002300.1 |
| 9 | HgAKR09 | Hg15G004360.1 | 21 | HgAKR21 | Hg465G000090.1 |
| 10 | HgAKR10 | Hg16G006840.1 | 22 | HgAKR22 | Hg53G002170.1 |
| 11 | HgAKR11 | Hg16G006850.1 | 23 | HgAKR42639 | Hg02G042639.1 |
| 12 | HgAKR12 | Hg16G006870.1 |
| 序号Number | 基因编号 Genetic code | 氨基酸数 Amino acid quantity (aa) | 等电点 Isoelectric point (PI) | 分子量 Molecular weight (Da) | 分子式 Molecular formula | 负电荷的残基总数Total number of negatively charged residues | 正电荷的残基总数Total number of positively charged residues | 脂肪 系数 Aliphatic index | 不稳定系数 Instability index | 亲水性平均值Grand average of hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HgAKR01 | 317 | 6.00 | 35036.93 | C1579H2455N419O465S9 | 34 | 30 | 89.53 | 43.19 | -0.240 |
| 2 | HgAKR02 | 316 | 5.57 | 34807.62 | C1562H2436N414O467S10 | 36 | 29 | 89.49 | 43.46 | -0.234 |
| 3 | HgAKR03 | 310 | 5.76 | 34512.44 | C1536H2435N421O460S11 | 41 | 34 | 92.81 | 27.01 | -0.215 |
| 4 | HgAKR04 | 311 | 5.84 | 34942.01 | C1573H2470N414O465S10 | 42 | 35 | 92.15 | 39.65 | -0.336 |
| 5 | HgAKR05 | 334 | 6.20 | 37468.25 | C1685H2659N447O488S15 | 38 | 35 | 93.65 | 45.44 | -0.244 |
| 6 | HgAKR06 | 324 | 6.34 | 35556.17 | C1606H2541N413O467S14 | 37 | 35 | 91.17 | 38.70 | -0.126 |
| 7 | HgAKR07 | 351 | 6.12 | 38937.70 | C1715H2739N469O521S21 | 43 | 39 | 84.96 | 34.53 | -0.300 |
| 8 | HgAKR08 | 350 | 5.66 | 38224.84 | C1700H2723N455O517S13 | 45 | 39 | 92.80 | 26.30 | -0.174 |
| 9 | HgAKR09 | 664 | 6.20 | 73942.76 | C3293H5210N898O977S29 | 90 | 80 | 85.78 | 40.27 | -0.320 |
| 10 | HgAKR10 | 338 | 5.70 | 37428.78 | C1664H2626N452O499S15 | 46 | 39 | 84.56 | 25.72 | -0.275 |
| 11 | HgAKR11 | 309 | 6.21 | 34774.88 | C1562H2453N415O459S12 | 43 | 39 | 90.91 | 22.12 | -0.238 |
| 12 | HgAKR12 | 165 | 6.20 | 18704.43 | C832H1313N227O247S8 | 21 | 19 | 87.45 | 25.62 | -0.250 |
| 13 | HgAKR13 | 338 | 5.68 | 37512.86 | C1668H2630N452O501S15 | 46 | 38 | 85.12 | 29.62 | -0.272 |
| 14 | HgAKR14 | 343 | 5.57 | 37951.12 | C1671H2652N462O516S15 | 48 | 39 | 83.06 | 37.63 | -0.385 |
| 15 | HgAKR15 | 317 | 8.38 | 35411.57 | C1582H2493N429O467S13 | 35 | 38 | 87.03 | 34.98 | -0.298 |
| 16 | HgAKR16 | 371 | 9.07 | 41209.57 | C1857H2926N488O538S16 | 28 | 36 | 91.48 | 34.66 | -0.149 |
| 17 | HgAKR17 | 322 | 5.48 | 35141.09 | C1563H2487N415O481S11 | 42 | 34 | 94.50 | 33.28 | -0.170 |
| 18 | HgAKR18 | 328 | 7.59 | 36492.74 | C1634H2569N439O484S12 | 37 | 38 | 87.68 | 34.03 | -0.295 |
| 19 | HgAKR19 | 298 | 9.03 | 33006.76 | C1487H2339N399O436S7 | 31 | 37 | 89.36 | 12.19 | -0.308 |
| 20 | HgAKR20 | 323 | 6.24 | 36545.87 | C1621H2552N454O475S17 | 44 | 39 | 84.18 | 41.19 | -0.401 |
| 21 | HgAKR21 | 220 | 5.71 | 24337.91 | C1080H1718N296O323S10 | 30 | 25 | 94.41 | 36.36 | -0.156 |
| 22 | HgAKR22 | 384 | 7.57 | 42245.83 | C1879H2974N518O575S7 | 46 | 47 | 87.89 | 24.76 | -0.396 |
| 23 | HgAKR42639 | 317 | 6.25 | 35151.21 | C1575H2473N419O468S12 | 36 | 34 | 90.41 | 32.06 | -0.219 |
Table 3 Physical and chemical properties of AKR gene family in H. glomeratus
| 序号Number | 基因编号 Genetic code | 氨基酸数 Amino acid quantity (aa) | 等电点 Isoelectric point (PI) | 分子量 Molecular weight (Da) | 分子式 Molecular formula | 负电荷的残基总数Total number of negatively charged residues | 正电荷的残基总数Total number of positively charged residues | 脂肪 系数 Aliphatic index | 不稳定系数 Instability index | 亲水性平均值Grand average of hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HgAKR01 | 317 | 6.00 | 35036.93 | C1579H2455N419O465S9 | 34 | 30 | 89.53 | 43.19 | -0.240 |
| 2 | HgAKR02 | 316 | 5.57 | 34807.62 | C1562H2436N414O467S10 | 36 | 29 | 89.49 | 43.46 | -0.234 |
| 3 | HgAKR03 | 310 | 5.76 | 34512.44 | C1536H2435N421O460S11 | 41 | 34 | 92.81 | 27.01 | -0.215 |
| 4 | HgAKR04 | 311 | 5.84 | 34942.01 | C1573H2470N414O465S10 | 42 | 35 | 92.15 | 39.65 | -0.336 |
| 5 | HgAKR05 | 334 | 6.20 | 37468.25 | C1685H2659N447O488S15 | 38 | 35 | 93.65 | 45.44 | -0.244 |
| 6 | HgAKR06 | 324 | 6.34 | 35556.17 | C1606H2541N413O467S14 | 37 | 35 | 91.17 | 38.70 | -0.126 |
| 7 | HgAKR07 | 351 | 6.12 | 38937.70 | C1715H2739N469O521S21 | 43 | 39 | 84.96 | 34.53 | -0.300 |
| 8 | HgAKR08 | 350 | 5.66 | 38224.84 | C1700H2723N455O517S13 | 45 | 39 | 92.80 | 26.30 | -0.174 |
| 9 | HgAKR09 | 664 | 6.20 | 73942.76 | C3293H5210N898O977S29 | 90 | 80 | 85.78 | 40.27 | -0.320 |
| 10 | HgAKR10 | 338 | 5.70 | 37428.78 | C1664H2626N452O499S15 | 46 | 39 | 84.56 | 25.72 | -0.275 |
| 11 | HgAKR11 | 309 | 6.21 | 34774.88 | C1562H2453N415O459S12 | 43 | 39 | 90.91 | 22.12 | -0.238 |
| 12 | HgAKR12 | 165 | 6.20 | 18704.43 | C832H1313N227O247S8 | 21 | 19 | 87.45 | 25.62 | -0.250 |
| 13 | HgAKR13 | 338 | 5.68 | 37512.86 | C1668H2630N452O501S15 | 46 | 38 | 85.12 | 29.62 | -0.272 |
| 14 | HgAKR14 | 343 | 5.57 | 37951.12 | C1671H2652N462O516S15 | 48 | 39 | 83.06 | 37.63 | -0.385 |
| 15 | HgAKR15 | 317 | 8.38 | 35411.57 | C1582H2493N429O467S13 | 35 | 38 | 87.03 | 34.98 | -0.298 |
| 16 | HgAKR16 | 371 | 9.07 | 41209.57 | C1857H2926N488O538S16 | 28 | 36 | 91.48 | 34.66 | -0.149 |
| 17 | HgAKR17 | 322 | 5.48 | 35141.09 | C1563H2487N415O481S11 | 42 | 34 | 94.50 | 33.28 | -0.170 |
| 18 | HgAKR18 | 328 | 7.59 | 36492.74 | C1634H2569N439O484S12 | 37 | 38 | 87.68 | 34.03 | -0.295 |
| 19 | HgAKR19 | 298 | 9.03 | 33006.76 | C1487H2339N399O436S7 | 31 | 37 | 89.36 | 12.19 | -0.308 |
| 20 | HgAKR20 | 323 | 6.24 | 36545.87 | C1621H2552N454O475S17 | 44 | 39 | 84.18 | 41.19 | -0.401 |
| 21 | HgAKR21 | 220 | 5.71 | 24337.91 | C1080H1718N296O323S10 | 30 | 25 | 94.41 | 36.36 | -0.156 |
| 22 | HgAKR22 | 384 | 7.57 | 42245.83 | C1879H2974N518O575S7 | 46 | 47 | 87.89 | 24.76 | -0.396 |
| 23 | HgAKR42639 | 317 | 6.25 | 35151.21 | C1575H2473N419O468S12 | 36 | 34 | 90.41 | 32.06 | -0.219 |
序号 Number | 盐生草AKR基因家族编号 Halophytes AKR gene family number | 信号肽 Signal peptides | 亲疏水性 Hydrophilicity | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HgAKR01 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 67.04 |
| 2 | HgAKR02 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 55.20 |
| 3 | HgAKR03 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 95.71 |
| 4 | HgAKR04 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 92.48 |
| 5 | HgAKR05 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 80.73 |
| 6 | HgAKR06 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 59.94 |
| 7 | HgAKR07 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 线粒体Mitochondrion 69.34 |
| 8 | HgAKR08 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 99.87 |
| 9 | HgAKR09 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞骨架Cytoskeleton 99.81 |
| 10 | HgAKR10 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞骨架Cytoskeleton 98.79 |
| 11 | HgAKR11 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 93.81 |
| 12 | HgAKR12 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 93.06 |
| 13 | HgAKR13 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 93.84 |
| 14 | HgAKR14 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 线粒体Mitochondrion 68.73 |
| 15 | HgAKR15 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 57.76 |
| 16 | HgAKR16 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 70.28 |
| 17 | HgAKR17 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 63.66 |
| 18 | HgAKR18 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 73.73 |
| 19 | HgAKR19 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 66.95 |
| 20 | HgAKR20 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 91.95 |
| 21 | HgAKR21 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 67.89 |
| 22 | HgAKR22 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 94.25 |
| 23 | HgAKR42639 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 60.90 |
Table 4 Prediction of AKR gene family signaling peptides, hydrophilicity, and subcellular localization in H. glomeratus
序号 Number | 盐生草AKR基因家族编号 Halophytes AKR gene family number | 信号肽 Signal peptides | 亲疏水性 Hydrophilicity | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HgAKR01 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 67.04 |
| 2 | HgAKR02 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 55.20 |
| 3 | HgAKR03 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 95.71 |
| 4 | HgAKR04 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 92.48 |
| 5 | HgAKR05 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 80.73 |
| 6 | HgAKR06 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 59.94 |
| 7 | HgAKR07 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 线粒体Mitochondrion 69.34 |
| 8 | HgAKR08 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 99.87 |
| 9 | HgAKR09 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞骨架Cytoskeleton 99.81 |
| 10 | HgAKR10 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞骨架Cytoskeleton 98.79 |
| 11 | HgAKR11 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 93.81 |
| 12 | HgAKR12 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 93.06 |
| 13 | HgAKR13 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 93.84 |
| 14 | HgAKR14 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 线粒体Mitochondrion 68.73 |
| 15 | HgAKR15 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 57.76 |
| 16 | HgAKR16 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 70.28 |
| 17 | HgAKR17 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 63.66 |
| 18 | HgAKR18 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 73.73 |
| 19 | HgAKR19 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 66.95 |
| 20 | HgAKR20 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 91.95 |
| 21 | HgAKR21 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 67.89 |
| 22 | HgAKR22 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 叶绿体Chloroplast 94.25 |
| 23 | HgAKR42639 | 无Without | 疏水性Hydrophobicity | 细胞质Cytoplasm 60.90 |
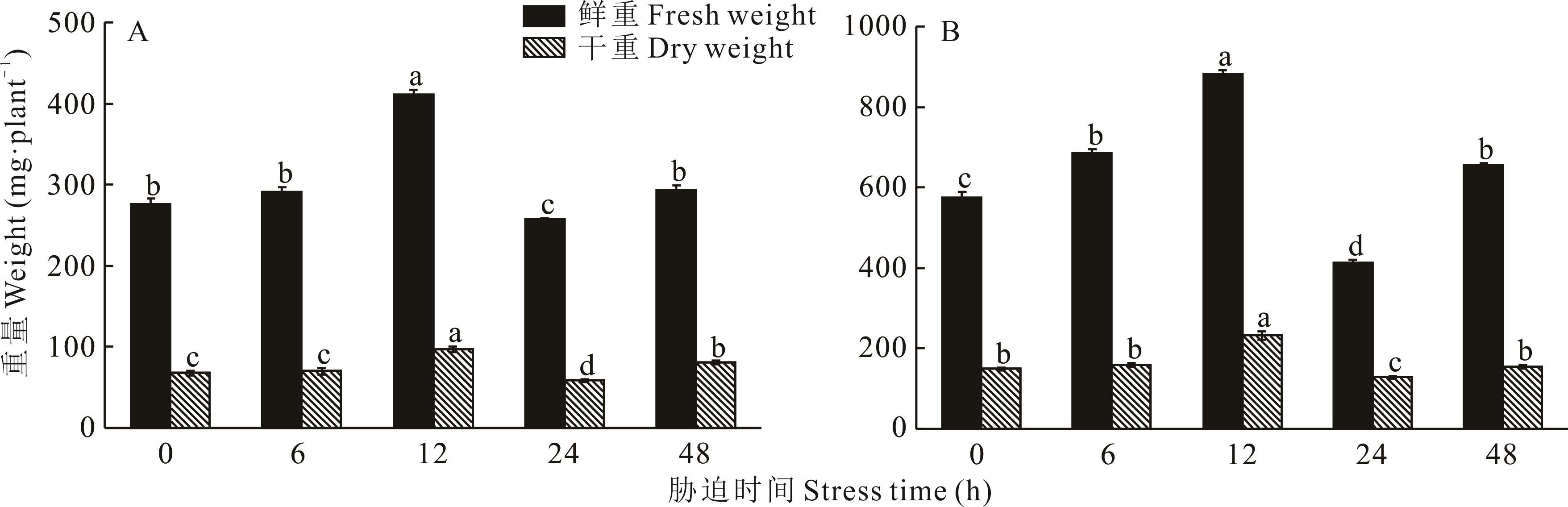
Fig.6 Changes in biomass of H. glomeratus roots (A) and A. thaliana transfer HgAKR42639 gene (B) treated at different times under 200 mmol·L-1 NaCl salt stress treatment
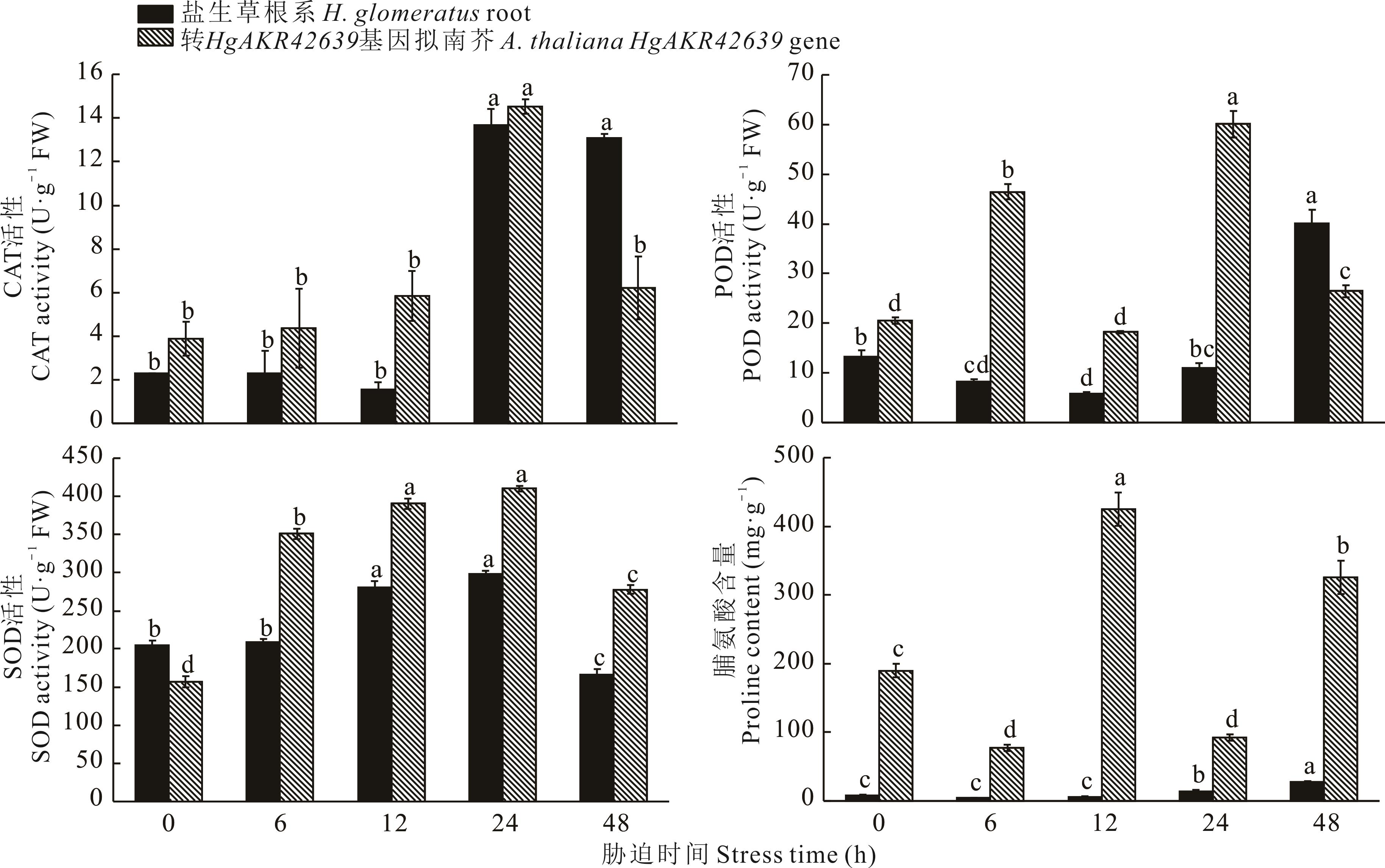
Fig.8 CAT, POD, SOD activity and proline content of H. glomeratus roots and A. thaliana transfer HgAKR42639 gene treated at different times under 200 mmol·L-1 NaCl salt stress treatment
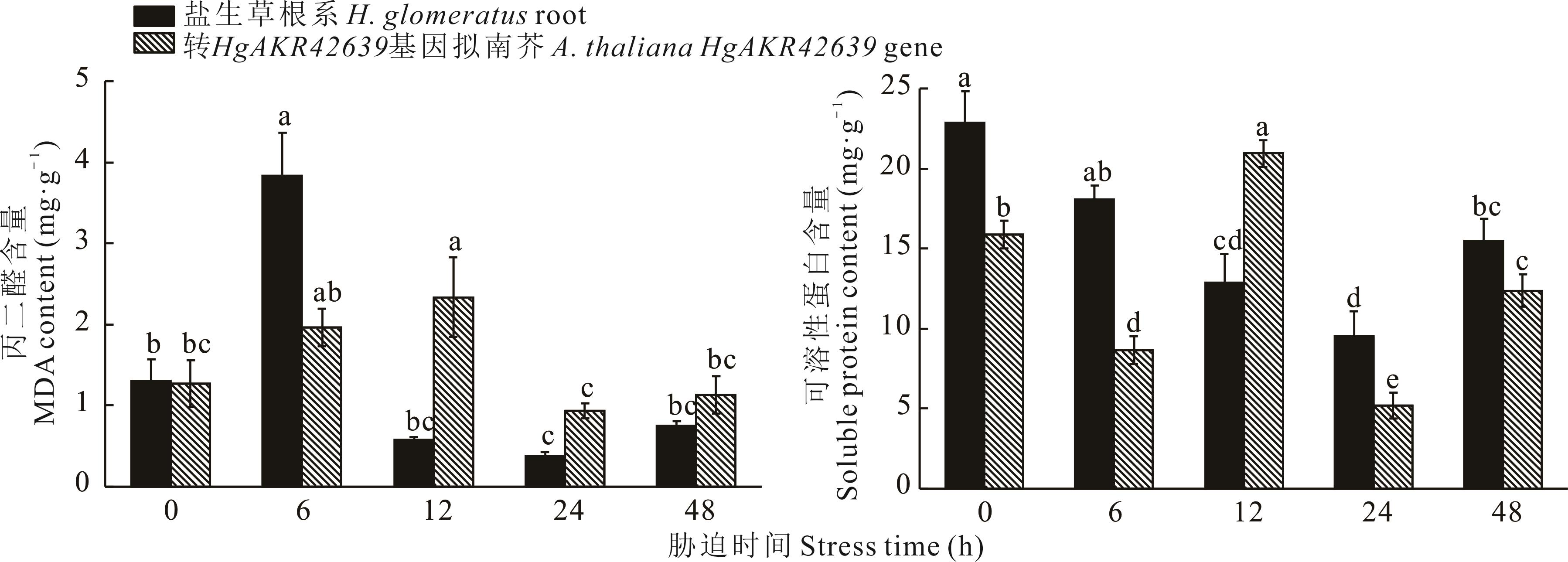
Fig.9 MDA and soluble protein content of H. glomeratus roots and A. thaliana transfer HgAKR42639 gene treated at different times under 200 mmol·L-1 NaCl salt stress treatment
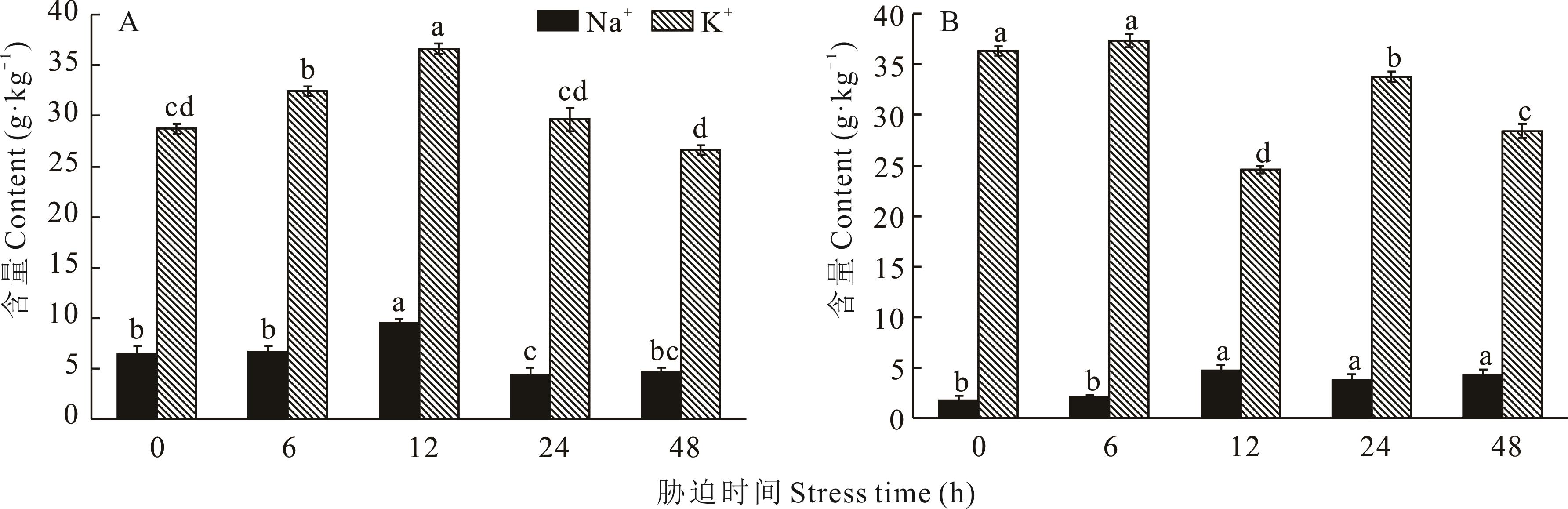
Fig.10 Changes in sodium-potassium ion content of H. glomeratus roots (A) and A. thaliana transfer HgAKR42639 gene (B) treated at different times under 200 mmol·L-1 NaCl salt stress treatment
| 1 | Li X, Jiao Y, Dai G, et al. Soil bacterial community diversity under different degrees of saline-alkaline in the Hetao Area of Inner Mongolia. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(1): 249-260. |
| 李新, 焦燕, 代钢, 等. 内蒙古河套灌区不同盐碱程度的土壤细菌群落多样性. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(1): 249-260. | |
| 2 | Yang J S, Yao R J, Wang X P, et al. Research on salt-affected soils in China: History, status quo and prospect. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2022, 59(1): 10-27. |
| 杨劲松, 姚荣江, 王相平, 等. 中国盐渍土研究: 历程、现状与展望. 土壤学报, 2022, 59(1): 10-27. | |
| 3 | Zhang H O. An analysis of the distribution and evolutionary characteristics of saline soils in China. Agriculture and Technology, 2022, 42(5): 104-107. |
| 张海欧. 浅析中国盐渍土分布及演变特征. 农业与技术, 2022, 42(5): 104-107. | |
| 4 | Pan J, Huang C H, Luo J, et al. Effects of salt stress on plant and the mechanism of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhancing salt tolerance of plants. Advances in Earth Science, 2018, 33(4): 361-372. |
| 潘晶, 黄翠华, 罗君, 等. 盐胁迫对植物的影响及AMF提高植物耐盐性的机制. 地球科学进展, 2018, 33(4): 361-372. | |
| 5 | Penning T M. The aldo-keto reductases (AKRs): Overview. Chemico Biological Interactions, 2015, 234(6): 236-246. |
| 6 | Sengupta D, Naik D, Reddy A R. Plant aldo-keto reductases (AKRs) as multi-tasking soldiers involved in diverse plant metabolic processes and stress defense: A structure-function update. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2015, 179(5): 40-55. |
| 7 | Noriaki O, Kazunori K, Masao H, et al. Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 is regulated by nucleos (t) ide analogues for chronic hepatitis B. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2023, 674(9): 133-139. |
| 8 | Tang R. Molecular mechanism of cholestanone metabolism mediated by aldo/keto reductase AKR2E9 in Mythimna separata. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2022. |
| 唐睿. 粘虫醛酮还原酶AKR2E9代谢胆甾烷酮的功能解析. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2022. | |
| 9 | Huo J X, Du B, Sun S F, et al. A novel aldo-keto reductase gene, IbAKR, from sweet potato confers higher tolerance to cadmium stress in tobacco. Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering, 2018, 5(2): 206-213. |
| 10 | Lee E H, Song D G, Lee J Y, et al. Inhibitory effect of the compounds isolated from Rhus verniciflua on aldose reductase and advanced glycation endproducts. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2008, 31(8): 1626-1630. |
| 11 | Jin Y, Penning T M. Aldo-keto reductases and bioactivation/detoxication. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 2007, 47(2): 263-292. |
| 12 | Shu N, Chen Z J. The research progress of aldo keto reductase. Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, 2017, 24(2): 175-179. |
| 舒楠, 陈子珺. 醛酮还原酶的研究进展. 药物生物技术, 2017, 24(2): 175-179. | |
| 13 | Bartels D, Engelhardt K, Roncarati R, et al. An ABA and GA modulated gene expressed in the barley embryo encodes in aldose reductase related protein. The EMBO Journal, 1991, 5(7): 1037-1043. |
| 14 | Roncarati R, Salamini F, Bartels D. An aldose reductase homologous gene from barley: Regulation and function. The Plant Journal, 1995, 7(5): 809-822. |
| 15 | Oberschall A, Deak M, Torok K, et al. A novel aldose/aldehyde reductase protects transgenic plants against lipid peroxidation under chemical and drought stress. The Plant Journal, 2000, 24(7): 437-446. |
| 16 | Hegedus A, Erdei S, Janda T, et al. Transgenic tobacco plants overproducing alfalfa aldose/aldehyde reductase show higher tolerance to low temperature and cadmium stress. Plant Science, 2004, 166(5): 1329-1333. |
| 17 | Turoczy Z, Kis P, Torok K, et al. Overproduction of a rice aldo-keto reductase increases oxidative and heat stress tolerance by malondialdehyde and methylglyoxal detoxification. Plant Molecular Biology, 2011, 75(1): 399-412. |
| 18 | Hideg E, Nagy T, Oberschall A, et al. Detoxification function of aldose/aldehyde reductase during drought and ultraviolet-B (230-320 nm) stresses. Plant, Cell and Environment, 2003, 26(4): 513-522. |
| 19 | Eva C, Zelenyanszki H, Farkas R T, et al. Transgenic barley expressing the Arabidopsis AKR4C9 aldo-keto reductase enzyme exhibits enhanced freezing tolerance and regenerative capacity. South African Journal of Botany, 2004, 93(7): 179-184. |
| 20 | Kanayama Y, Mizutani R, Yaguchi S, et al. Characterization of an uncharacterized aldo-keto reductase gene from peach and its role in abiotic stress tolerance. Phytochemistry, 2014, 104(8): 30-36. |
| 21 | Simpson P J, Tantitadapitak C, Reed A M, et al. Characterization of two novel aldo-keto reductases from Arabidopsis: Expression patterns, broad substrate specificity, and an open active-site structure suggest a role in toxicant metabolism following stress. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2009, 392(2): 465-480. |
| 22 | Zhao Q, Zhang X M. A preliminary study on the characteristics of population families of the halophilous herbaceous plants in Qira Gobi Desert, Xinjiang. Arid Zone Research, 2003(3): 221-225. |
| 赵强, 张希明. 策勒戈壁盐生草种群特征的初步研究. 干旱区研究, 2003(3): 221-225. | |
| 23 | Qiao R, Hu N, Zhou J, et al. Analysis and evaluation on seed nutrition of halophyte Halogeton glomeratus in arid region of Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2019, 41(6): 956-960. |
| 乔蕤, 胡娜, 周菁, 等. 西北旱区盐生植物盐生草籽营养成分分析与评价. 中国油料作物学报, 2019, 41(6): 956-960. | |
| 24 | He J J, Yao L R, Wang J C, et al. Effects of drought and salt stress on seed germination characteristics of Halogeton glomeratus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(11): 129-140. |
| 何建军, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 等. 干旱和盐胁迫对盐生植物盐生草种子萌发特性的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 129-140. | |
| 25 | Yao L R. Study on the salt uptake mechanisms of roots in halophyte Halogeton glomeratus. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 姚立蓉. 盐生草根系对盐分吸收机理的研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2018. | |
| 26 | Li S N, Zhao X W, Sun L P, et al. Identification and expression analysis of AKR superfamily in soybean (Glycine max). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2022, 30(11): 2061-2076. |
| 厉苏宁, 赵现伟, 孙丽萍, 等. 大豆醛酮还原酶超家族的鉴定及表达分析. 农业生物技术学报, 2022, 30(11): 2061-2076. | |
| 27 | Yu J. Cloning and functional analysis of aldehyde ketone reductase gene (MsAKR1) in response to salt stress in alfalfa. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2021. |
| 于洁. 苜蓿盐胁迫响应醛酮还原酶基因(MsAKR1)克隆及功能分析. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021. | |
| 28 | Ma Y N, Lu X, Wei Y C, et al. Identification and tissue specific expression analysis of AKR gene family in grape. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2021, 37(8): 141-151. |
| 马亚男, 卢旭, 魏云春, 等. 葡萄AKR基因家族的鉴定和组织特异性表达分析. 生物技术通报, 2021, 37(8): 141-151. | |
| 29 | Zhou X T, Liang G P, Lu S X, et al. Identification and expression analysis of adehlyde ktonee reductase (AKR) gene family in garpe. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2022, 42(11): 1851-1861. |
| 周雪婷, 梁国平, 卢世雄, 等. 葡萄醛酮还原酶(AKR)基因家族的鉴定与表达分析. 西北植物学报, 2022, 42(11): 1851-1861. | |
| 30 | Felsenstein J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: A maximum likelihood approach. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 1981, 17(6): 368-376. |
| 31 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 32 | Guo Y N, Ai J. Effects of salt stress on morphological and physiological indexes of Chinese cabbage. Journal of Yulin University, 2023, 33(2): 38-41. |
| 郭亚宁, 艾静. 盐胁迫对油白菜生长及其生理指标的影响. 榆林学院学报, 2023, 33(2): 38-41. | |
| 33 | Li H S. Principle and technology of plant physiology and biochemical experiments. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000. |
| 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. | |
| 34 | Wang Q Z, Liu Q, Gao Y N, et al. Review on the mechanisms of the response to salinity-alkalinity stress in plants. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(16): 5565-5577. |
| 王佺珍, 刘倩, 高娅妮, 等. 植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展. 生态学报, 2017, 37(16): 5565-5577. | |
| 35 | Wang J C. Study on the salt tolerance mechanisms of ion compartmentation in halophyte Halogeton glomeratus. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 汪军成. 盐生草盐分区隔化耐盐机制研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2017. | |
| 36 | Sun L J, He J J, Wang J C, et al. Development of SSR markers based on full-length transcriptome sequencing and genetic diversity analysis of Halogeton glomeratus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 199-210. |
| 孙禄娟, 何建军, 汪军成, 等. 全长转录组测序的盐生草SSR标记开发及其遗传多样性分析. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 199-210. | |
| 37 | Chen Q, Xu X Y, Wang J C, et al. Identification of a WRKY gene family based on full-length transcriptome sequences and analysis of response patterns under salt stress in Halogeton glomeratus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(12): 146-157. |
| 陈倩, 徐晓芸, 汪军成, 等. 基于全长转录组的盐生草WRKY基因家族的鉴定及其盐胁迫响应模式分析. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 146-157. | |
| 38 | Zhang Z H, Xu J Y, Song M N, et al. Effects of NaCl stress on seed germination of Halogeton glomeratus in different regions of Gansu Province. Grassland and Turf, 2022, 42(5): 132-141. |
| 张泽华, 许静玉, 宋美妮, 等. NaCl胁迫对甘肃省不同地区盐生草种子萌发特性的影响. 草原与草坪, 2022, 42(5): 132-141. | |
| 39 | Peng Y P. Functional study of HgS5 gene of salt stress response in Halogeton glomeratus. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2021. |
| 彭亚萍. 盐生草盐胁迫响应基因HgS5功能研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2021. | |
| 40 | Fu R, Zhang H Y, Liang X Y, et al. Physiological response of dandelion (Taraxacum mongolicum Hand.-Mazz. ) to single salt stress of NaCl and compound salt stress of seawater. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 52(2): 33-37. |
| 付娆, 张海洋, 梁晓艳, 等. 蒲公英对NaCl单盐和海水复合盐胁迫的生理响应. 山东农业科学, 2020, 52(2): 33-37. | |
| 41 | Xue T X, Ren Z B, Ren S F. Impacts of NaCl stress on physiological characteristics of Forsythia intermedia. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(11): 104-108. |
| 薛腾笑, 任子蓓, 任士福. NaCl胁迫对美国金钟连翘生理特性的影响. 江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(11): 104-108. | |
| 42 | Li Y X, Luo X L, Zhang T T, et al. Physiological changes and related gene expression analysis of Sesuvium portulacastrum under salt stress. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2022, 30(7): 1279-1289. |
| 李雨欣, 罗秀丽, 张婷婷, 等. 盐胁迫下海马齿生理指标变化及相关基因表达分析. 农业生物技术学报, 2022, 30(7): 1279-1289. | |
| 43 | Hao S H, Wang Y R, Yan Y X, et al. A review on plant responses to salt stress and their mechanisms of salt resistance. Horticulturae, 2021, 7(6): 132. |
| [1] | Yi WU, Ya-lan FENG, Tian-ning WANG, Ji-hao JU, Hui-shu XIAO, Chao MA, Jun ZHANG. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the Hsp70 gene family in wheat and its ancestral species [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(7): 53-67. |
| [2] | Hai-ming KONG, Jia-xing SONG, Jing YANG, Qian LI, Pei-zhi YANG, Yu-man CAO. Identification and transcript profiling of the CAMTA gene family under abiotic stress in alfalfa [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 143-154. |
| [3] | Meng WANG, Xue-li LU, Ju-ying WANG, Meng-chao ZHANG, Yi-ru SONG, Chen MENG, Li ZHANG, Zong-chang XU. Evaluation and screening of the salt tolerance of triticale germplasm at the germination and seedling stages [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 58-68. |
| [4] | Shang-qin HU, Jun-cheng WANG, Li-rong YAO, Er-jing SI, Xiao-le MA, Ke YANG, Hong ZHANG, Ya-xiong MENG, Hua-jun WANG, Bao-chun LI. Cloning and preliminary functional analysis of the root gene HgAKR6C of Halogeton glomeratus [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(1): 61-74. |
| [5] | Zhen-fen ZHANG, Rong HUANG, Xiang-yang LI, Bo YAO, Gui-qin ZHAO. Seed-borne bacterial diversity of oat and functional analysis based on Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 96-108. |
| [6] | Yan-lan ZHAO, Xin-yi ZENG, Jin-chao GONG, Xiang-jun LI, Xu-xu LI, Shan LIU, Xin-quan ZHANG, Ji-qiong ZHOU. Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the salt tolerance of Trifolium repens [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 179-188. |
| [7] | Chen MENG, Xue-li LU, Ju-ying WANG, Yun-chong WEI, Cheng-sheng ZHANG, Yi-qiang LI, Zong-chang XU. Effects of different salt stresses on triticale seed germination [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(12): 171-180. |
| [8] | Jiao-yun LU, Hong TIAN, He-shan ZHANG, Jun-bo XIONG, Yang LIU, Zhen-nan WANG. Effects of H2O2 immersion on seed germination and seedling growth of alfalfa under salt stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(10): 141-152. |
| [9] | Wen-hui XIE, Li-juan HUANG, Li-li ZHAO, Lei-ting WANG, Wen-wu ZHAO. Effects of calcium salt stress on seed germination and seedling physiological characteristics of three Pueraria lobata germplasm lines [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(7): 220-233. |
| [10] | Ya-nan LIU, Ren-jie YU, Yan-li GAO, Jun-mei KANG, Qing-chuan YANG, Zhi-hai WU, Zhen WANG. Expression pattern and biological functions of an annexin encoding gene MtANN2 in Medicago truncatula under salt stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(5): 124-134. |
| [11] | Zhi-heng WANG, Yu-qing WEI, Yan-rong ZHAO, Yue-juan WANG. A transcriptomic study of physiological responses to drought and salt stress in sweet sorghum seedlings [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 71-84. |
| [12] | Qian CHEN, Xiao-yun XU, Jun-cheng WANG, Li-rong YAO, Er-jing SI, Ke YANG, Xiao-ling WEI, Xiao-le MA, Bao-chun LI, Xun-wu SHANG, Ya-xiong MENG, Hua-jun WANG. Identification of a WRKY gene family based on full-length transcriptome sequences and analysis of response patterns under salt stress in Halogeton glomeratus [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(12): 146-157. |
| [13] | Na-na LI, Tong-ge LIU, Zhi-hui HUANG, Bao-jiang ZHENG, Yu-hong ZHANG. Physiological ecological and secondary metabolic responses of the herbaceous resource plant Thlaspi arvense to salt stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(11): 181-190. |
| [14] | Peng ZHANG, Xi REN, Si-yu MENG, Xiao-xing WEI, Gen-sheng BAO. Effects of Epichloё endophyte on seed germination and seedling growth of Stipa purpurea under salt stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 110-121. |
| [15] | An-qiao LU, Feng-ju ZHANG, Xing XU, Xue-qin WANG, Shan YAO. Effects of salt stress on growth and physiological characteristics of Echinochloa frumentacea seedlings [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(5): 84-93. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||