
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 80-93.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024093
Previous Articles Next Articles
Wen-qi CAI1( ), Shu-xia LI1,2,3(
), Shu-xia LI1,2,3( ), Xiao-tong WANG1, Wen-xue SONG1, Xu-xia MA1, Xiao-mei MA1, Xiao-hong LI1, Xin-yao DAI1
), Xiao-tong WANG1, Wen-xue SONG1, Xu-xia MA1, Xiao-mei MA1, Xiao-hong LI1, Xin-yao DAI1
Received:2024-03-25
Revised:2024-04-26
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Shu-xia LI
Wen-qi CAI, Shu-xia LI, Xiao-tong WANG, Wen-xue SONG, Xu-xia MA, Xiao-mei MA, Xiao-hong LI, Xin-yao DAI. Effects of interaction between exogenous melatonin and ethylene on the growth and physiological characteristics of Medicago sativa seedlings under salt stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(1): 80-93.
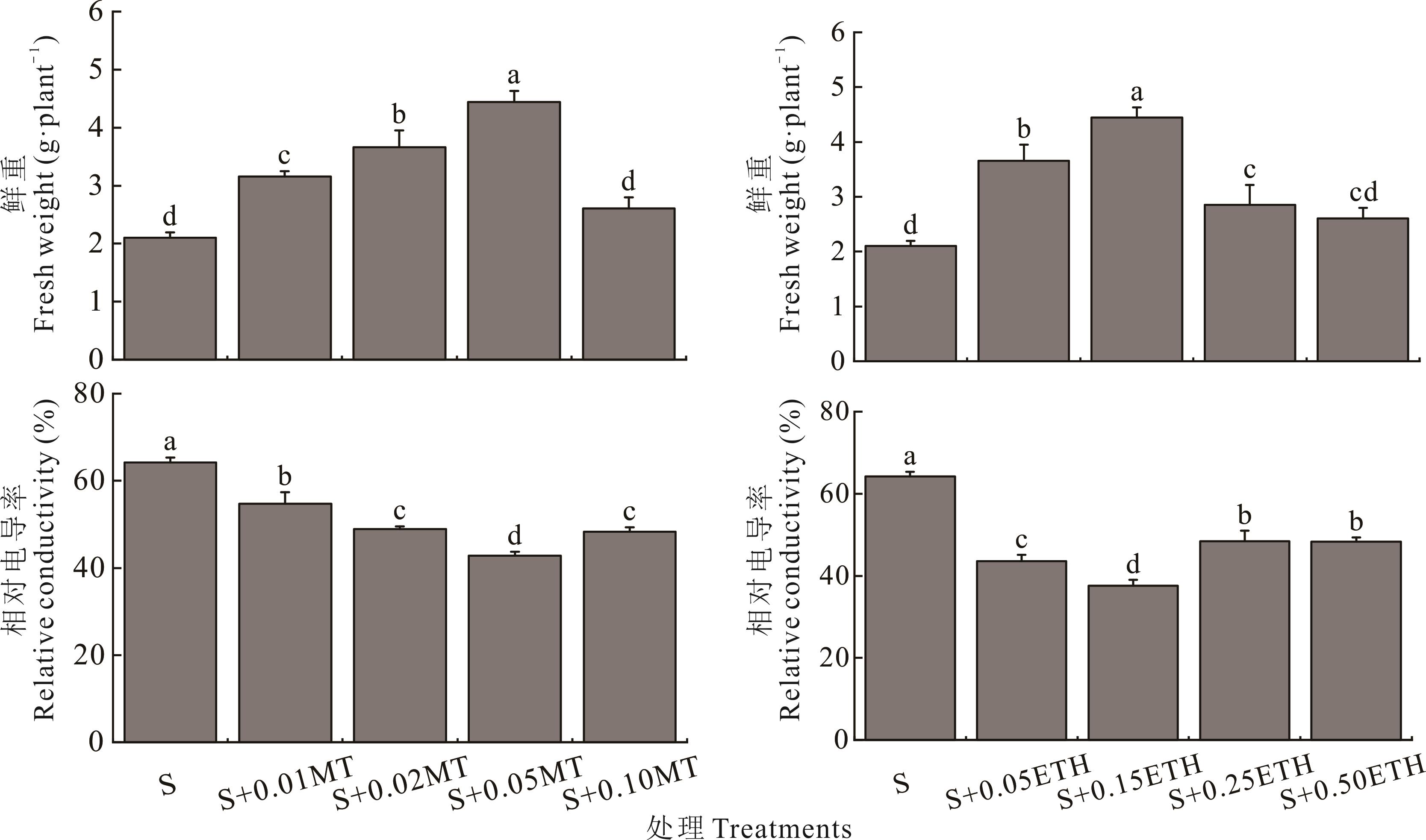
Fig.2 Effects of different concentrations of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) on fresh weight and relative conductivity of alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
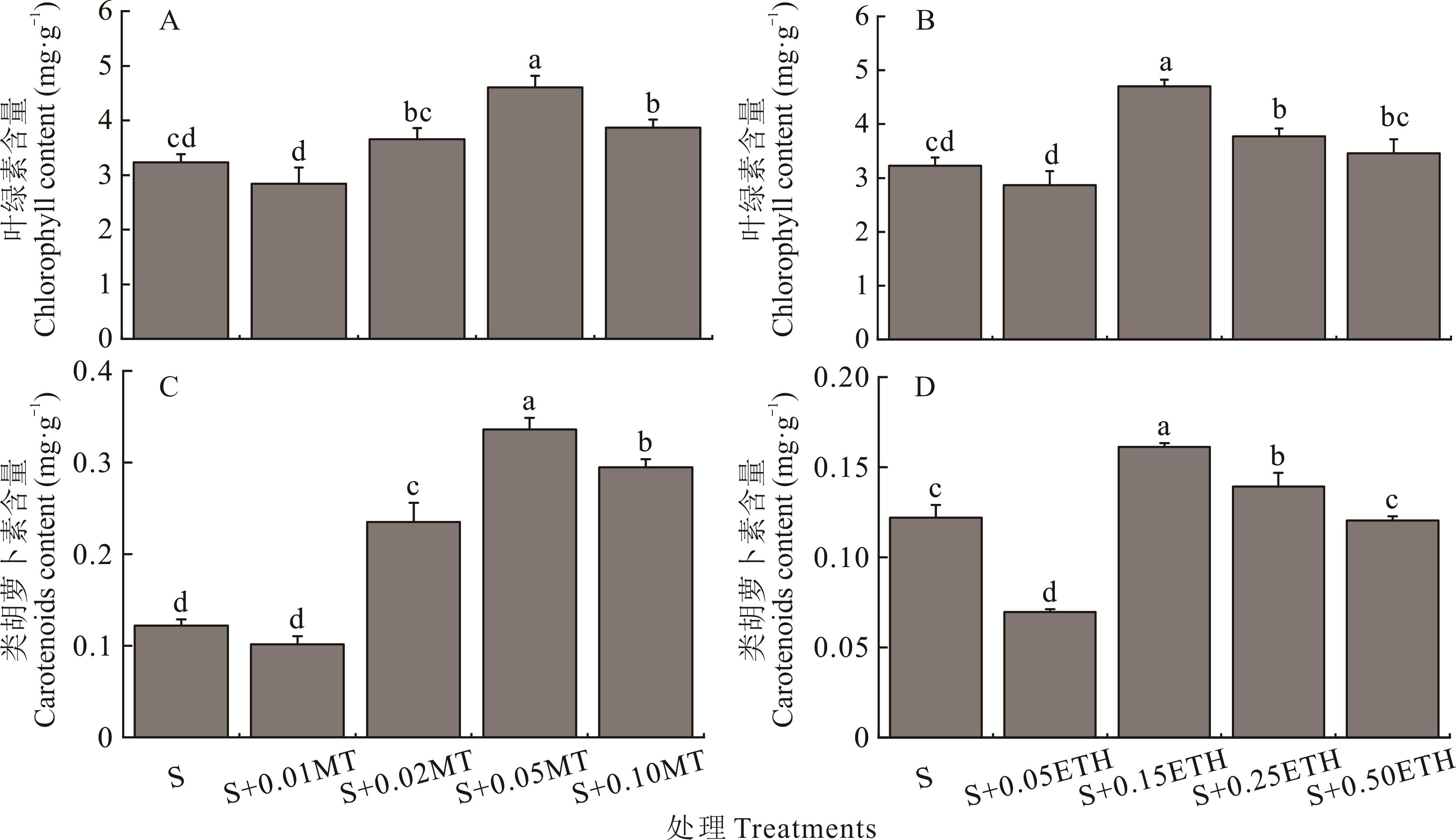
Fig.3 Effects of different concentrations of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) on the photosynthetic pigment content of alfalfa seedlings under salt stress

Fig.4 Effects of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) interaction on phenotype, plant height, leaf area and fresh weight of alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
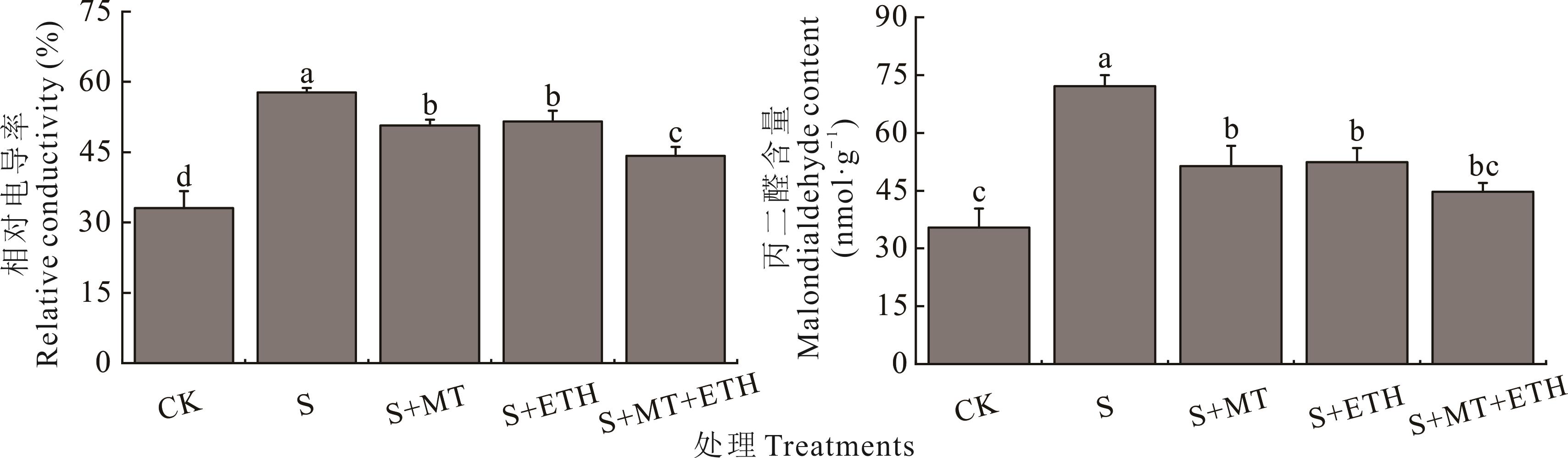
Fig.6 Effects of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) interaction on relative conductivity and malondialdehyde content in alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
| 项目Item | CK | S | S+MT | S+ETH | S+MT+ETH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ (mg·g-1) | 19.01±0.58d | 76.32±2.76a | 52.01±0.40b | 49.60±1.75b | 34.48±1.09c |
| K+ (mg·g-1) | 42.03±0.96a | 29.22±1.24d | 32.64±1.25cd | 36.69±0.72bc | 39.99±0.29ab |
| K+/Na+ | 2.22±0.11a | 0.40±0.02c | 0.59±0.04c | 0.69±0.07bc | 1.27±0.28b |
Table 1 Effects of melatonin (MT) and ethephon (ETH) interaction on Na+ and K+ content in alfalfa seedlings under salt stress
| 项目Item | CK | S | S+MT | S+ETH | S+MT+ETH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ (mg·g-1) | 19.01±0.58d | 76.32±2.76a | 52.01±0.40b | 49.60±1.75b | 34.48±1.09c |
| K+ (mg·g-1) | 42.03±0.96a | 29.22±1.24d | 32.64±1.25cd | 36.69±0.72bc | 39.99±0.29ab |
| K+/Na+ | 2.22±0.11a | 0.40±0.02c | 0.59±0.04c | 0.69±0.07bc | 1.27±0.28b |
| 1 | Zhao L J, Ma D M, Wang W J, et al. Effect of exogenous melatonin on antioxidant capacity and photosynthetic efficiency of alfalfa seedlings under salt stress. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2021, 41(8): 1355-1363. |
| 赵丽娟, 麻冬梅, 王文静, 等. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗抗氧化能力以及光合作用效率的影响. 西北植物学报, 2021, 41(8): 1355-1363. | |
| 2 | Yu H R, Jia Y S, Jia P F, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of growth, yield and quality of alfalfa in different saline-alkali soil. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(4): 143-149. |
| 于浩然, 贾玉山, 贾鹏飞, 等. 不同盐碱度对紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(4): 143-149. | |
| 3 | Wang Y, Yu R N, Ma X S, et al. Effects of ethylene on seed germination and seedling growth under salt stress in Medicago sativa. Journal of Inner Mongolia University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 52(1): 59-69. |
| 王月, 于若男, 马雪松, 等. 乙烯对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(1): 59-69. | |
| 4 | Zhang L S, Sun Y G, Ji J Q, et al. Flavonol synthase gene MsFLS13 regulates saline-alkali stress tolerance in alfalfa. The Crop Journal, 2023, 11(4): 1218-1229. |
| 5 | Jin M Y, Li X H, Li F Z, et al. Effects of mixed saline-alkali stress on germination of rice. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(4): 566-574. |
| 金梦野, 李小华, 李昉泽, 等. 盐碱复合胁迫对水稻种子发芽的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(4): 566-574. | |
| 6 | Tan Y, Yin H. Effects of root application of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and melatonin on the growth, photosynthetic characteristics, and antioxidant system of Medicago sativa under salt stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. |
| 谭英, 尹豪. 盐胁迫下根施AMF和褪黑素对紫花苜蓿生长、光合特征以及抗氧化系统的影响. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. | |
| 7 | Feng L C, Li Q, Zhou D Q, et al. B. subtilis CNBG-PGPR-1 induces methionine to regulate ethylene pathway and ROS scavenging for improving salt tolerance of tomato. The Plant Journal, 2023, 117(1): 193-211. |
| 8 | Yang H B, Yang S P. Effects of ABA and ethephon on salt tolerance of buckwheat seedlings. Journal of Jilin Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 39(1): 13-15, 29. |
| 杨洪兵, 杨世平. ABA和乙烯利对荞麦幼苗耐盐性的效应. 吉林农业科学, 2014, 39(1): 13-15, 29. | |
| 9 | Yuan R M, Peng J, Wang J A, et al. Melatonin regulates salicylic acid and ethylene metabolism to maintain shaguo quality during storage. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 37(9): 1798-1805. |
| 袁瑞敏, 彭静, 王佳傲, 等. 褪黑素调控水杨酸和乙烯代谢维持沙果贮藏品质. 核农学报, 2023, 37(9): 1798-1805. | |
| 10 | Lin Y H. Study on the growth, accumulation and distribution of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrients in Lanzhou edible lily. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019(12): 8-18. |
| 林玉红. 兰州食用百合生长发育及氮磷钾素养分吸收累积与分配规律研究. 甘肃农业科技, 2019(12): 8-18. | |
| 11 | Zhao F M. The mechanism of RhELIP3 and RhHY5 improving leaf freezing tolerance in the evergreen azalea. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2023. |
| 赵芳梦. 常绿杜鹃花RhELIP3和RhHY5提高叶片耐寒性的机制研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2023. | |
| 12 | Zhou H P, Shi H F, Yang Y Q, et al. Insights into plant salt stress signaling and tolerance. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2023, 51(1): 16-34. |
| 13 | Michard E, Simon A A. Melatonin’s antioxidant properties protect plants under salt stress. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2020, 43(11): 2587-2590. |
| 14 | Waadt R, Seller C A, Hsu P, et al. Plant hormone regulation of abiotic stress responses. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2022, 23(10): 680-694. |
| 15 | Zhao D H. Effects of exogenous abscisic acid and melatonin on physiological characteristics of alfalfa under salt stress. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2023. |
| 赵东豪. 外源脱落酸和褪黑素对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿生理特性的影响. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2023. | |
| 16 | Wang Y. Effects of ethylene on Madicago sativa L. seed germination and seedling growth under salt stress and investigation on the mechanism. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2019. |
| 王月. 乙烯对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响及其机制的研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2019. | |
| 17 | Xia J, Nan L L, Chen J, et al. Effects of low phosphorus stress on photosynthetic and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of alfalfa with different root types. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2024, 42(1): 169-176. |
| 夏静, 南丽丽, 陈洁, 等. 低磷胁迫对不同根型苜蓿光合及叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2024, 42(1): 169-176. | |
| 18 | Ma Y Y, Li G, He W, et al. Mitigating effects of exogenous melatonin on the physiological characteristics of strawberry seedlings under NaCl stress. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(10): 2486-2495. |
| 马媛媛, 李刚, 何旺, 等. 外源褪黑素对NaCl胁迫下草莓幼苗生理特性的缓解效应. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(10): 2486-2495. | |
| 19 | Sun H R, Sun M. Study on physiological response and salt tolerance of different parthenocissus plants. Journal of Zhongzhou University, 2019, 36(5): 114-118. |
| 孙浩冉, 孙淼. 盐胁迫下不同地锦属植物的生理响应及耐盐性研究. 中州大学学报, 2019, 36(5): 114-118. | |
| 20 | Li B F, Du H M. The effects of melation seed soak on growth of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne). Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2018, 36(4): 30-34, 40. |
| 李本峰, 杜红梅. 褪黑素浸种对多年生黑麦草种子发芽和幼苗生长的初步研究. 上海交通大学学报, 2018, 36(4): 30-34, 40. | |
| 21 | Li J C, Zhang Z W, Zhang J H, et al. The effect of spraying ethephon on low temperature stress in Zoysia japonica. Pratacultural Science, 2023, 40(12): 3000-3008. |
| 李进超, 张智韦, 张嘉航, 等. 乙烯利对结缕草响应低温胁迫的作用. 草业科学, 2023, 40(12): 3000-3008. | |
| 22 | Wang P T, Liu W C, Han C, et al. Reactive oxygen species: multidimensional regulators of plant adaptation to abiotic stress and development. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2023, 66(3): 330-367. |
| 23 | Wang J, Fu B Z, Li S X, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on growth and physiological characteristics of Agropyron mongolicum seedlings under drought stress. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(11): 2947-2957. |
| 王晶, 伏兵哲, 李淑霞, 等. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下沙芦草幼苗生长和生理特性的影响. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(11): 2947-2957. | |
| 24 | Hou W J, Ma D M, Zhang L, et al. Modulation of salt tolerance in Echinochloa frumentacea by foliar spraying of epibrassinolide. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2024, 44(4): 517-528. |
| 侯汶君, 麻冬梅, 张玲, 等. 叶面喷施表油菜素内酯对湖南稷子耐盐性的调控作用. 西北植物学报, 2024, 44(4): 517-528. | |
| 25 | Gao L Y, Liu B, Zhang R, et al. Effects of different concentrations of melatonin on photosynthetic and physiological characteristics of Malus halliana Koehne under saline-alkali stress. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2020, 55(2): 90-97. |
| 高立杨, 刘兵, 张瑞, 等. 褪黑素对盐碱复合胁迫下垂丝海棠光合及生理特性的影响. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2020, 55(2): 90-97. | |
| 26 | Ma P T, Su S P, Li Y, et al. Effects of exogenous proline on osmotic adjustment and antioxidant enzymes in the leaves of Nitraria tangutorum under natural drought. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2020, 55(4): 121-127, 136. |
| 马鹏图, 苏世平, 李毅, 等. 外源脯氨酸对自然干旱下白刺叶片渗透调节与抗氧化酶活性的影响. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2020, 55(4): 121-127, 136. | |
| 27 | Wang Y, Hou Y Y, Ma Y Q, et al. Effect of glycine betaine treatment on chilling injury and ascorbic acid-glutathione cycle metabolism in peach fruit. Food Science, 2021, 42(13): 158-165. |
| 王懿, 侯媛媛, 马钰晴, 等. 甘氨酸甜菜碱处理对桃果实冷害及抗坏血酸-谷胱甘肽循环代谢的影响. 食品科学, 2021, 42(13): 158-165. | |
| 28 | Wang X. The physiological response of the antioxidant system in Leymus chinensis to different alkali-saline stress. Changchun: Jilin University, 2015. |
| 王鑫. 羊草抗氧化系统对盐碱胁迫的响应特征. 长春: 吉林大学, 2015. | |
| 29 | Yan Z M, Sun J, Guo S R, et al. Effects of exogenous proline on the ascorbate-glutathione cycle in roots of Cucumis melo seedlings under salt stress. Plant Science Journal, 2014, 32(5): 502-508. |
| 颜志明, 孙锦, 郭世荣, 等. 外源脯氨酸对盐胁迫下甜瓜幼苗根系抗坏血酸-谷胱甘肽循环的影响. 植物科学学报, 2014, 32(5): 502-508. | |
| 30 | Li C Z Y. Effects of exogenous melatonin and ascorbic acid on physiological characteristics of apple rootstock M9T337 under NaCl stress. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2020. |
| 李晨智宇. 外源褪黑素和抗坏血酸对NaCl胁迫下苹果砧木M9T337生理特性的影响. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2020. | |
| 31 | Wei H J, He W Y, Wang Y, et al. The effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and melatonin on the heat tolerance of perennial ryegrass. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(12): 126-138. |
| 卫宏健, 贺文员, 王越, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌与褪黑素对多年生黑麦草耐热性的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 126-138. | |
| 32 | Ma X Y, Song C, Meng Y J, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on germination, antioxidant enzyme activity, and osmotic adjustment substance content of cotton seed under cadmium stress. Cotton Science, 2023, 35(4): 313-324. |
| 马鑫颖, 宋晨, 孟妍君, 等. 外源褪黑素对镉胁迫下棉花种子萌发、抗氧化酶活性及渗透调节物质含量的影响. 棉花学报, 2023, 35(4): 313-324. | |
| 33 | Gustavo C, Jessica M I, Alicia G, et al. Involvement of ethylene receptors in the salt tolerance response of Cucurbita pepo. Horticulture Research, 2021, 8(1): 73. |
| 34 | Wu C G, Zhang M, Liang Y F, et al. Salt stress responses in foxtail millet: Physiological and molecular regulation. The Crop Journal, 2023, 11(4): 1011-1021. |
| 35 | Sun Z J, Li J Y, Guo D M, et al. Melatonin enhances KCl salinity tolerance by maintaining K+ homeostasis in Malus hupehensis. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2023, 21(11): 2273-2290. |
| 36 | Bian F E, Xiao Q H, Hao G M, et al. Effects of root-applied melatonin on endogenous melatonin and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics in grapevine under NaCl stress. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(5): 952-963. |
| 卞凤娥, 肖秋红, 郝桂梅, 等. 根施褪黑素对NaCl胁迫下葡萄内源褪黑素及叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 中国农业科学, 2018, 51(5): 952-963. | |
| 37 | Hu X. Study on the effect of ethylene on fruit abscission in Camellia oleifera. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2021. |
| 胡潇. 乙烯对油茶果实脱落的影响研究. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2021. |
| [1] | Zhen-huan ZHANG, Li-rong YAO, Jun-cheng WANG, Er-jing SI, Hong ZHANG, Ke YANG, Xiao-le MA, Ya-xiong MENG, Hua-jun WANG, Bao-chun LI. Identification of AKR gene family members in Halogeton glomeratus and salt tolerance analysis of the root salt stress response gene HgAKR42639 [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(7): 68-83. |
| [2] | Wen-wen QI, Hong-yuan MA, Ya-xiao LI, Yan DU, Meng-dan SUN, Hai-tao WU. Progress in research on breeding methods to produce new, high-quality forage varieties [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(6): 187-202. |
| [3] | Ying TAN, Hao YIN. Effects of root application of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and melatonin on the growth, photosynthetic characteristics, and antioxidant system of Medicago sativa under salt stresss [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. |
| [4] | Meng WANG, Xue-li LU, Ju-ying WANG, Meng-chao ZHANG, Yi-ru SONG, Chen MENG, Li ZHANG, Zong-chang XU. Evaluation and screening of the salt tolerance of triticale germplasm at the germination and seedling stages [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 58-68. |
| [5] | Ying LUO, Cong LI, Pei WANG, Li-hua TIAN, Hui WANG, Qing-ping ZHOU, Ying-xia LEI. Responses of different oat cultivars to low-nitrogen stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(2): 164-184. |
| [6] | Abudilimu YUERENSA·, Wei ZHAO, Xiao-wei WANG, Yan HUANG, Ai-qin ZHNAG. Ovule development before and after fertilization and seed formation dynamics of Medicago sativa cv. Xinmu No.4 [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(12): 111-121. |
| [7] | Ze-bin LI, Yong-zheng QIU, Yan-jie LIU, Jin-qiu YU, Bai-ji WANG, Qian-ning LIU, Yue WANG, Guo-wen CUI. Identification of the BZR gene family in alfalfa and analysis of its transcriptional responses to abiotic stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(11): 106-122. |
| [8] | Yu-xin WANG, Jia-li TAO, Hui-sen ZHU, Tao XU, Yi-fei ZHANG, Hui-fang CEN. Heterologous expression of miR397-5p from Medicago sativa cv. ‘Pianguan’ improves the drought tolerance of tobacco [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(11): 123-134. |
| [9] | Zheng WANG, Xin LI, Jian-gui ZHANG, Ji-kuan CHAI, Gui-qin ZHAO, Kui-ju NIU. Exogenous melatonin mediates the antioxidant system and phenylpropanoid metabolism to induce resistance to leaf spot disease in oat [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(10): 135-146. |
| [10] | Xin-yue ZHOU, Qing-xue JIANG, Hui-li JIA, Lin MA, Lu FAN, Xue-min WANG. Cloning and salt-tolerance functional analysis of alfalfa MsBBX20 gene [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(10): 55-73. |
| [11] | Xu-qin BAI, Chun-yun JIA, Wen-shuan LI, Ya-min LI, Chang-feng LIU, Xiu-yun HAN, Mei-han CHU, Zong-qiang GONG, Xiao-jun LI. An investigation of foliar spraying of selenium fertilizer for selenium enrichment and cadmium reduction in alfalfa [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(1): 50-60. |
| [12] | Ying JIANG, Hui-hong ZHANG, Chang WEI, Zheng-yang XU, Ying ZHAO, Fang LIU, Ge-zi LI, Xue-hai ZHANG, Hai-tao LIU. Effects of exogenous melatonin on root development and physiological and biochemical characteristics of maize seedlings under drought stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(9): 143-159. |
| [13] | Jia LIANG, Zhao-yang HU, Zhi-ming XIE, Liu-feng MA, Yun CHEN, Zhi-gang FANG. Exogenous melatonin alleviates the physiological effects of drought stress in sweet sorghum seedlings [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 206-215. |
| [14] | Chao-nan LI, Lei WANG, Ji-qiang ZHOU, Chang-xing ZHAO, Xiao-rong XIE, Jin-rong LIU. Effect of microplastics on the growth and physiological characteristics of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(5): 138-146. |
| [15] | Zheng TIAN, Zheng-yu YANG, Zhong-jie LU, Ben LUO, Mao ZHANG, Rui DONG. Acid-aluminum adaptability and tolerance evaluation of 44 alfalfa cultivars [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 142-151. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||