

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 27-38.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020471
收稿日期:2020-10-20
修回日期:2021-01-27
出版日期:2021-11-11
发布日期:2021-11-11
通讯作者:
顾润源
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: gry0202@sina.com基金资助:
Wen-hui GUO( ), Run-yuan GU(
), Run-yuan GU( ), Feng DING
), Feng DING
Received:2020-10-20
Revised:2021-01-27
Online:2021-11-11
Published:2021-11-11
Contact:
Run-yuan GU
摘要:
基于2000-2015年山东省对蒲公英和车前草物候及气象观测资料,利用正交经验函数、相关分析、偏最小二乘回归研究了蒲公英及车前草在山东境内的春季物候变化特征及其对气候变化的响应规律。结果表明:1)2000-2015年蒲公英与车前草春季萌动与展叶总体表现为推迟的趋势且半岛沿海站点表现更明显,开花始期的年际变化具有局地性。2)冬季平均气温、2月平均气温升高会极显著促进两种植物的萌动、展叶。1月累积降水量与两种植物的萌动、展叶、开花始期总体显著负相关。鲁东地区两种草本植物的萌动、展叶与冬季日照时长显著负相关。在开花始期,除了冬季热量累积之外,从鲁东到鲁西3月平均气温及活动积温的影响逐渐加强,车前草表现更为明显。3)蒲公英与车前草偏最小二乘物候回归模型拟合结果表明,在萌动、展叶始期,2月平均气温、冬季平均气温、冬季0 cm平均地表温度、冬季正积温VIP值均大于1。在开花始期, 3月平均气温、3月活动积温、冬季平均气温、冬季0 cm平均地表温度在所有地区VIP值均大于1。
郭文慧, 顾润源, 丁锋. 蒲公英和车前草在山东境内的春季物候特征及对气候变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 27-38.
Wen-hui GUO, Run-yuan GU, Feng DING. Spring phenological characteristics of dandelion and plantain in Shandong Province and their responses to climate change[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(12): 27-38.
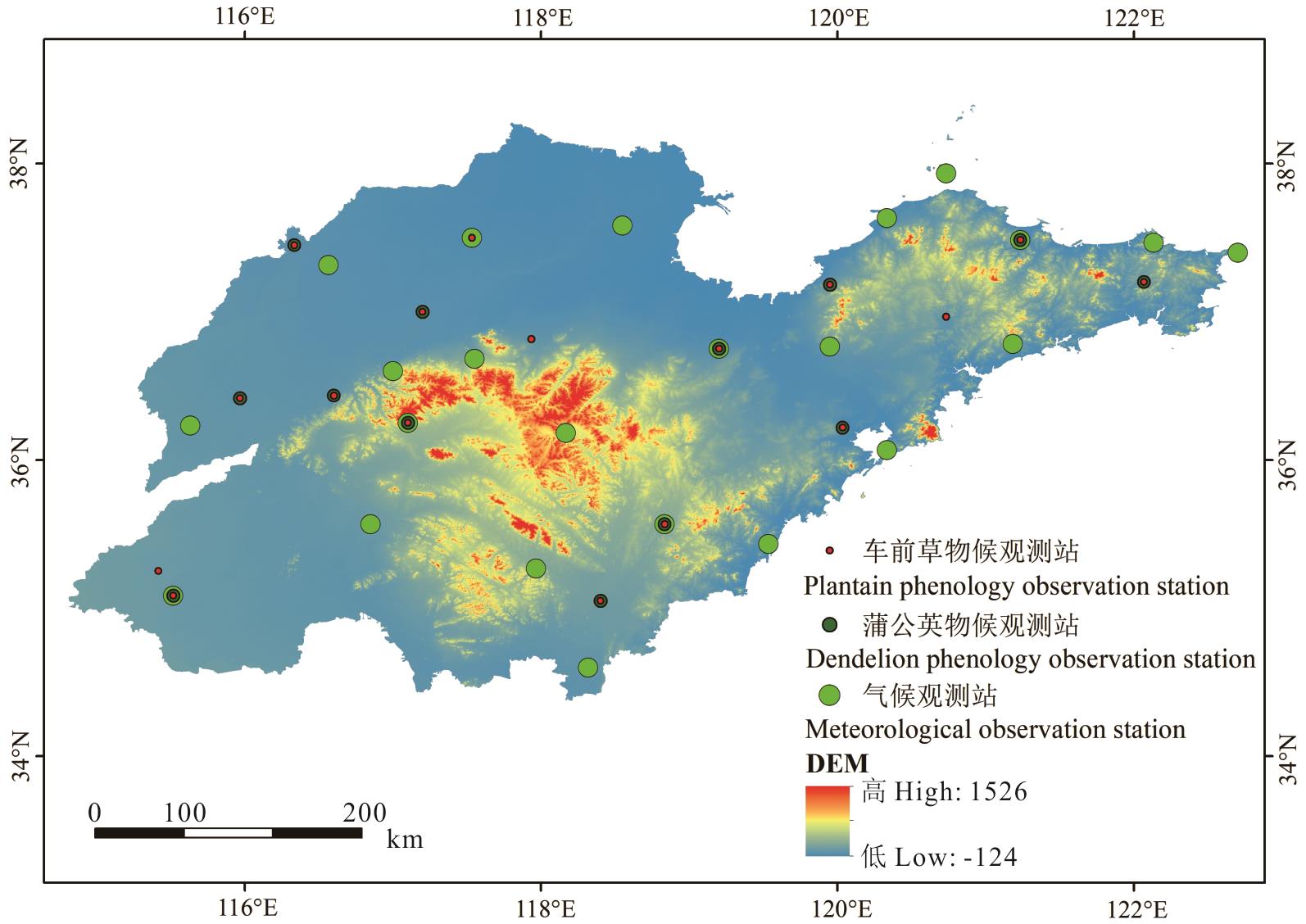
图1 山东地面高程及气象、物候观测站分布
Fig.1 Digital elevation map and the distribution of meteorological and phenological observation stations of the Shandong Province
分区 Partition | 站点 Station | 观测时间 Observation time | 蒲公英Dandelion | 车前草Plantain | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
萌动期 Germination period | 展叶始期 Early leaf expansion period | 开花始期 Early florescence period | 萌动期 Germination period | 展叶始期 Early leaf expansion period | 开花始期 Early florescence period | |||
鲁西 Western Shandong | 惠民Huimin | 1985-2015 | - | - | - | 73±14 | 78±15 | 119±16 |
| 德州Dezhou | 1985-2015 | 65±15 | 72±12 | 83±22 | 67±12 | 73±13 | 131±39 | |
| 菏泽Heze | 1991-2015 | - | - | - | 49±17 | 63±16 | 103±12 | |
| 曹县Caoxian | 1991-2015 | 55±15 | 61±13 | 78±18 | 56±16 | 63±15 | 127±18 | |
| 聊城Liaocheng | 2000-2015 | 68±22 | 75±23 | 93±17 | 65±14 | 77±19 | 102±14 | |
鲁中 Central Shandong | 潍坊Weifang | 1985-2015 | 78±13 | 83±13 | 107±17 | - | - | - |
| 泰安Taian | 1989-2015 | 44±13 | 53±15 | 86±15 | - | - | - | |
| 莒县Juxian | 1991-2015 | 51±17 | 61±17 | 85±24 | 55±19 | 64±16 | 111±12 | |
| 济宁Jining | 2000-2015 | 47±12 | 55±13 | 74±14 | 52±15 | 59±14 | 95±13 | |
| 济阳Jiyang | 1990-2015 | 71±14 | 76±16 | 97±13 | 69±14 | 75±15 | 108±11 | |
| 淄博Zibo | 1988-2015 | - | - | - | 67±23 | 70±22 | 113±19 | |
| 临沂Linyi | 1986-2015 | 48±16 | 57±16 | 91±19 | 60±20 | 70±14 | 116±13 | |
| 莱州Laizhou | 1990-2015 | 67±19 | 75±19 | 92±14 | 69±19 | 75±19 | 113±21 | |
鲁东 Eastern Shandong | 文登Wendeng | 1985-2015 | 67±14 | 74±15 | 103±13 | - | - | - |
| 莱阳Laiyang | 1994-2015 | - | - | - | 69±10 | 73±13 | 129±8 | |
| 胶州Jiaozhou | 1987-2015 | 72±13 | 81±13 | 105±21 | 77±15 | 82±14 | 132±23 | |
| 福山Fushan | 1994-2015 | 62±16 | 72±22 | 93±21 | 67±17 | 77±17 | 122±19 | |
表1 蒲公英与车前草物候观测站基本情况
Table1 The basic matter of dandelion and plantain phenology observation station (d)
分区 Partition | 站点 Station | 观测时间 Observation time | 蒲公英Dandelion | 车前草Plantain | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
萌动期 Germination period | 展叶始期 Early leaf expansion period | 开花始期 Early florescence period | 萌动期 Germination period | 展叶始期 Early leaf expansion period | 开花始期 Early florescence period | |||
鲁西 Western Shandong | 惠民Huimin | 1985-2015 | - | - | - | 73±14 | 78±15 | 119±16 |
| 德州Dezhou | 1985-2015 | 65±15 | 72±12 | 83±22 | 67±12 | 73±13 | 131±39 | |
| 菏泽Heze | 1991-2015 | - | - | - | 49±17 | 63±16 | 103±12 | |
| 曹县Caoxian | 1991-2015 | 55±15 | 61±13 | 78±18 | 56±16 | 63±15 | 127±18 | |
| 聊城Liaocheng | 2000-2015 | 68±22 | 75±23 | 93±17 | 65±14 | 77±19 | 102±14 | |
鲁中 Central Shandong | 潍坊Weifang | 1985-2015 | 78±13 | 83±13 | 107±17 | - | - | - |
| 泰安Taian | 1989-2015 | 44±13 | 53±15 | 86±15 | - | - | - | |
| 莒县Juxian | 1991-2015 | 51±17 | 61±17 | 85±24 | 55±19 | 64±16 | 111±12 | |
| 济宁Jining | 2000-2015 | 47±12 | 55±13 | 74±14 | 52±15 | 59±14 | 95±13 | |
| 济阳Jiyang | 1990-2015 | 71±14 | 76±16 | 97±13 | 69±14 | 75±15 | 108±11 | |
| 淄博Zibo | 1988-2015 | - | - | - | 67±23 | 70±22 | 113±19 | |
| 临沂Linyi | 1986-2015 | 48±16 | 57±16 | 91±19 | 60±20 | 70±14 | 116±13 | |
| 莱州Laizhou | 1990-2015 | 67±19 | 75±19 | 92±14 | 69±19 | 75±19 | 113±21 | |
鲁东 Eastern Shandong | 文登Wendeng | 1985-2015 | 67±14 | 74±15 | 103±13 | - | - | - |
| 莱阳Laiyang | 1994-2015 | - | - | - | 69±10 | 73±13 | 129±8 | |
| 胶州Jiaozhou | 1987-2015 | 72±13 | 81±13 | 105±21 | 77±15 | 82±14 | 132±23 | |
| 福山Fushan | 1994-2015 | 62±16 | 72±22 | 93±21 | 67±17 | 77±17 | 122±19 | |
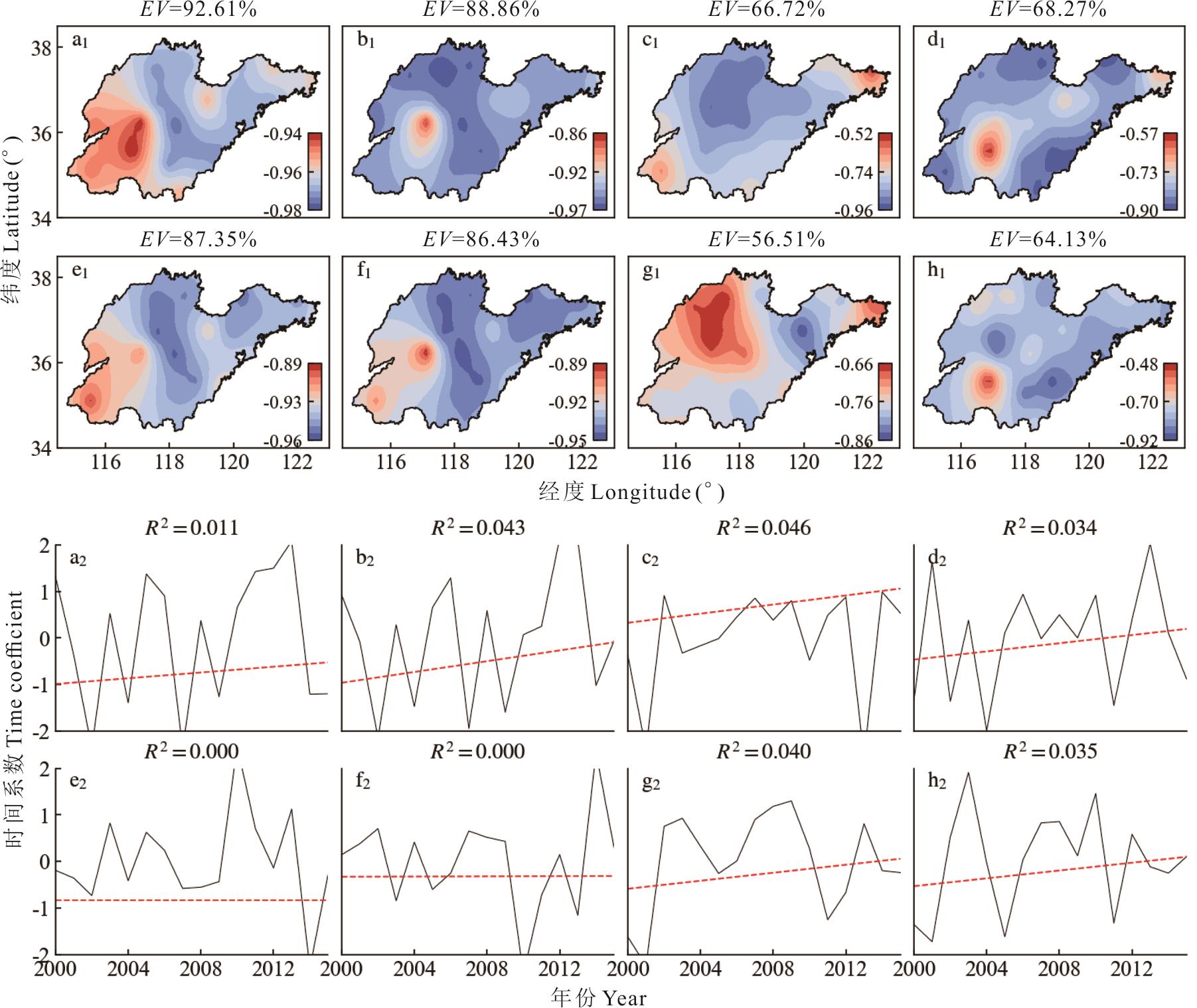
图2 2000-2015年山东省气象要素EOF-1模态EV: 各气象要素的EOF第1模态方差贡献率The contribution rate of the first mode variance of EOF; a: 冬季平均气温Average temperature in winter; b: 冬季正积温Winter cumulative positive temperature; c: 冬季累积降水量Accumulated precipitation in winter; d: 冬季日照时长Sunlight hours in winter; e: 春季平均气温Average temperature in spring; f: 春季正积温Positive accumulated temperature in spring; g: 春季累积降水量Accumulated precipitation in spring; h: 春季日照时长Sunlight hours in spring.
Fig.2 Meteorological factor EOF-1 modality of Shandong Province from 2000 to 2015
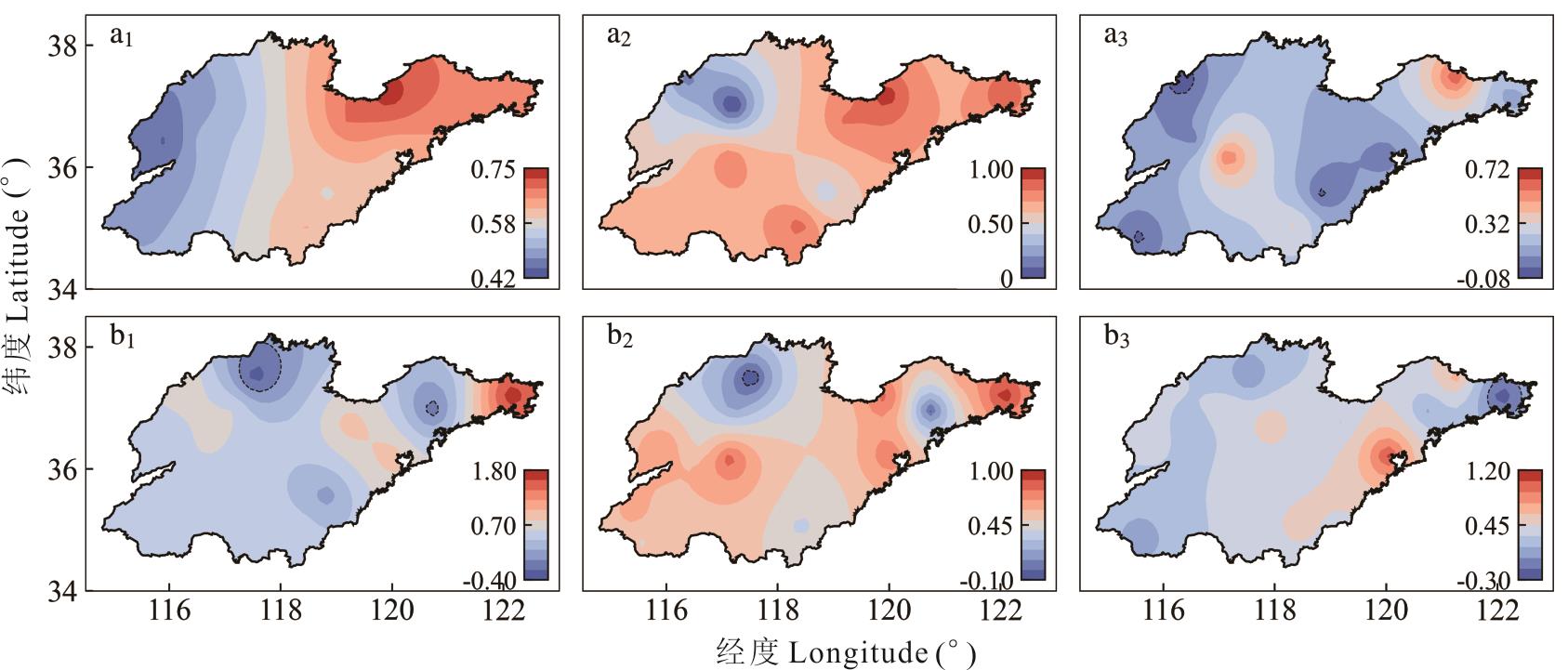
图3 2000-2015年蒲公英与车前草春季物候年际变化趋势a1: 蒲公英萌动期Dandelion germination period; a2: 蒲公英展叶始期Dandelion early leaf expansion period; a3: 蒲公英开花始期Dandelion early florescence period; b1:车前草萌动期Plantain germination period; b2: 车前草展叶始期Plantain early leaf expansion period; b3: 车前草开花始期Plantain early florescence period;图中不同颜色代表年际变化率The different colors represent the rate of interannual variation (d·a-1).
Fig.3 Interannual variation trend of spring phenological of dandelion and plantain from 2000 to 2015
生育期 Growth period | 气象要素 Meteorological factor | 鲁东Eastern Shandong | 鲁中Central Shandong | 鲁西Western Shandong | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蒲公英Dandelion | 车前草Plantain | 蒲公英Dandelion | 车前草Plantain | 蒲公英Dandelion | 车前草Plantain | ||
萌动期 Germination period | x1 | -0.331 | -0.441* | -0.450* | -0.468* | -0.385* | -0.630** |
| x2 | -0.714** | -0.712** | -0.717** | -0.788** | -0.569** | -0.831** | |
| x6 | -0.658** | -0.642** | -0.605** | -0.743** | -0.466* | -0.668** | |
| x7 | -0.817** | -0.735** | -0.632** | -0.738** | -0.685** | -0.745** | |
| x8 | -0.530* | -0.383 | -0.128 | -0.001 | -0.260 | 0.047 | |
| x9 | -0.713** | -0.706** | -0.568** | -0.666** | -0.624** | -0.764** | |
展叶始期 Early leaf expansion period | x1 | -0.302 | -0.455* | -0.445* | -0.414* | -0.376 | -0.613** |
| x2 | -0.692** | -0.745** | -0.778** | -0.803** | -0.370 | -0.756** | |
| x6 | -0.614** | -0.676** | -0.703** | -0.747** | -0.311 | -0.746** | |
| x7 | -0.772** | -0.823** | -0.684** | -0.762** | -0.562** | -0.769** | |
| x8 | -0.598** | -0.497* | 0.096 | 0.010 | -0.216 | 0.135 | |
| x9 | -0.744** | -0.724** | -0.657** | -0.728** | -0.480* | -0.760** | |
开花始期 Early florescence period | x1 | -0.407 | -0.449* | -0.476* | -0.102 | -0.322 | -0.353 |
| x2 | -0.644** | -0.598** | -0.518** | -0.353 | -0.448* | -0.444* | |
| x3 | -0.718** | -0.571** | -0.753** | -0.732** | -0.670** | -0.600** | |
| x4 | -0.556** | -0.460* | -0.788** | -0.626** | -0.606** | -0.657** | |
| x5 | -0.074 | 0.041 | 0.205 | 0.401* | 0.133 | -0.086 | |
| x6 | -0.792** | -0.597** | -0.595** | -0.339 | -0.671** | -0.630** | |
| x7 | -0.706** | -0.677** | -0.570** | -0.430* | -0.585** | -0.425 | |
| x9 | -0.727** | -0.565** | -0.506** | -0.492* | -0.567** | -0.377 | |
表2 春季物候期与气象要素的相关系数(2000-2015)
Table 2 The correlation coefficient between spring phenological period and meteorological factors (2000-2015 )
生育期 Growth period | 气象要素 Meteorological factor | 鲁东Eastern Shandong | 鲁中Central Shandong | 鲁西Western Shandong | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蒲公英Dandelion | 车前草Plantain | 蒲公英Dandelion | 车前草Plantain | 蒲公英Dandelion | 车前草Plantain | ||
萌动期 Germination period | x1 | -0.331 | -0.441* | -0.450* | -0.468* | -0.385* | -0.630** |
| x2 | -0.714** | -0.712** | -0.717** | -0.788** | -0.569** | -0.831** | |
| x6 | -0.658** | -0.642** | -0.605** | -0.743** | -0.466* | -0.668** | |
| x7 | -0.817** | -0.735** | -0.632** | -0.738** | -0.685** | -0.745** | |
| x8 | -0.530* | -0.383 | -0.128 | -0.001 | -0.260 | 0.047 | |
| x9 | -0.713** | -0.706** | -0.568** | -0.666** | -0.624** | -0.764** | |
展叶始期 Early leaf expansion period | x1 | -0.302 | -0.455* | -0.445* | -0.414* | -0.376 | -0.613** |
| x2 | -0.692** | -0.745** | -0.778** | -0.803** | -0.370 | -0.756** | |
| x6 | -0.614** | -0.676** | -0.703** | -0.747** | -0.311 | -0.746** | |
| x7 | -0.772** | -0.823** | -0.684** | -0.762** | -0.562** | -0.769** | |
| x8 | -0.598** | -0.497* | 0.096 | 0.010 | -0.216 | 0.135 | |
| x9 | -0.744** | -0.724** | -0.657** | -0.728** | -0.480* | -0.760** | |
开花始期 Early florescence period | x1 | -0.407 | -0.449* | -0.476* | -0.102 | -0.322 | -0.353 |
| x2 | -0.644** | -0.598** | -0.518** | -0.353 | -0.448* | -0.444* | |
| x3 | -0.718** | -0.571** | -0.753** | -0.732** | -0.670** | -0.600** | |
| x4 | -0.556** | -0.460* | -0.788** | -0.626** | -0.606** | -0.657** | |
| x5 | -0.074 | 0.041 | 0.205 | 0.401* | 0.133 | -0.086 | |
| x6 | -0.792** | -0.597** | -0.595** | -0.339 | -0.671** | -0.630** | |
| x7 | -0.706** | -0.677** | -0.570** | -0.430* | -0.585** | -0.425 | |
| x9 | -0.727** | -0.565** | -0.506** | -0.492* | -0.567** | -0.377 | |
| 1 | Chmielewski F M, Rotzer T. Response of tree phenology to climate change across Europe. Agricultural & Forest Meteorology, 2001, 108(2): 101-112. |
| 2 | Lu P L, Yu Q, Liu J D, et al. Effects of changes in spring temperature on flowering dates of woody plants across China. Botanical Studies, 2006, 47(2): 153-161. |
| 3 | Fu Y, Pan X B. Research advances in herbage plant phenology and phenological model of grassland. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2011, 32(3): 319-325. |
| 符瑜, 潘学标. 草本植物物候及其物候模拟模型的研究进展. 中国农业气象, 2011, 32(3): 319-325. | |
| 4 | Zhai J, Yuan F H, Wu J B. Research progress on vegetation phenological changes. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(11): 3237-3243. |
| 翟佳, 袁凤辉, 吴家兵. 植物物候变化研究进展. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(11): 3237-3243. | |
| 5 | Ma X F, Chen S Y, Deng J, et al. Vegetation phenology dynamics and its response to climate change on the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(1): 13-21. |
| 马晓芳, 陈思宇, 邓婕, 等. 青藏高原植被物候监测及其对气候变化的响应. 草业学报, 2016, 25(1): 13-21. | |
| 6 | Yu L X, Liu T X, Bu K, et al. Monitoring the long term vegetation phenology change in Northeast China from 1982 to 2015. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 14770 |
| 7 | Jonsson P, Eklundh L. Seasonality extraction by function fitting to time-series of satellite sensor data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(8): 1824-1832. |
| 8 | Gu R Y, Zhou W C, Bai M L, et al. Impacts of climate change on phenological phase of herb in the main grassland in Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(3): 767-776. |
| 顾润源, 周伟灿, 白美兰, 等.气候变化对内蒙古草原典型植物物候的影响. 生态学报, 2012, 32(3): 767-776. | |
| 9 | Miao B L, Liang C Z, Han F, et al. Responses of phenology to climate change over the major grassland types. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(23): 7689-7701. |
| 苗百岭, 梁存柱, 韩芳, 等. 内蒙古主要草原类型植物物候对气候波动的响应. 生态学报, 2016, 36(23): 7689-7701. | |
| 10 | Zhang X T. Spatial-temporal variation of grassland vegetation dynamics and its response to climate change in China’s temperate zone. Beijing: China Agriculture University, 2018. |
| 张煦庭. 中国温带地区草地植被动态时空特征及其对气候变化的响应. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2018. | |
| 11 | Ni L, Wu J, Li C B, et al. Temporal and spatial variations in natural grassland phenology in China over the last 30 years. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(1): 1-12. |
| 倪璐, 吴静, 李纯斌, 等. 近30年中国天然草地物候时空变化特征分析. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 1-12. | |
| 12 | Ge Q S, Dai J, Cui H, et al. Spatiotemporal variability in start and end of growing season in China related to climate variability. Remote Sensing, 2016, DOI: 10.3390/rs8050433. |
| 13 | Morin X, Roy J, Sonié L, et al. Changes in leaf phenology of three European oak species in response to experimental climate change. New Phytologist, 2010, 186(4): 900-910. |
| 14 | Han R Q, Bao W H, Zhao M H, et al. Temperature change and its influence on thermal conditions of agriculture in Shandong: Based on data of 52 years. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2017, 33(16): 112-122. |
| 韩荣青, 包维虎, 赵明华, 等. 1961-2012年山东省气温变化及对农业热量条件影响. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(16): 112-122. | |
| 15 | Dommenget D. A cautionary note on the interpretation of EOF. Journal of Climate, 2002, 15(2): 216-225. |
| 16 | Hou M T, Hu W, Qiao H L, et al. Application of partial least squares (PLS) regression method in attribution of vegetation change in Eastern China. Journal of Natural Resources, 2015, 30(3): 409-422. |
| 侯美亭, 胡伟, 乔海龙, 等. 偏最小二乘(PLS)回归方法在中国东部植被变化归因研究中的应用. 自然资源学报, 2015, 30(3): 409-422. | |
| 17 | Wang H W, Wu Z B, Meng J. Linear and nonlinear methods of partial least squares regression. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2006. |
| 王惠文, 吴载斌, 孟洁. 偏最小二乘回归的线性与非线性方法. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2006. | |
| 18 | Li R Y. Impacts of climate change on phenology of herbaceous plants in Heze. Desert and Oasis Meteorology, 2015, 9(1): 69-74. |
| 李瑞英. 气候变化对菏泽草本植物物候期的影响. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2015, 9(1): 69-74. | |
| 19 | Ge Q S, Zheng J Y, Hao Z X, et al. State-of-the-arts in the study of climate changes over China for the past 2000 years. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2014, 69(9): 1248-1258. |
| 葛全胜, 郑景云, 郝志新, 等. 过去2000年中国气候变化研究的新进展. 地理学报, 2014, 69(9): 1248-1258. | |
| 20 | Wang C, Cao R, Chen J, et al. Temperature sensitivity of spring vegetation phenology correlates to within-spring warming speed over the Northern Hemisphere. Ecological Indicators, 2015, 50: 62-68. |
| 21 | Gao Q, Chen J, Yan F, et al. Phenological characteristics of herbaceous plants in Hebei Province and their responses to climate warming. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2012, 31(3): 600-605. |
| 高祺, 陈静, 阎访, 等.河北省草本植物物候特征及其对气候变暖的响应. 生态学杂志, 2012, 31(3): 600-605. | |
| 22 | Zang H J, Li X Y, Li J, et al. Responses of woody plants’ spring phenology to climate changes in Shandong. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2011, 32(2): 167-173. |
| 臧海佳, 李星玉, 李俊, 等. 山东省木本植物春季物候对气候变化的响应. 中国农业气象, 2011, 32(2): 167-173. | |
| 23 | Shen M, Tang Y, Chen J, et al. Influences of temperature and precipitation before the growing season on spring phenology in grasslands of the central and eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2011, 151(12): 1711-1722. |
| 24 | Kong D D, Zhang Q, Huang W L, et al. Vegetation phenology change in Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2013 and its related meteorological factors. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(1): 39-52. |
| 孔冬冬, 张强, 黄文琳, 等. 1982-2013年青藏高原植被物候变化及气象因素影响. 地理学报, 2017, 72(1): 39-52. |
| [1] | 罗文蓉, 胡国铮, 干珠扎布, 高清竹, 李岩, 葛怡情, 李钰, 何世丞, 旦久罗布. 模拟干旱对藏北高寒草甸植物物候期和生产力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 82-92. |
| [2] | 林慧龙, 范迪, 冯琦胜, 梁天刚. 草地综合顺序分类法研究新热点:2008-2020年回顾与展望[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 201-213. |
| [3] | 郭强, 王玉琴, 鲍根生, 王宏生. 气象因子对高原鼢鼠种群数量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 188-194. |
| [4] | 马倩倩, 刘彤, 董合干, 王寒月, 赵文轩, 王瑞丽, 刘延, 陈乐. 气候变化下三裂叶豚草在新疆的潜在地理分布[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 73-85. |
| [5] | 倪璐, 吴静, 李纯斌, 秦格霞, 李政, 孔婕. 近30年中国天然草地物候时空变化特征分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 1-12. |
| [6] | 张智起, 张立旭, 徐炜, 汪浩, 王金洲, 王娓, 贺金生. 气候变暖背景下土壤呼吸研究的几个重要问题[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 164-173. |
| [7] | 王多斌, 籍常婷, 林慧龙. 基于DNDC模型的高寒草甸土壤有机碳含量动态研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 197-204. |
| [8] | 王迎新, 陈先江, 娄珊宁, 胡安, 任劲飞, 胡俊奇, 张静, 侯扶江. 草原灌丛化入侵:过程、机制和效应[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 219-227. |
| [9] | 马赫, 魏岩, 穆晨. 野榆钱菠菜三种异型种子幼苗的生长特性[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 126-134. |
| [10] | 郭丁, 郭文斐, 赵建, 特木其勒图, 李旭东, 傅华, 骆亦其. 黄土高原草地和农田系统碳动态对降雨、温度和CO2浓度变化响应的模拟[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 1-14. |
| [11] | 张仁平, 郭靖, 冯琦胜, 梁天刚. 新疆地区草地植被物候时空变化[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 66-75. |
| [12] | 耿元波, 王松, 胡雪荻. 高寒草甸草原净初级生产力对气候变化响应的模拟[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 1-13. |
| [13] | 王亚领, 李浩, 杨旋, 郭彦龙, 李维德. 基于MaxEnt模型和不同气候变化情景的单叶蔓荆潜在地理分布预测[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 1-10. |
| [14] | 张颖, 章超斌, 王钊齐, 杨悦, 张艳珍, 李建龙, 安如. 气候变化与人为活动对三江源草地生产力影响的定量研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(5): 1-14. |
| [15] | 陈奕兆, 李建龙, 孙政国, 刚成诚. 欧亚大陆草原带1982-2008年间净初级生产力时空动态及其对气候变化响应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(1): 1-12. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||