

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 62-71.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021012
李满有1( ), 杨彦军2, 王斌1, 沈笑天1, 曹立娟1, 李小云1, 倪旺1, 兰剑1(
), 杨彦军2, 王斌1, 沈笑天1, 曹立娟1, 李小云1, 倪旺1, 兰剑1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-01-13
修回日期:2021-03-10
出版日期:2022-04-20
发布日期:2022-01-25
通讯作者:
兰剑
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: ndlanjian@163.com基金资助:
Man-you LI1( ), Yan-jun YANG2, Bin WANG1, Xiao-tian SHEN1, Li-juan CAO1, Xiao-yun LI1, Wang NI1, Jian LAN1(
), Yan-jun YANG2, Bin WANG1, Xiao-tian SHEN1, Li-juan CAO1, Xiao-yun LI1, Wang NI1, Jian LAN1( )
)
Received:2021-01-13
Revised:2021-03-10
Online:2022-04-20
Published:2022-01-25
Contact:
Jian LAN
摘要:
采用单因素随机区组设计,研究了宁夏干旱地区滴灌条件下燕麦与光叶紫花苕按同行、间行、交叉和条撒4种混播模式对草地生产性能、种间关系的影响,并利用主成分分析(PCA)进行综合评价,探寻燕麦与光叶紫花苕最佳混播模式。结果表明,4种混播模式较单播均显著提高了牧草产量(P<0.05),其中,间行混播下鲜、干草产量最高,分别达36495和11906 kg·hm-2;混播草地较燕麦单播显著改善了牧草品质,其中间行混播牧草相对饲喂价值为115.89,仅低于光叶紫花苕单播;4种混播模式相对产量总和(RYT)均大于1,表现为种间竞争弱于种内竞争,燕麦和光叶紫花苕具有一定的生态位分化,其中间行混播尤为明显。经主成分分析(PCA),燕麦与光叶紫花苕间行混播模式综合性状表现最好。
李满有, 杨彦军, 王斌, 沈笑天, 曹立娟, 李小云, 倪旺, 兰剑. 宁夏干旱区滴灌条件下燕麦与光叶紫花苕不同混播模式的生产性能、品质及综合评价研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 62-71.
Man-you LI, Yan-jun YANG, Bin WANG, Xiao-tian SHEN, Li-juan CAO, Xiao-yun LI, Wang NI, Jian LAN. Yield, forage quality and a multivariate evaluation of Avena sativa and Vicia villosa in different mixed planting patterns under drip irrigation in an arid area of Ningxia[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(4): 62-71.
| 编号Number | 播种模式Sowing mode | 品种组合Variety combination | 播种量Sowing quantity (kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TH | 同行混播Peer mixed | 燕麦-光叶紫花苕A. sativa and V. villosa | 75-40 |
| JH | 间行混播Intercrop mixed | 燕麦-光叶紫花苕A. sativa and V. villosa | 75-40 |
| JC | 交叉混播Cross mixed | 燕麦-光叶紫花苕A. sativa and V. villosa | 75-40 |
| TS | 条撒混播Strip mixed | 燕麦-光叶紫花苕A. sativa and V. villosa | 75-40 |
| YD | 单播Unicast | 燕麦A. sativa | 120 |
| GD | 单播Unicast | 光叶紫花苕V. villosa | 60 |
表1 试验处理
Table 1 Test treatment
| 编号Number | 播种模式Sowing mode | 品种组合Variety combination | 播种量Sowing quantity (kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TH | 同行混播Peer mixed | 燕麦-光叶紫花苕A. sativa and V. villosa | 75-40 |
| JH | 间行混播Intercrop mixed | 燕麦-光叶紫花苕A. sativa and V. villosa | 75-40 |
| JC | 交叉混播Cross mixed | 燕麦-光叶紫花苕A. sativa and V. villosa | 75-40 |
| TS | 条撒混播Strip mixed | 燕麦-光叶紫花苕A. sativa and V. villosa | 75-40 |
| YD | 单播Unicast | 燕麦A. sativa | 120 |
| GD | 单播Unicast | 光叶紫花苕V. villosa | 60 |
处理 Treatment | 株高Plant height (cm) | 分蘖(枝)数Number of tillers (branches) (No.·m-2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 燕麦A. sativa (A) | 光叶紫花苕V. villosa (V) | 燕麦A. sativa | 光叶紫花苕V. villosa | 燕麦+光叶紫花苕(A+V) | |
| TH | 90.17±1.52bc | 75.88±2.72b | 985±95.67b | 271±46.89c | 1257±67.85b |
| JH | 102.35±1.03a | 82.88±2.38a | 1265±39.79a | 498±14.04b | 1763±95.77a |
| JC | 96.71±1.53ab | 79.58±2.62ab | 944±52.68b | 227±28.46c | 1171±45.32b |
| TS | 86.58±1.64c | 82.47±1.64a | 954±25.54b | 258±33.17c | 1212±55.79b |
| YD/GD | 84.11±2.05c | 75.82±1.88b | 885±59.67c | 616±45.14a | 885±35.18c/616±32.16d |
表2 混播模式对燕麦和光叶紫花苕株高和分蘖(枝)数的影响
Table 2 Effect of mixed sowing mode on plant height and number of tillers (branches) of A. sativa and V. villosa
处理 Treatment | 株高Plant height (cm) | 分蘖(枝)数Number of tillers (branches) (No.·m-2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 燕麦A. sativa (A) | 光叶紫花苕V. villosa (V) | 燕麦A. sativa | 光叶紫花苕V. villosa | 燕麦+光叶紫花苕(A+V) | |
| TH | 90.17±1.52bc | 75.88±2.72b | 985±95.67b | 271±46.89c | 1257±67.85b |
| JH | 102.35±1.03a | 82.88±2.38a | 1265±39.79a | 498±14.04b | 1763±95.77a |
| JC | 96.71±1.53ab | 79.58±2.62ab | 944±52.68b | 227±28.46c | 1171±45.32b |
| TS | 86.58±1.64c | 82.47±1.64a | 954±25.54b | 258±33.17c | 1212±55.79b |
| YD/GD | 84.11±2.05c | 75.82±1.88b | 885±59.67c | 616±45.14a | 885±35.18c/616±32.16d |
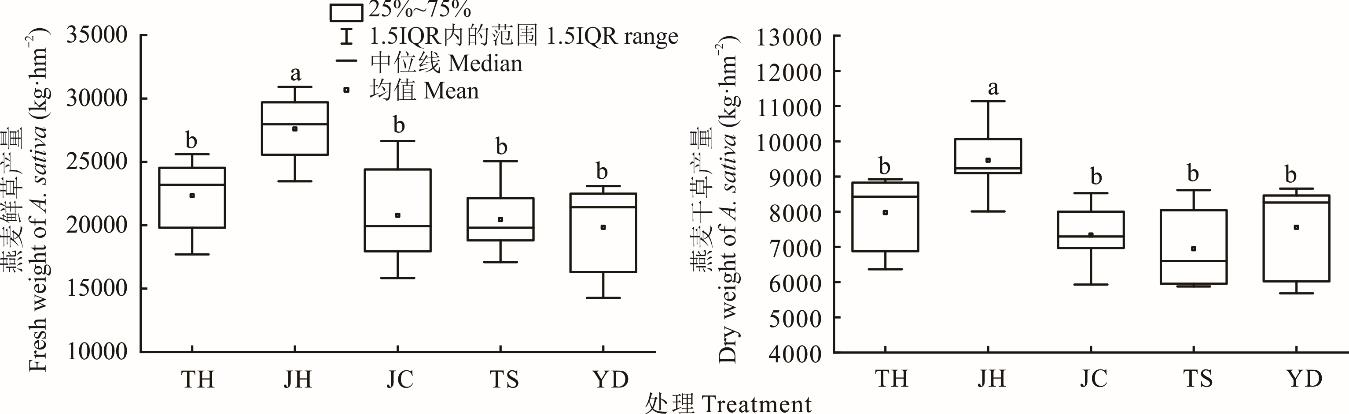
图2 混播模式对燕麦鲜、干草产量的影响不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05),25%~75%表示箱型图含有50%的数据,IQR表示第三四分位数与第一四分位数的差距,下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at 0.05 level, 25%-75% means that the box chart contains 50% of the data, and IQR means the difference between the third quartile and the first quartile, the same below.
Fig.2 Effect of the mixed sowing mode on A. sativa fresh and dry yields
处理 Treatment | 粗灰分 Crude ash (%) | 粗脂肪 Ether extract (%) | 粗蛋白 Crude protein (%) | 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber (%) | 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber (%) | 相对饲喂价值 Relative feeding value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TH | 5.57±0.14a | 1.36±0.04bc | 8.34±0.52bc | 55.25±1.81a | 33.90±0.81b | 105.22±4.66b |
| JH | 4.38±0.33ab | 1.74±0.21a | 9.80±0.93b | 53.30±3.35a | 29.39±1.25b | 115.89±5.61ab |
| JC | 5.20±1.13a | 1.65±0.14ab | 8.21±0.05bc | 53.97±0.43a | 32.69±0.49b | 109.34±1.41ab |
| TS | 2.83±0.12b | 1.42±0.03abc | 8.59±0.32bc | 53.48±0.80a | 33.44±0.65b | 109.32±1.87ab |
| YD | 4.88±0.23ab | 1.35±0.07bc | 6.24±0.93c | 53.36±6.06a | 40.12±2.89a | 99.38±12.71b |
| GD | 5.61±1.38a | 1.27±0.05c | 12.58±0.43a | 40.16±3.02b | 45.17±0.64a | 124.42±9.30a |
表3 混播模式对牧草营养品质的影响
Table 3 Effect of mixed sowing mode on the nutritional quality of forage
处理 Treatment | 粗灰分 Crude ash (%) | 粗脂肪 Ether extract (%) | 粗蛋白 Crude protein (%) | 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber (%) | 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber (%) | 相对饲喂价值 Relative feeding value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TH | 5.57±0.14a | 1.36±0.04bc | 8.34±0.52bc | 55.25±1.81a | 33.90±0.81b | 105.22±4.66b |
| JH | 4.38±0.33ab | 1.74±0.21a | 9.80±0.93b | 53.30±3.35a | 29.39±1.25b | 115.89±5.61ab |
| JC | 5.20±1.13a | 1.65±0.14ab | 8.21±0.05bc | 53.97±0.43a | 32.69±0.49b | 109.34±1.41ab |
| TS | 2.83±0.12b | 1.42±0.03abc | 8.59±0.32bc | 53.48±0.80a | 33.44±0.65b | 109.32±1.87ab |
| YD | 4.88±0.23ab | 1.35±0.07bc | 6.24±0.93c | 53.36±6.06a | 40.12±2.89a | 99.38±12.71b |
| GD | 5.61±1.38a | 1.27±0.05c | 12.58±0.43a | 40.16±3.02b | 45.17±0.64a | 124.42±9.30a |
| 指标Index | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X2 | 0.881* | ||||||
| X3 | 0.272 | 0.219 | |||||
| X4 | 0.792 | 0.783 | 0.085 | ||||
| X5 | 0.003 | -0.456 | -0.152 | -0.111 | |||
| X6 | -0.537 | -0.848* | -0.284 | -0.481 | 0.835* | ||
| X7 | 0.957** | 0.956** | 0.319 | 0.851* | -0.252 | -0.726 | |
| X8 | 0.056 | -0.399 | -0.100 | 0.031 | 0.982** | 0.802 | -0.175 |
表4 不同混播模式牧草主要性状的相关分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis of forage traits in different mixed patterns
| 指标Index | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X2 | 0.881* | ||||||
| X3 | 0.272 | 0.219 | |||||
| X4 | 0.792 | 0.783 | 0.085 | ||||
| X5 | 0.003 | -0.456 | -0.152 | -0.111 | |||
| X6 | -0.537 | -0.848* | -0.284 | -0.481 | 0.835* | ||
| X7 | 0.957** | 0.956** | 0.319 | 0.851* | -0.252 | -0.726 | |
| X8 | 0.056 | -0.399 | -0.100 | 0.031 | 0.982** | 0.802 | -0.175 |
| 指标Index | 因子1 Factor 1 | 因子2 Factor 2 | 指标Index | 因子1 Factor 1 | 因子2 Factor 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.456 | 0.857 | X7 | 0.472 | -0.841 |
| X2 | 0.821 | 0.545 | X8 | -0.862 | 0.506 |
| X3 | 0.353 | 0.335 | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 4.593 | 2.208 |
| X4 | 0.502 | 0.760 | 方差贡献率 Variance contribution rate (%) | 57.416 | 27.603 |
| X5 | -0.939 | 0.262 | 累积贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 57.416 | 85.019 |
| X6 | 0.964 | -0.253 |
表5 各因子特征值和累计贡献率
Table 5 Characteristic value and cumulative contribution rate of each factor
| 指标Index | 因子1 Factor 1 | 因子2 Factor 2 | 指标Index | 因子1 Factor 1 | 因子2 Factor 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.456 | 0.857 | X7 | 0.472 | -0.841 |
| X2 | 0.821 | 0.545 | X8 | -0.862 | 0.506 |
| X3 | 0.353 | 0.335 | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 4.593 | 2.208 |
| X4 | 0.502 | 0.760 | 方差贡献率 Variance contribution rate (%) | 57.416 | 27.603 |
| X5 | -0.939 | 0.262 | 累积贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 57.416 | 85.019 |
| X6 | 0.964 | -0.253 |
| 指标Index | A1 | A2 | 指标Index | A1 | A2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.377 | 0.370 | X5 | -0.269 | 0.542 |
| X2 | 0.456 | 0.085 | X6 | -0.427 | 0.264 |
| X3 | 0.155 | 0.005 | X7 | 0.436 | 0.234 |
| X4 | 0.353 | 0.323 | X8 | -0.236 | 0.578 |
表6 特征向量
Table 6 Feature vector
| 指标Index | A1 | A2 | 指标Index | A1 | A2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.377 | 0.370 | X5 | -0.269 | 0.542 |
| X2 | 0.456 | 0.085 | X6 | -0.427 | 0.264 |
| X3 | 0.155 | 0.005 | X7 | 0.436 | 0.234 |
| X4 | 0.353 | 0.323 | X8 | -0.236 | 0.578 |
| 处理Treatment | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TH | 0.353 | 0.436 | -0.649 | -0.563 | -0.294 | -0.586 | 0.231 | -0.611 |
| JH | 1.495 | 1.255 | 0.083 | 1.474 | 0.398 | -0.331 | 1.291 | 0.549 |
| JC | 0.159 | 0.309 | -0.458 | 0.991 | -0.355 | -0.421 | 0.486 | -0.132 |
| TS | 0.251 | 0.083 | 1.960 | -0.241 | -0.175 | -0.355 | 0.326 | -0.135 |
| YD | -1.164 | -0.348 | -0.268 | -0.616 | -1.288 | -0.339 | -0.841 | -1.290 |
| GD | -1.094 | -1.735 | -0.669 | -1.045 | 1.714 | 2.032 | -1.493 | 1.620 |
表7 数据标准化
Table 7 Data standardization
| 处理Treatment | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TH | 0.353 | 0.436 | -0.649 | -0.563 | -0.294 | -0.586 | 0.231 | -0.611 |
| JH | 1.495 | 1.255 | 0.083 | 1.474 | 0.398 | -0.331 | 1.291 | 0.549 |
| JC | 0.159 | 0.309 | -0.458 | 0.991 | -0.355 | -0.421 | 0.486 | -0.132 |
| TS | 0.251 | 0.083 | 1.960 | -0.241 | -0.175 | -0.355 | 0.326 | -0.135 |
| YD | -1.164 | -0.348 | -0.268 | -0.616 | -1.288 | -0.339 | -0.841 | -1.290 |
| GD | -1.094 | -1.735 | -0.669 | -1.045 | 1.714 | 2.032 | -1.493 | 1.620 |
| 处理Treatment | Y1 | Y2 | Y | 排名Ranking | 处理Treatment | Y1 | Y2 | Y | 排名Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TH | 0.607 | -0.631 | 0.205 | 4 | TS | 0.724 | -0.158 | 0.438 | 3 |
| JH | 2.137 | 1.884 | 2.055 | 1 | YD | -0.427 | -2.391 | -1.065 | 5 |
| JC | 0.998 | 0.137 | 0.719 | 2 | GD | -4.039 | 1.160 | -2.351 | 6 |
表8 不同混播模式综合排名
Table 8 Comprehensive ranking of different mixed sowing mode
| 处理Treatment | Y1 | Y2 | Y | 排名Ranking | 处理Treatment | Y1 | Y2 | Y | 排名Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TH | 0.607 | -0.631 | 0.205 | 4 | TS | 0.724 | -0.158 | 0.438 | 3 |
| JH | 2.137 | 1.884 | 2.055 | 1 | YD | -0.427 | -2.391 | -1.065 | 5 |
| JC | 0.998 | 0.137 | 0.719 | 2 | GD | -4.039 | 1.160 | -2.351 | 6 |
| 1 | Xie K Y, Zhao Y, Li X L, et al. Relationships between grasses and legumes in mixed grassland:a review. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(3): 284-296. |
| 谢开云, 赵云, 李向林, 等. 豆-禾混播草地种间关系研究进展. 草业学报, 2013, 22(3): 284-296. | |
| 2 | Tessema Z K, Feleke B S. Yield, yield dynamics and nutritional quality of grass-legume mixed pasture. Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 2018, 28(1): 155-164. |
| 3 | Berdahl J D, Karn J F, Hendrickson J R. Dry matter yields of cool-season grass monocultures and grass-alfalfa binary mixtures. Agronomy Journal, 2001, 93(2): 463-467. |
| 4 | Sheaffer C C, Miller D W, Marten G C. Grass dominance and mixture yield and quality in perennial grass-alfalfa mixtures. Journal of Production Agriculture, 1990, 3(4): 480-485. |
| 5 | Guan Z X, Na E K Z, Zhu Y Q, et al. Effect of different sowing patterns on production performance and soil nutrients in Avena sativa+Vicia sativa mixtures. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(3): 772-784. |
| 关正翾, 娜尔克孜, 朱亚琼, 等. 不同混播方式下燕麦+箭筈豌豆混播草地的生产性能及土壤养分特征. 草业科学, 2019, 36(3): 772-784. | |
| 6 | Xie K Y, Wang Y X, Wan J C, et al. Mechanisms and factors affecting nitrogen transfer in mixed legume/grass swards: A review. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(3): 157-170. |
| 谢开云, 王玉祥, 万江春, 等. 混播草地中豆科/禾本科牧草氮转移机理及其影响因素. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 157-170. | |
| 7 | Chen W, Mccaughey W P, Grant C A. Pasture type and fertilization effects on N2 fixation, N budgets and external energy inputs in western Canada. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2004, 36(8): 1205-1212. |
| 8 | Wang F Q, Xiang J, Guo B G, et al. Establishment of Vicia sativa-Secale cereale mixed and intercropping methods for the Lhasa valley area. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(8): 39-49. |
| 王富强, 向洁, 郭宝光, 等. 拉萨河谷区箭筈豌豆和黑麦混、间播建植方式研究. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 39-49. | |
| 9 | Liu M, Gong J R, Wang Y H, et al. Effects of legume-grass mixed sowing on forage grass yield and quality in artificial grassland. Arid Zone Research, 2016, 33(1): 179-185. |
| 刘敏, 龚吉蕊, 王忆慧, 等. 豆禾混播建植人工草地对牧草产量和草质的影响. 干旱区研究, 2016, 33(1): 179-185. | |
| 10 | Zheng W, Zhu J Z, Ku E B, et al. Dynamics of interspecific competition of legume-grass mixture under different mixed sowing patterns. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2010, 18(4): 568-575. |
| 郑伟, 朱进忠, 库尔班, 等. 不同混播方式下豆禾混播草地种间竞争动态研究. 草地学报, 2010, 18(4): 568-575. | |
| 11 | Liu Q, Wang H M, Fu P, et al. Effects of different mixture models of Italian ryegrass and smooth vetch on above ground biomass and quality. Pratacultural Science, 2013, 30(10): 1584-1588. |
| 柳茜, 王红梅, 傅平, 等. 多花黑麦草+光叶紫花苕混播草地生产力特征. 草业科学, 2013, 30(10): 1584-1588. | |
| 12 | Guo X, Qi S, Niu H, et al. Analysis on growing trends and forage nutrition of oat grass in single sowing and mixed sowing. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2020, 41(5): 61-65. |
| 郭孝, 齐爽, 牛晖, 等. 燕麦草在单播以及混播下牧草生长动态和营养价值的探讨. 家畜生态学报, 2020, 41(5): 61-65. | |
| 13 | Zhang X H, Zhu J Z, Ding H L. Effects of different mixed sowing patterns on productivity of legume/grass mixture. Grassland and Turf, 2014, 34(1): 44-48, 54. |
| 张鲜花, 朱进忠, 丁红领. 豆禾混播草地不同建植方式对草地生产性能的影响. 草原与草坪, 2014, 34(1): 44-48, 54. | |
| 14 | Zhu Y Q, Zheng W, Wang X, et al. Effect of mixed pattern on growth efficiency and mixed advantage of Bromus innermis+Onobrychis viciaefolia mixture pasture. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(11): 2335-2346. |
| 朱亚琼, 郑伟, 王祥, 等. 混播方式对无芒雀麦+红豆草混播草地植物生长效率及混播效应的影响. 草业科学, 2017, 34(11): 2335-2346. | |
| 15 | Xiang J, Wang F Q, Guo B G, et al. Effects of mixtures and intercropping of common vetch and oat in valley area of Tibet on the yield and quality. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 2018, 44(5): 555-564. |
| 向洁, 王富强, 郭宝光, 等. 西藏河谷区燕麦与箭筈豌豆混间作对产量和营养品质的影响. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2018, 44(5): 555-564. | |
| 16 | Liu P Q. Quality inspection methods and quality management of feed and feed additives. China Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Digest, 2017, 33(8): 228. |
| 刘沛钦. 饲料及饲料添加剂质量检测方法与品质管理. 中国畜牧兽医文摘, 2017, 33(8): 228. | |
| 17 | Zhang Y L, Gao K, Yu T F, et al. Effects of sowing patterns on productivity and interspecific relationship of alfalfa-grass mixture system. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 42(2): 47-57. |
| 张永亮, 高凯, 于铁峰, 等. 禾草种类与混播比例对苜蓿-禾草混播系统生产力及种间关系的影响. 中国草地学报, 2020, 42(2): 47-57. | |
| 18 | Zhang Y. Application of SPSS software and principle component analysis method in evaluation of forage nutrition value. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40(12): 7186-7188. |
| 张玉. SPSS软件和主成分分析法在牧草营养价值评价中的应用. 安徽农业科学, 2012, 40(12): 7186-7188. | |
| 19 | Qi J, Zheng W, Zhang X H, et al. Determination and comparison of the production performance of pastures among different spatial structure of legume-grass mixtures. Pratacultural Science, 2016, 33(1): 116-128. |
| 祁军, 郑伟, 张鲜花, 等. 不同豆禾混播模式的草地生产性能. 草业科学, 2016, 33(1): 116-128. | |
| 20 | Shi Y H, Wang Y Q, Gao X Z, et al. Studies on yield and quality of mixed-sown annual forage and feed crops inYanmenguan region. Pratacultural Science, 2009, 26(9): 119-123. |
| 石永红, 王运琦, 高新中, 等. 雁门关地区一年生牧草与饲料作物混播产量和品质研究. 草业科学, 2009, 26(9): 119-123. | |
| 21 | Zhang H Y, Yang H S, Li C H, et al. Research on the dynamics of productive forces of alfalfa+awnless brome man-made grassland under the different patterns of mixed sowing. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University(Natural Science Edition), 2008, 23(1): 55-58. |
| 张宏宇, 杨恒山, 李春辉, 等. 不同混播方式下苜蓿+无芒雀麦人工草地生产力动态研究. 内蒙古民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 23(1): 55-58. | |
| 22 | Gou R, You M H, Liu J P, et al. Effect of sowing methods on the productivity of mixed Avena sativa and Vicia sativa pastures. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(3): 804-812. |
| 苟蓉, 游明鸿, 刘金平, 等. 播种方式对燕麦和箭筈豌豆混播草地牧草生产性能的影响. 草业科学, 2019, 36(3): 804-812. | |
| 23 | Yao Z Y, Li J, Song L Z, et al. Study on the leguminous-gramineous grass mixed sowing in bashang area of Zhangjiakou. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(4): 1076-1082. |
| 姚泽英, 李军, 宋连昭, 等. 张家口坝上地区豆-禾牧草混播效果研究. 草地学报, 2020, 28(4): 1076-1082. | |
| 24 | Li J K, Sun T, Wang Z, et al. Effects on mixture sowing ratio on the yield and quality of both vetch and oat in Tibet. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2011, 19(5): 830-833. |
| 李佶恺, 孙涛, 旺扎, 等. 西藏地区燕麦与箭筈豌豆不同混播比例对牧草产量和质量的影响. 草地学报, 2011, 19(5): 830-833. | |
| 25 | Zheng W, Zhu J Z, Janaer G L. A comprehensive evaluation of the productive performance of legume-grass mixtures under different mixed sowing patterns. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(6): 242-251. |
| 郑伟, 朱进忠, 加娜尔古丽. 不同混播方式豆禾混播草地生产性能的综合评价. 草业学报, 2012, 21(6): 242-251. | |
| 26 | Liu J P, You M H, Zeng X L, et al. Correlation analysis of photosynthetic rate and biomass of different leaf positions with seed yield of Elymus sibiricus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(11): 118-127. |
| 刘金平, 游明鸿, 曾晓琳, 等. 老芒麦种子发育时小同位叶光合速率和生物量变化与种子产量的相关分析. 草业学报, 2015, 24(11): 118-127. | |
| 27 | Du X. Effect of mixture and interlacing drill modes on forage yield and quality of oat and alfalfa in Guanzhong region. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2011. |
| 杜欣. 关中地区燕麦与苜蓿混间条播模式对产量和品质的影响. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2011. | |
| 28 | Liu Q, Fu P, Ao X C, et al. Study on production performance and interspecific competition of Italian ryegrass and villose vetch mixed grassland in winter fallow farmlands. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2016, 24(1): 42-46. |
| 柳茜, 傅平, 敖学成, 等. 冬闲田多花黑麦草+光叶紫花苕混播系统生产性能与种间竞争的研究. 草地学报, 2016, 24(1): 42-46. | |
| 29 | Wang P, Zhou D W, Zhang B T. Coexistence and inter-specific competition in grass-legume mixture. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(5): 2560-2567. |
| 王平, 周道玮, 张宝田. 禾-豆混播草地种间竞争与共存. 生态学报, 2009, 29(5): 2560-2567. |
| [1] | 沈吉成, 王蕾, 赵彩霞, 叶发慧, 吕士凯, 刘德梅, 刘瑞娟, 张怀刚, 陈文杰. 77份裸燕麦品种籽粒相关性状分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 156-167. |
| [2] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 王静. 根系分隔方式下紫花苜蓿/燕麦间作氮素利用及种间互馈特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 73-85. |
| [3] | 袁英良, 唐丹, 鲁英, 冉桂霞, 郭艳芹. 吉林地区麦后复种饲用油菜与燕麦混播效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 167-178. |
| [4] | 李进, 陈仕勇, 赵旭, 田浩琦, 陈智华, 周青平. 基于SCoT标记的饲用燕麦品种遗传结构及指纹图谱分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 72-81. |
| [5] | 聂秀美, 慕平, 赵桂琴, 何海鹏, 吴文斌, 蔺豆豆, 苏伟娟, 张丽睿. 贮藏年限对裸燕麦种带真菌和真菌毒素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 106-120. |
| [6] | 高鹏, 魏江铭, 李瑶, 张丽红, 赵祥, 杜利霞, 韩伟. 山西省大同市早播饲用燕麦叶部真菌病害病原鉴定及影响因素分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 82-93. |
| [7] | 刘凯强, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 梁国玲, 马祥. 干旱胁迫对‘青燕1号’燕麦产量及干物质积累与分配的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 177-188. |
| [8] | 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 贾海燕, 卜婷, 李娜. NaHS引发提高裸燕麦种子活力的生理机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 135-142. |
| [9] | 张伟, 周青平, 陈有军, 潘静, 金晓明, 孙万斌, 贾志锋. 呼伦贝尔地区10个引进燕麦品种生产性能及饲草品质比较[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 129-142. |
| [10] | 蔺豆豆, 赵桂琴, 琚泽亮, 宫文龙. 15份燕麦材料苗期抗旱性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 108-121. |
| [11] | 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 贾海燕, 刘秀丽, 卜婷, 李娜. 外源半胱氨酸缓解裸燕麦镧胁迫的生理机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 122-131. |
| [12] | 古丽君, 段廷玉. 光叶紫花苕研究状况的文献分析——基于CNKI数据库的文献计量[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 221-228. |
| [13] | 旦增塔庆, Chapagain Purna Bhadra, Pant Shankar Raj, 杰布, 格桑顿珠, 陈少锋. 不同燕麦品种在尼泊尔北部山区的生长特性及其营养品质的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 73-82. |
| [14] | 牛欢欢, 王森森, 贾宏定, 陈桂华. 光叶紫花苕子浸提液对4种牧草种子萌发过程的化感作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 161-168. |
| [15] | 王苗苗, 周向睿, 梁国玲, 赵桂琴, 焦润安, 柴继宽, 高雪梅, 李娟宁. 5份燕麦材料苗期耐盐性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 143-154. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||