

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (8): 157-166.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021326
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
田吉鹏1,2( ), 刘蓓一1,2, 顾洪如1,2, 丁成龙1,2(
), 刘蓓一1,2, 顾洪如1,2, 丁成龙1,2( ), 程云辉1,2, 玉柱3
), 程云辉1,2, 玉柱3
收稿日期:2021-08-30
修回日期:2021-10-08
出版日期:2022-08-20
发布日期:2022-07-01
通讯作者:
丁成龙
作者简介:E-mail: dingcl@jaas.ac.cn基金资助:
Ji-peng TIAN1,2( ), Bei-yi LIU1,2, Hong-ru GU1,2, Cheng-long DING1,2(
), Bei-yi LIU1,2, Hong-ru GU1,2, Cheng-long DING1,2( ), Yun-hui CHENG1,2, Zhu YU3
), Yun-hui CHENG1,2, Zhu YU3
Received:2021-08-30
Revised:2021-10-08
Online:2022-08-20
Published:2022-07-01
Contact:
Cheng-long DING
摘要:
为研究乳酸菌及丙酸钙对全株玉米和燕麦青贮饲料发酵品质、营养品质、微生物数量、霉菌毒素含量及有氧稳定性的影响,利用蒸馏水(CK组)、复合乳酸菌(LAB组,添加量为5×105 CFU·g-1鲜样)、丙酸钙(PACA组,添加量为鲜草重的0.4%)以及乳酸菌和丙酸钙复合(LAB+PACA)分别添加进全株玉米和燕麦原料中青贮120 d。结果表明:全株玉米青贮饲料发酵品质优良而萎蔫后的燕麦青贮丁酸和氨态氮含量较高。添加剂在不同青贮饲料中表现不同。所有添加剂均显著提高了燕麦青贮饲料的乳酸和乙酸含量,降低了pH值、氨态氮、丁酸含量和酵母菌数量(P<0.05)。而PACA和LAB+PACA组则显著提高了玉米青贮饲料中的淀粉和可溶性碳水化合物含量和有氧稳定性并且降低了霉菌和酵母菌数量(P<0.05)。LAB和LAB+PACA的使用有效降低了玉米青贮饲料中的黄曲霉毒素B1含量(P<0.05)。在两种青贮饲料中丙酸含量只有PACA和LAB+PACA组能够显著增加。因此,添加剂尤其是LAB+PACA的复合添加对于提高玉米和燕麦青贮饲料的青贮品质和安全性具有重要作用。
田吉鹏, 刘蓓一, 顾洪如, 丁成龙, 程云辉, 玉柱. 乳酸菌及丙酸钙对全株玉米和燕麦青贮饲料发酵品质和霉菌毒素含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 157-166.
Ji-peng TIAN, Bei-yi LIU, Hong-ru GU, Cheng-long DING, Yun-hui CHENG, Zhu YU. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and calcium propionate on fermentation quality and mycotoxin contents of whole plant maize and oat silages[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 157-166.
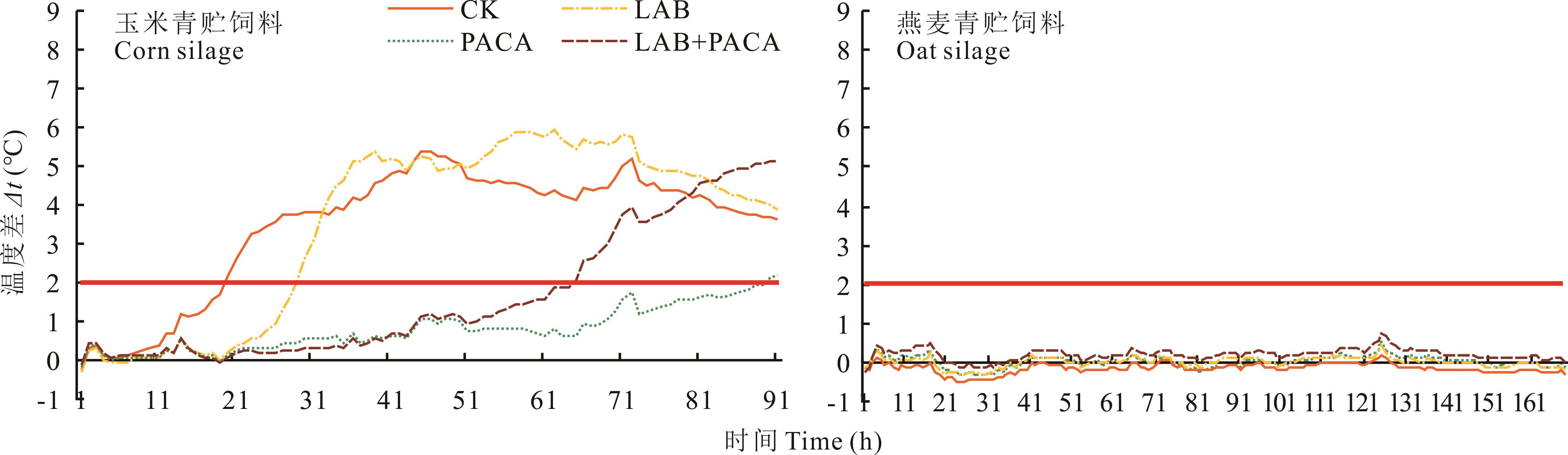
图1 玉米和燕麦青贮饲料有氧暴露期间温度差Δt(样品温度-室温)变化
Fig.1 Curve of Δt (temperature difference between sample temperature and room temperature) during aerobic exposure of corn and oat silages
原料 Material | 添加剂 Additive | pH值 pH value | 乳酸 Lactic acid (%DM) | 乙酸 Acetic acid (%DM) | 丙酸 Propionic acid (%DM) | 丁酸 Butyric acid (%DM) | 氨态氮 Ammoniacal nitrogen (%TN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
玉米青贮 Corn silage | CK | 3.71±0.01de | 4.53±0.15b | 0.70±0.06de | ND | ND | 6.50±0.16c |
| LAB | 3.69±0.01e | 4.54±0.18b | 0.37±0.09e | ND | ND | 4.62±0.21c | |
| PACA | 3.92±0.02c | 5.50±0.48a | 0.99±0.17cd | 0.57±0.04a | ND | 6.19±0.32c | |
| LAB+PACA | 3.84±0.02cd | 5.71±0.27a | 0.46±0.05e | 0.55±0.05a | ND | 4.66±0.21c | |
燕麦青贮 Oat silage | CK | 4.73±0.12a | 1.44±0.36e | 1.11±0.11c | 0.02±0.01d | 2.17±0.95a | 21.38±3.16a |
| LAB | 4.38±0.13b | 2.52±0.43d | 1.23±0.13c | 0.05±0.02d | 0.86±0.74b | 15.51±3.15b | |
| PACA | 4.22±0.02b | 4.19±0.30b | 1.63±0.19b | 0.27±0.03c | ND | 11.94±0.23b | |
| LAB+PACA | 4.36±0.03b | 3.30±0.16c | 2.40±0.16a | 0.42±0.06b | ND | 13.54±0.77b | |
| 标准误SEM | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 1.22 | |
总体显著性 Total significance | M | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| A | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| M×A | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
表1 添加剂对玉米和燕麦青贮饲料发酵品质的影响
Table 1 Effects of additives on fermentation quality of corn and oat silages
原料 Material | 添加剂 Additive | pH值 pH value | 乳酸 Lactic acid (%DM) | 乙酸 Acetic acid (%DM) | 丙酸 Propionic acid (%DM) | 丁酸 Butyric acid (%DM) | 氨态氮 Ammoniacal nitrogen (%TN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
玉米青贮 Corn silage | CK | 3.71±0.01de | 4.53±0.15b | 0.70±0.06de | ND | ND | 6.50±0.16c |
| LAB | 3.69±0.01e | 4.54±0.18b | 0.37±0.09e | ND | ND | 4.62±0.21c | |
| PACA | 3.92±0.02c | 5.50±0.48a | 0.99±0.17cd | 0.57±0.04a | ND | 6.19±0.32c | |
| LAB+PACA | 3.84±0.02cd | 5.71±0.27a | 0.46±0.05e | 0.55±0.05a | ND | 4.66±0.21c | |
燕麦青贮 Oat silage | CK | 4.73±0.12a | 1.44±0.36e | 1.11±0.11c | 0.02±0.01d | 2.17±0.95a | 21.38±3.16a |
| LAB | 4.38±0.13b | 2.52±0.43d | 1.23±0.13c | 0.05±0.02d | 0.86±0.74b | 15.51±3.15b | |
| PACA | 4.22±0.02b | 4.19±0.30b | 1.63±0.19b | 0.27±0.03c | ND | 11.94±0.23b | |
| LAB+PACA | 4.36±0.03b | 3.30±0.16c | 2.40±0.16a | 0.42±0.06b | ND | 13.54±0.77b | |
| 标准误SEM | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 1.22 | |
总体显著性 Total significance | M | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| A | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| M×A | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| 原料Material | 添加剂Additive | 乳酸菌Lactic acid bacteria | 酵母菌Yeast | 霉菌Mould |
|---|---|---|---|---|
玉米青贮 Corn silage | CK | 4.92±0.80b | 4.63±0.42a | 4.26±1.51a |
| LAB | 4.26±0.24b | 4.57±0.06a | 3.45±0.15a | |
| PACA | 4.50±0.20b | 3.48±1.07ab | 0.93±1.60b | |
| LAB+PACA | 2.00±0.01c | 2.60±0.11bc | ND | |
燕麦青贮 Oat silage | CK | 7.48±0.04a | 3.95±0.46a | 0.44±0.76b |
| LAB | 7.17±0.27a | 2.63±0.20bc | ND | |
| PACA | 7.40±0.18a | 2.79±0.09bc | ND | |
| LAB+PACA | 7.49±0.08a | 2.24±0.22c | ND | |
| 标准误SEM | 0.40 | 0.20 | 0.36 | |
总体显著性 Total significance | M | ** | ** | ** |
| A | ** | ** | ** | |
| M×A | ** | * | ** |
表2 添加剂对玉米和燕麦青贮饲料微生物数量的影响
Table 2 Effects of additives on microbial counts of corn and oat silages (lg CFU·g-1)
| 原料Material | 添加剂Additive | 乳酸菌Lactic acid bacteria | 酵母菌Yeast | 霉菌Mould |
|---|---|---|---|---|
玉米青贮 Corn silage | CK | 4.92±0.80b | 4.63±0.42a | 4.26±1.51a |
| LAB | 4.26±0.24b | 4.57±0.06a | 3.45±0.15a | |
| PACA | 4.50±0.20b | 3.48±1.07ab | 0.93±1.60b | |
| LAB+PACA | 2.00±0.01c | 2.60±0.11bc | ND | |
燕麦青贮 Oat silage | CK | 7.48±0.04a | 3.95±0.46a | 0.44±0.76b |
| LAB | 7.17±0.27a | 2.63±0.20bc | ND | |
| PACA | 7.40±0.18a | 2.79±0.09bc | ND | |
| LAB+PACA | 7.49±0.08a | 2.24±0.22c | ND | |
| 标准误SEM | 0.40 | 0.20 | 0.36 | |
总体显著性 Total significance | M | ** | ** | ** |
| A | ** | ** | ** | |
| M×A | ** | * | ** |
| 原料Material | 添加剂Additive | DM (%) | CP (%DM) | NDF (%DM) | ADF (%DM) | WSC (%DM) | 淀粉Starch (%DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
玉米青贮 Corn silage | CK | 32.25±0.91c | 7.34±0.28cd | 33.08±2.30b | 17.54±1.89b | 1.06±0.15c | 29.55±2.16b |
| LAB | 32.21±0.43c | 7.63±0.20bc | 32.04±2.23b | 16.97±1.63b | 1.01±0.05c | 37.94±3.46a | |
| PACA | 32.91±0.85c | 7.00±0.11d | 29.74±0.30b | 15.72±0.37b | 1.88±0.19b | 33.77±3.61ab | |
| LAB+PACA | 34.21±0.72bc | 6.85±0.19d | 29.56±2.04b | 16.87±0.15b | 5.99±0.65a | 35.69±3.37a | |
燕麦青贮 Oat silage | CK | 37.00±0.92a | 7.97±0.23ab | 58.93±2.76a | 34.60±1.86a | 0.39±0.08c | 11.79±1.15c |
| LAB | 38.13±0.76a | 8.30±0.13a | 55.62±0.87a | 31.83±0.87a | 0.51±0.04c | 15.46±1.78c | |
| PACA | 38.20±0.47a | 8.27±0.17a | 54.96±1.41a | 32.06±1.26a | 0.58±0.11c | 14.82±1.47c | |
| LAB+PACA | 35.04±1.14b | 8.07±0.30ab | 56.84±1.74a | 32.92±2.27a | 0.50±0.05c | 12.68±1.13c | |
| 标准误SEM | 0.51 | 0.12 | 2.69 | 1.71 | 0.37 | 2.24 | |
总体显著性 Total significance | M | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| A | NS | ** | * | NS | ** | ** | |
| M×A | ** | * | NS | NS | ** | NS |
表3 添加剂对玉米和燕麦青贮饲料化学成分的影响
Table 3 Effects of additives on chemical composition of corn and oat silages
| 原料Material | 添加剂Additive | DM (%) | CP (%DM) | NDF (%DM) | ADF (%DM) | WSC (%DM) | 淀粉Starch (%DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
玉米青贮 Corn silage | CK | 32.25±0.91c | 7.34±0.28cd | 33.08±2.30b | 17.54±1.89b | 1.06±0.15c | 29.55±2.16b |
| LAB | 32.21±0.43c | 7.63±0.20bc | 32.04±2.23b | 16.97±1.63b | 1.01±0.05c | 37.94±3.46a | |
| PACA | 32.91±0.85c | 7.00±0.11d | 29.74±0.30b | 15.72±0.37b | 1.88±0.19b | 33.77±3.61ab | |
| LAB+PACA | 34.21±0.72bc | 6.85±0.19d | 29.56±2.04b | 16.87±0.15b | 5.99±0.65a | 35.69±3.37a | |
燕麦青贮 Oat silage | CK | 37.00±0.92a | 7.97±0.23ab | 58.93±2.76a | 34.60±1.86a | 0.39±0.08c | 11.79±1.15c |
| LAB | 38.13±0.76a | 8.30±0.13a | 55.62±0.87a | 31.83±0.87a | 0.51±0.04c | 15.46±1.78c | |
| PACA | 38.20±0.47a | 8.27±0.17a | 54.96±1.41a | 32.06±1.26a | 0.58±0.11c | 14.82±1.47c | |
| LAB+PACA | 35.04±1.14b | 8.07±0.30ab | 56.84±1.74a | 32.92±2.27a | 0.50±0.05c | 12.68±1.13c | |
| 标准误SEM | 0.51 | 0.12 | 2.69 | 1.71 | 0.37 | 2.24 | |
总体显著性 Total significance | M | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| A | NS | ** | * | NS | ** | ** | |
| M×A | ** | * | NS | NS | ** | NS |
原料 Material | 添加剂 Additive | 有氧稳定性 Aerobic stability (h) | 黄曲霉毒素B1 Aflatoxin B1 (μg·kg-1 DM) | 玉米赤霉烯酮 Zearalenone (μg·kg-1 DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
玉米青贮 Corn silage | CK | 23.67±11.24d | 3.96±2.85a | 97.32±1.28ab |
| LAB | 29.67±2.08d | 1.07±0.80b | 95.30±1.77b | |
| PACA | 84.00±12.12b | 1.97±1.08ab | 97.35±2.98ab | |
| LAB+PACA | 63.67±8.74c | 0.87±0.61b | 95.84±1.61b | |
燕麦青贮 Oat silage | CK | >168.00a | 0.45±0.02b | 100.50±1.60ab |
| LAB | >168.00a | 0.30±0.15b | 99.99±2.36ab | |
| PACA | >168.00a | 0.43±0.08b | 101.34±1.09a | |
| LAB+PACA | >168.00a | 0.80±0.01b | 100.26±1.88ab | |
| 标准误SEM | 12.86 | 0.31 | 0.56 | |
总体显著性 Total significance | M | ** | ** | ** |
| A | ** | NS | NS | |
| M×A | ** | * | NS |
表4 添加剂对玉米和燕麦青贮饲料有氧稳定性和青贮开封时霉菌毒素含量的影响
Table 4 Effects of additives on aerobic stability of corn and oat silages and mycotoxin contents after silo opening
原料 Material | 添加剂 Additive | 有氧稳定性 Aerobic stability (h) | 黄曲霉毒素B1 Aflatoxin B1 (μg·kg-1 DM) | 玉米赤霉烯酮 Zearalenone (μg·kg-1 DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
玉米青贮 Corn silage | CK | 23.67±11.24d | 3.96±2.85a | 97.32±1.28ab |
| LAB | 29.67±2.08d | 1.07±0.80b | 95.30±1.77b | |
| PACA | 84.00±12.12b | 1.97±1.08ab | 97.35±2.98ab | |
| LAB+PACA | 63.67±8.74c | 0.87±0.61b | 95.84±1.61b | |
燕麦青贮 Oat silage | CK | >168.00a | 0.45±0.02b | 100.50±1.60ab |
| LAB | >168.00a | 0.30±0.15b | 99.99±2.36ab | |
| PACA | >168.00a | 0.43±0.08b | 101.34±1.09a | |
| LAB+PACA | >168.00a | 0.80±0.01b | 100.26±1.88ab | |
| 标准误SEM | 12.86 | 0.31 | 0.56 | |
总体显著性 Total significance | M | ** | ** | ** |
| A | ** | NS | NS | |
| M×A | ** | * | NS |
| 1 | Zhang J F. Experimental study on different proportion of oat hay and silage corn fed to beef cattle. Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 40(3): 64-66. |
| 张俊锋. 不同比例燕麦干草与青贮玉米饲喂肉牛试验研究. 畜牧兽医杂志, 2021, 40(3): 64-66. | |
| 2 | Wan X R, Wu J P, Lei Z M, et al. Effect of lactic acid bacteria on corn silage quality and stability after aerobic exposure. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(4): 204-211. |
| 万学瑞, 吴建平, 雷赵民, 等. 优良抑菌活性乳酸菌对玉米青贮及有氧暴露期微生物数量和pH的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(4): 204-211. | |
| 3 | Li P, Shen Y X, Bai S Q, et al. The effects of wilting on the fermentation quality of oat silage in pastoral area of Sichuan Northwest. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2020(1): 8-13. |
| 李平, 沈益新, 白史且, 等. 萎蔫对川西北高寒牧区燕麦青贮饲料发酵品质的影响. 草学, 2020(1): 8-13. | |
| 4 | Muck R E, Nadeau E M G, McAllister T A, et al. Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. Journal of Dairy Science, 2018, 101(5): 3980-4000. |
| 5 | Zhuang R F, Hua B J, Lin C C, et al. Application and efficacy of compound lactic acid bacteria preparation in whole corn silage. Animal Indusry and Environment, 2020(2): 85-86. |
| 庄茹菲, 华冰洁, 林呈呈, 等. 复合型乳酸菌制剂在全株玉米青贮的应用和功效. 畜牧业环境, 2020(2): 85-86. | |
| 6 | Lu D Y, Tian Y J, Ma Z X, et al. Effect of combination additive for fermentation characteristics and nutritional quality of whole corn silage. Feed Research, 2019, 42(9): 45-51. |
| 卢冬亚, 田雨佳, 马占霞, 等. 组合添加剂对全株玉米青贮发酵特性及营养品质的影响. 饲料研究, 2019, 42(9): 45-51. | |
| 7 | Lu X S. Analysis of forage commodity production situation in China in 2020 and outlook in 2021. Animal Agriculture, 2021(3): 31-36. |
| 卢欣石. 2020我国饲草商品生产形势分析与2021年展望. 畜牧产业, 2021(3): 31-36. | |
| 8 | Tian J P, Xu N X, Liu B Y, et al. Interaction effect of silo density and additives on the fermentation quality, microbial counts, chemical composition and in vitro degradability of rice straw silage. Bioresource Technology, 2020, DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122412. |
| 9 | Liu B Y, Huan H L, Gu H R, et al. Dynamics of a microbial community during ensiling and upon aerobic exposure in lactic acid bacteria inoculation-treated and untreated barley silages. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 273: 212-219. |
| 10 | Xu Q F, Yu Z, Han J G, et al. Determining organic acid in alfalfa silage by HPLC. Grassland and Turf, 2007(2): 63-65, 67. |
| 许庆方, 玉柱, 韩建国, 等. 高效液相色谱法测定紫花苜蓿青贮中的有机酸. 草原与草坪, 2007(2): 63-65, 67. | |
| 11 | Broderick G A, Kang J H. Automated simultaneous determination of ammonia and total amino acids in ruminal fluid and in vitro media. Journal of Dairy Science, 1980, 63(1): 64-75. |
| 12 | Kenneth H. Official methods of analysis (15th Edtion). Artington, Virginia, USA: Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 1990. |
| 13 | Van Soest P J, Robertson J B, Lewis B A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. Journal of Dairy Science, 1991, 74(10): 3583-3597. |
| 14 | Mcdonald P, Henderson A R. Determination of water-soluble carbohydrates in grass. Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture, 1964, 15(6): 395-398. |
| 15 | Rose R, Rose C L, Omi S K, et al. Starch determination by perchloric acid vs enzymes: Evaluating the accuracy and precision of six colorimetric methods. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 1991, 39(1): 2-11. |
| 16 | Silveira R C H, De Rezende A V, Silveira R F H, et al. Chemical composition, digestibility and aerobic stability of corn silages harvested at different maturity stages. Revista Caatinga, 2015, 28(2): 107-116. |
| 17 | Miao F, Zhang F, Wang X, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum, L. buchneri and Pediococcus acidilactici at low doses on the fermentation, aerobic stability and ruminal digestibility of corn silage. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 2019, 22(4): 655-664. |
| 18 | Iank B A V, Jobim C C, Rossi R M, et al. Wilting whole crop black oat with glyphosate for ensiling: Effects on nutritive, fermentative, and aerobic stability characteristics. Revista Brasileira De Zootecnia-Brazilian Journal of Animal Science, 2018, DOI: 10.1590/rbz4720170142. |
| 19 | Bergen W, Byrem T, Grant A. Ensiling characteristics of whole-crop small grains harvested at milk and dough stages. Journal of Animal Science, 1991, 69(4): 1766-1774. |
| 20 | Ge J, Yang C J, Yang Z M, et al. The effects of wilting and additives on silage quality of naked oats (Avena nuda). Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2015, 30(9): 18-23. |
| 葛剑, 杨翠军, 杨志敏, 等. 萎蔫处理和添加剂对裸燕麦青贮饲料品质的影响. 中国粮油学报, 2015, 30(9): 18-23. | |
| 21 | Wang S, Li J, Dong Z, et al. Effect of microbial inoculants on the fermentation characteristics, nutritive value, and in vitro digestibility of various forages. Animal Science Journal, 2019, 90(2): 178-188. |
| 22 | Gomes A L M, Jacovaci F A, Bolson D C, et al. Effects of light wilting and heterolactic inoculant on the formation of volatile organic compounds, fermentative losses and aerobic stability of oat silage. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2019, 247: 194-198. |
| 23 | Liu Q H, Wu J X, Dong Z H, et al. Effects of overnight wilting and additives on the fatty acid profile, alpha-tocopherol and beta-carotene of whole plant oat silages. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2020, DOI: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2019.114370. |
| 24 | Yu Z, Sun Q Z. Silage technology of grass and forage. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2011. |
| 玉柱, 孙启忠. 饲草青贮技术. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2011. | |
| 25 | Wilkinson J, Davies D. The aerobic stability of silage: Key findings and recent developments. Grass and Forage Science, 2013, 68(1): 1-19. |
| 26 | Wan X R, Dou S Y, Li Y, et al. Effect of lactic acid bacteria preparations on microbial population counts and silage quality in maize silage during fermentation and on aerobic exposure. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(11): 83-90. |
| 万学瑞, 豆思远, 李玉, 等. 复合乳酸菌对全株玉米青贮及有氧暴露后微生物及饲料品质的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 83-90. | |
| 27 | Zong C, Zhang J, Shao T, et al. Effects of additives on fermentation quality of alfalfa silage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 180-187. |
| 宗成, 张健, 邵涛, 等. 添加剂对紫花苜蓿青贮饲料发酵品质的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 180-187. | |
| 28 | Ju Z L, Zhao G Q, Chai J K. Effects of temperature and lactic acid bacteria additives on fermentation quality and aerobic stability of oat silage. Grassland and Turf, 2021, 41(2): 53-59, 69. |
| 琚泽亮, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽. 温度和乳酸菌添加剂对燕麦青贮发酵品质及有氧稳定性的影响. 草原与草坪, 2021, 41(2): 53-59, 69. | |
| 29 | Zhang Q Q, Liang Q W, Yang X F, et al. Effect of adding organic acids on fermentation and nutritional quality of oat silage. Feed Research, 2019, 42(4): 84-86. |
| 张晴晴, 梁庆伟, 杨秀芳, 等. 添加有机酸对燕麦青贮发酵和营养品质的影响. 饲料研究, 2019, 42(4): 84-86. | |
| 30 | Sun Z Q, Wu Z, Wang B, et al. The effect of different hybrids and lactic acid bacteria additives on the quality and aerobic stability of the whole plant corn silage. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(1): 83-88. |
| 孙志强, 吴哲, 王炳, 等. 不同品种和乳酸菌添加剂对全株玉米青贮品质和有氧稳定性的影响研究. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(1): 83-88. | |
| 31 | Jiang F, Cheng H, Liu D, et al. Treatment of whole-plant corn silage with lactic acid bacteria and organic acid enhances quality by elevating acid content, reducing pH, and inhibiting undesirable microorganisms. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.593088. |
| 32 | Oliveira A, Weinberg Z, Ogunade I, et al. Meta-analysis of effects of inoculation with homofermentative and facultative heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria on silage fermentation, aerobic stability, and the performance of dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science, 2017, 100(6): 4587-4603. |
| 33 | Jia T T, Wu Z, Yu Z. Effect of different lactic acid bacteria additives on the fermentation quality and aerobic stability of oat silage. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(5): 1266-1272. |
| 贾婷婷, 吴哲, 玉柱. 不同类型乳酸菌添加剂对燕麦青贮品质和有氧稳定性的影响. 草业科学, 2018, 35(5): 1266-1272. | |
| 34 | Zhu J G, Zhang J, Shao T, et al. The effects of additives on fermentation quality and aerobic stability of whole plant oat silage. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(6): 1756-1761. |
| 朱九刚, 张健, 邵涛, 等. 添加剂对全株燕麦青贮饲料发酵品质和有氧稳定性的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(6): 1756-1761. | |
| 35 | GB13078-2017. Hygienical standard for feeds. Beijing: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, 2017. |
| GB 13078-2017. 饲料卫生标准. 北京: 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2017. | |
| 36 | Payne G, Widstrom N. Aflatoxin in maize. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 1992, 10(5): 423-440. |
| 37 | Fu H, Jin J, Zhu X, et al. Effect of compound Lactobacillus preparation on quality of whole corn silage. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021(9): 221-224. |
| 付浩, 金晶, 朱欣, 等. 复合乳酸菌制剂对全株玉米青贮饲料品质的影响. 现代农业科技, 2021(9): 221-224. | |
| 38 | Guan H, Ke W, Yan Y, et al. Screening of natural lactic acid bacteria with potential effect on silage fermentation, aerobic stability and aflatoxin B1 in hot and humid area. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2020, 128(5): 1301-1311. |
| [1] | 蔺豆豆, 琚泽亮, 柴继宽, 赵桂琴. 青藏高原燕麦附着耐低温乳酸菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 103-114. |
| [2] | 杨德智, 王晨, 侯明杰, 王虎成. 饲用甜高粱和全株玉米青贮对肉羊前胃微生态的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 145-154. |
| [3] | 温媛媛, 张美琦, 刘桃桃, 沈宜钊, 高艳霞, 李秋凤, 曹玉凤, 李建国. 体外产气法评价生薯条加工副产品-稻草混贮与全株玉米青贮组合效应的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 154-163. |
| [4] | 杨冬梅, 李俊年, 陶双伦. 添加单宁酸对青贮葛藤有氧稳定性和霉菌毒素含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 164-170. |
| [5] | 张丹丹, 张元庆, 程景, 靳光, 李博, 王栋才, 徐芳, 孙锐锋. 不同粗饲料组合对晋南牛瘤胃体外发酵特性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 93-100. |
| [6] | 黄丽琴, 李松桥, 袁振中, 唐晶, 闫景彩, 唐启源. 全株水稻与平菇菌糠共发酵料对浏阳黑山羊屠宰性能、肉品质和器官指数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 133-140. |
| [7] | 余肖飞, 郭晓农, 张妍, 刘子威, 张喜闻, 徐可新, 吴治勇. 响应面法优化藜麦秸秆饲料发酵工艺的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 155-164. |
| [8] | 谢展, 穆麟, 张志飞, 陈桂华, 刘洋, 高帅, 魏仲珊. 乳酸菌或有机酸盐与尿素复配添加对紫花苜蓿混合青贮的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 165-173. |
| [9] | 吕竑建, 郭香, 陈德奎, 陈晓阳, 张庆. 植物乳酸菌和贮藏温度对辣木叶青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 121-128. |
| [10] | 陈鑫珠, 张建国. 不同茬次和高度热研四号王草的乳酸菌分布及青贮发酵品质[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 150-158. |
| [11] | 付锦涛, 王学凯, 倪奎奎, 杨富裕. 添加乳酸菌和糖蜜对全株构树和稻草混合青贮的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 121-128. |
| [12] | 万学瑞, 豆思远, 李玉, 何轶群, 王川, 张小丽, 雷赵民. 复合乳酸菌对全株玉米青贮及有氧暴露后微生物及饲料品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 83-90. |
| [13] | 毛翠, 刘方圆, 宋恩亮, 王亚芳, 王永军, 战翔, 李原, 成海建, 姜富贵. 不同乳酸菌添加量和发酵时间对全株玉米青贮营养价值及发酵品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 172-181. |
| [14] | 琚泽亮, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽, 贾志峰, 梁国玲. 不同燕麦品种在甘肃中部的营养价值及青贮发酵品质综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 77-86. |
| [15] | 张霞, 李妙善, 周恩光, 王虎成. 西北地区4种优质饲草的肉牛体外瘤胃发酵性能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 135-145. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||