

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3): 46-60.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023140
王安林( ), 马瑞(
), 马瑞( ), 马彦军, 刘腾, 田永胜, 董正虎, 柴巧弟
), 马彦军, 刘腾, 田永胜, 董正虎, 柴巧弟
收稿日期:2023-04-28
修回日期:2023-06-12
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2023-12-27
通讯作者:
马瑞
作者简介:E-mail: mr031103@126.com基金资助:
An-lin WANG( ), Rui MA(
), Rui MA( ), Yan-jun MA, Teng LIU, Yong-sheng TIAN, Zheng-hu DONG, Qiao-di CHAI
), Yan-jun MA, Teng LIU, Yong-sheng TIAN, Zheng-hu DONG, Qiao-di CHAI
Received:2023-04-28
Revised:2023-06-12
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2023-12-27
Contact:
Rui MA
摘要:
以流动沙丘地人工梭梭林土壤(Asd)为对照,选取尼龙网格沙障+人工梭梭林(Nn)和黏土沙障+人工梭梭林(Cy)2种复合型治沙措施区土壤为研究对象,采用Illumina高通量测序和PICRUSt2功能预测技术,探究复合型治沙措施对土壤细菌群落结构及功能的影响,并采用冗余分析解释影响土壤细菌群落及功能的主要理化因子。结果表明:1)2种复合型治沙措施区土壤细菌隶属于35门、90纲、172目、259科和436属。放线菌门、变形菌门和绿弯菌门是研究区土壤优势菌群,平均相对丰度累计达71.84%,其中放线菌门相对丰度最高,占32.16%~37.09%。Cy措施区土壤拟杆菌门和蓝藻菌门显著高于Asd样地(P<0.05)。2)2种措施区土壤细菌Chao1指数显著高于流动沙丘土壤(P<0.05),但主坐标分析显示,3组样地土壤细菌群落结构组成相似。3)在17个次级功能中,碳水化合物代谢功能等为土壤细菌的主要生态功能,且在治沙措施区表现出高度冗余特点。4)相较流动沙丘土壤,复合型治沙措施区土壤有机质等养分含量呈显著增加的共性趋势(P<0.05),且冗余分析表明土壤有机质和速效钾等理化因子显著影响细菌群落结构及生态功能。5)土壤优势菌门与绝大多数代谢功能呈显著相关,且Mantel检验表明土壤细菌群落结构差异与功能潜势差异之间呈显著正相关。综上,复合型治沙措施的实施有助于改善荒漠土壤微环境,研究结果可为沙化土壤微环境生态修复提供理论依据。
王安林, 马瑞, 马彦军, 刘腾, 田永胜, 董正虎, 柴巧弟. 复合型治沙措施对土壤细菌群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 46-60.
An-lin WANG, Rui MA, Yan-jun MA, Teng LIU, Yong-sheng TIAN, Zheng-hu DONG, Qiao-di CHAI. Effects of compound sand control measures on soil bacterial community structure and function[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(3): 46-60.
样地 Sample plot | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 沙障规格 Sandy specifications | 优势种 Dominant species | 高度 Height (cm) | 盖度 Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nn | 39°26′32″ | 103°26′29″ | 1 m×1 m | 梭梭H. ammodendron | 160.2±27.8a | 36.42±2.8a |
| Cy | 39°25′24″ | 103°16′16″ | 2 m×2 m | 177.3±42.3a | 39.77±3.1a | |
| Asd | 39°15′01″ | 103°16′54″ | - | 123.5±24.9b | 30.40±2.5b |
表1 采样地基本信息
Table 1 Basic information on sampling sites
样地 Sample plot | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 沙障规格 Sandy specifications | 优势种 Dominant species | 高度 Height (cm) | 盖度 Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nn | 39°26′32″ | 103°26′29″ | 1 m×1 m | 梭梭H. ammodendron | 160.2±27.8a | 36.42±2.8a |
| Cy | 39°25′24″ | 103°16′16″ | 2 m×2 m | 177.3±42.3a | 39.77±3.1a | |
| Asd | 39°15′01″ | 103°16′54″ | - | 123.5±24.9b | 30.40±2.5b |
试剂名称 The name of the reagent | 2×Premix Taq | 10 μmol·L-1 Primer-F | 10 μmol·L-1 Primer-R | DNA | 无核酸酶水 Nuclease-free water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 用量Use level | 25 μL | 1 μL | 1 μL | 50 ng | 加至50 μL Add to 50 μL |
表2 PCR反应体系
Table 2 PCR reaction system
试剂名称 The name of the reagent | 2×Premix Taq | 10 μmol·L-1 Primer-F | 10 μmol·L-1 Primer-R | DNA | 无核酸酶水 Nuclease-free water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 用量Use level | 25 μL | 1 μL | 1 μL | 50 ng | 加至50 μL Add to 50 μL |
环境因子 Environmental factors | 治沙措施 Sand control measures | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Asd | Nn | Cy | |
| pH | 8.22±0.30b | 8.83±0.19a | 8.96±0.22a |
| SOM (g·kg-1) | 1.04±0.07b | 1.41±0.13a | 1.53±0.30a |
| TN (g·kg-1) | 0.08±0.01b | 0.14±0.03a | 0.18±0.03a |
| TP (g·kg-1) | 0.18±0.02b | 0.22±0.04b | 0.26±0.03a |
| AP (mg·kg-1) | 1.25±0.19a | 1.33±0.25a | 1.36±0.34a |
| AK (mg·kg-1) | 112.29±11.34b | 148.96±14.51a | 155.77±18.29a |
| H (cm) | 125.33±11.30c | 155.01±8.01b | 187.65±17.55a |
| VG (%) | 30.40±2.49b | 36.42±2.82a | 39.77±3.08a |
表3 土壤因子和梭梭形态特征变化
Table 3 Changes of soil factors and morphological characteristics of H. ammodendron
环境因子 Environmental factors | 治沙措施 Sand control measures | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Asd | Nn | Cy | |
| pH | 8.22±0.30b | 8.83±0.19a | 8.96±0.22a |
| SOM (g·kg-1) | 1.04±0.07b | 1.41±0.13a | 1.53±0.30a |
| TN (g·kg-1) | 0.08±0.01b | 0.14±0.03a | 0.18±0.03a |
| TP (g·kg-1) | 0.18±0.02b | 0.22±0.04b | 0.26±0.03a |
| AP (mg·kg-1) | 1.25±0.19a | 1.33±0.25a | 1.36±0.34a |
| AK (mg·kg-1) | 112.29±11.34b | 148.96±14.51a | 155.77±18.29a |
| H (cm) | 125.33±11.30c | 155.01±8.01b | 187.65±17.55a |
| VG (%) | 30.40±2.49b | 36.42±2.82a | 39.77±3.08a |
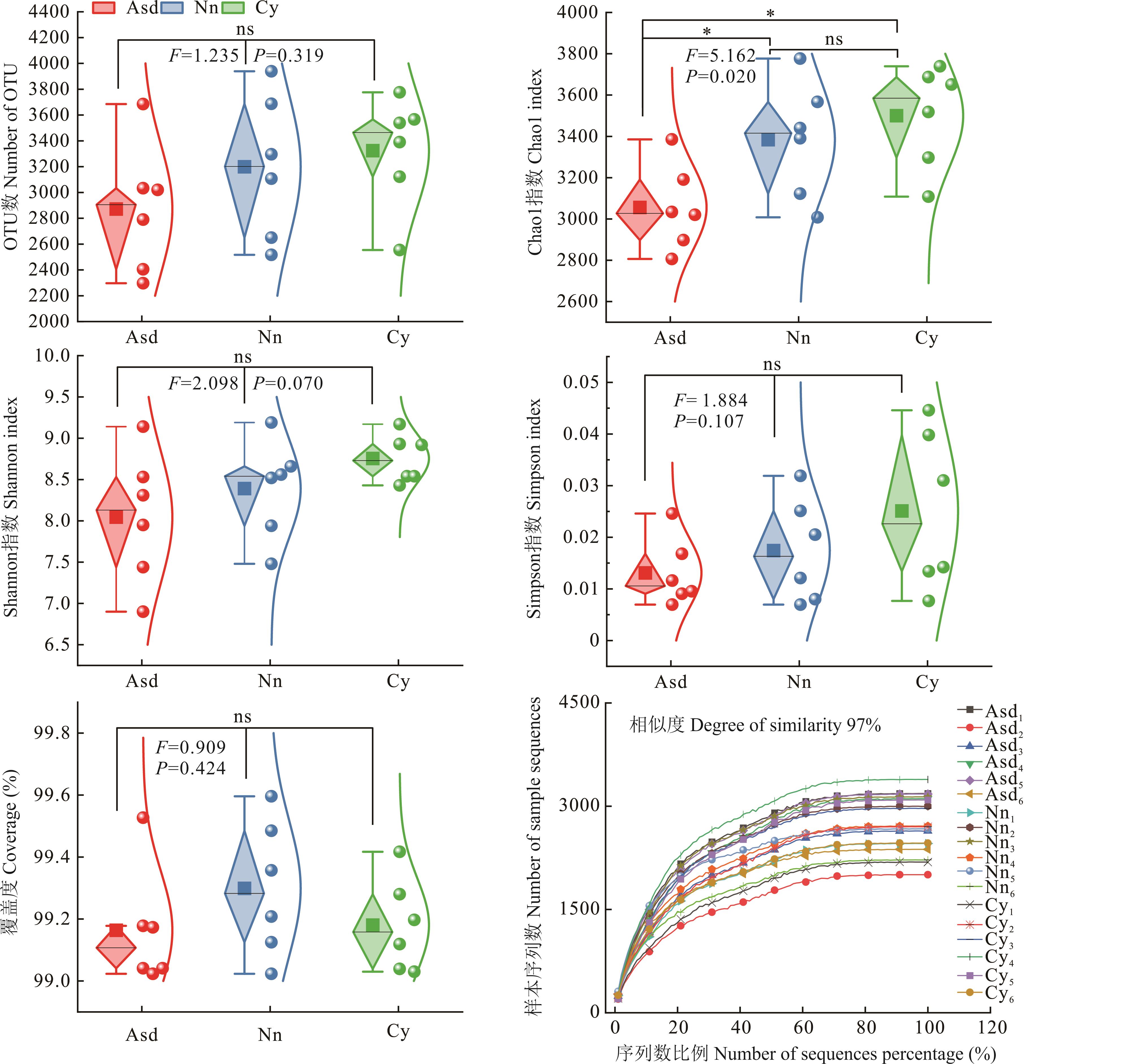
图1 土壤细菌Alpha多样性分析**:P<0.01;*:P<0.05;ns:P>0.05;Asd1~Asd6:流动沙丘梭梭林土壤Soil of mobile dune H. ammodendron forest;Nn1~Nn6:尼龙网格沙障区梭梭林土壤Soil of H. ammodendron forest in nylon grid sand barrier area;Cy1~Cy6:黏土沙障区梭梭林土壤Soil of H. ammodendron forest in clay sand barrier area;下同。The same below.
Fig.1 Analysis of Alpha diversity of soil bacterial
| 功能Function | Asd | Nn | Cy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 新陈代谢Metabolism | 81.98±0.36a | 81.73±0.15a | 81.78±0.20a |
| 遗传信息处理Genetic information processing | 11.74±0.24a | 11.75±0.38a | 11.78±0.33a |
| 细胞过程Cellular processes | 3.74±0.30a | 3.99±0.28a | 3.83±0.26a |
| 环境信息处理Environmental information processing | 1.98±0.08a | 2.06±0.11a | 2.03±0.07a |
表4 土壤细菌群落一级功能通路的相对丰度
Table 4 Relative abundance of primary functional pathways of soil bacterial community (%)
| 功能Function | Asd | Nn | Cy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 新陈代谢Metabolism | 81.98±0.36a | 81.73±0.15a | 81.78±0.20a |
| 遗传信息处理Genetic information processing | 11.74±0.24a | 11.75±0.38a | 11.78±0.33a |
| 细胞过程Cellular processes | 3.74±0.30a | 3.99±0.28a | 3.83±0.26a |
| 环境信息处理Environmental information processing | 1.98±0.08a | 2.06±0.11a | 2.03±0.07a |
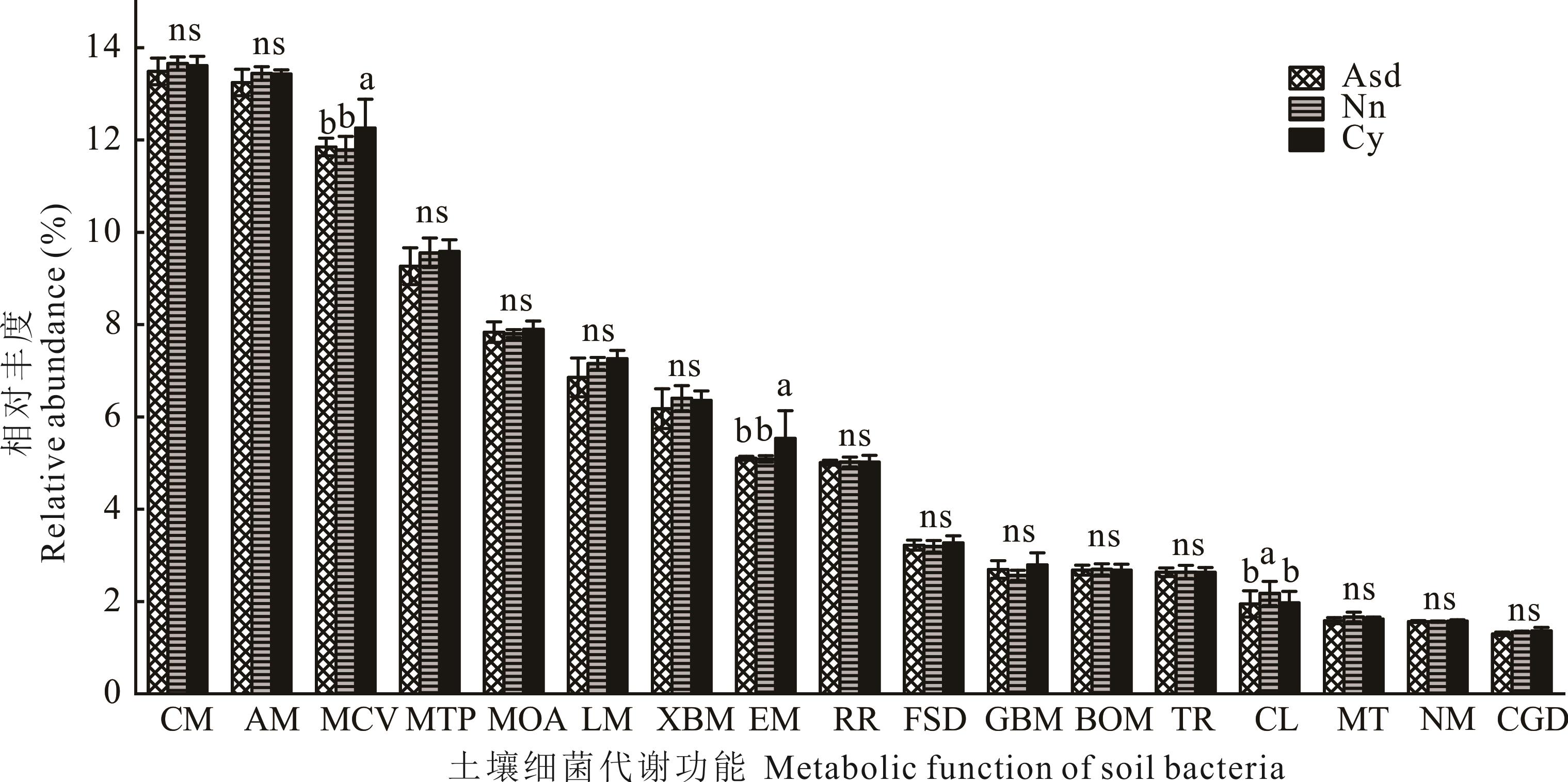
图5 土壤细菌二级功能相对丰度及差异不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);ns表示差异不显著(P>0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05); ns indicates no significant difference (P>0.05).CM:碳水化合物代谢Carbohydrate metabolism;AM:氨基酸代谢Amino acid metabolism;MCV:辅助因子和维生素代谢Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins;MTP:萜类和聚酮类化合物的代谢Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides;MOA:其他氨基酸的代谢Metabolism of other amino acids;LM:脂质代谢Lipid metabolism;XBM:外来生物的生物降解和代谢Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism;EM:能量代谢Energy metabolism;RR:复制和修复Replication and repair;FSD:折叠排序和降解Folding sorting and degradation;GBM:糖类的生物合成和代谢Glycan biosynthesis and metabolism;BOM:其他次级代谢物的生物合成Biosynthesis of other secondary metabolites;TR:翻译Translation;CL:细胞运动性Cell motility;MT:膜运输Membrane transport;NM:核苷酸代谢Nucleotide metabolism;CGD:细胞生长和死亡Cell growth and death.
Fig.5 Relative abundance and difference of secondary function of soil bacteria
项目 Item | 指标 Index | 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 轴3 Axis 3 | 轴4 Axis 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤细菌群落与理化因子Soil bacterial communities and physicochemical factors | 土壤细菌群落特征值Soil bacterial community characteristic values | 0.6824 | 0.0008 | 0.0004 | 0.0001 |
| 土壤细菌群落累计解释量Cumulative interpretation of soil bacterial community (%) | 68.24 | 68.32 | 68.36 | 68.37 | |
| 土壤细菌群落与环境因子的相关性Correlation between soil bacterial community and environmental factors | 0.8278 | 0.6393 | 0.5542 | 0.6547 | |
| 土壤细菌群落与环境因子累计解释量Cumulative explained amount of soil bacterial community and environmental factors (%) | 99.80 | 99.92 | 99.97 | 99.99 | |
| 典范特征值Canonical eigenvalue | 68.37 | ||||
| 总特征值Total eigenvalue | 99.99 | ||||
| 土壤细菌代谢功能与理化因子Soil bacterial metabolic functions and physicochemical factors | 土壤细菌代谢功能特征值Soil bacterial metabolic function characteristic values | 0.3787 | 0.0390 | 0.0250 | 0.0113 |
| 土壤细菌代谢功能累计解释量Cumulative interpretation of soil bacterial metabolic function (%) | 37.87 | 41.77 | 44.27 | 45.39 | |
| 土壤细菌代谢功能与环境因子的相关性Correlation between soil bacterial metabolic function and environmental factors | 0.7772 | 0.6107 | 0.5843 | 0.6210 | |
| 土壤细菌代谢功能与环境因子累计解释量Cumulative explained amount of soil bacterial metabolic functions and environmental factors (%) | 80.78 | 89.10 | 94.43 | 96.83 | |
| 典范特征值Canonical eigenvalue | 45.39 | ||||
| 总特征值Total eigenvalue | 96.83 | ||||
表5 土壤细菌群落及代谢功能RDA排序特征值及解释量
Table 5 Soil bacterial community and metabolic function RDA ordination characteristic value and interpretation amount
项目 Item | 指标 Index | 轴1 Axis 1 | 轴2 Axis 2 | 轴3 Axis 3 | 轴4 Axis 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤细菌群落与理化因子Soil bacterial communities and physicochemical factors | 土壤细菌群落特征值Soil bacterial community characteristic values | 0.6824 | 0.0008 | 0.0004 | 0.0001 |
| 土壤细菌群落累计解释量Cumulative interpretation of soil bacterial community (%) | 68.24 | 68.32 | 68.36 | 68.37 | |
| 土壤细菌群落与环境因子的相关性Correlation between soil bacterial community and environmental factors | 0.8278 | 0.6393 | 0.5542 | 0.6547 | |
| 土壤细菌群落与环境因子累计解释量Cumulative explained amount of soil bacterial community and environmental factors (%) | 99.80 | 99.92 | 99.97 | 99.99 | |
| 典范特征值Canonical eigenvalue | 68.37 | ||||
| 总特征值Total eigenvalue | 99.99 | ||||
| 土壤细菌代谢功能与理化因子Soil bacterial metabolic functions and physicochemical factors | 土壤细菌代谢功能特征值Soil bacterial metabolic function characteristic values | 0.3787 | 0.0390 | 0.0250 | 0.0113 |
| 土壤细菌代谢功能累计解释量Cumulative interpretation of soil bacterial metabolic function (%) | 37.87 | 41.77 | 44.27 | 45.39 | |
| 土壤细菌代谢功能与环境因子的相关性Correlation between soil bacterial metabolic function and environmental factors | 0.7772 | 0.6107 | 0.5843 | 0.6210 | |
| 土壤细菌代谢功能与环境因子累计解释量Cumulative explained amount of soil bacterial metabolic functions and environmental factors (%) | 80.78 | 89.10 | 94.43 | 96.83 | |
| 典范特征值Canonical eigenvalue | 45.39 | ||||
| 总特征值Total eigenvalue | 96.83 | ||||

图6 土壤细菌群落与理化因子RDA分析实线实心箭头Solid line solid arrow:环境因子Environmental factor. SOM:土壤有机质Soil organic matter;TN:土壤全氮Soil total nitrogen;TP:土壤全磷Soil total phosphorus;AP:土壤速效磷Soil available phosphorus;AK:土壤速效钾Soil available potassium;VG:梭梭林盖度H. ammodendron forest coverage;H:梭梭林高度Height of H. ammodendron forest;下同。The same below. 虚线空心箭头Dashed hollow arrow:土壤细菌群落及多样性指数Soil bacterial community and diversity index. 1:放线菌门Actinobacteria;2:变形菌门Proteobacteria;3:绿弯菌门Chloroflexi;4:拟杆菌门Bacteroidetes;5:酸杆菌门Acidobacteria;6:芽单胞菌门Gemmatimonadetes;7:蓝藻菌门Cyanobacteria;8:厚壁菌门Firmicutes;9:Chao1指数Chao1 index;10:Shannon指数Shannon index;11:Simpson指数Simpson index.
Fig.6 RDA analysis of soil bacterial community and physicochemical factors
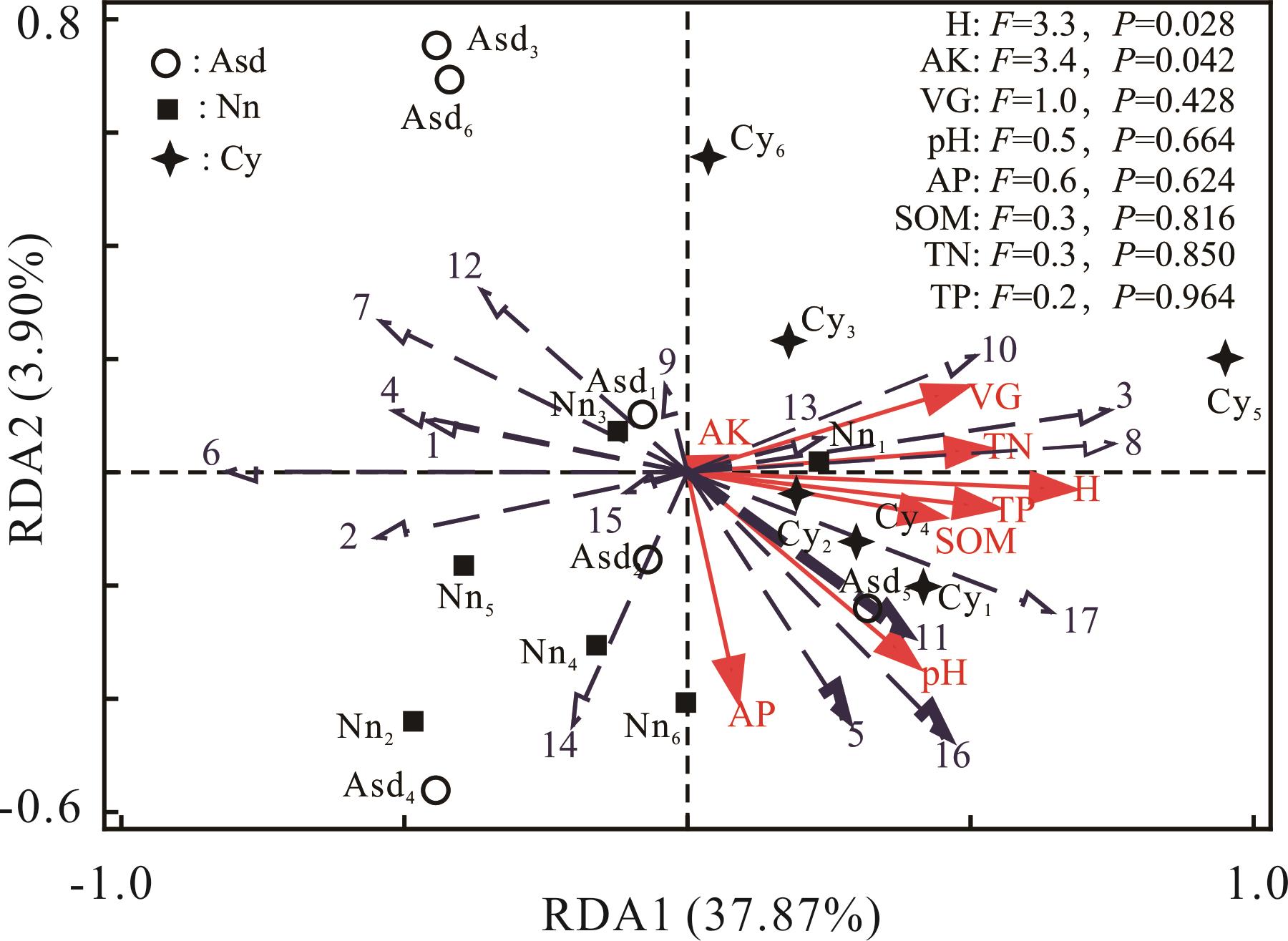
图7 土壤细菌功能基因与理化因子RDA分析虚线空心箭头Dashed hollow arrow:土壤细菌功能Soil bacterial function. 1:碳水化合物代谢Carbohydrate metabolism;2:氨基酸代谢Amino acid metabolism;3:辅助因子和维生素的代谢Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins;4:萜类和聚酮类化合物的代谢Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides;5:其他氨基酸的代谢Metabolism of other amino acids;6:脂质代谢Lipid metabolism;7:外来生物的生物降解和代谢Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism;8:能量代谢Energy metabolism;9:复制和修复Replication and repair;10:折叠排序和降解Folding sorting and degradation;11:糖类的生物合成和代谢Glycan biosynthesis and metabolism;12:其他次级代谢物的生物合成Biosynthesis of other secondary metabolites;13:翻译Translation;14:细胞运动性Cell motility;15:膜运输Membrane transport;16:核苷酸代谢Nucleotide metabolism;17:细胞生长和死亡Cell growth and death.
Fig.7 RDA analysis of functional genes and physicochemical factors of soil bacteria

图9 不同治沙措施下土壤细菌群落结构差异与功能基因丰度差异关系
Fig.9 Relationship between differences in soil bacterial community structure and differences in functional gene abundance under different sand control measures
| 1 | Guo B, Wei C, Yu Y, et al. The dominant influencing factors of desertification changes in the source region of Yellow River: Climate change or human activity? The Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 813(1): 152-170. |
| 2 | Yang J, Yang K, Wang C, et al. How desertification in northern China will change under a rapidly warming climate in the near future (2021-2050). Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2023, 151(1): 935-948. |
| 3 | Wang X, Song J L, Xiao Z, et al. Desertification in the Mu Us Sandy Land in China: Response to climate change and human activity from 2000 to 2020. Geography and Sustainability, 2022, 3(2): 177-189. |
| 4 | You Y, Zhou N, Wang Y, et al. Comparative study of desertification control policies and regulations in representative countries of the Belt and Road Initiative. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2021, 27(3): 157-169. |
| 5 | Zhang J, Guan Q Y, Du Q, et al. Spatial and temporal dynamics of desertification and its driving mechanism in Hexi region. Land Degradation & Development, 2022, 33(17): 3539-3556. |
| 6 | Zhao W Z, Ren H, Du J, et al. Thoughts and suggestions on oasis ecological construction and agricultural development in Hexi Corridor. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2023, 38(3): 424-434. |
| 赵文智, 任珩, 杜军, 等. 河西走廊绿洲生态建设和农业发展的若干思考与建议. 中国科学院院刊, 2023, 38(3): 424-434. | |
| 7 | Yong Z S, Wen Z Z, Pei X S, et al. Ecological effects of desertification control and desertified land reclamation in an oasis-desert ecotone in an arid region: A case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Ecological Engineering, 2007, 29(2): 117-124. |
| 8 | Xie Y, Dang X, Zhou Y, et al. Using sediment grain size characteristics to assess effectiveness of mechanical sand barriers in reducing erosion. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 149-163. |
| 9 | Liu Z Y, Dong Z B, Zhao J, et al. Effects of artificial sand fixation on sediment characteristics and soil nutrients. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(4): 1383-1391. |
| 刘铮瑶, 董治宝, 赵杰, 等. 人工固沙措施对沙丘沉积物特征及土壤养分的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(4): 1383-1391. | |
| 10 | Su Y Z, Liu T N. Soil evolution processes following establishment of artificial sandy-fixing Haloxylon ammodendron forest. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(1): 84-91. |
| 苏永中, 刘婷娜. 流动沙地建植人工固沙梭梭林的土壤演变过程. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(1): 84-91. | |
| 11 | Wang X Y, Ma L P, Cheng X Y, et al. Effects of different sand control measures on plant communities and soil factors in the desert-oasis ecotone. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(14): 5869-5883. |
| 王新源, 马立鹏, 程小云, 等. 不同治沙措施对荒漠绿洲过渡带植物群落与土壤因子的影响. 生态学报, 2022, 42(14): 5869-5883. | |
| 12 | Ma R, Wang J H, Qu J J, et al. Vegetation gradient characteristics of Minqin oasis-desert transition zone and its soil water environment. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2010, 29(6): 1075-1080. |
| 马瑞, 王继和, 屈建军, 等. 民勤绿洲-荒漠过渡带植被梯度特征及其土壤水环境. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29(6): 1075-1080. | |
| 13 | Liu X P, He Y H, Sun S S, et al. Restoration of sand-stabilizing vegetation reduces deep percolation of precipitation in semi-arid sandy lands, northern China. Catena, 2022, 208(20): 728-740. |
| 14 | Alamusa, Su Y H, Yin J, et al. Effect of sand-fixing vegetation on the hydrological regulation function of sand dunes and its practical significance. Journal of Arid Land, 2023, 15(1): 52-62. |
| 15 | Meng R B, Cai J, Xin H, et al. Spatio-temporal changes in land use and habitat quality of Hobq desert along the Yellow River section. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2023, 20(4): 3599-3610. |
| 16 | Yang H T, Li X R, Wang Z R, et al. Carbon sequestration capacity of shifting sand dune after establishing new vegetation in the Tengger Desert, northern China. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 478(15): 1-11. |
| 17 | Li H, Meng Z J, Dang X H, et al. Checkerboard barriers attenuate soil particle loss and promote nutrient contents of soil. Sustainability, 2022, 14(17): 157-175. |
| 18 | Guo Q J, Guo Z N, De Y J, et al. Effects of the Hedysarum laeve sand barriers on the microclimate of the Keerqin sand ground. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 28(2): 50-54. |
| 郭秋菊. 郭志年, 德永军, 等. 科尔沁沙地杨柴沙障对小气候的影响. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 28(2): 50-54. | |
| 19 | Chang Z F, Han F G, Zhong S N, et al. Responses of vegetations in Minqin desert area to climate change. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 2012, 23(5): 42-51. |
| 20 | Sun Z, Mao Z, Yang L, et al. Impacts of climate change and afforestation on vegetation dynamic in the Mu Us Desert, China. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 129(9): 108-121. |
| 21 | Wang Z H, Jiang X J. Contrasting responses of the microbial community structure and functional traits to soil pH in purple soils. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(7): 3876-3883. |
| 王智慧, 蒋先军. 紫色土中微生物群落结构及功能特征对土壤pH的差异响应.环境科学, 2022, 43(7): 3876-3883. | |
| 22 | Chen H S, Liu S P, Yang W Q, et al. Structure and diversity of bacterial community in rhizosphere soil of four dominant species along the bank of the lower reaches of Yarlung Zangbo River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(4): 1527-1537. |
| 陈海生, 刘守平, 杨万勤, 等. 雅鲁藏布江下游沿岸湿地建群种植物根际土壤细菌群落结构和多样性特征. 生态学报, 2022, 42(4): 1527-1537. | |
| 23 | Manuel D B, Jasmine G, Peter B, et al. Relative importance of soil properties and microbial community for soil functionality: Insights from a microbial swap experiment. Functional Ecology, 2016, 30(11): 1862-1873. |
| 24 | Ma X, Luo Z Z, Zhang Y Q, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological function predictions of soil bacterial communities in rainfed alfalfa fields on the Loess Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 54-67. |
| 马欣, 罗珠珠, 张耀全, 等. 黄土高原雨养区不同种植年限紫花苜蓿土壤细菌群落特征与生态功能预测. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 54-67. | |
| 25 | Sergio S, Vito R, Paolo R, et al. Soil inoculation with symbiotic microorganisms promotes plant growth and nutrient transporter genes expression in durum wheat. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6(4): 815-826. |
| 26 | Singh P, Singh R K, Li H B, et al. Nitrogen fixation and phytohormone stimulation of sugarcane plant through plant growth promoting diazotrophic Pseudomonas. Biotechnology & Genetic Engineering Reviews, 2023, 16(4): 1-21. |
| 27 | Li Y Y, Xu T T, Ai Z, et al. Diversity and predictive functional of Caragana jubata bacterial community in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil at different elevations. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(4): 2304-2314. |
| 李媛媛, 徐婷婷, 艾喆, 等. 不同海拔鬼箭锦鸡儿根际和非根际土壤细菌群落多样性及PICRUSt功能预测. 环境科学, 2023, 44(4): 2304-2314. | |
| 28 | Wang Z, Liu Y, Wang F, et al. Effects of vegetation types and seasonal dynamics on the diversity and function of soil bacterial communities in the upper reaches of the Heihe river. Environmental Science, 2023, DOI: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202210348. |
| 王竹, 刘扬, 王芳, 等. 黑河上游不同植被类型土壤细菌群落多样性、功能及季节动态. 环境科学, 2023, DOI: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202210348. | |
| 29 | Wei P, An S Z, Dong Y Q, et al. A high-throughput sequencing evaluation of bacterial diversity and community structure of the desert soil in the Junggar Basin. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(5): 182-190. |
| 魏鹏, 安沙舟, 董乙强, 等. 基于高通量测序的准噶尔盆地荒漠土壤细菌多样性及群落结构特征. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 182-190. | |
| 30 | Ding Y P, Du Y J, Gao G L, et al. Soil bacterial community structure and functional prediction of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations in the Hulun Buir Sandy Land. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(10): 4131-4139. |
| 丁钰珮, 杜宇佳, 高广磊, 等. 呼伦贝尔沙地樟子松人工林土壤细菌群落结构与功能预测. 生态学报, 2021, 41(10): 4131-4139. | |
| 31 | Cao H, Du Y, Gao G, et al. Afforestation with Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica remodelled soil bacterial community and potential metabolic function in the Horqin Desert. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2021, 29(2): 171-186. |
| 32 | An F J, Niu Z, Liu T N, et al. Succession of soil bacterial community along a 46-year choronsequence artificial revegetation in an arid oasis-desert ecotone. The Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 814(5): 152-162. |
| 33 | Yu J, Liu F, Tripathi B M, et al. Changes in the composition of soil bacterial and fungal communities after revegetation with Caragana microphylla in a desertified semiarid grassland. Journal of Arid Environments, 2020, 182(10): 44-55. |
| 34 | Gong X Q, Jarvie S, Zhang Q, et al. Community assembly of plant, soil bacteria, and fungi vary during the restoration of an ecosystem threatened by desertification. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2022, 23(1): 459-472. |
| 35 | Luo Y, Lu B L, Zhou G P, et al. Effects of returning the root of green manure on reducing N application in maize within their intercropping system in Hexi oasis irrigation area. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(12): 2125-2135. |
| 罗跃, 卢秉林, 周国朋, 等. 河西绿洲灌区玉米间作绿肥根茬还田的氮肥减施效应. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(12): 2125-2135. | |
| 36 | Bao S D. Agrochemical analysis of soil (3rd Edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000: 25-114. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 25-114. | |
| 37 | Jiang H M, Chen Y C, Hu Y, et al. Soil bacterial communities and diversity in alpine grasslands on the Tibetan Plateau based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2021, 9(2): 630-641. |
| 38 | Kim H, Kim S, Jung S. Instruction of microbiome taxonomic profiling based on 16S rRNA sequencing. Journal of Microbiology, 2020, 58(3): 193-205. |
| 39 | Douglas G M, Maffei V J, Zaneveld J R, et al. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(6): 685-688. |
| 40 | Wang X Y, Chen X S, Ding Q P, et al. Vegetation and soil environmental factor characteristics, and their relationship at different desertification stages: A case study in the Minqin desert-oasis ecotone. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(5): 1569-1580. |
| 王新源, 陈翔舜, 丁乾平, 等. 不同荒漠化阶段植被生态特征对土壤环境因子的响应——以民勤荒漠绿洲过渡带为例. 生态学报, 2018, 38(5): 1569-1580. | |
| 41 | Yuan W P, Cai W W, Liu D, et al. Satellite-based vegetation production models of terrestrial ecosystem: An overview.Advances in Earth Science, 2014, 29(5): 541-550. |
| 袁文平, 蔡文文, 刘丹, 等. 陆地生态系统植被生产力遥感模型研究进展. 地球科学进展, 2014, 29(5): 541-550. | |
| 42 | Zuo X A, Zhao X Y, Zhao H L, et al. Spatial heterogeneity of soil properties and vegetation-soil relationships following vegetation restoration of mobile dunes in Horqin Sandy Land, Northern China. Plant and Soil, 2009, 318(2): 153-167. |
| 43 | Li M J, Yu L F, Du M F, et al. C, N, and P stoichiometry and their interaction with plants, litter, and soil in a Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation with different ages. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(21): 7772-7781. |
| 李明军, 喻理飞, 杜明凤, 等. 不同林龄杉木人工林植物-凋落叶-土壤C、N、P化学计量特征及互作关系. 生态学报, 2018, 38(21): 7772-7781. | |
| 44 | Zemmrich A, Manthey M, Zerbe S, et al. Driving environmental factors and the role of grazing in grassland communities: A comparative study along an altitudinal gradient in Western Mongolia. Journal of Arid Environments, 2010, 74(10): 1271-1280. |
| 45 | Wang G H, Ren Y J, Gou Q Q. The changes of soil physical and chemical property during the enclosure process in a typical desert oasis ecotone of the Hexi Corridor in northwestern China. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(2): 222-231. |
| 王国华, 任亦君, 缑倩倩. 河西走廊荒漠绿洲过渡带封育对土壤和植被的影响. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 222-231. | |
| 46 | Yong Z S, Xue F W, Rong Y, et al. Effects of sandy desertified land rehabilitation on soil carbon sequestration and aggregation in an arid region in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 2010, 91(11): 2109-2116. |
| 47 | Xi J Q, Yang Z H, Guo S J, et al. Effects of artificial Haloxylon ammodendron forest on soil physical and chemical properties and microorganisms in sandy land. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(5): 44-52. |
| 席军强, 杨自辉, 郭树江, 等. 人工梭梭林对沙地土壤理化性质和微生物的影响. 草业学报, 2015, 24(5): 44-52. | |
| 48 | Sun L J, Qi Y C, Dong Y S, et al. Research progresses on the effects of global change on microbial community diversity of grassland soils. Progress in Geography, 2012, 31(12): 1715-1723. |
| 孙良杰, 齐玉春, 董云社, 等. 全球变化对草地土壤微生物群落多样性的影响研究进展. 地理科学进展, 2012, 31(12): 1715-1723. | |
| 49 | Sun Y, Shi Y L, Wang H, et al. Diversity of bacteria and the characteristics of actinobacteria community structure in Badain Jaran Desert and Tengger Desert of China. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9(10): 68-82. |
| 50 | Wang Z Y, Liu B R, Li Z H, et al. Characteristics of soil bacterial community structure in the different developmental stages of desert grassland Caragana korshinskii Kom. Nebkhas. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2022, 38(7): 205-214. |
| 王子寅, 刘秉儒, 李子豪, 等. 荒漠草原柠条灌丛堆不同发育阶段土壤细菌群落结构特征. 生物技术通报, 2022, 38(7): 205-214. | |
| 51 | Li S J, Wang F X, Cong W Q, et al. Microbial community structure and environmental response of desert soil in Hexi Corridor. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2022, 59(6): 1718-1728. |
| 李善家, 王福祥, 从文倩, 等. 河西走廊荒漠土壤微生物群落结构及环境响应. 土壤学报, 2022, 59(6): 1718-1728. | |
| 52 | Li T, Zhang W, Liu G X, et al. Advances in the study of microbical ecology in desert soil. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(2): 329-338. |
| 李婷, 张威, 刘光琇, 等. 荒漠土壤微生物群落结构特征研究进展. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(2): 329-338. | |
| 53 | Ren M. Microbial community structure in the Tarim Basin and its role in carbon and nitrogen cycling. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 任敏. 塔里木盆地微生物群落结构及其在碳氮元素循环中的作用. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018. | |
| 54 | Yang X D, Long Y X, Binoy S, et al. Influence of soil microorganisms and physicochemical properties on plant diversity in an arid desert of Western China. Journal of Forestry Research, 2021, 32: 2645-2659. |
| 55 | Vries F T, Griffiths R I, Mark B, et al. Soil bacterial networks are less stable under drought than fungal networks. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 30-33. |
| 56 | Du Y J, Gao G L, Chen L H, et al. Soil bacteria community structure and function prediction in the Hulun Buir Sandy Area. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(11): 4840-4848. |
| 杜宇佳, 高广磊, 陈丽华, 等. 呼伦贝尔沙区土壤细菌群落结构与功能预测. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(11): 4840-4848. | |
| 57 | Liu Z, Nan Z W, Lin S M, et al. Soil bacterial community structure and function prediction of millet/peanut intercropping farmland in the Lower Yellow River. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(8): 4575-4584. |
| 刘柱, 南镇武, 林松明, 等. 黄河下游谷子花生间作农田土壤细菌群落结构与功能预测. 环境科学, 2023, 44(8): 4575-4584. | |
| 58 | Falkowski P G, Fenchel T, Delong E F. The microbial engines that drive earth’s biogeochemical cycles. Science, 2008, 320(5879): 1034-1039. |
| 59 | Gema B M, Erland B, Johannes R. Functional implications of the pH-trait distribution of the microbial community in are-inoculation experiment across a pH gradient. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2016, 93: 69-78. |
| 60 | Wei H, Peng C H, Yang B, et al. Contrasting soil bacterial community, diversity, and function in two forests in China. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9(7): 169-183. |
| 61 | Lin H Y, Zhou J C, Zeng Q X, et al. Distribution pattern of soil bacterial community characteristics in a Pinus taiwanensis forest along an elevational gradient of Wuyi Mountains. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2022, 41(8): 1482-1492. |
| 林惠瑛, 周嘉聪, 曾泉鑫, 等. 武夷山黄山松林土壤细菌群落特征沿海拔梯度的分布模式. 生态学杂志, 2022, 41(8): 1482-1492. | |
| 62 | Liang Y T, Nuccio E E, Yuan M T, et al. Differentiation strategies of soil rare and abundant microbial taxa in response to changing climatic regimes. Environmental Microbiology, 2020, 22(4): 1327-1340. |
| [1] | 陈彦硕, 马彦平, 王红梅, 赵亚楠, 李志丽, 张振杰. 荒漠草原不同年限灌丛引入过程土壤细菌碳源利用特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 30-44. |
| [2] | 史正军, 潘松, 冯世秀, 袁峰均. 园林废弃物地表覆盖处理对植物生长及土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 153-160. |
| [3] | 王博, 张茹, 刘静, 李志刚. 翻埋与覆盖林木枝条对干旱区沙化土壤及紫花苜蓿根系丛枝菌根真菌的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 15-25. |
| [4] | 苏荣霞, 马彦平, 王红梅, 赵亚楠, 李志丽. 荒漠草原不同间距灌丛引入对土壤细菌碳源利用和胞外酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 93-105. |
| [5] | 周晓雷, 闫月娥, 张婧, 周旭姣, 闫永琴, 杨富强, 曹雪萍, 赵安, 赵艳丽, 苏静怡. 青藏高原东北边缘云杉-冷杉林火烧迹地不同坡向植物群落结构与多样性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 144-155. |
| [6] | 蒋嘉瑜, 连学, 唐希明, 刘任涛, 张安宁. 干旱与半干旱区红砂枯落物分解初期节肢动物群落结构特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 156-168. |
| [7] | 王亚妮, 胡宜刚, 王增如, 李以康, 张振华, 周华坤. 沙化和人工植被重建对高寒草地土壤细菌群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 26-39. |
| [8] | 田英, 许喆, 朱丽珍, 王俊, 温学飞. 生长季不同月份平茬对柠条人工林地土壤细菌群落特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 40-50. |
| [9] | 卢俊艳, 红梅, 赵巴音那木拉null, 赵乌英嘎, 王文东, 马尚飞, 杨殿林. 贝加尔针茅草原植物群落结构及生物量对长期养分添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 22-31. |
| [10] | 孙彩彩, 董全民, 刘文亭, 冯斌, 时光, 刘玉祯, 俞旸, 张春平, 张小芳, 李彩弟, 杨增增, 杨晓霞. 放牧方式对青藏高原高寒草地土壤节肢动物群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 62-75. |
| [11] | 靳旭妹, 王莹莹, 刘崇义, 陈新义, 龙明秀, 何树斌. 生草对关中地区有机猕猴桃园土壤养分及细菌群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 53-63. |
| [12] | 田翠翠, 卜书海, 周多良, 刘建泉, 周永祥, 郑雪莉. 安南坝野骆驼国家级自然保护区鼠类群落结构的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 62-71. |
| [13] | 马欣, 罗珠珠, 张耀全, 刘家鹤, 牛伊宁, 蔡立群. 黄土高原雨养区不同种植年限紫花苜蓿土壤细菌群落特征与生态功能预测[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 54-67. |
| [14] | 赵文, 尹亚丽, 李世雄, 刘燕, 刘晶晶, 董怡玲, 苏世锋, 吉凌鹤. 祁连山不同类型草地土壤细菌群落特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 161-171. |
| [15] | 何周窈, 王勇, 苏正安, 杨鸿琨, 周涛. 干热河谷冲沟沟头活跃度对植物群落结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 28-37. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||