

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3): 1-12.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023146
• 研究论文 •
油志远1( ), 马淑娟1(
), 马淑娟1( ), 王长庭1(
), 王长庭1( ), 丁路明1, 宋小艳1, 尹高飞2, 毛军1
), 丁路明1, 宋小艳1, 尹高飞2, 毛军1
收稿日期:2023-05-08
修回日期:2023-07-24
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2023-12-27
通讯作者:
王长庭
作者简介:E-mail: wangct@swun.edu.cn基金资助:
Zhi-yuan YOU1( ), Shu-juan MA1(
), Shu-juan MA1( ), Chang-ting WANG1(
), Chang-ting WANG1( ), Lu-ming DING1, Xiao-yan SONG1, Gao-fei YIN2, Jun MAO1
), Lu-ming DING1, Xiao-yan SONG1, Gao-fei YIN2, Jun MAO1
Received:2023-05-08
Revised:2023-07-24
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2023-12-27
Contact:
Chang-ting WANG
摘要:
为探究青藏高原高寒草甸生态系统不同主要功能群适宜生境的空间分布格局、主控气候因子及在气候变化背景下的变化趋势,基于青藏高原第2次科考数据(2019-2021年),利用MaxEnt模型预测川滇高原高寒草甸生态系统主要功能群的4种典型物种(莎草科-矮嵩草;禾本科-垂穗披碱草;杂类草-鹅绒委陵菜;豆科-异叶米口袋)在未来气候变化条件下空间分布格局及影响其分布的主要气候因子。结果表明,矮嵩草、垂穗披碱草、鹅绒委陵菜和异叶米口袋在当前气候条件下的适宜生境面积分别为11.09万、9.23万、17.12万和16.53万km2,主要位于川滇高原中部和北部区域。环境因子贡献率和响应曲线显示,4个物种生境适宜性对生存环境具有相似的生态要求,且影响其分布的主要气候因子均为气温年较差、等温性和年均温等与温度有关的环境因子。在未来气候背景下,4个物种适宜生境面积均呈扩张趋势且平均海拔均升高了100~200 m,但变化速率趋于减缓,高寒草甸生态系统的物种多样性、生物量和稳定性可能随着气候变化而增强。
油志远, 马淑娟, 王长庭, 丁路明, 宋小艳, 尹高飞, 毛军. 川滇高原高寒草甸生态系统不同功能群植物分布格局的MaxEnt模型预测[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 1-12.
Zhi-yuan YOU, Shu-juan MA, Chang-ting WANG, Lu-ming DING, Xiao-yan SONG, Gao-fei YIN, Jun MAO. Using the model MaxEnt to predict plant distribution patterns of different functional groups in the alpine meadow ecosystem on Sichuan-Yunnan Plateau[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(3): 1-12.
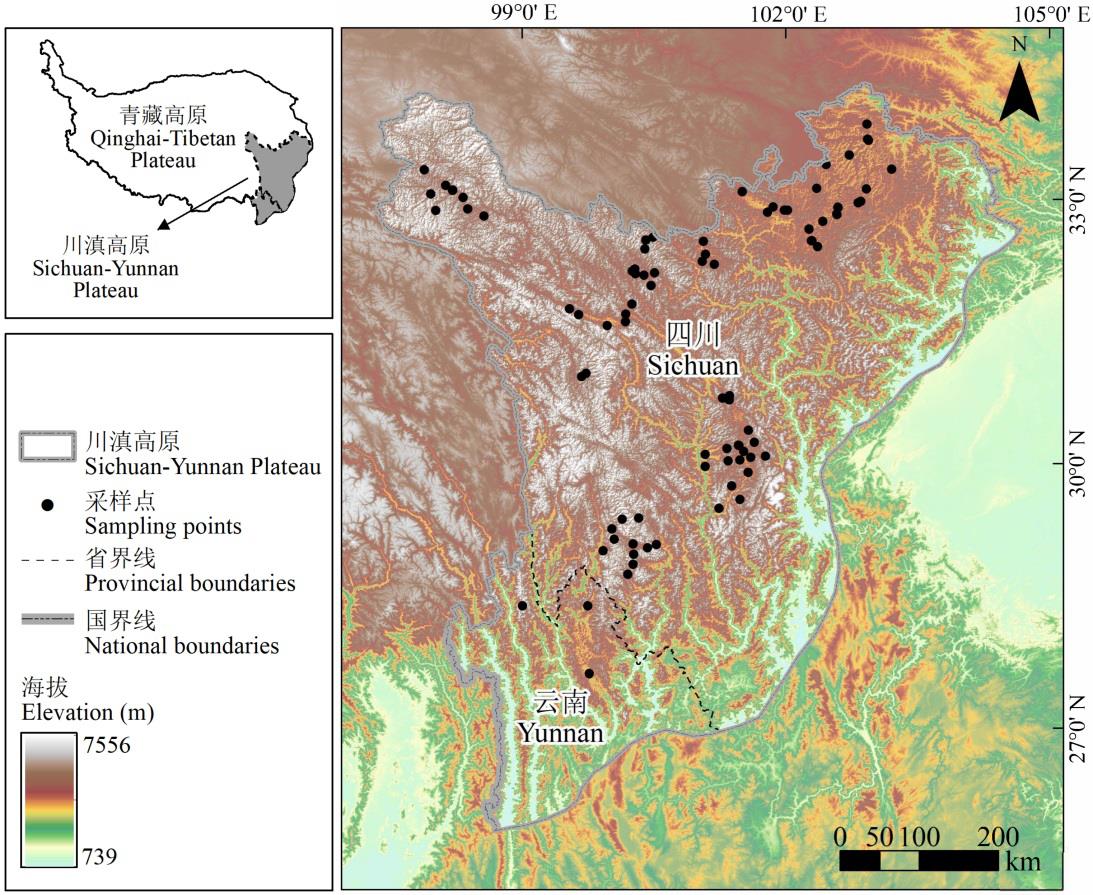
图1 川滇高原地形及采样位点示意青藏高原边界地图来源于时空三极环境大数据平台(https://poles.tpdc.ac.cn),该图基于审图号为GS(2016)1554号的标准地图制作,底图无修改。The boundary map of the Qinghai Tibet Plateau comes from A Big Earth Data Platform for Three Poles (https://poles.tpdc.ac.cn). The map was based on the standard map with the drawing review No. GS(2016)1554, and the base map was not modified.
Fig.1 Topography and sampling sites in Sichuan-Yunnan Plateau
| 模型评估指标Model evaluation metrics | 矮嵩草K. humilis | 垂穗披碱草E. nutans | 鹅绒委陵菜P. anserina | 异叶米口袋G. diversifolia |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集AUC值Training AUC | 0.9462 | 0.9503 | 0.9128 | 0.9082 |
| 测试集AUC值Testing AUC | 0.9309 | 0.9365 | 0.8701 | 0.8967 |
| AUC标准偏差AUC standard deviation (SD) | 0.0178 | 0.0187 | 0.0344 | 0.0311 |
表1 4个研究物种的AUC值及标准偏差
Table 1 AUC values and standard deviations of 4 study species
| 模型评估指标Model evaluation metrics | 矮嵩草K. humilis | 垂穗披碱草E. nutans | 鹅绒委陵菜P. anserina | 异叶米口袋G. diversifolia |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集AUC值Training AUC | 0.9462 | 0.9503 | 0.9128 | 0.9082 |
| 测试集AUC值Testing AUC | 0.9309 | 0.9365 | 0.8701 | 0.8967 |
| AUC标准偏差AUC standard deviation (SD) | 0.0178 | 0.0187 | 0.0344 | 0.0311 |

图2 当前及未来气候情景下4个物种适宜生境分布格局及重叠程度地图来源于时空三极环境大数据平台(https://poles.tpdc.ac.cn),该图基于审图号为GS(2016)1554号的标准地图制作,底图无修改。The boundary map of the Qinghai Tibet Plateau comes from A Big Earth Data Platform for Three Poles (https://poles.tpdc.ac.cn). The map was based on the standard map with the drawing review No. GS(2016)1554, and the base map was not modified.
Fig.2 Distribution pattern and overlap degree of suitable habitats for four species under current and future climate scenarios
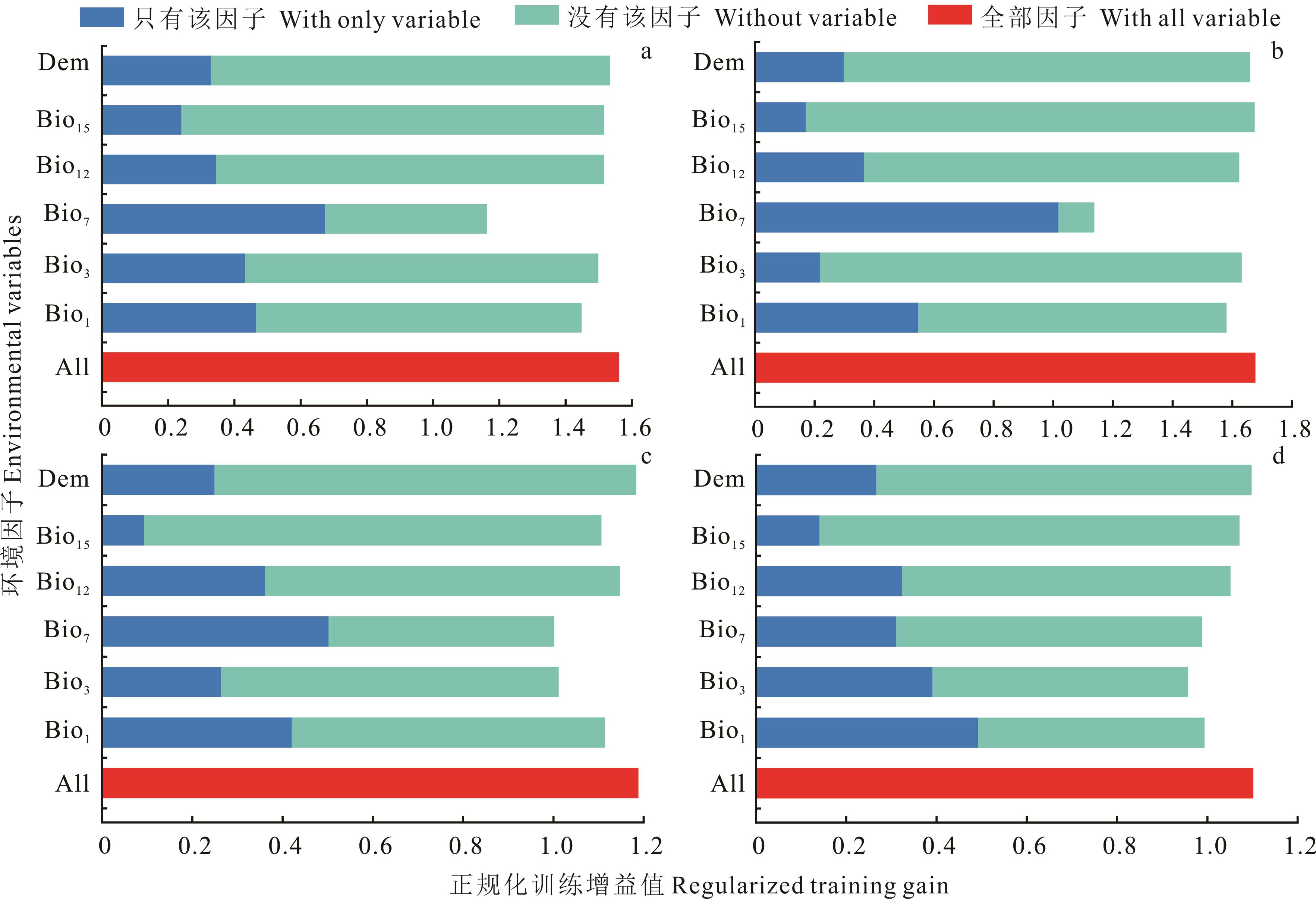
图4 环境因子正规化训练增益值a: 矮嵩草K. humilis; b: 垂穗披碱草E. nutans; c: 鹅绒委陵菜P. anserine;d: 异叶米口袋G. diversifolia; All: 全部因子With all variable; Bio1: 年均温Annual mean temperature; Bio3: 等温性Isothermality; Bio7: 气温年较差Temperature annual range; Bio12: 年均降水量Annual mean precipitation; Bio15: 降水季节性变异系数Precipitation seasonality; Dem: 海拔Elevation.
Fig.4 Regularized training gain of environmental factors
| 环境因子Variables | 矮嵩草K. humilis | 垂穗披碱草E. nutans | 鹅绒委陵菜P. anserina | 异叶米口袋G. diversifolia |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年均温Annual mean temperature | 13.4 | 13.2 | 15.1 | 17.8 |
| 等温性Isothermality | 31.5 | 15.8 | 27.2 | 40.3 |
| 气温年较差Temperature annual range | 49.1 | 63.7 | 48.0 | 33.8 |
| 年均降水量Annual mean precipitation | 1.6 | 6.7 | 6.2 | 4.8 |
| 降水季节性变异系数Precipitation seasonality | 3.8 | 0.2 | 3.4 | 2.4 |
| 海拔Elevation | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.9 |
表2 环境因子贡献率
Table 2 Contribution rate of environmental factors (%)
| 环境因子Variables | 矮嵩草K. humilis | 垂穗披碱草E. nutans | 鹅绒委陵菜P. anserina | 异叶米口袋G. diversifolia |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年均温Annual mean temperature | 13.4 | 13.2 | 15.1 | 17.8 |
| 等温性Isothermality | 31.5 | 15.8 | 27.2 | 40.3 |
| 气温年较差Temperature annual range | 49.1 | 63.7 | 48.0 | 33.8 |
| 年均降水量Annual mean precipitation | 1.6 | 6.7 | 6.2 | 4.8 |
| 降水季节性变异系数Precipitation seasonality | 3.8 | 0.2 | 3.4 | 2.4 |
| 海拔Elevation | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.9 |
| 1 | The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate change 2022: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Cambridge, UK and New York, USA: Cambridge University Press, 2022. |
| 2 | Jiang T, Zhai J Q, Luo Y, et al. Understandings of assessment reports on climate change impacts, adaptation and vulnerability: progress from IPCC AR5 to AR6. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2022, 45(4): 502-511. |
| 姜彤, 翟建青, 罗勇, 等. 气候变化影响适应和脆弱性评估报告进展: IPCC AR5到AR6的新认知. 大气科学学报, 2022, 45(4): 502-511. | |
| 3 | Chen D L, Xu B Q, Yao T D, et al. Assessment of past, present and future environmental changes on the Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(32): 3025-3035. |
| 陈德亮, 徐柏青, 姚檀栋, 等. 青藏高原环境变化科学评估: 过去、现在与未来. 科学通报, 2015, 60(32): 3025-3035. | |
| 4 | Yao T D. Tackling on environmental changes in Tibetan Plateau with focus on water, ecosystem and adaptation. Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(7): 417. |
| 5 | Walther G R, Post E, Convey P, et al. Ecological responses to recent climate change. Nature, 2022, 416(6879): 389-395. |
| 6 | Piao S L, Zhang X Z, Wang T, et al. Responses and feedback of the Tibetan Plateau’s alpine ecosystem to climate change. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(27): 2842-2855. |
| 朴世龙, 张宪洲, 汪涛, 等. 青藏高原生态系统对气候变化的响应及其反馈. 科学通报, 2019, 64(27): 2842-2855. | |
| 7 | Han M L, Bai S Q, Sun S N, et al. Simulation of Elymus sibiricus L. distribution in Tibetan Plateau based on MaxEnt model. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(2): 374-382. |
| 韩梦丽, 白史且, 孙盛楠, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型青藏高原老芒麦适生区模拟预测. 草地学报, 2021, 29(2): 374-382. | |
| 8 | Zhao W L, Chen H G, Yuan Y Y, et al. The impact of climate change on the distribution pattern of the suitable growing region for Tibetan medicine Lamiophlomis rotata. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(5): 956-964. |
| 赵文龙, 陈红刚, 袁永亚, 等. 气候变化对藏药独一味适生区分布格局的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(5): 956-964. | |
| 9 | Dong R, Chu B, Hua R, et al. Geographical distribution prediction of Stellera chamaejasme in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under future climate change scenarios. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(4): 10-20. |
| 董瑞, 楚彬, 花蕊, 等. 未来气候情景下青藏高原瑞香狼毒(Stellera chamaejasme)的地理分布预测. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(4): 10-20. | |
| 10 | Geng Y B, Wang S, Hu X D. Responses of aboveground net primary productivity of the alpine meadow steppe to climate change: simulations based on the CENTURY model. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(1): 1-13. |
| 耿元波, 王松, 胡雪荻. 高寒草甸草原净初级生产力对气候变化响应的模拟. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 1-13. | |
| 11 | Zhang F W, Li Y Q, Li Y N, et al. Short-term response of functional plant groups abundance to simulated climate change in alpine meadow ecosystems. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2010, 19(6): 72-78. |
| 张法伟, 李跃清, 李英年, 等. 高寒草甸不同功能群植被盖度对模拟气候变化的短期响应. 草业学报, 2010, 19(6): 72-78. | |
| 12 | Bengtsson J. Which species? What kind of diversity? Which ecosystem function? Some problems in studies of relations between biodiversity and ecosystem function. Applied Soil Ecology, 1998, 10(3): 191-199. |
| 13 | Wang C T, Long R J, Ding L M. The effects of differences in functional group diversity and composition on plant community productivity in four types of alpine meadow communities. Biodiversity Science, 2004, 12(4): 403-409. |
| 王长庭, 龙瑞军, 丁路明. 高寒草甸不同草地类型功能群多样性及组成对植物群落生产力的影响. 生物多样性, 2004, 12(4): 403-409. | |
| 14 | Yang X H, Bao Y J, Han G D, et al. Plant functional groups and their applications in ecology research. Journal of Dalian Minzu University, 2009, 11(5): 397-400, 409. |
| 杨晓慧, 鲍雅静, 韩国栋, 等. 植物功能群及其在生态学研究中的应用. 大连民族学院学报, 2009, 11(5): 397-400, 409. | |
| 15 | Yang Y J, Zhou H K, Yao B Q, et al. Effects of long-term simulated warming on soil physicochemical properties and plant chemical components of Kobresia humilis meadow. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(3): 781-789. |
| 杨月娟, 周华坤, 姚步青, 等. 长期模拟增温对矮嵩草草甸土壤理化性质与植物化学成分的影响. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(3): 781-789. | |
| 16 | Jiang Y B, Fan M, Zhang Y J. Effect of short-term warming on plant community features of alpine meadow in Northern Tibet. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(3): 616-622. |
| 姜炎彬, 范苗, 张扬建. 短期增温对藏北高寒草甸植物群落特征的影响. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(3): 616-622. | |
| 17 | Fick S E, Hijmans R J. WorldClim 2: new 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. International Journal of Climatology, 2017, 37(12): 4302-4315. |
| 18 | Fan X W, Miao C Y, Duan Q Y, et al. The performance of CMIP6 versus CMIP5 in simulating temperature extremes over the global land surface. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2020, 125(18): 1-16. |
| 19 | Zhang L X, Chen X L, Xin X G. Short commentary on CMIP6 Scenario Model Intercomparison Project (Scenario MIP). Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(5): 519-525. |
| 张丽霞, 陈晓龙, 辛晓歌. CMIP6情景模式比较计划(Scenario MIP)概况与评述. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(5): 519-525. | |
| 20 | Zhu G P, Liu G Q, Bu W J, et al. Ecological niche modeling and its applications in biodiversity conservation. Biodiversity Science, 2013, 21(1): 90-98. |
| 朱耿平, 刘国卿, 卜文俊, 等. 生态位模型的基本原理及其在生物多样性保护中的应用. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(1): 90-98. | |
| 21 | Guo Y L, Zhao Z F, Qiao H J, et al. Challenges and development trend of species distribution model. Advances in Earth Science, 2020, 35(12): 1292-1305. |
| 郭彦龙, 赵泽芳, 乔慧捷, 等. 物种分布模型面临的挑战与发展趋势. 地球科学进展, 2020, 35(12): 1292-1305. | |
| 22 | Xiong Q L, He Y L, Deng F Y, et al. Assessment of alpine mean response to climate change in Southwest China based on MaxEnt Model. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(24): 9033-9043. |
| 熊巧利, 何云玲, 邓福英, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型西南地区高山植被对气候变化的响应评估. 生态学报, 2019, 39(24): 9033-9043. | |
| 23 | Pan S A, Li X H, Feng Q H, et al. Response of Abies faxoniana to future climate change and its potential distribution patterns in Sichuan Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(10): 4055-4064. |
| 潘少安, 李旭华, 冯秋红, 等. 四川省岷江冷杉对气候变化的响应及其潜在分布格局. 生态学报, 2022, 42(10): 4055-4064. | |
| 24 | Myers N, Mittermeier R A, Mittermeier C G. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 2000, 403(6772): 853-858. |
| 25 | Zhang Y X, Li Y, Zhu G R. The effects of altitude on temperature, precipitation and climatic zone in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2019, 41(3): 505-515. |
| 张宇欣, 李育, 朱耿睿. 青藏高原海拔要素对温度、降水和气候型分布格局的影响. 冰川冻土, 2019, 41(3): 505-515. | |
| 26 | Yang X Q, Kushwaha S P S, Saran S. Maxent modeling for predicting the potential distribution of medicinal plant, Justicia adhatoda L. in Lesser Himalayan foothills. Ecological Engineering, 2013, 51: 83-87. |
| 27 | Yan W B, Wang Q, Wang C. Evaluation of potential breeding habitat distribution with Maxent model for crested ibis in the Qinling-Bashan region. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 2015, 50(2): 185-193. |
| 颜文博, 王琦, 王超. 应用Maxent模型分析秦巴地区朱鹮适宜繁殖地的分布. 动物学杂志, 2015, 50(2): 185-193. | |
| 28 | Swanepoel L H, Lindsey P, Somers M J, et al. Extent and fragmentation of suitable leopard habitat in South Africa. Animal Conservation, 2013, 16(1): 41-50. |
| 29 | Wang B Z, Zhu Y J, Liu Y S, et al. Potential distribution patterns of Stipa bungeana in China and the major factors influencing distribution. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(7): 3-13. |
| 王百竹, 朱媛君, 刘艳书, 等. 典型草原建群种长芒草(Stipa bungeana)在中国的潜在分布范围预测及主要影响因子分析. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 3-13. | |
| 30 | Li W Q, Xu Z F, Shi M M, et al. Prediction of potential geographical distribution patterns of Salix tetrasperma Roxb. in Asia under different climate scenarios. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(9): 3224-3234. |
| 李文庆, 徐洲锋, 史鸣明, 等. 不同气候情景下四子柳的亚洲潜在地理分布格局变化预测. 生态学报, 2019, 39(9): 3224-3234. | |
| 31 | Zhang M G, Slik J W F, Ma K P. Using species distribution modeling to delineate the botanical richness patterns and phytogeographical regions of China. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 22400. |
| 32 | Wu S J, Zhu T H, Qiao T M. Projections of Yunnan pine moth Dendrolimus houi in Sichuan Province under future climate change based on species distribution model. Journal of Plant Protection, 2021, 48(4): 882-890. |
| 吴思俊, 朱天辉, 谯天敏. 基于物种分布模型对未来气候变化下云南松毛虫在四川省适生区的预测. 植物保护学报, 2021, 48(4): 882-890. | |
| 33 | Wu T W, Lu Y X, Fang Y J, et al. The Beijing climate center climate system model (BCC-CSM): the main progress from CMIP5 to CMIP6. Geoscientific Model Development, 2019, 12(4): 1573-1600. |
| 34 | Xin X G, Wu T W, Zhang J, et al. Introduction of BCC models and its participation in CMIP6. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(5): 533-539. |
| 辛晓歌, 吴统文, 张洁, 等. BCC模式及其开展的CMIP6试验介绍. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(5): 533-539. | |
| 35 | Jin C X, Jiang C, Zhang X Y. Evaluation and projection of temperature in southwestern China by CMIP6 models. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2022, 43(8): 597-611. |
| 晋程绣, 姜超, 张曦月. CMIP6模式对中国西南地区气温的模拟与预估. 中国农业气象, 2022, 43(8): 597-611. | |
| 36 | Zhang J Y, Lun Y R, Liu L, et al. CMIP6 evaluation and projection of climate change in Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 2022, 58(1): 77-89. |
| 张佳怡, 伦玉蕊, 刘浏, 等. CMIP6多模式在青藏高原的适应性评估及未来气候变化预估. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 58(1): 77-89. | |
| 37 | Phillips S J, Dudík M. Modeling of species distributions with Maxent: new extensions and a comprehensive evaluation. Ecography, 2008, 31(2): 161-175. |
| 38 | Phillips S J, Anderson R P, Dudík M, et al. Opening the black box: an open-source release of Maxent. Ecography, 2017, 40(7): 887-893. |
| 39 | Swets J A. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science, 1988, 240(4857): 1285-1293. |
| 40 | Liu C, White M, Newell G. Selecting thresholds for the prediction of species occurrence with presence-only data. Journal of Biogeography, 2013, 40(4): 778-789. |
| 41 | Yu X, Chen J C, Wang B, et al. Population density estimation and habitat suitability assessment of Lophophorus lhuysii during breeding season in Xiaozhaizigou National Nature Reserve, Sichuan Province. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 2017, 36(4): 361-367. |
| 余翔, 陈俊橙, 王彬, 等. 四川小寨子沟国家级自然保护区绿尾虹雉种群密度调查与栖息地评价. 四川动物, 2017, 36(4): 361-367. | |
| 42 | Pearson R G, Dawson T P. Predicting the impacts of climate change on the distribution of species: Are bioclimate envelope models useful? Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2003, 12(5): 361-371. |
| 43 | Li J L, Li X L. Research progress on environmental adaptability of Kobresia humilis in alpine meadow. Ecological Science, 2016, 35(2): 156-165. |
| 李积兰, 李希来. 高寒草甸矮嵩草的环境适应性研究进展. 生态科学, 2016, 35(2): 156-165. | |
| 44 | Dandois J P, Olano M, Ellis E C. Optimal altitude, overlap, and weather conditions for computer vision UAV estimates of forest structure. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7(10): 13895-13920. |
| 45 | Li M J, He Z S, Jiang L, et al. Distribution pattern and driving factors of species diversity and phylogenetic diversity along altitudinal gradient on the south slope of Daiyun Mountain. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(3): 1148-1157. |
| 李梦佳, 何中声, 江蓝, 等. 戴云山物种多样性与系统发育多样性海拔梯度分布格局及驱动因子. 生态学报, 2021, 41(3): 1148-1157. | |
| 46 | Pan X, Qiu Q, Li J Y, et al. Physiological indexes of six plant species from the Tibetan plateau under drought stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(13): 3558-3567. |
| 潘昕, 邱权, 李吉跃, 等. 干旱胁迫对青藏高原6种植物生理指标的影响. 生态学报, 2014, 34(13): 3558-3567. | |
| 47 | Xu X K, Chen H, Levy J K. Spatiotemporal vegetation cover variations in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under global climate change. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(6): 915-922. |
| 48 | Qu T, Nan Z B. Research progress on responses and mechanisms of crop and grass under drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2008, 73(2): 126-135. |
| 曲涛, 南志标. 作物和牧草对干旱胁迫的响应及机理研究进展. 草业学报, 2008, 73(2): 126-135. | |
| 49 | Fan Q S, Sha Z J, Cao G C, et al. Assessment of ecology and environments on climate changing of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2005, 13(1): 12-18. |
| 樊启顺, 沙占江, 曹广超, 等.气候变化对青藏高原生态环境的影响评价. 盐湖研究, 2005, 13(1): 12-18. | |
| 50 | Liu W S, You J L, Zeng W B, et al. Prediction of the geographical distribution of Carex moorcroftii under global climate change based on MaxEnt model. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2018, 40(5): 43-49. |
| 刘文胜, 游简舲, 曾文斌, 等. 气候变化下青藏苔草地理分布的预测. 中国草地学报, 2018, 40(5): 43-49. | |
| 51 | Cai W T, Lai L M, Li H Y, et al. Progress of research on shrub encroachment in grassland. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2016, 22(4): 531-537. |
| 蔡文涛, 来利明, 李贺祎, 等. 草地灌丛化研究进展. 应用与环境生物学报, 2016, 22(4): 531-537. | |
| 52 | Ma W M, Liu J, Zhou Q P, et al. Stability of soil aggregates and soil organic carbon under shrub encroachment sites in alpine meadow. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2019, 50(5): 1108-1115. |
| 马文明, 刘军, 周青平, 等. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体稳定性及有机碳分布特征的影响. 土壤通报, 2019, 50(5): 1108-1115. |
| [1] | 马源, 王晓丽, 马玉寿, 张德罡. 高寒草甸退化程度对优势物种根际土壤真菌群落和生态网络的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 125-137. |
| [2] | 李林芝, 张德罡, 马源, 罗珠珠, 林栋, 海龙, 白兰鸽. 不同退化程度高寒草甸土壤团聚体养分及生态化学计量特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 48-60. |
| [3] | 廖小琴, 王长庭, 刘丹, 唐国, 毛军. 氮磷配施对高寒草甸植物根系特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 160-174. |
| [4] | 路欣, 祁娟, 师尚礼, 车美美, 李霞, 独双双, 赛宁刚, 贾燕伟. 阔叶类草抑制剂与氮素配施对高寒草甸土壤特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 38-48. |
| [5] | 刘彩凤, 段媛媛, 王玲玲, 王乙茉, 郭正刚. 高原鼠兔干扰对高寒草甸植物物种多样性与土壤生态化学计量比间关系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 157-166. |
| [6] | 孙玉, 杨永胜, 何琦, 王军邦, 张秀娟, 李慧婷, 徐兴良, 周华坤, 张宇恒. 三江源高寒草甸水源涵养功能及土壤理化性质对退化程度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 16-29. |
| [7] | 李紫晶, 高翠萍, 王忠武, 韩国栋. 中国草地固碳减排研究现状及其建议[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 191-200. |
| [8] | 周娟娟, 刘云飞, 王敬龙, 魏巍. 短期养分添加对西藏沼泽化高寒草甸地上生物量、植物多样性和功能性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 17-29. |
| [9] | 李江文, 裴婧宏, 韩国栋, 何邦印, 李彩. 基于植物功能性状分析异常降水对不同载畜率下荒漠草原功能群多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 212-222. |
| [10] | 吴旭东, 蒋齐, 王占军, 季波, 任小玢. 降水对荒漠草原地上生物量稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 30-39. |
| [11] | 游郭虹, 刘丹, 王艳丽, 王长庭. 高寒草甸植物叶片生态化学计量特征对长期氮肥添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 50-62. |
| [12] | 张玉琢, 杨志贵, 于红妍, 张强, 杨淑霞, 赵婷, 许画画, 孟宝平, 吕燕燕. 基于STARFM的草地地上生物量遥感估测研究——以甘肃省夏河县桑科草原为例[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 23-34. |
| [13] | 李洋, 王毅, 韩国栋, 孙建, 汪亚峰. 青藏高原高寒草地土壤微生物量碳氮含量特征及其控制要素[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 50-60. |
| [14] | 刘咏梅, 董幸枝, 龙永清, 朱志梅, 王雷, 盖星华, 赵樊, 李京忠. 退化高寒草甸狼毒群落分类特征及其环境影响因子[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 1-11. |
| [15] | 李鑫, 魏雪, 王长庭, 任晓, 吴鹏飞. 外源性养分添加对高寒草甸土壤节肢动物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 155-164. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||