

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 1-11.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023198
• 研究论文 •
秦瑞敏1,2( ), 程思佳1,3, 马丽1, 张中华1, 魏晶晶1,4, 苏洪烨1,2, 史正晨1,2, 常涛1,2, 胡雪1,2, 阿的哈则1,2, 袁访1, 李珊1, 周华坤1(
), 程思佳1,3, 马丽1, 张中华1, 魏晶晶1,4, 苏洪烨1,2, 史正晨1,2, 常涛1,2, 胡雪1,2, 阿的哈则1,2, 袁访1, 李珊1, 周华坤1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-04
修回日期:2023-07-24
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-01-15
通讯作者:
周华坤
作者简介:E-mail: hkzhou@nwipb.cas.cn基金资助:
Rui-min QIN1,2( ), Si-jia CHENG1,3, Li MA1, Zhong-hua ZHANG1, Jing-jing WEI1,4, Hong-ye SU1,2, Zheng-chen SHI1,2, Tao CHANG1,2, Xue HU1,2, De-ha-ze A1,2, Fang YUAN1, Shan LI1, Hua-kun ZHOU1(
), Si-jia CHENG1,3, Li MA1, Zhong-hua ZHANG1, Jing-jing WEI1,4, Hong-ye SU1,2, Zheng-chen SHI1,2, Tao CHANG1,2, Xue HU1,2, De-ha-ze A1,2, Fang YUAN1, Shan LI1, Hua-kun ZHOU1( )
)
Received:2023-06-04
Revised:2023-07-24
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-01-15
Contact:
Hua-kun ZHOU
摘要:
为探究不同恢复措施对退化高寒草甸的影响,研究了不同围封年限(0、4、13年)和长期施肥(N、P)下草甸群落特征和碳氮库的变化。结果表明:1)随着围封年限增加,物种丰富度指数和Shannon-Wiener指数显著降低,Simpson指数和Pielou指数呈先上升后下降的特征;长期N和P添加分别显著降低了物种丰富度指数和Shannon-Wiener指数。2)地上生物量和根系生物量在4和13年围封下均显著增加,且在4年围封时最高,而凋落物生物量则随围封年限增加而逐渐增加;长期施肥对生物量的影响不显著。3)围封后,植被碳和氮储量显著增加,其中地上生物量和根系碳、氮库均在4年围封时最高,凋落物碳、氮库则在13年围封时最高;长期施肥对植被碳储量无显著影响,仅长期N添加显著提高了地上生物量氮库。4)偏最小二乘(PLS)路径模型显示:围封和施肥导致环境因子发生变化,抑制了群落多样性,促进了植物生物量和植被碳库的积累,而植被氮库特征在施肥处理下发生变化。综上,围封整体上抑制了物种多样性,但能够促进群落生产力提高和植被碳氮库增汇;长期N添加对物种多样性和植被碳库无显著正效应,但促进了植被氮库增汇。
秦瑞敏, 程思佳, 马丽, 张中华, 魏晶晶, 苏洪烨, 史正晨, 常涛, 胡雪, 阿的哈则, 袁访, 李珊, 周华坤. 围封和施肥对高寒草甸群落特征和植被碳氮库的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 1-11.
Rui-min QIN, Si-jia CHENG, Li MA, Zhong-hua ZHANG, Jing-jing WEI, Hong-ye SU, Zheng-chen SHI, Tao CHANG, Xue HU, De-ha-ze A, Fang YUAN, Shan LI, Hua-kun ZHOU. Effects of grazing exclusion and fertilization on alpine meadow community characteristics and vegetation carbon and nitrogen pools[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(4): 1-11.
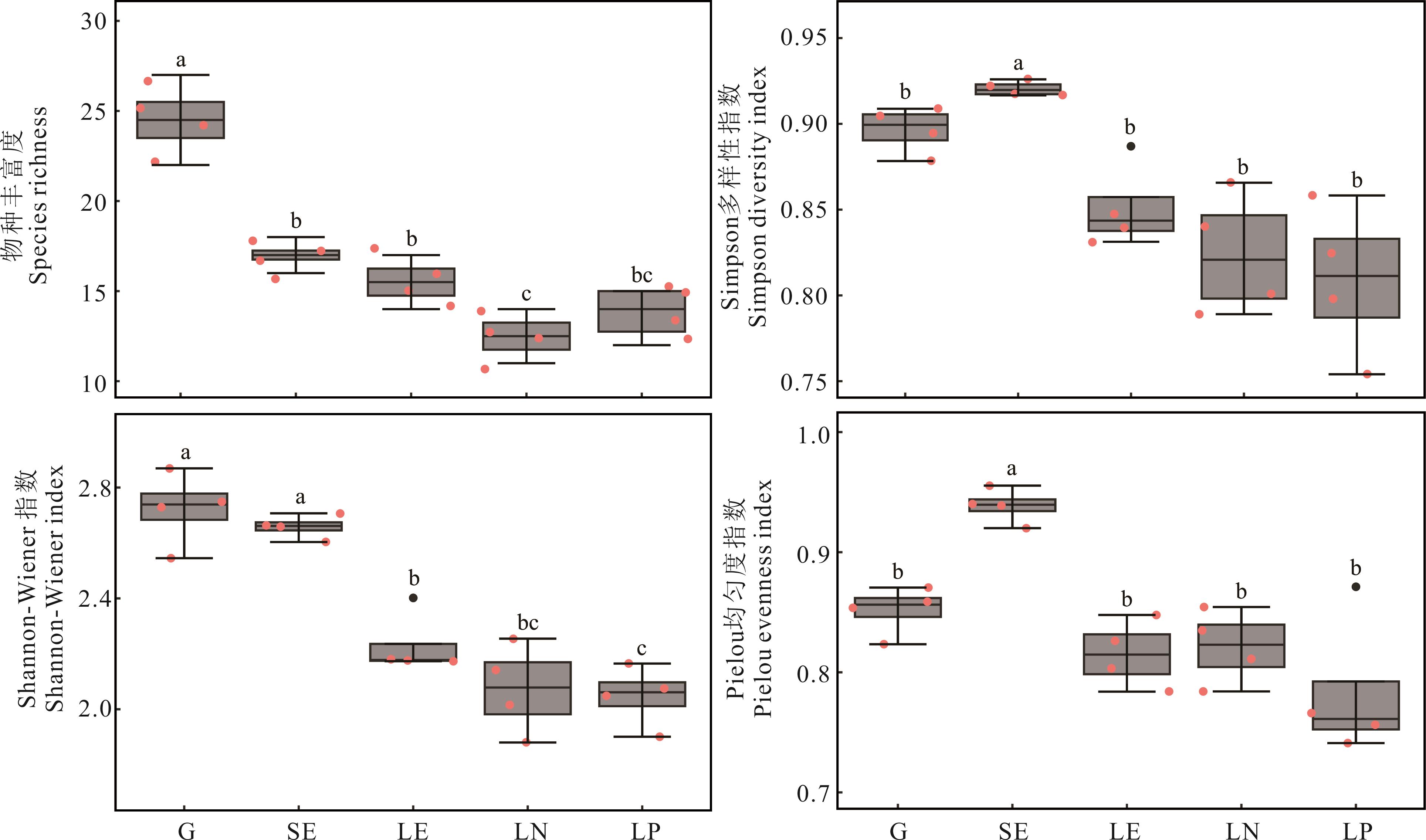
图1 围封和施肥对物种多样性的影响G: 自由放牧 Grazing; SE: 短期围封Short-term grazing exclusion (4 a); LE: 长期围封Long-term grazing exclusion (13 a); LN: 长期氮添加 Long-term N addition; LP: 长期磷添加Long-term P addition. 图中红点和黑点表示数据分布。不同小写字母表示不同处理之间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Red and black dots indicate data distribution. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Effect of grazing exclusion and fertilization on species diversity
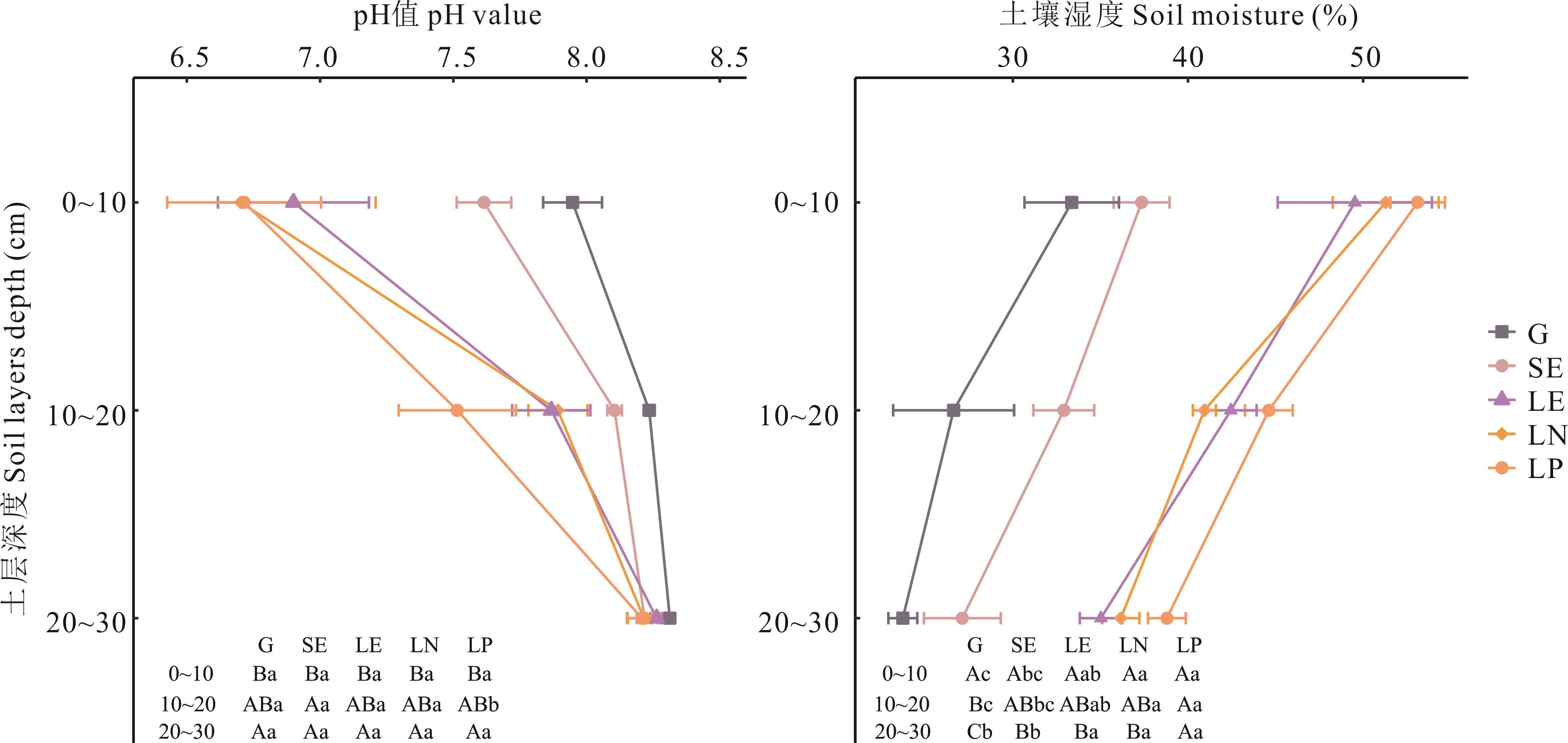
图3 围封和施肥对土壤pH值和湿度的影响不同大写字母表示同处理不同土层之间差异显著(P<0.05)Different capital letters indicate significant differences among different soil layers of the same treatment (P<0.05).
Fig.3 Effect of grazing exclusion and fertilization on soil pH value and moisture

图5 围封和施肥对植被碳和氮储量的影响机制环境因子: Environmental factor; 物种多样性指数: Species diversity index; 植物生物量: Plant biomass; 碳库储量: Carbon stocks; 氮库储量: Nitrogen stocks; 土壤湿度: Soil humidity; AGB: 地上生物量Aboveground biomass; Litter: 凋落物生物量Litter biomass; RB: 根系生物量Root biomass; *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001;实线和虚线分别表示正相关和负相关关系,箭头方向表示因果关系Solid and dashed lines indicate positive and negative correlations, respectively, and the direction of the arrow indicates causality.
Fig.5 Mechanisms of grazing exclusion and fertilization on vegetation carbon and nitrogen storage
| 1 | Bardgett R D, Bullock J M, Lavorel S, et al. Combatting global grassland degradation. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2021, 2(10): 720-735. |
| 2 | Gibson D J. Grasses and grassland ecology. New York: Oxford University Press, 2009. |
| 3 | Dong S K, Shang Z H, Gao J X, et al. Enhancing the ecological services of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau’s grasslands through sustainable restoration and management in era of global change. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2021.107756. |
| 4 | Sun J, Wang Y, Piao S L, et al. Toward a sustainable grassland ecosystem worldwide. The Innovation, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2022.100265. |
| 5 | Harris R B. Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau: A review of the evidence of its magnitude and causes. Journal of Arid Environments, 2010, 74(1): 1-12. |
| 6 | Zhou H K, Zhao X Q, Wen J, et al. The characteristics of soil and vegetation of degenerated alpine steppe in the Yellow River Source Region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(5): 1-11. |
| 周华坤, 赵新全, 温军, 等. 黄河源区高寒草原的植被退化与土壤退化特征. 草业学报, 2012, 21(5): 1-11. | |
| 7 | Lang Y Q, Yang X H, Cai H Y. Assessing the degradation of grassland ecosystems based on the advanced local net production scaling method-The case of Inner Mongolia, China. Land Degradation & Development, 2021, 32(2): 559-572. |
| 8 | Shi G X, Wang W Y, Jiang S J, et al. Effects of the spreading of Ligularia virgaurea on soil physicochemical property and microbial functional diversity. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2018, 42(1): 126-132. |
| 石国玺, 王文颖, 蒋胜竞, 等. 黄帚橐吾种群扩张对土壤理化特性与微生物功能多样性的影响. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(1): 126-132. | |
| 9 | Cheng J N, Jin H, Xu Z X, et al. Effects of degraded plant Stellera chamaejasme L. on the rhizosphere soil microbial communities in typical alpine grassland, Gansu Province. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2021, 61(11): 3686-3704. |
| 程济南, 金辉, 许忠祥, 等. 甘肃典型高寒草原退化植物瑞香狼毒对根际土壤微生物群落的影响研究. 微生物学报, 2021, 61(11): 3686-3704. | |
| 10 | Qin R M, Wei J J, Ma L, et al. Effects of Pedicularis kansuensis expansion on plant community characteristics and soil nutrients in an alpine grassland. Plants-Basel, 2022, doi: 10.3390/plants11131673. |
| 11 | Feng R Z, Zhou W H, Long R J, et al. Characteristics of soil physical, chemical and biological properties on degraded alpine meadows in the headwater areas of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2010, 41(2): 263-269. |
| 冯瑞章, 周万海, 龙瑞军, 等. 江河源区不同退化程度高寒草地土壤物理、化学及生物学特征研究. 土壤通报, 2010, 41(2): 263-269. | |
| 12 | Wang D J, Zhou H K, Zuo J, et al. Responses of soil microbial metabolic activity and community structure to different degraded and restored grassland gradients of the Tibetan Plateau. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.770315. |
| 13 | Ren J Z, Liang T G, Lin H L, et al. Study on grassland’s responses to global climate change and its carbon sequestration potentials. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2011, 20(2): 1-22. |
| 任继周, 梁天刚, 林慧龙, 等. 草地对全球气候变化的响应及其碳汇潜势研究. 草业学报, 2011, 20(2): 1-22. | |
| 14 | Feng J G, Zhang Q F, Yuan X, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil organic carbon: review and prospects. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2022, 46(8): 855-870. |
| 冯继广, 张秋芳, 袁霞, 等. 氮磷添加对土壤有机碳的影响: 进展与展望. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(8): 855-870. | |
| 15 | Sun J, Liu M, Fu B J, et al. Reconsidering the efficiency of grazing exclusion using fences on the Tibetan Plateau. Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(16): 1405-1414. |
| 16 | Zong N, Shi P L, Niu B, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorous fertilization on community structure and productivity of degraded alpine meadows in northern Tibet, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(12): 3458-3468. |
| 宗宁, 石培礼, 牛犇, 等. 氮磷配施对藏北退化高寒草甸群落结构和生产力的影响. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(12): 3458-3468. | |
| 17 | Wang D J, Zhou H K, Yao B Q, et al. Effects of nutrient addition on degraded alpine grasslands of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: A meta-analysis. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2020.106970. |
| 18 | Dong S K, Shang Z H, Gao J X, et al. Enhancing sustainability of grassland ecosystems through ecological restoration and grazing management in an era of climate change on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2019.106684. |
| 19 | Xiong D P, Shi P L, Zhang X Z, et al. Effects of grazing exclusion on carbon sequestration and plant diversity in grasslands of China-A meta-analysis. Ecological Engineering, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.124. |
| 20 | Wu X, Li Z S, Fu B J, et al. Restoration of ecosystem carbon and nitrogen storage and microbial biomass after grazing exclusion in semi-arid grasslands of Inner Mongolia. Ecological Engineering, 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.09.077. |
| 21 | Yan Y, Lu X Y. Is grazing exclusion effective in restoring vegetation in degraded alpine grasslands in Tibet, China. PeerJ, 2015, doi: 10.7717/peerj.1020. |
| 22 | Chen W J, Zhou H K, Wu Y, et al. Direct and indirect influences of long-term fertilization on microbial carbon and nitrogen cycles in an alpine grassland. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107922. |
| 23 | Fan Y J, Chang X Y, Zou H, et al. A study on the mechanisms of artificial fertilization on carbon cycling processes in grassland ecosystems. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(5): 95-96, 237. |
| 范月君, 畅喜云, 邹华, 等. 人工施肥对草地生态系统碳循环过程影响机制的研究. 安徽农业科学, 2015, 43(5): 95-96, 237. | |
| 24 | Chen H M, Shi F X, Yang G S, et al. Effects of nutrient addition on plant community composition and aboveground biomass in a marshy meadow in the Sanjiang Plain. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(6): 1440-1446. |
| 陈慧敏, 石福习, 杨桂生, 等. 养分添加对三江平原沼泽化草甸植物群落组成和地上生物量的影响. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(6): 1440-1446. | |
| 25 | Xiang X M, De K J, Zhang L, et al. Relationship between biomass and nutrients of alpine meadows in the short term under nitrogen addition. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(1): 53-61. |
| 向雪梅, 德科加, 张琳, 等. 氮素添加下短期内高寒草甸生物量与养分间的关系. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(1): 53-61. | |
| 26 | Jiang Y, Xu Z W, Wang R Z, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization and water addition on soil properties and plant community characteristics in a semiarid grassland. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(7): 2470-2480. |
| 姜勇, 徐柱文, 王汝振, 等. 长期施肥和增水对半干旱草地土壤性质和植物性状的影响. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(7): 2470-2480. | |
| 27 | Yang Y J, Zhou H K, Ye X, et al. Short-term responses of plant community structure and function to nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium additions in an alpine meadow of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2014, 34(11): 2317-2323. |
| 杨月娟, 周华坤, 叶鑫, 等. 青藏高原高寒草甸植物群落结构和功能对氮、磷、钾添加的短期响应. 西北植物学报, 2014, 34(11): 2317-2323. | |
| 28 | Lu C X, Xie G D, Xiao Y, et al. Ecosystem diversity and economic valuation of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(12): 2749-2755, 3011. |
| 鲁春霞, 谢高地, 肖玉, 等. 青藏高原生态系统服务功能的价值评估. 生态学报, 2004, 24(12): 2749-2755, 3011. | |
| 29 | Li L, Chen X G, Wang Z Y, et al. Climate change and its regional differences over the Tibetan Plateau. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2010, 6(3): 181-186. |
| 李林, 陈晓光, 王振宇, 等. 青藏高原区域气候变化及其差异性研究. 气候变化研究进展, 2010, 6(3): 181-186. | |
| 30 | Fu B J, Ouyang Z Y, Shi P, et al. Current condition and protection strategies of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau ecological security barrier. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021, 36(11): 1298-1306. |
| 傅伯杰, 欧阳志云, 施鹏, 等. 青藏高原生态安全屏障状况与保护对策. 中国科学院院刊, 2021, 36(11): 1298-1306. | |
| 31 | Zhang X S. The plateau zonality of vegetation in Xizang. Acta Botanica Sinica, 1978(2): 140-149. |
| 张新时. 西藏植被的高原地带性. 植物学报, 1978(2): 140-149. | |
| 32 | Ren F. The basic model of carbon cycle in alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and its response to simulated nitrogen deposition and nutrient addition. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016. |
| 任飞. 青藏高原高寒草甸碳循环基本模式及其对氮沉降和养分添加的响应. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2016. | |
| 33 | Ma L, Zhang Q, Zhang Z H, et al. Effects of gradient warming on species diversity and biomass in alpine meadows. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(5): 1395-1402. |
| 马丽, 张骞, 张中华, 等. 梯度增温对高寒草甸物种多样性和生物量的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(5): 1395-1402. | |
| 34 | Holdo R M, Holt R D, Coughenour M B, et al. Plant productivity and soil nitrogen as a function of grazing, migration and fire in an African savanna. Journal of Ecology, 2007, 95(1): 115-128. |
| 35 | Zhao W, Beng S H, Zhou X L, et al. Effects of short-term fertilization and enclosure on biomass and species richness in an alpine meadow. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2023, doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202311.002. |
| 赵维, 蚌绍豪, 周小龙, 等. 短期施肥和围封对高寒草甸生物量和物种丰富度的影响. 生态学杂志, 2023, doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202311.002. | |
| 36 | Semmartin M, Garibaldi L A, Chaneton E J. Grazing history effects on above- and below-ground litter decomposition and nutrient cycling in two co-occurring grasses. Plant and Soil, 2008, doi: 10.1007/s11104-007-9497-9. |
| 37 | Harpole W S, Sullivan L L, LindI E M, et al. Addition of multiple limiting resources reduces grassland diversity. Nature, 2016, 537(7618): 93-96. |
| 38 | Chen L, Tian X M, Ren Z W, et al. Effects of nutrient addition on plant diversity and above-ground biomass in alpine grasslands of Tianshan Mountains, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2022, 46(3): 280-289. |
| 陈丽, 田新民, 任正炜, 等. 养分添加对天山高寒草地植物多样性和地上生物量的影响. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(3): 280-289. | |
| 39 | Zhang P, Ma J J, Cheng J H, et al. Effects of enclosure on vegetation characteristics and soil physical and chemical properties of temperate grassland. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(5): 41-50. |
| 张攀, 马婧婧, 程军回, 等. 围封对天山北坡中段温性草原植被特征和土壤理化性质的影响. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(5): 41-50. | |
| 40 | Du K, Kang Y K, Zhang D G, et al. Effects of different grazing patterns on organic carbon and nitrogen pools in alpine meadow in the Qilian Mountains. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(5): 1412-1420. |
| 杜凯, 康宇坤, 张德罡, 等. 不同放牧方式对祁连山高寒草甸有机碳、氮库的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(5): 1412-1420. | |
| 41 | Bi X, Li B, Fu Q, et al. Effects of grazing exclusion on the grassland ecosystems of mountain meadows and temperate typical steppe in a mountain-basin system in Central Asia’s arid regions, China. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.055. |
| 42 | Qin J M, Wang C H, Cao Y, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition and mowing on plant carbon and nitrogen pools in typical grassland of Inner Mongolia. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(1): 12-20. |
| 秦加敏, 王常慧, 曹颖, 等. 氮添加和刈割对内蒙古典型草原植被碳氮库的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(1): 12-20. | |
| 43 | Zhang Y H, Lv X T, Isbell F, et al. Rapid plant species loss at high rates and at low frequency of N addition in temperate steppe. Global Change Biology, 2014, 20(11): 3520-3529. |
| 44 | Hou S L, Freschet G T, Yang J J, et al. Quantifying the indirect effects of nitrogen deposition on grassland litter chemical traits. Biogeochemistry, 2018, 139(3): 261-273. |
| 45 | Luo R Y, Fan J L, Wang W J, et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment accelerates soil organic carbon loss in alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.038. |
| 46 | Benner J W, Vitousek P M. Development of a diverse epiphyte community in response to phosphorus fertilization. Ecology Letters, 2007, 10(7): 628-636. |
| 47 | Song S S, Zhang J S, Zheng T L, et al. Effect of fencing on vegetation carbon storage in the Qinghai Haibei alpine meadows. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(12): 2414-2421. |
| 宋珊珊, 张建胜, 郑天立, 等. 围栏封育对青海海北高寒草甸植被碳储量的影响. 草业科学, 2020, 37(12): 2414-2421. | |
| 48 | Su S L, Li Y, Wang L Y, et al. Effect of fencing on plant biomass and functional group structure of different types of degraded grassland in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2014, 34(8): 1652-1657. |
| 苏淑兰, 李洋, 王立亚, 等. 围封与放牧对青藏高原草地生物量与功能群结构的影响. 西北植物学报, 2014, 34(8): 1652-1657. | |
| 49 | Yang X X, Ren F, Zhou H K, et al. Responses of plant community biomass to nitrogen and phosphorus additions in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(2): 159-166. |
| 杨晓霞, 任飞, 周华坤, 等. 青藏高原高寒草甸植物群落生物量对氮、磷添加的响应. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(2): 159-166. | |
| 50 | Jin S L, Diao Z Y, Lv S H, et al. Response characteristics of plant functional groups to enclosure and grazing in Hulunbuir grassland. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2022, 36(1): 151-158. |
| 靳三玲, 刁兆岩, 吕世海, 等. 呼伦贝尔草原植物功能群对围封及放牧的响应特征. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(1): 151-158. | |
| 51 | Zhang L, Zhang L W, Liu H L. Effects of nitrogen addition on the root morphology and biomass characteristics of ephemeral plants in a cold desert. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(10): 2003-2011. |
| 张岚, 张玲卫, 刘会良. 氮添加对荒漠草原一年生短命植物根系形态特征的影响及其生物量特征关系. 草业科学, 2020, 37(10): 2003-2011. | |
| 52 | Zhang Q, Wang Z C, Pu Q S, et al. Effects of different management modes on carbon storage in Gannan alpine meadow. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(2): 529-537. |
| 张倩, 王志成, 蒲强胜, 等. 不同管理模式对甘南高寒草甸碳储量的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(2): 529-537. |
| [1] | 油志远, 马淑娟, 王长庭, 丁路明, 宋小艳, 尹高飞, 毛军. 川滇高原高寒草甸生态系统不同功能群植物分布格局的MaxEnt模型预测[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 1-12. |
| [2] | 唐璎, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 董霖. 甘肃不同区域青贮紫花苜蓿乳酸菌群落特征及其驱动因子研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 112-124. |
| [3] | 马源, 王晓丽, 马玉寿, 张德罡. 高寒草甸退化程度对优势物种根际土壤真菌群落和生态网络的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 125-137. |
| [4] | 李林芝, 张德罡, 马源, 罗珠珠, 林栋, 海龙, 白兰鸽. 不同退化程度高寒草甸土壤团聚体养分及生态化学计量特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 48-60. |
| [5] | 廖小琴, 王长庭, 刘丹, 唐国, 毛军. 氮磷配施对高寒草甸植物根系特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 160-174. |
| [6] | 路欣, 祁娟, 师尚礼, 车美美, 李霞, 独双双, 赛宁刚, 贾燕伟. 阔叶类草抑制剂与氮素配施对高寒草甸土壤特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 38-48. |
| [7] | 刘彩凤, 段媛媛, 王玲玲, 王乙茉, 郭正刚. 高原鼠兔干扰对高寒草甸植物物种多样性与土壤生态化学计量比间关系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 157-166. |
| [8] | 孙玉, 杨永胜, 何琦, 王军邦, 张秀娟, 李慧婷, 徐兴良, 周华坤, 张宇恒. 三江源高寒草甸水源涵养功能及土壤理化性质对退化程度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 16-29. |
| [9] | 周娟娟, 刘云飞, 王敬龙, 魏巍. 短期养分添加对西藏沼泽化高寒草甸地上生物量、植物多样性和功能性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 17-29. |
| [10] | 游郭虹, 刘丹, 王艳丽, 王长庭. 高寒草甸植物叶片生态化学计量特征对长期氮肥添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 50-62. |
| [11] | 牛伟玲, 陈辉, 侯慧新, 郭晨睿, 马娇林, 武建双. 10年禁牧未改变藏西北高寒荒漠植物水氮利用效率[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 35-48. |
| [12] | 彭艳, 孙晶远, 马素洁, 王向涛, 魏学红, 孙磊. 藏北不同退化阶段高寒草甸植物群落特征与土壤养分特性[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 49-60. |
| [13] | 张玉琢, 杨志贵, 于红妍, 张强, 杨淑霞, 赵婷, 许画画, 孟宝平, 吕燕燕. 基于STARFM的草地地上生物量遥感估测研究——以甘肃省夏河县桑科草原为例[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 23-34. |
| [14] | 李洋, 王毅, 韩国栋, 孙建, 汪亚峰. 青藏高原高寒草地土壤微生物量碳氮含量特征及其控制要素[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 50-60. |
| [15] | 赵朋波, 邱开阳, 谢应忠, 刘王锁, 李小伟, 陈林, 王继飞, 孟文芬, 黄业芸, 李小聪, 杨浩楠. 海拔梯度对贺兰山岩羊主要活动区植物群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 79-90. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||