

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6): 227-235.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023258
• 研究简报 • 上一篇
丁维芹1,2( ), 孙永刚1,2(
), 孙永刚1,2( ), 韩银仓1,2, 刘亚倩1,2, 靳生伟1,2
), 韩银仓1,2, 刘亚倩1,2, 靳生伟1,2
收稿日期:2023-07-24
修回日期:2023-10-08
出版日期:2024-06-20
发布日期:2024-03-20
通讯作者:
孙永刚
作者简介:E-mail: sunyg2009@qq.com基金资助:
Wei-qin DING1,2( ), Yong-gang SUN1,2(
), Yong-gang SUN1,2( ), Yin-cang HAN1,2, Ya-qian LIU1,2, Sheng-wei JIN1,2
), Yin-cang HAN1,2, Ya-qian LIU1,2, Sheng-wei JIN1,2
Received:2023-07-24
Revised:2023-10-08
Online:2024-06-20
Published:2024-03-20
Contact:
Yong-gang SUN
摘要:
为鉴定不同饲养方式下牦牛皮下脂肪组织中差异表达的微小RNAs(miRNAs),本试验采用高通量测序对不同饲养方式下牦牛皮下脂肪组织中的miRNAs进行筛选,运用DESeq分别鉴定出自然放牧18月龄(G18) vs (从自然放牧18月龄开始舍饲育肥6个月至24月龄)F24、G18 vs (自然放牧至24月龄)G24和F24 vs G24皮下脂肪组织中差异表达的miRNAs,对差异表达的miRNAs进行靶基因预测分析。在9个牦牛皮下脂肪组织中共鉴定出1158个miRNAs,其中已知miRNAs 731个,新预测miRNAs 427个。在G18 vs F24中有43个差异miRNAs,预测到的靶基因2436 个; 在G18 vs G24中有68个差异miRNAs,预测到的靶基因3559个,在F24 vs G24中有31个差异miRNAs,预测到的靶基因1456个。对预测到的基因进行GO和KEGG富集分析,其主要富集到了脂肪酸代谢过程、脂肪酸生物合成过程、脂肪酸生物氧化、不饱和脂肪酸代谢过程和脂肪细胞分化调节等。因此,枯草期对牦牛进行补饲有利于牦牛皮下脂肪组织沉积。
丁维芹, 孙永刚, 韩银仓, 刘亚倩, 靳生伟. 牦牛皮下脂肪组织miRNA的鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 227-235.
Wei-qin DING, Yong-gang SUN, Yin-cang HAN, Ya-qian LIU, Sheng-wei JIN. Identification and analysis of miRNAs in subcutaneous fat tissue of yaks[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(6): 227-235.
| 项目Items | 比例Proportion (%) | 营养水平Nutrient levels | 含量Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| 玉米Corn | 43.71 | 综合净能Combined net energy(MJ·kg-1) | 4.28 |
| 浓缩料Concentrate | 10.93 | 粗蛋白Crude protein (%) | 16.63 |
| 油菜籽粕Rapeseed meal | 3.00 | 粗脂肪Ether extract (%) | 5.49 |
| 豆粕Soybean meal | 3.00 | 粗纤维Crude fiber (%) | 21.17 |
| 燕麦干草Oat hay | 10.93 | 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (%) | 28.61 |
| 青贮Silage | 27.33 | 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (%) | 46.09 |
| 食盐Salt | 0.55 | 钙Calcium (%) | 0.36 |
| 小苏打NaHCO3 | 0.55 | 总磷Total phosphorus (%) | 0.16 |
| 合计Total | 100.00 |
表1 基础饲粮组成及营养水平(干物质基础)
Table 1 Basal diet composition and nutrient levels (dry matter basis)
| 项目Items | 比例Proportion (%) | 营养水平Nutrient levels | 含量Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| 玉米Corn | 43.71 | 综合净能Combined net energy(MJ·kg-1) | 4.28 |
| 浓缩料Concentrate | 10.93 | 粗蛋白Crude protein (%) | 16.63 |
| 油菜籽粕Rapeseed meal | 3.00 | 粗脂肪Ether extract (%) | 5.49 |
| 豆粕Soybean meal | 3.00 | 粗纤维Crude fiber (%) | 21.17 |
| 燕麦干草Oat hay | 10.93 | 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (%) | 28.61 |
| 青贮Silage | 27.33 | 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (%) | 46.09 |
| 食盐Salt | 0.55 | 钙Calcium (%) | 0.36 |
| 小苏打NaHCO3 | 0.55 | 总磷Total phosphorus (%) | 0.16 |
| 合计Total | 100.00 |
样本 Sample | 原始数据 Raw reads | 质控数据 Clean reads | 错误率 Error rate (%) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC 含量 GC content (%) | 有效读数 Useful reads (18~32 nt) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G18_1 | 10750515 | 10148638 | 0.0234 | 98.60 | 95.90 | 48.28 | 9489991 |
| G18_2 | 10344153 | 10053329 | 0.0228 | 98.93 | 96.43 | 47.57 | 9500929 |
| G18_3 | 10984478 | 10809524 | 0.0242 | 98.04 | 95.35 | 46.06 | 10508432 |
| F24_1 | 10916818 | 10635810 | 0.0221 | 99.12 | 97.25 | 45.53 | 10095800 |
| F24_2 | 11840664 | 11204703 | 0.0221 | 99.18 | 97.29 | 47.62 | 10427912 |
| F24_3 | 9953508 | 9830901 | 0.0222 | 99.13 | 97.13 | 48.10 | 9286535 |
| G24_1 | 10513414 | 10431218 | 0.0217 | 99.38 | 97.64 | 46.04 | 8971547 |
| G24_2 | 10042097 | 9926786 | 0.0219 | 99.26 | 97.43 | 45.77 | 9632620 |
| G24_3 | 19642751 | 19531520 | 0.0227 | 98.96 | 96.46 | 47.40 | 17530772 |
表2 牦牛9个样本测序数据质控结果
Table 2 Quality control results of sequencing data from 9 samples of yak
样本 Sample | 原始数据 Raw reads | 质控数据 Clean reads | 错误率 Error rate (%) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC 含量 GC content (%) | 有效读数 Useful reads (18~32 nt) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G18_1 | 10750515 | 10148638 | 0.0234 | 98.60 | 95.90 | 48.28 | 9489991 |
| G18_2 | 10344153 | 10053329 | 0.0228 | 98.93 | 96.43 | 47.57 | 9500929 |
| G18_3 | 10984478 | 10809524 | 0.0242 | 98.04 | 95.35 | 46.06 | 10508432 |
| F24_1 | 10916818 | 10635810 | 0.0221 | 99.12 | 97.25 | 45.53 | 10095800 |
| F24_2 | 11840664 | 11204703 | 0.0221 | 99.18 | 97.29 | 47.62 | 10427912 |
| F24_3 | 9953508 | 9830901 | 0.0222 | 99.13 | 97.13 | 48.10 | 9286535 |
| G24_1 | 10513414 | 10431218 | 0.0217 | 99.38 | 97.64 | 46.04 | 8971547 |
| G24_2 | 10042097 | 9926786 | 0.0219 | 99.26 | 97.43 | 45.77 | 9632620 |
| G24_3 | 19642751 | 19531520 | 0.0227 | 98.96 | 96.46 | 47.40 | 17530772 |
样本 Sample | 总读数 Total reads | 总比对数 Total mapped | Mapped reads (+) | Mapped reads (-) | 样本 Sample | 总读数 Total reads | 总比对数 Total mapped | Mapped reads (+) | Mapped reads (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G18_1 | 9489991 | 5344527 | 4212651 | 1825475 | F24_3 | 9286535 | 4246707 | 3197390 | 1634626 |
| G18_2 | 9500929 | 5225765 | 3859662 | 1983461 | G24_1 | 8971547 | 5946435 | 2046646 | 4662344 |
| G18_3 | 10508432 | 8837041 | 6854643 | 3113029 | G24_2 | 9632620 | 8034727 | 6221424 | 2754939 |
| F24_1 | 10095800 | 8847347 | 6536930 | 3459607 | G24_3 | 17530772 | 9994961 | 7399388 | 3821385 |
| F24_2 | 10427912 | 7733935 | 5803836 | 3120208 |
表3 牦牛9个样本序列比对结果
Table 3 Sequence comparison results of 9 samples of yak
样本 Sample | 总读数 Total reads | 总比对数 Total mapped | Mapped reads (+) | Mapped reads (-) | 样本 Sample | 总读数 Total reads | 总比对数 Total mapped | Mapped reads (+) | Mapped reads (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G18_1 | 9489991 | 5344527 | 4212651 | 1825475 | F24_3 | 9286535 | 4246707 | 3197390 | 1634626 |
| G18_2 | 9500929 | 5225765 | 3859662 | 1983461 | G24_1 | 8971547 | 5946435 | 2046646 | 4662344 |
| G18_3 | 10508432 | 8837041 | 6854643 | 3113029 | G24_2 | 9632620 | 8034727 | 6221424 | 2754939 |
| F24_1 | 10095800 | 8847347 | 6536930 | 3459607 | G24_3 | 17530772 | 9994961 | 7399388 | 3821385 |
| F24_2 | 10427912 | 7733935 | 5803836 | 3120208 |
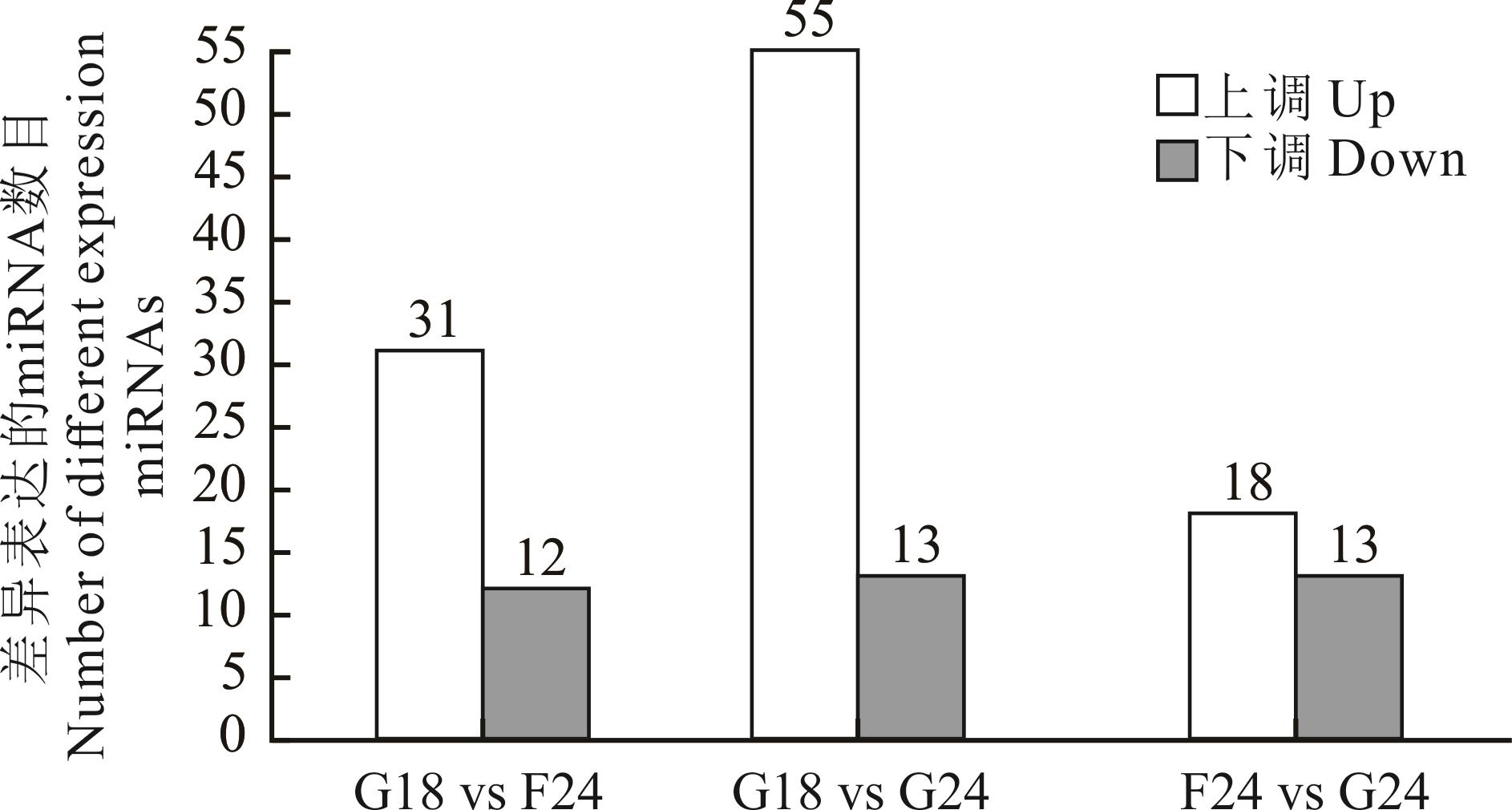
图1 表达量差异统计结果横坐标代表不同的差异比较组别,纵坐标代表对应的上下调差异miRNA数目。The horizontal coordinates represent the different difference comparison groups, and the vertical coordinates represent the corresponding number of up- and down-regulated differential miRNAs.
Fig.1 Expression variation statistics result
| miRNA身份编码miRNA ID | Log2FC (F24_SF/G18_SF) | P值P value | 显著性Significant | 上下调情况Regulate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bta-miR-1260b | 2.08031424948 | 0.0112727 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-24-3p | 1.02898643541 | 0.0466993 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-124a | 2.78762271924 | 0.0351538 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-885 | -3.95167430049 | 0.0207700 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-27a-5p | 2.36559870851 | 0.0016845 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
表4 G18 vs F24牦牛皮下脂肪差异倍数绝对值前5 位的miRNA
Table 4 G18 vs F24 miRNAs in the top 5 absolute values of subcutaneous fat differential ploidy in yaks
| miRNA身份编码miRNA ID | Log2FC (F24_SF/G18_SF) | P值P value | 显著性Significant | 上下调情况Regulate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bta-miR-1260b | 2.08031424948 | 0.0112727 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-24-3p | 1.02898643541 | 0.0466993 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-124a | 2.78762271924 | 0.0351538 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-885 | -3.95167430049 | 0.0207700 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-27a-5p | 2.36559870851 | 0.0016845 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| miRNA身份编码miRNA ID | Log2FC (G24_SF/G18_SF) | P值 P value | 显著性 Significant | 上下调情况Regulate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bta-miR-454 | 2.11532735063 | 0.014020 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-218 | 1.05553458799 | 0.043355 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-29b | 1.19292296058 | 0.039507 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-193b | -1.80868199849 | 0.010954 | 是Yes | 下调Down |
| bta-miR-335 | 1.59669329476 | 0.034489 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
表5 G18 vs G24牦牛皮下脂肪差异倍数绝对值前 5 位的 miRNA
Table 5 G18 vs G24 miRNAs in the top 5 absolute values of subcutaneous fat differential ploidy in yaks
| miRNA身份编码miRNA ID | Log2FC (G24_SF/G18_SF) | P值 P value | 显著性 Significant | 上下调情况Regulate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bta-miR-454 | 2.11532735063 | 0.014020 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-218 | 1.05553458799 | 0.043355 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-29b | 1.19292296058 | 0.039507 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-193b | -1.80868199849 | 0.010954 | 是Yes | 下调Down |
| bta-miR-335 | 1.59669329476 | 0.034489 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| miRNA身份编码miRNA ID | Log2FC(G24_SF/F24_SF) | P值 P value | 显著性Significant | 上下调情况Regulate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bta-miR-193b | -1.47024482126 | 0.038634 | 是Yes | 下调Down |
| bta-miR-454 | 1.89166293414 | 0.027869 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-340 | 1.82365577695 | 0.014773 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-20a | 1.55661838474 | 0.038220 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-147 | 3.89774495343 | 0.002327 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
表6 F24 vs G24牦牛皮下脂肪差异倍数绝对值前 5 位的 miRNA
Table 6 F24 vs G24 miRNAs in the top 5 absolute values of subcutaneous fat differential ploidy in yaks
| miRNA身份编码miRNA ID | Log2FC(G24_SF/F24_SF) | P值 P value | 显著性Significant | 上下调情况Regulate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bta-miR-193b | -1.47024482126 | 0.038634 | 是Yes | 下调Down |
| bta-miR-454 | 1.89166293414 | 0.027869 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-340 | 1.82365577695 | 0.014773 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-20a | 1.55661838474 | 0.038220 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
| bta-miR-147 | 3.89774495343 | 0.002327 | 是Yes | 上调Up |
miRNA名称 miRNA name | 预测到的靶基因 Predict target genes | miRNA名称 miRNA name | 预测到的靶基因 Predict target genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| bta-miR-1260 | MAP4K4、POU2F1、MRAS、STMP1、PACS2,et al | bta-miR-193b | ATL2、DYSF、AP5Z1、TMEM63A、FAT2,et al |
| bta-miR-124a | DISP1、ITSN2、CTSH、LRRC28、CEP68,et al | bta-miR-335 | TRIP12、NFIB、NRXN1、AGTPBP1、MYO1E,et al |
| bta-miR-24-3p | SPON1、CBFB、KIF18、CD163、ERG,et al | bta-miR-454 | VPS16、KIF14、DPY19L1、ECHDC1、VIRMA,et al |
| bta-miR-885 | FUS、RTRAF、DIDO1、ARHGAP20、SAMD8,et al | bta-miR-193b | ATL2、DYSF、AP5Z1、TMEM63A、FAT2,et al |
| bta-miR-27a-5p | CD163、KIF22、FAM43A、LRIF1、ACSS2,et al | bta-miR-340 | FEZZ、APP、CLIC1、PPP5C、ESPL1,et al |
| bta-miR-454 | VPS16、KIF14、DPY19L1、ECHDC1、VIRMA,et al | bta-miR-20a | ZNF484、UNC5A、ILF3、PFKP、CDC37,et al |
| bta-miR-218 | KIF3A、ZBTB6、ADCY6、SH3GL1、CCNG1,et al | bta-miR-147 | PLD、SLC20A2、ZNF608、PLEC、FASN,et al |
| bta-miR-29b | EPB41L3、ANKRD28、TOP2B、CASQ1、HERC4,et al |
表7 差异表达miRNA预测靶基因(部分)
Table 7 Differentially expressed miRNAs predict target genes (part)
miRNA名称 miRNA name | 预测到的靶基因 Predict target genes | miRNA名称 miRNA name | 预测到的靶基因 Predict target genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| bta-miR-1260 | MAP4K4、POU2F1、MRAS、STMP1、PACS2,et al | bta-miR-193b | ATL2、DYSF、AP5Z1、TMEM63A、FAT2,et al |
| bta-miR-124a | DISP1、ITSN2、CTSH、LRRC28、CEP68,et al | bta-miR-335 | TRIP12、NFIB、NRXN1、AGTPBP1、MYO1E,et al |
| bta-miR-24-3p | SPON1、CBFB、KIF18、CD163、ERG,et al | bta-miR-454 | VPS16、KIF14、DPY19L1、ECHDC1、VIRMA,et al |
| bta-miR-885 | FUS、RTRAF、DIDO1、ARHGAP20、SAMD8,et al | bta-miR-193b | ATL2、DYSF、AP5Z1、TMEM63A、FAT2,et al |
| bta-miR-27a-5p | CD163、KIF22、FAM43A、LRIF1、ACSS2,et al | bta-miR-340 | FEZZ、APP、CLIC1、PPP5C、ESPL1,et al |
| bta-miR-454 | VPS16、KIF14、DPY19L1、ECHDC1、VIRMA,et al | bta-miR-20a | ZNF484、UNC5A、ILF3、PFKP、CDC37,et al |
| bta-miR-218 | KIF3A、ZBTB6、ADCY6、SH3GL1、CCNG1,et al | bta-miR-147 | PLD、SLC20A2、ZNF608、PLEC、FASN,et al |
| bta-miR-29b | EPB41L3、ANKRD28、TOP2B、CASQ1、HERC4,et al |
| 组别Group | 通路名称Pathway name | 富集到该通路的基因Gene enrichment to this pathway |
|---|---|---|
| G18 vs F24 | 脂肪酸生物合成Fatty acid biosynthesis | ACACA、ACSL5、FASN、MECR、ACACB |
| G18 vs G24 | 不饱和脂肪酸生物合成Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | ACOX3、TECR、SCP2、 SCD、ACOX1、ELOVL5、ELOVL6、HACD3 |
| 脂肪酸生物合成Fatty acid biosynthesis | ACACA、FASN、MECR、ACACB、ACSL5 | |
| 脂肪酸降解Fatty acid degradation | ACOX3、ACSL5、TCP1、ADH5、EHHADH、ACOX1 | |
| F24 vs G24 | 不饱和脂肪酸生物合成Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | ACOX3、TECR、SCD、ELOVL5、ELOVL6、HACD3 |
| 脂肪酸生物合成Fatty acid biosynthesis | ACACA、FASN、MECR、ACSL5 | |
| 脂肪酸延长Fatty acid elongation | MECR、TECR、ELOVL5、ELOVL6、HACD3 | |
| 脂肪酸降解Fatty acid degradation | ACOX3、ACSL5、TCP1 |
表8 与脂肪有关的KEGG信号通路
Table 8 KEGG signaling pathway associated with adiposity
| 组别Group | 通路名称Pathway name | 富集到该通路的基因Gene enrichment to this pathway |
|---|---|---|
| G18 vs F24 | 脂肪酸生物合成Fatty acid biosynthesis | ACACA、ACSL5、FASN、MECR、ACACB |
| G18 vs G24 | 不饱和脂肪酸生物合成Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | ACOX3、TECR、SCP2、 SCD、ACOX1、ELOVL5、ELOVL6、HACD3 |
| 脂肪酸生物合成Fatty acid biosynthesis | ACACA、FASN、MECR、ACACB、ACSL5 | |
| 脂肪酸降解Fatty acid degradation | ACOX3、ACSL5、TCP1、ADH5、EHHADH、ACOX1 | |
| F24 vs G24 | 不饱和脂肪酸生物合成Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | ACOX3、TECR、SCD、ELOVL5、ELOVL6、HACD3 |
| 脂肪酸生物合成Fatty acid biosynthesis | ACACA、FASN、MECR、ACSL5 | |
| 脂肪酸延长Fatty acid elongation | MECR、TECR、ELOVL5、ELOVL6、HACD3 | |
| 脂肪酸降解Fatty acid degradation | ACOX3、ACSL5、TCP1 |
| 1 | Wiener G, Jianlin H, Long R. The yak. Bangkok: FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific, 2003. |
| 2 | Ba S W D, Hu P, Zhu Y B, et al. Current situation of herding and semi-herding yak breeding. Agriculture and Technology, 2018, 38(9): 116-117. |
| 巴桑旺堆, 胡萍, 朱彦滨, 等. 牦牛舍饲与半舍饲养殖的现状概况. 农业与技术, 2018, 38(9): 116-117. | |
| 3 | Cai R. The effect and mechanism of lnc-ORA on animal fat deposition and muscle development. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2021. |
| 蔡瑞. lnc-ORA对动物脂肪沉积与肌肉发育的作用及机制研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021. | |
| 4 | Ding W Q, Sun Y G, Han Y C. Research progress on fat metabolism and regulation mechanisms in yak. Feed Research, 2022(22): 156-159. |
| 丁维芹, 孙永刚, 韩银仓. 牦牛脂肪代谢和调控机理研究进展. 饲料研究, 2022(22): 156-159. | |
| 5 | Ding X Z, Guo X, Yan P, et al. Seasonal and nutrients intake regulation of lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity in grazing yak (Bos grunniens) in the alpine regions around Qinghai Lake. Livestock Science, 2012, 143(1): 29-34. |
| 6 | Wang Y Z. Research progress on mRNA N6-methyladenosine modification regulation and animal fat deposition. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2022, 34(11): 6801-6816. |
| 汪以真. mRNA N6-甲基腺嘌呤修饰调控与动物脂肪沉积的研究进展. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34(11): 6801-6816. | |
| 7 | Yin R H, Bai W L, Wang J M, et al. Development of an assay for rapid identification of meat from yak and cattle using polymerase chain reaction technique. Meat Science, 2009, 83(1): 38-44. |
| 8 | Ran H B, Zhao L L, Wang H, et al. Effect of lnc FAM200B on the lipid deposition in inntramuscular preadipocytes of yak. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(13): 2654-2666. |
| 冉宏标, 赵丽玲, 王会, 等. Lnc FAM200B对牦牛肌内前体脂肪细胞脂质沉积的影响. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(13): 2654-2666. | |
| 9 | Zhao L L. Studys of lnc FAM200B on the differentiation in yak pre-adipocytes. Chengdu: Southwest Minzu University, 2021. |
| 赵丽玲. lnc FAM200B对牦牛前体脂肪细胞分化的作用研究. 成都: 西南民族大学, 2021. | |
| 10 | Song L, Tuan R S. MicroRNAs and cell differentiation in mammalian development. Birth Defects Research Part C-Embryo Today-Reviews, 2006, 78(2): 140-149. |
| 11 | Griffiths-Jones S, Saini H K, Van Dongen S, et al. miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, 36: 154-158. |
| 12 | Wang H, Zheng Y, Wang G, et al. Identification of microRNA and bioinformatics target gene analysis in beef cattle intramuscular fat and subcutaneous fat. Molecular Biosystems, 2013, 9(8): 2154-2162. |
| 13 | Moore K J, Rayner K J, Suárez Y, et al. microRNAs and cholesterol metabolism. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2010, 21(12): 699-706. |
| 14 | He C, Zhang Q Y, Sun H W, et al. Role of miRNA and lncRNA in animal fat deposition-a review. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2020, 36(8): 1504-1514. |
| 何春, 张琦悦, 孙浩玮, 等. miRNA和lncRNA在动物脂肪沉积中的研究进展. 生物工程学报, 2020, 36(8): 1504-1514. | |
| 15 | Hu X, Xing Y S, Ren L, et al. Bta-miR-24-3p controls the myogenic differentiation and proliferation of fetal, bovine, skeletal muscle-derived progenitor cells by targeting ACVR1B. Animals, 2019, 9(11): 859. |
| 16 | Dey P, Soyer M A, Dey B K. MicroRNA-24-3p promotes skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration by regulating HMGA1. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2022, 79(3): 170. |
| 17 | Sun Q, Zhang Y, Yang G, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta-regulated miR-24 promotes skeletal muscle differentiation. Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, 36(8): 2690-2699. |
| 18 | Oladejo A O, Li Y, Shen W, et al. MicroRNA Bta-miR-24-3p suppressed galectin-9 expression through TLR4/NF-ĸB signaling pathway in LPS-stimulated bovine endometrial epithelial cells. Cells, 2021, 10(12): 3299. |
| 19 | Shen B, Yang Z, Han S, et al. Bta-miR-124a affects lipid metabolism by regulating PECR gene. Biomed Research Internation, 2019: 2596914. doi: 10.1155/2019/2596914. |
| 20 | Yang Z N N. Identification and functional validation of bta-miR-124a target gene in dairy cattle. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2019. |
| 杨卓妮娜. 奶牛Bta-miR-124a靶基因鉴定及功能验证的研究. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2019. | |
| 21 | Elsaeid Elnour I, Dong D, Wang X, et al. Bta-miR-885 promotes proliferation and inhibits differentiation of myoblasts by targeting MyoD1. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 2020, 235(10): 6625-6636. |
| 22 | Zhang M Q, Gao J L, Liao X D, et al. miR-454 regulates triglyceride synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells by targeting PPAR-γ. Gene, 2019, 691: 1-7. |
| 23 | Kang Z, Zhang S, Jiang E, et al. Mir-193b regulates the differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis of bovine adipose cells by targeting the ACSS2/AKT axis. Animals, 2020, 10(8): 1265. |
| [1] | 者玉琦, 武志娟, 王吉坤, 钟金城, 柴志欣, 信金伟. 基于mtDNA COX3基因对西藏特色牦牛群体遗传结构的分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 231-240. |
| [2] | 聂洪辛, 李毓敏, 庞凯悦, 柴沙驼, 申迪, 曾子铭, 廖扬, 王迅, 薛斌, 刘书杰, 王书祥, 杨英魁. 不同精粗比对牦牛粪便菌群结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 189-197. |
| [3] | 冯斌, 杨晓霞, 刘文亭, 刘玉祯, 吕卫东, 张振祥, 孙彩彩, 周沁苑, 王芳草, 于泽航, 董全民. 暖季草场不同放牧方式对牦牛藏羊生产力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 58-67. |
| [4] | 吴刀知才让, 裴成芳, 马志远, 刘红山, 曹旭亮, 刘虎, 周建伟. 燕麦干草不同饲喂水平对牦牛日增重、血液生理生化指标及瘤胃发酵参数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 119-129. |
| [5] | 段嘉钰, 张博, 操君, 刘书杰, 崔占鸿. 70~100 kg牦牛犊牛钠、钾、镁元素分布规律及生长需要量[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 130-139. |
| [6] | 贾晶莹, 刘宝宝, 马云, 段红娟, 蔡小艳. 苜蓿源miR168b跨界调控奶牛体内乳脂相关靶基因的筛选[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 173-186. |
| [7] | 马士龙, 李小伟, 李响, 谢书琼, 刘益丽, 唐娇, 江明锋. 基于GBS简化基因组测序评估3个麦洼牦牛保种群的遗传结构研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 183-194. |
| [8] | 游茵洁, 周浩珍, 刘垚, 王晨曦, 彭忠利. 燕麦干草、青贮燕麦与天然牧草饲喂牦牛的营养价值比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 99-110. |
| [9] | 杨兴云, 乔丹丹, 张雅洁, 王少青, 任俊才, 李明阳, 屈明好, 尚盼盼, 杨成, 黄琳凯, 曾兵. 鸭茅响应水淹胁迫的miRNA差异表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 150-162. |
| [10] | 戴东文, 庞凯悦, 王迅, 杨英魁, 柴沙驼, 王书祥. 精料补饲水平对暖季放牧牦牛瘤胃发酵和菌群结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 169-177. |
| [11] | 王永宏, 田黎明, 艾鷖, 陈仕勇, 泽让东科. 短期牦牛放牧对青藏高原高寒草地土壤真菌群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 41-52. |
| [12] | 李晨, Ahmad Anum Ali, 张剑搏, 梁泽毅, 丁学智, 阎萍. 冷季牦牛和黄牛采食行为、血清生化指标与瘤胃发酵参数的比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 162-169. |
| [13] | 纪会, 官久强, 王会, 周建旭, 阿农呷, 何宗伟, 樊珍详, 邱龙康, 曹诗晓, 安添午, 柏琴, 钟金城, 罗晓林. 亚丁牦牛和拉日马牦牛遗传多样性及遗传结构分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 134-145. |
| [14] | 潘发明, 常生华, 王国栋, 郝生燕, 刘佳, 张辉元, 徐银萍. 物候期对放牧牦牛瘤胃液、牧草中脂肪酸及乳脂中共轭亚油酸组成的影响及其相关性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 110-120. |
| [15] | 张强, 达娃央拉, 姬秋梅, 信金伟, 张成福, 朱勇, 洛桑顿珠, 次旦央吉, 孙光明, 姜辉. 西藏查吾拉地区不同性别牦牛产肉性能和肉营养成分的比较[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 193-198. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||