

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 73-83.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024037
曹秭琦1,2( ), 赵小庆1,3, 张向前1,3, 伍建辉3, 张帆3, 刘丹3, 路战远1,3(
), 赵小庆1,3, 张向前1,3, 伍建辉3, 张帆3, 刘丹3, 路战远1,3( ), 任永峰1,3(
), 任永峰1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-27
修回日期:2024-03-16
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-10-09
通讯作者:
路战远,任永峰
作者简介:renyongfeng_1984@163.com基金资助:
Zi-qi CAO1,2( ), Xiao-qing ZHAO1,3, Xiang-qian ZHANG1,3, Jian-hui WU3, Fan ZHANG3, Dan LIU3, Zhan-yuan LU1,3(
), Xiao-qing ZHAO1,3, Xiang-qian ZHANG1,3, Jian-hui WU3, Fan ZHANG3, Dan LIU3, Zhan-yuan LU1,3( ), Yong-feng REN1,3(
), Yong-feng REN1,3( )
)
Received:2024-01-27
Revised:2024-03-16
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-10-09
Contact:
Zhan-yuan LU,Yong-feng REN
摘要:
探究不同施钾水平对北方风沙区油莎豆生长、生理生化、块茎品质及产量的影响,将为油莎豆科学施钾提供理论依据和技术支撑。采用盆栽试验,以中油莎1号为供试材料,设置0(K0)、0.15(K1)、0.30(K2)和0.45 g·kg-1(K3)4个钾肥水平,对其生长、生理生化、块茎品质及产量进行了观测和分析。结果表明:与不施钾肥水平相比,施钾可以显著提高油莎豆株高、茎蘖数、单片叶面积、最大根长、根体积。在施钾量为0.15 g·kg-1(K1)时,乙酰辅酶A羧化酶、可溶性淀粉合成酶活性达到最大值,同时促进了块茎淀粉、粗脂肪的积累达到最大值,分别为229.03 mg·g-1、21.98%,但均与K2水平无显著差异。在施钾量为0.30 g·kg-1(K2)时,不饱和脂肪酸及总脂肪酸含量达到最大值,分别为16.53、20.07 g·100 g-1。总糖含量在施钾量为0.45 g·kg-1(K3)时达到最大值,为217.86 mg·g-1。油莎豆整株干重和产量随着施钾量的增加均有所增加,且在施钾0.45 g·kg-1(K3)水平下达到最大,但与K2无显著差异。因此,综合油莎豆品质、产量及养分利用率,认为施钾量为0.30 g·kg-1时,可促进北方风沙区油莎豆生长发育,提高其品质相关酶活性,促进品质形成,增加干物质积累及块茎产量。
曹秭琦, 赵小庆, 张向前, 伍建辉, 张帆, 刘丹, 路战远, 任永峰. 施钾水平对北方风沙区油莎豆生长、块茎品质及产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 73-83.
Zi-qi CAO, Xiao-qing ZHAO, Xiang-qian ZHANG, Jian-hui WU, Fan ZHANG, Dan LIU, Zhan-yuan LU, Yong-feng REN. Effects of potassium application level on the growth, tuber quality, and yield of Cyperus esculentus in the Northern wind-sand area[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(12): 73-83.
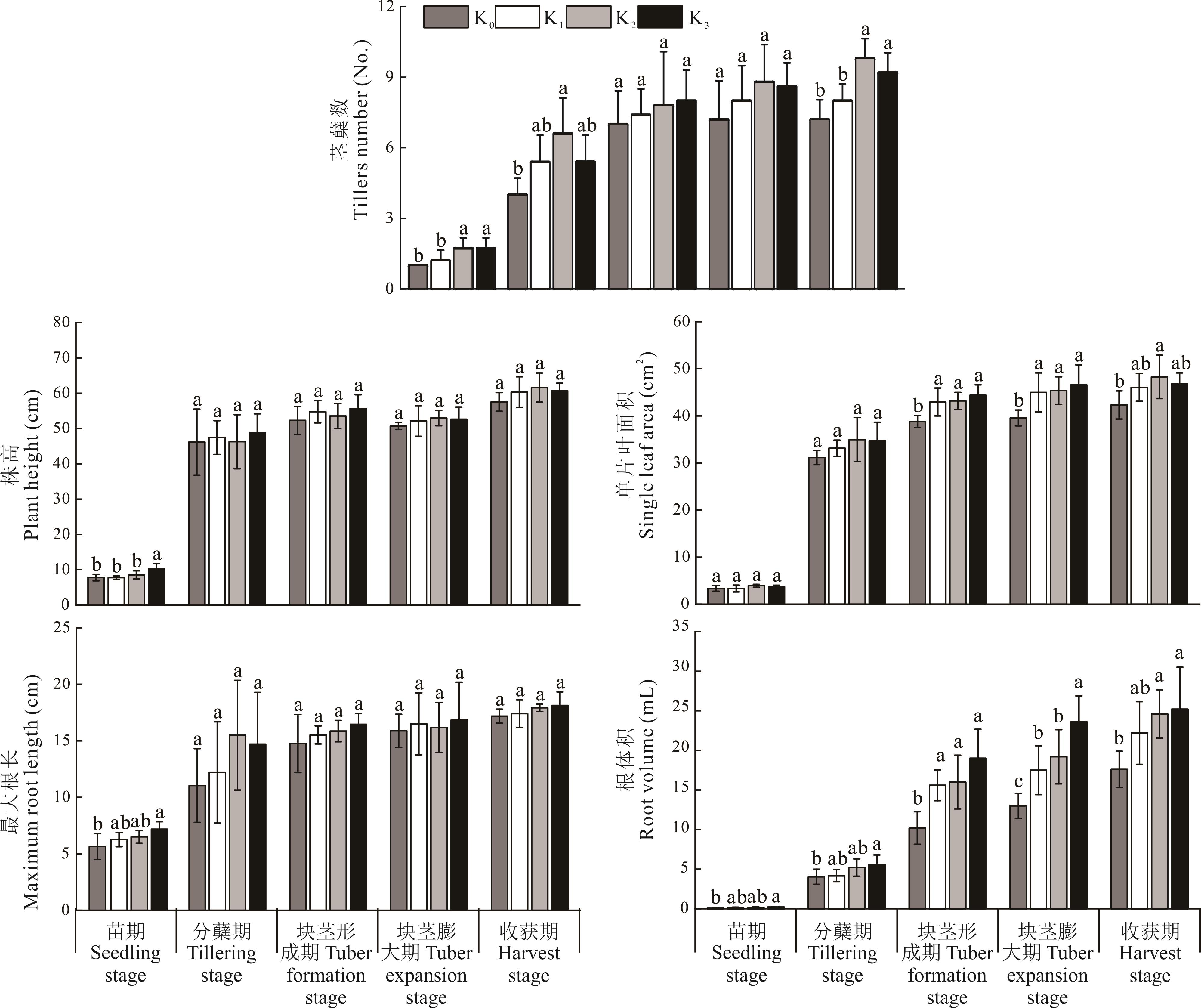
图1 不同施钾水平下油莎豆株高、茎蘖数、单片叶面积、最大根长和根体积K0~K3: 施钾量分别为0、0.15、0.30、0.45 g·kg-1 Potassium application rates were 0, 0.15, 0.30, 0.45 g·kg-1; 不同小写字母表示不同施钾水平间差异显著(P<0.05) Different lowercase letters indicated that there were significant differences among different potassium application levels (P<0.05); 下同The same below.
Fig.1 The plant height, tiller number, single leaf area, maximum root length and root volume of C. esculentus under different potassium application levels
| 项目 Item | K0 | K1 | K2 | K3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 十四碳酸(肉蔻酸)Myristic acid | 0.0094±0.0004b | 0.0082±0.0005b | 0.0143±0.0026a | 0.0141±0.0007a |
| 十六碳酸(棕榈酸)Palmitic acid | 1.9283±0.0715b | 1.9299±0.1280b | 2.3422±0.1699a | 2.3311±0.0937a |
| 顺-9-十六碳一烯酸(棕榈油酸)Palmitoleic acid | 0.0197±0.0020b | 0.0332±0.0036a | 0.0262±0.0073ab | 0.0254±0.0043ab |
| 十七碳酸(珠光脂酸)Margaric acid | 0.0097±0.0003c | 0.0095±0.0003c | 0.0122±0.0006a | 0.0111±0.0007b |
| 顺-10-十七碳一烯酸Heptadecenoic acid | 0.0075±0.0002b | 0.0072±0.0005b | 0.0112±0.0036a | 0.0091±0.0001ab |
| 十八碳酸(硬脂酸)Stearic acid | 0.5730±0.0288c | 0.5842±0.0277c | 0.9100±0.0526a | 0.6536±0.0294b |
| 顺-9-十八碳一烯酸(油酸)Oleic acid | 10.7614±0.4259b | 11.3937±0.6778b | 13.4113±0.8017a | 13.5707±0.6152a |
| 顺,顺-9,12-十八碳二烯酸(亚油酸)Linoleic acid | 1.7620±0.0657c | 1.7719±0.1237c | 2.9317±0.1840a | 2.0487±0.1007b |
| 顺,顺,顺-6,9,12-十八碳三烯酸(γ-亚麻酸)γ-Linolenic acid | 0.0280±0.0025b | 0.0436±0.0042a | 0.0287±0.0029b | 0.0172±0.0006c |
| 顺,顺,顺-9,12,15-十八碳三烯酸(α-亚麻酸)α-Linolenic acid | 0.0480±0.0013ab | 0.0450±0.0034bc | 0.0418±0.0028c | 0.0526±0.0020a |
| 二十碳酸(花生酸)Arachidic acid | 0.0874±0.0023c | 0.0909±0.0038c | 0.1246±0.0122a | 0.1067±0.0075b |
| 顺-11-二十碳一烯酸(花生一烯酸)Gadoleic acid | 0.0421±0.0031c | 0.0417±0.0031c | 0.0742±0.0056a | 0.0507±0.0032b |
| 二十二碳酸(山嵛酸)Docosanoic acid | 0.0183±0.0037b | 0.0178±0.0026b | 0.0760±0.0066a | 0.0245±0.0026b |
| 二十四碳酸(木腊酸)Tetracosanoic acid | 0.0321±0.0002c | 0.0309±0.0006c | 0.0683±0.0050a | 0.0454±0.0073b |
| 饱和脂肪酸总量Total saturated fatty acids | 2.6582±0.1020c | 2.6713±0.1603c | 3.5477±0.2456a | 3.1866±0.1307b |
| 不饱和脂肪酸总量Total unsaturated fatty acids | 12.6686±0.4899b | 13.3365±0.8134b | 16.5251±0.9953a | 15.7746±0.7206a |
| 脂肪酸总量Total fatty acids | 15.3268±0.5911b | 16.0079±0.9736b | 20.0728±1.2389a | 18.9612±0.8500a |
表1 不同施钾水平下油莎豆脂肪酸组分含量
Table 1 Fatty acid content of C. esculentus under different potassium application levels (g·100 g-1)
| 项目 Item | K0 | K1 | K2 | K3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 十四碳酸(肉蔻酸)Myristic acid | 0.0094±0.0004b | 0.0082±0.0005b | 0.0143±0.0026a | 0.0141±0.0007a |
| 十六碳酸(棕榈酸)Palmitic acid | 1.9283±0.0715b | 1.9299±0.1280b | 2.3422±0.1699a | 2.3311±0.0937a |
| 顺-9-十六碳一烯酸(棕榈油酸)Palmitoleic acid | 0.0197±0.0020b | 0.0332±0.0036a | 0.0262±0.0073ab | 0.0254±0.0043ab |
| 十七碳酸(珠光脂酸)Margaric acid | 0.0097±0.0003c | 0.0095±0.0003c | 0.0122±0.0006a | 0.0111±0.0007b |
| 顺-10-十七碳一烯酸Heptadecenoic acid | 0.0075±0.0002b | 0.0072±0.0005b | 0.0112±0.0036a | 0.0091±0.0001ab |
| 十八碳酸(硬脂酸)Stearic acid | 0.5730±0.0288c | 0.5842±0.0277c | 0.9100±0.0526a | 0.6536±0.0294b |
| 顺-9-十八碳一烯酸(油酸)Oleic acid | 10.7614±0.4259b | 11.3937±0.6778b | 13.4113±0.8017a | 13.5707±0.6152a |
| 顺,顺-9,12-十八碳二烯酸(亚油酸)Linoleic acid | 1.7620±0.0657c | 1.7719±0.1237c | 2.9317±0.1840a | 2.0487±0.1007b |
| 顺,顺,顺-6,9,12-十八碳三烯酸(γ-亚麻酸)γ-Linolenic acid | 0.0280±0.0025b | 0.0436±0.0042a | 0.0287±0.0029b | 0.0172±0.0006c |
| 顺,顺,顺-9,12,15-十八碳三烯酸(α-亚麻酸)α-Linolenic acid | 0.0480±0.0013ab | 0.0450±0.0034bc | 0.0418±0.0028c | 0.0526±0.0020a |
| 二十碳酸(花生酸)Arachidic acid | 0.0874±0.0023c | 0.0909±0.0038c | 0.1246±0.0122a | 0.1067±0.0075b |
| 顺-11-二十碳一烯酸(花生一烯酸)Gadoleic acid | 0.0421±0.0031c | 0.0417±0.0031c | 0.0742±0.0056a | 0.0507±0.0032b |
| 二十二碳酸(山嵛酸)Docosanoic acid | 0.0183±0.0037b | 0.0178±0.0026b | 0.0760±0.0066a | 0.0245±0.0026b |
| 二十四碳酸(木腊酸)Tetracosanoic acid | 0.0321±0.0002c | 0.0309±0.0006c | 0.0683±0.0050a | 0.0454±0.0073b |
| 饱和脂肪酸总量Total saturated fatty acids | 2.6582±0.1020c | 2.6713±0.1603c | 3.5477±0.2456a | 3.1866±0.1307b |
| 不饱和脂肪酸总量Total unsaturated fatty acids | 12.6686±0.4899b | 13.3365±0.8134b | 16.5251±0.9953a | 15.7746±0.7206a |
| 脂肪酸总量Total fatty acids | 15.3268±0.5911b | 16.0079±0.9736b | 20.0728±1.2389a | 18.9612±0.8500a |
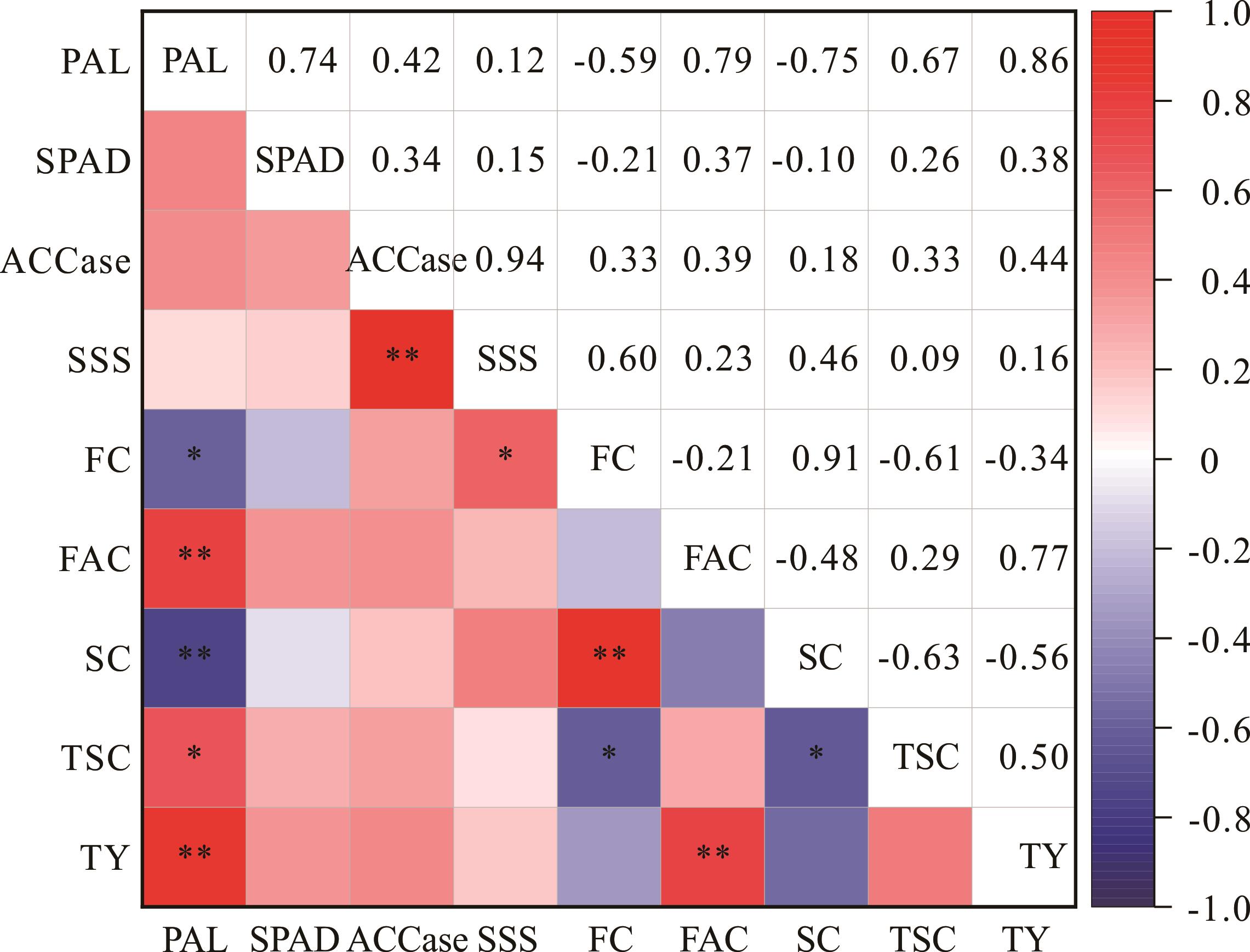
图6 不同施钾水平下油莎豆生理生化、品质及产量的相关性分析PAL: 施钾水平Potassium application level; SPAD: 相对叶绿素含量Relative chlorophyll content; ACCase: 乙酰辅酶A羧化酶活性Acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity; SSS; 可溶性淀粉合成酶活性Soluble starch synthase activity; FC: 粗脂肪含量Crude fat content; FAC: 脂肪酸含量Fatty acid content; SC: 淀粉含量Starch content; TSC: 总糖含量Total sugar content; TY: 块茎产量Tuber yield; *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01.
Fig.6 Correlation analysis of physiological and biochemical, quality and yield of C. esculentus under different potassium application levels
| 1 | Yang Z L. Characteristics and research progress of Cyperus esculentus. Northern Horticulture, 2017(17): 192-201. |
| 阳振乐. 油莎豆的特性及其研究进展. 北方园艺, 2017(17): 192-201. | |
| 2 | Zhang S G, Li P Z, Wei Z M, et al. Cyperus (Cyperus esculentus L.): A review of its compositions, medical efficacy, antibacterial activity and allelopathic potentials. Plants, 2022, 11(9): 1127. |
| 3 | Chou Y X, Li K J, Min Y, et al. Research progress in nutritional composition, biological and application of Cyperus esculentus. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2023, 14(15): 222-230. |
| 丑义宣, 李柯洁, 闵琰, 等. 油莎豆的营养成分、生物活性及其应用研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2023, 14(15): 222-230. | |
| 4 | Zhang Y M, Sun S D. Tiger nut (Cyperus esculentus L.) oil: A review of bioactive compounds, extraction technologies, potential hazards and applications. Food Chemistry: X, 2023, 19: 100868. |
| 5 | Cao Z Q, Ren Y F, Lu Z Y, et al. Research progress on the characteristics and development and utilization of Cyperus esculentus. Journal of Northern Agriculture, 2022, 50(1): 66-74. |
| 曹秭琦, 任永峰, 路战远, 等. 油莎豆的特性及其开发利用研究进展. 北方农业学报, 2022, 50(1): 66-74. | |
| 6 | Cui J, Tcherkez G. Potassium dependency of enzymes in plant primary metabolism. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 166: 522-530. |
| 7 | Li J, Hu W S, Lu Z F, et al. Imbalance between nitrogen and potassium fertilization influences potassium deficiency symptoms in winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) leaves. The Crop Journal, 2022, 10(2): 565-576. |
| 8 | Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan M H M B, Zulfiqar F, et al. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under abiotic stress: Revisiting the crucial role of a universal defense regulator. Antioxidants, 2020, 9(8): 681. |
| 9 | Xu X, Du X, Wang F, et al. Effects of potassium levels on plant growth, accumulation and distribution of carbon, and nitrate metabolism in apple dwarf rootstock seedlings. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 904. |
| 10 | Johnson R, Vishwakarma K, Hossen M S, et al. Potassium in plants: Growth regulation, signaling,and environmental stress tolerance. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2022, 172: 56-59. |
| 11 | Wang Y X, Zhang P, Ge B L, et al. Response of agronomic characters and active components of Lilium concolor to potassium. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(6): 205-213. |
| 王云霞, 张萍, 葛蓓蕾, 等. 渥丹百合农艺性状及活性成分对钾元素的响应. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 205-213. | |
| 12 | Zhang J L, Li J, Geng G T, et al. Combined application of nitrogen and potassium reduces seed yield loss of oilseed rape caused by Sclerotinia stem rot disease. Agronomy Journal, 2020, 112(6): 5143-5157. |
| 13 | Zhejiang Agricultural University. Plant nutrition and fertilizer. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1991: 101-109. |
| 浙江农业大学. 植物营养与肥料. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1991: 101-109. | |
| 14 | Li B B, Zhang F H, Zhao Y G, et al. Effects of different clipping degrees on non-structural carbohydrate metabolism and biomass of Cyperus esculentus. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2023, 47(1): 101-113. |
| 李变变, 张凤华, 赵亚光, 等. 不同刈割程度对油莎豆非结构性碳水化合物代谢及生物量的影响. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(1): 101-113. | |
| 15 | Yang Y J, Liang G L, Liu W H, et al. Effects of silicon fertilizer on lodging resistance traits and seed yield of Avena sativa in the alpine region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 2022, 39(3): 551-561. |
| 杨钰洁, 梁国玲, 刘文辉, 等. 硅肥对青藏高原高寒地区燕麦抗倒伏性状及种子产量的影响. 草业科学, 2022, 39(3): 551-561. | |
| 16 | National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. National standard for food safety determination of fatty acids in food, GB 5009.6-2016. Beijing: National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration, 2016. |
| 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中脂肪酸的测定, GB 5009.6-2016. 北京: 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局, 2016. | |
| 17 | National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. National standard for food safety determination of fatty acids in food, GB 5009.168-2016. Beijing: National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration, 2016. |
| 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中脂肪酸的测定, GB 5009.168-2016. 北京: 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局, 2016. | |
| 18 | Chen Y, Wang L, Bai Y L, et al. Quantitative relationship between effective accumulated temperature and plant height & leaf area index of summer maize under different nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium levels. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(22): 4761-4777. |
| 陈杨, 王磊, 白由路, 等. 有效积温与不同氮磷钾处理夏玉米株高和叶面积指数定量化关系. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(22): 4761-4777. | |
| 19 | Gou Z Y, Guo L Z, Gao Y H, et al. Effects of combined application of potassium and silicon fertilizers on root morphology and lodging resistance characteristics of oil flax. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2022, 57(1): 83-89, 97. |
| 苟振宇, 郭丽琢, 高玉红, 等. 钾硅肥配施对胡麻根系形态及抗倒伏特性的影响. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2022, 57(1): 83-89, 97. | |
| 20 | Hetherington F M, Kakkar M, Topping J F, et al. Gibberellin signaling mediates lateral root inhibition in response to K+-deprivation. Plant Physiology, 2021, 185(3): 1198-1215. |
| 21 | Kumar P, Singh T, Singh S, et al. Potassium: A key modulator for cell homeostasis. Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 324: 198-210. |
| 22 | Sun X, Qiu Y, Peng Y, et al. Close temporal relationship between oscillating cytosolic K+ and growth in root hairs of Arabidopsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(17): 6184. |
| 23 | Sustr M, Soukup A, Tylova E. Potassium in root growth and development. Plants, 2019, 8(10): 435. |
| 24 | Soumare A, Sarr D, Diédhiou A G. Potassium sources, microorganisms and plant nutrition: Challenges and future research directions. Pedosphere, 2023, 33(1): 105-115. |
| 25 | Tränkner M, Tavakol E, Jákli B. Functioning of potassium and magnesium in photosynthesis, photosynthate translocation and photoprotection. Physiologia Plantarum, 2018, 163(3): 414-431. |
| 26 | Ceylan Y, Kutman U B, Mengutay M, et al. Magnesium applications to growth medium and foliage affect the starch distribution, increase the grain size and improve the seed germination in wheat. Plant and Soil, 2016, 406(2): 145-156. |
| 27 | Ye T H, Xue X X, Lu J W, et al. Effects of potassium fertilization on crops yield, potassium uptake, and soil potassium fertility in rice-oilseed rape cropping systems. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2022, 68(7): 873-885. |
| 28 | Wang F, Liu C L, He C M, et al. Appropriate ratios of phosphate and potassium fertilizers and 50% return of rice straw enhanced yield and nutrient capture of Chinese milk vetch. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(12): 81-89. |
| 王飞, 刘彩玲, 何春梅, 等. 适宜磷、钾肥配比及稻秆半量还田提高紫云英产量与养分截获. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 81-89. | |
| 29 | Gu X, Liu Y, Li N, et al. Effects of the foliar application of potassium fertilizer on the grain protein and dough quality of wheat. Agronomy, 2021, 11(9): 1749. |
| 30 | Yang M, Tian L P, Xue L, et al. Effects of N, P, K combined application on yield and quality of Cyperus esculentus in arid climate region of Xinjiang. Northern Horticulture, 2013(6): 180-182. |
| 杨敏, 田丽萍, 薛琳, 等. 新疆干旱气候区不同氮磷钾肥配施对油莎豆产量与品质的影响. 北方园艺, 2013(6): 180-182. | |
| 31 | Guo A. Effects of different potassium application levels on fruit quality and sugar metabolism of fig fruit. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2019. |
| 郭傲. 不同施钾水平对无花果果实品质及糖代谢的影响. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2019. | |
| 32 | Guo Z G, Li W F, Mao J, et al. Effects of potassium fertilizer on endogenous hormone content and acid metabolism in fruit of apple cv. ‘Red Delicious’. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(10): 281-290. |
| 郭志刚, 李文芳, 毛娟, 等. 钾肥施用对元帅苹果果实内源激素含量及酸代谢的影响. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(10): 281-290. | |
| 33 | Lu Z F. Studies on mechanisms underlying the effects of potassium nutrition on leaf photosynthesis of Brassica napus. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 陆志峰. 钾素营养对冬油菜叶片光合作用的影响机制研究. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2017. | |
| 34 | Yang R L. Study on the effects of different light condition on the synthesis of lipids of Cyperus esculentus. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2013. |
| 杨若琳. 不同光照条件对油莎豆油脂合成作用的影响研究. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2013. | |
| 35 | Ma P, Yuan Y, Shen Q, et al. Evolution and expression analysis of starch synthase gene families in Saccharum spontaneum. Tropical Plant Biology, 2019, 12: 158-173. |
| 36 | Liu N, Xie C, Gao S J, et al. Effects of different potassium levels on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of peanut. Chinese Journal of Oil Crops Science, 2021, 43(5): 883-890. |
| 刘娜, 谢畅, 高世杰, 等. 不同钾水平对花生光合特性及产量的影响. 中国油料作物学报, 2021, 43(5): 883-890. | |
| 37 | Farooq M A, Ali S, Hassan A, et al. Biosynthesis and industrial applications of α-amylase: A review. Archives of Microbiology, 2021, 203(4): 1281-1292. |
| 38 | Zhu M Y, Kang Y J, Pu H T. Effects of potassium application rate on key enzyme activities of peanut fat formation. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017(20): 9-10. |
| 朱明玉, 康玉洁, 蒲海涛. 施钾量对花生脂肪形成关键酶活性的影响. 现代农业科技, 2017(20): 9-10. | |
| 39 | Long X Y, Yang X J, Yang S Y, et al. Effects of potassium application in summer on leaf growth and yield of Camellia oleifera. Tropical Forestry, 2021, 49(1): 35-41. |
| 龙雪燕, 杨小菊, 杨胜优, 等. 夏季施钾肥对油茶叶片生长和产量相关指标影响. 热带林业, 2021, 49(1): 35-41. | |
| 40 | Luo X L, Wu M Y, Tao L. Impacts of potassium fertilizer application at different stages on key enzyme activities and starch accumulation in starch synthesis of Cassava. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(16): 115-119. |
| 罗兴录, 吴美艳, 陶林. 木薯不同时期施钾对淀粉合成关键酶活性和淀粉积累的影响. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(16): 115-119. | |
| 41 | Pang Y L, Wang F X, Huang Z J, et al. Improving yield and quality of autumn tea with drip irrigation under appropriate nitrogen and potassium fertilization. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(24): 98-103. |
| 庞永磊, 王凤新, 黄泽军, 等. 适宜施氮钾水平提高滴灌秋茶的产量及品质. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(24): 98-103. | |
| 42 | Liu J, Fan Y F, Sun J Y, et al. Effects of straw return with potassium fertilizer on the stem lodging resistance, grain quality and yield of spring maize (Zea mays L.). Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 20307. |
| 43 | He P, Jin J Y, Li W J, et al. Comparison of potassium absorption, yield and quality between high-oil and common corn affected by potassium application. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2005, 11(5): 620-626. |
| 何萍, 金继运, 李文娟, 等. 施钾对高油玉米和普通玉米吸钾特性及子粒产量和品质的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2005, 11(5): 620-626. | |
| 44 | Hu W, Jiang N, Yang J, et al. Potassium (K) supply affects K accumulation and photosynthetic physiology in two cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars with different K sensitivities. Field Crops Research, 2016, 196: 51-63. |
| 45 | Yousef A F, Ali A M, Azab M A, et al. Improved plant yield of potato through exogenously applied potassium fertilizer sources and biofertilizer. AMB Express, 2023, 13(1): 124. |
| 46 | Sui X D. Effects of different amounts of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers on rice starch synthesis. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2020. |
| 隋晓东. 氮钾肥不同用量对水稻淀粉合成的影响. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2020. | |
| 47 | Shirani R A H, Eyni-Nargeseh H, Shiranirad S, et al. Effect of potassium silicate on seed yield and fatty acid composition of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) genotypes under different irrigation regimes.Silicon, 2022, 14(2): 11927-11938. |
| 48 | Li S T, Duan Y, Guo T W, et al. Sunflower response to potassium fertilization and nutrient requirement estimation. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2018, 17(12): 2802-2812. |
| 49 | Popp M P, Slaton N A, Norsworthy J S, et al. Rice yield response to potassium: An economic analysis. Agronomy Journal, 2020, 113(1): 287-297. |
| 50 | Zou T X, Dai T B, Jiang D, et al. Effects of nitrogen and potassium on key regulatory enzyme activities for grain starch in winter wheat. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(11): 3858-3864. |
| 邹铁祥, 戴廷波, 姜东, 等. 氮素和钾素对小麦籽粒淀粉合成关键酶活性的影响. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(11): 3858-3864. |
| [1] | 卜祥琪, 李姗姗, 段莹娜, 王迎春, 郑琳琳. 一氧化氮对盐碱胁迫下盐地碱蓬抗逆性及饲用品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 60-69. |
| [2] | 李中利, 蒋丛泽, 马仁诗, 高玮, 受娜, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 陇东旱塬区5个饲用甜高粱品种生产适宜性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 50-62. |
| [3] | 徐寿霞. 基于meta分析的丛枝菌根对小麦产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 192-204. |
| [4] | 李鸿飞, 周帮伟, 张淼, 施树楠, 李志坚. 不同燕麦品种在呼伦贝尔地区的引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 60-72. |
| [5] | 张瑞, 安雪姣, 李建烨, 卢曾奎, 牛春娥, 徐振飞, 张金霞, 耿智广, 岳耀敬, 杨博辉. 湖羊及其不同杂交组合生长性能、产肉性能及肌肉品质比较分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 186-197. |
| [6] | 张峰硕, 季秋蓉, 何婷莉, 苏曲杨昂毛, 王志有, 侯生珍, 桂林生. 低蛋白日粮中不同比例氨基酸对藏羊背腰最长肌肉品质、氨基酸和脂肪酸组成以及维生素和矿物质含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 198-208. |
| [7] | 张永亮, 滕泽, 郝凤, 于铁峰, 张玉霞. 苜蓿混播方式及比例对混播草地生产力和稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 185-197. |
| [8] | 白宇飞, 尹航, 杨海波, 冯振华, 李斐. 无人机多光谱和RGB影像融合的苜蓿产量估测[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 45-58. |
| [9] | 吕帅磊, 常单娜, 周国朋, 刘蕊, 赵鑫, 刘佳, 徐昌旭, 曹卫东. 江西红壤绿肥季施用磷矿粉的磷素效应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 149-160. |
| [10] | 侯铭辉, 孙延亮, 杨开鑫, 齐军仓, 张前兵. 基于响应曲面法确定水培大麦饲草高产优质的氮磷钾养分投入量[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 172-185. |
| [11] | 王凤宇, 梁国玲, 胡泽龙, 刘文辉. 地理因子对青藏高原野生垂穗披碱草表型及种子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 198-214. |
| [12] | 高兴发, 聂莹莹, 徐丽君, 杨敏, 徐树花, 朱孟. 干旱条件下乌蒙山区冬闲田燕麦引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 215-227. |
| [13] | 张仲鹃, 郝曦煜, 王雪, 李峰, 李文龙. 齐齐哈尔地区适宜青贮玉米品种的筛选及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 228-240. |
| [14] | 赵文军, 刘蕊, 王正旭, 冯瑜, 薛开政, 刘魁, 徐梓荷, 曹卫东, 付利波, 尹梅, 陈华. 烤烟-绿肥轮作对云南烟田土壤质量与微生物养分限制的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 147-158. |
| [15] | 黄佩珊, 臧美琪, 张炜灵, 陈俊戬, 刘立轩, 张庆. 黄梁木叶多酚提取工艺优化及其对柱花草青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 159-170. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||