

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (6): 181-192.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024297
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
姜沛沛1( ), 郭锦花1, 肖慧淑1, 彭彦珉1, 张军1, 田文仲2,3, 吕军杰2,3, 吴金芝1, 王贺正1, 付国占1, 黄明1(
), 郭锦花1, 肖慧淑1, 彭彦珉1, 张军1, 田文仲2,3, 吕军杰2,3, 吴金芝1, 王贺正1, 付国占1, 黄明1( ), 李友军1(
), 李友军1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-24
修回日期:2024-09-25
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-04-03
通讯作者:
黄明,李友军
作者简介:lyj@haust.edu.cn基金资助:
Pei-pei JIANG1( ), Jin-hua GUO1, Hui-shu XIAO1, Yan-min PENG1, Jun ZHANG1, Wen-zhong TIAN2,3, Jun-jie Lyu2,3, Jin-zhi WU1, He-zheng WANG1, Guo-zhan FU1, Ming HUANG1(
), Jin-hua GUO1, Hui-shu XIAO1, Yan-min PENG1, Jun ZHANG1, Wen-zhong TIAN2,3, Jun-jie Lyu2,3, Jin-zhi WU1, He-zheng WANG1, Guo-zhan FU1, Ming HUANG1( ), You-jun LI1(
), You-jun LI1( )
)
Received:2024-07-24
Revised:2024-09-25
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-04-03
Contact:
Ming HUANG,You-jun LI
摘要:
为探明不同轮耕模式对旱地夏玉米-冬小麦(简称玉-麦)两熟体系作物产量和品质的影响,利用始于2004年设置在中国农业科学院洛阳旱农试验基地的玉米季免耕+麦季免耕(MNWN)、玉米季深松+麦季免耕(MSWN)、玉米季免耕+麦季3年免耕1年翻耕(MNW3N1P)、玉米季深松+麦季3年免耕1年翻耕(MSW3N1P)和传统的两季均翻耕(CK)5个处理的定位试验,分析了2015-2021年度作物产量以及2020-2021年度作物籽粒氮、磷、钾含量,蛋白质产量和冬小麦籽粒蛋白质组分含量。结果表明:MNWN、MSWN、MNW3N1P和MSW3N1P下夏玉米和冬小麦籽粒产量的差异均不显著,但与CK相比均表现出不同程度的提升,且效应因降水年型而异,其与CK相比在干旱年使小麦和周年产量分别显著提高56.2%~65.2%和28.2%~32.6%,在平水年使夏玉米产量和周年产量分别显著提高47.5%~57.7%和25.7%~29.8%,在丰水年仅使冬小麦产量显著提高18.9%~31.2%。MSW3N1P提高夏玉米、冬小麦籽粒氮磷钾含量和蛋白质产量以及小麦籽粒蛋白组分含量的效果最优,与CK相比使夏玉米籽粒氮钾含量和蛋白质产量分别显著提高4.5%、15.6%和25.8%,冬小麦籽粒氮磷含量、蛋白质产量、谷蛋白含量、谷醇比和贮藏蛋白含量分别显著提高7.7%、15.2%、109.8%、16.1%、9.6%和11.9%,周年蛋白质产量显著提高38.5%。虽然MNW3N1P较CK也能使冬小麦籽粒谷蛋白含量、谷醇比和贮藏蛋白含量分别显著提高15.9%、14.4%和9.2%,但MSW3N1P较MNW3N1P可使冬小麦籽粒醇溶蛋白和贮藏蛋白含量分别显著提高5.4%和2.5%。综合来看,玉米季深松+麦季3年免耕1年翻耕是旱地玉-麦两熟体系高产优质栽培的适宜轮耕模式。
姜沛沛, 郭锦花, 肖慧淑, 彭彦珉, 张军, 田文仲, 吕军杰, 吴金芝, 王贺正, 付国占, 黄明, 李友军. 轮耕模式对旱地玉-麦两熟体系作物产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 181-192.
Pei-pei JIANG, Jin-hua GUO, Hui-shu XIAO, Yan-min PENG, Jun ZHANG, Wen-zhong TIAN, Jun-jie Lyu, Jin-zhi WU, He-zheng WANG, Guo-zhan FU, Ming HUANG, You-jun LI. Effect of rotational tillage patterns on the crop yield and quality in a maize-wheat (Zea mays-Triticum aestivum) double cropping system in dryland agriculture[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(6): 181-192.
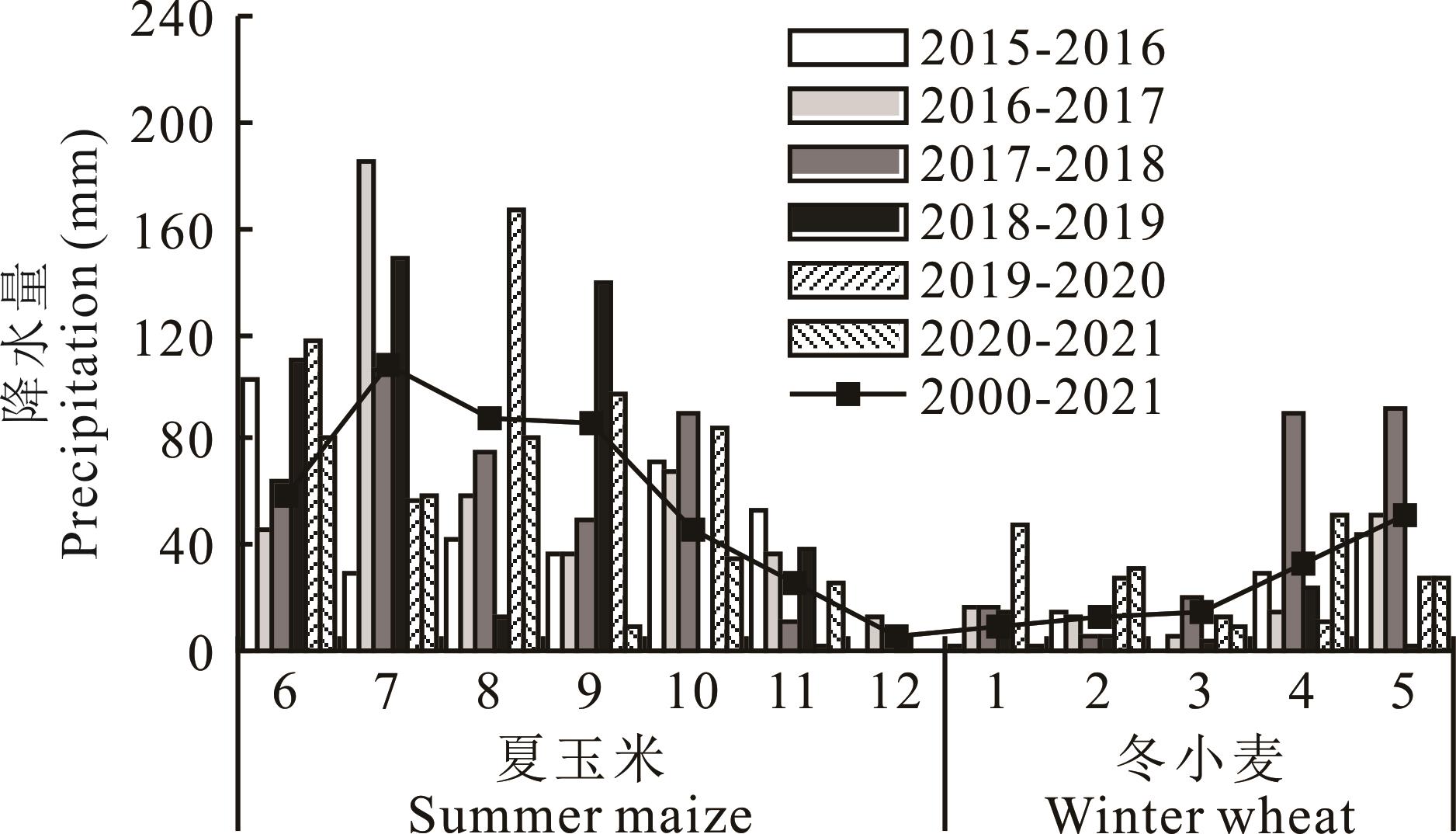
图1 2015-2021年逐月降水量和近21年的平均月降水量2000-2021代表2000年6月至2021年5月的平均月降水量。2000-2021 represents the average monthly precipitation from June 2000 to May 2021.
Fig.1 2015-2021 and latest 21-year average monthly precipitation
| 年度 Year | 夏玉米 Summer maize | 冬小麦 Winter wheat | 周年 Annual | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DI | 降水年型 Precipitation type | DI | 降水年型 Precipitation type | DI | 降水年型 Precipitation type | |
| 2015 (2015-2016) | -1.10 | 干旱年Dry year | 0.31 | 平水年Normal year | -0.72 | 干旱年Dry year |
| 2016 (2016-2017) | -0.16 | 平水年Normal year | 0.32 | 平水年Normal year | 0.02 | 平水年Normal year |
| 2017 (2017-2018) | -0.42 | 干旱年Dry year | 1.98 | 丰水年Rainy year | 0.48 | 丰水年Rainy year |
| 2018 (2018-2019) | 0.52 | 丰水年Rainy year | -1.67 | 干旱年Dry year | -0.24 | 平水年Normal year |
| 2019 (2019-2020) | 0.74 | 丰水年Rainy year | 0.21 | 平水年Normal year | 0.68 | 丰水年Rainy year |
| 2020 (2020-2021) | -0.96 | 干旱年Dry year | -0.30 | 平水年Normal year | -0.85 | 干旱年Dry year |
表1 2015-2021年试验区降水年型
Table 1 Precipitation year type in the experiment area from 2015 to 2021
| 年度 Year | 夏玉米 Summer maize | 冬小麦 Winter wheat | 周年 Annual | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DI | 降水年型 Precipitation type | DI | 降水年型 Precipitation type | DI | 降水年型 Precipitation type | |
| 2015 (2015-2016) | -1.10 | 干旱年Dry year | 0.31 | 平水年Normal year | -0.72 | 干旱年Dry year |
| 2016 (2016-2017) | -0.16 | 平水年Normal year | 0.32 | 平水年Normal year | 0.02 | 平水年Normal year |
| 2017 (2017-2018) | -0.42 | 干旱年Dry year | 1.98 | 丰水年Rainy year | 0.48 | 丰水年Rainy year |
| 2018 (2018-2019) | 0.52 | 丰水年Rainy year | -1.67 | 干旱年Dry year | -0.24 | 平水年Normal year |
| 2019 (2019-2020) | 0.74 | 丰水年Rainy year | 0.21 | 平水年Normal year | 0.68 | 丰水年Rainy year |
| 2020 (2020-2021) | -0.96 | 干旱年Dry year | -0.30 | 平水年Normal year | -0.85 | 干旱年Dry year |
项目 Item | 夏玉米 Summer maize | 冬小麦 Winter wheat | 周年 Annual | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
干旱年 Dry year | 平水年 Normal year | 丰水年 Rainy year | 干旱年 Dry year | 平水年 Normal year | 丰水年 Rainy year | 干旱年 Dry year | 平水年 Normal year | 丰水年 Rainy year | |||||||
| 籽粒产重Grain yield (kg·hm-2) | 4414c | 5649b | 8140a | 2193b | 3660a | 3900a | 7948b | 9380ab | 10625a | ||||||
| F值 F value | |||||||||||||||
| 年型 Year (Y) | 724.84** | 272.95** | 228.97** | ||||||||||||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | 44.46** | 33.73** | 71.83** | ||||||||||||
| 年型×处理 Y×T | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||
表2 不同降水年型籽粒产量均值及变异来源
Table 2 Annual average yield under different precipitation types and source of variation
项目 Item | 夏玉米 Summer maize | 冬小麦 Winter wheat | 周年 Annual | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
干旱年 Dry year | 平水年 Normal year | 丰水年 Rainy year | 干旱年 Dry year | 平水年 Normal year | 丰水年 Rainy year | 干旱年 Dry year | 平水年 Normal year | 丰水年 Rainy year | |||||||
| 籽粒产重Grain yield (kg·hm-2) | 4414c | 5649b | 8140a | 2193b | 3660a | 3900a | 7948b | 9380ab | 10625a | ||||||
| F值 F value | |||||||||||||||
| 年型 Year (Y) | 724.84** | 272.95** | 228.97** | ||||||||||||
| 处理 Treatment (T) | 44.46** | 33.73** | 71.83** | ||||||||||||
| 年型×处理 Y×T | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||

图2 不同降水年型下不同处理对夏玉米、冬小麦及周年产量的影响MNWN代表玉米季免耕+麦季免耕;MSWN代表玉米季深松+麦季免耕;MNW3N1P代表玉米季免耕+麦季3年免耕1年翻耕;MSW3N1P代表玉米季深松+麦季3年免耕1年翻耕;CK代表传统两季均翻耕。下同。误差线表示标准误,柱上不同小写字母表示同一降水年型下不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。MNWN represents no tillage in both maize season and wheat season; MSWN represents subsoiling in maize season and no tillage in wheat season; MNW3N1P represents no tillage in maize season plus consecutive 3-year no-tillage and 1-year plough in wheat season; MSW3N1P represents subsoiling in maize season plus consecutive 3-year no-tillage and 1-year plough in wheat season; CK represents conventional plough after wheat and maize harvest. The same below. The error line represents the standard error. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among treatments within the same precipitation year types (P<0.05).
Fig.2 Effects of different treatments on grain yield of summer maize, winter wheat and annual under different precipitation types
处理 Treatment | 夏玉米 Summer maize | 冬小麦 Winter wheat | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
氮含量 Nitrogen content | 磷含量 Phosphorus content | 钾含量 Potassium content | 氮含量 Nitrogen content | 磷含量 Phosphorus content | 钾含量 Potassium content | |
| MNWN | 1.33ab | 0.26a | 0.35ab | 2.21b | 2.76b | 2.19c |
| MSWN | 1.34ab | 0.25a | 0.34ab | 2.20b | 2.92ab | 2.47bc |
| MNW3N1P | 1.36ab | 0.27a | 0.37a | 2.31a | 2.88ab | 3.09a |
| MSW3N1P | 1.38a | 0.25a | 0.34ab | 2.38a | 3.18a | 2.70b |
| CK | 1.32b | 0.24a | 0.32b | 2.21b | 2.76b | 3.26a |
表3 不同轮耕模式对旱地玉-麦两熟体系作物籽粒氮磷钾含量的影响
Table 3 Effects of different rotational tillage modes on nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium contents in grains in dryland maize-wheat double cropping system (%)
处理 Treatment | 夏玉米 Summer maize | 冬小麦 Winter wheat | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
氮含量 Nitrogen content | 磷含量 Phosphorus content | 钾含量 Potassium content | 氮含量 Nitrogen content | 磷含量 Phosphorus content | 钾含量 Potassium content | |
| MNWN | 1.33ab | 0.26a | 0.35ab | 2.21b | 2.76b | 2.19c |
| MSWN | 1.34ab | 0.25a | 0.34ab | 2.20b | 2.92ab | 2.47bc |
| MNW3N1P | 1.36ab | 0.27a | 0.37a | 2.31a | 2.88ab | 3.09a |
| MSW3N1P | 1.38a | 0.25a | 0.34ab | 2.38a | 3.18a | 2.70b |
| CK | 1.32b | 0.24a | 0.32b | 2.21b | 2.76b | 3.26a |

图3 不同轮耕模式对旱地玉-麦两熟体系作物籽粒蛋白质产量的影响误差线表示标准误,柱上不同小写字母表示相同作物或周年下不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。The error line represents the standard error. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among treatments within the same crop or annual (P<0.05).
Fig.3 Effects of different rotational tillage patterns on grain protein yield in dryland maize-wheat double cropping system
处理 Treatment | 清蛋白 Albumin | 球蛋白 Globulin | 醇溶蛋白 Gliadin | 谷蛋白 Glutelin | 谷醇比 Glutelin/gliadin | 贮藏蛋白 Storage protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNWN | 2.33b | 1.71ab | 3.33b | 4.14b | 1.24c | 7.46c |
| MSWN | 2.36b | 1.76ab | 3.36b | 4.07b | 1.21c | 7.43c |
| MNW3N1P | 2.54a | 1.85a | 3.36b | 4.81a | 1.43a | 8.16b |
| MSW3N1P | 2.36b | 1.78ab | 3.54a | 4.82a | 1.37b | 8.36a |
| CK | 2.32b | 1.66b | 3.32b | 4.15b | 1.25c | 7.47c |
表4 不同轮耕模式对旱地玉-麦两熟体系冬小麦籽粒蛋白质组分特征的影响
Table 4 Effects of different rotational tillage patterns on the properties of protein components in winter wheat grains in dryland maize-wheat double cropping system (%)
处理 Treatment | 清蛋白 Albumin | 球蛋白 Globulin | 醇溶蛋白 Gliadin | 谷蛋白 Glutelin | 谷醇比 Glutelin/gliadin | 贮藏蛋白 Storage protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNWN | 2.33b | 1.71ab | 3.33b | 4.14b | 1.24c | 7.46c |
| MSWN | 2.36b | 1.76ab | 3.36b | 4.07b | 1.21c | 7.43c |
| MNW3N1P | 2.54a | 1.85a | 3.36b | 4.81a | 1.43a | 8.16b |
| MSW3N1P | 2.36b | 1.78ab | 3.54a | 4.82a | 1.37b | 8.36a |
| CK | 2.32b | 1.66b | 3.32b | 4.15b | 1.25c | 7.47c |
| 1 | Jia M Y, Huang L M, Li Q C, et al. Effects of tillage methods on physico-chemical and microbial characteristics of farmland soil and nutritional quality of wheat. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(11): 1964-1976. |
| 贾梦圆, 黄兰媚, 李琦聪, 等. 耕作方式对农田土壤理化性质、微生物学特性及小麦营养品质的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(11): 1964-1976. | |
| 2 | Yan W, Sun J B, Lyu H G, et al. Effects of foliar applications of fertilizers containing different zinc sources on grain yield and grain nutritional quality of winter wheat and summer maize. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2024, 43(3): 504-515. |
| 颜为, 孙金鞭, 吕洪国, 等. 不同锌源叶面喷施对冬小麦和夏玉米产量及籽粒营养品质的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2024, 43(3): 504-515. | |
| 3 | Liu J, Liu J, Su R G, et al. Current status, problems and countermeasures of wheat and maize production in Henan province. Journal of Agriculture, 2015, 5(1): 5-9. |
| 刘娇, 刘举, 苏瑞光, 等. 河南省小麦、玉米生产现状、问题与对策. 农学学报, 2015, 5(1): 5-9. | |
| 4 | Zhang J J, Wang Y, Fan T L, et al. Effects of different tillage and fertilization modes on the soil physical and chemical properties and crop yield under winter wheat/spring corn rotation on dryland of east Gansu, Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(4): 1001-1008. |
| 张建军, 王勇, 樊廷录, 等. 耕作方式与施肥对陇东旱塬冬小麦-春玉米轮作农田土壤理化性质及产量的影响. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(4): 1001-1008. | |
| 5 | Wang Q L, Yu F X, Gao L, et al. Regulation of tillage on grain matter accumulation in maize. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2024, 15: 1373624. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2024.1373624. |
| 6 | Zhang Y J, Wang R, Wang H, et al. Soil water use and crop yield increase under different long-term fertilization practices incorporated with two-year tillage rotations. Agricultural Water Management, 2019, 221(11): 362-370. |
| 7 | Wang Y L, Li J. Study of tillage patterns suitable for soil physicochemical properties and crop yields in wheat/maize fields. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2014, 20(5): 1139-1150. |
| 王玉玲, 李军. 利于小麦-玉米轮作田土壤理化性状和作物产量的耕作方式研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(5): 1139-1150. | |
| 8 | Sun K, Liu Z, Hu H Y, et al. Effect of organic fertilizer and rotational tillage practices on soil carbon and nitrogen and maize yield in wheat-maize cropping system. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(3): 401-410. |
| 孙凯, 刘振, 胡恒宇, 等. 有机培肥与轮耕方式对夏玉米田土壤碳氮和产量的影响. 作物学报, 2019, 45(3): 401-410. | |
| 9 | Izumi Y, Yoshida T, Iijima M. Effects of subsoiling to the non-tilled field of wheat-soybean rotation on the root system development, water uptake, and yield. Plant Production Science, 2009, 12(3): 327-335. |
| 10 | Yan L, Jiang X X, Ji X N, et al. Distribution of water-stable aggregates under soil tillage practices in a black soil hillslope cropland in Northeast China. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2020, 20(1): 24-31. |
| 11 | Nie L P, Guo L W, Niu H Y, et al. Effects of rotational tillage on tilth soil structure and crop yield and quality in maize-wheat croping system. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2015, 41(3): 468-478. |
| 聂良鹏, 郭利伟, 牛海燕, 等. 轮耕对小麦-玉米两熟农田耕层构造及作物产量与品质的影响. 作物学报, 2015, 41(3): 468-478. | |
| 12 | Sun M, Ge X M, Gao Z Q, et al. Relationship between water storage conservation in fallow period and grains protein formation in dryland wheat in different precipitation years. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2014, 47(9): 1692-1704. |
| 孙敏, 葛晓敏, 高志强, 等. 不同降水年型休闲期耕作蓄水与旱地小麦籽粒蛋白质形成的关系. 中国农业科学, 2014, 47(9): 1692-1704. | |
| 13 | Guo S L, Zhu H H, Dang T H, et al. Winter wheat grain yield associated with precipitation distribution under long-term nitrogen fertilization in the semiarid Loess Plateau in China. Geoderma, 2012, 189(20): 442-450. |
| 14 | Xin N Q, Zhang Y Q, Wang L X. The study on dryland agriculture in North China. Beijing: Chinese Agriculture Press, 2002. |
| 信乃诠, 张燕卿, 王立祥. 中国北方旱区农业研究. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2002. | |
| 15 | Wu J Z, Wang H T, Hou Y Q, et al. Optimum tillage pattern with high crop productivity and soil nitrate-N accumulation in rain-fed summer maize and winter wheat double cropping system. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(4): 614-627. |
| 吴金芝, 汪洪涛, 侯园泉, 等. 提升雨养夏玉米-冬小麦两熟体系生产力和土壤硝态氮累积的最优耕作模式. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(4): 614-627. | |
| 16 | He G, Wang Z H, Li F C, et al. Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium requirement and their physiological efficiency for winter wheat affected by soil surface managements in dryland. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(9): 1657-1671. |
| 何刚, 王朝辉, 李富翠, 等. 地表覆盖对旱地小麦氮磷钾需求及生理效率的影响. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(9): 1657-1671. | |
| 17 | Huang M, Wu J Z, Li Y J, et al. Effects of tillage method and straw mulching on grain yield and protein content in wheat and soil nitrate residue under a winter wheat and summer soybean crop rotation in drylands. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(9): 34-44. |
| 黄明, 吴金芝, 李友军, 等. 耕作方式和秸秆覆盖对旱地麦豆轮作下小麦籽粒产量、蛋白质含量和土壤硝态氮残留的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 34-44. | |
| 18 | Yao X Y, Qiu W, Lu H H, et al. Optimum combination of planting density and fertilization mode for high yield, quality and nitrogen utilization of spring-sown fresh waxy maize. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(12): 2258-2271. |
| 姚霄宇, 邱纹, 陆虎华, 等. 种植密度和施肥方式对春播鲜食糯玉米产量、品质及氮素吸收利用的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(12): 2258-2271. | |
| 19 | He Z F. Quality and analysis techniques of grain and oilseeds. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1985: 87-92. |
| 何照范. 粮油籽粒品质及其分析技术. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1985: 87-92. | |
| 20 | Shi Y, Chen M X, Yu Z W, et al. Effects of shading at different phases of grain-filling on wheat grain protein components contents and processing quality. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(10): 2504-2510. |
| 石玉, 陈茂学, 于振文, 等. 灌浆期不同阶段遮光对小麦籽粒蛋白质组分含量和加工品质的影响. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(10): 2504-2510. | |
| 21 | Yimer T, Abera G, Beyene S, et al. Optimizing fertilization schemes to narrow the maize yield gap in smallholder farming systems in southern Ethiopia. Heliyon, 2024, 10(13): e33926. |
| 22 | Ding J L, Wei H Y, Yang Y H, et al. Effects of conservation tillage on soil water condition and winter wheat yield in farmland. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(8): 2501-2508. |
| 丁晋利, 魏红义, 杨永辉, 等. 保护性耕作对农田土壤水分和冬小麦产量的影响. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(8): 2501-2508. | |
| 23 | Li N, Zhou C, Sun X, et al. Effects of ridge tillage and mulching on water availability, grain yield, and water use efficiency in rain-fed winter wheat under different rainfall and nitrogen conditions. Soil and Tillage Research, 2018, 179(9): 86-95. |
| 24 | Zhao K N, Wang H T, Wu J Z, et al. One-off irrigation improves water and nitrogen use efficiency and productivity of wheat as mediated by nitrogen rate and tillage in drought-prone areas. Field Crops Research, 2023, 295(6): 108898. |
| 25 | Li N N, Sun M, Gao Z Q, et al. A study on the relationship between water consumption and nitrogen absorption, utilization under sub-soiling during the fallow period plus mulched-sowing in humid and dry years of dryland wheat. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(18): 3455-3469. |
| 李念念, 孙敏, 高志强, 等. 极端年型旱地麦田深松和覆盖播种水分消耗与植株氮素吸收、利用关系的研究. 中国农业科学, 2018, 51(18): 3455-3469. | |
| 26 | Guo X Y, Wang H, Yu Q, et al. Effects of tillage on soil moisture and yield of wheat-maize rotation field in Weibei upland plateau. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(14): 2977-2990. |
| 郭星宇, 王浩, 于琦, 等. 耕作对渭北旱塬小麦-玉米轮作田土壤水分和产量的影响. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(14): 2977-2990. | |
| 27 | Yu Q, Li J, Zhou D, et al. Effects of no-tillage/subsoiling rotational tillage system on increasing soil water storage and crop yield under different precipitation patterns of winter wheat in the Loess Plateau. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(11): 1870-1882. |
| 于琦, 李军, 周栋, 等. 不同降水年型黄土旱塬冬小麦免耕与深松轮耕蓄墒增收效应. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(11): 1870-1882. | |
| 28 | Sun M, Wen F F, Gao Z Q, et al. Effects of farming practice during fallow period on soil water storage and yield of dryland wheat in different rainfall years. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(8): 1459-1469. |
| 孙敏, 温斐斐, 高志强, 等. 不同降水年型旱地小麦休闲期耕作的蓄水增产效应. 作物学报, 2014, 40(8): 1459-1469. | |
| 29 | Xin Y, Xie Y, Liu Y X, et al. Residue cover effects on soil erosion and the infiltration in black soil under simulated rainfall experiments. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 543(12): 651-658. |
| 30 | Zhao Z X, Wang X Y, Tian Y J, et al. Effects of straw returning and nitrogen fertilizer types on summer maize yield and soil ammonia volatilization under future climate change. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2023, 56(1): 104-117. |
| 赵政鑫, 王晓云, 田雅洁, 等. 未来气候条件下秸秆还田和氮肥种类对夏玉米产量及土壤氨挥发的影响. 中国农业科学, 2023, 56(1): 104-117. | |
| 31 | Zhang X T, Wang J, Feng X Y, et al. Effects of tillage on soil organic carbon and crop yield under straw return. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2023, 354(14): 108543. |
| 32 | Zhao Y H, Yin H K, Hu X C, et al. Effects of long-term straw returning on soil organic carbon and nitrogen components and maize yield in brown soil farmland. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2024, 42(3): 80-88. |
| 赵宇航, 殷浩凯, 胡雪纯, 等. 长期秸秆还田对褐土农田土壤有机碳、氮组分及玉米产量的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2024, 42(3): 80-88. | |
| 33 | Chen Y Z, Chai S X, Cheng H B, et al. Effects of straw-incorporation combined with autumn plastic mulching on soil water consumption characteristics and winter wheat yield in arid farming areas. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(2): 256-266. |
| 陈玉章, 柴守玺, 程宏波, 等. 秸秆还田结合秋覆膜对旱地冬小麦耗水特性和产量的影响. 作物学报, 2019, 45(2): 256-266. | |
| 34 | Fang B T, Li Y J, Yan G X, et al. Effects of tillage methods on wheat yield, nutilization and soil nitrate-N residue in dryland wheat-maize rotation system. Journal of Henan Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(5): 1-9. |
| 方保停, 李友军, 闫广轩, 等. 耕作方式对旱作区麦-玉轮作体系小麦产量、氮素利用和土壤硝态氮残留的影响. 河南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(5): 1-9. | |
| 35 | Xiong S P, Wang J, Wang X C, et al. Effects of tillage and nitrogen addition rate on nitrogen metabolism, grain yield and protein content in wheat in lime concretion black soil region. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(7): 767-775. |
| 熊淑萍, 王静, 王小纯, 等. 耕作方式及施氮量对砂姜黑土区小麦氮代谢及籽粒产量和蛋白质含量的影响. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(7): 767-775. | |
| 36 | Li W Q, Han M M, Zhang H J, et al. Effects of tillage practices and nitrogen rates on grain yield, grain protein content and nitrogen use efficiency in wheat. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2024, 40(14): 1-12. |
| 李文倩, 韩明明, 张海军, 等. 耕作措施和施氮量对小麦籽粒产量、籽粒蛋白质含量和氮素利用率的影响.中国农学通报, 2024, 40(14): 1-12. | |
| 37 | Zhang D X, Ma S K, Zhang J, et al. Influences of different tillage methods on soil nutrient evolution, grain nutrient and yield of dryland wheat after anthesis. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(24): 73-78. |
| 张冬霞, 马嵩科, 张静, 等. 不同耕作方式对旱作小麦花后土壤养分演变与籽粒养分和产量的影响. 江苏农业科学, 2022, 50(24): 73-78. | |
| 38 | Wen M J, Wang C B, Huo L, et al. Effects of subsoiling and straw returning on soil physical properties and maize production in Yellow River irrigation area of Gansu, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(1): 224-232. |
| 温美娟, 王成宝, 霍琳, 等. 深松和秸秆还田对甘肃引黄灌区土壤物理性状和玉米生产的影响. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(1): 224-232. | |
| 39 | Wang X Z, Fu Z L, Zhang Q K, et al. Short-term subsoiling effects with different wing mounting heights before winter wheat on soil properties and wheat growth in Northwest China. Soil and Tillage Research, 2021, 213(9): 105151. |
| 40 | Wang Q Y, Yu Z W, Shi Y, et al. Strip rotary tillage combining with every two-year subsoiling increases the nitrogen use efficiency and yield of winter wheat. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2024, 30(5): 863-872. |
| 王庆源, 于振文, 石玉, 等. 隔两年深松配合条旋耕显著提升冬小麦的氮素吸收利用效率和产量. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2024, 30(5): 863-872. | |
| 41 | Li W Y, Yan S H, Wang Z L. Comparison of grain protein components and processing quality in responses to dim light during grain filling between strong and weak gluten wheat cultivars. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(1): 265-273. |
| 李文阳, 闫素辉, 王振林. 强筋与弱筋小麦籽粒蛋白质组分与加工品质对灌浆期弱光的响应. 生态学报, 2012, 32(1): 265-273. | |
| 42 | Zhang L J, Zhang Y H, Lu Q L, et al. Effect of tillage model and nitrogen rate on grain quality of dryland winter wheat. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 31(8): 1567-1575. |
| 张礼军, 张耀辉, 鲁清林, 等. 耕作方式和氮肥水平对旱地冬小麦籽粒品质的影响. 核农学报, 2017, 31(8): 1567-1575. | |
| 43 | Sun M, Gao Z Q, Zhao W F, et al. Effect of subsoiling in fallow period and nitrogen application on soil moisture and grain protein accumulation in dryland wheat. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(7): 1286-1295. |
| 孙敏, 高志强, 赵维峰, 等. 休闲期深松配施氮肥对旱地土壤水分及小麦籽粒蛋白质积累的影响. 作物学报, 2014, 40(7): 1286-1295. | |
| 44 | Zhao H M, Gao Z Q, Zhao W F, et al. Effect of tillage in fallow period on grain protein and its related enzyme activity in dryland wheat. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2013, 33(2): 331-338. |
| 赵红梅, 高志强, 赵维峰, 等. 休闲期耕作对旱地小麦籽粒蛋白质形成及其相关酶活性的影响. 麦类作物学报, 2013, 33(2): 331-338. |
| [1] | 冯雅琪, 陈嘉慧, 张静妮, 隋超, 陈基伟, 刘志鹏, 周强, 刘文献. 基于重测序紫花苜蓿高蛋白、高产关联InDel分子标记开发[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 137-149. |
| [2] | 王腾飞, 马霞, 刘金龙, 王斌, 张译尹, 李佳旺, 马江萍, 王小兵, 兰剑. 引黄灌区复种饲用燕麦种植模式产量、品质及经济效益分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 27-37. |
| [3] | 蒋鹏, 李磊, 解昊郡, 徐得甲, 王锐, 虎强, 孙权. 净化沼液滴灌对砂壤土质量、青贮玉米生产力的影响及安全消纳容量分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 64-81. |
| [4] | 王新友, 王小兰, 张万昌, 李颖, 马永玲, 王晓寅, 王建刚, 王海青, 岳贝凡, 刘永福, 王永宏, 刘珊, 白美婷. 陇东南部林缘山区青贮玉米品种筛选及其高效栽培研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 191-202. |
| [5] | 徐寿霞. 基于meta分析的丛枝菌根对小麦产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 192-204. |
| [6] | 张俊豪, 柴雪茹, 马嵩科, 张冬霞, 张静, 乔唱唱, 李爽, 黄明, 王贺正. 秸秆还田配施磷肥对豫西旱地小麦碳同化物积累的影响及其生理机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 89-104. |
| [7] | 张永亮, 滕泽, 郝凤, 于铁峰, 张玉霞. 苜蓿混播方式及比例对混播草地生产力和稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 185-197. |
| [8] | 白宇飞, 尹航, 杨海波, 冯振华, 李斐. 无人机多光谱和RGB影像融合的苜蓿产量估测[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 45-58. |
| [9] | 曹秭琦, 赵小庆, 张向前, 伍建辉, 张帆, 刘丹, 路战远, 任永峰. 施钾水平对北方风沙区油莎豆生长、块茎品质及产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 73-83. |
| [10] | 吕帅磊, 常单娜, 周国朋, 刘蕊, 赵鑫, 刘佳, 徐昌旭, 曹卫东. 江西红壤绿肥季施用磷矿粉的磷素效应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 149-160. |
| [11] | 侯铭辉, 孙延亮, 杨开鑫, 齐军仓, 张前兵. 基于响应曲面法确定水培大麦饲草高产优质的氮磷钾养分投入量[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 172-185. |
| [12] | 王凤宇, 梁国玲, 胡泽龙, 刘文辉. 地理因子对青藏高原野生垂穗披碱草表型及种子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 198-214. |
| [13] | 张仲鹃, 郝曦煜, 王雪, 李峰, 李文龙. 齐齐哈尔地区适宜青贮玉米品种的筛选及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 228-240. |
| [14] | 赵文军, 刘蕊, 王正旭, 冯瑜, 薛开政, 刘魁, 徐梓荷, 曹卫东, 付利波, 尹梅, 陈华. 烤烟-绿肥轮作对云南烟田土壤质量与微生物养分限制的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 147-158. |
| [15] | 张睿, 韩重阳, 蔡家邦, 汪阳, 黄琳凯, 张新全, 聂刚. 6个苇状羊茅(型)品种在成都平原区的生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 138-148. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||