

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 15-24.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023360
候腾思1( ), 沈艳1,2,3,4(
), 沈艳1,2,3,4( ), 马红彬1,2,3,4, 方鹏1, 曹颖1
), 马红彬1,2,3,4, 方鹏1, 曹颖1
收稿日期:2023-09-25
修回日期:2023-11-13
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-05-13
通讯作者:
沈艳
作者简介:E-mail: nxshenyan@163.com基金资助:
Teng-si HOU1( ), Yan SHEN1,2,3,4(
), Yan SHEN1,2,3,4( ), Hong-bin MA1,2,3,4, Peng FANG1, Ying CAO1
), Hong-bin MA1,2,3,4, Peng FANG1, Ying CAO1
Received:2023-09-25
Revised:2023-11-13
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-05-13
Contact:
Yan SHEN
摘要:
平茬是荒漠草原人工柠条优化管理的重要手段。探究柠条平茬方式对土壤水分特征及水量平衡的影响,可为研究区柠条的合理平茬提供理论依据和实践指导。以宁夏荒漠草原区人工柠条林为对象,设置未平茬(WP)、隔1带平茬1带(G1P1)、隔3带平茬3带(G3P3)、隔5带平茬5带(G5P5)4种平茬方式,分析不同平茬方式对土壤水分和水分平衡特征的影响,结果表明:1) G3P3处理土壤含水量最高,0~200 cm土壤含水量随土壤深度的增加而升高;2) 与未种植柠条天然草地相比,WP、G1P1、G3P3和G5P5处理均有一定程度的土壤水分亏缺,其中G3P3处理水分亏缺指数最低,减缓了土壤水分消耗;3) 受环境和平茬方式的影响,4种平茬方式植被蒸腾量表现为G3P3<G1P1<G5P5<WP,棵间蒸散量表现为G3P3<G1P1<WP<G5P5,G3P3的蒸散量与降水量的比值最小。基于土壤水分和水量平衡特征方面,G3P3处理更有利于种植柠条林的荒漠草原水分保持和水量平衡。
候腾思, 沈艳, 马红彬, 方鹏, 曹颖. 柠条平茬对荒漠草原土壤水分特征及水量平衡的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 15-24.
Teng-si HOU, Yan SHEN, Hong-bin MA, Peng FANG, Ying CAO. Effects of Caragana intermedia stubble on soil water characteristics and water balance on the desert steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(8): 15-24.
处理 Treatment | 盖度 Coverage (%) | 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | Margalef丰富度指数Margalef richness index | Simpson优势度指数Simpson dominance index | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数Shannon-Wiener diversity index | Pielou均匀度指数Pielou evenness index | 重要值比例Proportion of importance (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木Bush | PH | AH | |||||||
| WP | 79.67±3.38a | 89.46±5.90ab | 1.30±0.10ab | 0.25±0.02a | 1.90±0.13ab | 1.08±0.07ab | 10.05 | 87.09 | 2.86 |
| G1P1 | 58.67±3.18b | 115.85±2.79a | 1.37±0.11a | 0.17±0.02ab | 2.13±0.09ab | 1.03±0.09ab | 28.20 | 66.21 | 5.59 |
| G3P3 | 59.67±2.33b | 58.82±4.35b | 1.09±0.05b | 0.15±0.03b | 2.27±0.09a | 1.18±0.04a | 26.06 | 73.94 | 0.00 |
| G5P5 | 76.67±6.06a | 73.58±6.53b | 1.13±0.08ab | 0.25±0.04a | 1.80±0.12b | 0.99±0.04b | 23.78 | 59.09 | 17.13 |
表1 样地植物群落特征
Table 1 Characteristics of plant community in sample plots
处理 Treatment | 盖度 Coverage (%) | 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | Margalef丰富度指数Margalef richness index | Simpson优势度指数Simpson dominance index | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数Shannon-Wiener diversity index | Pielou均匀度指数Pielou evenness index | 重要值比例Proportion of importance (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木Bush | PH | AH | |||||||
| WP | 79.67±3.38a | 89.46±5.90ab | 1.30±0.10ab | 0.25±0.02a | 1.90±0.13ab | 1.08±0.07ab | 10.05 | 87.09 | 2.86 |
| G1P1 | 58.67±3.18b | 115.85±2.79a | 1.37±0.11a | 0.17±0.02ab | 2.13±0.09ab | 1.03±0.09ab | 28.20 | 66.21 | 5.59 |
| G3P3 | 59.67±2.33b | 58.82±4.35b | 1.09±0.05b | 0.15±0.03b | 2.27±0.09a | 1.18±0.04a | 26.06 | 73.94 | 0.00 |
| G5P5 | 76.67±6.06a | 73.58±6.53b | 1.13±0.08ab | 0.25±0.04a | 1.80±0.12b | 0.99±0.04b | 23.78 | 59.09 | 17.13 |
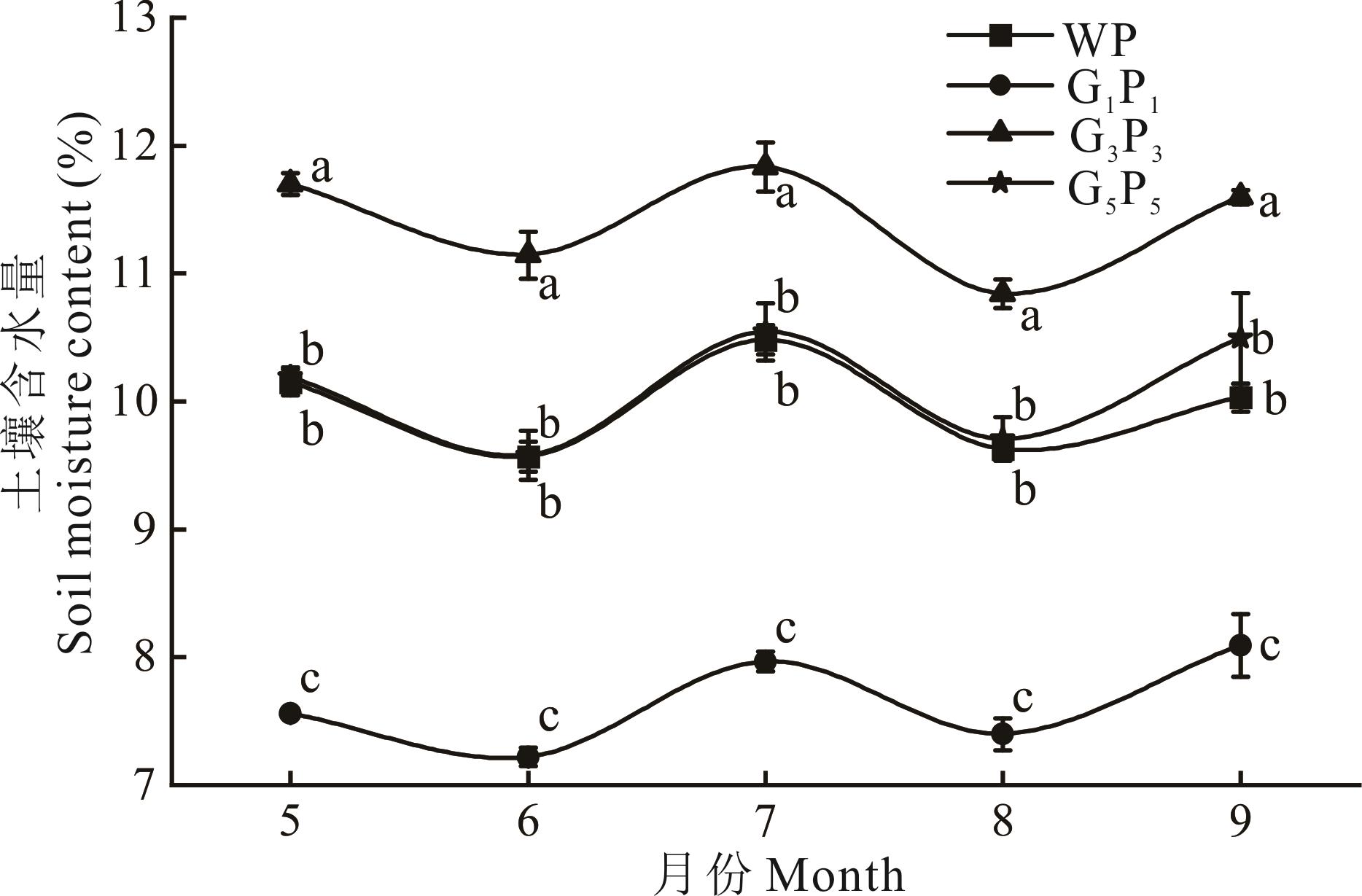
图3 荒漠草原生长季土壤水分特征不同小写字母表示相同月份不同处理间在P<0.05水平上差异显著,下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences of different treatments in the same month at P<0.05level, the same below.
Fig.3 Soil water characteristics in the growing season of desert steppe
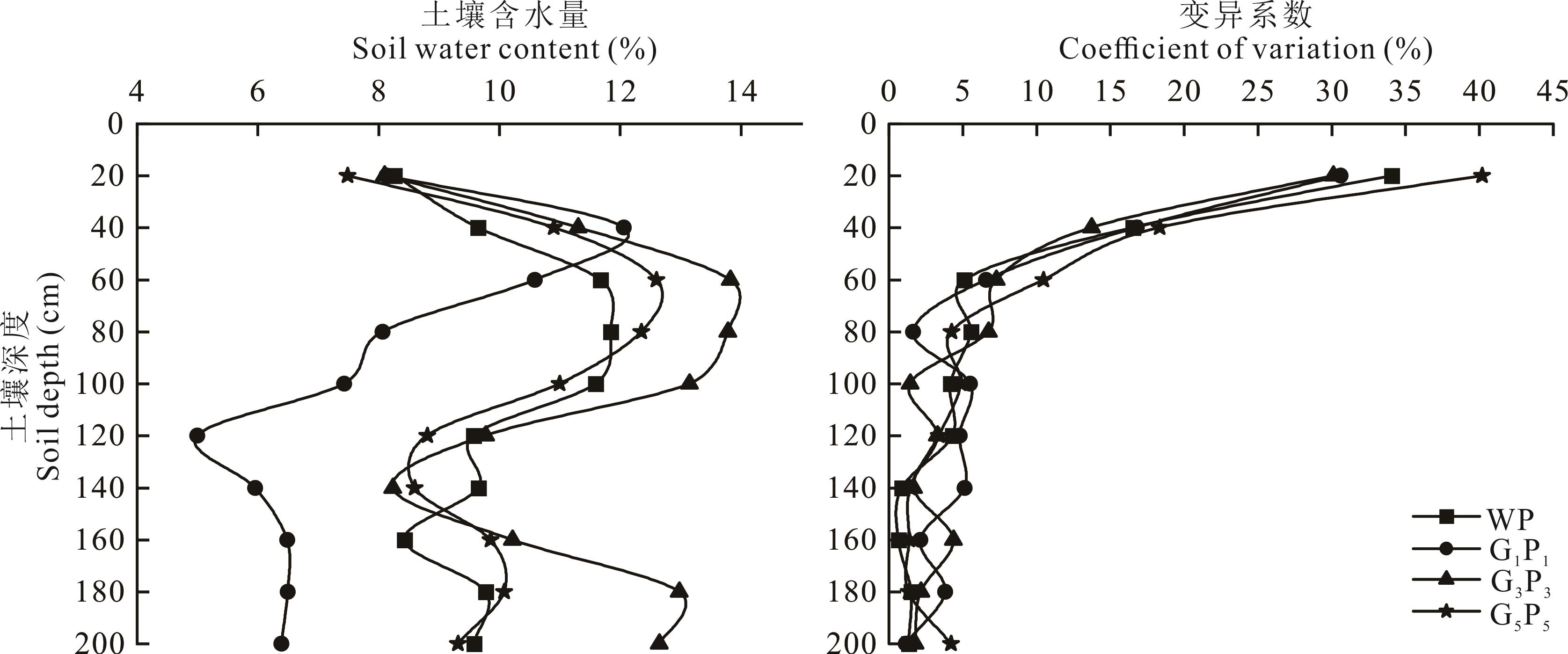
图4 荒漠草原生长季0~200 cm土壤含水量垂直变化及其变异系数
Fig. 4 Vertical variation and coefficient of variation of 0-200 cm soil water content in desert steppe during the growing season
处理 Treatment | 降水量 Precipitation (P, mm) | 植被蒸腾量 Vegetation transpiration (mm) | 棵间蒸散量 Evapotranspiration among trees (mm) | 蒸散量 Evapotranspiration (ET, mm) | 储水变化量 Change in water storage (mm) | 蒸散量/降水量 ET/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WP | 336.80 | 225.06 | 64.21 | 380.20 | -43.40 | 1.13 |
| G1P1 | 336.80 | 185.86 | 58.11 | 334.90 | 1.90 | 0.99 |
| G3P3 | 336.80 | 182.72 | 52.97 | 326.63 | 10.17 | 0.97 |
| G5P5 | 336.80 | 204.66 | 66.33 | 361.92 | -25.12 | 1.07 |
表2 不同平茬方式下荒漠草原水量平衡
Table 2 Water balance in desert steppe under different stubble methods
处理 Treatment | 降水量 Precipitation (P, mm) | 植被蒸腾量 Vegetation transpiration (mm) | 棵间蒸散量 Evapotranspiration among trees (mm) | 蒸散量 Evapotranspiration (ET, mm) | 储水变化量 Change in water storage (mm) | 蒸散量/降水量 ET/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WP | 336.80 | 225.06 | 64.21 | 380.20 | -43.40 | 1.13 |
| G1P1 | 336.80 | 185.86 | 58.11 | 334.90 | 1.90 | 0.99 |
| G3P3 | 336.80 | 182.72 | 52.97 | 326.63 | 10.17 | 0.97 |
| G5P5 | 336.80 | 204.66 | 66.33 | 361.92 | -25.12 | 1.07 |
| 1 | Lu F, Hu H F, Sun W J, et al. Effects of national ecological restoration projects on carbon sequestration in China from 2001 to 2010. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2018, 115(16): 4039-4044. |
| 2 | Wang B R, Zhao X D, Liu Y, et al. Using soil aggregate stability and erodibility to evaluate the sustainability of large-scale afforestation of Robinia pseudoacacia and Caragana korshinskii in the Loess Plateau. Forest Ecology and Management, 2019, 450: 117491. |
| 3 | Ma C C, Guo H Y, Wu J B, et al. Acclimation of photosynthetic traits of Caragana species to desert environment in Inner Mongolian Plateau. Arid Land Research and Management, 2014, 28(1): 87-101. |
| 4 | Jia X Y, Zhou J J, Su T T, et al. Effects of different cropping densities on the habitat of artificial Caragana intermedia in desert steppe. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(12): 4126-4136. |
| 贾希洋, 周静静, 宿婷婷, 等. 平茬密度对荒漠草原人工柠条林间生境的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(12): 4126-4136. | |
| 5 | Tang Y K, Wu X, Chen Y M, et al. Water use strategies for two dominant tree species in pure and mixed plantations of the semiarid Chinese Loess Plateau. Ecohydrology, 2018, 11(4): e1943. |
| 6 | Zhou T R, Han C, Qiao L J, et al. Seasonal dynamics of soil water content in the typical vegetation and its response to precipitation in a semi-arid area of Chinese Loess Plateau. Journal of Arid Land, 2021, 35(21): 1015-1025. |
| 7 | Zhang Q D, Wei W, Chen L D, et al. Plant traits in influencing soil moisture in semiarid grasslands of the Loess Plateau, China. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 82: 153297. |
| 8 | Dou Y X, Yang Y, An S S, et al. Effects of different vegetation restoration measures on soil aggregate stability and erodibility on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena, 2019, 185: 104294. |
| 9 | Su T T, Han B F, Ma H B, et al. Effects of contour trenches engineering measures on soil moisture dynamics and balance of typical in Loess Hilly Region. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(21): 125-134. |
| 宿婷婷, 韩丙芳, 马红彬, 等. 水平沟整地措施对黄土丘陵区草原土壤水分动态平衡的影响. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(21): 125-134. | |
| 10 | Xu R, Zhang Y F, Pan Z B, et al. Impact of planting density of Caragana intermedia on soil moisture in the restoration of degraded grassland. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2004, 22(1): 172-175. |
| 徐荣, 张玉发, 潘占兵, 等. 不同柠条密度在退化草地恢复过程中对土壤水分的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2004, 22(1): 172-175. | |
| 11 | Fan R Y, Li Q F, He Y M, et al. Response of the herb layer community to the density of Caragana microphylla plantation. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2019, 33(2): 177-182. |
| 樊如月, 李青丰, 贺一鸣, 等. 柠条林分密度对林带间草本群落的影响. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019, 33(2): 177-182. | |
| 12 | Li Z F, Kang Y Q, He Z, et al. The effects of stumping technology on soil water and plant growth of Caragana intermedia. Journal of Gansu Forestry Science and Technology, 2018, 43(2): 4-7, 12. |
| 李振峰, 康永前, 何榛, 等. 平茬措施对柠条生长和土壤水分的影响研究. 甘肃林业科技, 2018, 43(2): 4-7, 12. | |
| 13 | Yang Y, Liu B R. Effects of planting Caragana shrubs on soil nutrients and stoichiometries in desert steppe of Northwest China. Catena, 2019, 183(10): 104213. |
| 14 | Kang J, Zhang W J, Li J. The calibration of TRIME-T3 tubular TDR for measurement of soil water content in Jingyuan Region. Ningxia Engineering Technology, 2015, 14(2): 146-148. |
| 康洁, 张维江, 李娟. TRIME-T3管式TDR土壤水分测定系统在宁夏泾源地区的标定研究. 宁夏工程技术, 2015, 14(2): 146-148. | |
| 15 | She D L, Liu Y Y, Shao M A, et al. Simulated effects and adaptive evaluation of different canopies rainfall interception models in Loess Plateau. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(16): 115-120. |
| 佘冬立, 刘营营, 邵明安, 等. 黄土坡面不同植被冠层降雨截留模型模拟效果及适用性评价. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(16): 115-120. | |
| 16 | Deng J F, Ding G D, Zhao Y Y, et al. The transpiration rates of three typical trees in Yanchi district. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2014, 28(7): 161-165. |
| 邓继峰, 丁国栋, 赵媛媛, 等. 盐池地区三种典型树种蒸腾速率的研究. 干旱区资源与环境, 2014, 28(7): 161-165. | |
| 17 | Guan T, Fan M S, Jia L G. Estimation of evaporation between plants based on micro-evaporators: Research progress. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(2): 63-67. |
| 关婷, 樊明寿, 贾立国. 基于微型蒸发器估算不同作物棵间蒸发的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(2): 63-67. | |
| 18 | He K J, Huang Y M, Qi Y, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on vegetation and soil and its linkages to plant diversity and productivity in a semi-arid steppe. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 778: 146299. |
| 19 | Han X S, Liu G Q, Xu H, et al. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of soil moisture under three land use types in the semiarid loess region of Southern Ningxia. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 36(6): 250-259. |
| 韩新生, 刘广全, 许浩, 等. 宁夏南部半干旱黄土区3种土地利用类型的土壤水分时空变化特征. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(6): 250-259. | |
| 20 | Zhao Y N, Yu L, Zhou Y R, et al. Soil moisture dynamics and deficit of desert grassland with anthropogenic introduced shrub encroachment in the eastern Ningxia, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(4): 1305-1315. |
| 赵亚楠, 于露, 周玉蓉, 等. 宁夏东部荒漠草原灌丛引入对土壤水分动态及亏缺的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(4): 1305-1315. | |
| 21 | Liu W H, Wang X, Duan W B, et al. Water balance characters of Pinus tabuliformis plantation in Xining city of China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2023, 59(4): 46-56. |
| 刘文浩, 王晓, 段文标, 等. 西宁市油松人工林生长季水量平衡特征. 林业科学, 2023, 59(4): 46-56. | |
| 22 | Wu G L, Yang Z, Cui Z, et al. Mixed artificial grasslands with more roots improved mine soil infiltration capacity. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 535: 54-60. |
| 23 | Gou Q P, Zhu Q K. Response of deep soil moisture to different vegetation types in the Loess Plateau of northern Shannxi, China. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 15098. |
| 24 | Jia X X, Shao M G, Yu D X, et al. Spatial variations in soil-water carrying capacity of three typical revegetation species on the Loess Plateau, China. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2019, 273: 25-35. |
| 25 | Gao Y H, Guo Y F, Yao Y F, et al. Influence of the structural features of Caragana korshinskii root system of soil water content and taproot diameter. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 2020, 29(6): 4624-4633. |
| 26 | Sun Y, Yan X F, Zhou L B, et al. Effect of light intensity and clipping treatment on the compensatory growth of Caragana korshinskii seedings. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(1): 75-83. |
| 孙毅, 闫兴富, 周立彪, 等. 光强和刈割处理对柠条幼苗补偿生长的影响. 草业科学, 2017, 34(1): 75-83. | |
| 27 | Wang L L, Luo Z Z, Li L L, et al. Land use affects soil water balance and soil desiccation within the soil profile: evidence from the western Loess Plateau case. Land, 2022, 11(8): 1136. |
| 28 | Yu R X, Wang L, Yang X G, et al. Soil moisture dynamics and physiological characteristics of moving of Caragana intermedia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(19): 7249-7257. |
| 于瑞鑫, 王磊, 杨新国, 等. 平茬柠条的土壤水分动态及生理特征. 生态学报, 2019, 39(19): 7249-7257. | |
| 29 | Zhang L H, Wang X Q, Jia Z Q, et al. Root distribution characteristics of Caragana intermedia plantations at different ages in alpine sandy land. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2018, 32(11): 163-168. |
| 张立恒, 王学全, 贾志清, 等. 高寒沙地不同林龄中间锦鸡儿人工林根系分布特征. 干旱区资源与环境, 2018, 32(11): 163-168. | |
| 30 | Cui Z, Wu G L, Huang Z, et al. Fine roots determine soil infiltration potential than soil water content in semi-arid grassland soils. Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 578: 124023. |
| 31 | Li H F, Wei W, Chen L D, et al. Progress in the study of soil water balance under forest and grassland covers on the Loess Plateau. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 20(1): 287-293. |
| 李海防, 卫伟, 陈利顶, 等. 黄土高原林草地覆盖土壤水量平衡研究进展. 水土保持研究, 2013, 20(1): 287-293. | |
| 32 | Ma L H, Wang X, Gao Z Y, et al. Canopy pruning as a strategy for saving water in a dry land jujube plantation in a loess hilly region of China. Agricultural Water Management, 2019, 216: 436-443. |
| 33 | Shi S L, Zhao F Y, Ren X M, et al. Soil infiltration properties are affected by typical plant communities in a semi-arid desert grassland in China. Water, 2022, 14(20): 3301. |
| [1] | 曹颖, 聂明鹤, 沈艳, 胡艳, 马登宝, 李东, 候腾思, 方鹏, 王学琴. 宁夏干旱风沙区荒漠草原不同退化阶段植被土壤变化特征及其相关性[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 1-14. |
| [2] | 佘洁, 沈爱红, 石云, 赵娜, 张风红, 何洪源, 吴涛, 李红霞, 马益婷, 朱晓雯. 基于无人机遥感影像和面向对象技术的荒漠草原植被分类[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 1-14. |
| [3] | 姜海鑫, 周瑶, 胡科, 丁占胜, 马红彬. 不同放牧时间对荒漠草原土壤颗粒组成及分形维数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 17-28. |
| [4] | 赵亚楠, 王红梅, 李志丽, 张振杰, 陈彦硕, 苏荣霞. 荒漠草原灌丛转变过程土壤水分亏缺空间特征及影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 22-34. |
| [5] | 李俊瑶, 蒋星驰, 胡晋瑜, 魏栋光, 赵学勇, 王少昆. 生物有机肥施加对荒漠草原植被-土壤-微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 34-45. |
| [6] | 鲍平安, 邱开阳, 黄业芸, 王思瑶, 崔璐瑶, 骆欣怡, 杨云涛, 谢应忠. 荒漠草原植物在氮磷添加下叶功能性状特征及其可塑性[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 97-106. |
| [7] | 赵敏, 赵坤, 王赟博, 殷国梅, 刘思博, 闫宝龙, 孟卫军, 吕世杰, 韩国栋. 长期放牧干扰降低了短花针茅荒漠草原植物多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 39-49. |
| [8] | 刘欣雷, 杜鹤强, 刘秀帆, 范亚伟. 内蒙古荒漠草原地表风沙活动对放牧强度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 1-11. |
| [9] | 陈彦硕, 马彦平, 王红梅, 赵亚楠, 李志丽, 张振杰. 荒漠草原不同年限灌丛引入过程土壤细菌碳源利用特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 30-44. |
| [10] | 胡宇霞, 龚吉蕊, 朱趁趁, 矢佳昱, 张子荷, 宋靓苑, 张魏圆. 基于生态系统服务簇的内蒙古荒漠草原生态系统服务的空间分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 1-14. |
| [11] | 黄业芸, 邱开阳, 朱亚超, 谢应忠, 刘王锁, 杨壹, 王思瑶, 崔璐瑶, 鲍平安. 贺兰山不同海拔植被生物量与土壤分形特征和土壤水分的相关关系[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 24-35. |
| [12] | 曲文杰, 赵文智, 王磊, 屈建军, 杨新国. 两种旱生灌木种子萌发与幼苗复活对模拟干湿处理的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 179-187. |
| [13] | 李江文, 裴婧宏, 韩国栋, 何邦印, 李彩. 基于植物功能性状分析异常降水对不同载畜率下荒漠草原功能群多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 212-222. |
| [14] | 吴旭东, 蒋齐, 王占军, 季波, 任小玢. 降水对荒漠草原地上生物量稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 30-39. |
| [15] | 朱志昊, 孟晨, 王兴, 宋乃平, 王丽, 徐苗苗, 杜灵通. 荒漠草原人工柠条引入后土壤团聚体几何分布及拓扑结构演变特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 53-64. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||