

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 93-106.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025057
收稿日期:2025-02-26
修回日期:2025-04-03
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2025-11-13
通讯作者:
南丽丽
作者简介:E-mail: nanll@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Jun-shi FU( ), Li-li NAN(
), Li-li NAN( ), Ze-long ZHANG, Shi-wen WU
), Ze-long ZHANG, Shi-wen WU
Received:2025-02-26
Revised:2025-04-03
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2025-11-13
Contact:
Li-li NAN
摘要:
为探究不同猫尾草种质资源的光合能力及筛选高光效猫尾草种质,本研究对21份猫尾草种质分蘖期、拔节期、抽穗期和成熟期4个生育时期的叶绿素体色素含量、光合及叶绿素荧光参数进行了对比研究。结果表明,供试猫尾草16项光合指标中,叶绿素a、叶绿素b、类胡萝卜素、总叶绿素、蒸腾速率、气孔导度、净光合速率、胞间二氧化碳浓度、PSⅡ最大光合效率、PSⅡ潜在光化学效率、光化学淬灭系数、表观电子传递效率、PSⅡ光化学量子产量均呈先升后降趋势,并在抽穗期达最大值。基于4个生育时期各指标的均值进行主成分分析,将16项指标经降维提取出5个综合因子,累积贡献率为78.76%;利用逐步回归分析筛选出PSⅡ潜在光化学效率、PSⅡ光化学量子产量、总叶绿素、净光合速率、类胡萝卜素、气孔限制值、表观电子传递效率和非光化学淬灭系数8项可作为高光效猫尾草种质筛选的关键指标。21份猫尾草可聚为4类,其中材料9451、10676和9657均属第Ⅰ类,综合评价值较高,可作为猫尾草高光效新品种选育和改良的优异亲本材料。
傅俊士, 南丽丽, 张泽龙, 吴世文. 21份猫尾草种质不同生育时期光合特性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 93-106.
Jun-shi FU, Li-li NAN, Ze-long ZHANG, Shi-wen WU. Multivariate evaluation of the photosynthetic characteristics of 21 timothy germplasm lines at different growth stages[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(1): 93-106.
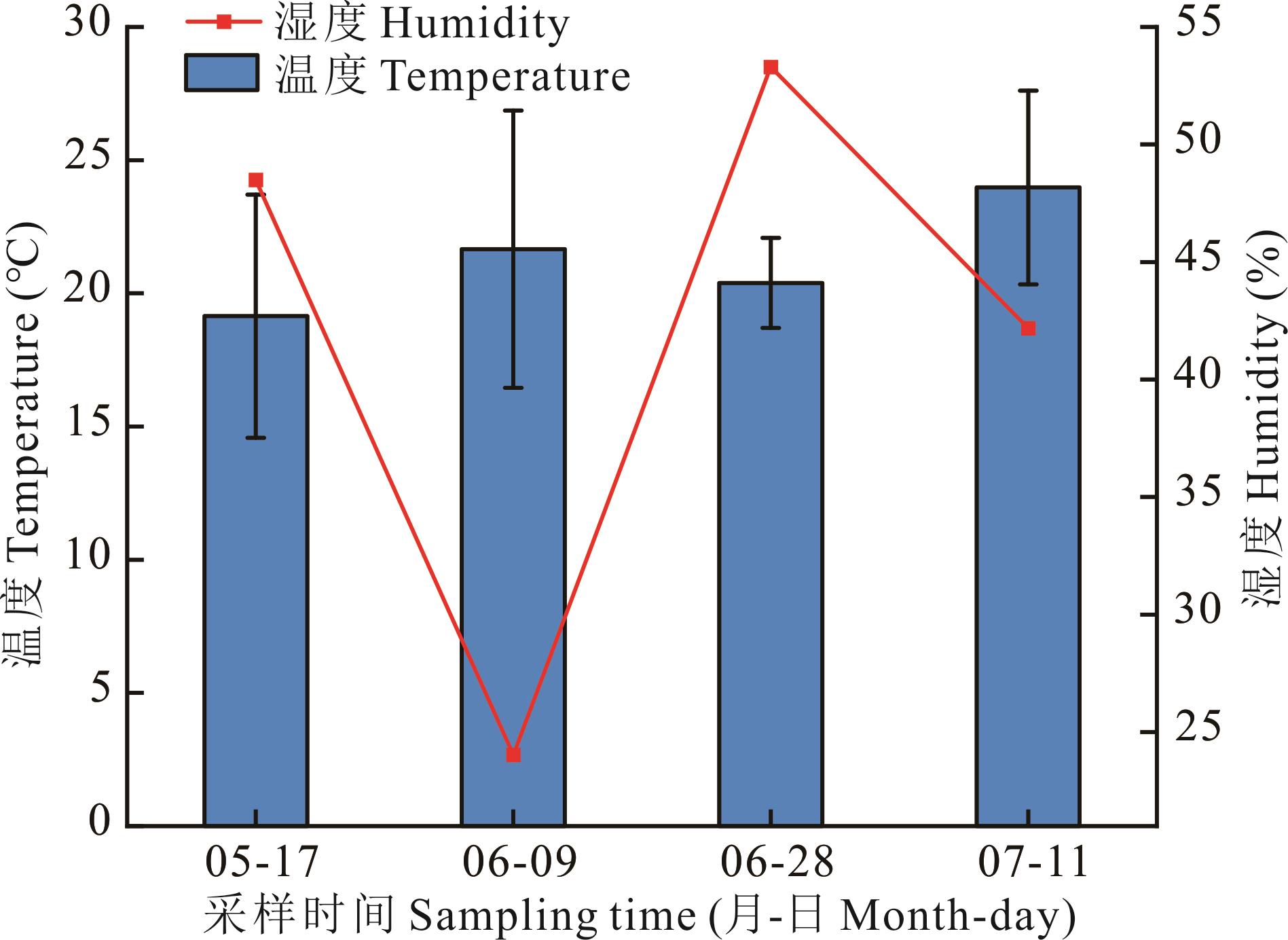
图1 采样时间及当日天气状况05-17为分蘖期,06-09为拔节期,06-28为抽穗期,07-11为成熟期。05-17 is the tillering stage, 06-09 is the jointing stage, 06-28 is the heading stage, and 07-11 is the maturity stage.
Fig.1 Sampling time and weather conditions of the day

图2 猫尾草种质叶绿素体色素含量CX: ‘川西’猫尾草P. pratense ‘Chuanxi’; MS: ‘岷山’猫尾草P. pratense ‘Minshan’. 下同The same below.
Fig.2 Chloroplast pigment content in timothy germplasm
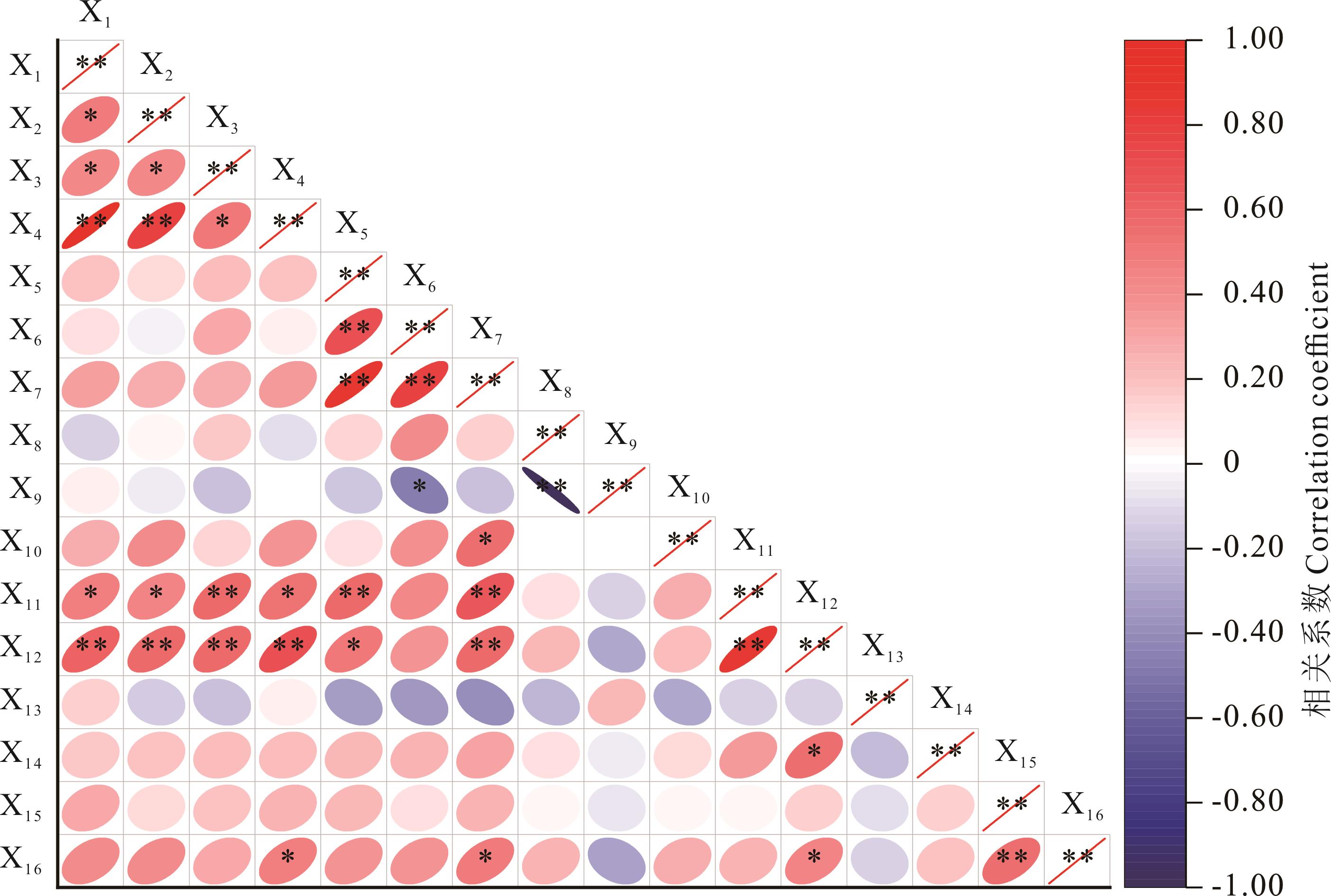
图6 猫尾草种质光合特性各指标间相关性分析**: P<0.01; *: P<0.05. X1: 叶绿素a含量Chl a content; X2: 叶绿素b含量Chl b content; X3: 类胡萝卜素含量Car content; X4: 总叶绿素含量TChl content; X5: 蒸腾速率Tr; X6: 气孔导度Gs; X7: 净光合速率Pn; X8; 胞间二氧化碳浓度Ci; X9: 气孔限制值Ls; X10: 水分利用效率WUE; X11: PSⅡ最大光合效率Fv/Fm; X12: PSⅡ潜在光化学效率Fv/Fo; X13: 非光化学淬灭系数qN; X14: 光化学淬灭系数qP; X15: 表观电子传递效率ETR; X16: PSⅡ光化学量子产量Yield. 下同The same below.
Fig.6 Correlation analysis among indicators of photosynthetic properties of timothy germplasm
指标 Index | 主成分Principal component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| X1 | 0.658 | 0.567 | -0.173 | 0.099 | 0.077 |
| X2 | 0.610 | 0.435 | -0.216 | -0.021 | -0.389 |
| X3 | 0.617 | 0.142 | -0.224 | -0.234 | 0.001 |
| X4 | 0.735 | 0.586 | -0.218 | 0.062 | -0.113 |
| X5 | 0.656 | -0.372 | 0.431 | 0.032 | 0.294 |
| X6 | 0.602 | -0.625 | 0.222 | 0.005 | -0.018 |
| X7 | 0.809 | -0.315 | 0.424 | 0.124 | -0.041 |
| X8 | 0.251 | -0.695 | -0.628 | -0.132 | -0.077 |
| X9 | -0.308 | 0.676 | 0.640 | 0.107 | 0.032 |
| X10 | 0.466 | 0.018 | 0.234 | 0.217 | -0.706 |
| X11 | 0.799 | 0.083 | 0.153 | -0.417 | 0.094 |
| X12 | 0.849 | 0.205 | -0.054 | -0.361 | 0.212 |
| X13 | -0.282 | 0.422 | -0.254 | -0.081 | 0.364 |
| X14 | 0.462 | 0.013 | 0.192 | -0.210 | 0.292 |
| X15 | 0.344 | 0.029 | -0.123 | 0.719 | 0.399 |
| X16 | 0.637 | -0.069 | -0.260 | 0.553 | 0.084 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 5.726 | 2.676 | 1.658 | 1.338 | 1.203 |
| 贡献率Rate of contribution (%) | 35.78 | 16.72 | 10.36 | 8.36 | 7.52 |
| 累计贡献率Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 35.78 | 52.51 | 62.87 | 71.24 | 78.76 |
表1 基于主成分分析的各指标特征值及贡献率
Table 1 Eigenvalue and contribution rate from principal component analysis of photosynthetic traits
指标 Index | 主成分Principal component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| X1 | 0.658 | 0.567 | -0.173 | 0.099 | 0.077 |
| X2 | 0.610 | 0.435 | -0.216 | -0.021 | -0.389 |
| X3 | 0.617 | 0.142 | -0.224 | -0.234 | 0.001 |
| X4 | 0.735 | 0.586 | -0.218 | 0.062 | -0.113 |
| X5 | 0.656 | -0.372 | 0.431 | 0.032 | 0.294 |
| X6 | 0.602 | -0.625 | 0.222 | 0.005 | -0.018 |
| X7 | 0.809 | -0.315 | 0.424 | 0.124 | -0.041 |
| X8 | 0.251 | -0.695 | -0.628 | -0.132 | -0.077 |
| X9 | -0.308 | 0.676 | 0.640 | 0.107 | 0.032 |
| X10 | 0.466 | 0.018 | 0.234 | 0.217 | -0.706 |
| X11 | 0.799 | 0.083 | 0.153 | -0.417 | 0.094 |
| X12 | 0.849 | 0.205 | -0.054 | -0.361 | 0.212 |
| X13 | -0.282 | 0.422 | -0.254 | -0.081 | 0.364 |
| X14 | 0.462 | 0.013 | 0.192 | -0.210 | 0.292 |
| X15 | 0.344 | 0.029 | -0.123 | 0.719 | 0.399 |
| X16 | 0.637 | -0.069 | -0.260 | 0.553 | 0.084 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 5.726 | 2.676 | 1.658 | 1.338 | 1.203 |
| 贡献率Rate of contribution (%) | 35.78 | 16.72 | 10.36 | 8.36 | 7.52 |
| 累计贡献率Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 35.78 | 52.51 | 62.87 | 71.24 | 78.76 |
材料 Material | 主成分得分Principal component score | 综合评价得分 Discriminant score | 排名 Ranking | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| 10067 | 4.366 | 0.020 | -0.366 | 0.693 | 0.190 | 0.325 | 10 |
| 7259 | 2.687 | -1.110 | -0.074 | 0.470 | 0.693 | 0.175 | 19 |
| 4190 | 5.109 | 0.139 | 0.587 | 0.377 | 0.440 | 0.402 | 5 |
| 9451 | 7.826 | 0.178 | -0.294 | -0.191 | 0.180 | 0.568 | 1 |
| 9038 | 4.372 | 0.807 | -0.405 | 0.402 | 0.553 | 0.352 | 7 |
| 7019 | 3.817 | 1.128 | -1.154 | -0.231 | 0.340 | 0.293 | 13 |
| 8050 | 3.708 | 1.203 | 0.573 | 0.637 | 0.522 | 0.341 | 8 |
| 13688 | 3.918 | 1.260 | -0.547 | 0.829 | 0.044 | 0.331 | 9 |
| 10101 | 4.580 | -0.663 | 0.502 | 0.024 | 0.054 | 0.322 | 11 |
| 7122 | 2.833 | 0.682 | -0.170 | -0.372 | 0.194 | 0.222 | 18 |
| 8334 | 5.055 | 1.308 | -0.276 | 0.536 | 0.838 | 0.428 | 4 |
| 8383 | 3.491 | 1.820 | 0.565 | 0.141 | -0.596 | 0.321 | 12 |
| 2547 | 3.049 | 0.913 | 0.826 | 0.153 | 0.385 | 0.279 | 14 |
| 8460 | 3.570 | 0.698 | -0.006 | -0.614 | 0.328 | 0.278 | 15 |
| 9657 | 6.880 | 0.247 | -0.063 | 0.543 | 0.161 | 0.519 | 3 |
| 7629 | 2.233 | -0.540 | -0.578 | 0.420 | -0.160 | 0.137 | 21 |
| 10227 | 4.046 | 1.728 | 0.629 | 0.442 | 0.476 | 0.381 | 6 |
| CX | 3.227 | 0.112 | 0.245 | -0.036 | 0.498 | 0.251 | 17 |
| 10676 | 7.535 | 0.230 | -0.447 | 0.260 | 0.289 | 0.555 | 2 |
| 8735 | 2.664 | 1.609 | 0.017 | 0.272 | 0.799 | 0.266 | 16 |
| MS | 2.295 | -0.481 | 0.093 | -0.146 | 0.423 | 0.156 | 20 |
表2 猫尾草种质主成分得分及综合评价
Table 2 Principal component scores and comprehensive evaluation of timothy germplasm
材料 Material | 主成分得分Principal component score | 综合评价得分 Discriminant score | 排名 Ranking | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| 10067 | 4.366 | 0.020 | -0.366 | 0.693 | 0.190 | 0.325 | 10 |
| 7259 | 2.687 | -1.110 | -0.074 | 0.470 | 0.693 | 0.175 | 19 |
| 4190 | 5.109 | 0.139 | 0.587 | 0.377 | 0.440 | 0.402 | 5 |
| 9451 | 7.826 | 0.178 | -0.294 | -0.191 | 0.180 | 0.568 | 1 |
| 9038 | 4.372 | 0.807 | -0.405 | 0.402 | 0.553 | 0.352 | 7 |
| 7019 | 3.817 | 1.128 | -1.154 | -0.231 | 0.340 | 0.293 | 13 |
| 8050 | 3.708 | 1.203 | 0.573 | 0.637 | 0.522 | 0.341 | 8 |
| 13688 | 3.918 | 1.260 | -0.547 | 0.829 | 0.044 | 0.331 | 9 |
| 10101 | 4.580 | -0.663 | 0.502 | 0.024 | 0.054 | 0.322 | 11 |
| 7122 | 2.833 | 0.682 | -0.170 | -0.372 | 0.194 | 0.222 | 18 |
| 8334 | 5.055 | 1.308 | -0.276 | 0.536 | 0.838 | 0.428 | 4 |
| 8383 | 3.491 | 1.820 | 0.565 | 0.141 | -0.596 | 0.321 | 12 |
| 2547 | 3.049 | 0.913 | 0.826 | 0.153 | 0.385 | 0.279 | 14 |
| 8460 | 3.570 | 0.698 | -0.006 | -0.614 | 0.328 | 0.278 | 15 |
| 9657 | 6.880 | 0.247 | -0.063 | 0.543 | 0.161 | 0.519 | 3 |
| 7629 | 2.233 | -0.540 | -0.578 | 0.420 | -0.160 | 0.137 | 21 |
| 10227 | 4.046 | 1.728 | 0.629 | 0.442 | 0.476 | 0.381 | 6 |
| CX | 3.227 | 0.112 | 0.245 | -0.036 | 0.498 | 0.251 | 17 |
| 10676 | 7.535 | 0.230 | -0.447 | 0.260 | 0.289 | 0.555 | 2 |
| 8735 | 2.664 | 1.609 | 0.017 | 0.272 | 0.799 | 0.266 | 16 |
| MS | 2.295 | -0.481 | 0.093 | -0.146 | 0.423 | 0.156 | 20 |
| [1] | Yuan H, Zhang X H, Han X Q, et al. Effects of salt and alkali stresses on biomass and physiological characteristics of four Phleum pratense at seedling stage. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(4): 1184-1193. |
| 袁惠, 张鲜花, 韩禧卿, 等. 盐、碱胁迫对4份梯牧草苗期生物量及生理特性的影响. 草地学报, 2024, 32(4): 1184-1193. | |
| [2] | Fu J S, Nan L L, Zhang Z L, et al. Evaluation of morphological characteristics and SSR genetic diversity of 21 accessions of timothy seeds. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2024, 46(9): 23-33. |
| 傅俊士, 南丽丽, 张泽龙, 等. 21份猫尾草种子形态特征及SSR遗传多样性评价. 中国草地学报, 2024, 46(9): 23-33. | |
| [3] | Shi S L, Cao W X, Chen Y, et al. Analysis of current situation and prospect of characteristic forage industry of timothy in China. Grassland and Turf, 2020, 40(5): 1-7. |
| 师尚礼, 曹文侠, 陈耀, 等. 猫尾草产业发展现状与前景分析. 草原与草坪, 2020, 40(5): 1-7. | |
| [4] | Chu H L, Ma W X, Tian X H, et al. Study on drought resistance of a new strain of timothy. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(11): 52-59. |
| 褚红丽, 马文馨, 田新会, 等. 猫尾草新品系的抗旱性研究. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(11): 52-59. | |
| [5] | Zhang W X, Li R Z, Tian X H, et al. Effects of sowing method and nitrogen fertilizing rate on production performance of timothy genotypes in alpine and humid regions of Gansu. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 910-921. |
| 张文轩, 李瑞珍, 田新会, 等. 甘肃高寒阴湿区播种方式和氮肥施用量对猫尾草种质生产性能的影响. 西北农业学报, 2024, 33(5): 910-921. | |
| [6] | Yang P N, An X Z, Ma W X, et al. The study on the production performance and nutritional value of a new line of Phleum pretense in central Gansu Province. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(9): 44-51. |
| 杨鹏年, 安学忠, 马文馨, 等. 猫尾草新品系在甘肃省中部地区的生产性能和营养价值研究. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(9): 44-51. | |
| [7] | Zhang W X, Li R Z, Tian X H, et al. Effects of sowing method on the production performance and nutrient composition of timothy grass genotypes in alpine and shaded areas of Gansu. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(7): 15-22. |
| 张文轩, 李瑞珍, 田新会, 等. 甘肃高寒阴湿区播种方式对猫尾草种质生产性能和营养成分的影响. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(7): 15-22. | |
| [8] | Xue W, Lindner S, Nay-Htoon B, et al. Nutritional and developmental influences on components of rice crop light use efficiency. Agricultural & Forest Meteorology, 2016, 223: 1-16. |
| [9] | Zhu X G, Long P S, Ort R D. Improving photosynthetic efficiency for greater yield. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010, 61(1): 235-261. |
| [10] | Ort D R, Merchant S S, Alric J, et al. Redesigning photosynthesis to sustainably meet global food and bioenergy demand. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(28): 8529-8536. |
| [11] | Zhang Y W, Zhao X G, Guan Z B, et al. Difficulties and solutions to rape high photosynthetic efficiency breeding. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2018, 27(1): 1-9. |
| 张耀文, 赵小光, 关周博, 等. 油菜高光效育种的难点及解决策略. 西北农业学报, 2018, 27(1): 1-9. | |
| [12] | Wang J W, Wang J L, Liu J L, et al. Study on photosynthetic physiological characteristics of 7 new varieties (strains) of Leymus chinensis. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2021(8): 110-113, 118. |
| 王嘉雯, 王建丽, 刘杰淋, 等. 7个羊草新品种(品系)光合特性研究. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2021(8): 110-113, 118. | |
| [13] | Hu S S. Compared study on photosynthesis and production performance of 15 alfalfa (Medicago sativa) cultivars in Nanjing. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2010: 21-22. |
| 胡莎莎. 15个紫花苜蓿(Medicago sativa)品种在南京地区光合及生产性能比较. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2010: 21-22. | |
| [14] | Wu F. The study on feeding performance and photosynthetic characteristics of 61 Lotus corniculatus germplasm materials from Russia. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2018: 45-46. |
| 吴芳. 61份俄罗斯百脉根种质材料饲用性能及光合特性研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2018: 45-46. | |
| [15] | Du W H, Tian X H, Cao Z Z. Hay yield and adaptability of different Phleum pratense varieties. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2004, 13(2): 56-60. |
| 杜文华, 田新会, 曹致中. 猫尾草不同品种的草产量和适应性评价. 草业学报, 2004, 13(2): 56-60. | |
| [16] | Zhang R Z, Shao L H,Ma T, et al. Study on the regional adaptability of new variety of “Chuanxi” timothy grass. Journal of Southwest Minzu University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 46(3): 221-228. |
| 张瑞珍, 邵麟惠, 马涛, 等. “川西”猫尾草新品种区域适应性研究. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 46(3): 221-228. | |
| [17] | Zou Q. Experimental guidance of plant physiology. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House, 2003: 110-174. |
| 邹琦. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2003: 110-174. | |
| [18] | Sun Z R, Zhu N N, Cheng L L, et al. Comparison of photosynthesis and fluorescent parameters between Dendrobium officinale and Dendrobium loddigesii. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 2015, 8(8): 13163-13170. |
| [19] | Yang Z F, Tian J C, Feng K P, et al. Application of a hyperspectral imaging system to quantify leaf-scale chlorophyll, nitrogen and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in grapevine. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021(1): 723-737. |
| [20] | Hong Z Q, Zhang Z Z, Zhou T, et al. Optimal potassium dosage for high fluorescence parameters and target yield of spring maize under drip fertigation. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2024, 30(8): 1461-1476. |
| 洪自强, 张正珍, 周甜, 等. 水肥一体化下钾肥用量对春玉米光合荧光参数的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2024, 30(8): 1461-1476. | |
| [21] | Liao H Q, Xie W G. Advanced in the mechanism of forage grass responding to low temperature stress. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(12): 99-111. |
| 廖浩钦, 谢文刚. 牧草应对低温胁迫机制研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(12): 99-111. | |
| [22] | Jiang J H, Gao P F, Ding N N, et al. Physio-ecological response strategies of the endangered medicinal plant Sinopodophyllum hexandrum (Royle)Ying to altitudes. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(20): 9342-9353. |
| 江金花, 高鹏斐, 丁娜娜, 等. 濒危药用植物桃儿七对海拔的生理生态响应策略. 生态学报, 2024, 44(20): 9342-9353. | |
| [23] | Zhao F Y, Cao H X, Ma L N, et al. Effects of supplementary irrigation on growth, yield, and water use efficiency of millet in the Loess Plateau. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2024, 42(5): 44-53, 84. |
| 赵方洋, 曹红霞, 马丽娜, 等. 补充灌溉对黄土高原谷子生长、产量及水分利用效率的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2024, 42(5): 44-53, 84. | |
| [24] | Yang X T, Cai J W, Ren Y J, et al. Physiological and metabolic stage-specific characteristics of coloration in the autumn leaves of Acer mono Maxim. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2024, 52(11): 47-55. |
| 杨晓童, 蔡静雯, 任艳君, 等. 五角枫秋季叶片呈色生理及代谢阶段性特征. 东北林业大学学报, 2024, 52(11): 47-55. | |
| [25] | Sukenik A, Beardall J, Kromkamp J C, et al. Photosynthetic performance of outdoor Nannochloropsis mass cultures under a wide range of environmental conditions. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 2009, 56(2): 297-308. |
| [26] | Ren M F, Mao G L, Liu S Z, et al. Research progress on the effects of light quality on plant growth and development, photosynthesis, and carbon and nitrogen metabolism. Plant Physiology Journal, 2023, 59(7): 1211-1228. |
| 任毛飞, 毛桂玲, 刘善振, 等. 光质对植物生长发育、光合作用和碳氮代谢的影响研究进展. 植物生理学报, 2023, 59(7): 1211-1228. | |
| [27] | Alexei S, Konstantin N. Carotenogenic response in photosynthetic organisms: a colorful story. Photosynthesis Research, 2017, 133(1/3): 31-47. |
| [28] | Lv C G, Li X, Zong S Y, et al. Analysis of the eurytopicity of super hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(3): 191-205. |
| 吕川根, 李霞, 宗寿余, 等. 超级杂交稻两优培九的广适性分析. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(3): 191-205. | |
| [29] | Zhang H, Hu H Y, Li H X, et al. Physiological response and transcriptome analysis of the desert steppe dominant plant Lespedeza potaninii to drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 188-205. |
| 张浩, 胡海英, 李惠霞, 等. 荒漠草原优势植物牛枝子对干旱胁迫的生理响应与转录组分析. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 188-205. | |
| [30] | Yu H R, Guo Y, Zhu A M, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer level on non-structural carbon and nitrogen metabolite levels in oats grown in sandy desert soil. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(5): 61-72. |
| 于华荣, 郭园, 朱爱民, 等. 氮素水平对沙地燕麦叶片非结构性碳氮代谢的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 61-72. | |
| [31] | Meng S Y, Wang Q, Wei Y, et al. Effects of salt stress on the growth and photosynthetic production of Euonymus hamiltonianus. Journal of Shandong University (Natural Science), 2019, 54(7): 26-34. |
| 孟诗原, 王倩, 韦业, 等. 盐胁迫对西南卫矛生长及光合特性的影响. 山东大学学报(理学版), 2019, 54(7): 26-34. | |
| [32] | Zhao P T, Gao S X, Zhao X G, et al. Comparison of photosynthetic characteristics of different wheat evolution materials at late growth stage and their response to environmental factors. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2019, 39(3): 299-307. |
| 赵鹏涛, 苟升学, 赵小光, 等. 不同小麦进化材料生育后期的光合特性及其对环境因子响应的比较. 麦类作物学报, 2019, 39(3): 299-307. | |
| [33] | Peng Y Y, Yan H H, Guo L C, et al. Evaluation and selection on drought-resistance of germplasm resources of Avena species with different types of ploidy. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(9): 2478-2491. |
| 彭远英, 颜红海, 郭来春, 等. 燕麦属不同倍性种质资源抗旱性状评价及筛选. 生态学报, 2011, 31(9): 2478-2491. | |
| [34] | Wang W, Zhao H, Huang X, et al. Relationship between leaf hydraulic and economic traits and biomass of poplar clones. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2023, 59(10): 89-98. |
| 王薇, 赵涵, 黄欣, 等. 白杨无性系叶片水力及经济性状与生物量的关系. 林业科学, 2023, 59(10): 89-98. | |
| [35] | Kalaji H M, Jajoo A, Oukarroum A, et al. Chlorophyll a fluorescence as a tool to monitor physiological status of plants under abiotic stress conditions. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2016, 38(4): 1-11. |
| [36] | Tao Y, Xu Y N, Ye C, et al. Research progress on correlation of rice leaf senescence and discoloration with nitrogen reuse and volatilization. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 553-562. |
| 陶怡, 徐亚楠, 叶昌, 等. 水稻叶片衰老转色与氮循环利用及挥发关系的研究进展. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 553-562. | |
| [37] | Wei X D, Zhang Y D, Song X M, et al. Photosynthetic physiological characteristics of high yield super rice variety Nanjing 5718. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(11): 2879-2890. |
| 魏晓东, 张亚东, 宋雪梅, 等. 超级稻品种南粳5718高产的光合生理特性研究. 作物学报, 2022, 48(11): 2879-2890. | |
| [38] | Yang W Q, Lin R C, Duanmu D Q, et al. Multiple of important progress on photosynthesis in the last 10 years. Plant Physiology Journal, 2024, 60(2): 211-247. |
| 杨文强, 林荣呈, 端木德强, 等. 近10年光合作用领域若干重要研究进展. 植物生理学报, 2024, 60(2): 211-247. | |
| [39] | Wei X W, Pan X Y, Wang P F, et al. Responses of chlorophyll fluorescence of alfalfa with various phosphorus utilization efficiencies to phosphorus deficiency. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(4): 690-703. |
| 卫先伟, 潘新雅, 王鹏飞, 等.不同磷效率紫花苜蓿叶绿素荧光参数对低磷胁迫的响应. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(4): 690-703. | |
| [40] | Li Y Y, Zhang Z W, Huang W, et al. Leaf structure and chlorophyll fluorescence of Lantana camara. Journal of Biology, 2022, 39(2): 29-33. |
| 李焰焰, 张紫薇, 黄薇, 等. 马缨丹光合色素及叶绿素荧光参数分析. 生物学杂志, 2022, 39(2): 29-33. | |
| [41] | Hong K, Li M, Xu S S, et al. Effect of elevated CO2 on growth, photosynthetic characteristics and nutrient concentration of Cunninghamia lanceolata seedlings. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2020, 40(6): 1011-1021. |
| 洪凯, 李茂, 许珊珊, 等. CO2浓度升高对杉木幼苗生长及其光合特性和养分含量的影响. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(6): 1011-1021. | |
| [42] | Cai J H, Xue L. Advances on photosynthesis characteristics of alpine plants. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(1): 245-254. |
| 蔡金桓, 薛立. 高山植物的光合生理特性研究进展. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(1): 245-254. | |
| [43] | He Y T, Hu Y, Duan H R, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of four Elymus varieties at seedling stage. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(1): 77-87. |
| 何永涛, 胡宇, 段慧荣, 等. 披碱草属4个牧草品种苗期抗旱性综合评价. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(1): 77-87. |
| [1] | 胡泽龙, 梁国玲, 刘文辉, 王文虎. 两种粒色燕麦籽粒色素与光合特性动态变化[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(12): 145-156. |
| [2] | 侯文璐, 康文娟, 陆保福, 韩宜霖, 关键, 王晶晶. 不同共生效应根瘤菌株对紫花苜蓿光合特性和呼吸代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(11): 66-80. |
| [3] | 张盈盈, 胡丹丹, 马春晖, 张前兵. 苜蓿叶片结构和光合特性对菌磷添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 133-144. |
| [4] | 申琴, 郑荣春, 南志标, 段廷玉. 猫尾草种带真菌多样性及其对种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 108-122. |
| [5] | 韩金秀, 陈斌, 刘晏廷, 孟儒, 金利妍, 何淼. 神农香菊CibHLH1的鉴定及对光合特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 89-101. |
| [6] | 柳文蔚, 刘鑫, 雷映霞, 周青平, 刘志峰, 王沛. 老芒麦种质资源抗寒性综合评价及冷胁迫下的生理反应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 152-163. |
| [7] | 张适阳, 刘凤民, 崔均涛, 何磊, 冯月燕, 张伟丽. 三种外源物质对低温胁迫下柱花草生理与荧光特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 85-99. |
| [8] | 叶婷, 吴晓娟, 芦奕晓, 刘生娟, 姜卓慧, 杨惠敏. 混播比例对两种苜蓿混播草地产量和种群密度稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 127-137. |
| [9] | 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 安晓霞, 马春晖, 张前兵. 施磷和接种解磷菌对紫花苜蓿光合特性及生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 189-199. |
| [10] | 王静, 孔令莹, 徐建风, 康静, 沈振峰, 刘婷. 不同粒度猫尾草对羔羊体外发酵特性和微生物数量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 224-233. |
| [11] | 周晓瑾, 黄海霞, 张君霞, 马步东, 陆刚, 齐建伟, 张婷, 朱珠. 盐胁迫对裸果木幼苗光合特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 75-83. |
| [12] | 钱文武, 郭鹏, 朱慧森, 张士敏, 李德颖. 草地早熟禾叶片表皮特征、解剖结构及光合特性对不同施氮量的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 131-143. |
| [13] | 周泽东, 马晖玲, 韩煦, 李元恒, 李西良, 李坤娜. 温性典型草原羊草光合特性对模拟放牧因素分解的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 81-89. |
| [14] | 董梦宇, 王金鑫, 吴萌, 周子瑶, 程顺, 李彦慧. 两种香花芥属植物叶片结构及光合特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 172-184. |
| [15] | 金祎婷, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 梁国玲, 贾志锋. 全生育期干旱胁迫对‘青燕1号’燕麦叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 112-126. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||