

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 95-106.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025092
彭辉1,2( ), 穆麟1,2, 沈佳欣1,2, 王靖轩1,2, 黄菁2,3, 黄雨珣2,3, 张志飞1,2(
), 穆麟1,2, 沈佳欣1,2, 王靖轩1,2, 黄菁2,3, 黄雨珣2,3, 张志飞1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-20
修回日期:2025-05-21
出版日期:2026-02-20
发布日期:2025-12-24
通讯作者:
张志飞
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: zhangzf@hunau.edu.cn基金资助:
Hui PENG1,2( ), Lin MU1,2, Jia-xin SHEN1,2, Jing-xuan WANG1,2, Jing HUANG2,3, Yu-xun HUANG2,3, Zhi-fei ZHANG1,2(
), Lin MU1,2, Jia-xin SHEN1,2, Jing-xuan WANG1,2, Jing HUANG2,3, Yu-xun HUANG2,3, Zhi-fei ZHANG1,2( )
)
Received:2025-03-20
Revised:2025-05-21
Online:2026-02-20
Published:2025-12-24
Contact:
Zhi-fei ZHANG
摘要:
扁穗牛鞭草是禾本科牛鞭草属多年生草本植物,生长速度快,适应性和抗逆性强,是南方地区重要的饲草资源。本研究以扁穗牛鞭草种茎为试验材料,设置甲基磺酸乙酯(EMS)不同浓度(0%、0.2%、0.4%、0.6%、0.8%、1.0%)和处理时间(2、4、6 h)的双因素完全随机试验,明确了扁穗牛鞭草种茎EMS诱变最佳处理浓度和处理时间分别为0.6%和6 h。在扁穗牛鞭草EMS诱变群体中通过表型评价筛选获得了1株优良突变体(编号5-5-4)。对突变体5-5-4进行低磷胁迫试验发现,5-5-4较野生型生根数和根尖数更多,最长根长和总根长更大,根毛结构更发达。低磷胁迫导致扁穗牛鞭草磷吸收量大幅下降,但磷利用效率大幅提高,且5-5-4根部和地上部磷利用效率均高于野生型。低磷胁迫下,5-5-4根系中酸性磷酸酶、超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化物酶活性更高,富集了解磷菌芽孢杆菌、沙壤土杆菌、红育菌。本研究基于EMS化学诱变技术,解析了扁穗牛鞭草突变体耐受低磷胁迫的生理学机理,创制出耐低磷的新型种质资源,为南方低磷地区草牧业品种选育提供了理论依据与育种材料储备。
彭辉, 穆麟, 沈佳欣, 王靖轩, 黄菁, 黄雨珣, 张志飞. 扁穗牛鞭草种茎EMS化学诱变突变体创制[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(2): 95-106.
Hui PENG, Lin MU, Jia-xin SHEN, Jing-xuan WANG, Jing HUANG, Yu-xun HUANG, Zhi-fei ZHANG. Creation of ethyl methanesulfonate chemical mutants of Hemarthria compressa seed stem[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(2): 95-106.
EMS浓度 EMS concentration (%) | 7 d出芽率7 days germination rate | 14 d出芽率14 days germination rate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 h | 4 h | 6 h | 2 h | 4 h | 6 h | |
| 0 | 8.33±2.36Aa | 10.00±4.08Aa | 30.00±18.71Aa | 95.00±4.08ABa | 88.33±2.36Ba | 96.67±2.36Aa |
| 0.2 | 8.33±8.50Aa | 11.67±2.36Aa | 15.00±12.25Aab | 81.67±12.47Aab | 86.67±2.36Aa | 86.67±8.50Aa |
| 0.4 | 8.33±6.24Aa | 6.67±2.36Aab | 5.00±4.08Ab | 76.67±8.50Aab | 78.33±14.34Aa | 33.33±6.24Bb |
| 0.6 | 0Aa | 5.00±4.08Aab | 6.67±4.71Ab | 83.33±9.43Aab | 78.33±6.24Aa | 41.67±6.24Bb |
| 0.8 | 0Aa | 1.67±2.36Ab | 0Ab | 58.33±6.24Abc | 50.00±7.07Ab | 1.67±2.36Bc |
| 1.0 | 0Aa | 0Ab | 0Ab | 41.67±18.41Ac | 11.67±2.36Bc | 3.33±2.36Bc |
表1 不同EMS处理下扁穗牛鞭草7 和14 d出芽率
Table 1 The germination rate of H. compressa on the 7 and 14 days under different EMS treatment (%)
EMS浓度 EMS concentration (%) | 7 d出芽率7 days germination rate | 14 d出芽率14 days germination rate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 h | 4 h | 6 h | 2 h | 4 h | 6 h | |
| 0 | 8.33±2.36Aa | 10.00±4.08Aa | 30.00±18.71Aa | 95.00±4.08ABa | 88.33±2.36Ba | 96.67±2.36Aa |
| 0.2 | 8.33±8.50Aa | 11.67±2.36Aa | 15.00±12.25Aab | 81.67±12.47Aab | 86.67±2.36Aa | 86.67±8.50Aa |
| 0.4 | 8.33±6.24Aa | 6.67±2.36Aab | 5.00±4.08Ab | 76.67±8.50Aab | 78.33±14.34Aa | 33.33±6.24Bb |
| 0.6 | 0Aa | 5.00±4.08Aab | 6.67±4.71Ab | 83.33±9.43Aab | 78.33±6.24Aa | 41.67±6.24Bb |
| 0.8 | 0Aa | 1.67±2.36Ab | 0Ab | 58.33±6.24Abc | 50.00±7.07Ab | 1.67±2.36Bc |
| 1.0 | 0Aa | 0Ab | 0Ab | 41.67±18.41Ac | 11.67±2.36Bc | 3.33±2.36Bc |
编号 Number | 分蘖数 Tiller number (个·株-1 No.·plant-1) | 最长分蘖长度 Longest tiller length (cm) | 叶长 Leaf length (cm) | 叶宽 Leaf width (mm) | 生物量 Biomass (kg·plant-1) | D值 D value | 排名 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-5-4 | 106 | 312.73 | 13.12 | 6.1 | 2.45 | 0.95 | 1 |
| 3-8-10 | 91 | 243.53 | 8.79 | 3.4 | 2.30 | 0.64 | 2 |
| 7-10-10 | 86 | 194.57 | 13.10 | 5.1 | 3.07 | 0.49 | 3 |
| 4-7-1 | 50 | 237.63 | 8.20 | 3.9 | 1.20 | 0.44 | 4 |
| 4-1-8 | 62 | 210.44 | 14.15 | 5.3 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 5 |
| 3-3-1 | 45 | 222.36 | 12.23 | 4.3 | 2.99 | 0.40 | 6 |
| 5-4-3 | 61 | 206.72 | 9.00 | 4.0 | 1.35 | 0.40 | 7 |
| CK | 40 | 228.97 | 12.51 | 5.1 | 1.07 | 0.39 | 8 |
| 5-4-2 | 36 | 229.88 | 13.35 | 4.6 | 2.51 | 0.39 | 9 |
| 5-1-1 | 85 | 173.45 | 6.12 | 4.2 | 1.71 | 0.38 | 10 |
| 9-8-3 | 37 | 230.46 | 7.27 | 5.0 | 1.00 | 0.36 | 11 |
| 5-3-1 | 61 | 182.45 | 12.81 | 5.5 | 1.67 | 0.34 | 12 |
| 7-8-10 | 47 | 203.21 | 8.14 | 4.2 | 2.76 | 0.33 | 13 |
| 9-7-6 | 25 | 226.04 | 8.93 | 5.1 | 0.43 | 0.30 | 14 |
| 3-6-6 | 32 | 192.33 | 9.56 | 3.6 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 15 |
| 6-9-10 | 52 | 157.34 | 11.21 | 4.8 | 0.42 | 0.21 | 16 |
| 6-7-8 | 30 | 180.64 | 9.50 | 3.9 | 0.41 | 0.18 | 17 |
| 5-10-1 | 28 | 178.71 | 7.75 | 4.0 | 0.34 | 0.16 | 18 |
| 6-8-9 | 31 | 136.43 | 10.88 | 5.0 | 0.53 | 0.05 | 19 |
| 最大值Maximum value | 106 | 312.73 | 14.15 | 6.1 | 3.07 | - | - |
| 最小值Minimum value | 25 | 136.43 | 6.12 | 3.4 | 0.34 | - | - |
| 变异系数Coefficient of variation | 0.44 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.67 | - | - |
表2 扁穗牛鞭草长势评价
Table 2 Growth evaluation of H. compressa
编号 Number | 分蘖数 Tiller number (个·株-1 No.·plant-1) | 最长分蘖长度 Longest tiller length (cm) | 叶长 Leaf length (cm) | 叶宽 Leaf width (mm) | 生物量 Biomass (kg·plant-1) | D值 D value | 排名 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-5-4 | 106 | 312.73 | 13.12 | 6.1 | 2.45 | 0.95 | 1 |
| 3-8-10 | 91 | 243.53 | 8.79 | 3.4 | 2.30 | 0.64 | 2 |
| 7-10-10 | 86 | 194.57 | 13.10 | 5.1 | 3.07 | 0.49 | 3 |
| 4-7-1 | 50 | 237.63 | 8.20 | 3.9 | 1.20 | 0.44 | 4 |
| 4-1-8 | 62 | 210.44 | 14.15 | 5.3 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 5 |
| 3-3-1 | 45 | 222.36 | 12.23 | 4.3 | 2.99 | 0.40 | 6 |
| 5-4-3 | 61 | 206.72 | 9.00 | 4.0 | 1.35 | 0.40 | 7 |
| CK | 40 | 228.97 | 12.51 | 5.1 | 1.07 | 0.39 | 8 |
| 5-4-2 | 36 | 229.88 | 13.35 | 4.6 | 2.51 | 0.39 | 9 |
| 5-1-1 | 85 | 173.45 | 6.12 | 4.2 | 1.71 | 0.38 | 10 |
| 9-8-3 | 37 | 230.46 | 7.27 | 5.0 | 1.00 | 0.36 | 11 |
| 5-3-1 | 61 | 182.45 | 12.81 | 5.5 | 1.67 | 0.34 | 12 |
| 7-8-10 | 47 | 203.21 | 8.14 | 4.2 | 2.76 | 0.33 | 13 |
| 9-7-6 | 25 | 226.04 | 8.93 | 5.1 | 0.43 | 0.30 | 14 |
| 3-6-6 | 32 | 192.33 | 9.56 | 3.6 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 15 |
| 6-9-10 | 52 | 157.34 | 11.21 | 4.8 | 0.42 | 0.21 | 16 |
| 6-7-8 | 30 | 180.64 | 9.50 | 3.9 | 0.41 | 0.18 | 17 |
| 5-10-1 | 28 | 178.71 | 7.75 | 4.0 | 0.34 | 0.16 | 18 |
| 6-8-9 | 31 | 136.43 | 10.88 | 5.0 | 0.53 | 0.05 | 19 |
| 最大值Maximum value | 106 | 312.73 | 14.15 | 6.1 | 3.07 | - | - |
| 最小值Minimum value | 25 | 136.43 | 6.12 | 3.4 | 0.34 | - | - |
| 变异系数Coefficient of variation | 0.44 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.67 | - | - |
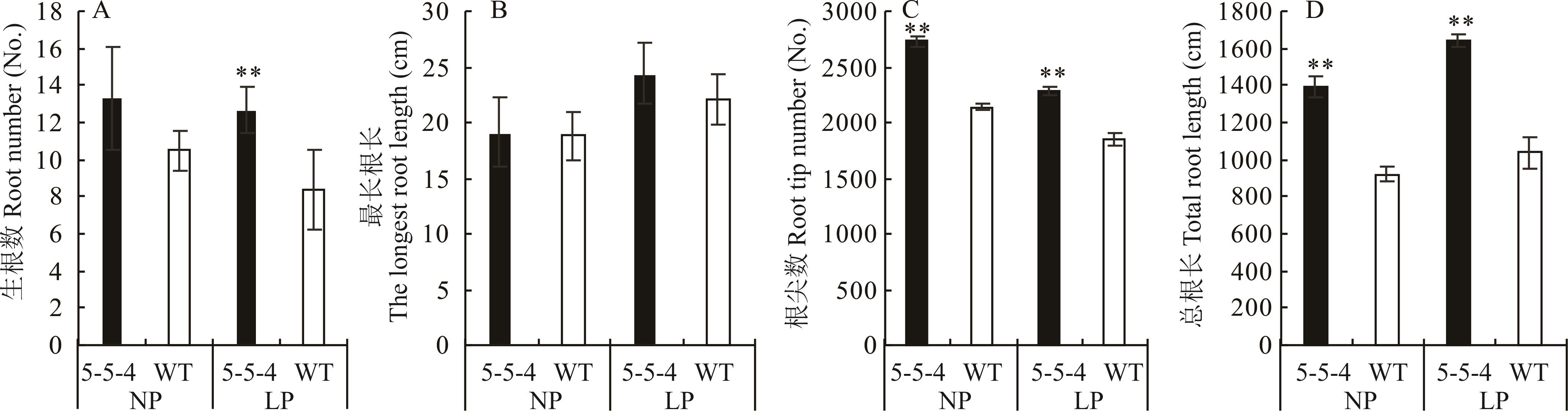
图2 突变体5-5-4与野生型在不同处理下30 d根系参数比较WT: 野生型。*表示同一处理下两份材料间差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01),下同。WT: Wild type. * indicate significant difference (P<0.05) between two materials under the same treatment, ** indicate extremely significant difference (P<0.01). The same below.
Fig.2 Comparison of the total root trait parameters of mutant 5-5-4 and wild type on 30 days under different treatments
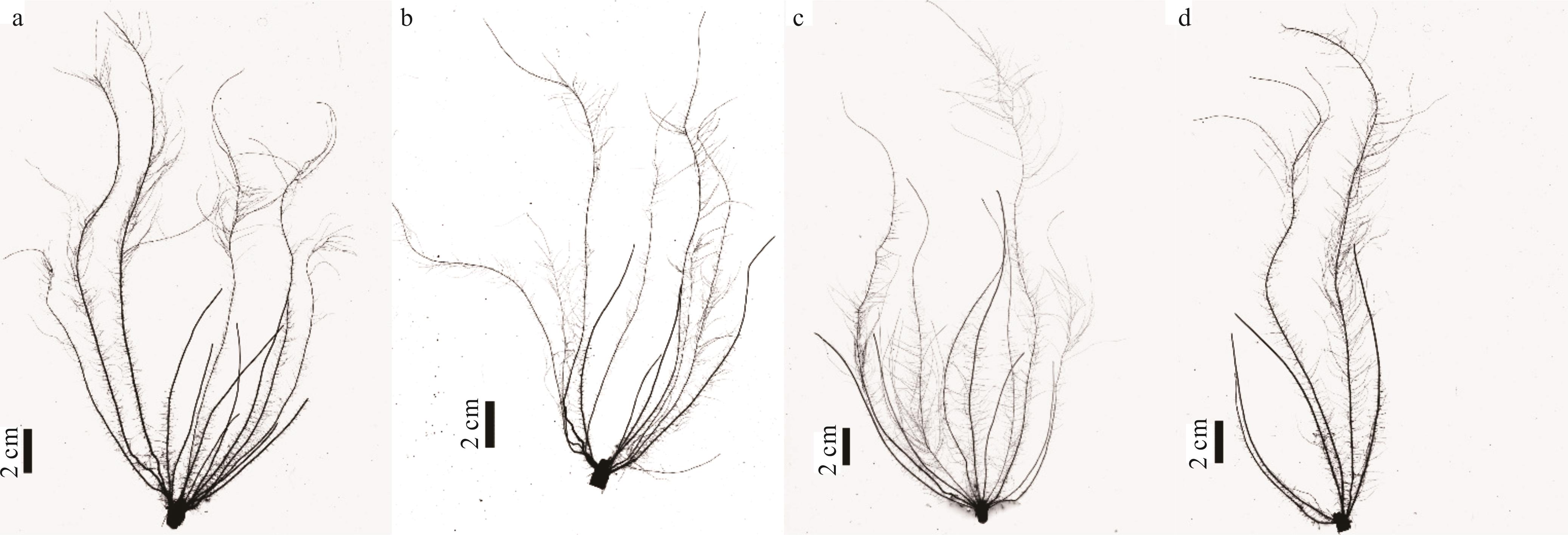
图3 突变体5-5-4与野生型在不同处理下30 d的根系扫描结果图a、c为突变体5-5-4,图b、d为野生型,图a、b为正常供磷处理,图c、d为低磷胁迫处理。Figs a and c are mutant 5-5-4, Figs b and d are wild type, Figs a and b are normal phosphorus supply treatment, Figs c and d are low phosphorus stress treatment.
Fig.3 The root scanning of mutant 5-5-4 and wild type on 30 days under different treatments
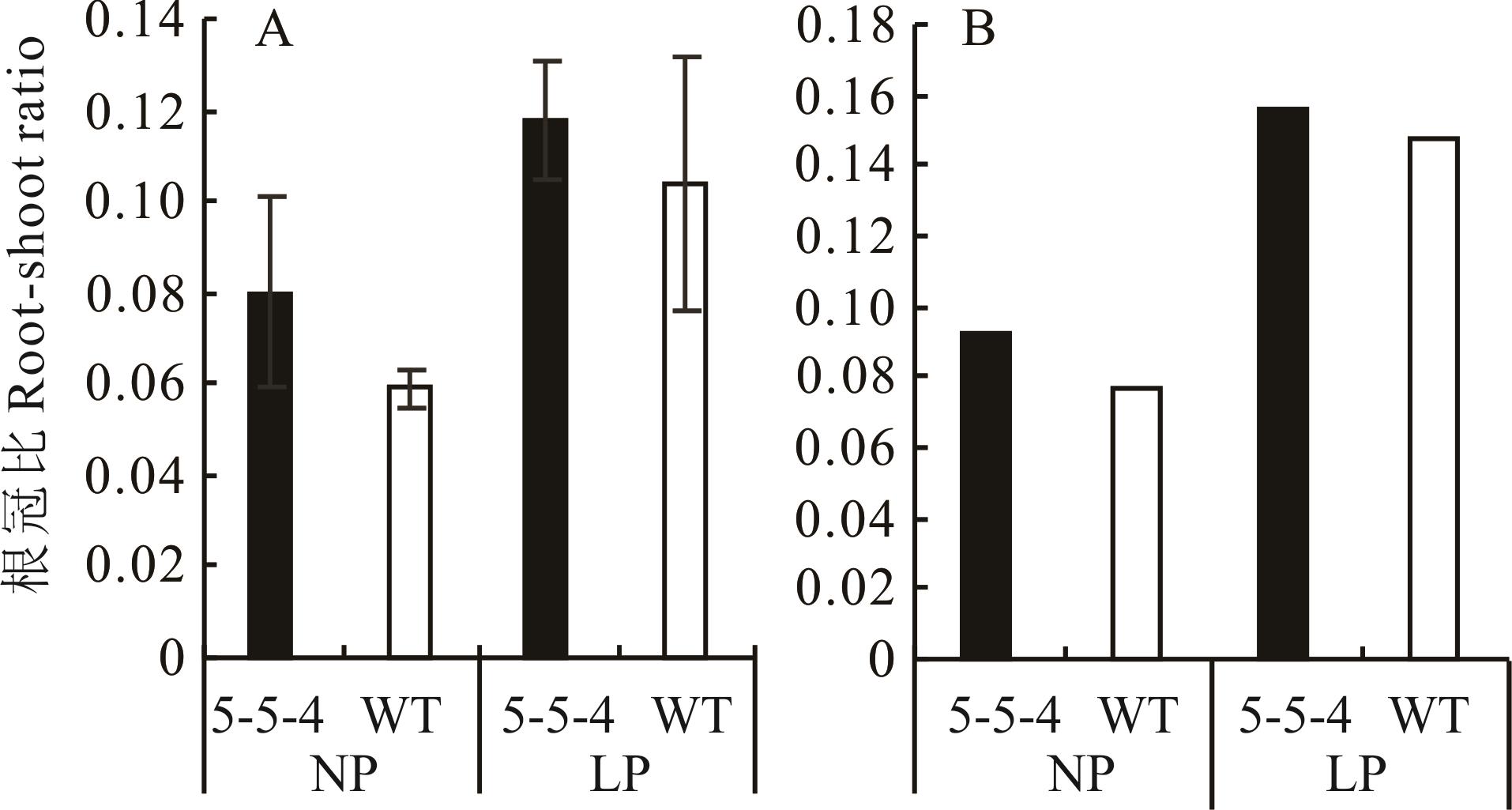
图4 突变体5-5-4与野生型在不同处理下30 d(A)和60 d(B)根冠比60 d时因根系难以分开,根冠比由所有植株根的总干重比茎的总干重计算得出,因此未进行显著性分析,图中未标注误差线。At 60 days, because the roots were difficult to separate, the root-shoot ratio was calculated by dividing the total dry weight of roots of all plants by the total dry weight of stems, so no significant analysis was performed, and the error line was not marked in the figure.
Fig.4 The root-shoot ratios of mutants 5-5-4 and wild-type on 30 days (A) and 60 days (B) under different treatments
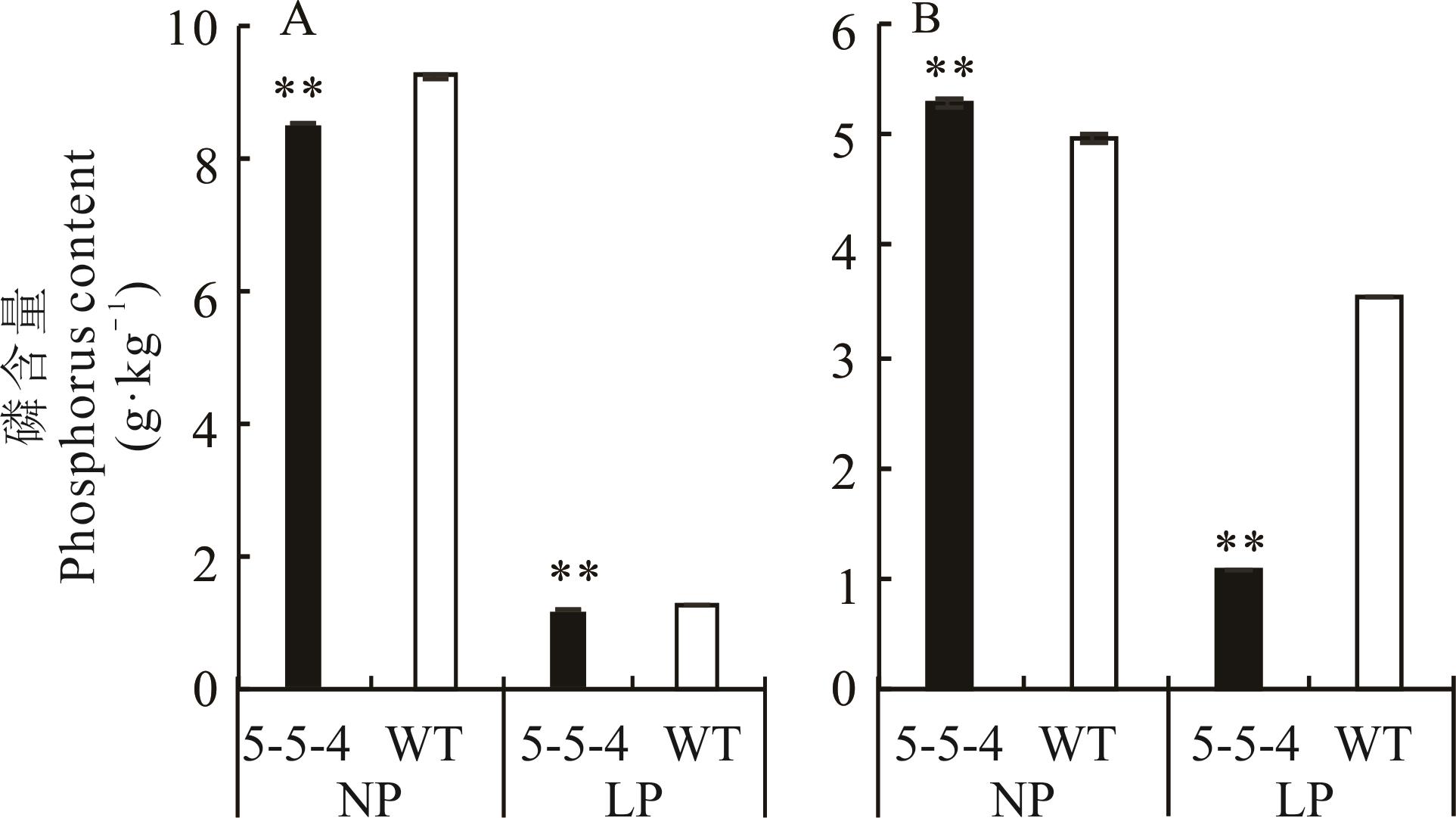
图5 5-5-4与野生型(60 d)在不同处理下根部(A)和地上部(B)全磷含量比较
Fig.5 Comparison of total phosphorus content in roots (A) and shoots (B) between 5-5-4 and wild type (60 d) under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 编号 Number | 根部 Root part | 地上部 Overground part | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
干物质 Dry matter (g) | 磷吸收量 Phosphorus uptake (mg) | 磷利用效率 Phosphorus utilization efficiency (g·mg-1) | 干物质 Dry matter (g) | 磷吸收量 Phosphorus uptake (mg) | 磷利用效率 Phosphorus utilization efficiency (g·mg-1) | ||
| NP | 5-5-4 | 0.525 | 4.478 | 0.117 | 5.665 | 30.025 | 0.189 |
| WT | 0.484 | 4.482 | 0.108 | 6.275 | 31.187 | 0.201 | |
| LP | 5-5-4 | 0.786 | 0.927 | 0.847 | 5.017 | 5.418 | 0.926 |
| WT | 0.541 | 0.687 | 0.787 | 3.675 | 13.009 | 0.282 | |
表3 低磷胁迫对扁穗牛鞭草磷吸收量、利用效率的影响
Table 3 Effects of low phosphorus stress on phosphorus uptake and utilization efficiency of H. compressa
处理 Treatment | 编号 Number | 根部 Root part | 地上部 Overground part | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
干物质 Dry matter (g) | 磷吸收量 Phosphorus uptake (mg) | 磷利用效率 Phosphorus utilization efficiency (g·mg-1) | 干物质 Dry matter (g) | 磷吸收量 Phosphorus uptake (mg) | 磷利用效率 Phosphorus utilization efficiency (g·mg-1) | ||
| NP | 5-5-4 | 0.525 | 4.478 | 0.117 | 5.665 | 30.025 | 0.189 |
| WT | 0.484 | 4.482 | 0.108 | 6.275 | 31.187 | 0.201 | |
| LP | 5-5-4 | 0.786 | 0.927 | 0.847 | 5.017 | 5.418 | 0.926 |
| WT | 0.541 | 0.687 | 0.787 | 3.675 | 13.009 | 0.282 | |
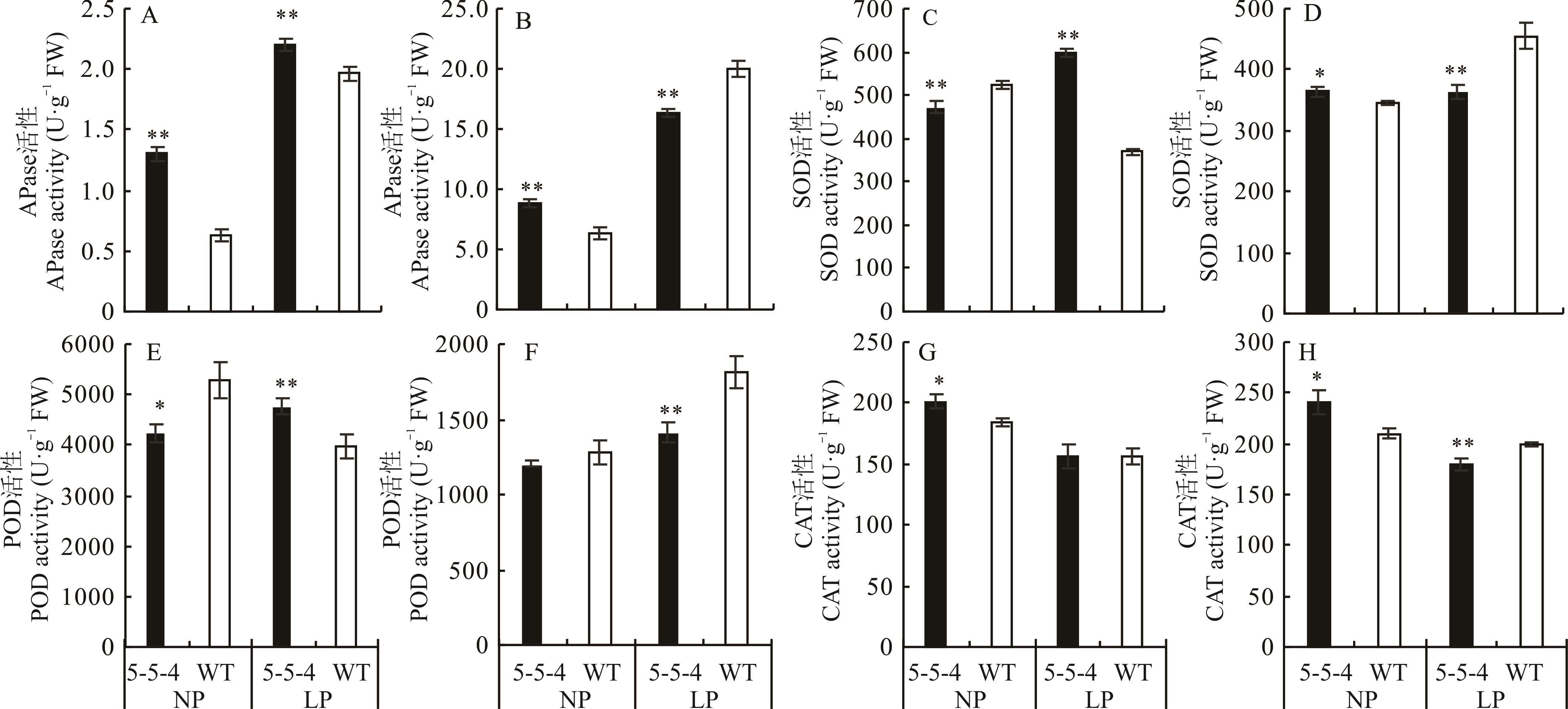
图6 5-5-4与野生型在不同处理下60 d的APase、SOD、POD、CAT活性A、C、E、G是根中的APase、SOD、POD、CAT活性,B、D、F、H是叶片中的APase、SOD、POD、CAT活性。A, C, E, and G are the activities of APase, SOD, POD, and CAT in the root, B, D, F, H are the activities of APase, SOD, POD, and CAT in the blade.
Fig.6 APase, SOD, POD, and CAT activities of mutant 5-5-4 and wild-type on 60 days under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 编号 Number | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | 覆盖度 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP | 5-5-4 | 441.60±40.76 | 457.35±55.87 | 0.79±0.02** | 3.78±0.17** | 0.99 |
| WT | 457.62±31.49 | 463.31±32.81 | 0.96±0.01 | 5.76±0.21 | 0.99 | |
| LP | 5-5-4 | 433.58±19.39 | 434.94±25.25 | 0.91±0.03* | 5.12±0.26** | 0.99 |
| WT | 416.30±4.10 | 424.64±17.66 | 0.82±0.01 | 3.56±0.04 | 0.99 |
表4 5-5-4与野生型细菌群落Alpha多样性指数
Table 4 Alpha diversity index of bacterial community in mutant 5-5-4 and wild-type
处理 Treatment | 编号 Number | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | 覆盖度 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP | 5-5-4 | 441.60±40.76 | 457.35±55.87 | 0.79±0.02** | 3.78±0.17** | 0.99 |
| WT | 457.62±31.49 | 463.31±32.81 | 0.96±0.01 | 5.76±0.21 | 0.99 | |
| LP | 5-5-4 | 433.58±19.39 | 434.94±25.25 | 0.91±0.03* | 5.12±0.26** | 0.99 |
| WT | 416.30±4.10 | 424.64±17.66 | 0.82±0.01 | 3.56±0.04 | 0.99 |

图8 细菌群落门和属水平组成分析A、B分别为门和属水平的物种组成分析。A,B are the composition of the bacteria community at phyla and genus level, respectively.
Fig.8 Composition of the bacteria community at phyla and genus level
| [1] | He W, Zhang X Q, Yang C H, et al. The distribution characters and planting technology of Hemarthia spp. SICHUAN CAOYUAN, 2003(5): 42-44. |
| 何玮, 张新全, 杨春华, 等. 牛鞭草种质资源在中国的分布及其人工草地建植技术. 四川草原, 2003(5): 42-44. | |
| [2] | Li F, Zhang X Q, Ma X, et al. Comparative study on the agronomic traits of new whipgrass lines. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 48(5): 1210-1213. |
| 李芳, 张新全, 马啸, 等. 扁穗牛鞭草新品系的农艺性状比较研究. 湖北农业科学, 2009, 48(5): 1210-1213. | |
| [3] | Chen Y X, Zhang X Q, Yang C H, et al. Breeding and cultivation techniques of a new variety Hemarthria compressa cv. Ya’an. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2012, 34(3): 109-112. |
| 陈永霞, 张新全, 杨春华, 等. 扁穗牛鞭草新品种选育及栽培技术. 中国草地学报, 2012, 34(3): 109-112. | |
| [4] | Yang C. Waterlogging resistance and root microstructure analysis of different Hemarthria compressa germplasm resources under flooding stress. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2022. |
| 杨成. 淹水胁迫下不同扁穗牛鞭草种质资源耐涝性能及其根部显微结构分析. 重庆: 西南大学, 2022. | |
| [5] | Zeng J, Huang L K, Zhang X Q, et al. Study on phenotype mutation of Hemarthria compressa and dose selection of 60Co-γ irradiation. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2014, 22(4): 828-833. |
| 曾捷, 黄琳凯, 张新全, 等. 60Co-γ辐射扁穗牛鞭草剂量筛选及表型变异研究. 草地学报, 2014, 22(4): 828-833. | |
| [6] | Chen L Z, Duan L, Sun M H, et al. Current trends and insights on EMS mutagenesis application to studies on plant abiotic stress tolerance and development. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 13: 1052569. |
| [7] | Zhang J. Spatial and temporal changes of soil nutrients in typical red soil erosion region of southern China. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University, 2021. |
| 张婧. 南方典型红壤侵蚀区土壤养分时空变异特征研究. 福州: 福建师范大学, 2021. | |
| [8] | Zhao C. Study on characteristics and physiological mechanism of phosphorus efficient utilization of switchgrass in saline-alkali soil. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2023. |
| 赵匆. 盐碱地柳枝稷磷高效利用特征及其生理机制研究. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2023. | |
| [9] | Wu R X, Li Y, You Y L, et al. Study on drought resistance identification and evaluation methods of alfalfa during whole growth period. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(5): 1444-1453. |
| 武瑞鑫, 李源, 游永亮, 等. 紫花苜蓿全生育期抗旱性鉴定评价方法探讨. 草地学报, 2020, 28(5): 1444-1453. | |
| [10] | Xu W W. Construction of sugarcane mutant library induced by EMS and sereening of SSR primers. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2018. |
| 许雯雯. EMS诱变甘蔗突变体库的构建及其SSR引物的筛选. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2018. | |
| [11] | Li M, Wang Y F, Xu K J, et al. Construction of mutant library by EMS induction with Panicum virgatum spike buds. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2016, 25(2): 203-208. |
| 李毛, 王勇锋, 徐开杰, 等. 利用EMS诱变构建柳枝稷穗芽无性系突变体库的初步研究. 西北农业学报, 2016, 25(2): 203-208. | |
| [12] | Yang Q, Zhang F, Wang D, et al. Selection of salt-tolerant variants from potato in vitro micro-cuttings induced by EMS. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 25(4): 673-678. |
| 杨乾, 张峰, 王蒂, 等. EMS诱变筛选马铃薯茎段离体耐盐变异体. 核农学报, 2011, 25(4): 673-678. | |
| [13] | Guo S Y. EMS mutagenesis creates Lilium davidii var. unicolor mutants. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020. |
| 郭思雨. EMS诱变创建兰州百合突变体. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2020. | |
| [14] | Feng S Z, Chen X B, He X Y, et al. Effects of land use and fertilization on lignin accumulation in red soil. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(9): 1761-1768. |
| 冯书珍, 陈香碧, 何寻阳, 等. 不同土地利用方式及施肥措施对红壤木质素积累特性的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(9): 1761-1768. | |
| [15] | Liu Z P. Quality characteristics and regulation technique of sugarcane cultivated-layer in red soil slope farmland. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2018. |
| 刘志鹏. 红壤坡耕地甘蔗耕层质量特征及调控技术研究. 重庆: 西南大学, 2018. | |
| [16] | Sun Z W, Xu Y M, Xu R Y, et al. Research advance in the response of rice to low phosphorus stress and its regulation mechanism. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 37(8): 1562-1570. |
| 孙志伟, 徐月梅, 许荣越, 等. 水稻低磷胁迫响应及其调控机制的研究进展. 核农学报, 2023, 37(8): 1562-1570. | |
| [17] | Dong L. Root developmental responses to phosphorus nutrition. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(6): 1065-1090. |
| [18] | Yugandhar P, Veronica N, Ai H, et al. NH787 EMS mutant of rice variety Nagina22 exhibits higher phosphate use efficiency. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 9156. |
| [19] | Zhang Y. Molecular regulation of phosphate starvation-induced acid phosphatase activity. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2014. |
| 张烨. 低磷胁迫诱导植物酸性磷酸酶的分子调控机制. 北京: 清华大学, 2014. | |
| [20] | Li P C, Ma X L, Wang J C, et al. Integrated analysis of metabolome and transcriptome reveals insights for low phosphorus tolerance in wheat seedling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(19): 14840. |
| [21] | Sewelam N, Kazan K, Schenk P M. Global plant stress signaling: reactive oxygen species at the cross-road. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7(187): 187. |
| [22] | Shuvasish C, Piyalee P, Lingaraj S, et al. Reactive oxygen species signaling in plants under abiotic stress. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2013, 8(4): e23681. |
| [23] | Yugandhar P, Sun Y, Liu L. Characterization of the loss-of-function mutant NH101 for yield under phosphate deficiency from EMS-induced mutants of rice variety Nagina22. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2018, 130: 1-13. |
| [24] | Oburger E, Dell’mour M, Hann S, et al. Evaluation of a novel tool for sampling root exudates from soil-grown plants compared to conventional techniques. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2013, 87: 235-247. |
| [25] | Zheng Y F, Cao X W, Zhou Y, et al. Purines enrich root-associated Pseudomonas and improve wild soybean growth under salt stress. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 3520. |
| [1] | 曾燕霞, 陈志龙, 尚继红, 沙晓弟, 吴娟, 陈彩锦. 太空诱变对PEG-6000模拟干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿材料苗期生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 59-69. |
| [2] | 张鹤山, 陆姣云, 朱伟, 田宏, 熊军波, 吴新江, 刘洋. N+和Ar+注入红三叶种子的诱变效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 160-171. |
| [3] | 亓雯雯, 马红媛, 李亚晓, 杜艳, 孙梦丹, 武海涛. 优质牧草新品种选育方法研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 187-202. |
| [4] | 余静菠, 张慧丽, 李进, 关皓, 周青平, 陈仕勇. 38份饲用燕麦品种苗期磷利用效率综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 161-171. |
| [5] | 徐宗昌, 鲁雪莉, 魏云冲, 孟晨, 张梦超, 张缘杨, 王萌, 王菊英, 张成省, 李义强. 航天诱变野大豆SP1群体苗期耐盐性鉴定与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 168-178. |
| [6] | 王升升, 段珍, 周培, 张吉宇. 白花草木樨结瘤缺失型突变体的结瘤表型及生物量分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 247-256. |
| [7] | 李小铃, 关皓, 帅杨, 李小梅, 彭安琪, 李昌华, 蒲棋, 闫艳红, 张新全. 单一和复合乳酸菌添加剂对扁穗牛鞭草青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 119-127. |
| [8] | 李振松, 栗振义, 张绮芯, 何峰, 王宇菲, 万里强, 李向林, 仝宗永. 敖汉和维多利亚紫花苜蓿对低磷环境应激机制的比较[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 50-59. |
| [9] | 刘攀道, 郇恒福, 刘一明, 刘国道, 白昌军, 陈志坚. 低磷胁迫对太空诱变耐低磷柱花草酸性磷酸酶活性和磷效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 78-85. |
| [10] | 冯鹏, 孙力, 申晓慧, 李如来, 李增杰, 李志民, 郑海燕, 姜成, 杨鹤, 刘俊刚, 郭伟, 张英俊. 不同诱变处理对苜蓿叶片细胞显微和超微结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(6): 72-80. |
| [11] | 武炳超, 张欢, 童磊, 杜昭昌, 胡家菱, 陈燚, 张新全, 刘伟, 黄琳凯. 象草不同辐射剂量诱变系表型及遗传变异研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(11): 77-86. |
| [12] | 靳军英, 张卫华, 王大可, 寇青青, 运剑苇, 黄建国. 扁穗牛鞭草的水肥耦合效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 106-114. |
| [13] | 王昶, 贺春贵, 张丽娟, 杨晓明. 豌豆抗豌豆象育种及其综合防治研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 213-224. |
| [14] | 李娟, 雷霞, 钟理, 王小利, 杨春燕, 吴佳海. 高温胁迫对高羊茅航天诱变新品系生理特性研究及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(3): 121-131. |
| [15] | 李娟, 雷霞, 王小利, 牟琼, 杨春燕, 吴佳海. 干旱胁迫对高羊茅航天诱变新品系生理特性的影响及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(10): 87-98. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||