

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (2): 14-31.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020112
收稿日期:2020-03-12
修回日期:2020-06-08
出版日期:2021-02-20
发布日期:2021-01-19
作者简介:蒋翔(1995-),男,陕西咸阳人,在读硕士。E-mail:jiangxiang@llas.ac.cn基金资助:
Xiang JIANG1,2,3( ), Jian-xia MA1,2,3(
), Jian-xia MA1,2,3( )
)
Received:2020-03-12
Revised:2020-06-08
Online:2021-02-20
Published:2021-01-19
摘要:
草地覆盖了大于40%的陆地面积,其生态退化问题受到了极大的关注。近年来在各个地区采取了一系列草地恢复措施,但是具体的恢复效果无从得知。从论文数据库中收集整理关于中国草地恢复的中英文文献共86篇用于Meta分析,对中国草地生物多样性和生态系统服务的恢复效果进行了定量评估。通过亚组分析,分别得到了恢复时间、恢复方法、恢复地区、草地类型和草地退化程度对恢复效果的响应,以及各生态类型对草地恢复的响应。结果表明,草地恢复措施使得退化草地得到了不同程度的恢复。恢复时间对恢复效果具有较大的影响,恢复时间越长恢复效果越好;主动的人工措施可以有效提高草地的恢复速度,但是自然恢复才能使草地恢复到接近退化前的状态;在不同的生态区域中,湿润地区草地的恢复效果相对更好;温性草地的恢复效果总体好于高寒草地;经过恢复后的中度退化草地与恢复前相比改善效果最为明显;在草地的恢复过程中,生物多样性和生态系统服务都能得到恢复,生物多样性的恢复速度快于生态系统服务。
蒋翔, 马建霞. 我国草地生态恢复对不同因素响应的Meta分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 14-31.
Xiang JIANG, Jian-xia MA. The impact of different factors on the outcomes of grassland ecological restoration to in China: A Meta-analysis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(2): 14-31.
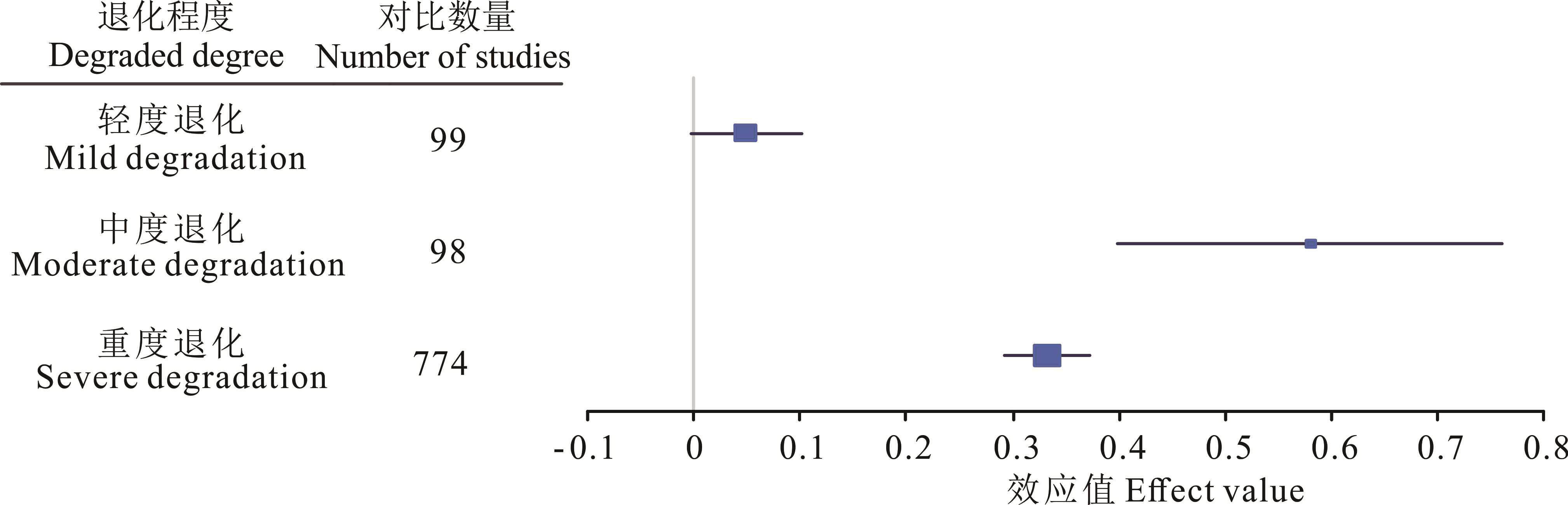
图15 不同草地退化程度对草地恢复的响应(恢复草地/退化草地)
Fig.15 Response of different grassland degraded degree to grassland restoration (recovered grassland/degrade grassland)
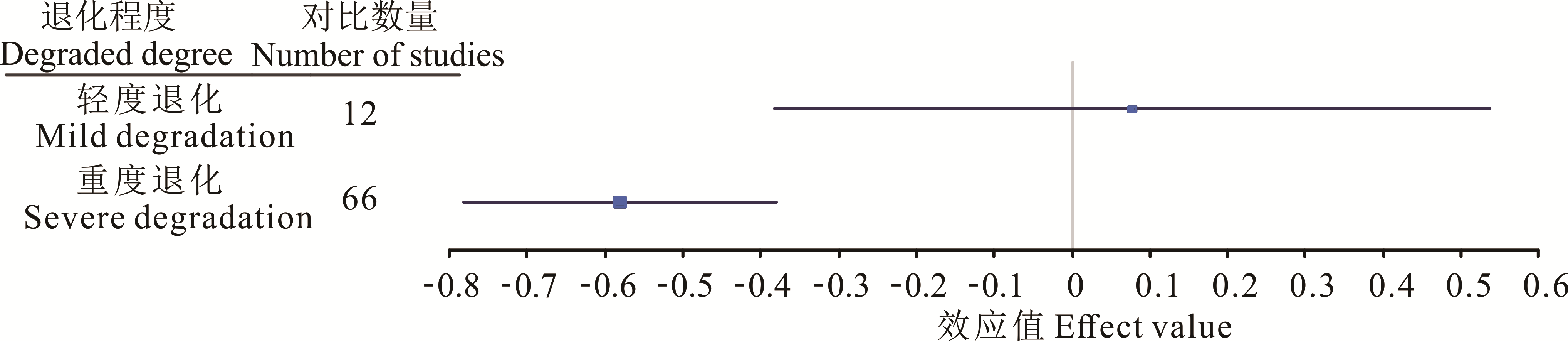
图16 不同草地退化程度对草地恢复的响应(恢复草地/参考草地)
Fig.16 Response of different grassland degraded degree to grassland restoration (recovered grassland/reference grassland)
| 1 | Kang L, Han X, Zhang Z, et al. Grassland ecosystems in China: Review of current knowledge and research advancement. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2007, 362(1482): 997-1008. |
| 2 | Wen L, Dong S, Li Y, et al. Effect of degradation intensity on grassland ecosystem services in the alpine region of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. PLoS One, 2013, 8(3): e58432. |
| 3 | CoxGeorge W. Readings in conservation ecology. New York: Appleton Century Crofts, 1974. |
| 4 | Ye D Z, Chou J F, Liu J Y, et al. Causes of sand-stormy weather in Northern China and contral measures. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2000, 15(5): 513-521. |
| 叶笃正, 丑纪范, 刘纪远, 等. 关于我国华北沙尘天气的成因与治理对策. 地理学报, 2000, 15(5): 513-521. | |
| 5 | Straton A. A complex systems approach to the value of ecological resources. Ecological Economics, 2006, 56(3): 402-411. |
| 6 | Wade M R, Gurr G M, Wratten S D. Ecological restoration of farmland: Progress and prospects. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2007, 363(1492): 831-847. |
| 7 | Zhang J T, Dong Y. Factors affecting species diversity of plant communities and the restoration process in the loess area of China. Ecological Engineering, 2010, 36(3): 345-350. |
| 8 | Liu J P, Xia Y. Quality appraisal of systematic reviews or Meta-analysis on traditional Chinese medicine published in Chinese Journals. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2007, 27(4): 306-311. |
| 刘建平, 夏芸. 中文期刊发表的中医药系统综述或Meta-分析文章的质量评价. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2007, 27(4): 306-311. | |
| 9 | Ren Y, Lv Y, Fu B. Quantifying the impacts of grassland restoration on biodiversity and ecosystem services in China: A meta-analysis. Ecological Engineering, 2016, 95: 542-550. |
| 10 | Chang X, Chai Q, Wu G, et al. Soil organic carbon accumulation in abandoned croplands on the Loess Plateau. Land Degradation & Development, 2017, 28(5): 1519-1527. |
| 11 | Song Z, Wang J, Liu G, et al. Changes in nitrogen functional genes in soil profiles of grassland under long-term grazing prohibition in a semiarid area. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 673: 92-101. |
| 12 | Chen J, Tang H. Effect of grazing exclusion on vegetation characteristics and soil organic carbon of Leymus chinensis grassland in Northern China. Sustainability, 2016, 8(1): 1-10. |
| 13 | Li P, Zhang X, Hao M, et al. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil bacterial communities, enzyme activities, and nutrients of reconstructed soil in a mining area on the Loess Plateau, China. Sustainability, 2019, 11(8): 2295. |
| 14 | Wang K, Deng L, Ren Z, et al. Grazing exclusion significantly improves grassland ecosystem C and N pools in a desert steppe of Northwest China. Catena, 2016, 137: 441-448. |
| 15 | Wang X, Song N, Yang X, et al. Grazing exclusion-induced shifts, the relative importance of environmental filtering, biotic interactions and dispersal limitation in shaping desert steppe communities, Northern China. Journal of Arid Land, 2018, 10(3): 402-415. |
| 16 | Wang T, Zhang Z, Li Z, et al. Grazing management affects plant diversity and soil properties in a temperate steppe in Northern China. Catena, 2017, 158: 141-147. |
| 17 | Borjigin S, Cheng Y, Nomura N, et al. Effect of abandonment on diversity and abundance of free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria and total bacteria in the cropland soils of Hulun Buir, Inner Mongolia. PLoS One, 2014, 9(9): e106714. |
| 18 | Li J, Zhang C, Yang Z, et al. Grazing and fertilization influence plant species richness via direct and indirect pathways in an alpine meadow of the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Grass and Forage Science, 2017, 72(2): 343-354. |
| 19 | Li J, Zheng Z, Xie H, et al. Increased soil nutrition and decreased light intensity drive species loss after eight years grassland enclosures. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 44525. |
| 20 | Zhong L, Zhou X, Wang Y, et al. Mixed grazing and clipping is beneficial to ecosystem recovery but may increase potential N2O emissions in a semi-arid grassland. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2017, 114: 42-51. |
| 21 | Luo D. Effects of different improved measures on vegetation and soil in the Stipa breviflora desert steppe. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2016. |
| 罗冬. 不同改良措施对短花针茅荒漠草原植被和土壤的影响. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2016. | |
| 22 | Zhang W N. The plant and soil characteristics of the alpine meadow under different periods of grazing ban in Northern Tibet. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2015. |
| 张伟娜. 不同年限禁牧对藏北高寒草甸植被及土壤特征的影响. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2015. | |
| 23 | Bai X. Effect of enclosure duration on offspring recruitment and bud bank in semiarid steppe on the Loess Plateau. Luoyang: Henan University of Science and Technology, 2017. |
| 白欣. 封育年限对黄土高原典型草原繁殖更新与芽库的影响. 洛阳: 河南科技大学, 2017. | |
| 24 | Li Y L. A study on the insect diversity of different exclosure period in degraded typical steppe of Inner Mongolia. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2017. |
| 李云龙. 内蒙古退化典型草原不同封育年限样地昆虫多样性研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2017. | |
| 25 | Li Y Q. Influence of enclosure grazing on Stipa klemenzii steppe community and soil. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2017. |
| 李雅琼. 围封禁牧对小针茅草原群落和土壤的影响. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2017. | |
| 26 | Xiong D, Shi P, Sun Y, et al. Effects of grazing exclusion on plant productivity and soil carbon, nitrogen storage in alpine meadows in Northern Tibet, China. Chinese Geographical Science, 2014, 24(4): 488-498. |
| 27 | Liu R, Zhao H, Zhao X, et al. Effects of cultivation and grazing exclusion on the soil macro-faunal community of semiarid sandy grasslands in Northern China. Arid Land Research and Management, 2013, 27(4): 377-393. |
| 28 | Pei S, Fu H, Wan C. Changes in soil properties and vegetation following exclosure and grazing in degraded Alxa desert steppe of Inner Mongolia, China. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2008, 124(1/2): 33-39. |
| 29 | Liu R T, Zhao H L, Zhao X Y. Community structure and diversity of soil arthropods in naturally restored sandy grasslands after grazing. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2010, 21(11): 2849-2855. |
| 刘任涛, 赵哈林, 赵学勇. 放牧后自然恢复沙质草地土壤节肢动物群落结构与多样性. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(11): 2849-2855. | |
| 30 | Yuan J, Ouyang Z, Zheng H, et al. Effects of different grassland restoration approaches on soil properties in the southeastern Horqin sandy land, Northern China. Applied Soil Ecology, 2012, 61: 34-39. |
| 31 | Wu X, Li Z, Fu B, et al. Effects of grazing exclusion on soil carbon and nitrogen storage in semi-arid grassland in Inner Mongolia, China. Chinese Geographical Science, 2014, 24(4): 479-487. |
| 32 | Zeng Z G, Bi J H, Li S R, et al. Effects of habitat alteration on lizard community and food web structure in a desert steppe ecosystem. Biological Conservation, 2014, 179: 86-92. |
| 33 | Shi F, Chen H, Wu Y, et al. Effects of livestock exclusion on vegetation and soil properties under two topographic habitats in an alpine meadow on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Polish Journal of Ecology, 2010, 58(1): 125-133. |
| 34 | Gao Y Z, Giese M, Gao Q, et al. Community level offset of rain use-and transpiration efficiency for a heavily grazed ecosystem in Inner Mongolia grassland. PLoS One, 2013, 8(9): e74841. |
| 35 | Giese M, Brueck H, Gao Y Z, et al. N balance and cycling of Inner Mongolia typical steppe: A comprehensive case study of grazing effects. Ecological Monographs, 2013, 83(2): 195-219. |
| 36 | Wang D, Wu G L, Zhu Y J, et al. Grazing exclusion effects on above-and below-ground C and N pools of typical grassland on the Loess Plateau (China). Catena, 2014, 123: 113-120. |
| 37 | Su Y Z, Li Y L, Cui J Y, et al. Influences of continuous grazing and livestock exclusion on soil properties in a degraded sandy grassland, Inner Mongolia, Northern China. Catena, 2005, 59(3): 267-278. |
| 38 | Li Y, Zhao H, Zhao X, et al. Effects of grazing and livestock exclusion on soil physical and chemical properties in desertified sandy grassland, Inner Mongolia, Northern China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 63(4): 771-783. |
| 39 | Lv X T, Freschet G T, Kazakou E, et al. Contrasting responses in leaf nutrient-use strategies of two dominant grass species along a 30-yr temperate steppe grazing exclusion chronosequence. Plant and Soil, 2015, 387(1/2): 69-79. |
| 40 | Ma H, Yang H, Liang Z, et al. Effects of 10-year management regimes on the soil seed bank in saline-alkaline grassland. PLoS One, 2015, 10(4): e0122319. |
| 41 | Wu X, Li Z, Fu B, et al. Restoration of ecosystem carbon and nitrogen storage and microbial biomass after grazing exclusion in semi-arid grasslands of Inner Mongolia. Ecological Engineering, 2014, 73: 395-403. |
| 42 | Zhan X, Li L, Cheng W. Restoration of Stipa kryloviisteppes in Inner Mongolia of China: Assesment of seed banks and vegetation composition. Journal of Arid Environments, 2007, 68(2): 298-307. |
| 43 | Rong Y, Yuan F, Ma L. Effectiveness of exclosures for restoring soils and vegetation degraded by overgrazing in the Junggar Basin, China. Grassland Science, 2014, 60(2): 118-124. |
| 44 | Wu L, He N, Wang Y, et al. Storage and dynamics of carbon and nitrogen in soil after grazing exclusion in Leymus chinensis grasslands of Northern China. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2008, 37(2): 663-668. |
| 45 | Su Y Z, Li Y L, Zhao H L. Soil properties and their spatial pattern in a degraded sandy grassland under post-grazing restoration, Inner Mongolia, Northern China. Biogeochemistry, 2006, 79(3): 297-314. |
| 46 | Su Y Y, Guo L D. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in non-grazed, restored and over-grazed grassland in the Inner Mongolia steppe. Mycorrhiza, 2007, 17(8): 689-693. |
| 47 | Wang C T, Wang G X, Liu W, et al. Effects of establishing an artificial grassland on vegetation characteristics and soil quality in a degraded meadow. Israel Journal of Ecology & Evolution, 2013, 59(3): 141-153. |
| 48 | Peng S L, Tang X Y. Meta-analysis and its application in ecology. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 1998, 17(5): 74-79. |
| 彭少麟, 唐小焱. Meta分析及其在生态学上的应用. 生态学杂志, 1998, 17(5): 74-79. | |
| 49 | Yan Y, Lu X. Is grazing exclusion effective in restoring vegetation in degraded alpine grasslands in Tibet, China. Blank, 2015, 3: e1020. |
| 50 | Zhang H, Gilbert B, Zhang X X, et al. Community assembly along a successional gradient in sub-alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Oikos, 2013, 122: 952-960. |
| 51 | Zhou Z Y, Sun O J, Huang J H, et al. Soil carbon and nitrogen stores and storage potential as affected by land-use in an agro-pastoral ecotone of Northern China. Biogeochemistry, 2006, 82: 127-138. |
| 52 | Wang H, Wang H, Huang R, et al. Effects of different exclosure management on soil and plant characteristics of sandy grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(6): 15. |
| 王蕙, 王辉, 黄蓉, 等. 不同封育管理对沙质草地土壤与植被特征的影响. 草业学报, 2012, 21(6): 15. | |
| 53 | Zhang X, Hu Y L, Li W J, et al. Effects of different improvement measures on plant community and soil of typical pasture. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2013, 31(2): 106-110. |
| 张信, 胡艳莉, 李维军, 等. 不同改良措施对典型草原植物群落及土壤的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2013, 31(2): 106-110. | |
| 54 | Yang L N, Baoyin T G T. Effect of different improving measures on degenerated steppe of Leymus chinensis. Journal of Desert Research, 2008, 28(2): 312-317. |
| 杨丽娜, 宝音陶格涛. 不同改良措施对退化羊草 (Leymus chinensis) 草原的影响. 中国沙漠, 2008, 28(2): 312-317. | |
| 55 | Yang L N. Effect of different improving measures on degenerated steppe of Leymus chinensis. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2008. |
| 杨丽娜. 不同改良措施对退化羊草草原的影响. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2008. | |
| 56 | Yang B. Research on the effect of different restoration measures on degenerated Leymus chinensis steppe. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2014. |
| 杨波. 不同恢复措施对退化羊草(Leymus chinensis)草原影响研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2014. | |
| 57 | Zhao J M. Study on the soil and water conservation ecological services under different land use patterns in alpine area. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2010. |
| 赵锦梅. 不同土地利用方式对高寒地区水土保持生态服务功能的影响研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2010. | |
| 58 | Ao Y M. Study on soil ecological stoichiometey of enclosing life in typical steppe. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Normal University, 2012. |
| 敖伊敏. 不同围封年限下典型草原土壤生态化学计量特征研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2012. | |
| 59 | Li F R, Liu J L, Hua W, et al. Trophic group responses of ground arthropods to land-cover change and management disturbance. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(15): 4169-4181. |
| 李锋瑞, 刘继亮, 化伟, 等. 地面节肢动物营养类群对土地覆被变化和管理扰动的响应. 生态学报, 2011, 31(15): 4169-4181. | |
| 60 | Wu D H, Yin W Y, Yan R Q. Effects of vegetation reclamation practices on soil mite communities in seriously alkalinized and degraded grasslands of Songnen, Northeastern China. Zoological Research, 2007, 28(5): 519-525. |
| 吴东辉, 尹文英, 阎日青. 东北松嫩草原重度退化草地两种典型植被恢复处理方式间土壤螨类群落特征比较. 动物学研究, 2007, 28(5): 519-525. | |
| 61 | Liu R, Zhu F, An H, et al. Effect of naturally vs manually managed restoration on ground-dwelling arthropod communities in a desertified region. Ecological Engineering, 2014, 73: 545-552. |
| 62 | Yang X H, Zhang K B, Hou R P. Impacts of exclusion on vegetative features and aboveground biomass in semi-arid degraded rangeland. Ecology and Environmnet, 2005, 14(5): 730-734. |
| 杨晓晖, 张克斌, 侯瑞萍. 封育措施对半干旱沙地草场植被群落特征及地上生物量的影响. 生态环境, 2005, 14(5): 730-734. | |
| 63 | Liu X D, Zhang K B, Wang L L, et al. How enclosure affects community characteristics of the sandy grassland in semi-arid areas of Northwestern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2015, 37(2): 48-54. |
| 刘小丹, 张克斌, 王黎黎, 等. 封育对半干旱区沙化草地群落特征的影响. 北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(2): 48-54. | |
| 64 | Zhang J L, Wang H N, Bi Y F, et al. Effects of enclosure management on soil seed bank and vegetation diversity of degraded grassland in dry-hot valley of Jinsha River. Grassland and Turf, 2008(1): 6-12. |
| 张建利, 王海宁, 毕玉芬, 等. 封育对干热河谷稀树灌草丛退化草地土壤种子库和植物多样性的影响. 草原与草坪, 2008(1): 6-12. | |
| 65 | Jiang D M, Miao R H, Toshio O, et al. Effects of fence enclosure on vegetation restoration and soil properties in Horqin sandy land. Ecology and Enviromental Sciences, 2013, 22(1): 40-46. |
| 蒋德明, 苗仁辉, 押田敏雄, 等. 封育对科尔沁沙地植被恢复和土壤特性的影响. 生态环境学报, 2013, 22(1): 40-46. | |
| 66 | Jin Y X, Zhou H K, Yao B Q, et al. Characteristics and recovery capacity of plant community in grave-soil-taken field during natural restoration in alpine steppe. Pratacultural Science, 2014, 31(8): 1528-1537. |
| 金艳霞, 周华坤, 姚步青, 等. 高寒草原取土场自然恢复过程中植物群落的特征和恢复力. 草业科学, 2014, 31(8): 1528-1537. | |
| 67 | Zhao C Z, Dong X G, Shi F X, et al. Community stability under different vegetations restored of abandoned lands in alpine areas. Journal of Mountain Research, 2011, 29(1): 6-11. |
| 赵成章, 董小刚, 石福习, 等. 高寒山区退耕地不同植被恢复方式下群落稳定性. 山地学报, 2011, 29(1): 6-11. | |
| 68 | Li G, Wang L J, Li Y J, et al. Effects of different vegetation restoration patterns on the diversity of soil nitrogen-fixing microbes in Hulunbeier sandy land, Inner Mongolia of North China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(6): 1639-1646. |
| 李刚, 王丽娟, 李玉洁, 等. 呼伦贝尔沙地不同植被恢复模式对土壤固氮微生物多样性的影响. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(6): 1639-1646. | |
| 69 | Li G, Xiu W M, Wang J, et al. Community structure and diversity of soil ammonia-oxidizing bacteria under different vegetation restoration patterns in Hulunbeier sandy land, Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(1): 111. |
| 李刚, 修伟明, 王杰, 等. 呼伦贝尔沙地不同植被恢复模式土壤氨氧化细菌群落结构及多样性. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(1): 111. | |
| 70 | Jin X M, Liu J D, Ai L, et al. Study on the community trends of fenced vegetation in Hulunbeier sandy land. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 31(1): 15-20. |
| 金晓明, 刘及东, 艾琳, 等. 呼伦贝尔沙地封育植被群落动态研究. 內蒙古农业大学学报 (自然科学版), 2010, 31(1): 15-20. | |
| 71 | Lv S H. Study on the characteristics of desertification grassland ecosystem and the effect of fencing improvement in Hulunbeir steppe. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2005. |
| 吕世海. 呼伦贝尔沙化草地系统退化特征及围封效应研究. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2005. | |
| 72 | Liu R T, Yang X G, Chai Y Q, et al. Response of ground-dwelling arthropod guilds to reseeding and cutting in artificial Caragana korshinskii plantations in desert steppe. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(3): 78. |
| 刘任涛, 杨新国, 柴永青, 等. 荒漠草原区柠条林地地面节肢动物功能群对补播牧草和平茬措施的响应. 草业学报, 2013, 22(3): 78. | |
| 73 | Shan G L, Xue S M, Chen G, et al. Influence of seasonal exclosure on vegetation restoration in typical steppe, Inner Mongolia. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2012, 20(5): 812-818. |
| 单贵莲, 薛世明, 陈功, 等. 季节性围封对内蒙古典型草原植被恢复的影响. 草地学报, 2012, 20(5): 812-818. | |
| 74 | Sun T, Bi Y F, Zhao X S, et al. Study on different recover measures of degraded grassland in arid-hot valleys along the Jinshajiang River. Grassland and Turf, 2006(3): 39-44. |
| 孙涛, 毕玉芬, 赵小社, 等. 金沙江干热河谷退化草地植被恢复技术的研究. 草原与草坪, 2006(3): 39-44. | |
| 75 | Zuo X A, Zhao H L, Zhao X Y, et al. Species diversity of degraded vegetation in different age restorations in Horqin Sandy Land, Northern China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2009, 18(4): 9-16. |
| 左小安, 赵哈林, 赵学勇, 等. 科尔沁沙地不同恢复年限退化植被的物种多样性. 草业学报, 2009, 18(4): 9-16. | |
| 76 | Liu F C. Effect of enclosing on degenerative typical steppe of Zhengxiangbaiqi County in Inner Mongolia. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2013. |
| 刘凤婵. 内蒙古正镶白旗退化典型草原封育效应. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2013. | |
| 77 | Liu J. Study on the vegetation change of sandy grassland and the effect of fencing in Yanchi of Ningxia. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2011. |
| 刘建. 宁夏盐池县沙化草地植被变化及围封措施效果研究. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2011. | |
| 78 | Mao L, Zhou J, Guo Z G. Effect of areas of land used for engineering construction on features of restorable plant communities in the alpine steppe regions of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(11): 3547-3554. |
| 毛亮, 周杰, 郭正刚. 青藏高原高寒草原区工程迹地面积对其恢复植物群落特征的影响. 生态学报, 2013, 33(11): 3547-3554. | |
| 79 | Lin G H, Zhao F, Chen G C, et al. Effects of different land-use types on larger-size soil animal communities in the northern region of Qinghai Lake. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(2): 180-186. |
| 林恭华, 赵芳, 陈桂琛, 等. 青海湖北岸不同土地利用方式对大型土壤动物群落的影响. 草业学报, 2012, 21(2): 180-186. | |
| 80 | Liu B W, Jiang Z G. Impacts of grassland fencing on plant communities and conservation of a rare gazelle, the Przewalski's gazelle. Biodiversity Science, 2002, 10(3): 326-331. |
| 刘丙万, 蒋志刚. 青海湖草原围栏对植物群落的影响兼论濒危动物普氏原羚的保护. 生物多样性, 2002, 10(3): 326-331. | |
| 81 | Jin S Y. Study on the soil fauna communities structure of degraded alpine meadow under restoration in the Three River Source region. Xining: Qinghai University, 2014. |
| 金生英. 三江源区退化高寒草甸恢复与重建中土壤动物群落结构的研究. 西宁: 青海大学, 2014. | |
| 82 | Wu D H, Yin W Y, Yin X Q. Comparisons among soil collembola community characteristics in relation to different vegetation restoration treatments in the moderate degraded grasslands in the Songnen Plain of Northeast China. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2008, 51(5): 509-515. |
| 吴东辉, 尹文英, 殷秀琴. 松嫩草原中度退化草地不同植被恢复方式下土壤跳虫群落特征比较. 昆虫学报, 2008, 51(5): 509-515. | |
| 83 | Wu D H, Yin W Y, Bu Z Y. Changes among soil nematode community characteristics in relation to different vegetation restoration practices in the moderate degraded grasslands of Songnen. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(1): 1-12. |
| 吴东辉, 尹文英, 卜照义. 松嫩草原中度退化草地不同植被恢复方式下土壤线虫的群落特征. 生态学报, 2008, 28(1): 1-12. | |
| 84 | Li F R, Liu J L, Kang L F, et al. Responses of soil seed banks and above-ground plant communities to grazing exclusion in a degraded sandy grassland. Journal of Desert Research, 2008, 28(6): 1078-1085. |
| 李锋瑞, 刘继亮, 康玲芬, 等. 退化沙质草地土壤种子库和地上植被对封育的响应机理. 中国沙漠, 2008, 28(6): 1078-1085. | |
| 85 | Si G C, Yuan Y L, Wang J, et al. Effects of fencing on microbial communities and soil enzyme activities in Damxung alpine grassland. Pratacultural Science, 2015, 32(1): 1-10. |
| 斯贵才, 袁艳丽, 王建, 等. 围封对当雄县高寒草原土壤微生物和酶活性的影响. 草业科学, 2015, 32(1): 1-10. | |
| 86 | Liu X D, Zhang K B, Wang X, et al. Influence of enclosure ages on community structure and species diversity of sandy grassland. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 35(3): 39-43. |
| 刘小丹, 张克斌, 王晓, 等. 围封年限对沙化草地群落结构及物种多样性的影响. 水土保持通报, 2015, 35(3): 39-43. | |
| 87 | Liu J, Zhang K B, Cheng Z Q, et al. Influences of fencing on vegetation and soil properties in sandy grassland. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 31(4): 180-184. |
| 刘建, 张克斌, 程中秋, 等. 围栏封育对沙化草地植被及土壤特性的影响. 水土保持通报, 2011, 31(4): 180-184. | |
| 88 | Yu X J, Jing Y Y, Duan C H, et al. Influence of enclosure and grazing intensity on alpine meadow vegetation and soil characteristics in the Eastern Qilian Mountains. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2015, 33(1): 252-257. |
| 鱼小军, 景媛媛, 段春华, 等. 围栏与不同放牧强度对东祁连山高寒草甸植被和土壤的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2015, 33(1): 252-257. | |
| 89 | Wang Y S, Shi G H, Xu Z Q, et al. Study on the restoration process of enclosed grassland in Xilinguole. Pratacultural Science, 2010, 27(8): 10-14. |
| 王英舜, 师桂花, 许中旗, 等. 锡林郭勒放牧草地封育后植被恢复过程的研究. 草业科学, 2010, 27(8): 10-14. | |
| 90 | Li Y J. Effects of rest grazing on plant diversity and organic carbon storage on Stipa baicalensis steppe in Inner Mongolia. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2013. |
| 李玉洁. 休牧对贝加尔针茅草原群落植物多样性和有机碳储量的影响. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2013. | |
| 91 | Li W J. Restoration succession and ecological mechanism of old-fields in subalpine meadow. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2010. |
| 李文金. 亚高寒草甸弃耕地恢复演替过程及其生态学机制研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2010. | |
| 92 | Wang J F, Sha Z P, Guan F C, et al. Effects of transplanting on the grassland biomass and the plant diversity in the region of the Brahmaputra River in Tibet. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2015, 20(1): 103-109. |
| 王军峰, 沙志鹏, 关法春, 等. 移栽措施对西藏退化草地生物量和植物多样性的影响. 中国农业大学学报, 2015, 20(1): 103-109. | |
| 93 | Jing Z B. Mechanism for restoration and regulatory of degraded grassland ecosystem in Yunwu Mountain. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2014. |
| 井赵斌. 云雾山退化草地生态系统恢复与调控机理. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2014. | |
| 94 | Zhou W P, Xiang D, Hu Y J, et al. Influences of long-term enclosure on the restoration of plant and AM fungal communities on grassland under different grazing intensities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(11): 3383-3393. |
| 周文萍, 向丹, 胡亚军, 等. 长期围封对不同放牧强度下草地植物和AM真菌群落恢复的影响. 生态学报, 2013, 33(11): 3383-3393. | |
| 95 | Wu D H, Yin W Y, Yan R Q. Effects of vegetation recovery practices on the characteristics of soil nematode communities on seriously degraded grasslands in Songnen Plain. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007(12): 2783-2790. |
| 吴东辉, 尹文英, 阎日青. 植被恢复方式对松嫩草原重度退化草地土壤线虫群落特征的影响. 应用生态学报, 2007(12): 2783-2790. | |
| 96 | Benayas J M R, Newton A C, Diaz A, et al. Enhancement of biodiversity and ecosystem services by ecological restoration: A meta-analysis. Science, 2009, 325(5944): 1121-1124. |
| 97 | Meli P, Benayas J M R, Balvanera P, et al. Restoration enhances wetland biodiversity and ecosystem service supply, but results are context-dependent: A meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2014, 9(4): e93507. |
| 98 | Leemans R, De Groot R S. Millennium ecosystem assessment: Ecosystems and human well-being: A framework for assessment. Washington, DC: Island Press, 2003. |
| 99 | Xie G, Zhang C S, Zhang L B, et al. China’s county-scale ecological regionalization. Journal of Natural Resources, 2012, 27(1): 154-162. |
| 100 | Liu X N, Zhang D G, Wang H X, et al. GIS-based analysis of the compatibility of two grassland classification systems in China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(6): 1-18. |
| 柳小妮, 张德罡, 王红霞, 等.基于GIS的中国2大草地分类系统类的兼容性分析.草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 1-18. | |
| 101 | Xu P. Grassland resources survey and planning. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000: 11-24. |
| 许鹏. 草地资源调查规划学. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 11-24. |
| [1] | 孙忠超, 郭天斗, 于露, 马彦平, 赵亚楠, 李雪颖, 王红梅. 宁夏东部荒漠草原向灌丛地人为转变过程土壤粒径分形特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 34-45. |
| [2] | 张金青, 牛奎举, 李玉珠, 马晖玲. 植物无融合生殖发生因素解析及其在草地早熟禾育种中的应用前景展望[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 205-217. |
| [3] | 张茹, 李建平, 彭文栋, 王芳, 李志刚. 柠条枝条覆盖对宁夏荒漠草原土壤水热及补播牧草生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 58-67. |
| [4] | 张超, 闫瑞瑞, 梁庆伟, 娜日苏, 李彤, 杨秀芳, 包玉海, 辛晓平. 不同利用方式下草地土壤理化性质及碳、氮固持研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 90-98. |
| [5] | 王辛有, 曹文侠, 王小军, 刘玉祯, 高瑞, 王世林, 安海涛, 邓秀霞, 王文虎. 河西地区豆禾混播草地生产性能对刈割高度与施肥的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 99-110. |
| [6] | 陈宸, 井长青, 邢文渊, 邓小进, 付皓宇, 郭文章. 近20年新疆荒漠草地动态变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 1-14. |
| [7] | 张宁, 曹允馨, 徐伟, 常智慧. 干旱胁迫下污泥对草地早熟禾生长及激素代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 167-176. |
| [8] | 李洁, 潘攀, 王长庭, 胡雷, 陈科宇, 杨文高. 三江源区不同建植年限人工草地根系动态特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 28-40. |
| [9] | 刘斯莉, 王长庭, 张昌兵, 胡雷, 唐立涛, 潘攀. 川西北高原3种禾本科牧草根系特征比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 41-53. |
| [10] | 孙华方, 李希来, 金立群, 李成一, 张静. 黄河源人工草地土壤微生物多样性对建植年限的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 46-58. |
| [11] | 季波, 何建龙, 吴旭东, 王占军, 谢应忠, 蒋齐. 宁夏典型天然草地土壤有机碳及其活性组分变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 24-35. |
| [12] | 李聪聪, 周亚星, 谷强, 杨明新, 朱传鲁, 彭子原, 薛凯, 赵新全, 王艳芬, 纪宝明, 张静. 三江源区典型高寒草地丛枝菌根真菌多样性及构建机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 46-58. |
| [13] | 丛一鸣, 高小叶, 侯扶江. 黄土高原-青藏高原过渡带农户生产系统的能量平衡分析——以“通渭-渭源-夏河”样带为例[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 5-19. |
| [14] | 陈红, 马文明, 周青平, 杨智, 刘超文, 刘金秋, 杜中曼. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体稳定性及其铁铝氧化物分异的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 73-84. |
| [15] | 郭剑波, 赵国强, 贾书刚, 董俊夫, 陈龙, 王淑平. 施肥对高寒草原草地质量指数及土壤性质影响的综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 85-93. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||