

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 47-56.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020477
荆佳强1,2( ), 萨仁其力莫格null2, 秦洁2, 张海芳2, 李明2, 杨殿林2(
), 萨仁其力莫格null2, 秦洁2, 张海芳2, 李明2, 杨殿林2( )
)
收稿日期:2020-10-20
修回日期:2020-12-28
出版日期:2021-12-01
发布日期:2021-12-01
通讯作者:
杨殿林
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: yangdianlin@caas.cn基金资助:
Jia-qiang JING1,2( ), Ren-qi-li-mo-ge SA2, Jie QIN2, Hai-fang ZHANG2, Ming LI2, Dian-lin YANG2(
), Ren-qi-li-mo-ge SA2, Jie QIN2, Hai-fang ZHANG2, Ming LI2, Dian-lin YANG2( )
)
Received:2020-10-20
Revised:2020-12-28
Online:2021-12-01
Published:2021-12-01
Contact:
Dian-lin YANG
摘要:
土壤活性有机碳能够准确反映土壤有效性,表征土壤质量变化,是探索可持续草地管理措施的关键指标之一。以内蒙古贝加尔针茅草原为研究对象,采用围封、放牧和刈割野外控制试验,探讨不同利用方式对土壤有机碳(SOC)和活性有机碳的影响,发现不同利用方式下土壤SOC含量表现为围封>刈割>放牧,其中围封区和刈割区土壤SOC含量显著大于放牧区,围封区与刈割区土壤SOC含量差异不显著,在土壤活性有机碳中土壤可溶性有机碳(DOC)含量表现为放牧>围封>刈割。土壤微生物量碳(MBC)和土壤易氧化有机碳(ROC)含量均表现为围封>刈割>放牧,围封区与刈割区土壤MBC和土壤ROC平均含量差异不显著,且均显著大于放牧区。土壤MBC、ROC和SOC之间呈极显著相关性(P<0.01)。土壤ROC和土壤MBC与土壤全氮和土壤全磷呈极显著相关性(P<0.01)。围封与刈割有利于土壤SOC、MBC、ROC的提升,放牧对土壤DOC有一定累积作用。围封和刈割增强了土壤SOC的稳定性,活性有机碳与土壤有机碳和土壤理化性质密切相关,能够敏感地反映土壤有机碳的变化。
荆佳强, 萨仁其力莫格null, 秦洁, 张海芳, 李明, 杨殿林. 不同利用方式对贝加尔针茅草原土壤活性有机碳的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 47-56.
Jia-qiang JING, Ren-qi-li-mo-ge SA, Jie QIN, Hai-fang ZHANG, Ming LI, Dian-lin YANG. Effects of different land-use patterns on soil active organic carbon in Stipa baicalensis steppe in Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 47-56.
利用方式 Land use patterns | pH | 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon (SOC, g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (TN, g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (TP, g·kg-1) | 铵态氮 NH4+-N (mg·kg-1) | 硝态氮 NO3--N (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 围封Enclosure | 6.72±0.05b | 13.54±0.03a | 2.46±0.10a | 0.41±0.00a | 4.52±0.05b | 1.19±0.04b |
| 放牧Grazing | 6.74±0.03b | 13.01±0.07b | 2.46±0.10a | 0.42±0.00a | 5.15±0.23a | 1.56±0.04a |
| 刈割Mowing | 7.26±0.11a | 13.30±0.11a | 2.61±0.03a | 0.41±0.01a | 4.74±0.05ab | 1.23±0.04b |
表1 不同利用方式下贝加尔针茅草原土壤理化因子
Table 1 Soil organic carbon content and basic physical and chemical properties of S. baicalensis steppe under different land use patterns
利用方式 Land use patterns | pH | 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon (SOC, g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (TN, g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (TP, g·kg-1) | 铵态氮 NH4+-N (mg·kg-1) | 硝态氮 NO3--N (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 围封Enclosure | 6.72±0.05b | 13.54±0.03a | 2.46±0.10a | 0.41±0.00a | 4.52±0.05b | 1.19±0.04b |
| 放牧Grazing | 6.74±0.03b | 13.01±0.07b | 2.46±0.10a | 0.42±0.00a | 5.15±0.23a | 1.56±0.04a |
| 刈割Mowing | 7.26±0.11a | 13.30±0.11a | 2.61±0.03a | 0.41±0.01a | 4.74±0.05ab | 1.23±0.04b |

图1 不同利用方式下贝加尔针茅草原土壤可溶性有机碳含量不同大写字母表示不同利用方式在相同土层0.05水平差异显著,不同小写字母表示相同利用方式不同土层在0.05水平差异显著。下同。Different capital letters indicate that different land use types have significant differences at the 0.05 level in the same soil layer, and different lowercase letters indicate that the same land use types have significant differences at 0.05 level in different soil layers. The same below.
Fig.1 Changes of soil dissolved organic carbon (DOC) content under different land use patterns in S. baicalensis steppe
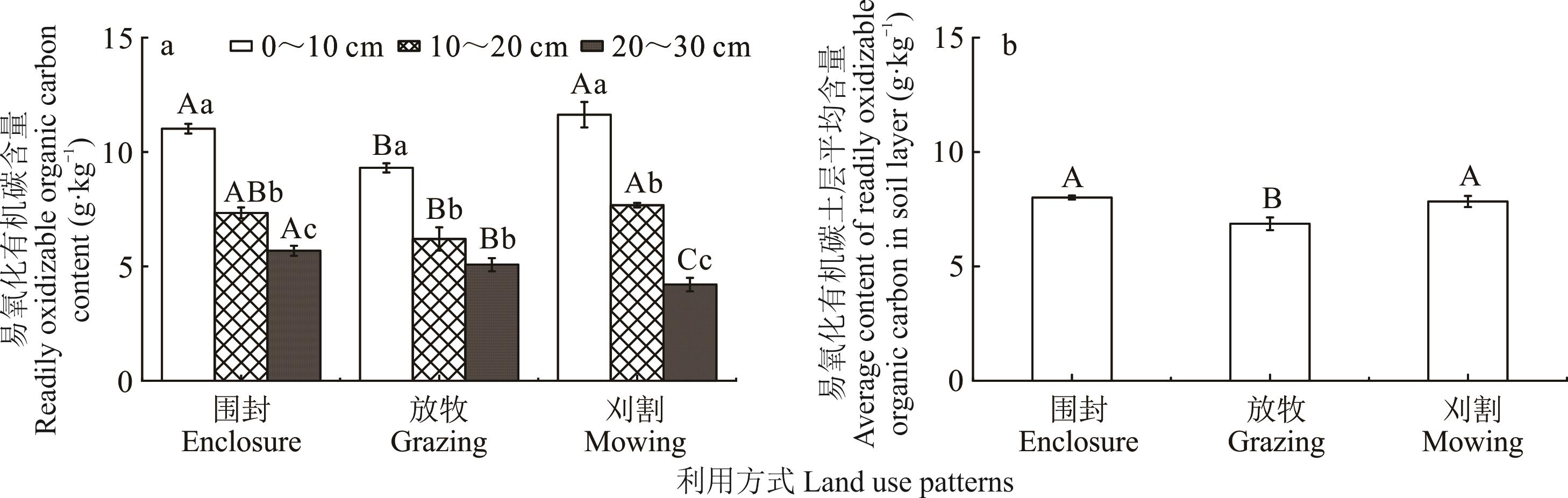
图2 不同利用方式下贝加尔针茅草原土壤易氧化有机碳含量
Fig.2 Changes of soil readily oxidizable organic carbon (ROC) content under different land use patterns in S. baicalensis steppe
利用方式 Land use patterns | 可溶性有机碳 比例 DOC/SOC | 易氧化有机碳比例 ROC/SOC | 微生物生物量碳比例 MBC/SOC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 围封Enclosure | 0.61±0.01b | 59.15±0.51a | 4.92±0.19a |
| 放牧Grazing | 0.70±0.01a | 52.75±2.38b | 3.59±0.05b |
| 刈割Mowing | 0.55±0.05b | 58.93±1.44a | 4.83±0.25a |
表2 不同利用方式下土壤活性有机碳的分配比例
Table 2 Distribution ratio of soil active organic carbon under different utilization methods (%)
利用方式 Land use patterns | 可溶性有机碳 比例 DOC/SOC | 易氧化有机碳比例 ROC/SOC | 微生物生物量碳比例 MBC/SOC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 围封Enclosure | 0.61±0.01b | 59.15±0.51a | 4.92±0.19a |
| 放牧Grazing | 0.70±0.01a | 52.75±2.38b | 3.59±0.05b |
| 刈割Mowing | 0.55±0.05b | 58.93±1.44a | 4.83±0.25a |
| 指标Index | 易氧化有机碳ROC | 微生物生物量碳MBC | 土壤有机碳SOC | pH | 全氮TN | 全磷TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 可溶性有机碳DOC | -0.20 | -0.32 | -0.25 | -0.30 | -0.24 | -0.08 |
| 易氧化有机碳ROC | 0.92** | 0.95** | -0.24 | 0.95** | 0.58** | |
| 微生物生物量碳MBC | 0.90** | -0.08 | 0.89** | 0.51** |
表3 土壤活性有机碳含量与土壤理化指标之间的相关系数
Table 3 Correlation coefficients between soil active organic carbon content and soil physical and chemical indexes
| 指标Index | 易氧化有机碳ROC | 微生物生物量碳MBC | 土壤有机碳SOC | pH | 全氮TN | 全磷TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 可溶性有机碳DOC | -0.20 | -0.32 | -0.25 | -0.30 | -0.24 | -0.08 |
| 易氧化有机碳ROC | 0.92** | 0.95** | -0.24 | 0.95** | 0.58** | |
| 微生物生物量碳MBC | 0.90** | -0.08 | 0.89** | 0.51** |
| 1 | Grace P, Ladd J, Robertson G, et al. SOCRATES-A simple model for predicting long-term changes in soil organic carbon in terrestrial ecosystems. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2006, 38(5): 1172-1176. |
| 2 | Lalitha M, Kumar P. Soil carbon fractions influenced by temperature sensitivity and land use management. Agroforestry Systems, 2016, 90(6): 961-964. |
| 3 | Lal R. Soil processes and greenhouse effect. Boca Raton, Florida. (USA): CRC Press, 1997. |
| 4 | Conant R T, Ogle S M, Paul E A, et al. Measuring and monitoring soil organic carbon stocks in agricultural lands for climate mitigation. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2011, 9(3): 169-173. |
| 5 | Shen H, Cao Z H, Hu Z Y. Characterization of soil active organic carbon and its ecological effects. Journal of Ecology, 1999, 18(3): 32-38. |
| 沈宏, 曹志洪, 胡正义. 土壤活性有机碳的表征及其生态效应. 生态学杂志, 1999, 18(3): 32-38. | |
| 6 | Nieder R, Harden T, Martens R, et al. Microbial biomass in arable soils of Germany during the growth period of annual crops. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2008, 171(6): 878-885. |
| 7 | Byrd K, Ratliff J, Bliss N, et al. Quantifying climate change mitigation potential in the United States Great Plains wetlands for three greenhouse gas emission scenarios. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 2015, 20(3): 439-465. |
| 8 | Liu M, Yu W T, Jiang Z S, et al. A research review on soil active organic carbon. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2006, 25(11): 1412-1417. |
| 柳敏, 宇万太, 姜子绍, 等. 土壤活性有机碳. 生态学杂志, 2006, 25(11): 1412-1417. | |
| 9 | Zou X M, Ruan H H, Fu Y, et al. Estimating soil labile organic carbon and potential turnover rates using a sequential fumigation-incubation procedure. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2005, 37(10): 1923-1928. |
| 10 | Naklang K, Whitbread A, Lefroy R, et al. The management of rice straw, fertilisers and leaf litters in rice cropping systems in Northeast Thailand. Plant and Soil, 1999, 209(1): 21-28. |
| 11 | Wang L L, Lou Y L, Shi Y L, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil active organic carbon indicators. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2008, 39(4): 752-755. |
| 王玲莉, 娄翼来, 石元亮, 等. 长期施肥对土壤活性有机碳指标的影响. 土壤通报, 2008, 39(4): 752-755. | |
| 12 | Saviozzi A, Levi M R, Cardelli R, et al. A comparison of soil quality in adjacent cultivated, forest and native grassland soils. Plant and Soil, 2001, 233(2): 251-259. |
| 13 | Yang C, Yang L, Ouyang Z. Organic carbon and its fractions in paddy soil as affected by different nutrient and water regimes. Geoderma, 2005, 124(1/2): 133-142. |
| 14 | Cambaradella C A, Elliott E T. Particulate soil organic-matter changes across a grassland cultivation sequence. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1992, 56(3): 777-783. |
| 15 | Breulmann M, Schulz E, Weißhuhn K, et al. Impact of the plant community composition on labile soil organic carbon, soil microbial activity and community structure in semi-natural grassland ecosystems of different productivity. Plant and Soil, 2012, 352(1/2): 253-265. |
| 16 | Turner B L, Meyer W B, Skole D L. Global land-use/land-cover change: Towards an integrated study. Ambio, 1994, 23(1): 91-95. |
| 17 | Pu N N, Sun Z J, Fan Y M, et al. Influence of grazing intensity on the soil organic carbon and microbial biomass carbon of meadow steppe in Zhaosu area. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2013, 36(1): 66-70. |
| 蒲宁宁, 孙宗玖, 范燕敏, 等. 放牧强度对昭苏草甸草原土壤有机碳及微生物碳的影响. 新疆农业大学学报, 2013, 36(1): 66-70. | |
| 18 | Yang H L, Sun Z J, Fan Y M, et al. Effects of short-period grazing on soil active organic carbon fractions in Zhaosu meadow steppe. Pratacultural Science, 2013, 30(12): 1926-1932. |
| 杨合龙, 孙宗玖, 范燕敏, 等. 短期放牧对昭苏草甸草原土壤活性有机碳组分的影响. 草业科学, 2013, 30(12): 1926-1932. | |
| 19 | Xu H F. The impact of different utilization methods on the organic carbon content of Longli grassland. South China Agriculture, 2017, 11(28): 80-82. |
| 徐海峰. 不同利用方式对龙里草地有机碳含量的影响. 南方农业, 2017, 11(28): 80-82. | |
| 20 | Hao G, Yan Y Z, Li Y, et al. Effects of different mowing frequencies on soil carbon and nitrogen changes in Leymus chinensis steppe of Hunlun Buir. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2018, 24(2): 195-199. |
| 郝广, 闫勇智, 李阳, 等. 不同刈割频次对呼伦贝尔羊草草原土壤碳氮变化的影响. 应用与环境生物学报, 2018, 24(2): 195-199. | |
| 21 | Zhao N, Zhuang Y, Zhao J. Effects of grassland managements on soil organic carbon and microbial biomass carbon. Pratacultural Science, 2014, 31(3): 367-374. |
| 赵娜, 庄洋, 赵吉. 放牧和补播对草地土壤有机碳和微生物量碳的影响. 草业科学, 2014, 31(3): 367-374. | |
| 22 | Wang Y S, Zhao N S, Xu Z R, et al. The relationship between the yield of Stipa baicalensis grassland and ecological factors in Northeastern China and its prediction model. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 1991, 15(3): 286-295. |
| 王昱生, 赵妮珊, 徐中儒, 等. 中国东北部贝加尔针茅(Stipa baicalensis)草原生产量与生态因素的关系及其预测模型. 植物生态学报, 1991, 15(3): 286-295. | |
| 23 | Li W J, Liu H M, Zhao J N, et al. Effects of nitrogen and water addition on plant species diversity and biomass of common species in the Stipa baicalensis steppe, Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(19): 6460-6469. |
| 李文娇, 刘红梅, 赵建宁, 等. 氮素和水分添加对贝加尔针茅草原植物多样性及生物量的影响. 生态学报, 2015, 35(19): 6460-6469. | |
| 24 | Bao S D . Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis (3rd Edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2005: 45-52. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第3版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2005: 45-52. | |
| 25 | Jones D, Willett V. Experimental evaluation of methods to quantify dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2006, 38(5): 991-999. |
| 26 | Zhang L M, Xu M G, Lou Y L, et al. Soil organic carbon fractionation methods. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2014(4): 1-6. |
| 张丽敏, 徐明岗, 娄翼来, 等. 土壤有机碳分组方法概述. 中国土壤与肥料, 2014(4): 1-6. | |
| 27 | Vance E D, Brookes P C, Jenkinson D S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1987, 19(6): 703-707. |
| 28 | Ji X. Changes of soil organic carbon in Hulunbuir grassland under the policy of return grazing to grassland. Kashgar: Kashgar University, 2019. |
| 纪翔. 退牧还草政策影响下呼伦贝尔草地土壤有机碳变化. 喀什: 喀什大学, 2019. | |
| 29 | Zhang J N, Lai X, Li G, et al. Response of plant diversity and soil nutrient condition to grazing disturbance in Stipa baicalensis Roshev. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2010, 18(2): 177-182. |
| 张静妮, 赖欣, 李刚, 等. 贝加尔针茅草原植物多样性及土壤养分对放牧干扰的响应. 草地学报, 2010, 18(2): 177-182. | |
| 30 | Qiu X, Zhao J N, Li W Y, et al. Effects of different land-use types on soil active organic carbon in the Stipa klemenaii desert steppe of Inner Mongolia. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(9): 1-9. |
| 邱璇, 赵建宁, 李文亚, 等. 不同利用方式对小针茅荒漠草原土壤活性有机碳的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(9): 1-9. | |
| 31 | Zhang L, Sun X Y, Qiao Y, et al. Distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon and its stable carbon isotope composition in desertification grassland under different grazing intensities. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 23(6): 149-153. |
| 张林, 孙向阳, 乔永, 等. 不同放牧强度下荒漠草原土壤有机碳及其δ~(13) C值分布特征. 水土保持学报, 2009, 23(6): 149-153. | |
| 32 | Wang H Y, Dong Z, Guo J Y, et al. Effects of different grazing intensities on total and light fraction organic carbon and nitrogen storages of soil in Stipa grandis steppe. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 29(6): 101-106, 207. |
| 王合云, 董智, 郭建英, 等. 不同放牧强度对大针茅草原土壤全土及轻组碳氮储量的影响. 水土保持学报, 2015, 29(6): 101-106, 207. | |
| 33 | Lan R J, Guo J Y, Yin Z D, et al. Effects of soil erosion on the soil organic carbon of typical steep under different grazing intensities. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(4): 172-177. |
| 兰瑞君, 郭建英, 尹忠东, 等. 不同放牧强度下土壤侵蚀对典型草原土壤有机碳的影响. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(4): 172-177. | |
| 34 | An H, Xu K. The effect of grazing disturbance on soil properties in desert steppe. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(4): 35-42. |
| 安慧, 徐坤. 放牧干扰对荒漠草原土壤性状的影响. 草业学报, 2013, 22(4): 35-42. | |
| 35 | Feyisa K, Beyene S, Angassa A, et al. Effects of enclosure management on carbon sequestration, soil properties and vegetation attributes in East African rangelands. Catena, 2017, 159: 9-19. |
| 36 | Maidinuer A, Li D P, Sun T, et al. Effects of utilization modes on soil organic carbon components in alpine meadow. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2018, 41(1): 55-60. |
| 买迪努尔·阿不来孜, 李典鹏, 孙涛, 等. 利用方式对高寒草地土壤有机碳组分的影响. 新疆农业大学学报, 2018, 41(1): 55-60. | |
| 37 | Guan G Y, Fan Y M, Wu H Q, et al. Effects of fencing on soil active organic carbon and carbon pool management index in mountain meadow steppe. Pratacultural Science, 2014, 31(9): 1618-1622. |
| 管光玉, 范燕敏, 武红旗, 等. 封育对山地草甸草原土壤活性有机碳及碳库管理指数的影响. 草业科学, 2014, 31(9): 1618-1622. | |
| 38 | Socher S A, Prati D, Boch S, et al. Direct and productivity-mediated indirect effects of fertilization, mowing and grazing on grassland species richness. The Journal of Ecology, 2012, 100(6): 1391-1399. |
| 39 | Belay T A, Zhou X, Su B, et al. Labile, recalcitrant, and microbial carbon and nitrogen pools of a tallgrass prairie soil in the US Great Plains subjected to experimental warming and clipping. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2009, 41(1): 110-116. |
| 40 | Nie C, Niu L, Zhang X B, et al. Effects of grazing on soil respiration in typical steppe during growing season in Inner Mongolia. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(3): 402-411. |
| 聂成, 牛磊, 张旭博, 等. 放牧模式对内蒙古典型草原生长季土壤呼吸速率的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(3): 402-411. | |
| 41 | Milchunas D G, Lauenroth W K. Quantitative effects of grazing on vegetation and soils over a global range of environments: Ecological archives M063-001. Ecological Monographs, 1993, 63(4): 327-366. |
| 42 | Prieto L H, Bertiller M B, Carrera A L, et al. Soil enzyme and microbial activities in a grazing ecosystem of Patagonian Monte, Argentina. Geoderma, 2011, 162(3/4): 281-287. |
| 43 | Bai T X, Bai Y, Liu A N, et al. The effect of mowing and nutrient adding back on the biomass and compositions of Leymus chinensis grassland plant community. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2017, 25(6): 1206-1211. |
| 白天晓, 白杨, 刘安娜, 等. 刈割和养分回添对羊草草原植物群落生物量及其构成的影响. 草地学报, 2017, 25(6): 1206-1211. | |
| 44 | Wang Z R, Yang S, Ma R A, et al. Responses of soil physicochemical properties and microbial characteristics to mowing and nitrogen addition in a meadow steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(9): 3010-3018. |
| 王志瑞, 杨山, 马锐骜, 等. 内蒙古草甸草原土壤理化性质和微生物学特性对刈割与氮添加的响应. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(9): 3010-3018. | |
| 45 | Wang B, Sun G, Luo P, et al. Labile and recalcitrant carbon and nitrogen pools of an alpine meadow soil from the Eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau subjected to experimental warming and grazing. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(6): 1506-1514. |
| 王蓓, 孙庚, 罗鹏, 等. 模拟升温和放牧对高寒草甸土壤有机碳氮组分和微生物生物量的影响. 生态学报, 2011, 31(6): 1506-1514. | |
| 46 | Li J C, Gao M, Tian D, et al. Effects of straw and biochar on soil organic carbon and its active components. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(5): 39-50. |
| 黎嘉成, 高明, 田冬, 等. 秸秆及生物炭还田对土壤有机碳及其活性组分的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 39-50. | |
| 47 | Luo M, Tian D, Gao M, et al. Soil organic carbon of purple soil as affected by different application of biochar. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(9): 4327-4337. |
| 罗梅, 田冬, 高明, 等. 紫色土壤有机碳活性组分对生物炭施用量的响应. 环境科学, 2018, 39(9): 4327-4337. | |
| 48 | Xu M L, Wu W, Yan Z M, et al. Content and vertical distribution of soil labile organic carbons in different land use types in the tidal flat area. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 44(4): 167-175. |
| 许梦璐, 吴炜, 颜铮明, 等. 滨海滩涂不同土地利用类型土壤活性有机碳含量与垂直分布. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(4): 167-175. | |
| 49 | Wang C Y, Zhang J J, Lv Y L, et al. Effects of long-term grazing exclusion on soil organic carbon fractions in the grasslands of Inner Mongolia. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(5): 31-39. |
| 王春燕, 张晋京, 吕瑜良, 等. 长期封育对内蒙古羊草草地土壤有机碳组分的影响. 草业学报, 2014, 23(5): 31-39. | |
| 50 | Zhang W M, Wu M, Shao X X, et al. Changes in soil organic carbon and its active fractions during different reclamation period on the South Coast of Hangzhou Bay. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 28(2): 226-231. |
| 张文敏, 吴明, 邵学新, 等. 杭州湾南岸不同围垦年限农田土壤有机碳及其活性组分变化. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(2): 226-231. | |
| 51 | Ma S W. Study on the regulation mechanism of different grass-managements practices to soil carbon pool behavior and the response of plant photosynthesis in apple orchard. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2016. |
| 马思文. 草域管理对自然生草苹果园碳库行为调控及植株光合生理响应研究. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2016. | |
| 52 | Wang Y, Ruan H, Huang L, et al. Soil labile organic carbon with different land uses in reclaimed land area from Taihu Lake. Soil Science, 2010, 175(12): 624-630. |
| 53 | Wang G B, Zhao X L, Wang M H, et al. Effects of land use change on soil readily oxidizable carbon in a coastal area of Northern Jiangsu Province, East China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(4): 921-926. |
| 王国兵, 赵小龙, 王明慧, 等. 苏北沿海土地利用变化对土壤易氧化碳含量的影响. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(4): 921-926. | |
| 54 | Xie Z M, Ni J Z, Xu J M. Advances in soil water-soluble organic carbon research. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2003, 12(1): 71-75. |
| 谢正苗, 倪进治, 徐建民. 土壤水溶性有机碳的研究进展. 生态环境学报, 2003, 12(1): 71-75. | |
| 55 | Liu X D. Characteristics of soil labile organic carbon fractions in different communities of desert steppe. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2017. |
| 刘学东. 荒漠草原不同群落类型土壤活性有机碳组分特征研究. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2017. | |
| 56 | Hu H Q, Lu X, Sun L. Research review on soil active organic carbon fractionation and analytical methods. Forest Engineering, 2012, 28(5): 18-22. |
| 胡海清, 陆昕, 孙龙. 土壤活性有机碳分组及测定方法. 森林工程, 2012, 28(5): 18-22. | |
| 57 | Xiao Y, Zhang Y G, Zhang X Q. Effects of land use change on soil organic carbon and microbial biomass carbon in Miyaluo forest area. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2006, 17(11): 2029-2033. |
| 肖烨, 张于光, 张小全. 米亚罗林区土地利用变化对土壤有机碳和微生物量碳的影响. 应用生态学报, 2006, 17(11): 2029-2033. | |
| 58 | Kallenbach C M, Wallenstein M D, Schipanksi M E, et al. Managing agroecosystems for soil microbial carbon use efficiency: Ecological unknowns, potential outcomes, and a path forward. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 1146. |
| 59 | Hu Y, Jiang S, Yuan S, et al. Changes in soil organic carbon and its active fractions in different desertification stages of alpine-cold grassland in the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(1): 348. |
| 60 | Lu Y, Xu H W. Research progress on soil carbon mineralization and active organic carbon influencing factors. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(10): 4-7. |
| 卢妍, 徐洪文. 土壤碳矿化及活性有机碳影响因子研究进展. 江苏农业科学, 2014, 42(10): 4-7. | |
| 61 | Liu X D, Chen L, Yang X G, et al. Characteristics of soil labile organic carbon fractions and their relationship with soil enzyme activities in four typical communities in desert steppe. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2016, 36(9): 1882-1890. |
| 刘学东, 陈林, 杨新国, 等. 荒漠草原典型植物群落土壤活性有机碳组分特征及其与酶活性的关系. 西北植物学报, 2016, 36(9): 1882-1890. |
| [1] | 徐睿智, 吴晓娟, 杨惠敏. 刈割后追肥对建植当年紫花苜蓿生长和生产性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 195-204. |
| [2] | 付刚, 王俊皓, 李少伟, 何萍. 藏北高寒草地牧草营养品质对放牧的响应机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 38-50. |
| [3] | 赵京东, 乌云娜, 宋彦涛. 短期围封对辽西北退化草地群落牧草品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 51-61. |
| [4] | 郭丰辉, 丁勇, 马文静, 李贤松, 李西良, 侯向阳. 母体放牧经历对羊草克隆后代干旱敏感性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 119-126. |
| [5] | 赵京东, 宋彦涛, 徐鑫磊, 乌云娜. 施氮和刈割对辽西北退化草地牧草产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 36-48. |
| [6] | 徐鑫磊, 宋彦涛, 赵京东, 乌云娜. 施肥和刈割对呼伦贝尔草甸草原牧草品质的影响及其与植物多样性的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 1-10. |
| [7] | 李晨, Ahmad Anum Ali, 张剑搏, 梁泽毅, 丁学智, 阎萍. 冷季牦牛和黄牛采食行为、血清生化指标与瘤胃发酵参数的比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 162-169. |
| [8] | 吕广一, 徐学宝, 高翠萍, 于志慧, 王新雅, 王成杰. 放牧对内蒙古不同类型草原植物和土壤总氮与稳定氮同位素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 208-214. |
| [9] | 王红林, 左艳春, 严旭, 周晓康, 寇晶, 杨希智, 郭俊英, 蒲军, 张浩仁, 杜周和. 刈割高度与施氮量对饲料桑全株产量及营养品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 203-211. |
| [10] | 季波, 何建龙, 吴旭东, 王占军, 谢应忠, 蒋齐. 宁夏典型天然草地土壤有机碳及其活性组分变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 24-35. |
| [11] | 鲍根生, 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 尹亚丽, 王宏生. 围封和防除狼毒对狼毒斑块土壤理化性质和微生物量影响的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 63-72. |
| [12] | 刘红梅, 张海芳, 赵建宁, 王慧, 秦洁, 杨殿林, 张乃芹. 氮添加对贝加尔针茅草原土壤活性有机碳和碳库管理指数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 18-26. |
| [13] | 孙世贤, 丁勇, 李夏子, 吴新宏, 闫志坚, 尹强, 李金卓. 放牧强度季节调控对荒漠草原土壤风蚀的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 23-29. |
| [14] | 孔凡林, 刁其玉, 渠建江, 屠焰. 构树在肉牛瘤胃中降解特性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 179-189. |
| [15] | 任昱鑫, 代寒凌, 田新会, 杜文华. 添加剂对甘肃省高寒牧区不同刈割期小黑麦青贮饲料营养品质和青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 197-206. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||