

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 12-21.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021007
金玲1( ), 陆颖1, 马红彬1,2,3, 谢应忠1,2,3, 沈艳1,2,3(
), 陆颖1, 马红彬1,2,3, 谢应忠1,2,3, 沈艳1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2021-01-05
修回日期:2021-04-06
出版日期:2022-04-20
发布日期:2022-01-25
通讯作者:
沈艳
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: nxshenyan@163.com基金资助:
Ling JIN1( ), Ying LU1, Hong-bin MA1,2,3, Ying-zhong XIE1,2,3, Yan SHEN1,2,3(
), Ying LU1, Hong-bin MA1,2,3, Ying-zhong XIE1,2,3, Yan SHEN1,2,3( )
)
Received:2021-01-05
Revised:2021-04-06
Online:2022-04-20
Published:2022-01-25
Contact:
Yan SHEN
摘要:
了解草地群落类型、分布及其与土壤环境的关系,对草地科学管理及生物多样性保护具有重要意义。以内蒙古鄂托克前旗荒漠草原的100个样地为研究对象,通过野外调查与室内分析相结合的方法,对试验区内100个样地的植物群落数量特征进行观测和分析,测定土壤理化因子,采用双向指示种法(two-way indicator species analysis,TWINSPAN),对植物群落数量进行分类,并采用典范对应分析法(CCA)分析植物群落与土壤因子的关系,结果表明: 1)研究区内荒漠草原分为黑沙蒿+短花针茅群落,短花针茅+芨芨草群落,冰草+芨芨草群落,黑沙蒿+苦豆子群落,中间锦鸡儿+牛枝子群落,短花针茅+猫头刺群落,苦豆子+短花针茅群落,大针茅+白刺群落8个类型。2)CCA排序结果表明,土壤主要理化因子与排序轴的相关性由大到小分别为碱解氮、速效钾、全磷、土壤容重、全氮、速效磷、有机质和总碳。碱解氮和速效钾对内蒙古鄂托克前旗荒漠草原植物群落分布影响较大。3)TWINSPAN分类与CCA排序结合反映了群落分布特征与环境因子之间的关系,可为内蒙古鄂托克前旗荒漠草原生态建设和可持续利用提供参考。
金玲, 陆颖, 马红彬, 谢应忠, 沈艳. 内蒙古鄂托克前旗荒漠草原植物群落的数量分类与排序[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 12-21.
Ling JIN, Ying LU, Hong-bin MA, Ying-zhong XIE, Yan SHEN. Numerical classification and ordination of the desert steppe plant community in Etuokeqianqi, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(4): 12-21.
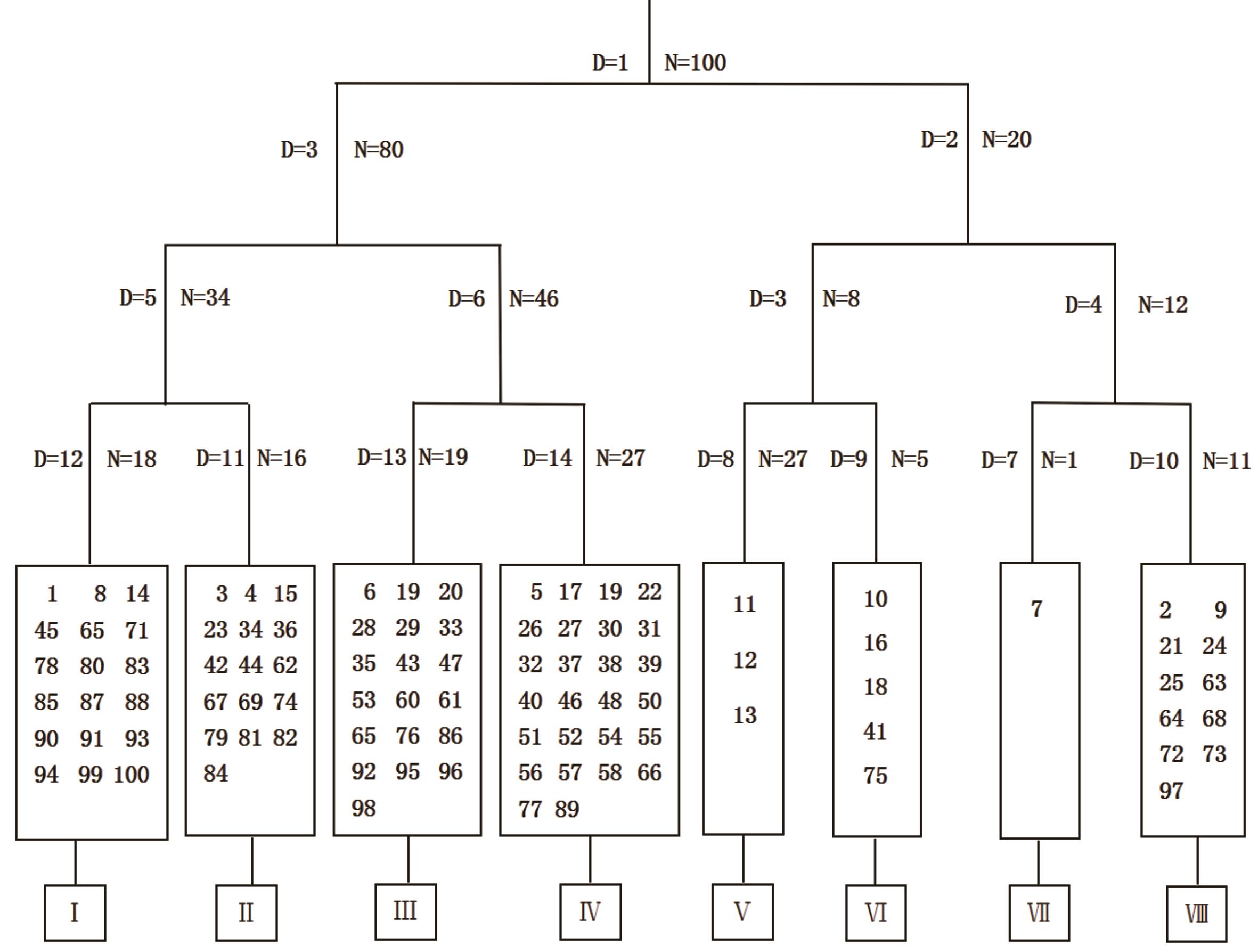
图2 内蒙古鄂托克前旗荒漠草原100个样地群落的双向指示种分类树状图D: 分类次序Sort order; N: 组内样地数Number of plots in the group; 1~100: 样地编号Sample number; Ⅰ~Ⅷ: 群落编号Community number.
Fig.2 Dendrogram of two-way indicator species classification of 100 sample plots in desert steppe in Etuokeqianqi, Inner Mongolia
| 指标Index | 第1轴The first axis | 第2轴The second axis | 第3轴The third axis | 第4轴The fourth axis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值Eigenvalues | 0.4998 | 0.3147 | 0.1953 | 0.1465 |
| 累计解释变量Explained variation cumulative | 5.03 | 8.20 | 10.17 | 11.65 |
| 非典型相关Pseudo-canonical correlation | 0.7898 | 0.7781 | 0.7153 | 0.6216 |
| 累计解释拟合变量Explained fitted variation cumulative (%) | 33.87 | 55.20 | 68.44 | 78.37 |
表1 CCA排序统计
Table 1 CCA sorting statistics
| 指标Index | 第1轴The first axis | 第2轴The second axis | 第3轴The third axis | 第4轴The fourth axis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值Eigenvalues | 0.4998 | 0.3147 | 0.1953 | 0.1465 |
| 累计解释变量Explained variation cumulative | 5.03 | 8.20 | 10.17 | 11.65 |
| 非典型相关Pseudo-canonical correlation | 0.7898 | 0.7781 | 0.7153 | 0.6216 |
| 累计解释拟合变量Explained fitted variation cumulative (%) | 33.87 | 55.20 | 68.44 | 78.37 |
土壤因子 Soil factor | 解释变量 Explains (%) | 贡献值 Contribution (%) | 置换检验 Pseudo-F | 显著性 P | 土壤因子 Soil factor | 解释变量 Explains (%) | 贡献值 Contribution (%) | 置换检验 Pseudo-F | 显著性 P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H6 | 4.6 | 30.8 | 4.7 | 0.006 | H7 | 1.4 | 9.1 | 1.4 | 0.064 |
| H 3 | 2.9 | 19.4 | 3.0 | 0.002 | H4 | 1.0 | 6.8 | 1.1 | 0.324 |
| H8 | 1.7 | 11.3 | 1.8 | 0.010 | H5 | 1.0 | 6.6 | 1.1 | 0.376 |
| H1 | 1.6 | 11.1 | 1.8 | 0.008 | H2 | 0.7 | 4.9 | 0.8 | 0.780 |
表2 内蒙古鄂托克前旗荒漠草原土壤因子与CCA排序轴相关分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis between soil factors and CCA ordination axis of desert steppe in Etuokeqianqi, Inner Mongolia
土壤因子 Soil factor | 解释变量 Explains (%) | 贡献值 Contribution (%) | 置换检验 Pseudo-F | 显著性 P | 土壤因子 Soil factor | 解释变量 Explains (%) | 贡献值 Contribution (%) | 置换检验 Pseudo-F | 显著性 P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H6 | 4.6 | 30.8 | 4.7 | 0.006 | H7 | 1.4 | 9.1 | 1.4 | 0.064 |
| H 3 | 2.9 | 19.4 | 3.0 | 0.002 | H4 | 1.0 | 6.8 | 1.1 | 0.324 |
| H8 | 1.7 | 11.3 | 1.8 | 0.010 | H5 | 1.0 | 6.6 | 1.1 | 0.376 |
| H1 | 1.6 | 11.1 | 1.8 | 0.008 | H2 | 0.7 | 4.9 | 0.8 | 0.780 |
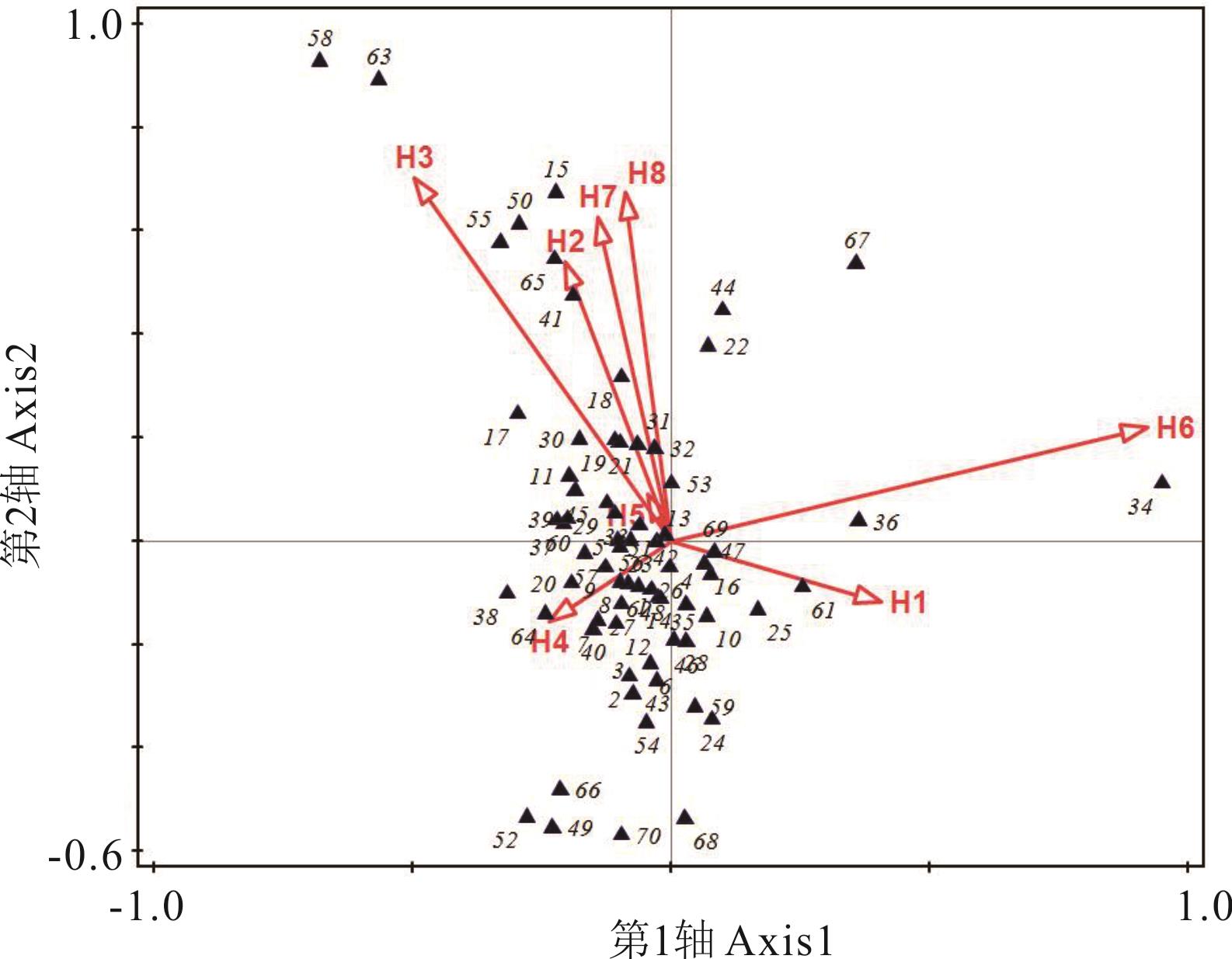
图5 内蒙古鄂托克前旗荒漠草原CCA物种排序1: 猪毛蒿A. scoparia; 2: 黑沙蒿A. ordosica; 3: 甘遂E. kansui; 4: 苦豆子S. alopecuroides; 5: 骆驼蓬P. harmala; 6: 华北白前C. mongolicum;7: 蒙古虫实C. mongolicum; 8: 牛枝子L. potaninii ; 9: 冰草A. cristatum; 10: 砂蓝刺头E. gmelini; 11: 赖草L. secalinus; 12: 雾冰藜B. dasyphylla; 13: 白草P. flaccidum;14: 刺藜C. aristatum;15: 芨芨草A. splendens; 16: 二色棘豆O. bicolor; 17: 短花针茅S. breviflora; 18: 芦苇P. australis; 19: 碱蓬S. glauca; 20: 披针叶野决明T. lanceolata; 21: 猪毛菜S. collina; 22: 长芒草S. bungeana; 23: 丛生隐子草C. caespitosa; 24: 中间锦鸡儿C. intermedia; 25: 狭叶锦鸡儿C. stenophylla; 26: 阿尔泰狗娃花A. altaicus; 27: 圆头藜C. strictum; 28: 狗尾草S. viridis; 29: 甘草G. uralensis; 30: 猫头刺O. aciphylla; 31:白刺N. tangutorum; 32: 早熟禾P. annua; 33: 北莎草C. fuscus; 34: 冷蒿A. frigida; 35: 冬青叶兔唇花L. ilicifolius; 36: 蒺藜T. terrester; 37: 蒙古韭A. mongolicum; 38: 银灰旋花C. ammannii; 39: 沙蓬A. squarrosum; 40: 细枝山竹子C. scoparium; 41: 艾蒿A. argyi; 42: 蒲公英T. mongolicum; 43: 倒羽叶风毛菊S. runcinata; 44: 斜茎黄耆A. laxmannii; 45: 西伯利亚蓼P. sibiricum; 46: 苦苣菜S. oleraceus; 47: 脓疮草P. alaschanica; 48: 角茴香H. erectum; 49: 硬阿魏F. bungeana; 50: 蓼子朴I. salsoloides; 51: 车前P. asiatica; 52: 节节草E. ramosissimum; 53: 少花米口袋G. verna; 54: 大针茅S. grandis; 55: 苦荬菜I. polycephala; 56: 盐爪爪K. foliatum; 57: 细裂叶莲蒿A. gmelinii; 58: 远志P. tenuifolia; 59: 滨藜A. patens; 60: 角蒿I. sinensis; 61: 女娄菜S. aprica; 62: 唐松草T. sibiricum; 63: 兴安天门冬A. dauricus; 64: 二裂委陵菜P. bifurca; 65: 二色补血草L. bicolor; 66: 黄花补血草L. aureum; 67: 尖头叶藜C. acuminatum; 68: 藜C. album; 69: 草木犀M. officinalis; 70: 鼠掌老鹳草G. sibiricum.
Fig.5 CCA species ordination of desert steppe in Etuokeqianqi, Inner Mongolia
| 1 | Fernando V, Bastias C C, Oscar G. Species coexistence in a changing world. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 1-15. |
| 2 | Zhao C J, Kang M Y, Lei J Q. Relationships between plant community characteristics and environmental factors in the typical profiles from Dzungaria Basin. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(10): 2669-2677. |
| 赵从举, 康慕谊, 雷加强. 准噶尔盆地典型地段植物群落及其与环境因子的关系. 生态学报, 2011, 31(10): 2669-2677. | |
| 3 | Zhang F, Zhang J T, Zhang F. Pattern of forest vegetation and its environmental interpretation in Zhuweigou, Lishan Mountain Nature Reserve, Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2003, 23(3): 421-427. |
| 张峰, 张金屯, 张峰. 历山自然保护区猪尾沟森林群落植被格局及环境解释. 生态学报, 2003, 23(3): 421-427. | |
| 4 | Ahmad S S, Quratulann. Vegetation classification in Ayubia National Park, Pakistan using ordination methods. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 2011, 43(5): 2315-2321. |
| 5 | Bai X H, Zhang J T, Cao K, et al. Relationship between forest communities and the environment in the Xiaowutai Mountain National Nature Reserve, Hebei. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(11): 3683-3696. |
| 白晓航, 张金屯, 曹科, 等. 河北小五台山国家级自然保护区森林群落与环境的关系. 生态学报, 2017, 37(11): 3683-3696. | |
| 6 | Liu R H, Tu H R, Li J F, et al. Numerical classification and ordination of Cyclobalanopsis glauca communities in karst hills of Guilin, Southwest China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(22): 8595-8605. |
| 刘润红, 涂洪润, 李娇凤, 等. 桂林岩溶石山青冈群落数量分类与排序. 生态学报, 2019, 39(22): 8595-8605. | |
| 7 | Zhang J T. Quantitative ecology. Beijing: Science Press, 2004. |
| 张金屯. 数量生态学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004. | |
| 8 | Han J W, Wang J, Zhang X, et al. Numerical classification and ordination of the plant community in Xiaoqinling National Nature Reserve. Henan Science, 2015, 33(4): 547-552. |
| 韩军旺, 王进, 张旭, 等. 小秦岭国家级自然保护区植物群落数量分类与排序. 河南科学, 2015, 33(4): 547-552. | |
| 9 | Ma K P, Chen L Z, Yu S L, et al. Study on the diversity of plant communities in Dongling Mountain area of Beijing Ⅰ. basic types of plant communities//Research progress of biodiversity- proceedings of the first national symposium on biodiversity conservation and sustainable utilization biodiversity committee. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1994. |
| 马克平, 陈灵芝, 于顺利, 等. 北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性的研究Ⅰ植物群落的基本类型//生物多样性研究进展——首届全国生物多样性保护与持续利用研讨会论文集.北京: 中国科学院, 1994. | |
| 10 | Lai J S, Mi X C. Ordination analysis of ecological data using Vegan package in R//Proceedings of the 9th national biodiversity conservation and sustainable utilization symposium. Xiamen: International Biodiversity Program China Committee, Bureau of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2010. |
| 赖江山, 米湘成. 基于Vegan软件包的生态学数据排序分析//第九届全国生物多样性保护与持续利用研讨会论文集. 厦门: 国际生物多样性计划中国委员会, 中国科学院生命科学与生物技术局, 2010. | |
| 11 | Vittoz P, Bayfield N, Brooker R, et al. Reproducibility of species lists, visual cover estimates and frequency methods for recording high‐mountain vegetation. Journal of Vegetation Science, 2010, 21(6): 1035-1047. |
| 12 | Lu B, Bu L G, Si Q B L G. Countermeasures and suggestions for promoting the sustainable development of family farms and pastures in Inner Mongolia——A case study of Etuoke Qianqi in Ordos city. Modern Agriculture, 2019(8): 12-14. |
| 陆斌, 布拉格, 斯庆毕力格.推进内蒙古家庭农牧场可持续发展的对策建议——以鄂尔多斯市鄂托克前旗为例. 现代农业, 2019(8): 12-14. | |
| 13 | Ermakov N, Makhatkov I. Classification and ordination of north boreal light-coniferous forests of the West Siberian Plain. Plant Biosystems, 2011, 145(S): 199-207. |
| 14 | Liu B, Pan C D, Li G H, et al. Quantitative classification and sequencing of communities in pyrogenic succession of Kanas Taiga. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(10): 1961-1973. |
| 刘博, 潘存德, 李贵华, 等. 喀纳斯泰加林火成演替群落数量分类与排序.生态环境学报, 2019, 28(10): 1961-1973. | |
| 15 | Bao X T, Ding L B, Yao S C, et al. Quantitative classification and ordination of grassland communities on the Lhasa River Basin, 2019, 39(3): 779-786. |
| 包小婷, 丁陆彬, 姚帅臣, 等. 拉萨河流域植物群落的数量分类与排序.生态学报, 2019, 39(3): 779-786. | |
| 16 | Wang L, Song N P, Chen L, et al. Increase in soil coarse sand content and decrease in soil nutrient levels accompany the transformation of perennial communities to annual communities in desert grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(11): 183-189. |
| 王磊, 宋乃平, 陈林, 等. 荒漠草原土壤粗质化和养分减少伴随多年生群落转变为一年生群落. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 183-189. | |
| 17 | Liu B, Zhao W Z, Liu Z L, et al. Changes in species diversity, aboveground biomass,and vegetation cover along an afforestation successional gradient in a semiarid desert steppe of China. Ecological Engineering, 2015, 81(4): 301-311. |
| 18 | Wang T, Wang J S, Ding Y K, et al. Quantitative classification and ordination of plant communities in the upper and middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2019, 10(4): 389-396. |
| 19 | Zhao P, Qu J J, Xu X Y, et al. Desert vegetation distribution and species-environment relationships in an oasis-desert ecotone of northwestern China. Journal of Arid Land, 2019, 11(3): 461-476. |
| 20 | Wang Z R, Yang G J, Yi S H, et al. Effects of environmental factors on the distribution of plant communities in a semi-arid region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecological Research, 2012, 27(4): 667-675. |
| 21 | Wu H, Zhang M X, Wang D X, et al. Diversity characteristics in different layers of the of Pinus tabuliformis-Quercus aliena var. accuteserrata mixed forest and environmental interpretation in the southern slope of Qinling Mountains. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2013, 33(10): 2086-2094. |
| 吴昊, 张明霞, 王得祥, 等. 秦岭南坡油松-锐齿槲栎混交林群落不同层次多样性特征及环境解释. 西北植物学报, 2013, 33(10): 2086-2094. | |
| 22 | Suriguga, Zhang J T, Zhang B, et al. Numerical classification and ordination of forest communities in the Songshan Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(10): 2621-2629. |
| 苏日古嘎, 张金屯, 张斌, 等. 松山自然保护区森林群落的数量分类和排序.生态学报, 2010, 30(10): 2621-2629. | |
| 23 | Xinjiang Comprehensive Investigation Team of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Xinjiang vegetation and its utilization. Beijing: Science Press, 1978: 44-65. |
| 中国科学院新疆综合考察队, 中国科学院植物研究所. 新疆植被及其利用. 北京: 科学出版社, 1978: 44-65. | |
| 24 | Wang Y C, Zhou Y F, Wang D X. The quantitative classification and environmental interpretation of forest communities in the middle area of south slope of Qinling Mountains. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 2016, 25(6): 965-972. |
| 王宇超, 周亚福, 王得祥.秦岭南坡中段主要森林群落类型划分及环境梯度解释.生态环境学报, 2016, 25(6): 965-972. | |
| 25 | Zheng T Y, Wang D, Ji L T, et al. Classification, ordination and diversity pattern of typical forest communities in Taibai Mountain Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(20): 7353-7361. |
| 郑天义, 王丹, 姬柳婷, 等.太白山自然保护区典型森林群落数量分类、排序及多样性格局.生态学报, 2020, 40(20): 7353-7361. | |
| 26 | Yao S C, Wang J S, Ding L B, et al. Quantitative classification and ordination of grassland communities in Lhasa River Valley. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(13): 4779-4788. |
| 姚帅臣, 王景升, 丁陆彬, 等. 拉萨河谷草地群落的数量分类与排序.生态学报, 2018, 38(13): 4779-4788. | |
| 27 | Tang Z H, Yu Q S, Liu H J, et al. Characteristics of alpine vegetation community and its relationship to topographical climate factors in the eastern Qilian Mountain. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(1): 223-232. |
| 唐志红, 尉秋实, 刘虎俊, 等. 祁连山东段高寒植被群落特征及其与地形气候因子关系研究.生态学报, 2020, 40(1): 223-232. | |
| 28 | Dong L S, Zhang X D, Zhou J X, et al. Quantitative classification and ordination of shrub species and communities in a loess landscape of western Shanxi. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(7): 3072-3080. |
| 董林水, 张旭东, 周金星, 等. 晋西黄土丘陵与土石山区交错地带灌木种的数量分类与排序. 生态学报, 2007, 27(7): 3072-3080. | |
| 29 | Kneitel J M, Lessin C L. Ecosystem-phase interactions: aquatic eutrophication decreases terrestrial plant diversity in California vernal pools. Oecologia, 2010, 163(2): 461-469. |
| 30 | Zhang J Q, Li Q, Ren Z W, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on species richness and relationship between species richness and aboveground productivity of alpine meadow of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2010,34(10): 1125-1131. |
| 张杰琦, 李奇, 任正炜, 等. 氮素添加对青藏高原高寒草甸植物群落物种丰富度及其与地上生产力关系的影响. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(10): 1125-1131. | |
| 31 | Wang Y Q, Yin Y L, Li S X. Physicochemical properties and enzymatic activities of alpine meadow at different degradation degrees. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(6): 1108-1116. |
| 王玉琴, 尹亚丽, 李世雄. 不同退化程度高寒草甸土壤理化性质及酶活性分析. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(6): 1108-1116. | |
| 32 | Jin W, Alistair R, Albert L P, et al. Leaf reflectance spectroscopy captures variation in carboxylation capacity across species, canopy environment and leaf age in lowland moist tropical forests. New Phytologist, 2019, 224: 663-674. |
| 33 | Wang T, Yang Y H, Ma W H, Storage,patterns and environmental controls of soil phosphorus in China.Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2008, 44(6): 945-952. |
| 汪涛, 杨元合, 马文红. 中国土壤磷库的大小、分布及其影响因素. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 44(6): 945-952. | |
| 34 | Li T T, Zhang Q D, Duan X M, et al. Comparative study concerning the effects of rare species treatment on RDA ordination. Guihaia, 2015, 35(4): 539-545. |
| 李婷婷, 张钦弟, 段晓梅, 等. 稀有种处理对RDA排序结果影响的比较研究. 广西植物, 2015, 35(4): 539-545. | |
| 35 | Xu G C, Kang M Y, Ma M, et al. The relationship between herbaceous vegetation and environment in middle reach of Halaqingou stream valley, Mt. Daqingshan, Inner Mongolia. Journal of Mountain Science, 2007, 25(4): 393-399. |
| 徐广才, 康慕谊, 马敏, 等. 内蒙古大青山哈拉沁沟流域中游草本植被与环境的关系. 山地学报, 2007, 25(4): 393-399. |
| [1] | 倪芳芳, 吕世杰, 屈志强, 白璐, 孟彪, 张博涵, 李治国. 不同载畜率下荒漠草原非生长季植物群落特征对近地面风沙通量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 26-33. |
| [2] | 张峰, 孙嘉伟, 孙宇, 郑佳华, 乔荠瑢, 赵萌莉. 不同载畜率对短花针茅荒漠草原优势物种间关系及其空间分布特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 1-11. |
| [3] | 吴旭东, 蒋齐, 任小玢, 俞鸿千, 王占军, 何建龙, 季波, 杜建民. 降水水平对荒漠草原生物土壤结皮碳、氮和微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 34-43. |
| [4] | 孙忠超, 郭天斗, 于露, 马彦平, 赵亚楠, 李雪颖, 王红梅. 宁夏东部荒漠草原向灌丛地人为转变过程土壤粒径分形特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 34-45. |
| [5] | 蒙仲举, 陈颜洁, 包斯琴. 苏尼特右旗荒漠草原三种放牧方式下群落斑块特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 13-23. |
| [6] | 顾继雄, 郭天斗, 王红梅, 李雪颖, 梁丹妮, 杨青莲, 高锦月. 宁夏东部荒漠草原向灌丛地转变过程土壤微生物响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 46-57. |
| [7] | 熊梅, 乔荠瑢, 杨阳, 张峰, 郑佳华, 吴建新, 赵萌莉. 不同载畜率下短花针茅和土壤生态化学计量特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 212-219. |
| [8] | 张静静, 刘尊驰, 鄢创, 王云霞, 刘凯, 时新荣, 袁志友. 土壤pH值变化对3种草原类型土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 69-81. |
| [9] | 罗超, 郭小平, 冯昶栋, 叶金鹏, 薛东明. 乌海周边土壤种子库特征及其与地上植被和土壤因子的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 13-28. |
| [10] | 李静, 红梅, 闫瑾, 张宇晨, 梁志伟, 叶贺, 高海燕, 赵巴音那木拉. 短花针茅荒漠草原植被群落结构及生物量对水氮变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 38-48. |
| [11] | 万芳, 蒙仲举, 党晓宏, 王瑞东, 张慧敏. 封育措施下荒漠草原针茅植物-土壤C、N、P化学计量特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 49-55. |
| [12] | 孙世贤, 丁勇, 李夏子, 吴新宏, 闫志坚, 尹强, 李金卓. 放牧强度季节调控对荒漠草原土壤风蚀的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 23-29. |
| [13] | 于露, 周玉蓉, 赵亚楠, 郭天斗, 孙忠超, 王红梅. 荒漠草原土壤种子库对灌丛引入和降水梯度的响应特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 41-50. |
| [14] | 许爱云, 许冬梅, 曹兵, 刘金龙, 于双, 郭艳菊, 马晓静. 宁夏荒漠草原不同群落蒙古冰草种群空间格局及种间关联性[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 171-178. |
| [15] | 谢莉, 宋乃平, 孟晨, 吴婷, 陈晓莹, 李敏岚, 岳健敏. 不同封育年限对宁夏荒漠草原土壤粒径及碳氮储量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 1-10. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||