

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 64-74.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021378
收稿日期:2021-10-19
修回日期:2021-12-29
出版日期:2022-10-20
发布日期:2022-09-14
通讯作者:
刘吉利
作者简介:E-mail: tim11082003@163.com基金资助:
Hai-feng HE1( ), Na WU1, Ji-li LIU1,2,3(
), Na WU1, Ji-li LIU1,2,3( ), Xing XU1
), Xing XU1
Received:2021-10-19
Revised:2021-12-29
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-09-14
Contact:
Ji-li LIU
摘要:
为了探究不同施磷水平对宁夏银北盐碱地区柳枝稷生长发育及耐盐性的影响,通过田间试验,以2种生态型柳枝稷品种“Alamo”和“Pathfinder”为供试材料,采用裂区试验设计,设置不施磷(0) 、施低磷(30 kg·hm-2 P2O5) 和施高磷(90 kg·hm-2 P2O5) 共3个施磷水平,每个处理设3个重复,共计18个小区。分析比较了各生育时期内柳枝稷生长指标、渗透调节物质及抗氧化酶活性的变化,同时采用隶属函数法综合评价了盐碱地柳枝稷的耐盐性。结果表明,随着施磷水平的提高,两种生态型柳枝稷开花期株高、分蘖数、叶面积指数、干物质积累和生物产量等农艺性状和相对叶绿素、丙二醛、可溶性糖含量、过氧化物酶活性等生理特性均呈逐渐升高的总趋势。与不施磷处理相比,分别提高了7.74%、10.21%、14.64%、11.88%、22.22%、3.85%、74.29%、14.70%和57.77%。隶属函数分析结果表明,施低磷处理下柳枝稷各抗盐指标隶属函数值的均值最大。因此,施磷量为30 kg·hm-2 处理时,既可以提高两种生态型柳枝稷的生理特性及生物产量,又能在一定程度上提高其耐盐性,是较为理想的施磷水平。
何海锋, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 许兴. 盐碱条件下施磷对柳枝稷生长发育及耐盐性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 64-74.
Hai-feng HE, Na WU, Ji-li LIU, Xing XU. Effects of phosphorus application on the growth and salt resistance of switchgrass under saline alkali conditions[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 64-74.
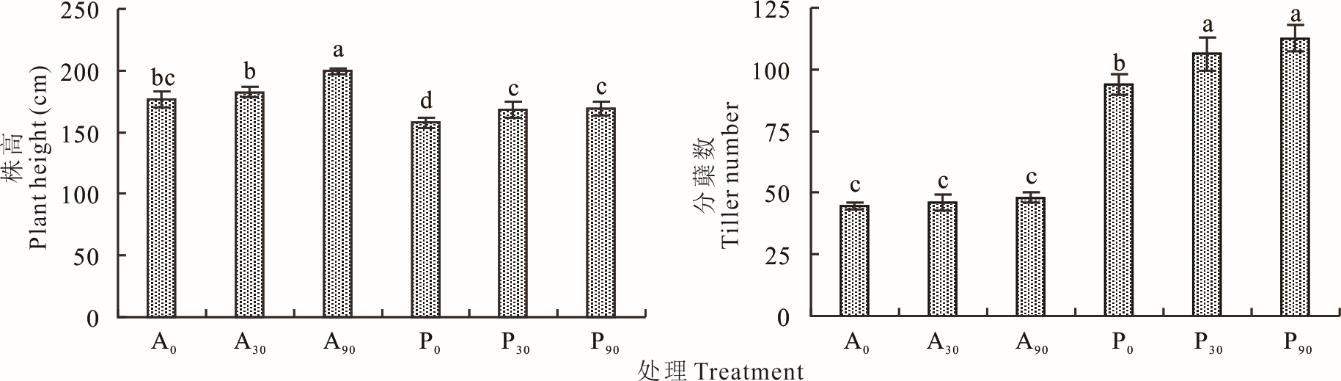
图2 不同施磷水平对柳枝稷株高、分蘖数的影响不同小写字母表示不同处理之间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。 Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig. 2 Effect of different phosphorus application levels on plant height and tiller number of switchgrass
| 处理Treatment | 过氧化物酶POD (U·g-1·FW·min-1) | 过氧化氢酶CAT (U·g-1·FW·min-1) | 超氧化物歧化酶SOD (U·g-1·FW·h-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | 129.17±2.67e | 152.86±5.38c | 1136.08±25.31a |
| A30 | 197.64±1.01d | 204.43±7.91bc | 1271.06±44.20a |
| A90 | 256.92±7.43c | 382.92±3.26a | 1352.84±78.29a |
| P0 | 203.19±1.92d | 182.16±9.37c | 1173.00±50.56a |
| P30 | 271.67±3.61b | 286.20±9.75b | 1278.39±21.94a |
| P90 | 322.50±5.28a | 175.52±3.54c | 1143.46±43.71a |
表1 不同施磷水平对柳枝稷抗氧化酶活性的影响
Table 1 Effect of different phosphorus application levels on the antioxidant enzyme activity of switchgrass
| 处理Treatment | 过氧化物酶POD (U·g-1·FW·min-1) | 过氧化氢酶CAT (U·g-1·FW·min-1) | 超氧化物歧化酶SOD (U·g-1·FW·h-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | 129.17±2.67e | 152.86±5.38c | 1136.08±25.31a |
| A30 | 197.64±1.01d | 204.43±7.91bc | 1271.06±44.20a |
| A90 | 256.92±7.43c | 382.92±3.26a | 1352.84±78.29a |
| P0 | 203.19±1.92d | 182.16±9.37c | 1173.00±50.56a |
| P30 | 271.67±3.61b | 286.20±9.75b | 1278.39±21.94a |
| P90 | 322.50±5.28a | 175.52±3.54c | 1143.46±43.71a |
| 指标Index | PH | TN | LAI | DMA | BY | Pro | MDA | SS | POD | CAT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | -0.68** | |||||||||
| LAI | 0.88** | -0.80** | ||||||||
| DMA | 0.81** | -0.41 | 0.73** | |||||||
| BY | 0.80** | -0.49* | 0.77** | 0.78** | ||||||
| Pro | -0.33 | 0.46 | -0.46 | -0.01 | -0.51* | |||||
| MDA | 0.60* | -0.05 | 0.44 | 0.66** | 0.75** | -0.18 | ||||
| SS | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.53* | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.61* | |||
| POD | -0.02 | 0.67** | -0.21 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.31 | 0.59* | 0.77** | ||
| CAT | 0.70** | -0.29 | 0.54* | 0.67** | 0.46 | 0.25 | 0.57* | 0.61* | 0.26 | |
| SOD | 0.29 | -0.08 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
表2 柳枝稷开花期各生长指标与生理指标之间的相关系数矩阵
Table 2 Correlation coefficient matrix between growth indexes and physiological indexes at flowering stage of switchgrass
| 指标Index | PH | TN | LAI | DMA | BY | Pro | MDA | SS | POD | CAT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | -0.68** | |||||||||
| LAI | 0.88** | -0.80** | ||||||||
| DMA | 0.81** | -0.41 | 0.73** | |||||||
| BY | 0.80** | -0.49* | 0.77** | 0.78** | ||||||
| Pro | -0.33 | 0.46 | -0.46 | -0.01 | -0.51* | |||||
| MDA | 0.60* | -0.05 | 0.44 | 0.66** | 0.75** | -0.18 | ||||
| SS | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.53* | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.61* | |||
| POD | -0.02 | 0.67** | -0.21 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.31 | 0.59* | 0.77** | ||
| CAT | 0.70** | -0.29 | 0.54* | 0.67** | 0.46 | 0.25 | 0.57* | 0.61* | 0.26 | |
| SOD | 0.29 | -0.08 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
处理 Treatment | 相对电导率RC | 脯氨酸 Pro | 丙二醛MDA | 可溶性糖 SS | 过氧化物酶POD | 过氧化氢酶CAT | 超氧化物歧 化酶SOD | 平均值 Mean | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | 0.392 | 0.372 | 0.403 | 0.374 | 0.376 | 0.312 | 0.388 | 0.374 | 6 |
| A30 | 0.759 | 0.217 | 0.229 | 0.892 | 0.354 | 0.224 | 0.623 | 0.471 | 3 |
| A90 | 0.421 | 0.487 | 0.514 | 0.464 | 0.401 | 0.479 | 0.485 | 0.464 | 4 |
| P0 | 0.641 | 0.538 | 0.623 | 0.674 | 0.383 | 0.589 | 0.543 | 0.571 | 2 |
| P30 | 0.652 | 0.572 | 0.613 | 0.524 | 0.737 | 0.580 | 0.657 | 0.619 | 1 |
| P90 | 0.726 | 0.331 | 0.215 | 0.396 | 0.502 | 0.299 | 0.332 | 0.401 | 5 |
表3 盐碱胁迫下柳枝稷各抗盐指标隶属函数值
Table 3 Membership function values of each drought resistance index under saline alkali stress in switchgrass
处理 Treatment | 相对电导率RC | 脯氨酸 Pro | 丙二醛MDA | 可溶性糖 SS | 过氧化物酶POD | 过氧化氢酶CAT | 超氧化物歧 化酶SOD | 平均值 Mean | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | 0.392 | 0.372 | 0.403 | 0.374 | 0.376 | 0.312 | 0.388 | 0.374 | 6 |
| A30 | 0.759 | 0.217 | 0.229 | 0.892 | 0.354 | 0.224 | 0.623 | 0.471 | 3 |
| A90 | 0.421 | 0.487 | 0.514 | 0.464 | 0.401 | 0.479 | 0.485 | 0.464 | 4 |
| P0 | 0.641 | 0.538 | 0.623 | 0.674 | 0.383 | 0.589 | 0.543 | 0.571 | 2 |
| P30 | 0.652 | 0.572 | 0.613 | 0.524 | 0.737 | 0.580 | 0.657 | 0.619 | 1 |
| P90 | 0.726 | 0.331 | 0.215 | 0.396 | 0.502 | 0.299 | 0.332 | 0.401 | 5 |
| 1 | Tang W, Yu Y X. Adaptation mechanisms of legume to phosphorus deficiency. Pratacultural Science, 2014, 31(8): 1538-1548. |
| 唐伟, 玉永雄. 豆科植物低磷胁迫的适应机制. 草业科学, 2014, 31(8): 1538-1548. | |
| 2 | Shen J B, Yuan L X, Zhang J L, et al. Phosphorus dynamics: From soil to plant. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(3): 997-1005. |
| 3 | Cordell D, White S. Life’s bottleneck: Sustaining the world’s phosphorus for a food secure future. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 2014, 39(1): 161-188. |
| 4 | Qin X M, Nong Y Q, Luo Y F, et al. Effects of phosphorus application on inorganic phosphorus forms and phosphorus absorption in rhizosphere red soil of maize soybean intercropping. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021-08-21: 1-12. http: //kns. cnki. net/kcms/detail/11. 5498. S. 20210813. 1044. 002. html. |
| 覃潇敏, 农玉琴, 骆妍飞, 等. 施磷量对玉米-大豆间作根际红壤无机磷形态及磷吸收的影响.中国土壤与肥料, 2021-08-21: 1-12. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.5498.S.20210813.1044.002.html. | |
| 5 | Zhang X Y, Wang S S, Li X L, et al. Effects of potassium application rates on carbohydrate content and resistance to thrips (Thripidae) in alfalfa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(10): 153-162. |
| 张晓燕, 王森山, 李小龙, 等. 不同施钾量对苜蓿碳水化合物含量及抗蓟马的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(10): 153-162. | |
| 6 | He P, Wu M, Wei J S, et al. Effects of different phosphorus levels on nitrogen and potassium absorption, distribution and utilization of rubber seedlings. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27 (16): 1-6. |
| 何鹏, 吴敏, 韦家少, 等. 不同磷水平对橡胶树幼苗氮钾吸收、分配与利用的影响. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(16): 1-6. | |
| 7 | Hu G X, Peng R, Cui X N, et al. Effects of phosphorus application on distribution of photosynthetic products in roots, stems and leaves of alfalfa and resistance to thrips. Chinese Journal of Ecological Agriculture, 2020, 28 (7): 969-978. |
| 胡桂馨, 彭然, 崔晓宁, 等. 施磷对苜蓿光合产物在根茎叶的分配及抗蓟马的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(7): 969-978. | |
| 8 | Rodriguez D, Andrade F H, Goudriaan J. Effect of phosphorus nutrition on tiller emergence in wheat. Plant and Soil, 1999, 202(2): 283-295. |
| 9 | Kang L Y, Li S Q. Effects of phosphorus application in layered water supply on growth and water use efficiency of winter wheat. China Agricultural Science, 2012, 45(1): 85-92. |
| 康利允, 李世清. 分层供水施磷对冬小麦生长及水分利用效率的影响. 中国农业科学, 2012, 45(1): 85-92. | |
| 10 | Lu M, Sun M, Gao Z Q, et al. Effects of different phosphorus application levels on dryland wheat yield and its components. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2018, 37(7): 13-19. |
| 陆梅, 孙敏, 高志强, 等. 不同施磷水平对旱地小麦产量及其构成要素的影响. 灌溉排水学报, 2018, 37(7): 13-19. | |
| 11 | Du Q J, Li J M, Pan T H, et al. Effects of drought stress on leaf water and reactive oxygen metabolism in tomato seedlings under subfreezing temperatures. Journal of Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(12): 151-159. |
| 杜清洁, 李建明, 潘铜华, 等. 亚低温下干旱胁迫对番茄幼苗叶片水分及活性氧代谢的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(12): 151-159. | |
| 12 | Liang Y, Shi Y, Jin X, et al. Effect of light quality on growth and physiological resistance of tomato seedlings under low phosphorus stress. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(1): 56-61. |
| 梁颖, 石玉, 靳琇, 等.低磷胁迫下光质对番茄幼苗生长及生理抗性的影响. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(1): 56-61. | |
| 13 | Feng G, Li X L, Zhang F S, et al. Effect of phosphorus application and AM fungal inoculation on salt tolerance in maize. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2000, 9(2): 22-26. |
| 冯固, 李晓林, 张福锁, 等. 施磷和接种AM真菌对玉米耐盐性的影响. 植物资源与环境学报, 2000, 9(2): 22-26. | |
| 14 | Liu J L, Wu N. Biomass production of switchgrass in saline-alkali land. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 3383(2): 93-96. |
| 15 | Ma Y Q, An Y, Shui J F, et al. Adaptability evaluation of switchgrass cultivars on the Loess Plateau of China. Plant Science, 2011, 181(6): 638-643. |
| 16 | He H F, Wu N, Liu J L, et al. Effect of planting years of switchgrass on physical and chemical properties of saline alkali soil. Journal of Ecological Environment, 2020, 29(2): 285-292. |
| 何海锋, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 等. 柳枝稷种植年限对盐碱土壤理化性质的影响. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(2): 285-292. | |
| 17 | Xiao H, Wang X, Song Y, et al. Research progress in the production of fuel ethanol from energy forage switchgrass. Pratacultural Science, 2011,28 (3): 487-492. |
| 肖晖, 王珣, 宋洋, 等. 利用能源牧草柳枝稷生产燃料乙醇的研究进展. 草业科学, 2011, 28(3): 487-492. | |
| 18 | Ma Y Q, Hao Z Q, Xiong S J, et al. Present status and future of switchgrass going to scale plantation in China. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2012, 17(6): 133-137. |
| 马永清, 郝智强, 熊韶峻, 等. 我国柳枝稷规模化种植现状与前景. 中国农业大学学报, 2012, 17(6): 133-137. | |
| 19 | He H F, Yan C H, Wu N, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics and dry matter accumulation of switchgrass leaves. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29 (11): 141-150. |
| 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 等. 施氮量对柳枝稷叶片叶绿素荧光特性及干物质积累的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 141-150. | |
| 20 | Gao Z L. Experimental technology of plant physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1990. |
| 高志良. 植物生理学实验技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1990. | |
| 21 | Zhang C Y, Xu G F. Comprehensive evaluation of heat resistance of four ground cover plants by membership function method. Pratacultural Science, 2009, 26(2): 57-60. |
| 张朝阳, 许桂芳. 利用隶属函数法对4种地被植物的耐热性综合评价. 草业科学, 2009, 26(2): 57-60. | |
| 22 | Shi Y H, Wan L Q, Liu J N, et al. Analysis of drought resistance principal components and membership function of perennial ryegrass. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2010, 18(5): 669-672. |
| 石永红, 万里强, 刘建宁, 等. 多年生黑麦草耐盐性主成分及隶属函数分析. 草地学报, 2010, 18(5): 669-672. | |
| 23 | He H F, Yan C H, Wu N, et al. Effects of different nitrogen application levels on photosynthetic characteristics and drought resistance of switchgrass. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30 (1): 107-115. |
| 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 等. 不同施氮水平对柳枝稷光合特性及耐盐性的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 107-115. | |
| 24 | Yu Q S, Zhao M, Li C L, et al. Growth and biomass allocation of chilopsis linearis under different soil water stresses. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2006, 25(1): 7-12. |
| 尉秋实, 赵明, 李昌龙, 等. 不同土壤水分胁迫下沙漠葳的生长及生物量的分配特征. 生态学杂志, 2006, 25(1): 7-12. | |
| 25 | Long J R, Ma G H, Wan Y Z, et al. Effect of nitrogen application rate on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of flag leaf in late growth stage of super hybrid medium rice. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(5): 501-507. |
| 龙继锐, 马国辉, 万宜珍, 等. 施氮量对超级杂交中稻生育后期剑叶叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(5): 501-507. | |
| 26 | Ge X L, Yang H S, Liu J, et al. Effects of phosphorus application level on alfalfa growth and grass yield. Journal of Inner Mongolia University for Nationalities (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 24(5): 509-513. |
| 葛选良, 杨恒山, 刘晶, 等. 施磷水平对紫花苜蓿生长及草产量的影响. 内蒙古民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 24(5): 509-513. | |
| 27 | Chen Y X, Li H H, Zhou T, et al. Effects of phosphorus application on leaf area index, dry matter accumulation and distribution and phosphorus fertilizer utilization efficiency of intercropping maize. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(10): 2799-2806. |
| 陈远学, 李汉邯, 周涛, 等. 施磷对间套作玉米叶面积指数、干物质积累分配及磷肥利用效率的影响. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(10): 2799-2806. | |
| 28 | Lian H D, Pei H B, Zhang Y Q, et al. Effects of phosphorus application on morphological and physiological characteristics of different varieties of red adzuki bean. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2015, 21(3): 792-799. |
| 连慧达, 裴红宾, 张永清, 等. 施磷量对不同品种红小豆形态和生理特性的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(3): 792-799. | |
| 29 | Li P, Zhang Y Q. Effect of low phosphorous stress on photosynthesis properties of different broomcorn millet varieties. Heilongjiang Agricultural Science, 2012, 1(7): 35-39. |
| 李鹏, 张永清. 低磷胁迫对不同黍稷品种光合特性的影响. 黑龙江农业科学, 2012, 1(7): 35-39. | |
| 30 | He P, Gao L, Wei J S, et al. Study on the protective enzyme activity of the hevea seedling under low phosphorus stress. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2012, 33(12): 2225-2229. |
| 何鹏, 高乐, 韦家少, 等. 低磷胁迫对巴西橡胶树幼苗保护酶活性的影响. 热带作物学报, 2012, 33(12): 2225-2229. | |
| 31 | Pang C H, Hua Y H, Zhang Y Q, et al. Effects of humic acid on physiological characteristics and yield of quinoa under different phosphorus levels. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 21(4): 143-150. |
| 庞春花, 华艳宏, 张永清, 等. 不同磷水平下施加腐植酸对藜麦生理特性及产量的影响. 中国农业科技导报, 2019, 21(4): 143-150. | |
| 32 | Zhang Y Q. Study on adaptability of switchgrass in saline alkali land in Yinbei area of Ningxia. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2018. |
| 张永乾. 宁夏银北地区盐碱地柳枝稷适应性研究. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2018. | |
| 33 | Zhang K, Chen N L, Gu Q Y, et al. Gas exchange characteristics and biomass accumulation and distribution response to water and nitrogen in different drought resistant wheat. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture Sciences, 2016, 30(4): 797-804. |
| 张凯, 陈年来, 顾群英, 等. 不同抗旱性小麦气体交换特性和生物量积累与分配对水氮的响应. 核农学报, 2016, 30(4): 797-804. | |
| 34 | Zhang K, Chen N L, Gu Q Y. Trade-offs among light, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of wheat cultivars under different water and nitrogen application levels. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(7): 2273-2282. |
| 张凯, 陈年来, 顾群英. 不同水氮水平下小麦品种对光、水和氮利用效率的权衡. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(7): 2273-2282. | |
| 35 | Guo P W, Zhao J Y, Shi Y, et al. Effects of water and fertilizer integration on water use and photosynthetic characteristics of winter wheat. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(4): 1170-1178. |
| 郭培武, 赵俊晔, 石玉, 等. 水肥一体化对小麦水分利用和光合特性的影响. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(4): 1170-1178. | |
| 36 | Zhang S Q, Shan L. Effects of nitrogen nutrition on drought adaptation and water use of spring wheat. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 1995, 2(1): 31-35. |
| 张岁歧, 山仑. 氮素营养对春小麦抗旱适应性及其水分利用的影响. 水土保持研究, 1995, 2(1): 31-35. |
| [1] | 杨志新, 郑旭, 陈来宝, 于泳鑫, 张凤华, 李鲁华, 王家平. 干旱区盐碱地食叶草根系形态分布适应策略研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 15-27. |
| [2] | 李宏伟, 郑琪, 李滨, 赵茂林, 李振声. 一种耐盐碱牧草——长穗偃麦草研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 190-199. |
| [3] | 王晔, 陈慧萍, 李润枝, 彭真, 范希峰, 武菊英, 段留生. 奇岗微繁技术建立及幼苗耐盐性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 214-220. |
| [4] | 陈雅琦, 苏楷淇, 陈泰祥, 李春杰. 混合盐碱胁迫对醉马草种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 137-157. |
| [5] | 李倩, 李晓霞, 程丽琴, 陈双燕, 齐冬梅, 杨伟光, 高利军, 新巴音, 刘公社. 羊草LcCBF6基因的表达特性和功能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 105-115. |
| [6] | 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 贾瑜琀. 不同施氮水平对柳枝稷光合特性及抗旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 107-115. |
| [7] | 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 常雯雯. 施氮量对柳枝稷叶片叶绿素荧光特性及干物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 141-150. |
| [8] | 胡冰钰, 方志刚, 娄来清, 蔡庆生. 14份柳枝稷种质资源苗期耐镉性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 27-36. |
| [9] | 熊雪, 桂维阳, 刘沫含, 陈继辉, 张英俊. 不同紫花苜蓿品种在均匀与不均匀盐胁迫下的耐盐性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 67-76. |
| [10] | 柯丹霞, 彭昆鹏, 夏远君, 朱玉莹, 张丹丹. 盐胁迫应答基因GmWRKY6的克隆及转基因百脉根的抗盐分析[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 95-106. |
| [11] | 麻冬梅, 秦楚. AtSOS基因在紫花苜蓿中的表达及其耐盐性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(6): 81-91. |
| [12] | 才华, 孙娜, 宋婷婷. 人工改造野生大豆GsDREB2基因对植物耐盐和耐渗透胁迫能力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(6): 168-176. |
| [13] | 祁泽文, 孙鑫博, 樊波, 张雪, 袁建波, 韩烈保. PEG介导的柳枝稷叶肉细胞原生质体瞬时表达体系的建立[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 113-120. |
| [14] | 柴艳, 孙宗玖, 李培英, 巴德木其其格, 张向向, 杨静. 新疆狗牙根种质芽期耐盐性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 154-167. |
| [15] | 伍国强, 冯瑞军, 李善家, 王春梅, 焦琦, 刘海龙. 盐处理对甜菜生长和渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(4): 169-177. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||