

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 72-84.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022338
收稿日期:2022-08-26
修回日期:2022-10-07
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-05-26
通讯作者:
张林刚
作者简介:E-mail: lingangzhang@imu.edu.cn基金资助:
Xiao-dong YU( ), Hao-yang YU(
), Hao-yang YU( ), Xu YANG, Dong-xu ZHAO, Lin-gang ZHANG(
), Xu YANG, Dong-xu ZHAO, Lin-gang ZHANG( )
)
Received:2022-08-26
Revised:2022-10-07
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-05-26
Contact:
Lin-gang ZHANG
摘要:
羊草是广泛分布于我国内蒙古草原上的一种优质牧草,根据叶色差异可将其分为灰绿和黄绿两种生态型,前期研究发现二者的叶绿体存在差异,但是造成羊草叶色趋异的分子机理还不清楚。选取内蒙古敕勒川草原的两种生态型羊草,利用Denovo测序平台对二者的叶绿体基因组进行测序和特征分析。结果表明,灰绿型羊草全长136816 bp,大单拷贝区80973 bp,拥有一对长21560 bp的反向重复序列,黄绿型羊草全长136809 bp,大单拷贝区80962 bp,拥有一对长21562 bp的反向重复序列,二者均含有12723 bp的小单拷贝区;二者的叶绿体基因组皆包含131个基因,编码84个蛋白质、8个rRNA和39个tRNA基因;二者都具有丰富的重复序列并存在差异,且大多位于基因间隔区;二者的叶绿体基因组序列相比共发现14个突变区,导致二者反向重复区域收缩/扩张的不同;此外,系统发育分析证明两种生态型羊草与祖先新麦草依然保持较近的亲缘关系。所以,两种生态型羊草的叶绿体基因组序列为解析二者叶色差异提供了分子信息,更为推动羊草叶绿体转化技术奠定了基础。
于晓东, 余浩洋, 杨旭, 赵东旭, 张林刚. 内蒙古两种生态型羊草叶绿体基因组序列差异分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 72-84.
Xiao-dong YU, Hao-yang YU, Xu YANG, Dong-xu ZHAO, Lin-gang ZHANG. Difference analysis of chloroplast genome sequence between two ecotypes of Leymus chinensis in Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 72-84.
项目 Item | 灰绿型羊草 GG L. chinensis | 黄绿型羊草 YG L. chinensis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长度Length (bp) | 百分比Percent (%) | 长度Length (bp) | 百分比Percent (%) | |
| 全长 Total length | 136816 | 100.00 | 136809 | 100.00 |
| 大单拷贝区 Large single-copy (LSC) | 80973 | 59.18 | 80962 | 59.18 |
| 反向重复序列a Inverted repeats a (IRa) | 21560 | 15.76 | 21562 | 15.76 |
| 小单拷贝区 Small single-copy (SSC) | 12723 | 9.30 | 12723 | 9.30 |
| 反向重复序列b Inverted repeats b (IRb) | 21560 | 15.76 | 21562 | 15.76 |
| 蛋白编码基因 Protein coding genes | 59235 | 43.29 | 59235 | 43.30 |
| 转运RNA tRNA | 3046 | 2.23 | 3046 | 2.23 |
| 核糖体RNA rRNA | 9192 | 6.72 | 9192 | 6.72 |
表1 两种生态型羊草的叶绿体基因组特征
Table 1 Characteristics of two ecotypes of L. chinensis chloroplast genome
项目 Item | 灰绿型羊草 GG L. chinensis | 黄绿型羊草 YG L. chinensis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长度Length (bp) | 百分比Percent (%) | 长度Length (bp) | 百分比Percent (%) | |
| 全长 Total length | 136816 | 100.00 | 136809 | 100.00 |
| 大单拷贝区 Large single-copy (LSC) | 80973 | 59.18 | 80962 | 59.18 |
| 反向重复序列a Inverted repeats a (IRa) | 21560 | 15.76 | 21562 | 15.76 |
| 小单拷贝区 Small single-copy (SSC) | 12723 | 9.30 | 12723 | 9.30 |
| 反向重复序列b Inverted repeats b (IRb) | 21560 | 15.76 | 21562 | 15.76 |
| 蛋白编码基因 Protein coding genes | 59235 | 43.29 | 59235 | 43.30 |
| 转运RNA tRNA | 3046 | 2.23 | 3046 | 2.23 |
| 核糖体RNA rRNA | 9192 | 6.72 | 9192 | 6.72 |

图1 两种生态型羊草的叶绿体基因组图谱A: 黄绿型羊草叶绿体基因组图谱; B: 灰绿型羊草叶绿体基因组图谱。图谱外部的基因是以顺时针方向转录的,图谱内部的基因是以逆时针方向转录的,颜色区分了不同的基因,内圈较暗的灰色表示基因组的GC含量,较浅的灰色对应基因组的AT含量。A: Gene map of YG L. chinensis chloroplast genome; B: Gene map of GG L. chinensis chloroplast genome. Genes lying outside of the outer circle are transcribed in the clockwise direction whereas genes inside are transcribed in the counterclockwise direction. Genes belonging to different functional groups are color-coded. Area dashed darker gray in the inner circle indicates GC content while the lighter gray corresponds to AT content of the genome.
Fig.1 Gene map of two ecotypes of L. chinensis chloroplast genome
| 基因分类 Gene classification | 灰绿型GG | 黄绿型YG | 基因分类 Gene classification | 灰绿型GG | 黄绿型YG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基因总数 Total genes | 131 | 131 | tRNA基因 tRNA genes | 39 | 39 |
| 蛋白质编码基因 Protein-coding genes | 84 | 84 | 内含子中的基因 Genes with introns | 12 | 12 |
| rRNA基因 rRNA genes | 8 | 8 | IR区重复的基因 Genes duplicated by IR | 18 | 18 |
表2 两种生态型羊草叶绿体基因组的基因数量
Table 2 Number of genes found in two ecotypes of L. chinensis chloroplast genome
| 基因分类 Gene classification | 灰绿型GG | 黄绿型YG | 基因分类 Gene classification | 灰绿型GG | 黄绿型YG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基因总数 Total genes | 131 | 131 | tRNA基因 tRNA genes | 39 | 39 |
| 蛋白质编码基因 Protein-coding genes | 84 | 84 | 内含子中的基因 Genes with introns | 12 | 12 |
| rRNA基因 rRNA genes | 8 | 8 | IR区重复的基因 Genes duplicated by IR | 18 | 18 |
基因分类 Category for genes | 基因分组 Group of genes | 基因名称 Name of genes |
|---|---|---|
| 光合作用相关基因Genes for photosynthesis | 光合系统Ⅰ基因Genes of photosystem I | psaB, psaA, psaI, psaJ, psaC |
| 光合系统Ⅱ基因Genes of photosystem II | psbA, psbK, psbI, psbD, psbC, psbZ, psbM, psbJ, psbB, psbT, pbfI, psbH, psbF, psbE, psbL | |
| ATP合酶基因Genes of ATP synthase | atpI, atpH, atpF, atpA, atpE, atpB | |
| 细胞色素复合物基因Genes of cytochrome b/f complex | petN, petA, petL, petD, petB, petG | |
| NADH脱氢酶基因Genes of NADH-dehydrogenase | ndhJ, ndhK, ndhC, ndhB, ndhF, ndhD, ndhE, ndhG, ndhI, ndhA, ndhH | |
| 二磷酸核酮羧化酶大亚基基因Large subunit genes of RuBisco | rbcL | |
表达相关基因 Genes for expression | rRNA基因rRNA genes | rrn16S, rrn23S, rrn4.5S, rrn5S |
| tRNA基因tRNA genes | trnK-UUU, trnQ-UUG, trnS-GCU, trnG-GCC, trnM-CAU, trnS-CGA, trnT-GGU, trnE-UUC, trnY-GUA, trnD-GUC, trnC-GCA, trnR-UCU, trnL-UAA, trnF-GAA, trnV-UAC, trnW-CCA, trnP-UGG, trnH-GUG, trnI-GAU, trnA-UGC, trnN-GUU, trnN-GUU, trnL-UAG, trnL-CAA, trnS-UGA, trnT-UGU, trnV-GAC, trnR-ACG, trnR-ACG, trnS-GGA | |
| 核糖体小亚基基因Small subunit genes of ribosomal | rps16, rps2, rps14, rps4, rps3, rps18, rps11, rps8, rps19, rps7, rps12, rps15 | |
| 核糖体大亚基基因Large subunit genes of ribosomal | rpl33, rpl20, rpl36, rpl14, rpl16, rpl22, rpl2, rpl23, rpl32 | |
| 依赖DNA的RNA聚合酶亚基基因DNA dependent RNA polymerase | rpoB, rpoC1, rpoC2, rpoA | |
其他基因 Other genes | C型细胞色素合成基因C-type cytochrome synthesis gene | ccsA |
| 外膜蛋白基因Envelope membrane protein gene | cemA | |
| 成熟酶基因Maturase gene | matK | |
| 蛋白酶基因Protease gene | clpP | |
| 转录起始因子基因Translation initiation factor gene | infA | |
| 未知功能基因Genes of unknown function | 假定叶绿体基因和保守开放阅读框Conserved hypothetical chloroplast reading frames | bptG, ycf3, ycf4 |
表3 两种生态型羊草叶绿体基因组的基因
Table 3 Genes found in two ecotypes of L. chinensis chloroplast genome
基因分类 Category for genes | 基因分组 Group of genes | 基因名称 Name of genes |
|---|---|---|
| 光合作用相关基因Genes for photosynthesis | 光合系统Ⅰ基因Genes of photosystem I | psaB, psaA, psaI, psaJ, psaC |
| 光合系统Ⅱ基因Genes of photosystem II | psbA, psbK, psbI, psbD, psbC, psbZ, psbM, psbJ, psbB, psbT, pbfI, psbH, psbF, psbE, psbL | |
| ATP合酶基因Genes of ATP synthase | atpI, atpH, atpF, atpA, atpE, atpB | |
| 细胞色素复合物基因Genes of cytochrome b/f complex | petN, petA, petL, petD, petB, petG | |
| NADH脱氢酶基因Genes of NADH-dehydrogenase | ndhJ, ndhK, ndhC, ndhB, ndhF, ndhD, ndhE, ndhG, ndhI, ndhA, ndhH | |
| 二磷酸核酮羧化酶大亚基基因Large subunit genes of RuBisco | rbcL | |
表达相关基因 Genes for expression | rRNA基因rRNA genes | rrn16S, rrn23S, rrn4.5S, rrn5S |
| tRNA基因tRNA genes | trnK-UUU, trnQ-UUG, trnS-GCU, trnG-GCC, trnM-CAU, trnS-CGA, trnT-GGU, trnE-UUC, trnY-GUA, trnD-GUC, trnC-GCA, trnR-UCU, trnL-UAA, trnF-GAA, trnV-UAC, trnW-CCA, trnP-UGG, trnH-GUG, trnI-GAU, trnA-UGC, trnN-GUU, trnN-GUU, trnL-UAG, trnL-CAA, trnS-UGA, trnT-UGU, trnV-GAC, trnR-ACG, trnR-ACG, trnS-GGA | |
| 核糖体小亚基基因Small subunit genes of ribosomal | rps16, rps2, rps14, rps4, rps3, rps18, rps11, rps8, rps19, rps7, rps12, rps15 | |
| 核糖体大亚基基因Large subunit genes of ribosomal | rpl33, rpl20, rpl36, rpl14, rpl16, rpl22, rpl2, rpl23, rpl32 | |
| 依赖DNA的RNA聚合酶亚基基因DNA dependent RNA polymerase | rpoB, rpoC1, rpoC2, rpoA | |
其他基因 Other genes | C型细胞色素合成基因C-type cytochrome synthesis gene | ccsA |
| 外膜蛋白基因Envelope membrane protein gene | cemA | |
| 成熟酶基因Maturase gene | matK | |
| 蛋白酶基因Protease gene | clpP | |
| 转录起始因子基因Translation initiation factor gene | infA | |
| 未知功能基因Genes of unknown function | 假定叶绿体基因和保守开放阅读框Conserved hypothetical chloroplast reading frames | bptG, ycf3, ycf4 |
| 项目 Item | 灰绿型GG | 黄绿型YG |
|---|---|---|
| 总GC含量 Total GC content | 38.41 | 38.42 |
| 蛋白质编码区的GC含量 GC content in protein-coding regions | 38.98 | 38.98 |
| 基因间隔区的GC含量 GC content in inter genic spacer | 37.98 | 37.99 |
| tRNA中的GC含量 GC content in tRNA | 52.27 | 52.27 |
| rRNA中的GC含量 GC content in rRNA | 54.72 | 54.72 |
表4 两种生态型羊草叶绿体基因组的GC含量
Table 4 GC content of two ecotypes of L. chinensis chloroplast genome (%)
| 项目 Item | 灰绿型GG | 黄绿型YG |
|---|---|---|
| 总GC含量 Total GC content | 38.41 | 38.42 |
| 蛋白质编码区的GC含量 GC content in protein-coding regions | 38.98 | 38.98 |
| 基因间隔区的GC含量 GC content in inter genic spacer | 37.98 | 37.99 |
| tRNA中的GC含量 GC content in tRNA | 52.27 | 52.27 |
| rRNA中的GC含量 GC content in rRNA | 54.72 | 54.72 |
基因 Gene | 灰绿型GG | 黄绿型YG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 位置Location | 内含子ⅠIntron Ⅰ | 内含子ⅡIntron Ⅱ | 位置Location | 内含子ⅠIntron Ⅰ | 内含子ⅡIntron Ⅱ | |
| trnK-UUU | LSC | 2480 | - | LSC | 2480 | - |
| trnS-CGA | LSC | 664 | - | LSC | 664 | - |
| trnL-UAA | LSC | 565 | - | LSC | 565 | - |
| trnV-UAC | LSC | 598 | - | LSC | 598 | - |
| atpF | LSC | 831 | - | LSC | 831 | - |
| petD | LSC | 749 | - | LSC | 749 | - |
| petB | LSC | 749 | - | LSC | 748 | - |
| rps16 | LSC | 838 | - | LSC | 838 | - |
| ndhB | IRa | 712 | - | IRa | 712 | - |
| rps12 | IRa | 540 | - | IRa | 540 | - |
| rpl2 | IRa | 663 | - | IRa | 663 | - |
| ycf3 | LSC | 727 | 751 | LSC | 727 | 751 |
表5 两种生态型羊草叶绿体基因组中含有内含子的基因以及内含子的长度
Table 5 Genes with introns in the chloroplast genomes of two ecotypes L. chinensis as well as the lengths of the introns (bp)
基因 Gene | 灰绿型GG | 黄绿型YG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 位置Location | 内含子ⅠIntron Ⅰ | 内含子ⅡIntron Ⅱ | 位置Location | 内含子ⅠIntron Ⅰ | 内含子ⅡIntron Ⅱ | |
| trnK-UUU | LSC | 2480 | - | LSC | 2480 | - |
| trnS-CGA | LSC | 664 | - | LSC | 664 | - |
| trnL-UAA | LSC | 565 | - | LSC | 565 | - |
| trnV-UAC | LSC | 598 | - | LSC | 598 | - |
| atpF | LSC | 831 | - | LSC | 831 | - |
| petD | LSC | 749 | - | LSC | 749 | - |
| petB | LSC | 749 | - | LSC | 748 | - |
| rps16 | LSC | 838 | - | LSC | 838 | - |
| ndhB | IRa | 712 | - | IRa | 712 | - |
| rps12 | IRa | 540 | - | IRa | 540 | - |
| rpl2 | IRa | 663 | - | IRa | 663 | - |
| ycf3 | LSC | 727 | 751 | LSC | 727 | 751 |
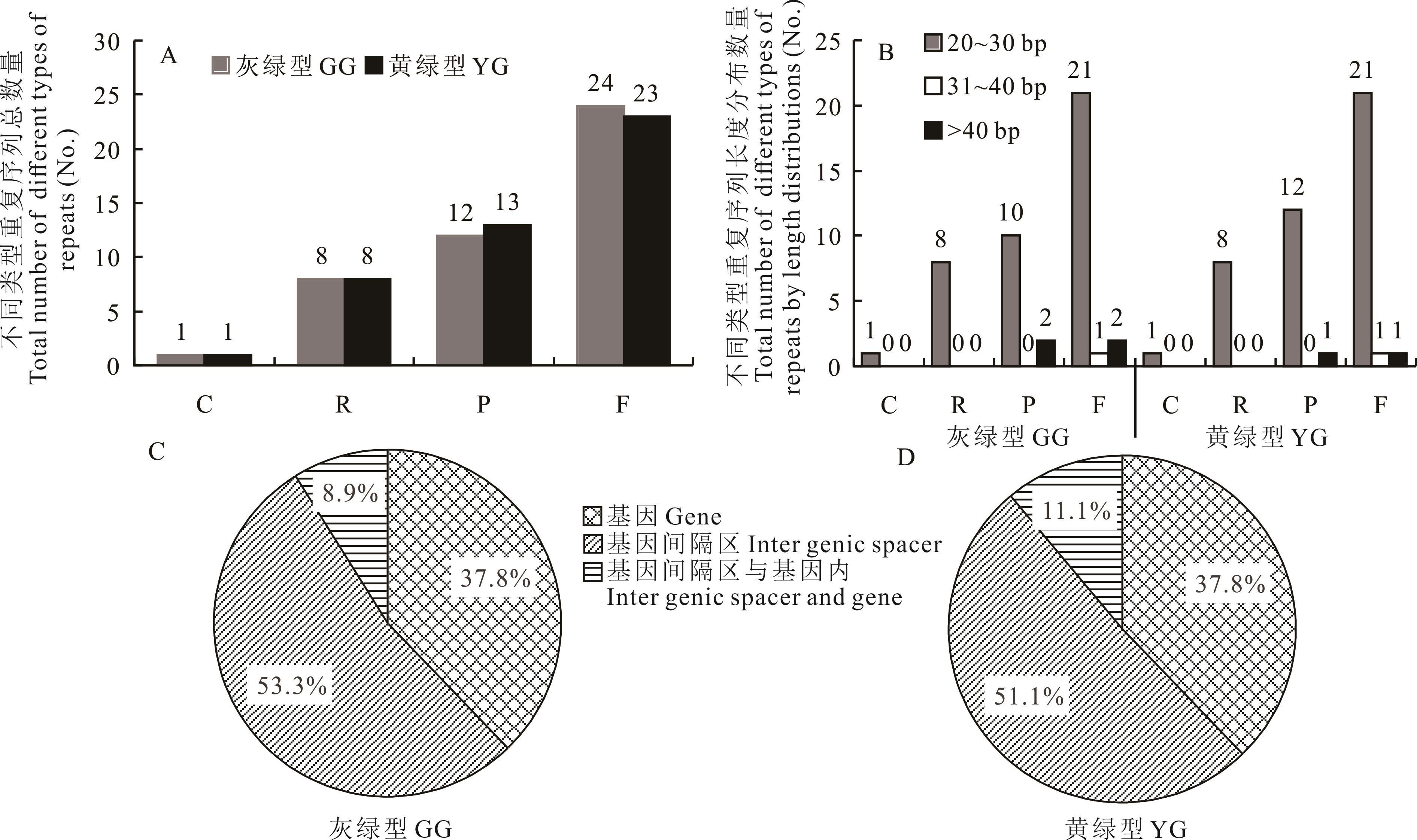
图2 两种生态型羊草叶绿体基因组的分散重复序列分析A: 不同类型分散重复序列总数; B: 不同类型重复序列长度分布数; C: 灰绿型羊草分散重复序列的位置分布; D: 黄绿型羊草分散重复序列的位置分布; “C” 代表互补重复序列, “R” 代表反向重复序列, “P” 代表回文重复序列, “F” 代表正向重复序列。A: Total number of different types of dispersed repeats; B: Total number of different types of repeats by length distributions; C: Positional distribution of dispersed repeats in GG L. chinensis; D: Positional distribution of dispersed repeats in YG L. chinensis. “C” means complement repeats; “R” means reverse repeats; “P” means palindromic repeats; “F” means forward repeats.
Fig.2 Analysis of dispersed repeats of two ecotypes of L. chinensis chloroplast genome
生态型 Ecotypes | 长度 Length (bp) | 重复类型 Repeat type | 1次重复位置 Repeat 1 start position (bp) | 2次重复位置 Repeat 2 start position (bp) | 1次重复定位 Repeat 1 location | 2次重复定位 Repeat 2 location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灰绿型GG | 114 | F | 56537 | 134440 | rps3 | rpl23-D |
| 171 | F | 56652 | 134555 | rps3_psaI | rpl23-D | |
| 114 | P | 56537 | 83235 | rps3 | rpl23 | |
| 171 | P | 56652 | 83063 | rps3_psaI | rpl2_rpl23 (rpl23) | |
| 黄绿型YG | 286 | F | 56526 | 134431 | rps3 | rpl23-D |
| 30 | P | 16914 | 16914 | psbM_petN (psbM) | psbM_petN (psbM) | |
| 286 | P | 56526 | 83054 | rps3 | rpl2_rpl23 (rpl2) | |
| 30 | P | 130206 | 130206 | ndhB-D (intron) | ndhB-D (intron) |
表6 两种生态型羊草叶绿体基因组中的差异分散重复序列
Table 6 Differential dispersed repeats in two ecotypes of L. chinensis chloroplast genome
生态型 Ecotypes | 长度 Length (bp) | 重复类型 Repeat type | 1次重复位置 Repeat 1 start position (bp) | 2次重复位置 Repeat 2 start position (bp) | 1次重复定位 Repeat 1 location | 2次重复定位 Repeat 2 location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灰绿型GG | 114 | F | 56537 | 134440 | rps3 | rpl23-D |
| 171 | F | 56652 | 134555 | rps3_psaI | rpl23-D | |
| 114 | P | 56537 | 83235 | rps3 | rpl23 | |
| 171 | P | 56652 | 83063 | rps3_psaI | rpl2_rpl23 (rpl23) | |
| 黄绿型YG | 286 | F | 56526 | 134431 | rps3 | rpl23-D |
| 30 | P | 16914 | 16914 | psbM_petN (psbM) | psbM_petN (psbM) | |
| 286 | P | 56526 | 83054 | rps3 | rpl2_rpl23 (rpl2) | |
| 30 | P | 130206 | 130206 | ndhB-D (intron) | ndhB-D (intron) |

图3 两种生态型羊草叶绿体基因组的SSR分析A: 不同类型SSR总数量; B: 灰绿型羊草SSR的位置分布; C: 黄绿型羊草SSR的位置分布。A: Total number of different types of SSR; B: Positional distribution of SSR in GG L. chinensis; C: Positional distribution of SSR in YG L. chinensis.
Fig.3 Analysis of SSR of two ecotypes of L. chinensis chloroplast genome
生态型 Ecotypes | 序号 No. | 类型 Type | 重复基序 Repeat motif | 长度 Length (bp) | 起止位置 Start-end (bp) | 定位 Location | 区域 Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灰绿型GG | 1 | p1 | (A)10 | 10 | 33569~33578 | AtpF (intron) | LSC |
| 2 | p1 | (A)10 | 10 | 71835~71844 | PetB (intron) | LSC | |
| 3 | p1 | (A)11 | 11 | 29775~29785 | rpoC2 | LSC | |
| 4 | p1 | (A)12 | 12 | 44046~44057 | ycf3 (intron) | LSC | |
| 5 | p1 | (T)10 | 10 | 43056~43065 | ycf3 (intron) | LSC | |
| 6 | c | (T)10ctctccta(T)10ctgtcata(T)10 | 46 | 76955~77000 | infA+IGS | LSC | |
| 黄绿型YG | 1 | p1 | (A)10 | 10 | 33564~33573 | AtpF (intron) | LSC |
| 2 | p1 | (A)10 | 10 | 71824~71833 | PetB (intron) | LSC | |
| 3 | p1 | (A)11 | 11 | 29770~29780 | rpoC2 | LSC | |
| 4 | p1 | (A)12 | 12 | 44041~44052 | ycf3 (intron) | LSC | |
| 5 | p1 | (T)10 | 10 | 43051~43060 | ycf3 (intron) | LSC | |
| 6 | c | (T)10ctctccta(T)10ctgtcata(T)10 | 46 | 76944~76989 | infA+IGS | LSC |
表7 两种生态型羊草叶绿体基因组中存在于基因内的SSR
Table 7 Intragenic SSRs in chloroplast genomes of two ecotypes of L. chinensis
生态型 Ecotypes | 序号 No. | 类型 Type | 重复基序 Repeat motif | 长度 Length (bp) | 起止位置 Start-end (bp) | 定位 Location | 区域 Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灰绿型GG | 1 | p1 | (A)10 | 10 | 33569~33578 | AtpF (intron) | LSC |
| 2 | p1 | (A)10 | 10 | 71835~71844 | PetB (intron) | LSC | |
| 3 | p1 | (A)11 | 11 | 29775~29785 | rpoC2 | LSC | |
| 4 | p1 | (A)12 | 12 | 44046~44057 | ycf3 (intron) | LSC | |
| 5 | p1 | (T)10 | 10 | 43056~43065 | ycf3 (intron) | LSC | |
| 6 | c | (T)10ctctccta(T)10ctgtcata(T)10 | 46 | 76955~77000 | infA+IGS | LSC | |
| 黄绿型YG | 1 | p1 | (A)10 | 10 | 33564~33573 | AtpF (intron) | LSC |
| 2 | p1 | (A)10 | 10 | 71824~71833 | PetB (intron) | LSC | |
| 3 | p1 | (A)11 | 11 | 29770~29780 | rpoC2 | LSC | |
| 4 | p1 | (A)12 | 12 | 44041~44052 | ycf3 (intron) | LSC | |
| 5 | p1 | (T)10 | 10 | 43051~43060 | ycf3 (intron) | LSC | |
| 6 | c | (T)10ctctccta(T)10ctgtcata(T)10 | 46 | 76944~76989 | infA+IGS | LSC |
| 序号No. | 突变位置Mutation position (bp) | 灰绿型GG | 黄绿型YG | 定位Location | 区域Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5351 | T | G | rps16 (intron) | LSC |
| 2 | 5792 | G | T | rps16_trnQ-UUG | LSC |
| 3 | 15200 | TTCTAT | - | trnT-GGU_trnE-UUG | LSC |
| 4 | 16289 | A | C | trnD-GUC_psbM | LSC |
| 5 | 19080 | - | T | trnC-GCA_rpoB | LSC |
| 6 | 44490 | A | C | ycf3_trnS-GGA | LSC |
| 7 | 50634 | AAAAA | - | ndhC_trnV-UAC | LSC |
| 8 | 56407 | A | - | rbcL_rps3 | LSC |
| 9 | 56653 | G | A | rps3_psaI | LSC |
| 10 | 65895 | T | G | rpl33_rps18 | LSC |
| 11 | 72162 | A | - | petB (intron) | LSC |
| 12 | 74711 | - | A | petD_rpoA | LSC |
| 13 | 80980 | - | TT | rpl22_rps19 | IRa |
| 14 | 136815 | - | AA | rps19-D_psbA | IRb |
表8 两种生态型羊草叶绿体基因组之间的突变分析
Table 8 Mutation analysis of two ecotypes of L. chinensis chloroplast genomes
| 序号No. | 突变位置Mutation position (bp) | 灰绿型GG | 黄绿型YG | 定位Location | 区域Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5351 | T | G | rps16 (intron) | LSC |
| 2 | 5792 | G | T | rps16_trnQ-UUG | LSC |
| 3 | 15200 | TTCTAT | - | trnT-GGU_trnE-UUG | LSC |
| 4 | 16289 | A | C | trnD-GUC_psbM | LSC |
| 5 | 19080 | - | T | trnC-GCA_rpoB | LSC |
| 6 | 44490 | A | C | ycf3_trnS-GGA | LSC |
| 7 | 50634 | AAAAA | - | ndhC_trnV-UAC | LSC |
| 8 | 56407 | A | - | rbcL_rps3 | LSC |
| 9 | 56653 | G | A | rps3_psaI | LSC |
| 10 | 65895 | T | G | rpl33_rps18 | LSC |
| 11 | 72162 | A | - | petB (intron) | LSC |
| 12 | 74711 | - | A | petD_rpoA | LSC |
| 13 | 80980 | - | TT | rpl22_rps19 | IRa |
| 14 | 136815 | - | AA | rps19-D_psbA | IRb |
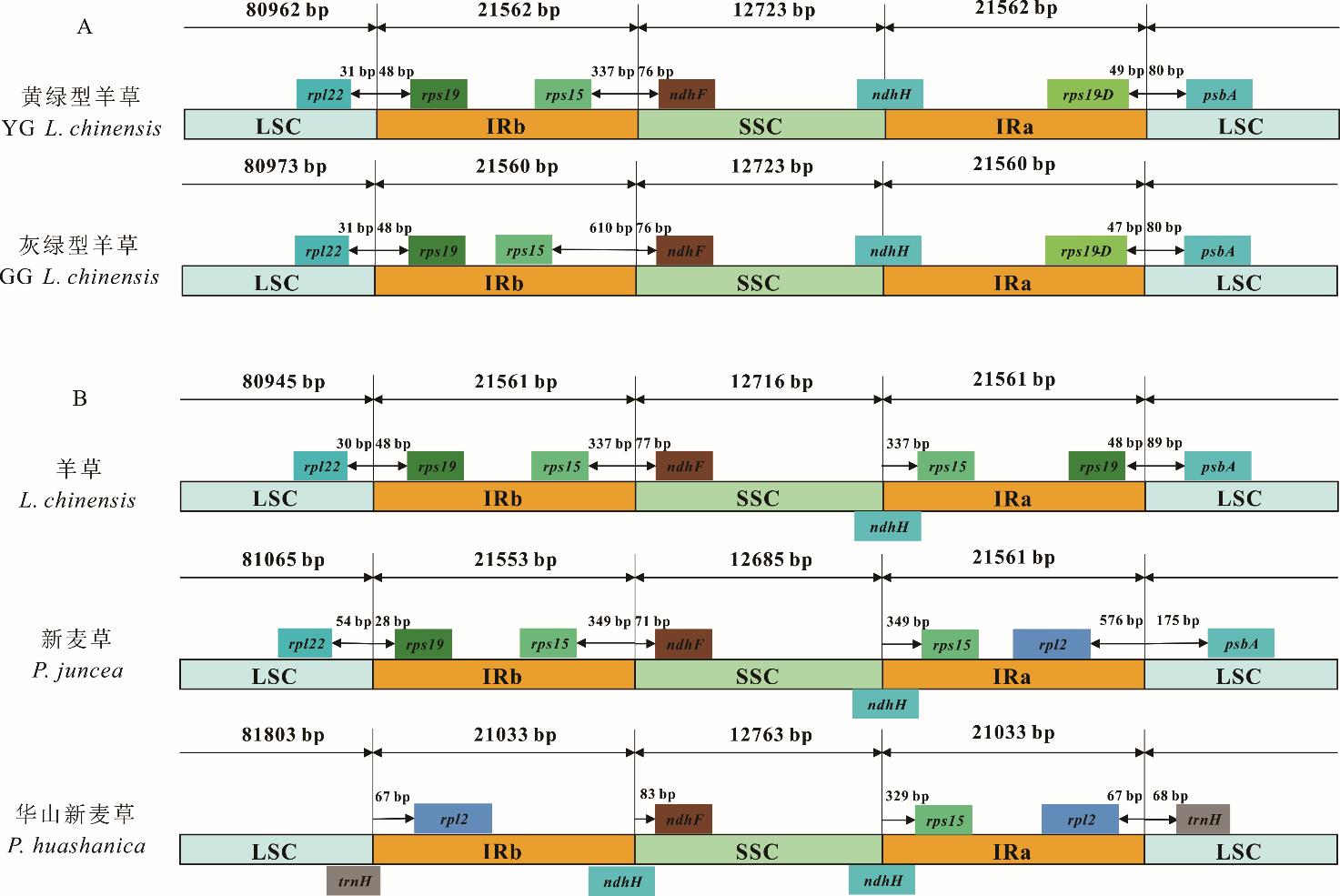
图4 两种生态型羊草、羊草、新麦草和华山新麦草叶绿体基因组LSC、IR和SSC交界区的比较SSC: 小单拷贝区 Small single-copy; LSC: 大单拷贝区 Large single-copy;IRa/b: 反向重复序列 Inverted repeats.
Fig.4 Comparison of the border regions of LSC, IR and SSC among two ecotypes of L. chinensis, L. chinensis, P. juncea and P. huashanica
| 1 | Zhou C, Yang Y F. Edaphic factors of differentiation for two ecotypes Leymus chinensis in North China. Progress in Natural Science, 2006, 16(11): 1150-1155. |
| 2 | Cui J Z, Qu L Y, Zu Y G. Genetic diversity and differentiation of two ecotypes of Leymus chinensis populations in microhabitat-Allozyme analysis. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2000, 20(3): 434-439. |
| 崔继哲, 曲来叶, 祖元刚. 微生境下羊草两种生态型种群的遗传多样性及遗传分化-等位酶分析. 生态学报, 2000, 20(3): 434-439. | |
| 3 | Zhou C. Study on divergent adaptative characteristics and evolutional mechanism of two ecotypes Leymus chinensis in northeastern plain in China. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2004. |
| 周婵. 东北草原两个生态型羊草趋异适应特性及其进化机理的研究. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2004. | |
| 4 | Zhang B Y. Differential proteomic analysis of chloroplasts in two ecotypes of Leymus chinensis. Harbin: Harbin Normal University, 2017. |
| 张宝懿. 两种生态型羊草叶绿体的差异蛋白质组分析. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨师范大学, 2017. | |
| 5 | Ma L J, Fan J Q, Narengaowa, et al. Comparative study on chloroplast pigment concentration and morphology between two ecotypes of Leymus chinensis in Inner Mongolia. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(9): 1779-1786. |
| 马利娟, 范精琦, 娜仁高娃, 等. 内蒙古两种生态型羊草叶绿体色素含量以及形态特征的对比. 草业科学, 2020, 37(9): 1779-1786. | |
| 6 | Lohse M, Drechsel O, Bock R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW): A tool for the easy generation of high-quality custom graphical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes. Current Genetics, 2007, 52(5/6): 267-274. |
| 7 | Kurtz S, Choudhuri J, Ohlebusch E, et al. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Research, 2001, 29(22): 4633-4642. |
| 8 | Yang J X, Hu G X, Hu G W. Comparative genomics and phylogenetic relationships of two endemic and endangered species (Handeliodendron bodinieri and Eurycorymbus cavaleriei) of two monotypic genera within Sapindales. BMC Genomics, 2022, 23(1): 1-22. |
| 9 | Wang R J, Cheng C L, Chang C C, et al. Dynamics and evolution of the inverted repeat-large single copy junctions in the chloroplast genomes of monocots. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 2008, 8(1): 1-14. |
| 10 | Huang H, Shi C, Liu Y, et al. Thirteen Camellia chloroplast genome sequences determined by high-throughput sequencing: Genome structure and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 2014, 14(1): 1-17. |
| 11 | Liu C K, Lei J Q, Jiang Q P, et al. The complete plastomes of seven Peucedanum plants: Comparative and phylogenetic analyses for the Peucedanum genus. BMC Plant Biology, 2022, 22(1): 1-14. |
| 12 | Zhang H B, Dvorak J. The genome origin of tetraploid species of Leymus (Poaceae: Triticeae) inferred from variation in repeated nucleotide sequences. American Journal of Botany, 1991, 78(7): 871-884. |
| 13 | Wang R R C, Jensen K B. Absence of the J genome in Leymus species (Poaceae: Triticeae): Evidence from DNA hybridization and meiotic pairing. Genome, 1994, 37(2): 231-235. |
| 14 | Hole D J, Jensen K B, Wang R R C, et al. Molecular marker analysis of Leymus flavescens and chromosome pairing in Leymus flavescens hybrids (Poaceae: Triticeae). International Journal of Plant Sciences, 1999, 160(2): 371-376. |
| 15 | Jonsson K A, Bodvarsdottir S K. Genomic and genetic relationships among species of Leymus (Poaceae: Triticeae) inferred from 18S-26S ribosomal genes. American Journal of Botany, 2001, 88(4): 553-559. |
| 16 | Civan P, Foster P G, Embley M T, et al. Analyses of charophyte chloroplast genomes help characterize the ancestral chloroplast genome of land plants. Genome Biology and Evolution, 2014, 6(4): 897-911. |
| 17 | Wang S, Gao L Z. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of green foxtail (Setaria viridis), a promising model system for C4 photosynthesis. Mitochondrial DNA Part A, 2016, 27(5): 3707-3708. |
| 18 | Timme R E, Kuehi J V, Boore J L, et al. A comparative analysis of the Lactuca and Helianthus (Asteraceae) plastid genomes: Identification of divergent regions and categorization of shared repeats. The Botanical Society of America, 2007, 94(3): 302-312. |
| 19 | Weng M L, Blazier J C, Govindu M, et al. Reconstruction of the ancestral plastid genome in Geraniaceae reveals a correlation between genome rearrangements, repeats, and nucleotide substitution rates. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2014, 31(3): 645-659. |
| 20 | Saski C, Lee S B, Fjellheim S, et al. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Hordeum vulgare, Sorghum bicolor and Agrostis stolonifera, and comparative analyses with other grass genomes. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2007, 115(4): 571-590. |
| 21 | Wang W C, Chen S Y, Zhang X Z. Whole-genome comparison reveals heterogeneous divergence and mutation hotspots in chloroplast genome of Eucommia ulmoides oliver. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(4): 1-16. |
| 22 | Morton B R, Clegg M T. Neighboring base composition is strongly correlated with base substitution bias in a region of the chloroplast genome. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 1995, 41(5): 597-603. |
| 23 | Morton B R, Oberholzer V M, Clegg M T. The influence of specific neighboring bases on substitution bias in noncoding regions of the plant chloroplast genome. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 1997, 45(3): 227-231. |
| 24 | Li W Q, Liu Y L, Yang Y, et al. Interspecific chloroplast genome sequence diversity and genomic resources in Diospyros. BMC Plant Biology, 2018, 18(1): 1-11. |
| 25 | Dong W P, Liu H, Xu C, et al. A chloroplast genomic strategy for designing taxon specific DNA mini-barcodes: A case study on ginsengs. BMC Genetics, 2014, 15(1): 1-8. |
| 26 | Zong D, Gan P H, Zhou A P, et al. Plastome sequences help to resolve deep-level relationships of Populus in the family salicaceae. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 5. |
| 27 | Sang T, Crawford D J, Stuessy T F. Chloroplast DNA phylogeny, reticulate evolution, and biogeography of Paeonia (Paeoniaceae). American Journal of Botany, 1997, 84(8): 1120-1136. |
| 28 | Mason-Gamer R J, Orme N L, Anderson C M. Phylogenetic analysis of North American Elymus and the monogenomic Triticeae (Poaceae) using three chloroplast DNA data sets. Genome, 2002, 45(6): 991-1002. |
| 29 | Xu D H, Ban T. Phylogenetic and evolutionary relationships between Elymus humidus and other Elymus species based on sequencing of non-coding regions of cpDNA and AFLP of nuclear DNA. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2004, 108(8): 1443-1448. |
| 30 | Alvarez I, Wendel J F. Ribosomal ITS sequences and plant phylogenetic inference. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 2003, 29(3): 417-434. |
| 31 | Mansion G, Struwe L. Generic delimitation and phylogenetic relationships within the subtribe Chironiinae (Chironieae: Gentianaceae), with special reference to Centaurium: Evidence from nrDNA and cpDNA sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 2004, 32(3): 951-977. |
| 32 | Liu Z, Hao G, Luo Y B, et al. Phylogeny and androecial evolution in Schisandraceae, inferred from sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA its and chloroplast DNA trnL-F regions. International Journal of Plant Sciences, 2006, 167(3): 539-550. |
| 33 | Asano T, Tsudzuki T, Takahashi S, et al. Complete nucleotide sequence of the sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) chloroplast genome: A comparative analysis of four monocot chloroplast genomes. DNA Research, 2004, 11(2): 93-99. |
| 34 | Wu Y, Liu F, Yang D G, et al. Comparative chloroplast genomics of Gossypium species: Insights into repeat sequence variations and phylogeny. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 376. |
| 35 | Yae-Eun L E E, Yoonkyung L E E, Sangtae K I M. A report of the second chloroplast genome sequence in Veronica nakaiana (Plantaginaceae), an endemic species in Korea. Korean Journal of Plant Taxonomy, 2021, 51(1): 109-114. |
| 36 | Fukuda T, Ashizawa H, Suzuki R, et al. Molecular phylogeny of the genus Asparagus (Asparagaceae) inferred from plastid petB intron and petD-rpoA intergenic spacer sequences. Plant Species Biology, 2010, 20(2): 121-132. |
| 37 | Choi K S, Chung M G, Park S J. The complete chloroplast genome sequences of three Veroniceae species (Plantaginaceae): Comparative analysis and highly divergent regions. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 355. |
| 38 | Qin Q L, Li J L, Zeng S Y, et al. The complete plastomes of red fleshed pitaya (Selenicereus monacanthus) and three related Selenicereus species: Insights into gene losses, inverted repeat expansions and phylogenomic implications. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2022, 28(1): 123-137. |
| [1] | 张适阳, 刘凤民, 崔均涛, 何磊, 冯月燕, 张伟丽. 三种外源物质对低温胁迫下柱花草生理与荧光特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 85-99. |
| [2] | 周晓瑾, 黄海霞, 张君霞, 马步东, 陆刚, 齐建伟, 张婷, 朱珠. 盐胁迫对裸果木幼苗光合特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 75-83. |
| [3] | 金祎婷, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 梁国玲, 贾志锋. 全生育期干旱胁迫对‘青燕1号’燕麦叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 112-126. |
| [4] | 刘丽英, 贾玉山, 范文强, 尹强, 成启明, 王志军. 影响苜蓿自然干燥的主要环境因子研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 121-132. |
| [5] | 张永超, 梁国玲, 秦燕, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 刘勇, 马祥. 老芒麦衰老过程中叶片叶绿素和光合作用变化特征及对养分的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 229-237. |
| [6] | 吴路遥, 张建国, 常闻谦, 张少磊, 常青. 三种荒漠植物叶绿素荧光参数日变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 203-213. |
| [7] | 单立文, 张强, 朱瑞芬, 孔晓蕾, 陈积山. 氮、磷添加下AMF对羊草和苜蓿生长与光合生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 46-57. |
| [8] | 王玉萍, 郜春晓, 王盛祥, 何晓童. 低温弱光胁迫下芸豆叶片光抑制与类囊体膜脂构成变化[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 116-125. |
| [9] | 张利霞, 常青山, 薛娴, 刘伟, 张巧明, 陈苏丹, 郑轶琦, 李景林, 陈婉东, 李大钊. 酸胁迫对夏枯草叶绿素荧光特性和根系抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 134-142. |
| [10] | 刘文文, 崔会婷, 尉春雪, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 王珍. 蒺藜苜蓿叶绿素酸酯a加氧酶(MtCAO)基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 171-181. |
| [11] | 赵小强, 陆晏天, 白明兴, 徐明霞, 彭云玲, 丁永福, 庄泽龙, 陈奋奇, 张大志. 不同株型玉米基因型对干旱胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 149-162. |
| [12] | 程守丰, 梁巧兰, 魏列新, 桑旭文, 姜玉玲. 苜蓿不同品种AMV和WCMV带毒检测及生理生化特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 140-149. |
| [13] | 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 常雯雯. 施氮量对柳枝稷叶片叶绿素荧光特性及干物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 141-150. |
| [14] | 李文彬, 宁楚涵, 李伟, 李峰, 郭绍霞. 菲和芘胁迫下AMF和PGPR对高羊茅生理生态的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 84-94. |
| [15] | 刘领, 李冬, 马宜林, 王丽君, 赵世民, 周俊学, 申洪涛, 王艳芳. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下烤烟幼苗生长的缓解效应与生理机制研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 95-105. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 310
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 337
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||