

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 138-153.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023108
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
段鹏1( ), 韦鎔宜1, 王芳萍1, 姚步青2(
), 韦鎔宜1, 王芳萍1, 姚步青2( ), 赵之重1,3(
), 赵之重1,3( ), 胡碧霞1, 宋词2,4, 杨萍2,4, 王婷1
), 胡碧霞1, 宋词2,4, 杨萍2,4, 王婷1
收稿日期:2023-04-06
修回日期:2023-05-12
出版日期:2024-02-20
发布日期:2023-12-12
通讯作者:
姚步青,赵之重
作者简介:qdwjm@126.com基金资助:
Peng DUAN1( ), Rong-yi WEI1, Fang-ping WANG1, Bu-qing YAO2(
), Rong-yi WEI1, Fang-ping WANG1, Bu-qing YAO2( ), Zhi-zhong ZHAO1,3(
), Zhi-zhong ZHAO1,3( ), Bi-xia HU1, Ci SONG2,4, Ping YANG2,4, Ting WANG1
), Bi-xia HU1, Ci SONG2,4, Ping YANG2,4, Ting WANG1
Received:2023-04-06
Revised:2023-05-12
Online:2024-02-20
Published:2023-12-12
Contact:
Bu-qing YAO,Zhi-zhong ZHAO
摘要:
土壤微生物碳源利用能力是退化湿地修复过程中的重要评判指标,但在高寒退化湿地修复过程中,养分添加对土壤微生物碳源利用的影响仍不明确。为探究不同养分添加对黄河源区退化高寒湿地土壤微生物碳源利用能力的影响,本研究对黄河源区退化高寒湿地进行了氮、磷添加和有机掺混肥添加处理,采用常规实验室分析法和Biolog-Eco法,分析了不同养分添加处理对湿地不同退化阶段植被特征、土壤理化性质和土壤微生物碳源利用的影响。结果表明:氮添加可以显著提高中度退化阶段土壤微生物碳源利用能力,磷添加和有机掺混肥添加后退化湿地土壤微生物碳源利用能力没有显著提高。不同养分添加处理可以影响土壤微生物对不同种类碳源的利用能力,其中氮添加和有机掺混肥添加可以提高退化湿地土壤微生物脂类和醇类碳源的利用占比,降低酸类碳源的利用占比。不同养分添加下退化高寒湿地土壤微生物总体碳源利用能力主要取决于土壤微生物对酯类、醇类和胺类碳源的利用。结构方程模型分析显示,退化高寒湿地氮添加和有机掺混肥添加都可以通过提升植被地上生物量促进土壤微生物碳源利用,但有机掺混肥对土壤微生物碳源利用的提升作用受土壤水分含量降低的限制。该结果可为高寒退化湿地修复技术研发和退化高寒湿地修复效果评判提供科学依据。
段鹏, 韦鎔宜, 王芳萍, 姚步青, 赵之重, 胡碧霞, 宋词, 杨萍, 王婷. 不同养分添加对黄河源区退化高寒湿地土壤微生物碳源利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 138-153.
Peng DUAN, Rong-yi WEI, Fang-ping WANG, Bu-qing YAO, Zhi-zhong ZHAO, Bi-xia HU, Ci SONG, Ping YANG, Ting WANG. Effects of adding different nutrients on soil microbial carbon source utilization in degraded alpine wetland in the source region of the Yellow River[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(2): 138-153.
指标 Indicators | 退化 Degradation | 养分添加 Nutrient addition | 退化+养分添加 Degradation+nutrient addition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 植被性质Properties of vegetation | |||
| 盖度Coverage | 10.985** | 0.649 | 0.093 |
| 地上生物量Aboveground biomass | 2.211 | 1.390 | 0.226 |
| 地下生物量Under ground biomass | 25.350*** | 11.810** | 18.480*** |
| 土壤性质Properties of soil | |||
| 全氮Total nitrogen | 54.215*** | 3.659 | 0.007 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus | 13.647*** | 0.187 | 1.199 |
| 有机碳Total organic carbon | 2.833 | 1.176 | 0.610 |
| 含水量Moisture content | 259.000*** | 44.640*** | 15.260*** |
| pH | 3.485 | 10.614** | 0.005 |
| 微生物性质Properties of microorganism | |||
| 颜色平均变化率Average well color development | 9.520** | 5.551* | 2.938 |
表1 植被、土壤和微生物状况的双因素方差分析(F值)
Table 1 Two-factor ANOVA analysis of vegetation, soil and microbial status (F value)
指标 Indicators | 退化 Degradation | 养分添加 Nutrient addition | 退化+养分添加 Degradation+nutrient addition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 植被性质Properties of vegetation | |||
| 盖度Coverage | 10.985** | 0.649 | 0.093 |
| 地上生物量Aboveground biomass | 2.211 | 1.390 | 0.226 |
| 地下生物量Under ground biomass | 25.350*** | 11.810** | 18.480*** |
| 土壤性质Properties of soil | |||
| 全氮Total nitrogen | 54.215*** | 3.659 | 0.007 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus | 13.647*** | 0.187 | 1.199 |
| 有机碳Total organic carbon | 2.833 | 1.176 | 0.610 |
| 含水量Moisture content | 259.000*** | 44.640*** | 15.260*** |
| pH | 3.485 | 10.614** | 0.005 |
| 微生物性质Properties of microorganism | |||
| 颜色平均变化率Average well color development | 9.520** | 5.551* | 2.938 |
项目 Item | 退化梯度 Degraded gradient | 处理Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
对照 Control (CK) | 氮添加 Nitrogen addition (N) | 磷添加 Phosphorus addition (P) | 有机掺混肥添加 Organic mixed fertilizer addition(S) | ||
盖度 Coverage (%) | LD | 80.10±0.36Ad | 90.57±0.74Ac | 94.90±0.56Ab | 98.10±0.66Aa |
| MD | 69.80±0.40Bb | 79.60±0.53Ba | 50.47±0.45Cd | 60.40±0.87Cc | |
| SD | 60.00±0.35Cc | 79.77±0.78Ba | 80.77±0.75Ba | 74.77±0.25Bb | |
| 平均Average | 70.78 | 83.31 | 75.38 | 77.76 | |
地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | LD | 116.00±1.44Ac | 174.60±2.20Aa | 116.20±0.96Bc | 168.36±2.76Ab |
| MD | 90.00±0.79Bc | 148.20±2.29Ca | 67.99±2.17Cd | 129.31±2.87Bb | |
| SD | 84.00±1.76Bd | 169.60±2.12Ba | 127.87±2.41Ab | 112.00±1.83Cc | |
| 平均Average | 96.93 | 164.13 | 104.02 | 136.56 | |
地下生物量 Underground biomass (g·m-2) | LD | 175.85±0.99Aa | 110.63±0.64Ad | 124.01±0.51Ac | 135.58±0.91Bb |
| MD | 89.33±0.58Bc | 100.53±0.67Bb | 76.13±0.33Cd | 166.48±0.68Aa | |
| SD | 40.03±0.66Cd | 96.14±0.60Cb | 83.45±0.77Bc | 132.13±0.82Ca | |
| 平均Average | 101.73 | 102.43 | 94.53 | 144.73 | |
表 2 2018年退化高寒湿地不同养分添加下植被群落特征
Table 2 Characteristics of vegetation community in degraded alpine wetland with different nutrients in 2018
项目 Item | 退化梯度 Degraded gradient | 处理Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
对照 Control (CK) | 氮添加 Nitrogen addition (N) | 磷添加 Phosphorus addition (P) | 有机掺混肥添加 Organic mixed fertilizer addition(S) | ||
盖度 Coverage (%) | LD | 80.10±0.36Ad | 90.57±0.74Ac | 94.90±0.56Ab | 98.10±0.66Aa |
| MD | 69.80±0.40Bb | 79.60±0.53Ba | 50.47±0.45Cd | 60.40±0.87Cc | |
| SD | 60.00±0.35Cc | 79.77±0.78Ba | 80.77±0.75Ba | 74.77±0.25Bb | |
| 平均Average | 70.78 | 83.31 | 75.38 | 77.76 | |
地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g·m-2) | LD | 116.00±1.44Ac | 174.60±2.20Aa | 116.20±0.96Bc | 168.36±2.76Ab |
| MD | 90.00±0.79Bc | 148.20±2.29Ca | 67.99±2.17Cd | 129.31±2.87Bb | |
| SD | 84.00±1.76Bd | 169.60±2.12Ba | 127.87±2.41Ab | 112.00±1.83Cc | |
| 平均Average | 96.93 | 164.13 | 104.02 | 136.56 | |
地下生物量 Underground biomass (g·m-2) | LD | 175.85±0.99Aa | 110.63±0.64Ad | 124.01±0.51Ac | 135.58±0.91Bb |
| MD | 89.33±0.58Bc | 100.53±0.67Bb | 76.13±0.33Cd | 166.48±0.68Aa | |
| SD | 40.03±0.66Cd | 96.14±0.60Cb | 83.45±0.77Bc | 132.13±0.82Ca | |
| 平均Average | 101.73 | 102.43 | 94.53 | 144.73 | |
项目 Item | 退化梯度 Degraded gradient | 处理Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
对照 Control (CK) | 氮添加 Nitrogen addition (N) | 磷添加 Phosphorus addition (P) | 有机肥掺混肥添加 Organic mixed fertilizer addition(S) | ||
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | LD | 1.43±0.10Abc | 1.10±0.07Ac | 1.91±0.24Aa | 1.63±0.24Aab |
| MD | 1.12±0.11Ba | 1.04±0.08Aab | 1.19±0.06Ba | 0.86±0.06Bb | |
| SD | 0.62±0.05Cb | 0.74±0.07Bab | 0.72±0.06Cb | 1.07±0.23Ba | |
| 平均Average | 1.06 | 0.96 | 1.28 | 1.18 | |
全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | LD | 0.44±0.04Ab | 1.10±0.10Aa | 1.01±0.09Aa | 0.55±0.05Ab |
| MD | 0.46±0.05Aa | 0.45±0.05Ba | 0.43±0.05Ba | 0.46±0.04Aa | |
| SD | 0.34±0.03Ba | 0.37±0.04Ba | 0.40±0.04Ba | 0.39±0.03Ba | |
| 平均Average | 0.41 | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.47 | |
有机碳 Organic carbon (g·kg-1) | LD | 40.36±4.90ABa | 39.51±0.19ABa | 41.07±4.52Aa | 39.55±4.50Aa |
| MD | 45.12±3.51Aa | 43.08±3.24Aa | 42.32±4.81Aa | 36.60±6.91Aa | |
| SD | 36.27±2.30Ba | 36.34±2.69Ba | 35.22±4.96Aa | 38.56±2.40Aa | |
| 平均Average | 40.58 | 39.65 | 39.54 | 38.34 | |
含水量 Moisture content (m3·m-3) | LD | 0.43±0.01Aa | 0.37±0.01Ab | 0.37±0.01Ab | 0.33±0.01Ab |
| MD | 0.38±0.01Ba | 0.31±0.01Bb | 0.27±0.01Bc | 0.28±0.01Bc | |
| SD | 0.23±0.01Cab | 0.24±0.01Cab | 0.25±0.02Ba | 0.23±0.03Cb | |
| 平均Average | 0.40 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.28 | |
| pH | LD | 8.88±0.02Ba | 8.77±0.04Aa | 8.55±0.12Ab | 8.60±0.03Bb |
| MD | 8.52±0.02Cb | 8.94±0.15Aa | 8.40±0.06Ab | 8.39±0.03Cb | |
| SD | 9.04±0.02Aa | 8.97±0.27Aab | 8.58±0.19Ab | 8.83±0.02Aab | |
| 平均Average | 8.81 | 8.89 | 8.51 | 8.61 | |
表 3 2018年退化高寒湿地不同养分添加下土壤理化特征
Table 3 Physical-chemical characteristics of soil under different nutrients in degraded alpine wetland in 2018
项目 Item | 退化梯度 Degraded gradient | 处理Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
对照 Control (CK) | 氮添加 Nitrogen addition (N) | 磷添加 Phosphorus addition (P) | 有机肥掺混肥添加 Organic mixed fertilizer addition(S) | ||
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | LD | 1.43±0.10Abc | 1.10±0.07Ac | 1.91±0.24Aa | 1.63±0.24Aab |
| MD | 1.12±0.11Ba | 1.04±0.08Aab | 1.19±0.06Ba | 0.86±0.06Bb | |
| SD | 0.62±0.05Cb | 0.74±0.07Bab | 0.72±0.06Cb | 1.07±0.23Ba | |
| 平均Average | 1.06 | 0.96 | 1.28 | 1.18 | |
全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | LD | 0.44±0.04Ab | 1.10±0.10Aa | 1.01±0.09Aa | 0.55±0.05Ab |
| MD | 0.46±0.05Aa | 0.45±0.05Ba | 0.43±0.05Ba | 0.46±0.04Aa | |
| SD | 0.34±0.03Ba | 0.37±0.04Ba | 0.40±0.04Ba | 0.39±0.03Ba | |
| 平均Average | 0.41 | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.47 | |
有机碳 Organic carbon (g·kg-1) | LD | 40.36±4.90ABa | 39.51±0.19ABa | 41.07±4.52Aa | 39.55±4.50Aa |
| MD | 45.12±3.51Aa | 43.08±3.24Aa | 42.32±4.81Aa | 36.60±6.91Aa | |
| SD | 36.27±2.30Ba | 36.34±2.69Ba | 35.22±4.96Aa | 38.56±2.40Aa | |
| 平均Average | 40.58 | 39.65 | 39.54 | 38.34 | |
含水量 Moisture content (m3·m-3) | LD | 0.43±0.01Aa | 0.37±0.01Ab | 0.37±0.01Ab | 0.33±0.01Ab |
| MD | 0.38±0.01Ba | 0.31±0.01Bb | 0.27±0.01Bc | 0.28±0.01Bc | |
| SD | 0.23±0.01Cab | 0.24±0.01Cab | 0.25±0.02Ba | 0.23±0.03Cb | |
| 平均Average | 0.40 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.28 | |
| pH | LD | 8.88±0.02Ba | 8.77±0.04Aa | 8.55±0.12Ab | 8.60±0.03Bb |
| MD | 8.52±0.02Cb | 8.94±0.15Aa | 8.40±0.06Ab | 8.39±0.03Cb | |
| SD | 9.04±0.02Aa | 8.97±0.27Aab | 8.58±0.19Ab | 8.83±0.02Aab | |
| 平均Average | 8.81 | 8.89 | 8.51 | 8.61 | |

图 2 退化高寒湿地不同养分添加下土壤微生物AWCD不同大写字母表示相同处理下不同退化阶段间差异显著;不同小写字母表示相同退化阶段不同处理间差异显著; CK为对照;N为添加氮肥;P为添加磷肥;S为添加有机掺混肥。下同。Different capital letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level in different degradation stages under the same treatment; Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level under different treatments in the same degradation stage; CK: Control; N: Nitrogen fertilizer; P: Phosphorus fertilizer; S: Organic mixed fertilizer addition. The same below.
Fig.2 Soil microbial AWCD in different degradation stages of alpine wetlands under different human disturbances
样地 Samples | 单糖/糖苷/聚合物类 Carbohydrates | 氨基酸类 Amino acids | 酯类 Ester | 醇类 Alcohol | 胺类 Amines/amides | 酸类 Acids | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWCD | P (%) | AWCD | P (%) | AWCD | P (%) | AWCD | P (%) | AWCD | P (%) | AWCD | P (%) | |
| LD | 1.10±0.28ab | 19.43 | 0.83±0.12bc | 14.64 | 1.16±0.11a | 20.42 | 0.97±0.05abc | 17.12 | 0.87±0.03abc | 15.35 | 0.74±0.17c | 13.04 |
| LD+N | 0.28±0.44a | 7.67 | 0.74±0.70a | 20.35 | 1.01±0.91a | 27.96 | 0.66±0.80a | 18.24 | 0.44±0.18a | 12.20 | 0.49±0.54a | 13.58 |
| LD+P | 0.49±0.20a | 16.13 | 0.51±0.30a | 16.73 | 0.48±0.37a | 15.72 | 0.65±0.30a | 21.38 | 0.52±0.25a | 17.05 | 0.39±0.28a | 12.98 |
| LD+S | 0.19±0.18c | 4.13 | 0.94±0.11ab | 20.11 | 1.21±0.18a | 25.92 | 0.87±0.03b | 18.64 | 0.67±0.09b | 14.31 | 0.79±0.18b | 16.89 |
| MD | 0.54±0.06c | 12.21 | 0.98±0.11ab | 22.07 | 1.05±0.05a | 23.80 | 0.66±0.14bc | 14.91 | 0.53±0.20c | 11.93 | 0.67±0.06bc | 15.07 |
| MD+N | 0.78±0.12b | 14.04 | 1.02±0.13ab | 18.35 | 1.09±0.07a | 19.61 | 0.91±0.12ab | 16.39 | 0.99±0.14ab | 17.74 | 0.77±0.05b | 13.86 |
| MD+P | 0.05±0.02d | 2.50 | 0.39±0.14b | 21.07 | 0.65±0.10a | 34.91 | 0.34±0.03b | 18.25 | 0.13±0.02cd | 7.02 | 0.30±0.01bc | 16.25 |
| MD+S | 0.28±0.25c | 8.73 | 0.69±0.11ab | 21.57 | 0.87±0.06a | 27.13 | 0.47±0.11bc | 14.71 | 0.32±0.19c | 10.08 | 0.57±0.12bc | 17.78 |
| SD | 0.04±0.04d | 1.08 | 0.85±0.12a | 23.23 | 1.00±0.11a | 27.37 | 0.55±0.04bc | 15.05 | 0.52±0.05c | 14.33 | 0.69±0.05b | 18.94 |
| SD+N | 0.05±0.03d | 1.91 | 0.64±0.23a | 24.55 | 0.62±0.10ab | 23.91 | 0.58±0.04ab | 22.12 | 0.39±0.07bc | 14.83 | 0.33±0.12c | 12.68 |
| SD+P | 0.20±0.19b | 4.03 | 1.13±0.39a | 23.07 | 1.18±0.48a | 24.12 | 0.85±0.36ab | 17.37 | 0.77±0.36ab | 15.75 | 0.77±0.17ab | 15.66 |
| SD+S | 0.46±0.04b | 14.82 | 0.34±0.01b | 11.11 | 0.82±0.22a | 26.75 | 0.54±0.07b | 17.61 | 0.41±0.06b | 13.48 | 0.50±0.06b | 16.23 |
表 4 退化高寒湿地不同养分添加下土壤微生物对各类碳源的利用情况
Table 4 Utilization of various carbon sources by soil microorganisms in different degradation stages of alpine wetlands
样地 Samples | 单糖/糖苷/聚合物类 Carbohydrates | 氨基酸类 Amino acids | 酯类 Ester | 醇类 Alcohol | 胺类 Amines/amides | 酸类 Acids | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWCD | P (%) | AWCD | P (%) | AWCD | P (%) | AWCD | P (%) | AWCD | P (%) | AWCD | P (%) | |
| LD | 1.10±0.28ab | 19.43 | 0.83±0.12bc | 14.64 | 1.16±0.11a | 20.42 | 0.97±0.05abc | 17.12 | 0.87±0.03abc | 15.35 | 0.74±0.17c | 13.04 |
| LD+N | 0.28±0.44a | 7.67 | 0.74±0.70a | 20.35 | 1.01±0.91a | 27.96 | 0.66±0.80a | 18.24 | 0.44±0.18a | 12.20 | 0.49±0.54a | 13.58 |
| LD+P | 0.49±0.20a | 16.13 | 0.51±0.30a | 16.73 | 0.48±0.37a | 15.72 | 0.65±0.30a | 21.38 | 0.52±0.25a | 17.05 | 0.39±0.28a | 12.98 |
| LD+S | 0.19±0.18c | 4.13 | 0.94±0.11ab | 20.11 | 1.21±0.18a | 25.92 | 0.87±0.03b | 18.64 | 0.67±0.09b | 14.31 | 0.79±0.18b | 16.89 |
| MD | 0.54±0.06c | 12.21 | 0.98±0.11ab | 22.07 | 1.05±0.05a | 23.80 | 0.66±0.14bc | 14.91 | 0.53±0.20c | 11.93 | 0.67±0.06bc | 15.07 |
| MD+N | 0.78±0.12b | 14.04 | 1.02±0.13ab | 18.35 | 1.09±0.07a | 19.61 | 0.91±0.12ab | 16.39 | 0.99±0.14ab | 17.74 | 0.77±0.05b | 13.86 |
| MD+P | 0.05±0.02d | 2.50 | 0.39±0.14b | 21.07 | 0.65±0.10a | 34.91 | 0.34±0.03b | 18.25 | 0.13±0.02cd | 7.02 | 0.30±0.01bc | 16.25 |
| MD+S | 0.28±0.25c | 8.73 | 0.69±0.11ab | 21.57 | 0.87±0.06a | 27.13 | 0.47±0.11bc | 14.71 | 0.32±0.19c | 10.08 | 0.57±0.12bc | 17.78 |
| SD | 0.04±0.04d | 1.08 | 0.85±0.12a | 23.23 | 1.00±0.11a | 27.37 | 0.55±0.04bc | 15.05 | 0.52±0.05c | 14.33 | 0.69±0.05b | 18.94 |
| SD+N | 0.05±0.03d | 1.91 | 0.64±0.23a | 24.55 | 0.62±0.10ab | 23.91 | 0.58±0.04ab | 22.12 | 0.39±0.07bc | 14.83 | 0.33±0.12c | 12.68 |
| SD+P | 0.20±0.19b | 4.03 | 1.13±0.39a | 23.07 | 1.18±0.48a | 24.12 | 0.85±0.36ab | 17.37 | 0.77±0.36ab | 15.75 | 0.77±0.17ab | 15.66 |
| SD+S | 0.46±0.04b | 14.82 | 0.34±0.01b | 11.11 | 0.82±0.22a | 26.75 | 0.54±0.07b | 17.61 | 0.41±0.06b | 13.48 | 0.50±0.06b | 16.23 |

图 3 土壤微生物对碳源利用与各影响因子的 Mantel检验分析A为未添加肥料;B为氮肥添加;C为磷肥添加;D为有机掺混肥添加;N为全氮;TOC为有机碳;G为盖度;DX为地下生物量;P为全磷;DS为地上生物量;W为含水量;r表示解释变量和被解释变量之间的线性相关程度;P表示相关性显著水平。* P<0.05; ** P<0.01. A represent no-adding fertilizer; B represent adding nitrogen fertilizer; C represent adding phosphate fertilizer; D represent adding organic mixed fertilizer; N represent total nitrogen; TOC represent total organic carbon; G represent coverage; DX represent underground biomass; P represent total phosphorus; DS represent aboveground biomass; W represent moisture; r represent the degree of linear correlation between the explanatory variable and the explained variable; P represents a significant level of correlation.
Fig.3 Mantel test analysis of soil microorganism’s utilization of carbon source and its influencing factors
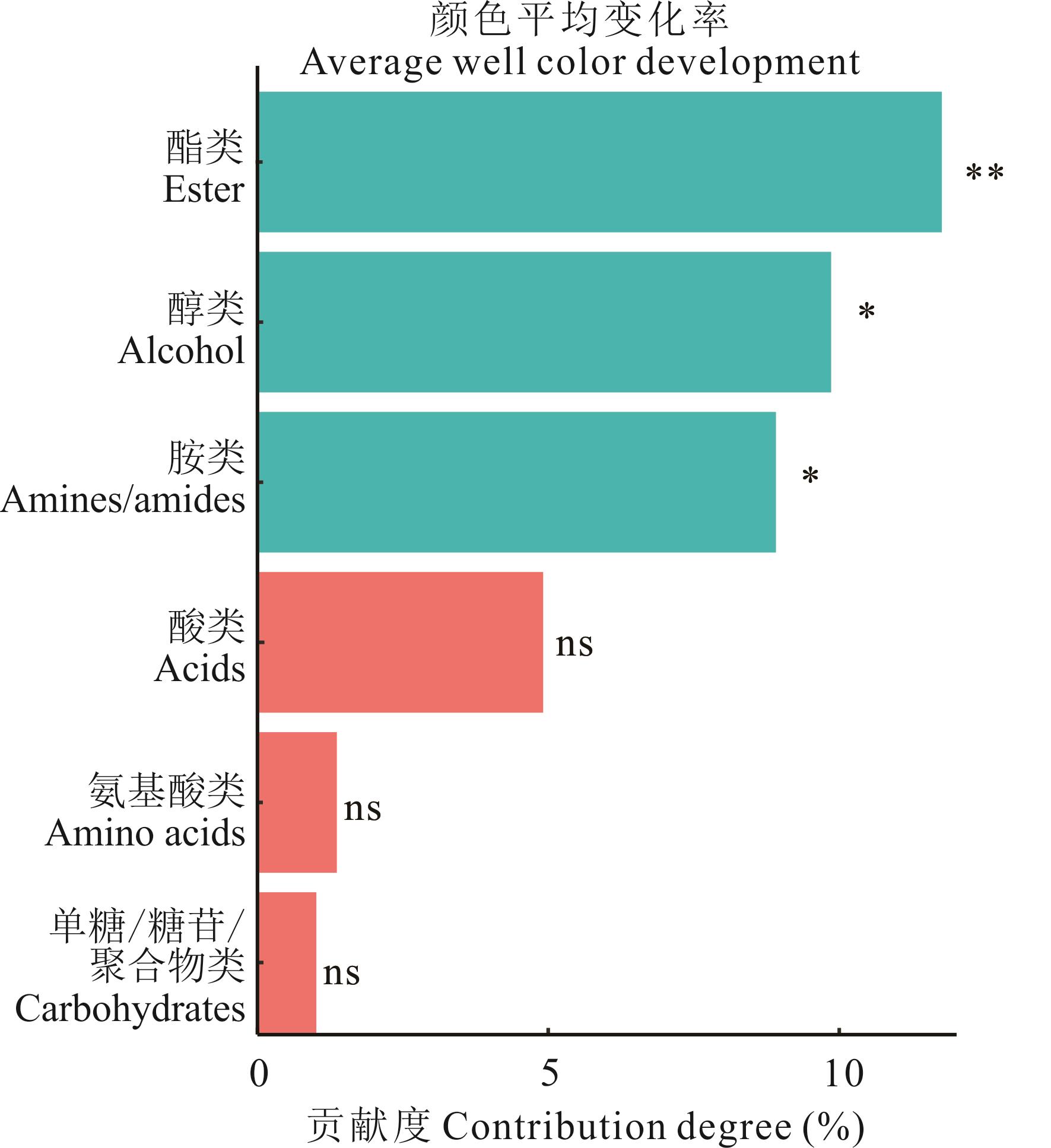
图4 土壤微生物各类碳源的利用对土壤微生物AWCD变化相对重要性排序*表示显著相关(P<0.05);**表示极显著相关(P<0.01),“ns”表示无显著相关。下同。* means significant correlation at the 0.05 level; ** means extremely significant correlation at the 0.01 level, “ns” means no significant correlation. The same below.
Fig.4 Ranking of relative importance of utilization of various carbon sources of soil microorganisms to changes of AWCD of soil microorganisms

图 7 不同养分下退化湿地各环境因子对土壤微生物AWCD调控机制结构方程模型黑色线为正效应,红色线为负效应,实线为显著影响,虚线为非显著影响。The black line indicate positive; The red line indicate negative; The solid line indicate significant; The dotted line indicate non-significant.
Fig.7 Piecewise structural equation model of AWCD regulation mechanism of environmental factors in degraded wetland under different nutrients
| 1 | Xing Y, Jiang Q G, Li W Q, et al. Landscape spatial patterns changes of the wetland in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecology and Environment, 2009, 18(3): 1010-1015. |
| 邢宇, 姜琦刚, 李文庆, 等. 青藏高原湿地景观空间格局的变化. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(3): 1010-1015. | |
| 2 | Xie G D, Lu C X, Leng Y F, et al. Ecological assets valuation of the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Natural Resources, 2003, 18(2): 189-196. |
| 谢高地, 鲁春霞, 冷允法, 等. 青藏高原生态资产的价值评估. 自然资源学报, 2003, 18(2): 189-196. | |
| 3 | Wang Y Y, Pei W W, Xin Y, et al. Change characteristics and influencing factors of soil organic carbon in alpine meadow from 2008 to 2015. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(12): 47-54. |
| 王云英, 裴薇薇, 辛莹, 等. 2008~2015年高寒草甸土壤有机碳变化特征及影响因素解析. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(12): 47-54. | |
| 4 | Wang S Q, Zhou C H. Estimating soil carbon reservior of terrestrial ecosystem in China. Geographical Research, 1999, 18(4): 349-354. |
| 王绍强, 周成虎. 中国陆地土壤有机碳库估算. 地理研究, 1999, 18(4): 349-354. | |
| 5 | Li K R, Wang S Q, Cao M K. Microbial China vegetation and soil carbon storage. Science in China (Series D), 2003, 33(1): 72-80. |
| 李克让, 王绍强, 曹明奎. 中国植被和土壤碳贮量. 中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(1): 72-80. | |
| 6 | Feng L. Effects of fertilization on plant community structure and soil organic matter in Qilian mountain wetland. Xining: Qinghai Normal University, 2015. |
| 冯璐. 养分添加对祁连山湿地植物群落结构及土壤有机质的影响. 西宁: 青海师范大学, 2015. | |
| 7 | Zhang X L, Li P Y. Discussion on standard of wetland degradation. Wetland Science, 2004, 2(1): 36-41. |
| 张晓龙, 李培英. 湿地退化标准的探讨. 湿地科学, 2004, 2(1): 36-41. | |
| 8 | Li C Y, Li X L, Sun H F, et al. Drought processes of alpine wetland and their influences on CO2 exchange. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(3): 750-758. |
| 李成一, 李希来, 孙华方, 等. 高寒湿地旱化过程及其对CO2交换的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(3): 750-758. | |
| 9 | Song X Y, Wang C T, Hu L, et al. Changes in soil aggregate-associated organic carbon of degraded alpine meadow in the Zoigê Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(4): 1538-1548. |
| 宋小艳, 王长庭, 胡雷, 等. 若尔盖退化高寒草甸土壤团聚体结合有机碳的变化. 生态学报, 2022, 42(4): 1538-1548. | |
| 10 | Wang D. Effects of Zoige alpine wetland degradation on the soil non-labile organic carbon. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 王丹. 若尔盖湿地退化对土壤惰性有机碳的影响. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2018. | |
| 11 | Lin C Y. Degradation process and mechanism of alpine swamp wetland in the source of Yellow River based on soil carbon and nitrogen. Xining: Qinghai University, 2021. |
| 林春英. 基于土壤碳氮的黄河源高寒沼泽湿地退化过程与机理研究. 西宁: 青海大学, 2021. | |
| 12 | Shi M M, Zhou B R, Duo J Z M, et al. Characteristics of vegetation and its evaluation index system in the swamp degradation process over three-river resource region. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2020, 40(10): 1751-1758. |
| 石明明, 周秉荣, 多杰卓么, 等.三江源区沼泽湿地退化过程中植被变化特征及评价指标体系. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(10): 1751-1758. | |
| 13 | Lin C Y, Li X L, Liu K, et al. Vegetation evolutional characteristics of floodplain wetlands during degradation succession in the Yellow River Source Zone. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2016, 32(19): 115-119. |
| 林春英, 李希来, 刘凯, 等. 黄河源区河漫滩湿地退化过程植被变化特征. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(19): 115-119. | |
| 14 | Wang S Y. Analysis on change of physical characteristics of degraded wetland soils in Sanjiang plain. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2004, 18(3): 167-170, 174. |
| 王世岩. 三江平原退化湿地土壤物理特征变化分析. 水土保持学报, 2004, 18(3): 167-170, 174. | |
| 15 | Lu M, Tian K, Chen Y H, et al. Studies on soil nutrients and enzyme activities of degraded wetland in Napahai. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 2004, 24(1): 34-37. |
| 陆梅, 田昆, 陈玉惠, 等. 高原湿地纳帕海退化土壤养分与酶活性研究. 西南林学院学报, 2004, 24(1): 34-37. | |
| 16 | Yang Y, Chen K L, Zhang N, et al. Responses of soil microbial community to different precipitation gradients in the alpine wetlands of Qinghai Lake Basin. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2022, 28(2): 290-299. |
| 杨阳, 陈克龙, 章妮, 等. 青海湖流域高寒湿地土壤微生物群落对不同降水梯度的响应. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(2): 290-299. | |
| 17 | Wu X Z, Liu B R, Yan X, et al. Response of soil microbial biomass and microbial entropy to desertification in desert grassland. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(8): 2691-2698. |
| 吴秀芝, 刘秉儒, 阎欣, 等. 荒漠草地土壤微生物生物量和微生物熵对沙漠化的响应. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(8): 2691-2698. | |
| 18 | Fritze H, Smolander A, Levula T, et al. Wood-ash fertilization and fire treatments in a Scots pine forest stand: effects on the organic layer, microbial biomass, and microbial activity. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 1994, 17(1): 57-63. |
| 19 | Wang S Q, Li T X, Zheng Z C, et al. Soil aggregate-associated bacterial metabolic activity and community structure in different aged tea plantations. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 65(4): 1023-1032. |
| 20 | Yao X X, Gong X Y, Bai B, et al. Study of grassland vegetation characteristics and soil nutrient and their correlation between different grassland types in alpine pastoral area of Qilian Mountains. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(2): 371-379. |
| 姚喜喜, 宫旭胤, 白滨, 等. 祁连山高寒牧区不同类型草地植被特征与土壤养分及其相关性研究. 草地学报, 2018, 26(2): 371-379. | |
| 21 | Yao H Y, Huang C Y. Soil microbial ecology and its experimental techniques. Beijing: Science Press, 2006. |
| 姚槐应, 黄昌勇. 土壤微生物生态学及其实验技术. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006. | |
| 22 | Tuergong X M X N R, Zhang J B, Dong Z W, et al. The soil microbial community structure under retrogressive succession of an alpine wetland in the arid area. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2023, 63(4): 1603-1617. |
| 谢姆西努尔·图尔贡, 张经博, 董正武, 等. 干旱区高寒湿地逆行演替下土壤微生物群落结构的研究. 微生物学报, 2023, 63(4): 1603-1617. | |
| 23 | Xu H F, Liu X T, Bai J H, et al. Dynamic change and environmental effects of soil microorganism in marsh soils from Carex meyeriana wetlands in Changbai Mountain. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2004, 18(3): 115-118. |
| 徐惠风, 刘兴土, 白军红, 等. 长白山沟谷湿地乌拉苔草沼泽湿地土壤微生物动态及环境效应研究. 水土保持学报, 2004, 18(3): 115-118. | |
| 24 | Bell T, Newman J A, Silverman B W, et al. The contribution of species richness and composition to bacterial services. Nature, 2005, 436(7054): 1157-1160. |
| 25 | Liu B R, Jia G M, Chen J, et al. A review of methods for studying microbial diversity in soils. Pedosphere, 2006, 16(1): 18-24. |
| 26 | Fierer N, Jackson R B. The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(3): 626-631. |
| 27 | Pankhurst C E, Ophelkeller K, Doube B M, et al. Biodiversity of soil microbial communities in agricultural systems. Biodiver-sity and Conservation, 1996, 5(2): 197-209. |
| 28 | Schloter M, Dilly O, Munch J C. Indicators of evaluating soil quality. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2003, 98(1/2/3): 255-262. |
| 29 | Zhang Y K, Peng S, Song Q Y, et al. Effects of different fertilizers regimes on the functional diversity of soil microbes under poplar plantation. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 40(5): 1-8. |
| 张雅坤, 彭赛, 宋倩云, 等. 不同施肥模式对杨树人工林土壤微生物功能多样性的影响. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 40(5): 1-8. | |
| 30 | Li H L, Hu J G, Xiao F, et al. Responses of soil water content of degraded alpine wetland to growing-season fencing and nitrogen addition. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(11): 2523-2529. |
| 李宏林, 胡竞格, 肖锋, 等. 生长季封育和氮添加对退化高寒沼泽湿地土壤水分状况的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(11): 2523-2529. | |
| 31 | Lovell R D, Jarvis S C, Bardgett R D. Soil microbial biomass and activity in long-term grassland: Effects of management changes. Soil Biology & Biochemistry,1995, 27: 969-975. |
| 32 | Hatch D J, Lovell R D, Antil R S, et al. Nitrogen mineralization and microbial activity in permanent pastures amended with nitrogen fertilizer or dung. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2000, 30: 288-293. |
| 33 | Hartmann M, Frey B, Mayer J, et al. Distinct soil microbial diversity under long-term organic and conventional farming. ISME J, 2015, 9(5): 1177-1194. |
| 34 | Liu L L, Shang Y M, Zhang J, et al. Effects of different fertilization treatments on soil microbial functional diversity of dry tableland wheat field in south Shanxi Province. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(3): 671-678. |
| 刘莲莲, 尚妍萌, 张杰, 等. 不同施肥处理对晋南旱塬麦田土壤微生物功能多样性的影响. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(3): 671-678. | |
| 35 | He W, Ye W H, Sun M J, et al. Soil phosphorus availability and stoichiometry determine microbial activity and functional diversity of fluvo-aquic soils under long-term fertilization regimes. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2022, 22: 1214-1227. |
| 36 | Dai H, Zeng Q X, Zhou J C, et al. Responses of soil microbial carbon use efficiency to short-term nitrogen addition in Castanopsis fabri forest. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(10): 2611-2618. |
| 戴辉, 曾泉鑫, 周嘉聪, 等. 罗浮栲林土壤微生物碳利用效率对短期氮添加的响应. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(10): 2611-2618. | |
| 37 | Fei Y C, Liu L, Chen G, et al. Effects of different organic fertilizer treatments on carbon source utilization of soil microbial communities of Camellia oleifera plantation in purple soil area. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China, 2020(5): 101-108. |
| 费裕翀, 刘丽, 陈钢, 等. 不同有机肥处理对紫色土油茶林土壤微生物碳源利用的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2020(5): 101-108. | |
| 38 | Xu W, Wang G, Deng F, et al. Responses of soil microbial biomass, diversity and metabolic activity to biochar applications in managed poplar plantations on reclaimed coastal saline soil. Soil Use and Management, 2018, 34: 597-605. |
| 39 | Hao M M, Hu H Y, Liu Z, et al. Shifts in microbial community and carbon sequestration in farmland soil under long-term conservation tillage and straw returning. Applied Soil Ecology, 2019, 136: 43-54. |
| 40 | Wu S Q, Wang C Z, Li M S. On soil functional diversity of native coastal wetland under simulated nitrogen deposition. Soils, 2017, 49(6): 1153-1158. |
| 吴松芹, 汪成忠, 李梦莎. 模拟氮沉降对滨海湿地土壤微生物功能多样性的影响. 土壤, 2017, 49(6): 1153-1158. | |
| 41 | Liu K, Li X L, Jin L Q, et al. Characteristics of soil and vegetation in the process of lacustrine wetland degradation in the Yellow River source zone. Ecological Science, 2017, 36(3): 23-30. |
| 刘凯, 李希来, 金立群, 等. 黄河源湖泊湿地退化过程土壤和植被的变化特征. 生态科学, 2017, 36(3): 23-30. | |
| 42 | Liu Y H, Li X L, Li C H, et al. Vegetation decline and reduction of soil organic carbon stock in high-altitude meadow grasslands in the source area of Three Major Rivers of China. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2009, 28(12): 2559-2567. |
| 刘育红, 李希来, 李长慧, 等. 三江源区高寒草甸湿地植被退化与土壤有机碳损失. 农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(12): 2559-2567. | |
| 43 | Duan P, Zhang Y C, Wang J G, et al. Functional diversity of soil microbial communities during degradation of alpine wetlands in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(3): 759-767. |
| 段鹏, 张永超, 王金贵, 等. 青藏高原高寒湿地退化过程中土壤微生物群落功能多样性特征. 草地学报, 2020, 28(3): 759-767. | |
| 44 | Ma W W, Wang H, Li G, et al. Changes in plant biomass and its seasonal dynamics during degradation succession in the Gahai wetland. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(15): 5091-5101. |
| 马维伟, 王辉, 李广, 等. 甘南尕海湿地退化过程中植被生物量变化及其季节动态. 生态学报, 2017, 37(15): 5091-5101. | |
| 45 | Li J W. Degenrrated characterization and mechanism of wetland commties on floodplan in typical steppe region of Inner Mongolia Plateau. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2012. |
| 李建玮. 内蒙古高原典型草原区河漫滩湿地植物群落退化表征及退化机制研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2012. | |
| 46 | Chen W Y, Wang L, Geng Q B M, et al. Effect of N and P addition on production performance of aging artificial pasture. Journal of Qinghai University, 2019, 37(2): 15-21. |
| 陈伟元, 王玲, 更求巴毛, 等. 氮、磷添加对老龄人工草地生产性能的影响. 青海大学学报, 2019, 37(2): 15-21. | |
| 47 | Wang T. Characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus and community succession during typical alpine wetland degradation and response to the interference. Xining: Qinghai University, 2020. |
| 王婷. 退化高寒典型湿地土壤碳氮磷和群落演替特征及其对干扰的响应. 西宁: 青海大学, 2020. | |
| 48 | Zhang C, Wang M, Zhang Y, et al. Effects of root cutting and organic fertilizer application on aboveground biomass and soil nutrients in the mowing ggrassland of Leymus chinensis meadow. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(1): 220-228. |
| 张楚, 王淼, 张宇, 等. 切根与施有机肥对羊草草甸草原打草场地上生物量与土壤养分的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(1): 220-228. | |
| 49 | Duan P, Yao B Q, Zhao Z Z, et al. Effects of seasonal lake wetland degradation on the utilization of soil microbial carbon source in the source region of the Yellow River. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(11): 2975-2985. |
| 段鹏, 姚步青, 赵之重, 等. 黄河源区季节性湖泊湿地退化对土壤微生物碳源利用的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(11): 2975-2985. | |
| 50 | Lu R K. Methods of soil agrochemical analysis. Nanjing: Hehai University Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 南京: 河海大学出版社, 2000. | |
| 51 | Garland J L, Mills A L. Classification and characterization of het erotrophic microbial communities on the basis of patterns of community-level sole carbon source utilization. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1991, 57(18): 2351-2359. |
| 52 | Zabinski C A, Gannon J E. Effects of recreational impacts on soil microbial communities. Environmental Management, 1997, 21(2): 233-238. |
| 53 | Bossio D A, Scow K M. Impact of carbon and flooding on the metabolic diversity of microbial communities in soils. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1995, 61(11): 4043-4050. |
| 54 | Zhang R, Zhang G L, Chen D Q, et al. The effects of different fertilization on the functional diversity of soil microbial community. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(2): 133-139. |
| 张瑞, 张贵龙, 陈冬青, 等. 不同养分添加对农田土壤微生物功能多样性的影响. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(2): 133-139. | |
| 55 | Diao C, Lu X K, Tian J, et al. Effects of long-term nitrogen addition on the metabolic diversity of microbial carbon sources in subtropical forest soils. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(18): 1-9. |
| 刁婵, 鲁显楷, 田静, 等. 长期氮添加对亚热带森林土壤微生物碳源代谢多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2019, 39(18): 1-9. | |
| 56 | Weng X H, Sui X, Li M S, et al. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil microbial carbon metabolism in Calamagrostis angustifolia wetland in Sanjiang Plain. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(9): 4674-4683. |
| 翁晓虹, 隋心, 李梦莎, 等. 模拟氮沉降对三江平原小叶樟湿地土壤微生物碳源利用能力的影响. 环境科学, 2022, 43(9): 4674-4683. | |
| 57 | Liu H M, An K R, Wang H, et al. Effects of fertilization regimes on the metabolic diversity of microbial carbon sources in a maize field of fluvo-aquic soil in North China. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(10): 2336-2344. |
| 刘红梅, 安克锐, 王慧, 等. 不同养分添加措施对华北潮土区玉米田土壤微生物碳源代谢多样性的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(10): 2336-2344. | |
| 58 | Li M, Zhang E P, Zhang S H, et al. Comparison of soil enzyme activities and microbial C metabolism in installed vegetable fields under long-term different fertilization. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(1): 44-53. |
| 李猛, 张恩平, 张淑红, 等. 长期不同施肥设施菜地土壤酶活性与微生物碳源利用特征比较. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(1): 44-53. | |
| 59 | Zhu F, Li T P, Yu P Y, et al. Carbon source utilization of soil microbial communities in response to nitrogen addition in the Cinnamomum camphora plantation. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2014, 50(8): 82-89. |
| 朱凡, 李天平, 郁培义, 等. 施氮对樟树林土壤微生物碳源代谢的影响. 林业科学, 2014, 50(8): 82-89. | |
| 60 | Guo Y, Wang Y M, Wu P, et al. Influence of long-term manure application in paddy soil on the functional diversity of microbial community. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2019, 25(3): 593-602. |
| 郭莹, 王一明, 巫攀, 等. 长期施用粪肥对水稻土中微生物群落功能多样性的影响. 应用与环境生物学报, 2019, 25(3): 593-602. | |
| 61 | Blum U. Effects of microbial utilization of phenolic acids and their phenolic acid breakdown products on allelopathic interactions. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 1998, 24(4): 685-708. |
| 62 | Ji L, Yang Y C, Wang J, et al. Relationship between soil phenolic acids and the soil microbial community under different land uses. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(18): 6710-6720. |
| 及利, 杨雨春, 王君, 等. 不同土地利用方式下酚酸物质与土壤微生物群落的关系. 生态学报, 2019, 39(18): 6710-6720. | |
| 63 | Chen X J, Wu X H, Liu S L, et al. Microbial activity and community structure analysis under the different land use patterns in farmland soils: Based on the methods PLFA and MicroRespTM. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(6): 2375-2382. |
| 陈晓娟, 吴小红, 刘守龙, 等. 不同耕地利用方式下土壤微生物活性及群落结构特性分析:基于PLFA和MicroRespTM方法. 环境科学, 2013, 34(6): 2375-2382. | |
| 64 | Weng X H, Sui X, Liu Y N, et al. Effect of nitrogen addition on the carbon metabolism of soil microorganisms in a Calamagrostis angustifolia wetland of the San Jiang plain, northeastern China. Annals of Microbiology, 2022, 72: 18. |
| 65 | Wei X R, Hao M D, Zhang C X. Effects of long-term fixed fertilization on soil water. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2003, 10(1): 95-97. |
| 魏孝荣, 郝明德, 张春霞. 旱地长期施肥对土壤水分的影响. 水土保持研究, 2003, 10(1): 95-97. | |
| 66 | Liu Z G. Plant biomass, soil water content and soil N∶P ratio regulating soil microbial functional diversity in a temperate steppe: A regional scale study. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2010, 42(3): 445-450. |
| 67 | Zhao X C, Liu H M, Huangfu C H, et al. Responses of functional diversity of soil microbial communities to nutrient additions in Stipa baicalensis steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(10): 1933-1939. |
| 赵晓琛, 刘红梅, 皇甫超河, 等. 贝加尔针茅草原土壤微生物功能多样性对养分添加的响应. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(10): 1933-1939. | |
| 68 | Yu P Y, Zhu F, Wang Z Y, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on metabolic function of microbial communitynin red soil of Cinnamomum camphora forest. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2013, 33(3): 70-74. |
| 郁培义, 朱凡, 王志勇, 等. 氮添加对樟树林红壤微生物群落代谢功能的影响. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2013, 33(3): 70-74. | |
| 69 | Luo X X, Hao X H, Chen T, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on functional diversity of soil microbial communities in paddy fields. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(2): 740-748. |
| 罗希茜, 郝晓晖, 陈涛, 等. 长期不同养分添加对稻田土壤微生物群落功能多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2009, 29(2): 740-748. | |
| 70 | Wu X S, Du G H, Mu C L, et al. Effects of different fertilization on structure and function of soil bacterial community. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2014, 20(1): 99-109. |
| 武晓森, 杜广红, 穆春雷, 等. 不同施肥处理对农田土壤微生物区系和功能的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(1): 99-109. | |
| 71 | Wang J H, Wang Y, Yu H B. Relationship between acidification and organic matter stability of black soil in Jilin maize belt. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2022, 44(6): 657-664. |
| 王继红, 王洋, 于洪波. 吉林玉米带黑土酸化与有机质稳定性关系. 吉林农业大学学报, 2022, 44(6): 657-664. | |
| 72 | Li C L, Li Q, Zhao L, et al. Responses of plant community biomass to nitrogen and phosphorus additions in natural and restored grasslands around Qinghai Lake Basin. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2016, 40(10): 1015-1027. |
| 李春丽, 李奇, 赵亮, 等. 环青海湖地区天然草地和退耕恢复草地植物群落生物量对氮、磷添加的响应. 植物生态学报, 2016, 40(10): 1015-1027. |
| [1] | 李思媛, 崔雨萱, 孙宗玖, 刘慧霞, 冶华薇. 封育对蒿类荒漠草地土壤有机碳及土壤微生物生物量生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 58-70. |
| [2] | 江奥, 敬路淮, 泽让东科, 田黎明. 放牧影响草地凋落物分解研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 208-220. |
| [3] | 苏荣霞, 马彦平, 王红梅, 赵亚楠, 李志丽. 荒漠草原不同间距灌丛引入对土壤细菌碳源利用和胞外酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 93-105. |
| [4] | 张永超, 魏小星, 梁国玲, 秦燕, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 刘勇, 马祥. 老芒麦衰老过程形态特征变化规律及对养分添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 101-111. |
| [5] | 李洋, 王毅, 韩国栋, 孙建, 汪亚峰. 青藏高原高寒草地土壤微生物量碳氮含量特征及其控制要素[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 50-60. |
| [6] | 卢俊艳, 红梅, 赵巴音那木拉null, 赵乌英嘎, 王文东, 马尚飞, 杨殿林. 贝加尔针茅草原植物群落结构及生物量对长期养分添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 22-31. |
| [7] | 张永超, 梁国玲, 秦燕, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 刘勇, 马祥. 老芒麦衰老过程中叶片叶绿素和光合作用变化特征及对养分的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 229-237. |
| [8] | 顾继雄, 郭天斗, 王红梅, 李雪颖, 梁丹妮, 杨青莲, 高锦月. 宁夏东部荒漠草原向灌丛地转变过程土壤微生物响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 46-57. |
| [9] | 孙华方, 李希来, 金立群, 李成一, 张静. 黄河源人工草地土壤微生物多样性对建植年限的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 46-58. |
| [10] | 宋达成, 王理德, 吴昊, 吴春荣, 赵赫然, 韩生慧, 胥宝一. 民勤退耕区次生草地土壤特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 59-68. |
| [11] | 周诗晶, 罗佳宁, 刘仲淼, 董超, 秦燕, 吴淑娟, 甘红军, 谢菲, 庄光辉, 伏兵哲, 牛得草. 箭筈豌豆种植密度对土壤微生物养分代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 63-72. |
| [12] | 鲍根生, 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 尹亚丽, 王宏生. 围封和防除狼毒对狼毒斑块土壤理化性质和微生物量影响的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 63-72. |
| [13] | 徐绮雯, 马淑敏, 朱波, 张小短, 邢毅, 段美春, 王龙昌. 生物炭与化肥配施对紫色土肥力与微生物特征及油菜产量品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 121-131. |
| [14] | 张建军, 党翼, 赵刚, 王磊, 樊廷录, 李尚中, 雷康宁. 留膜留茬免耕栽培对旱作玉米田土壤养分、微生物数量及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 123-133. |
| [15] | 帅林林, 周青平, 陈有军, 苟小林, 周蓉. 高寒半湿润沙地草本修复期土壤微生物变化研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 11-22. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||