

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 74-82.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023466
收稿日期:2023-12-01
修回日期:2023-12-25
出版日期:2024-10-20
发布日期:2024-07-15
作者简介:亓琳(1985-),女,河南洛阳人,副教授,博士。E-mail: linq@haust.edu.cn
基金资助:
Lin QI1,2( ), Yun BAO2, Ying-bo YANG3, Xiao-ling WANG2, Wei ZHAO2
), Yun BAO2, Ying-bo YANG3, Xiao-ling WANG2, Wei ZHAO2
Received:2023-12-01
Revised:2023-12-25
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-07-15
摘要:
为探明硝态氮对燕麦锶富集能力的影响,以燕麦内蒙科艺1号为试验材料,采用土培盆栽试验,施加3个水平的金属锶(0、400和800 mg·kg-1)和两个水平的硝态氮(0和100 mmol·L-1)处理,在硝态氮处理30 d后,研究硝态氮在锶污染条件下对燕麦锶的富集和分布特征,生长指标以及叶片细胞分裂素浓度的影响。结果表明:1)燕麦幼苗的干重随着锶浓度的升高呈现降低的趋势,硝态氮缓解了金属锶对燕麦生长的抑制作用;2)燕麦富集锶的能力表现为根>叶>茎,硝态氮促进了燕麦对锶的富集作用,提高了燕麦对锶的转运系数;3)细胞分裂素含量随着硝态氮施加浓度增加而增加。细胞分裂素含量与转运系数呈正相关。综上所述,燕麦根部富集锶的能力最强;硝态氮可以诱导燕麦中细胞分裂素含量增加,促进其对锶的抗性。此研究可为强化植物修复锶污染土壤的研究提供理论依据。
亓琳, 包云, 杨莹博, 王晓凌, 赵威. 硝态氮诱导细胞分裂素强化燕麦锶富集机制的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 74-82.
Lin QI, Yun BAO, Ying-bo YANG, Xiao-ling WANG, Wei ZHAO. A study of the mechanism of nitrate nitrogen-induced cytokinin enhancement of strontium enrichment in Avena sativa[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(10): 74-82.
| pH | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 阳离子交换量 Cation exchange capacity (cmol·kg-1) | 锶 Strontium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.05 | 12.85 | 0.96 | 12.52 | 155.13 | 19.23 | 5.78 |
表1 试验土壤的基本理化性质
Table 1 Basic physicochemical properties of the test soil
| pH | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 阳离子交换量 Cation exchange capacity (cmol·kg-1) | 锶 Strontium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.05 | 12.85 | 0.96 | 12.52 | 155.13 | 19.23 | 5.78 |
硝态氮处理 Nitrate nitrogen treatment (mmol·L-1) | 锶处理 Strontium treatment (mg·kg-1) | 干重Dry weight (mg) | 根冠比 Root to shoot ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根 Root | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | |||
| 0 | 0 | 60±1Aa | 71±12Aa | 74±11Ba | 0.41Ac |
| 400 | 57±2Bb | 52±8Bb | 61±4Bb | 0.50Ab | |
| 800 | 54±1Bc | 44±11Bb | 52±6Bc | 0.56Aa | |
| 10 | 0 | 62±1Aa | 76±14Aa | 84±9Aa | 0.39Bc |
| 400 | 59±3Aab | 71±8Ab | 75±4Ab | 0.40Bb | |
| 800 | 58±1Ab | 68±11Ab | 68±7Ab | 0.43Ba | |
表2 不同硝态氮和锶处理对燕麦生物量的影响
Table 2 The effects of different nitrate nitrogen and strontium treatments on oat biomass
硝态氮处理 Nitrate nitrogen treatment (mmol·L-1) | 锶处理 Strontium treatment (mg·kg-1) | 干重Dry weight (mg) | 根冠比 Root to shoot ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根 Root | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | |||
| 0 | 0 | 60±1Aa | 71±12Aa | 74±11Ba | 0.41Ac |
| 400 | 57±2Bb | 52±8Bb | 61±4Bb | 0.50Ab | |
| 800 | 54±1Bc | 44±11Bb | 52±6Bc | 0.56Aa | |
| 10 | 0 | 62±1Aa | 76±14Aa | 84±9Aa | 0.39Bc |
| 400 | 59±3Aab | 71±8Ab | 75±4Ab | 0.40Bb | |
| 800 | 58±1Ab | 68±11Ab | 68±7Ab | 0.43Ba | |
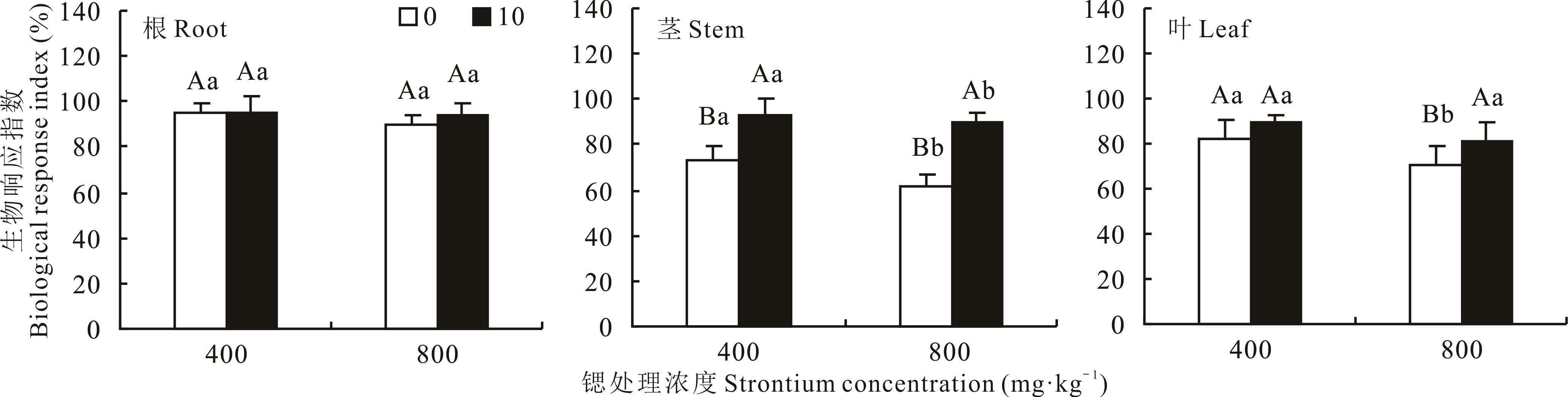
图1 燕麦生物量对硝态氮和锶处理的生物响应指数不同小写字母表示同一硝态氮处理的不同锶浓度间差异显著(P<0.05),不同大写字母表示同一金属锶处理的不同硝态氮浓度间差异显著(P<0.05)。□0:表示无硝态氮添加处理,■10:表示10 mmol·L-1硝态氮处理。下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different strontium treatments of the same nitrate nitrogen treatment (P<0.05), and different uppercaes letters indicate significant differences between nitrate nitrogen treatments of the same metal strontium concentrations (P<0.05). In the figure, □0: represents no nitrate addition treatment, ■10: represents 10 mmol·L-1 nitrate nitrogen treatment. The same below.
Fig.1 The biological response index of oat biomass under nitrate nitrogen and strontium treatments
硝态氮处理 Nitrate nitrogen treatment (mmol·L-1) | 锶处理 Strontium treatment (mg·kg-1) | 富集浓度 Accumulation concentration (mg·kg-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根 Root | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | ||
| 0 | 0 | 5±1Ac | 2±1Ac | 2±1Ac |
| 400 | 186±3Bb | 77±8Bb | 89±4Bb | |
| 800 | 274±31Ba | 112±11Ba | 151±12Ba | |
| 10 | 0 | 6±1Ac | 3±1Ac | 3±1Ac |
| 400 | 226±12Ab | 97±8Ab | 139±4Ab | |
| 800 | 324±31Aa | 152±11Aa | 221±12Aa | |
表3 不同硝态氮和锶处理下燕麦植株各器官中锶的富集特征
Table 3 Strontium accumulation characteristics in organs of oats under different nitrate and strontium treatments
硝态氮处理 Nitrate nitrogen treatment (mmol·L-1) | 锶处理 Strontium treatment (mg·kg-1) | 富集浓度 Accumulation concentration (mg·kg-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根 Root | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | ||
| 0 | 0 | 5±1Ac | 2±1Ac | 2±1Ac |
| 400 | 186±3Bb | 77±8Bb | 89±4Bb | |
| 800 | 274±31Ba | 112±11Ba | 151±12Ba | |
| 10 | 0 | 6±1Ac | 3±1Ac | 3±1Ac |
| 400 | 226±12Ab | 97±8Ab | 139±4Ab | |
| 800 | 324±31Aa | 152±11Aa | 221±12Aa | |
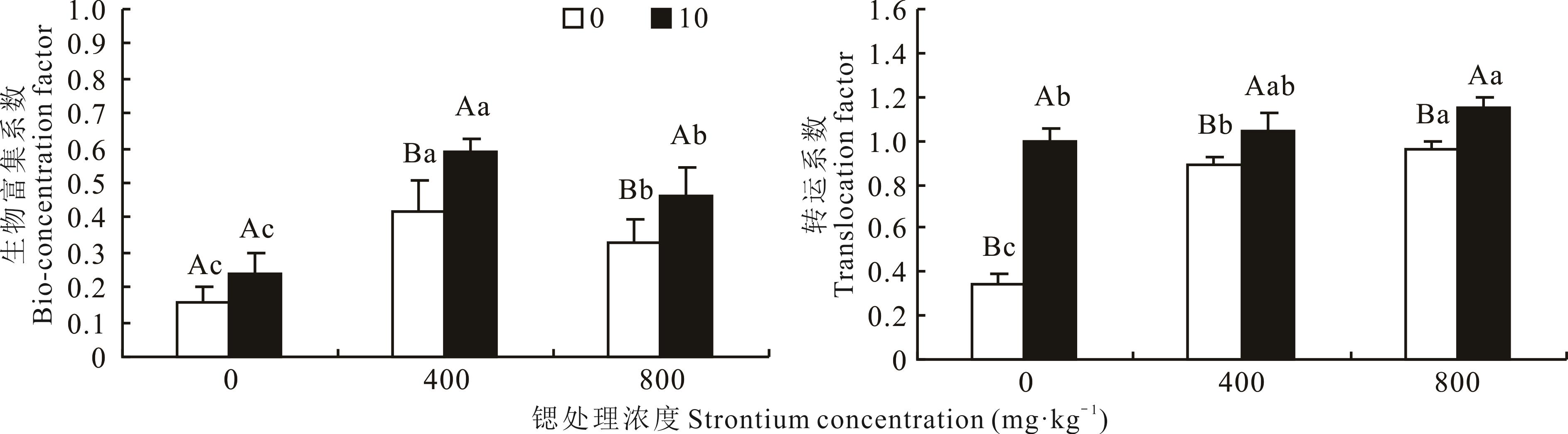
图2 不同硝态氮和锶处理下燕麦对锶的生物富集系数和转运系数
Fig.2 Bio-concentration factor and translocation factor of oat under different nitrate nitrogen and strontium treatments
硝态氮处理 Nitrate nitrogen treatment (mmol·L-1) | 锶处理 Strontium treatment (mg·kg-1) | 土壤pH值 Soil pH value |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 8.3±0.2Aa |
| 400 | 8.1±0.3Aa | |
| 800 | 7.9±0.2Aa | |
| 10 | 0 | 6.3±0.5Ba |
| 400 | 6.4±0.3Ba | |
| 800 | 6.2±0.3Ba |
表4 不同硝态氮和锶处理下土壤pH值
Table 4 The soil pH values under different nitrate nitrogen and strontium treatments
硝态氮处理 Nitrate nitrogen treatment (mmol·L-1) | 锶处理 Strontium treatment (mg·kg-1) | 土壤pH值 Soil pH value |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 8.3±0.2Aa |
| 400 | 8.1±0.3Aa | |
| 800 | 7.9±0.2Aa | |
| 10 | 0 | 6.3±0.5Ba |
| 400 | 6.4±0.3Ba | |
| 800 | 6.2±0.3Ba |
硝态氮处理 Nitrate nitrogen treatment (mmol·L-1) | 锶处理 Strontium treatment (mg·kg-1) | 细胞分裂素浓度 Cytokinin concentration (ng·g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 95±13Ba |
| 400 | 79±9Bb | |
| 800 | 66±11Bc | |
| 10 | 0 | 115±7Ac |
| 400 | 128±8Ab | |
| 800 | 139±11Aa |
表5 不同硝态氮和锶处理下燕麦叶片细胞分裂素含量
Table 5 The cytokinin concentration in oat leaves under different nitrate nitrogen and strontium treatments
硝态氮处理 Nitrate nitrogen treatment (mmol·L-1) | 锶处理 Strontium treatment (mg·kg-1) | 细胞分裂素浓度 Cytokinin concentration (ng·g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 95±13Ba |
| 400 | 79±9Bb | |
| 800 | 66±11Bc | |
| 10 | 0 | 115±7Ac |
| 400 | 128±8Ab | |
| 800 | 139±11Aa |
类型 Type | 指标 Index | 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | 金属锶 Strontium | 硝态氮×金属锶 Nitrate nitrogen×strontium | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
P值 P value | F值 F value | P值 P value | F值 F value | P值 P value | F值 F value | ||
生物量 Biomass | 根 Root | 0.12 | 2.54 | <0.001 | 56.99 | <0.001 | 108.47 |
| 茎 Stem | 0.04 | 119.20 | <0.001 | 443.21 | 0.040 | 15.81 | |
| 叶 Leaf | <0.001 | 126.06 | 0.03 | 21.66 | <0.001 | 25.04 | |
| 根冠比 Root to shoot ratio | <0.001 | 90.33 | <0.001 | 53.33 | 0.530 | <0.001 | |
锶浓度 Strontium concentration | 根Root | <0.001 | 59.81 | <0.001 | 33.16 | 0.02 | 18.47 |
| 茎 Stem | <0.001 | 25.33 | <0.001 | 213.43 | <0.001 | 128.12 | |
| 叶 Leaf | <0.001 | 41.29 | <0.001 | 113.66 | <0.001 | 146.20 | |
| 转运系数 Translocation factor (TLF) | <0.001 | 26.33 | <0.001 | 543.33 | <0.001 | 1128.53 | |
| 生物富集系数 Bio-concentration factor (BCF) | <0.001 | 41.29 | <0.001 | 113.66 | <0.001 | 186.20 | |
| 土壤pH Soil pH | <0.001 | 513.72 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.030 | 18.47 | |
| 细胞分裂素Cytokinin | <0.001 | 33.14 | 0.34 | 0.01 | <0.001 | 1108.13 | |
表6 采用双因素方差分析比较硝态氮处理、金属锶处理及其相互作用对各项指标的影响
Table 6 The effects of nitrate nitrogen treatment, metal strontium treatment and their interactions on each indicators by two-way ANOVA
类型 Type | 指标 Index | 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | 金属锶 Strontium | 硝态氮×金属锶 Nitrate nitrogen×strontium | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
P值 P value | F值 F value | P值 P value | F值 F value | P值 P value | F值 F value | ||
生物量 Biomass | 根 Root | 0.12 | 2.54 | <0.001 | 56.99 | <0.001 | 108.47 |
| 茎 Stem | 0.04 | 119.20 | <0.001 | 443.21 | 0.040 | 15.81 | |
| 叶 Leaf | <0.001 | 126.06 | 0.03 | 21.66 | <0.001 | 25.04 | |
| 根冠比 Root to shoot ratio | <0.001 | 90.33 | <0.001 | 53.33 | 0.530 | <0.001 | |
锶浓度 Strontium concentration | 根Root | <0.001 | 59.81 | <0.001 | 33.16 | 0.02 | 18.47 |
| 茎 Stem | <0.001 | 25.33 | <0.001 | 213.43 | <0.001 | 128.12 | |
| 叶 Leaf | <0.001 | 41.29 | <0.001 | 113.66 | <0.001 | 146.20 | |
| 转运系数 Translocation factor (TLF) | <0.001 | 26.33 | <0.001 | 543.33 | <0.001 | 1128.53 | |
| 生物富集系数 Bio-concentration factor (BCF) | <0.001 | 41.29 | <0.001 | 113.66 | <0.001 | 186.20 | |
| 土壤pH Soil pH | <0.001 | 513.72 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.030 | 18.47 | |
| 细胞分裂素Cytokinin | <0.001 | 33.14 | 0.34 | 0.01 | <0.001 | 1108.13 | |
| 1 | Mangano J, Gaus K S, Mousseau T A, et al. Strontium-90 in baby teeth as a basis for estimating US cancer deaths from nuclear weapons fallout. International Journal of Social Determinants of Health and Health Services, 2023, 28(3): 374-384. |
| 2 | Alsharef S, Alanazi M, Alharthi F, et al. Review about radiopharmaceuticals: preparation, radioactivity, and applications. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2020, 12(3): 8-15. |
| 3 | Coudert F X. Strontium’s scarlet sparkles. Nature Chemistry, 2015, 7(11): 940. |
| 4 | Tsukada H, Takeda A, Takahashi T, et al. Uptake and distribution of 90Sr and stable Sr in rice plants. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2005, 81(2/3): 221-231. |
| 5 | Bhat S A, Bashir O, Haq S A U, et al. Phytoremediation of heavy metals in soil and water: An eco-friendly, sustainable and multidisciplinary approach. Chemosphere, 2022, 303(1): 134788. |
| 6 | Kafle A, Timilsina A, Gautam A, et al. Phytoremediation: Mechanisms, plant selection and enhancement by natural and synthetic agents. Environmental Advances, 2022, 8(1): 100203. |
| 7 | Shi L, Li J, Palansooriya K N, et al. Modeling phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils through machine learning. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 441(1): 129904. |
| 8 | Zhu Y, Wang Y, He X, et al. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria: A good companion for heavy metal phytoremediation. Chemosphere, 2023, 338(1): 139475. |
| 9 | Saini S, Kaur N, Pati P K. Phytohormones: Key players in the modulation of heavy metal stress tolerance in plants. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 223(1): 112578. |
| 10 | Sharma A, Kapoor D, Gautam S, et al. Heavy metal induced regulation of plant biology: Recent insights. Physiologia Plantarum, 2022, 174(3): e13688. |
| 11 | Sameena P P, Puthur J T. Exogenous application of cytokinins confers copper stress tolerance in Ricinus communis L. seedlings. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2021, 41(1): 3395-3409. |
| 12 | Wang X L, Duan P L, Sun R H, et al. Effects of soil nitrification on compensatory growth upon post-drought rewatering of corns based on cytokinin. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 2020, 23(5): 882-888. |
| 13 | Gu J, Li Z, Mao Y, et al. Roles of nitrogen and cytokinin signals in root and shoot communications in maximizing of plant productivity and their agronomic applications. Plant Science, 2018, 274(1): 320-331. |
| 14 | Khan T A, Nadeem F, Gao Y, et al. A larger root system in oat (Avena nuda L.) is coupled with enhanced biomass accumulation and hormonal alterations under low nitrogen. Applied Ecology & Environmental Research, 2019, 17(2): 4631-4653. |
| 15 | Lu R K. Analysis methods for soil and agrochemistry. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. | |
| 16 | Tang Y J, Luo X G, Zeng F, et al. The responses of plants to high concentrations of strontium, cesium stress and the screening of remediation plants. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(5): 960-965. |
| 唐永金, 罗学刚, 曾峰, 等. 不同植物对高浓度Sr、Cs胁迫的响应与修复植物筛选. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(5): 960-965. | |
| 17 | Liu Z L, Jie L, Yang Y Q, et al. Research and application of microwave assisted digestion procedure for the determination of 23 elements in sediments by ICP-AES/ICP-MS. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(12): 2370-2377. |
| 18 | Soudek P, Valenová Š, Vavříková Z, et al. 137Cs and 90Sr uptake by sunflower cultivated under hydroponic conditions. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2006, 88(3): 236-250. |
| 19 | Wang X L, Duan P L, Yang S J, et al. Corn compensatory growth upon post-drought re-watering based on the effects of rhizosphere soil nitrification on cytokinin. Agricultural Water Management, 2020, 241(1): 106436. |
| 20 | Yang T, Zhong Q L, Li B Y, et al. Effects of short-term combined application of ammonium nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen on the growth and leaf traits of Machilus pauhoi seedlings. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(1): 25-32. |
| 杨婷, 钟全林, 李宝银, 等. 短期铵态氮与硝态氮配施对刨花楠幼苗生长及叶片性状的影响. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(1): 25-32. | |
| 21 | Lu Y, Dong F, Tian T, et al. Effects of nitrogen nutrition on wheat seedling root growth and drought resistance. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 53(1): 39-45. |
| 卢毅, 董放, 田田, 等. 不同氮素营养对小麦苗期根系发育及抗旱性的影响. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 53(1): 39-45. | |
| 22 | Zhang Q Z, Hao G, Li H Y. Effects of availability and form of exogenous nitrogen on plant growth and physiology: Progress and prospects. Chinese Journal of Ecology, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20230309.1116.016.html. |
| 张秦泽, 郝广, 李洪远. 外源输入氮的有效性及形态对植物生长与生理影响的研究进展. 生态学杂志, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20230309.1116.016.html. | |
| 23 | Gao Y, Song X, Liu K, et al. Mixture of controlled-release and conventional urea fertilizer application changed soil aggregate stability, humic acid molecular composition, and maize nitrogen uptake. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 789(1): 147778. |
| 24 | Hatamian M, Nejad A R, Kafi M, et al. Nitrate improves hackberry seedling growth under cadmium application. Heliyon, 2020, 6(1): e03247. |
| 25 | Zu Q X, Nie Z Y, Lin S, et al. Effects of ammonium nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen ratio on growth and ion balance of flue-cured tobacco. Crops, 2023, 39(3): 154-158. |
| 祖庆学, 聂忠扬, 林松, 等. 铵态氮和硝态氮配比对烤烟生长及离子平衡的影响. 作物杂志, 2023, 39(3): 154-158. | |
| 26 | Liu N, Zhang L, Meng X X, et al. Effect of nitrate/ammonium ratios on growth, root morphology and nutrient elements uptake of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) seedlings. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2014, 37(11): 1859-1872. |
| 27 | Wei X Q, Jia W F, Ma J H, et al. Review on the effects of plant growth regulators on plant growth and development. Northern Horticulture, 2022(4): 118-125. |
| 魏晓琼, 贾文飞, 马靖恒, 等. 植物生长调节剂对植株生长发育的影响概述. 北方园艺, 2022(4): 118-125. | |
| 28 | Ramireddy E, Nelissen H, Leuendorf J E, et al. Root engineering in maize by increasing cytokinin degradation causes enhanced root growth and leaf mineral enrichment. Plant Molecular Biology, 2021, 106(1): 555-567. |
| 29 | Qin R R, Wang X L. Effects of crown height on the compensatory growth of Italian ryegrass based on combined effects of stored organic matter and cytokinin. Grassland Science, 2019, 66(1): 29-39. |
| 30 | Fang Z G, Yang Q, Xie J T, et al. The role and mechanism of cytokinin in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(8): 3056-3065. |
| 方治国, 杨青, 谢俊婷, 等. 重金属污染土壤植物修复中细胞分裂素的作用与机制. 生态学报, 2022, 42(8): 3056-3065. | |
| 31 | Li P, Guo X F, Xu L L, et al. Influence of exogenous cytokinins on uptake and translocation of cadmium in corn seedlings. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 25(1): 119-122. |
| 李萍, 郭喜丰, 徐莉莉, 等. 细胞分裂素类物质对玉米幼苗镉吸收和转运的影响. 水土保持学报, 2011, 25(1): 119-122. | |
| 32 | Zhang Q, Xing J, Yao J M, et al. The role of a cytokinin signaling pathway type-B ARR transcription factor, LpARR10, in cadmium tolerance of perennial ryegrass. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(5): 135-143. |
| 张晴, 邢静, 姚佳明, 等. 多年生黑麦草细胞分裂素信号通路B类ARR转录因子LpARR10的耐镉功能分析. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 135-143. |
| [1] | 王宝, 谢占玲, 郭璟, 唐永鹏, 孟清, 彭清青, 杨家宝, 董德誉, 徐鸿雁, 高太侦, 张凡, 段迎珠. 真菌发酵液浸种燕麦对其抗旱性及根际真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 126-139. |
| [2] | 关皓, 许多, 李海萍, 贾志锋, 马祥, 刘文辉, 陈有军, 李欣洋, 黄艳玲, 周青平, 陈仕勇. 高寒地区17个燕麦品种营养品质及瘤胃降解特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 185-198. |
| [3] | 米春娇, 洪流, 马馼, 毛培胜. 谷胱甘肽引发对老化燕麦种胚线粒体抗氧化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 51-59. |
| [4] | 马圆, 刘欢, 赵桂琴, 王敬龙, 张然, 姚瑞瑞. 燕麦sHSP基因家族的鉴定及其响应高温及老化的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 145-158. |
| [5] | 杜文盼, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽, 杨莉, 张建贵, 史怡超, 张官禄. 根系分隔方式对燕麦/豌豆间作地上生物量、土壤养分及根系性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 25-36. |
| [6] | 桑瑞娟, 崔超杰, 何云, 张晓霞, 姚晋, 董春阳, 孙浩, 史莹华, 朱晓艳, 李德锋. 豫北地区18个秋播饲用燕麦品种抗倒伏特性及生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 74-85. |
| [7] | 张昭, 伏莹莹, 孙浩文, 孙逢雪, 闫慧芳. 不同品种燕麦种子活力鉴定与耐贮藏性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 165-174. |
| [8] | 李鸿飞, 周帮伟, 张淼, 施树楠, 李志坚. 不同燕麦品种在呼伦贝尔地区的引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 60-72. |
| [9] | 慕平, 柴继宽, 苏玮娟, 章海龙, 赵桂琴. 燕麦不同组合正、反交杂种后代的表型及遗传参数分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 73-86. |
| [10] | 冯琴, 何小莉, 王斌, 王腾飞, 倪旺, 马霞, 明雪花, 邓建强, 兰剑. 宁夏引黄灌区燕麦与箭筈豌豆的混播效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 107-119. |
| [11] | 鲍根生, 李媛, 冯晓云, 张鹏, 孟思宇. 高寒区氮添加和间作种植互作对燕麦和豌豆根系构型影响的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 73-84. |
| [12] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 王静, 吴勇, 童长春. 连续间作下的紫花苜蓿/燕麦根系与碳氮代谢特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 85-96. |
| [13] | 罗颖, 李聪, 王沛, 田莉华, 汪辉, 周青平, 雷映霞. 低氮胁迫下不同皮燕麦品种早期的响应研究及耐低氮性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 164-184. |
| [14] | 王正, 李新, 张建贵, 柴继宽, 赵桂琴, 牛奎举. 外源褪黑素介导抗氧化和苯丙烷代谢提高燕麦叶斑病抗性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 135-146. |
| [15] | 周青平, 胡晓炜, 汪辉, 陈有军. 燕麦在维护国家粮食安全中的重要作用[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 171-182. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||