

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (9): 65-77.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024378
赵聪1,2,3,4( ), 吴文慧5, 王娟玲2(
), 吴文慧5, 王娟玲2( ), 梁改梅1,2,3,4,5(
), 梁改梅1,2,3,4,5( ), 李娜娜1,2,3,4,5, 黄学芳1,2,3,4
), 李娜娜1,2,3,4,5, 黄学芳1,2,3,4
收稿日期:2024-09-27
修回日期:2024-10-31
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-07-02
通讯作者:
王娟玲,梁改梅
作者简介:Juanling_Wang@sxau.edu.cn基金资助:
Cong ZHAO1,2,3,4( ), Wen-hui WU5, Juan-ling WANG2(
), Wen-hui WU5, Juan-ling WANG2( ), Gai-mei LIANG1,2,3,4,5(
), Gai-mei LIANG1,2,3,4,5( ), Na-na LI1,2,3,4,5, Xue-fang HUANG1,2,3,4
), Na-na LI1,2,3,4,5, Xue-fang HUANG1,2,3,4
Received:2024-09-27
Revised:2024-10-31
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-07-02
Contact:
Juan-ling WANG,Gai-mei LIANG
摘要:
为比较结球甘蓝对3种适宜在山西冷凉区旱作栽培的作物种子萌发及幼苗生长的化感效应差异,并从生理学层面揭示其作用机制,本研究采用培养皿滤纸法和盆栽培养法,开展结球甘蓝风干叶水提液对西葫芦、菜豆和玉米种子萌发、幼苗生长与生理特性的影响研究。结果表明,一定浓度的结球甘蓝叶水提液会对3种作物种子萌发与幼苗生长产生显著的抑制作用(P<0.05),且该作用随浓度增加而增强。同一浓度处理,对西葫芦和玉米胚根伸长的抑制作用均强于胚芽,仅当水提液浓度为0.04 g·mL-1时,对菜豆胚根伸长的抑制作用小于胚芽。化感物质处理后菜豆和玉米幼苗的丙二醛含量均高于对照。当处理液浓度为0.06、0.08 g·mL-1时,受体作物幼苗抗氧化物酶如超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)及过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性有所增强。3种受体作物的化感综合抑制作用强弱顺序为西葫芦>玉米>菜豆,该差异与作物体内丙二醛含量和抗氧化物酶活性变化有关。因此,结球甘蓝茬衔接菜豆的种植模式可能是缓解该茬口化感负效应的方法之一。在采收结球甘蓝时,建议将地上部完全去除,避免化感物质累积于土壤中,进而影响下茬作物生长。
赵聪, 吴文慧, 王娟玲, 梁改梅, 李娜娜, 黄学芳. 结球甘蓝叶对3种作物芽期与苗期生长的化感效应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 65-77.
Cong ZHAO, Wen-hui WU, Juan-ling WANG, Gai-mei LIANG, Na-na LI, Xue-fang HUANG. Allelopathic effects of cabbage leaf on germination and seedling stages of three crops[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(9): 65-77.

图1 结球甘蓝叶水提液质量浓度对3种作物种子发芽势与发芽率的影响不同小写字母表示相同供试作物不同质量浓度处理间差异达显著水平(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters mean significant differences at 0.05 level among different concentration treatments of the same tested crop. The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of mass concentrations of cabbage-leaf water extracts on the seed germination potential and rate of three crop seeds
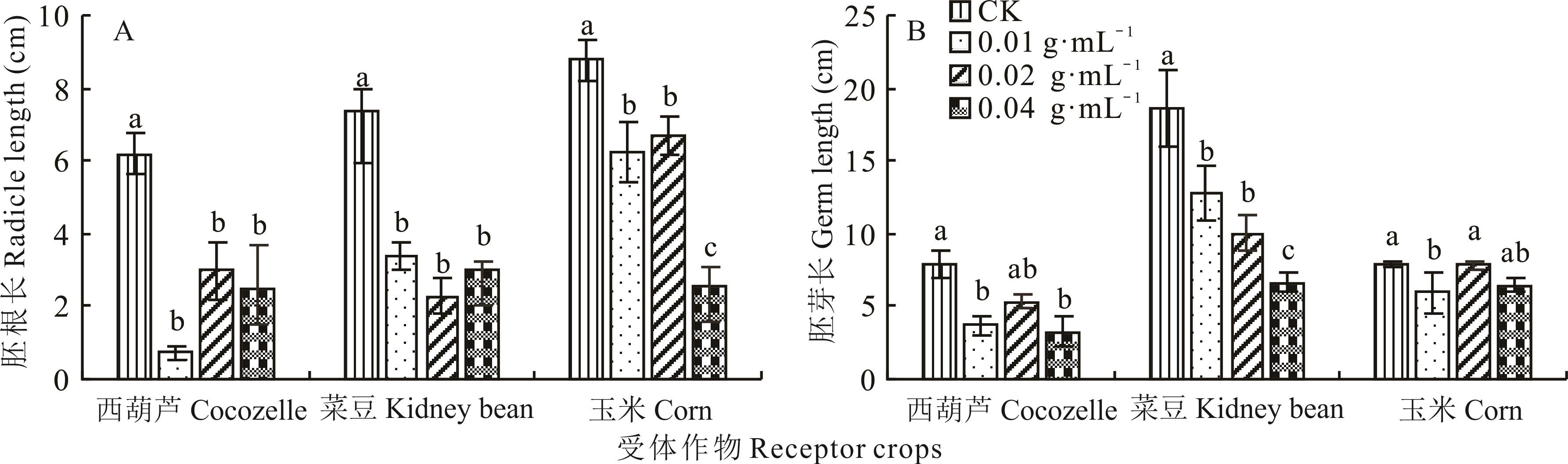
图2 结球甘蓝叶水提液质量浓度对3种作物种子胚根长与胚芽长的影响
Fig.2 Effects of mass concentrations of cabbage-leaf water extracts on the radicle and germ length of three crop seeds

图3 结球甘蓝叶水提液质量浓度对3种作物种子胚根与胚芽干重的影响
Fig.3 Effects of mass concentrations of cabbage-leaf water extracts on the radicle and germ dry weight of three crop seeds
受体作物 Receptor crops | 质量浓度 Mass concentration (g·mL-1) | 化感效应指数Index of allelopathic effect | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
发芽势 Germination potential | 发芽率 Germination rate | 胚根长 Radicle length | 胚芽长 Germ length | 胚芽干重 Dry weight of germ | 胚根干重 Dry weight of radicle | ||
西葫芦 Cocozelle | 0.01 | -0.568 | -0.494 | -0.880 | -0.532 | 0.107 | -0.537 |
| 0.02 | -0.635 | -0.701 | -0.516 | -0.325 | 0.088 | -0.103 | |
| 0.04 | -0.946 | -0.948 | -0.593 | -0.589 | -0.272 | 0.250 | |
菜豆 Kidney bean | 0.01 | -0.347 | -0.200 | -0.535 | -0.309 | 0.109 | -0.224 |
| 0.02 | -0.458 | -0.294 | -0.688 | -0.458 | 0.124 | -0.425 | |
| 0.04 | -0.625 | -0.482 | -0.586 | -0.644 | 0.229 | -0.390 | |
玉米 Corn | 0.01 | -0.211 | -0.159 | -0.290 | -0.248 | -0.249 | -0.245 |
| 0.02 | -0.296 | -0.207 | -0.240 | -0.016 | -0.150 | -0.371 | |
| 0.04 | -0.408 | -0.378 | -0.707 | -0.187 | -0.336 | -0.670 | |
表1 不同结球甘蓝叶水提液质量浓度时3种作物种子萌发的化感指数
Table 1 Allelopathic index of the seed germination of three crops under different mass concentrations of cabbage-leaf water extracts
受体作物 Receptor crops | 质量浓度 Mass concentration (g·mL-1) | 化感效应指数Index of allelopathic effect | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
发芽势 Germination potential | 发芽率 Germination rate | 胚根长 Radicle length | 胚芽长 Germ length | 胚芽干重 Dry weight of germ | 胚根干重 Dry weight of radicle | ||
西葫芦 Cocozelle | 0.01 | -0.568 | -0.494 | -0.880 | -0.532 | 0.107 | -0.537 |
| 0.02 | -0.635 | -0.701 | -0.516 | -0.325 | 0.088 | -0.103 | |
| 0.04 | -0.946 | -0.948 | -0.593 | -0.589 | -0.272 | 0.250 | |
菜豆 Kidney bean | 0.01 | -0.347 | -0.200 | -0.535 | -0.309 | 0.109 | -0.224 |
| 0.02 | -0.458 | -0.294 | -0.688 | -0.458 | 0.124 | -0.425 | |
| 0.04 | -0.625 | -0.482 | -0.586 | -0.644 | 0.229 | -0.390 | |
玉米 Corn | 0.01 | -0.211 | -0.159 | -0.290 | -0.248 | -0.249 | -0.245 |
| 0.02 | -0.296 | -0.207 | -0.240 | -0.016 | -0.150 | -0.371 | |
| 0.04 | -0.408 | -0.378 | -0.707 | -0.187 | -0.336 | -0.670 | |
受体作物 Receptor crops | 质量浓度 Mass concentration (g·mL-1) | 相对胚根长 Relative radicle length (%) | 相对胚芽长 Relative germ length (%) | 相对胚根干重 Relative radicle dry weight (%) | 相对胚芽干重 Relative germ dry weight (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
西葫芦 Cocozelle | 0.01 | 12.00±1.11b | 46.85±2.57b | 47.92±8.57c | 112.91±1.51a |
| 0.02 | 48.35±2.96a | 67.51±3.96a | 93.85±5.15b | 110.58±2.97a | |
| 0.04 | 40.67±2.15a | 60.09±10.22ab | 138.10±7.14a | 73.39±8.95b | |
菜豆 Kidney bean | 0.01 | 46.48±5.28a | 69.06±12.55a | 78.23±10.23a | 112.08±4.88b |
| 0.02 | 31.21±3.14b | 54.15±10.67a | 57.97±14.16a | 113.95±2.96b | |
| 0.04 | 41.40±2.62a | 35.56±3.10b | 61.47±9.86a | 129.53±3.53a | |
玉米 Corn | 0.01 | 71.04±9.56a | 75.19±10.48b | 77.04±11.05a | 75.61±12.41a |
| 0.02 | 76.02±5.21a | 98.41±5.01a | 64.14±9.87a | 85.58±4.33a | |
| 0.04 | 29.34±3.58b | 81.36±4.39b | 33.67±7.24b | 66.87±2.15a |
表2 结球甘蓝叶水提液质量浓度对3种作物种子胚根与胚芽相对生长的影响
Table 2 Effects of mass concentrations of cabbage-leaf water extracts on the relative growth of radicle and germ of three crop seeds
受体作物 Receptor crops | 质量浓度 Mass concentration (g·mL-1) | 相对胚根长 Relative radicle length (%) | 相对胚芽长 Relative germ length (%) | 相对胚根干重 Relative radicle dry weight (%) | 相对胚芽干重 Relative germ dry weight (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
西葫芦 Cocozelle | 0.01 | 12.00±1.11b | 46.85±2.57b | 47.92±8.57c | 112.91±1.51a |
| 0.02 | 48.35±2.96a | 67.51±3.96a | 93.85±5.15b | 110.58±2.97a | |
| 0.04 | 40.67±2.15a | 60.09±10.22ab | 138.10±7.14a | 73.39±8.95b | |
菜豆 Kidney bean | 0.01 | 46.48±5.28a | 69.06±12.55a | 78.23±10.23a | 112.08±4.88b |
| 0.02 | 31.21±3.14b | 54.15±10.67a | 57.97±14.16a | 113.95±2.96b | |
| 0.04 | 41.40±2.62a | 35.56±3.10b | 61.47±9.86a | 129.53±3.53a | |
玉米 Corn | 0.01 | 71.04±9.56a | 75.19±10.48b | 77.04±11.05a | 75.61±12.41a |
| 0.02 | 76.02±5.21a | 98.41±5.01a | 64.14±9.87a | 85.58±4.33a | |
| 0.04 | 29.34±3.58b | 81.36±4.39b | 33.67±7.24b | 66.87±2.15a |
受体作物 Receptor crops | 质量浓度 Mass concentration (g·mL-1) | 株高 Plant height | 根长 Root length | 地下部干重 Underground dry weight | 地上部干重 Aboveground dry weight | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
测定值 Measured value (cm) | 化感效应 指数Response index (RI) | 测定值 Measured value (cm) | 化感效应 指数Response index (RI) | 测定值 Measured value (g·plant-1) | 化感效应指数Response index (RI) | 测定值 Measured value (g·plant-1) | 化感效应指数Response index (RI) | ||
西葫芦 Cocozelle | 0 | 12.78±1.65a | - | 9.78±0.76a | - | 0.059±0.009a | - | 0.163±0.006a | - |
| 0.06 | 9.89±0.86ab | -0.226 | 8.28±0.81ab | -0.153 | 0.043±0.005b | -0.271 | 0.149±0.008ab | -0.086 | |
| 0.08 | 9.31±0.52b | -0.272 | 6.53±0.92ab | -0.332 | 0.040±0.009b | -0.322 | 0.139±0.009b | -0.147 | |
| 0.10 | 8.23±0.91b | -0.356 | 5.10±0.55b | -0.479 | 0.028±0.006c | -0.525 | 0.094±0.005c | -0.423 | |
菜豆 Kidney bean | 0 | 25.12±0.86a | - | 11.98±0.85a | - | 0.116±0.006a | - | 0.289±0.012a | - |
| 0.06 | 21.30±1.17a | -0.152 | 10.52±1.23a | -0.122 | 0.083±0.009b | -0.285 | 0.215±0.043a | -0.256 | |
| 0.08 | 19.85±2.25ab | -0.210 | 8.75±1.86ab | -0.270 | 0.078±0.075b | -0.328 | 0.186±0.027b | -0.356 | |
| 0.10 | 14.59±1.32b | -0.419 | 6.16±0.59b | -0.486 | 0.056±0.007c | -0.517 | 0.162±0.038b | -0.439 | |
玉米 Corn | 0 | 46.69±3.31a | - | 17.80±1.95a | - | 0.131±0.007a | - | 0.355±0.005a | - |
| 0.06 | 32.27±1.47b | -0.309 | 9.30±1.24b | -0.478 | 0.109±0.005b | -0.168 | 0.186±0.009c | -0.476 | |
| 0.08 | 31.63±2.27b | -0.323 | 9.10±0.95b | -0.489 | 0.095±0.009c | -0.275 | 0.228±0.011b | -0.358 | |
| 0.10 | 26.92±1.97c | -0.423 | 7.50±0.80c | -0.579 | 0.074±0.005c | -0.435 | 0.157±0.004c | -0.558 | |
表3 结球甘蓝叶水提液质量浓度对3种作物幼苗生长的影响
Table 3 Effects of mass concentrations of cabbage-leaf water extracts on the seedling growth of three crops
受体作物 Receptor crops | 质量浓度 Mass concentration (g·mL-1) | 株高 Plant height | 根长 Root length | 地下部干重 Underground dry weight | 地上部干重 Aboveground dry weight | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
测定值 Measured value (cm) | 化感效应 指数Response index (RI) | 测定值 Measured value (cm) | 化感效应 指数Response index (RI) | 测定值 Measured value (g·plant-1) | 化感效应指数Response index (RI) | 测定值 Measured value (g·plant-1) | 化感效应指数Response index (RI) | ||
西葫芦 Cocozelle | 0 | 12.78±1.65a | - | 9.78±0.76a | - | 0.059±0.009a | - | 0.163±0.006a | - |
| 0.06 | 9.89±0.86ab | -0.226 | 8.28±0.81ab | -0.153 | 0.043±0.005b | -0.271 | 0.149±0.008ab | -0.086 | |
| 0.08 | 9.31±0.52b | -0.272 | 6.53±0.92ab | -0.332 | 0.040±0.009b | -0.322 | 0.139±0.009b | -0.147 | |
| 0.10 | 8.23±0.91b | -0.356 | 5.10±0.55b | -0.479 | 0.028±0.006c | -0.525 | 0.094±0.005c | -0.423 | |
菜豆 Kidney bean | 0 | 25.12±0.86a | - | 11.98±0.85a | - | 0.116±0.006a | - | 0.289±0.012a | - |
| 0.06 | 21.30±1.17a | -0.152 | 10.52±1.23a | -0.122 | 0.083±0.009b | -0.285 | 0.215±0.043a | -0.256 | |
| 0.08 | 19.85±2.25ab | -0.210 | 8.75±1.86ab | -0.270 | 0.078±0.075b | -0.328 | 0.186±0.027b | -0.356 | |
| 0.10 | 14.59±1.32b | -0.419 | 6.16±0.59b | -0.486 | 0.056±0.007c | -0.517 | 0.162±0.038b | -0.439 | |
玉米 Corn | 0 | 46.69±3.31a | - | 17.80±1.95a | - | 0.131±0.007a | - | 0.355±0.005a | - |
| 0.06 | 32.27±1.47b | -0.309 | 9.30±1.24b | -0.478 | 0.109±0.005b | -0.168 | 0.186±0.009c | -0.476 | |
| 0.08 | 31.63±2.27b | -0.323 | 9.10±0.95b | -0.489 | 0.095±0.009c | -0.275 | 0.228±0.011b | -0.358 | |
| 0.10 | 26.92±1.97c | -0.423 | 7.50±0.80c | -0.579 | 0.074±0.005c | -0.435 | 0.157±0.004c | -0.558 | |
受体作物 Receptor crops | 结球甘蓝叶水提液浓度Concentrations of cabbage-leaf water extracts (g·mL-1) | 平均 Average | 排名 Ranking | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.10 | |||
| 西葫芦Cocozelle | -0.484 | -0.366 | -0.516 | -0.185 | -0.267 | -0.447 | -0.378 | 1 |
| 菜豆Kidney bean | -0.251 | -0.367 | -0.416 | -0.204 | -0.291 | -0.465 | -0.332 | 3 |
| 玉米Corn | -0.234 | -0.213 | -0.448 | -0.356 | -0.358 | -0.497 | -0.351 | 2 |
表4 结球甘蓝叶水提液质量浓度对3种作物种子萌发与幼苗生长的化感综合效应
Table 4 Allelopathic comprehensive effects of mass concentrations of cabbage-leaf water extracts on the seed germination and seedling growth of three crops
受体作物 Receptor crops | 结球甘蓝叶水提液浓度Concentrations of cabbage-leaf water extracts (g·mL-1) | 平均 Average | 排名 Ranking | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.10 | |||
| 西葫芦Cocozelle | -0.484 | -0.366 | -0.516 | -0.185 | -0.267 | -0.447 | -0.378 | 1 |
| 菜豆Kidney bean | -0.251 | -0.367 | -0.416 | -0.204 | -0.291 | -0.465 | -0.332 | 3 |
| 玉米Corn | -0.234 | -0.213 | -0.448 | -0.356 | -0.358 | -0.497 | -0.351 | 2 |
受体作物 Receptor crop | 质量浓度Mass concentration (g·mL-1) | MDA含量Malondialdehyde content (μmol·g-1) | 酶活性Enzyme activity (U·g-1·min-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOD | POD | CAT | |||
西葫芦 Cocozelle | 0 | 3.92±0.16b | 51.2±1.9b | 20.1±2.6b | 1.6±0.2c |
| 0.06 | 3.78±0.49b | 53.8±3.1b | 28.5±4.1ab | 5.3±0.8a | |
| 0.08 | 5.06±1.84a | 65.4±2.6a | 32.8±3.9a | 3.9±1.6b | |
| 0.10 | 7.89±0.61a | 39.5±4.8c | 14.2±5.4c | 3.4±1.1b | |
菜豆 Kidney bean | 0 | 2.56±0.11a | 146.2±10.8b | 2085±105.0b | 428.7±20.0a |
| 0.06 | 2.79±0.08a | 149.4±9.9b | 2118±158.0b | 439.1±11.0a | |
| 0.08 | 3.16±0.12a | 171.9±5.1a | 2104±102.0b | 465.5±6.0a | |
| 0.10 | 3.65±0.06a | 143.6±4.2b | 2499±162.0a | 450.6±13.0a | |
玉米 Corn | 0 | 2.96±0.28b | 22.8±1.3b | 52.8±6.4b | 70.2±2.7b |
| 0.06 | 3.37±1.05b | 34.6±4.1a | 63.9±5.2a | 72.5±3.5b | |
| 0.08 | 4.96±2.29a | 28.2±3.2ab | 56.7±2.8b | 89.3±6.7a | |
| 0.10 | 6.09±1.18a | 20.1±2.4b | 41.3±3.5c | 52.5±7.4c | |
表5 不同质量浓度甘蓝叶水提液对3种作物幼苗生理指标的影响
Table 5 Effect of different mass concentrations of cabbage-leaf water extracts on the seedling physiological index of three crops
受体作物 Receptor crop | 质量浓度Mass concentration (g·mL-1) | MDA含量Malondialdehyde content (μmol·g-1) | 酶活性Enzyme activity (U·g-1·min-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOD | POD | CAT | |||
西葫芦 Cocozelle | 0 | 3.92±0.16b | 51.2±1.9b | 20.1±2.6b | 1.6±0.2c |
| 0.06 | 3.78±0.49b | 53.8±3.1b | 28.5±4.1ab | 5.3±0.8a | |
| 0.08 | 5.06±1.84a | 65.4±2.6a | 32.8±3.9a | 3.9±1.6b | |
| 0.10 | 7.89±0.61a | 39.5±4.8c | 14.2±5.4c | 3.4±1.1b | |
菜豆 Kidney bean | 0 | 2.56±0.11a | 146.2±10.8b | 2085±105.0b | 428.7±20.0a |
| 0.06 | 2.79±0.08a | 149.4±9.9b | 2118±158.0b | 439.1±11.0a | |
| 0.08 | 3.16±0.12a | 171.9±5.1a | 2104±102.0b | 465.5±6.0a | |
| 0.10 | 3.65±0.06a | 143.6±4.2b | 2499±162.0a | 450.6±13.0a | |
玉米 Corn | 0 | 2.96±0.28b | 22.8±1.3b | 52.8±6.4b | 70.2±2.7b |
| 0.06 | 3.37±1.05b | 34.6±4.1a | 63.9±5.2a | 72.5±3.5b | |
| 0.08 | 4.96±2.29a | 28.2±3.2ab | 56.7±2.8b | 89.3±6.7a | |
| 0.10 | 6.09±1.18a | 20.1±2.4b | 41.3±3.5c | 52.5±7.4c | |
| [1] | Liu J, Zhu K L, Yue H W, et al. Effects of seed coat on seed germination and physiological characteristics of maize. Seed, 2021, 40(9): 40-47. |
| 刘京, 朱凯丽, 岳海旺, 等. 玉米果种皮对其种子萌发及生理特性的影响. 种子, 2021, 40(9): 40-47. | |
| [2] | Zhang Z Y, Lin W X. Continuous cropping obstacle and allelopathic autotoxicity of medicinal plants. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2009, 17(1): 189-196. |
| 张重义, 林文雄. 药用植物的化感自毒作用与连作障碍. 中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(1): 189-196. | |
| [3] | Cao P, Shen Y X. Study on allelopathic effects of bermudagrass on five gramineous weeds. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2010, 18(3): 452-455. |
| 曹璞, 沈益新. 狗牙根对5种禾本科杂草化感作用的研究. 草地学报, 2010, 18(3): 452-455. | |
| [4] | Wang T T, Wang Q, Wang H Z, et al. Autotoxicity of Angelica sinens and allelopathy on tested plants. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2012, 20(6): 1132-1138. |
| 王田涛, 王琦, 王惠珍, 等. 当归自毒作用和其对不同作物的化感效应. 草地学报, 2012, 20(6): 1132-1138. | |
| [5] | Li Y F, Chu X H, Li J Y, et al. Allelopathic effects of Euphorbia jolkinii on seed germination and seedling growth of alfalfa. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(2): 394-402. |
| 李彦飞, 初晓辉, 李嘉懿, 等. 大狼毒对紫花苜蓿种子萌发及幼苗生长的化感效应研究. 草地学报, 2022, 30(2): 394-402. | |
| [6] | Fan L H, Wang P B, Wang Y X, et al. The allelopathy effect of Artemisia scoparia water extracts on grassland plants seeds germination. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(1): 96-103. |
| 范丽花, 汪鹏斌, 王玉霞, 等. 猪毛蒿枯落物水浸提液对5种草地植物种子萌发的化感作用. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(1): 96-103. | |
| [7] | Zhang Z L, Wang W Q, Yang J Z, et al. Effects of continuous Panax notoginseng cropping soil on P. notoginseng seed germination and seedling growth. Soils, 2010, 42(6): 1009-1014. |
| 张子龙, 王文全, 杨建忠, 等. 三七连作土壤对其种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 土壤, 2010, 42(6): 1009-1014. | |
| [8] | Gao X X, Li M, Gao Z J, et al. Allelopathic potential of Xanthium sibiricum on seeds germination and seedling growth of different plants. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2009, 18(2): 95-101. |
| 高兴祥, 李美, 高宗军, 等. 苍耳对不同植物幼苗的化感作用研究. 草业学报, 2009, 18(2): 95-101. | |
| [9] | Xu Y F, Huang B, Zhu C M, et al. Allelopathic effects of aqueous extract from composted tomato residues on the growth of cucumber and Chinese cabbage. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2017, 34(2): 276-282. |
| 徐勇峰, 黄斌, 朱陈名, 等. 堆制番茄秸秆浸提液对黄瓜和大白菜的化感作用. 浙江农林大学学报, 2017, 34(2): 276-282. | |
| [10] | Zhao H, Wang T, Yu L. Allelopathic effects of garlic bulb aqueous extracts on seed germination and seedling growth of soybean. Soybean Science, 2019, 38(4): 548-553. |
| 赵红, 王婷, 余李. 大蒜鳞茎浸提液对大豆种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感效应. 大豆科学, 2019, 38(4): 548-553. | |
| [11] | Yao L B, Han H X, Li Q W, et al. Research on allelopathy of Allium fistulosum L. aqueous extracts and its physiological mechanism on Raphanus sativus L. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 46(8): 115-120. |
| 姚岭柏, 韩海霞, 李倩雯, 等. 大葱水浸液对萝卜的化感效应及其生理机制研究. 河南农业科学, 2017, 46(8): 115-120. | |
| [12] | You H X. Study on the environmental effects of different planting patterns and the allelopathy mechanism of cucumber in facility condition. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2007. |
| 由海霞. 设施黄瓜不同种植模式的环境效应及其化感作用研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2007. | |
| [13] | Guan A Q. Preliminary study on allelopathy of amaranth (Amaranthus tricolorll L.). Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2015. |
| 管安琴. 苋菜化感作用的初步研究. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2015. | |
| [14] | Tong F, Cheng Z H, Jin R, et al. Allelopathy of methanol dissolved ingredient from garlic plant aqueous extracts. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 35(6): 119-124. |
| 佟飞, 程智慧, 金瑞, 等. 大蒜植株水浸液醇溶成分的化感作用. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 35(6): 119-124. | |
| [15] | Zhao C, Zhao M, Huang X F, et al. Allelopathic effect of water extract of Brassica oleracea var. capitata leaves on seedling growth of Zea mays and Cucurbita pepo. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2022, 39(4): 838-844. |
| 赵聪, 赵敏, 黄学芳, 等. 结球甘蓝叶片水提液对糯玉米和西葫芦幼苗生长的化感作用. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(4): 838-844. | |
| [16] | Kural L, Özkan R Y. Allelopathic potential of white cabbage on some plants. Plant, Soil and Environment, 2020, 66 (11): 559-563. |
| [17] | Ma A M, Wang F, Pan G Y, et al. Analysis on the main processing and utilization ways of cabbage. China Fruit and Vegetable, 2018, 38(5): 5-8. |
| 马爱民, 王峰, 潘国云, 等. 结球甘蓝主要加工利用途径分析. 中国果菜, 2018, 38(5): 5-8. | |
| [18] | Tang L, Paonessa J D, Zhang Y, et al. Total isothiocyanate yield from raw cruciferous vegetables commonly consumed in the United States. Journal of Functional Foods, 2013, 5(4): 1996-2001. |
| [19] | Delchier N, Herbig A, Rychlik M, et al. Folates in fruits and vegetables: contents, processing and stability. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 2016, 15(3): 506-528. |
| [20] | Cartea M E, Francisco M, Soengas P, et al. Phenolic compounds in Brassica vegetables. Molecules, 2010, 16(1): 251-280. |
| [21] | Singh S V, Singh K. Cancer chemoprevention with dietary isothiocyanates mature for clinical translational research. Carcinogenesis, 2012, 33(10): 1833-1842. |
| [22] | Jennings B A, Willis G. How folate metabolism affects colorectal cancer development and treatment: a story of heterogeneity and pleiotropy. Cancer Letters, 2015, 356(2): 224-230. |
| [23] | Sevgi K, Tepe B, Sarikurkcu C. Antioxidant and DNA damage protection potentials of selected phenolic acids. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2015, 77: 12-21. |
| [24] | Merkl R, Hrádkov I, Filip V. Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of phenolic acids alkyl esters. Czech Journal of Food Sciences, 2010, 28(4): 275-279. |
| [25] | Lin C M, Preston J F, Cheng I W. Antibacterial mechanism of allyl isothiocyanate. Journal of Food Protection, 2000, 63(6): 727-734. |
| [26] | Yang H T, Lee M, Hong K S, et al. Efficacy of folic acid supplementation in cardiovascular disease prevention: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. European Journal of Internal Medicine, 2012, 23(8): 745-754. |
| [27] | Nooyens A C, Mesquita H B B, Boxtel M P J, et al. Fruit and vegetable intake and cognitive decline in middle-aged men and women: the Doetinchem Cohort Study. The British Journal of Nutrition, 2011, 106(5): 752-761. |
| [28] | Zhou S F, Tang Y, Pan L, et al. Effect of fulvic acid on barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crusgalli) seedling growth under flooding conditions. Weed Science, 2021, 69(2): 192-202. |
| [29] | Xu C C, Zhao S J, Zou Q. Separation and identification of malondialdehyde in plant tissue. Plant Physiology Communications, 1992, 28(4): 288-290. |
| 许长成, 赵世杰, 邹琦. 植物组织内丙二醛的分离与鉴定. 植物生理学通讯, 1992, 28(4): 288-290. | |
| [30] | Zou Q. Experimental direction of plant physiology. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2001: 223-224. |
| 邹琦. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2001: 223-224. | |
| [31] | Rice E L. Allelopathy (the second edition). Orlando: Academic Press, 1984: 1-7. |
| [32] | Jiang H Y, Zhang Y N, Feng P Z, et al. Allelopathic effects of Lycoris radiate on radish, cucumber, tomato and rape seedlings. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2006, 17(9): 1655-1659. |
| 蒋红云, 张燕宁, 冯平章, 等. 石蒜对萝卜、黄瓜、番茄和油菜幼苗的化感效应. 应用生态学报, 2006, 17(9): 1655-1659. | |
| [33] | Yu J G, Gu Y, Chang Z Z, et al. Allelopathic effects of wheat straw extract and decomposition liquid on rice. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2013, 50(2): 349-356. |
| 于建光, 顾元, 常志州, 等. 小麦秸秆浸提液和腐解液对水稻的化感效应. 土壤学报, 2013, 50(2): 349-356. | |
| [34] | Luo Q, Ma Z Y, Niu Q M, et al. Allelopathic effect and physiological mechanism of extracts from different parts of Euphorbia jolkinii on growth of Loium perenne seedlings. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(10): 3212-3199. |
| 罗钦, 马祖艳, 牛琼梅, 等. 大狼毒不同部位浸提液对多年生黑麦草幼苗生长的化感效应及生理机制. 草地学报, 2023, 31(10): 3212-3199. | |
| [35] | Zuo L, Wang S S, Ma Y M, et al. Effect of torch tree extract on seeds germination in two types of turfgrass. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(9): 1927-1933. |
| 左郎, 王树森, 马迎梅, 等. 火炬树浸提液对两种草坪草种子萌发的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(9): 1927-1933. | |
| [36] | Chen H Z, Xu M S, Zhou T Y, et al. Allelopathic effects of extract from Rabdosia serra (Maxim.) Hara on seed germination and seedling growth of two weeds. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(7): 2118-2127. |
| 陈幻真, 许明爽, 周天宇, 等. 溪黄草浸提液对2种杂草种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用. 草地学报, 2024, 32(7): 2118-2127. | |
| [37] | Gao Y L, Chang J, Wang Y H, et al. Allelopathic effects of Stellera chamaejasme on seed germination and growth of three crops. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(10): 83-91. |
| 高玉莲, 常静, 王贻卉, 等. 瑞香狼毒根提取物对3种作物种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 83-91. | |
| [38] | Guo Y Z, Jia W Q, He S L, et al. Allelopathic effects of extracts of Sonchus asper on seed germination and seedling growth of three herbaceous flower species. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 96-106. |
| 郭英姿, 贾文庆, 何松林, 等. 花叶滇苦菜浸提液对3种花卉种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 96-106. | |
| [39] | Yang Z Y, Zou J Q, Ni H J, et al. Effects of aqueous extract from Sesamun indicum L. on seed germination and physiological characteristics of Phyllostachys edulis. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2023, 51(1): 11-17. |
| 杨振亚, 邹景泉, 倪惠菁, 等. 芝麻浸提液对毛竹种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响. 东北林业大学学报, 2023, 51(1): 11-17. |
| [1] | 何邦印, 裴婧宏, 野起瑞, 胡佳佳, 郑彩雪, 李江文. 不同人工经济林凋落叶浸提液对豆禾草种的化感效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 199-208. |
| [2] | 阮坤非, 王天琪, 毕宁宁, 师劭彤, 李森, 刘忠华. 元宝枫凋落叶浸提液对3种中草药化感作用的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 151-159. |
| [3] | 郭英姿, 贾文庆, 何松林, 王政. 花叶滇苦菜浸提液对3种花卉种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 96-106. |
| [4] | 李春杰, 郎鸣晓, 陈振江, 陈泰祥, 刘静, 金媛媛, 魏学凯. Epichloë内生真菌对禾草种子萌发影响研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 192-206. |
| [5] | 陈金慧, 马慧燕, 陈煜, 何禾. 五爪金龙两种化感作用途径释放的化学成分分析及其效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 88-100. |
| [6] | 臧真凤, 白婕, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿形态和生理指标响应干旱胁迫的品种特异性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 73-81. |
| [7] | 包赛很那, 王向涛, 武俊喜, 苗彦军, 贾祥, 田彦婷. 苗期劲直黄芪根浸提液对8种西藏野生植物化感作用的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 211-220. |
| [8] | 高玉莲, 常静, 王贻卉, 李锋, 李海平, 马崇勇. 瑞香狼毒根提取物对3种作物种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 83-91. |
| [9] | 牛欢欢, 王森森, 贾宏定, 陈桂华. 光叶紫花苕子浸提液对4种牧草种子萌发过程的化感作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 161-168. |
| [10] | 李凤兰, 武佳文, 姚树宽, 赵梓颐, 赵潇璨, 贺付蒙, 朱元芳, 石奇海, 周磊, 徐永清. 假苍耳不同部位水浸提液对5种土著植物化感作用的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 169-178. |
| [11] | 王桔红, 史生晶, 陈文, 李云, 崔现亮. 鬼针草与含羞草化感作用及其入侵性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 81-91. |
| [12] | 张金羽, 周忠泽, 叶晓馨. 陌上菅对三种禾本科植物的化感潜势研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 103-111. |
| [13] | 王宇轩, 唐宗寿, 曹梦琳, 李雅馨, 张天宝, 杜慧玲. 八宝景天花对三种杂草的化感作用及潜在化感物质鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 175-182. |
| [14] | 刘雅婧, 蒙仲举, 党晓宏, 宋文娟, 翟波. 狼毒浸提液对3种牧草种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 130-138. |
| [15] | 伍国强, 李辉, 雷彩荣, 蔺丽媛, 金娟, 李善家. 添加KCl对高盐胁迫下红豆草生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 45-55. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||