

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 158-171.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021350
姜渊博( ), 康燕霞, 齐广平(
), 康燕霞, 齐广平( ), 银敏华, 马彦麟, 汪精海, 贾琼, 康瑶, 张宏斌, 唐仲霞, 汪爱霞
), 银敏华, 马彦麟, 汪精海, 贾琼, 康瑶, 张宏斌, 唐仲霞, 汪爱霞
收稿日期:2021-09-22
修回日期:2021-11-03
出版日期:2022-11-20
发布日期:2022-10-01
通讯作者:
齐广平
作者简介:E-mail: qigp@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Yuan-bo JIANG( ), Yan-xia KANG, Guang-ping QI(
), Yan-xia KANG, Guang-ping QI( ), Min-hua YIN, Yan-lin MA, Jing-hai WANG, Qiong JIA, Yao KANG, Hong-bin ZHANG, Zhong-xia TANG, Ai-xia WANG
), Min-hua YIN, Yan-lin MA, Jing-hai WANG, Qiong JIA, Yao KANG, Hong-bin ZHANG, Zhong-xia TANG, Ai-xia WANG
Received:2021-09-22
Revised:2021-11-03
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2022-10-01
Contact:
Guang-ping QI
摘要:
合理的水分调控模式有助于提升人工草地生产力、改善牧草品质和提高水资源利用效率。以无芒雀麦为试验材料,对比分析河西走廊地区两种水分调控模式[分生育期调亏灌溉(I1);全生育期调亏灌溉(I2)]下灌水量对其产量和品质的影响,综合考虑大田试验和典型枯水年灌溉制度模拟结果进行灌溉制度优选,为当地生产实践提供理论依据。结果表明:随着灌水量增加,I1模式下无芒雀麦产量呈先增加后减小趋势,I2模式下则逐渐增加,两种模式下无芒雀麦粗蛋白含量均逐渐减小,但酸性洗涤纤维和中性洗涤纤维含量均缓慢增加。与I2相比,I1模式下无芒雀麦产量平均提升23.11%,粗蛋白含量平均提升6.09%,因此,I1水分调控模式较优。由大田试验分析及典型枯水年灌溉制度模拟结果可知,I1DF1处理下[返青期(75%~85% θFC),拔节期(65%~85% θFC),抽穗期(65%~85% θFC)],灌水次数12次,灌溉定额521.76 mm的灌溉制度可为河西走廊地区无芒雀麦节水稳产提供参考。
姜渊博, 康燕霞, 齐广平, 银敏华, 马彦麟, 汪精海, 贾琼, 康瑶, 张宏斌, 唐仲霞, 汪爱霞. 基于产量与品质的无芒雀麦灌溉制度研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 158-171.
Yuan-bo JIANG, Yan-xia KANG, Guang-ping QI, Min-hua YIN, Yan-lin MA, Jing-hai WANG, Qiong JIA, Yao KANG, Hong-bin ZHANG, Zhong-xia TANG, Ai-xia WANG. Irrigation scheduling based on yield and quality in Bromus inermis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(11): 158-171.
水分调控模式 Water regulation mode | 处理 Treatment | 水分处理Moisture treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 建植期/返青期Planting stage/greening stage | 拔节期Jointing stage | 抽穗期Tasseling stage | ||
分生育期调亏灌溉 Regulated deficit irrigation at different growth stages (I1) | CK | 75~85 | 75~85 | 75~85 |
| F1 | 75~85 | 65~85 | 65~85 | |
| F2 | 75~85 | 55~85 | 55~85 | |
| F3 | 75~85 | 45~85 | 45~85 | |
全生育期调亏灌溉 Regulated deficit irrigation in whole growth period (I2) | CK | 75~85 | 75~85 | 75~85 |
| Q1 | 65~75 | 65~75 | 65~75 | |
| Q2 | 55~65 | 55~65 | 55~65 | |
| Q3 | 45~55 | 45~55 | 45~55 | |
表1 无芒雀麦水分调控试验灌水上下限
Table 1 Upper and lower limits of irrigation for B. inermis moisture regulation trial (%)
水分调控模式 Water regulation mode | 处理 Treatment | 水分处理Moisture treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 建植期/返青期Planting stage/greening stage | 拔节期Jointing stage | 抽穗期Tasseling stage | ||
分生育期调亏灌溉 Regulated deficit irrigation at different growth stages (I1) | CK | 75~85 | 75~85 | 75~85 |
| F1 | 75~85 | 65~85 | 65~85 | |
| F2 | 75~85 | 55~85 | 55~85 | |
| F3 | 75~85 | 45~85 | 45~85 | |
全生育期调亏灌溉 Regulated deficit irrigation in whole growth period (I2) | CK | 75~85 | 75~85 | 75~85 |
| Q1 | 65~75 | 65~75 | 65~75 | |
| Q2 | 55~65 | 55~65 | 55~65 | |
| Q3 | 45~55 | 45~55 | 45~55 | |
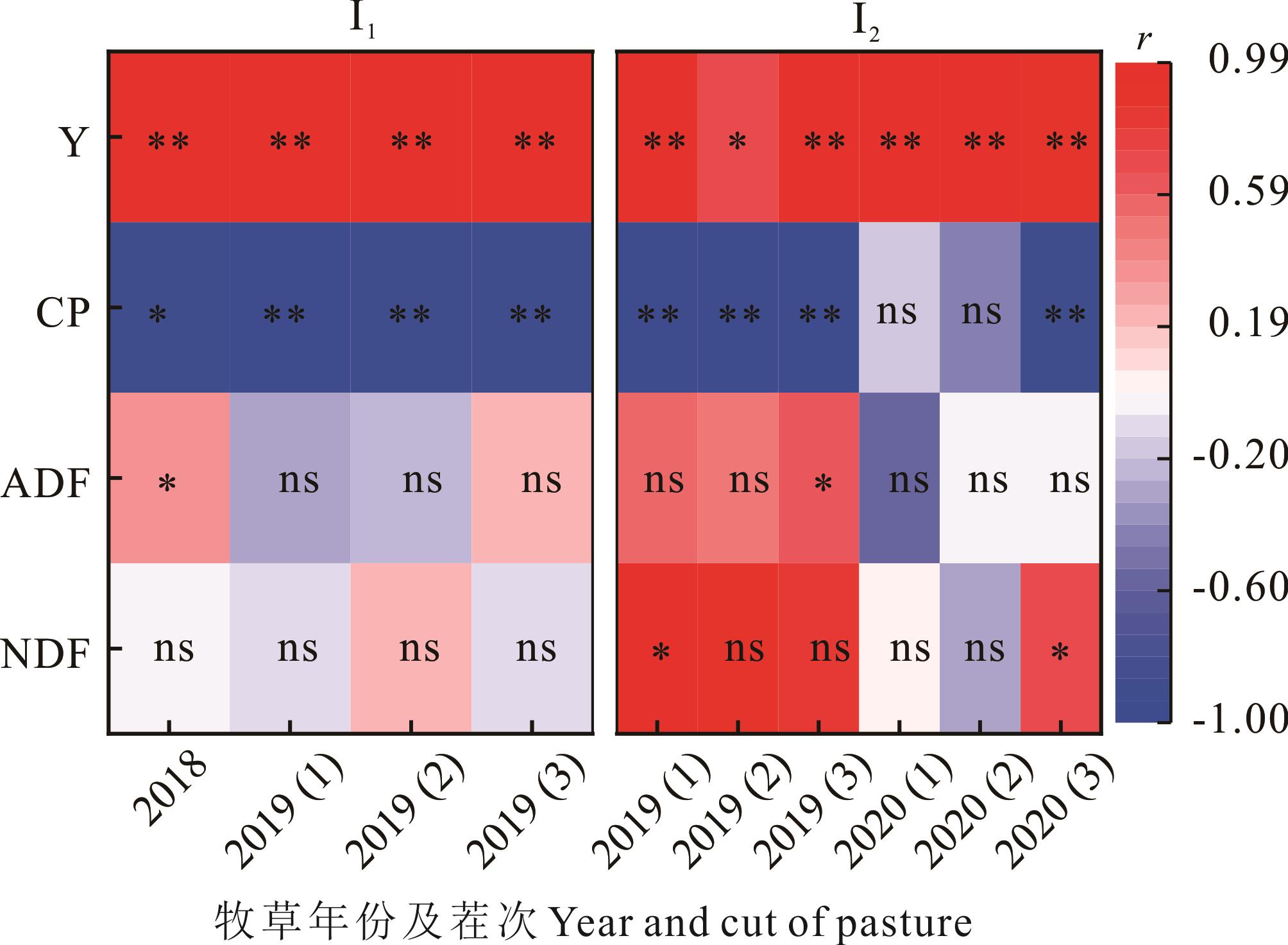
图2 灌水量与无芒雀麦各指标间的相关性分析I1为分生育期调亏灌溉,I2为全生育期调亏灌溉,Y为产量,CP为粗蛋白,ADF为酸性洗涤纤维,NDF为中性洗涤纤维;r为相关系数,r>0为正相关,r<0为负相关;*表示在P<0.05水平显著相关,**表示在P<0.01水平极显著相关,ns表示无显著相关性。I1 is regulated deficit irrigation at different growth stages, I2 is regulated deficit irrigation in whole growth period, Y is yield, CP is crude protein, ADF is acid detergent fiber, NDF is neutral detergent fiber; r is the correlation coefficient, r>0 is positive correlation, r<0 is negative correlation; * indicates significant correlation at P<0.05 level, ** indicates highly significant correlation at P<0.01 level, and ns indicates no significance.
Fig.2 Correlation analysis between irrigation amount and various indicators of B. inermis
指标 Index | 主成分Principal components | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
| 产量Y | -0.740 | 0.385 |
| 水分利用效率WUE | 0.883 | -0.022 |
| 灌溉水利用效率IWUE | 0.961 | -0.189 |
| 粗蛋白CP | 0.960 | -0.212 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维ADF | 0.341 | 0.916 |
| 中性洗涤纤维NDF | 0.436 | 0.865 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 3.480 | 1.817 |
| 方差贡献率Variance contribution rate (%) | 58.005 | 30.275 |
| 累计方差贡献率Cumulative variance contribution rate (%) | 58.005 | 88.280 |
表2 不同灌水处理下无芒雀麦各指标主成分分析
Table 2 Principal component analysis of each index of B. inermis with different irrigation treatments
指标 Index | 主成分Principal components | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
| 产量Y | -0.740 | 0.385 |
| 水分利用效率WUE | 0.883 | -0.022 |
| 灌溉水利用效率IWUE | 0.961 | -0.189 |
| 粗蛋白CP | 0.960 | -0.212 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维ADF | 0.341 | 0.916 |
| 中性洗涤纤维NDF | 0.436 | 0.865 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 3.480 | 1.817 |
| 方差贡献率Variance contribution rate (%) | 58.005 | 30.275 |
| 累计方差贡献率Cumulative variance contribution rate (%) | 58.005 | 88.280 |
| 处理Treatment | 综合得分Overall score | 排序Sorting | 处理Treatment | 综合得分Overall score | 排序Sorting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1CK | -0.3212 | 7 | I2CK | -0.6052 | 8 |
| I1F1 | 0.7016 | 1 | I2Q1 | -0.1331 | 4 |
| I1F2 | 0.3436 | 3 | I2Q2 | -0.1671 | 5 |
| I1F3 | 0.3904 | 2 | I2Q3 | -0.2090 | 6 |
表3 不同灌水处理无芒雀麦综合得分
Table 3 Overall score of B. inermis with different irrigation treatments
| 处理Treatment | 综合得分Overall score | 排序Sorting | 处理Treatment | 综合得分Overall score | 排序Sorting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1CK | -0.3212 | 7 | I2CK | -0.6052 | 8 |
| I1F1 | 0.7016 | 1 | I2Q1 | -0.1331 | 4 |
| I1F2 | 0.3436 | 3 | I2Q2 | -0.1671 | 5 |
| I1F3 | 0.3904 | 2 | I2Q3 | -0.2090 | 6 |
品质指标 Quality index | 信息熵值 Information entropy value (E j ) | 信息效用值 Information utility value (D j ) | 权重系数 Weight coefficient (W j ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 酸性洗涤纤维含量ADF content | 85.79 | 14.21 | 20.84 |
| 中性洗涤纤维含量NDF content | 86.29 | 13.71 | 20.12 |
| 粗蛋白含量CP content | 59.76 | 40.24 | 59.04 |
表4 熵权法计算结果汇总
Table 4 Summary of calculation results of entropy method (%)
品质指标 Quality index | 信息熵值 Information entropy value (E j ) | 信息效用值 Information utility value (D j ) | 权重系数 Weight coefficient (W j ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 酸性洗涤纤维含量ADF content | 85.79 | 14.21 | 20.84 |
| 中性洗涤纤维含量NDF content | 86.29 | 13.71 | 20.12 |
| 粗蛋白含量CP content | 59.76 | 40.24 | 59.04 |
处理 Treatment | 茬次 Cut | 真实值 Real value (mm) | 预测值 Predicted value (mm) | 相对误差 Relative error (%) | 平均相对误差MRE (%) | 决定系数R2 | 均方根误差RMSE (mm) | 标准均方根误差 nRMSE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 充分灌溉CK | 第1茬The first cut | 222.40 | 195.568 | -12.06 | 13.84 | 0.985 | 24.56 | 13.58 |
| 第2茬The second cut | 139.56 | 161.882 | 15.99 | |||||
| 第3茬The third cut | 180.63 | 156.306 | -13.47 |
表5 灌水量的真实值与预测值
Table 5 Real and predicted values of irrigation amount
处理 Treatment | 茬次 Cut | 真实值 Real value (mm) | 预测值 Predicted value (mm) | 相对误差 Relative error (%) | 平均相对误差MRE (%) | 决定系数R2 | 均方根误差RMSE (mm) | 标准均方根误差 nRMSE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 充分灌溉CK | 第1茬The first cut | 222.40 | 195.568 | -12.06 | 13.84 | 0.985 | 24.56 | 13.58 |
| 第2茬The second cut | 139.56 | 161.882 | 15.99 | |||||
| 第3茬The third cut | 180.63 | 156.306 | -13.47 |
日期Date (月-日Month-day) | 逐旬参照作物蒸散量 Reference crop evapotranspiration by decade (mm) | 日期Date (月-日Month-day) | 逐旬参照作物蒸散量 Reference crop evapotranspiration by decade (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 04-11-04-20 | 46.03 | 07-01-07-10 | 65.21 |
| 04-21-04-30 | 46.60 | 07-11-07-20 | 53.41 |
| 05-01-05-10 | 50.25 | 07-21-07-31 | 59.62 |
| 05-11-05-20 | 49.02 | 08-01-08-10 | 60.91 |
| 05-21-05-31 | 60.40 | 08-11-08-20 | 54.88 |
| 06-01-06-10 | 64.64 | 08-21-08-31 | 44.56 |
| 06-11-06-20 | 59.29 | 09-01-09-10 | 43.68 |
| 06-21-06-30 | 63.85 |
表6 典型枯水年逐旬参照作物蒸散量
Table 6 Reference crop evapotranspiration by decade in a typical dry year
日期Date (月-日Month-day) | 逐旬参照作物蒸散量 Reference crop evapotranspiration by decade (mm) | 日期Date (月-日Month-day) | 逐旬参照作物蒸散量 Reference crop evapotranspiration by decade (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 04-11-04-20 | 46.03 | 07-01-07-10 | 65.21 |
| 04-21-04-30 | 46.60 | 07-11-07-20 | 53.41 |
| 05-01-05-10 | 50.25 | 07-21-07-31 | 59.62 |
| 05-11-05-20 | 49.02 | 08-01-08-10 | 60.91 |
| 05-21-05-31 | 60.40 | 08-11-08-20 | 54.88 |
| 06-01-06-10 | 64.64 | 08-21-08-31 | 44.56 |
| 06-11-06-20 | 59.29 | 09-01-09-10 | 43.68 |
| 06-21-06-30 | 63.85 |
模拟情景 Simulation scenarios | 灌水设计Irrigation design (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
返青期 Greening stage | 拔节期 Jointing stage | 抽穗期 Tasseling stage | |
| DCK | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| DF1 | 75 | 65 | 65 |
| DF2 | 75 | 55 | 55 |
| DF3 | 75 | 45 | 45 |
表7 灌溉制度模拟情景
Table 7 Simulation scenarios of irrigation scheduling
模拟情景 Simulation scenarios | 灌水设计Irrigation design (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
返青期 Greening stage | 拔节期 Jointing stage | 抽穗期 Tasseling stage | |
| DCK | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| DF1 | 75 | 65 | 65 |
| DF2 | 75 | 55 | 55 |
| DF3 | 75 | 45 | 45 |
模拟情景 Simulation scenarios | 项目 Item | 灌溉制度 Irrigation scheduling | TIA (mm) | IWUE (kg·m-3) | APDA (%) | RCP (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCK | 灌水次序Number of irrigations | SI | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 601.49 | 1.61 | 0 | 0 |
| 灌水定额Irrigation quota (mm) | 70.00 | 61.10 | 22.17 | 21.73 | 21.72 | 23.08 | 23.38 | 21.29 | 22.91 | 22.03 | 22.48 | 20.51 | |||||
| 灌水日期Irrigation date (Month-day) | - | 04-12 | 04-29 | 05-06 | 05-14 | 05-20 | 05-25 | 05-31 | 06-04 | 06-21 | 06-26 | 06-30 | |||||
| 灌水次序Number of irrigations | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | WI | ||||||||
| 灌水定额Irrigation quota (mm) | 22.38 | 24.65 | 22.96 | 23.37 | 20.92 | 21.81 | 20.43 | 22.57 | 70.00 | ||||||||
| 灌水日期Irrigation date (Month-day) | 07-04 | 07-09 | 07-14 | 07-20 | 07-28 | 08-13 | 08-21 | 08-28 | - | ||||||||
| DF1 | 灌水次序Number of irrigations | SI | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | WI | 521.76 | 1.71 | 7.88 | 3.03 |
| 灌水定额Irrigation quota (mm) | 70.00 | 61.10 | 45.91 | 30.52 | 23.27 | 46.83 | 44.83 | 45.05 | 21.14 | 20.58 | 42.53 | 70.00 | |||||
| 灌水日期Irrigation date (Month-day) | - | 04-12 | 05-21 | 05-29 | 06-04 | 06-26 | 07-05 | 07-15 | 07-21 | 08-02 | 08-25 | - | |||||
| DF2 | 灌水次序Number of irrigations | SI | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | WI | 463.53 | 1.77 | 15.12 | 6.24 | |||
| 灌水定额Irrigation quota (mm) | 70.00 | 61.10 | 61.38 | 26.54 | 21.55 | 63.49 | 66.37 | 23.10 | 70.00 | ||||||||
| 灌水日期Irrigation date (Month-day) | - | 04-12 | 05-26 | 06-01 | 06-07 | 07-01 | 07-20 | 07-28 | - | ||||||||
| DF3 | 灌水次序Number of irrigations | SI | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | WI | 405.20 | 1.87 | 21.88 | 8.89 | ||||||
| 灌水定额Irrigation quota (mm) | 70.00 | 61.10 | 58.09 | 82.41 | 63.60 | 70.00 | |||||||||||
| 灌水日期Irrigation date (Month-day) | - | 04-12 | 05-29 | 07-04 | 07-21 | - | |||||||||||
表8 典型枯水年无芒雀麦灌溉制度模拟
Table 8 Simulation of irrigation scheduling for B. inermis in a typical dry water year
模拟情景 Simulation scenarios | 项目 Item | 灌溉制度 Irrigation scheduling | TIA (mm) | IWUE (kg·m-3) | APDA (%) | RCP (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCK | 灌水次序Number of irrigations | SI | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 601.49 | 1.61 | 0 | 0 |
| 灌水定额Irrigation quota (mm) | 70.00 | 61.10 | 22.17 | 21.73 | 21.72 | 23.08 | 23.38 | 21.29 | 22.91 | 22.03 | 22.48 | 20.51 | |||||
| 灌水日期Irrigation date (Month-day) | - | 04-12 | 04-29 | 05-06 | 05-14 | 05-20 | 05-25 | 05-31 | 06-04 | 06-21 | 06-26 | 06-30 | |||||
| 灌水次序Number of irrigations | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | WI | ||||||||
| 灌水定额Irrigation quota (mm) | 22.38 | 24.65 | 22.96 | 23.37 | 20.92 | 21.81 | 20.43 | 22.57 | 70.00 | ||||||||
| 灌水日期Irrigation date (Month-day) | 07-04 | 07-09 | 07-14 | 07-20 | 07-28 | 08-13 | 08-21 | 08-28 | - | ||||||||
| DF1 | 灌水次序Number of irrigations | SI | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | WI | 521.76 | 1.71 | 7.88 | 3.03 |
| 灌水定额Irrigation quota (mm) | 70.00 | 61.10 | 45.91 | 30.52 | 23.27 | 46.83 | 44.83 | 45.05 | 21.14 | 20.58 | 42.53 | 70.00 | |||||
| 灌水日期Irrigation date (Month-day) | - | 04-12 | 05-21 | 05-29 | 06-04 | 06-26 | 07-05 | 07-15 | 07-21 | 08-02 | 08-25 | - | |||||
| DF2 | 灌水次序Number of irrigations | SI | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | WI | 463.53 | 1.77 | 15.12 | 6.24 | |||
| 灌水定额Irrigation quota (mm) | 70.00 | 61.10 | 61.38 | 26.54 | 21.55 | 63.49 | 66.37 | 23.10 | 70.00 | ||||||||
| 灌水日期Irrigation date (Month-day) | - | 04-12 | 05-26 | 06-01 | 06-07 | 07-01 | 07-20 | 07-28 | - | ||||||||
| DF3 | 灌水次序Number of irrigations | SI | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | WI | 405.20 | 1.87 | 21.88 | 8.89 | ||||||
| 灌水定额Irrigation quota (mm) | 70.00 | 61.10 | 58.09 | 82.41 | 63.60 | 70.00 | |||||||||||
| 灌水日期Irrigation date (Month-day) | - | 04-12 | 05-29 | 07-04 | 07-21 | - | |||||||||||
| 1 | Chen R, Chen H B. Current situation and countermeasures of grassland resource utilization in Sunan County. China Animal Industry, 2019(17): 50-52. |
| 陈荣, 陈怀斌. 肃南县草地资源利用现状及对策. 中国畜牧业, 2019(17): 50-52. | |
| 2 | Niu S L, Jiang G M. Function of artificial grassland in restoration of degraded natural grassland and its research advance. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2004, 15(9): 1662-1666. |
| 牛书丽, 蒋高明. 人工草地在退化草地恢复中的作用及其研究现状. 应用生态学报, 2004, 15(9): 1662-1666. | |
| 3 | Wu Z L, Jia W X, Zhao Z, et al. Spatial-temporal variations of vegetation and its correlation with climatic factors in Qilian Mountains from 2000 to 2012. Arid Land Geography, 2015, 38(6): 1241-1252. |
| 武正丽, 贾文雄, 赵珍, 等. 2000-2012年祁连山植被覆盖变化及其与气候因子的相关性. 干旱区地理, 2015, 38(6): 1241-1252. | |
| 4 | Xu R G, Ren J Z, Nan Z B, et al. Strategies and policies for the ecological and food security of China’s grassland. Strategic Study of CAE, 2016, 18(1): 8-16. |
| 旭日干, 任继周, 南志标, 等. 保障我国草地生态与食物安全的战略和政策. 中国工程科学, 2016, 18(1): 8-16. | |
| 5 | Ren J Z, Hou F J. System coupling of mountain-oasis-desert plays a key role in the protection of water resource in Qilian mountains. Pratacultural Science, 2010, 27(2): 4-7. |
| 任继周, 侯扶江. 山地-绿洲-荒漠的系统耦合是祁连山水资源保护的关键措施. 草业科学, 2010, 27(2): 4-7. | |
| 6 | Dang Z Q, Huang Z, Tian F P, et al. Five-year soil moisture response of typical cultivated grasslands in a semiarid area: Implications for vegetation restoration. Land Degradation and Development, 2020, 31(9): 1078-1085. |
| 7 | Pang X M, Kang S Z, Wang M X. Theory and technology research development and prospect of regulated deficit irrigation on crops. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 33(6): 141-146. |
| 庞秀明, 康绍忠, 王密侠. 作物调亏灌溉理论与技术研究动态及其展望. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 33(6): 141-146. | |
| 8 | Shahrabian E, Soleymani A. Response of forage maize hybrids to different regimes of irrigation. Research on Crops, 2011, 12(1): 53-59. |
| 9 | Wang Y D, Kou D, Muneer M A, et al. The effects of irrigation regimes on soil moisture dynamics, yield and quality of lucerne under subsurface drip irrigation. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 2020, 18(3): 4179-4194. |
| 10 | Jia S X. Forage plants of China (the First Volume). Beijing: Agricultural Press, 1987: 53-54. |
| 贾慎修. 中国饲用植物志(第一卷). 北京: 农业出版社, 1987: 53-54. | |
| 11 | Gong K, Jin G L, Sui X Q, et al. Analysis on the distribution, breeding and utilization of Bromus inermis germplasm resources in China. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2019(21): 29-32, 36. |
| 宫珂, 靳瑰丽, 隋晓青, 等. 我国无芒雀麦种质资源分布、育种及利用现状分析. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2019(21): 29-32, 36. | |
| 12 | Zhang J, Li S H, Song H Y, et al. Growth and photosynthetic physiological responses of Lolium perenne L. to water stress in the simulated karst soil habitats. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(4): 1240-1248. |
| 张静, 李素慧, 宋海燕, 等. 模拟喀斯特不同土壤生境下黑麦草对水分胁迫的生长和光合生理响应. 生态学报, 2020, 40(4): 1240-1248. | |
| 13 | Zhu Y Q, Peng D D, Peng Y, et al. Physiological response and comparison of Sorghum sudanense and S. bicolor×S. sudanense seedlings under drought stress. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(5): 1361-1370. |
| 朱永群, 彭丹丹, 彭燕, 等. 苏丹草及高丹草幼苗对干旱胁迫的生理响应与抗旱性比较. 草业科学, 2019, 36(5): 1361-1370. | |
| 14 | Zhang J G, Tian F P, Miao H T, et al. Expressions of morphological and physiological features of 4 forage species under water stress and re-watering process. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(1): 193-201. |
| 张静鸽, 田福平, 苗海涛, 等. 水分胁迫及复水过程4种牧草形态及其生理特征表达. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(1): 193-201. | |
| 15 | Lu J Y, Xiong J B, Zhang H S, et al. Effects of water stress on yield, quality and trace element composition of alfalfa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 126-133. |
| 陆姣云, 熊军波, 张鹤山, 等. 水分胁迫对紫花苜蓿产量、品质和微量元素的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 126-133. | |
| 16 | Zhang H B, Qi G P, Kang Y X, et al. Effects of water regulation on yield, quality and water use of mixed artificial grassland. Water Resources Planning and Design, 2021, 34(4): 63-69. |
| 张宏斌, 齐广平, 康燕霞, 等. 水分调控对混播人工草地产量、品质与水分利用的影响. 水利规划与设计, 2021, 34(4): 63-69. | |
| 17 | Ni Y, Guo Y J, Lv J, et al. Physiological-biological changes of legumes under drought stress. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2004, 35(3): 275-278. |
| 倪郁, 郭彦军, 吕俊, 等. 水分胁迫下豆科牧草的生理生化变化. 土壤通报, 2004, 35(3): 275-278. | |
| 18 | Huang W. Study on drought resistance of four gramineae herbage varieties at seedling stage. South China Agriculture, 2015, 9(33): 246-248. |
| 黄顽. 四个禾本科牧草品种的苗期抗旱性能研究. 南方农业, 2015, 9(33): 246-248. | |
| 19 | Wang H Q, Tian Y H, Huang W L, et al. Analyzing the impact of irrigation quantity on biomass and water use efficiency of main grasses in artificial grassland in Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(10): 3225-3232. |
| 王海青, 田育红, 黄薇霖, 等. 不同灌溉量对内蒙古人工草地主要牧草产量和水分利用效率的影响. 生态学报, 2015, 35(10): 3225-3232. | |
| 20 | Dong G F, Cheng Z Y, Zhang Z H, et al. Effects of regulated deficit irrigation on water use efficiency and quality of alfalfa. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2006, 35(5): 201-203. |
| 董国锋, 成自勇, 张自和, 等. 调亏灌溉对苜蓿水分利用效率和品质的影响. 农业工程学报, 2006, 35(5): 201-203. | |
| 21 | Chen C F, Liu S H, Guo D X, et al. Growth simulation and optimization of irrigation scheme for summer maize using AquaCrop model. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2019, 37(3): 72-82. |
| 陈超飞, 柳双环, 郭大辛, 等. 基于AquaCrop模型的夏玉米生长模拟及灌溉制度优化. 干旱地区农业研究, 2019, 37(3): 72-82. | |
| 22 | Shang S H. Simulation-optimization method for crop irrigation scheduling with limited water supplies. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2005, 45(9): 1179-1183. |
| 尚松浩. 作物非充分灌溉制度的模拟优化方法. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 45(9): 1179-1183. | |
| 23 | Huang H W, Cheng J L, Wang M D, et al. Optimization method of irrigation schedule for paddy field in southern large-scale irrigation districts. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2019, 38(S1): 51-56. |
| 黄慧雯, 程吉林, 王明东, 等. 南方大型灌区水稻田灌溉制度实时优化方法研究. 灌溉排水学报, 2019, 38(S1): 51-56. | |
| 24 | Qu W. Study on the dynamic water production function and the optimal irrigation schedule of artificial glassland in the west of Jilin Province. Changchun: Jilin University, 2011. |
| 曲武. 吉林省西部人工草地动态水分生产函数及优化灌溉制度研究. 长春: 吉林大学, 2011. | |
| 25 | Wang Z Q. A study on simulating approach for water requirement of grass and on irrigation schedule of grass planted by man in the Otinday Sandy area. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2006. |
| 王志强. 浑善达克沙地牧草需水量的模拟计算方法及人工牧草灌溉制度研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2006. | |
| 26 | Liu L F, Huang G H, He J P, et al. Simulation of irrigation requirements of typical cool season turfgrass in Beijing area. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2009, 25(1): 64-68. |
| 刘丽芳, 黄冠华, 何建平, 等. 北京地区典型冷季型草坪草灌水量模拟. 农业工程学报, 2009, 25(1): 64-68. | |
| 27 | Wang Y D. Effects of different the amount of water on the evapotranspiration and turf quality of three cool-season turfgrass. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2010. |
| 王跃栋. 不同灌水量对三种冷型草坪草蒸散量和草坪质量的影响研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2010. | |
| 28 | Wang J H, Li G, Yu X X, et al. Effects of regulated deficit micro-sprinkler irrigation on the yield, quality and water utilization of artificial grassland in alpine desert area. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 35(4): 200-207, 216. |
| 汪精海, 李广, 余晓雄, 等. 调亏微喷灌对高寒荒漠区人工草地产量、品质及水分利用的影响. 水土保持学报, 2021, 35(4): 200-207, 216. | |
| 29 | Shi H B, Tian J C, Liu Q H, et al. Irrigation and drainage engineering. Beijing: China Water and Power Press, 2006: 47-53. |
| 史海滨, 田军仓, 刘庆华, 等. 灌溉排水工程学. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2006: 47-53. | |
| 30 | Liu Y, Fernando R M, Pereira L S. Water balance simulation with ISAREG considering water table interactions//World congress of computers in agriculture and natural resources. Brazil: ASAE Publication, 2002: 857-863. |
| 31 | Wang H Z, Zhang X P. Advances in crop water ecology and physiology under regulated deficit irrigation. Irrigation and Drainage, 2001, 20(4): 73-75. |
| 王和洲, 张晓萍. 调亏灌溉条件下的作物水分生态生理研究进展. 灌溉排水, 2001, 20(4): 73-75. | |
| 32 | Xi Y Z, Li G, Chen G P, et al. Impact of water regulation on growth process of spring wheat. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2019, 54(2): 73-80, 88. |
| 席元章, 李广, 陈国鹏, 等. 水分调控对春小麦生长过程的影响. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2019, 54(2): 73-80, 88. | |
| 33 | Cao C Y, Dang H K, Zheng C L, et al. Effects of different irrigation regime on yield, water consumption and water use efficiency of winter wheat. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2016, 31(S1): 17-24. |
| 曹彩云, 党红凯, 郑春莲, 等. 不同灌溉模式对小麦产量、耗水及水分利用效率的影响. 华北农学报, 2016, 31(S1): 17-24. | |
| 34 | Feng F X, Mu P, Zhao G Q, et al. Water consumption characteristics and yields of fodder oat under different irrigation and nitrogen fertilization regimes in the northwest oasis irrigation area. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(8): 74-84. |
| 冯福学, 慕平, 赵桂琴, 等. 西北绿洲灌区饲用燕麦耗水特性及产量变化对水氮耦合的响应. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 74-84. | |
| 35 | Ayijiang H B, Ma Y J, Hong M, et al. Experimental study of the water consumption of alfalfa subsurface drip irrigation. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 49(7): 1301-1306. |
| 阿依江·哈比, 马英杰, 洪明, 等. 地下滴灌条件下紫花苜蓿耗水规律试验研究. 新疆农业科学, 2012, 49(7): 1301-1306. | |
| 36 | Ren R, Lv Z Y, Guo K Z, et al. Application of regulated deficit irrigation in pasture planting. Inner Mongolia Water Resources, 2011, 32(2): 58-59. |
| 任蓉, 吕志远, 郭克贞, 等. 调亏灌溉在牧草种植中的应用. 内蒙古水利, 2011, 32(2): 58-59. | |
| 37 | Yu X X, Qi G P, Kang Y X, et al. Effect of irrigation mode on the yield and water consumption of mixed artificial grassland in alpine desert area. Water Resources Planning and Design, 2020, 33(3): 130-134, 178. |
| 余晓雄, 齐广平, 康燕霞, 等. 灌水模式对高寒荒漠区混播人工草地产量及耗水特性的影响. 水利规划与设计, 2020, 33(3): 130-134, 178. | |
| 38 | Wang J R, Liu W X, Chen Y L, et al. Regulatory effect of different irrigation regimes on grain yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2018, 38(10): 1229-1236. |
| 王家瑞, 刘卫星, 陈雨露, 等. 不同灌水模式对冬小麦产量及水分利用的调控效应. 麦类作物学报, 2018, 38(10): 1229-1236. | |
| 39 | Wang J, Li G, Nie Z G, et al. Simulation study of response of spring wheat yield to drought stress in the Loess Plateau of central Gansu. Arid Land Geography, 2021, 44(2): 494-506. |
| 王钧, 李广, 聂志刚, 等. 陇中黄土高原区旱地春小麦产量对干旱胁迫响应的模拟研究. 干旱区地理, 2021, 44(2): 494-506. | |
| 40 | Liu M, Gong J R, Wang Y H, et al. Effects of legume-grass mixed sowing on forage grass yield and quality in artificial grassland. Arid Zone Research, 2016, 33(1): 179-185. |
| 刘敏, 龚吉蕊, 王忆慧, 等. 豆禾混播建植人工草地对牧草产量和草质的影响. 干旱区研究, 2016, 33(1): 179-185. | |
| 41 | Li W J, Wang J F, Gao X D, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on the hay yield and quality of Leymus chinensis under drought conditions. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(4): 743-748. |
| 李文晶, 王俊锋, 高晓荻, 等. 干旱条件下氮磷添加对羊草干草产量及饲用品质的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(4): 743-748. | |
| 42 | Fariaszewska A, Aper J, Van Huylenbroeck J, et al. Mild drought stress-induced changes in yield, physiological processes and chemical composition in Festuca, Lolium and Festulolium. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 2016, 203(2): 103-116. |
| 43 | Olszewska M. Response of cultivars of meadow fescue (Festuca pratensis) and timothy (Phleum prantense L.) grown on organic soil to moisture deficiency. Acta Scientiarum Polonorum-Agricultura, 2009, 8(1): 37-46. |
| 44 | Jin J Y, Zhang W H, Yuan L. Physiological responses of three forages to drought stress and evaluation of their drought resistance. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(10): 157-165. |
| 靳军英, 张卫华, 袁玲. 三种牧草对干旱胁迫的生理响应及抗旱性评价. 草业学报, 2015, 24(10): 157-165. | |
| 45 | Ma Q H, Zhang X M, Wang Z K, et al. Optimizing oat irrigation schedules in an alpine region using APSIM. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(7): 1-10. |
| 马千虎, 张学梅, 王自奎, 等. 基于APSIM模型的高寒地区燕麦灌溉制度优化. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 1-10. | |
| 46 | Xu B, Tang P C, Li Q, et al. Research on optimal irrigation schedule of oats by CROPWAT in Lhasa of Tibet. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2015, 33(6): 35-39, 183. |
| 徐冰, 汤鹏程, 李奇, 等. 基于CROPWAT模型的拉萨地区燕麦优化灌溉制度研究. 干旱地区农业研究, 2015, 33(6): 35-39, 183. |
| [1] | 陈映霞, 杜雨, 王玉祥, 张博, 阿迪莱·阿布都热合曼. 生境对无芒雀麦幼穗分化进程及生殖格局的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 112-121. |
| [2] | 王珊珊, 谷海涛, 谢慧芳, 何绍冬, 甘长波, 卫小勇, 孔广超. 113份饲草型六倍体小黑麦种质饲草产量与品质性状的评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 192-202. |
| [3] | 李瑞强, 王玉祥, 孙玉兰, 张磊, 陈爱萍. 盐胁迫对5份无芒雀麦苗期生长和生理生化的影响及综合性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 99-111. |
| [4] | 张耀, 黄小云, 陈鑫珠, 黄勤楼, 黄秀声, 韩海东. 海鲜菇菌糠发酵饲料对山羊屠宰性能及肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 195-205. |
| [5] | 银敏华, 马彦麟, 康燕霞, 贾琼, 齐广平, 汪精海. 氮素添加对中国苜蓿产量与品质效应的Meta分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 36-49. |
| [6] | 孙延亮, 赵俊威, 刘选帅, 李生仪, 马春晖, 王旭哲, 张前兵. 施氮对苜蓿初花期光合日变化、叶片形态及干物质产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 63-75. |
| [7] | 王星, 黄薇, 余淑艳, 李小云, 高雪芹, 伏兵哲. 宁夏地区地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿种子产量及构成因素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 76-85. |
| [8] | 付东青, 贾春英, 张力, 张凡凡, 马春晖. 南疆干旱灌溉区青贮玉米农艺性状和发酵品质动态分析及评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 111-125. |
| [9] | 李影正, 程榆林, 徐璐璐, 李万松, 严旭, 李晓锋, 何如钰, 周阳, 郑军军, 汪星宇, 张德龙, 程明军, 夏运红, 何建美, 唐祈林. 不同玉米品种(系)的全株、果穗与秸秆青贮特性比较[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 144-156. |
| [10] | 吴永杰, 丁浩, 邵涛, 赵杰, 董东, 代童童, 尹雪敬, 宗成, 李君风. 酶制剂对水稻秸秆青贮发酵品质及体外消化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 167-177. |
| [11] | 戈建珍, 傅文慧, 张露, 蔺宝珺, 赵帅, 白玛噶翁, 寇建村. 多菌灵在果园白三叶青贮中的降解及其对微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 64-75. |
| [12] | 李君风, 赵杰, 唐小月, 代童童, 董东, 宗成, 邵涛. 瘤胃纤维素降解菌系对灭菌水稻秸秆结构性碳水化合物降解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 85-95. |
| [13] | 张铎, 李岚涛, 林迪, 郑龙辉, 耿赛男, 石纹碹, 盛开, 苗玉红, 王宜伦. 施磷水平对菊芋块茎产量、品质、植株生理特性与磷利用率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 139-149. |
| [14] | 郭香, 吴硕, 郑明扬, 陈德奎, 邹璇, 陈晓阳, 周玮, 张庆. 添加黄梁木叶和壳寡糖对甘蔗梢青贮饲料发酵品质及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 202-210. |
| [15] | 金有顺, 侯扶江. 放牧家畜养分消化率的测定[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 200-212. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||