

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 36-49.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022127
银敏华( ), 马彦麟, 康燕霞(
), 马彦麟, 康燕霞( ), 贾琼, 齐广平, 汪精海
), 贾琼, 齐广平, 汪精海
收稿日期:2022-03-18
修回日期:2022-04-18
出版日期:2022-09-20
发布日期:2022-08-12
通讯作者:
康燕霞
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: yanxiakang@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Min-hua YIN( ), Yan-lin MA, Yan-xia KANG(
), Yan-lin MA, Yan-xia KANG( ), Qiong JIA, Guang-ping QI, Jing-hai WANG
), Qiong JIA, Guang-ping QI, Jing-hai WANG
Received:2022-03-18
Revised:2022-04-18
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-08-12
Contact:
Yan-xia KANG
摘要:
氮素在苜蓿产量累积与品质提升中发挥着重要作用,但其不合理添加不仅会造成资源浪费,还会加剧环境污染,且其添加效应因试验区域、添加模式和种植管理等因素不同存在较大差异。本研究通过整合已发表的相关田间试验数据,利用Meta分析方法定量研究了氮素添加对苜蓿产量与品质(粗蛋白含量、酸性和中性洗涤纤维含量)的效应及主要影响因素。结果表明,与不添加氮素相比,添加氮素可显著提高苜蓿产量与品质,其中产量和粗蛋白含量分别平均提高12.6%(置信区间9.0%~16.2%)和7.3%(置信区间4.1%~10.6%),酸性和中性洗涤纤维含量分别平均降低5.6%(置信区间3.5%~7.8%)和3.0%(置信区间1.0%~4.9%)。在甘肃,年平均气温<8 ℃和年平均降水量200~400 mm的地区,采用硝酸铵分次施肥及灌溉和播种量为26~30 kg·hm-2时,更有利于添加氮素对苜蓿产量和粗蛋白含量的提高效应及对酸性和中性洗涤纤维含量的降低效应;但适宜的施氮量及生长年限在产量与品质方面存在差异。该研究可为苜蓿生产力提升及氮营养高效利用提供参考。
银敏华, 马彦麟, 康燕霞, 贾琼, 齐广平, 汪精海. 氮素添加对中国苜蓿产量与品质效应的Meta分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 36-49.
Min-hua YIN, Yan-lin MA, Yan-xia KANG, Qiong JIA, Guang-ping QI, Jing-hai WANG. Effects of nitrogen application on alfalfa yield and quality in China-A Meta-analysis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 36-49.

图1 添加与不添加氮素条件下苜蓿产量和品质的频率分布NA: 氮素添加Nitrogen application; CP: 粗蛋白Crude protein; ADF: 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber; NDF: 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber. 下同The same below.
Fig.1 Frequency distribution of alfalfa yield and quality with or without nitrogen application

图2 苜蓿产量和品质的区域变化方框的内部水平线、上边缘和下边缘分别表示中位数、1/4分位数和3/4分位数。垂直线的下端和上端分别表示最小值和最大值。方框内外的实心点分别代表平均值和异常值。IM为内蒙古。下同。The horizontal lines in the boxes and the lower and upper ends of the boxes indicate the 50th, 25th and 75th percentiles, respectively. The lower and upper ends of the vertical lines indicate the minimum value and maximum value, respectively. The solid dot inside and outside the box represents the mean value and outlier, respectively. IM means Inner Mongolia. The same below.
Fig.2 Regional changes of alfalfa yield and quality
指标 Index | 模型 Model | 提高(降低)率 Increase (decrease) rate (%) | 95%置信区间 95% CI (%) | 效应量检验 Effect size test | 异质性检验 Heterogeneity test | 发表偏倚检验 Publication test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限LL | 上限UL | Z | P | Q | PQ | ZB | PB | |||
| 产量Yield | 随机效应模型REM | 12.6 | 9.0 | 16.2 | 7.17 | 0.000 | 8829810 | 0.000 | -0.246 | 0.806 |
| 粗蛋白含量CP content | 随机效应模型REM | 7.3 | 4.1 | 10.6 | 4.62 | 0.000 | 9532 | 0.000 | -0.408 | 0.683 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维含量ADF content | 随机效应模型REM | -5.6 | -7.8 | -3.5 | -5.03 | 0.000 | 750 | 0.000 | -0.874 | 0.382 |
| 中性洗涤纤维含量NDF content | 随机效应模型REM | -3.0 | -4.9 | -1.0 | -3.00 | 0.003 | 511 | 0.000 | -1.241 | 0.215 |
表1 氮素添加对苜蓿产量与品质的综合效应量
Table 1 Comprehensive effect size of nitrogen application on yield and quality of alfalfa
指标 Index | 模型 Model | 提高(降低)率 Increase (decrease) rate (%) | 95%置信区间 95% CI (%) | 效应量检验 Effect size test | 异质性检验 Heterogeneity test | 发表偏倚检验 Publication test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限LL | 上限UL | Z | P | Q | PQ | ZB | PB | |||
| 产量Yield | 随机效应模型REM | 12.6 | 9.0 | 16.2 | 7.17 | 0.000 | 8829810 | 0.000 | -0.246 | 0.806 |
| 粗蛋白含量CP content | 随机效应模型REM | 7.3 | 4.1 | 10.6 | 4.62 | 0.000 | 9532 | 0.000 | -0.408 | 0.683 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维含量ADF content | 随机效应模型REM | -5.6 | -7.8 | -3.5 | -5.03 | 0.000 | 750 | 0.000 | -0.874 | 0.382 |
| 中性洗涤纤维含量NDF content | 随机效应模型REM | -3.0 | -4.9 | -1.0 | -3.00 | 0.003 | 511 | 0.000 | -1.241 | 0.215 |
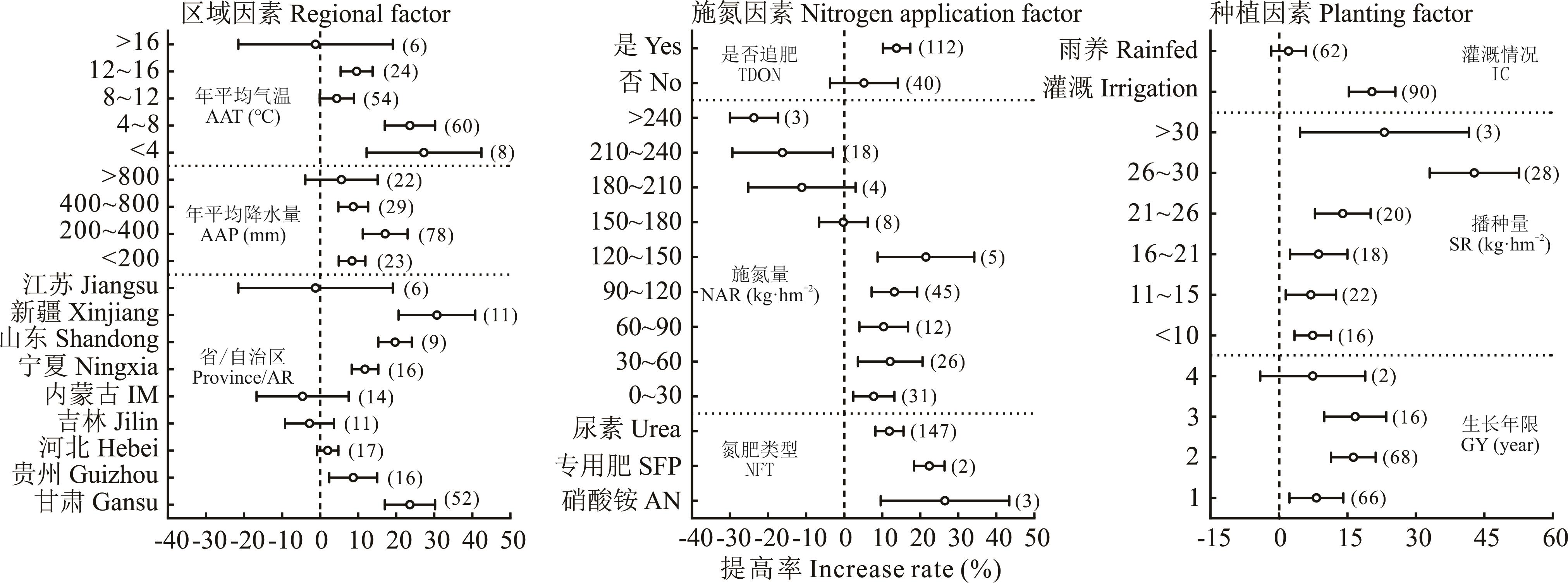
图4 氮素添加对苜蓿产量的影响因素分析误差线和圆点分别表示95%置信区间和平均提高率,误差线右侧的数字表示相应分组的样本数量。Error bar and dot represents 95% confidence interval and increase rate, respectively. The number at the right of the error bar indicates the number of samples. AAT: 年平均气温Average annual temperature; AAP: 年平均降水量Average annual precipitation; AR: 自治区Autonomous region; SFP: 牧草专用肥Special fertilizer for pasture; AN: 硝酸铵Ammonium nitrate; TDON: 是否施肥Top dressed or not; NAR: 施氮量Nitrogen application rate; NFT: 氮肥类型Nitrogen fertilizer type; IC: 灌溉情况Irrigation condition; SR: 播种量Seeding rate; GY: 生长年限Growth year. 下同The same below.
Fig.4 Analysis of factors affecting alfalfa yield with nitrogen application
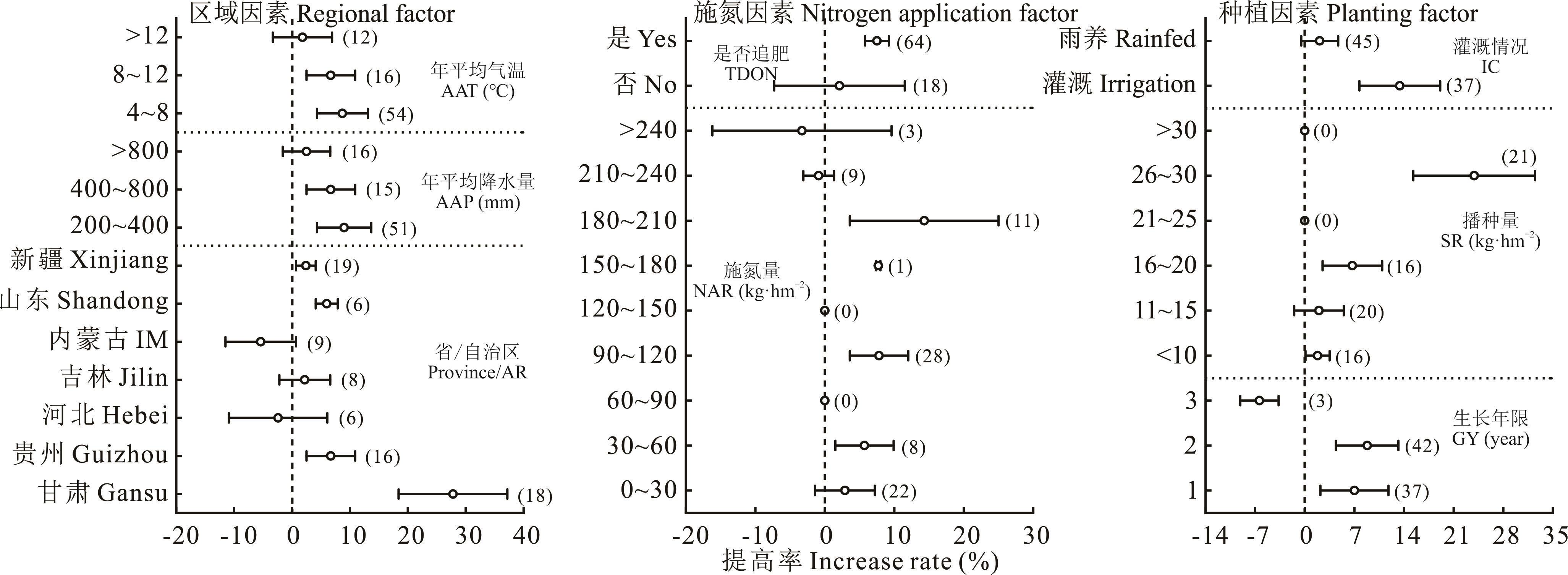
图5 氮素添加对苜蓿粗蛋白含量的影响因素分析苜蓿粗蛋白含量的样本中仅涉及尿素一种氮肥,故因素中不包含氮肥类型。下同。The samples of crude protein content of alfalfa only involve urea, so nitrogen fertilizer type is not included in the influencing factors. The same below.
Fig.5 Analysis of factors affecting crude protein content of alfalfa with nitrogen application
| 1 | Wei Z B, Bai Z H, Ma L, et al. Spatial characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus flow in cultivated grassland of China. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(3): 535-555. |
| 魏志标, 柏兆海, 马林, 等. 中国栽培草地氮磷流动空间特征. 中国农业科学, 2018, 51(3): 535-555. | |
| 2 | Shen H H, Zhu Y K, Zhao X, et al. Analysis of current grassland resources in China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(2): 139-154. |
| 沈海花, 朱言坤, 赵霞, 等. 中国草地资源的现状分析. 科学通报, 2016, 61(2): 139-154. | |
| 3 | The third national land survey leading group office of the state council. Main data Bulletin of the third national land survey. (2021-08-25) [2022-03-11]. http://www.mnr.gov.cn/dt/ywbb/202108/t20210826_2678340.html. |
| 国务院第三次全国国土调查领导小组办公室. 第三次全国国土调查主要数据公报. (2021-08-25) [2022-03-11]. http://www.mnr.gov.cn/dt/ywbb/202108/t20210826_2678340.html. | |
| 4 | Mcdonald I, Baral R, Min D. Effects of alfalfa and alfalfa-grass mixtures with nitrogen fertilization on dry matter yield and forage nutritive value. Journal of Animal Science and Technology, 2021, 63(2): 305-318. |
| 5 | Osterholz W R, Renz M J, Jokela W E, et al. Interseeded alfalfa reduces soil and nutrient runoff losses during and after corn silage production. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 74(1): 85-90. |
| 6 | Gu Y J, Han C L, Kong M, et al. Plastic film mulch promotes high alfalfa production with phosphorus-saving and low risk of soil nitrogen loss. Field Crops Research, 2018, 229: 44-54. |
| 7 | Liu R, Zhang Y H, Ge Y Q, et al. Alfalfa growth simulation model based on water and nitrogen factors in Ningxia irrigation area of Yellow River. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(13): 102-112. |
| 刘瑞, 张亚红, 葛永琪, 等. 基于水氮因子的宁夏引黄灌区紫花苜蓿生长模拟模型. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(13): 102-112. | |
| 8 | Wang W X. Countermeasures for the development of alfalfa planting industry in China. Journal of Beijing University of Agriculture, 2022, 37(1): 117-120. |
| 王文信. 中国苜蓿种植业发展的对策. 北京农学院学报, 2022, 37(1): 117-120. | |
| 9 | Han S X, Wang S, Gao Z L, et al. Impact of N application on the yield of alfalfa, N accumulation and nitrogen use efficiency. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2014, 29(6): 220-225. |
| 韩思训, 王森, 高志岭, 等. 不同施肥条件下苜蓿产量、氮素累积量及肥料氮素利用率研究. 华北农学报, 2014, 29(6): 220-225. | |
| 10 | Wang Y Q, Shen Y, Qian J, et al. Effects of nitrogen forms on plant growth, expression of nitrate transporter gene MtNRT1.3 and nitrogen absorption in Medicago sativa L. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(5): 1172-1180. |
| 王玉强, 沈宇, 钱进, 等. 不同形态氮肥对紫花苜蓿生长、硝酸盐转运蛋白基因MtNRT1.3表达及氮吸收的影响. 草地学报, 2019, 27(5): 1172-1180. | |
| 11 | Wang J, Li F M, Jia Y, et al. Dynamics of soil nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in alfalfa-crop rotated farmland in semiarid area of Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2005, 16(3): 439-444. |
| 王俊, 李凤民, 贾宇, 等. 半干旱黄土区苜蓿草地轮作农田土壤氮、磷和有机质变化. 应用生态学报, 2005, 16(3): 439-444. | |
| 12 | Gao L M, Su J, Tian Q, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on nitrogen accumulation and root nitrogenase activity in Medicago sativa at different soil water contents. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(3): 130-136. |
| 高丽敏, 苏晶, 田倩, 等. 施氮对不同水分条件下紫花苜蓿氮素吸收及根系固氮酶活性的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 130-136. | |
| 13 | Liu X J, Zhao Y J, Hao F, et al. Detection and characterization of nitrogen efficiency in alfalfa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(12): 90-102. |
| 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 郝凤, 等. 紫花苜蓿氮效率及其类型特征研究. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 90-102. | |
| 14 | Liu X J, Liu Y N, Kuai J L, et al. Effects of different N levels on productivity and quality of alfalfa varieties. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2013, 21(4): 702-707. |
| 刘晓静, 刘艳楠, 蒯佳林, 等. 施供氮水平对不同紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响. 草地学报, 2013, 21(4): 702-707. | |
| 15 | Zhang J X, Liu X J, Hao F, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus regulation on alfalfa nitrogen accumulation and the nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients of soil. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2016, 24(1): 61-68. |
| 张进霞, 刘晓静, 郝凤, 等. 氮磷调控对紫花苜蓿氮积累与土壤氮磷营养的影响. 草地学报, 2016, 24(1): 61-68. | |
| 16 | Zhu T Q, Liu X J, Zhang X L. Effects of nitrogen on root morphology and anatomical structure of alfalfa. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2016, 24(6): 1290-1295. |
| 朱天琦, 刘晓静, 张晓玲. 氮营养调控对紫花苜蓿根系形态及其解剖结构的影响. 草地学报, 2016, 24(6): 1290-1295. | |
| 17 | Xu R R, Chang S H, Jia Q M, et al. Effects of nitrogen application and utilization methods on yield, quality and water use of grass-legume mixed grassland in Loess Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(6): 1744-1755. |
| 徐然然, 常生华, 贾倩民, 等. 施氮和利用方式对黄土高原禾豆混播草地产量、品质和水分利用的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(6): 1744-1755. | |
| 18 | Li H, Chang W Y. Exploring optimal film mulching to enhance potato yield in China: A Meta-analysis. Agronomy Journal, 2020, 113(5): 4099-4115. |
| 19 | Zhang F M, Shen S H. A study on dry/wet conditions and changes of dry/wet climate boundary in China. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 2008, 4: 574-579. |
| 张方敏, 申双和. 中国干湿状况和干湿气候界限变化研究. 南京气象学院学报, 2008, 4: 574-579. | |
| 20 | Hedges L V, Gurevitch J, Curtis P S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology, 1999, 80(4): 1150-1156. |
| 21 | Qi G P, Kang Y X, Yin M H, et al. Yield responses of wheat to crop residue returning in China: A Meta-analysis. Crop Science, 2019, 59(5): 2185-2200. |
| 22 | Card N A. Applied meta-analysis for social science research. New York: Guilford Press, 2011. |
| 23 | Egger M, Smith G D, Schneider M, et al. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. British Medical Journal, 1997, 315(7109): 629-634. |
| 24 | Yang Y Y, Gao Z L, Wang X J. Impacts of organic and inorganic fertilizations on alfalfa yield, soil nitrate and greenhouse gas emissions. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(3): 822-828. |
| 杨园园, 高志岭, 王雪君. 有机、无机氮肥施用对苜蓿产量、土壤硝态氮和温室气体排放的影响. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(3): 822-828. | |
| 25 | Zhang K, Qu H, Xue Z, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on the forage dry matter yield and quality of alfalfa with seasonal cultivation. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2015, 23(4): 844-849. |
| 张昆, 渠晖, 薛峥, 等. 施氮水平对季节性栽培紫花苜蓿饲草干物质产量和品质的影响. 草地学报, 2015, 23(4): 844-849. | |
| 26 | Wu Y, Liu X J, Lin F, et al. Nitrogen application effect and soil carbon and nitrogen characteristics of rotation alfalfa in vegetable field in Hexi irrigated area, Gansu Province, Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(11): 4011-4020. |
| 吴勇, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 等. 河西灌区蔬菜地轮作紫花苜蓿的施氮效应及土壤碳氮特征. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(11): 4011-4020. | |
| 27 | Wen Y, Zhang J, Feng M, et al. Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilizer on alfalfa quality. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(10): 76-83. |
| 文雅, 张静, 冯萌, 等. 水氮互作对河西走廊紫花苜蓿品质的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 76-83. | |
| 28 | Wei X B, Wang Z F, Yu H Z, et al. Effects of alfalfa with different growth years on soil fertility in saline-alkali land. Pratacultural Science, 2013, 30(10): 1502-1507. |
| 魏晓斌, 王志锋, 于洪柱, 等. 不同生长年限苜蓿对盐碱地土壤肥力的影响. 草业科学, 2013, 30(10): 1502-1507. | |
| 29 | Hao F, Yu T F, Liu X J, et al. Relationship between nitrogen uptake and root morphology of alfalfa with different nitrogen efficiency and its response to nitrogen. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(11): 2428-2434. |
| 郝凤, 于铁峰, 刘晓静, 等. 不同氮效率型苜蓿氮素吸收差异与根系形态的关系及其对氮的响应. 草地学报, 2021, 29(11): 2428-2434. | |
| 30 | Liu X J, Ye F, Zhang X L. Effects of exogenous nitrogen forms on root characteristics of alfalfa at different growth stages. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(6): 53-63. |
| 刘晓静, 叶芳, 张晓玲. 外源氮素形态对紫花苜蓿不同生育期根系特性的影响. 草业学报, 2015, 24(6): 53-63. | |
| 31 | Yin M H, Li Y N, Li H, et al. Effects of nitrogen application rates on root growth and nitrogen use of summer maize. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(6): 129-138. |
| 银敏华, 李援农, 李昊, 等. 氮肥运筹对夏玉米根系生长与氮素利用的影响. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(6): 129-138. | |
| 32 | He F, Han D M, Wan L Q, et al. The nutrient situations in the major alfalfa producing areas of China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2014, 20(2): 503-509. |
| 何峰, 韩冬梅, 万里强, 等. 我国主产区紫花苜蓿营养状况分析. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(2): 503-509. | |
| 33 | Xu R Z, Wu X J, Yang H M. Effect of topdressing after cutting on alfalfa growth and production. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 195-204. |
| 徐睿智, 吴晓娟, 杨惠敏. 刈割后追肥对建植当年紫花苜蓿生长和生产性能的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 195-204. | |
| 34 | Wang Y, Cui G W, Yin H, et al. Effects of different fertilization schemes on alfalfa performance and nutritional quality. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(3): 793-803. |
| 王洋, 崔国文, 尹航, 等. 施肥对紫花苜蓿生产性能及营养品质的影响. 草业科学, 2019, 36(3): 793-803. | |
| 35 | Xiao Z X, Wang Y, Liu G F, et al. Effects of fertilizing time in early spring on alfalfa (Medicago sativa) production performance and nutritional quality in Mollisol area in cold region. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(13): 2668-2677. |
| 肖知新, 王洋, 刘国富, 等. 寒地黑土区春季施肥期对紫花苜蓿生产性能及营养品质的影响. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(13): 2668-2677. | |
| 36 | Ge J M, Fan J, Yuan H Y, et al. Soil water depletion and restoration under inter-conversion of food crop and alfalfa with three consecutive wet years. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 585: 124851. |
| 37 | Zheng R, Kang S Z, Hu X T, et al. Effects of water and nitrogen conditions on the diurnal variation of photosynthesis characteristic and yield of grapevine in arid oasis region. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2013, 29(4): 133-141. |
| 郑睿, 康绍忠, 胡笑涛, 等. 水氮处理对荒漠绿洲区酿酒葡萄光合特性与产量的影响. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(4): 133-141. | |
| 38 | Wen X. Study on water and fertilizer effects on productivity and quality of alfalfa. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2010. |
| 文霞. 水肥对紫花苜蓿生产性能和品质的影响研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2010. | |
| 39 | Ahmad J, Iqbal A, Mahmood A, et al. Effect of cutting management, seeding rate and sowing method on seed yield of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Pakistan Journal of Botany, 2020, 52(4): 1449-1454. |
| 40 | Wang Y H, Wang C Z, Li D F, et al. Effects of seeding rate on plant number, production performance, and quality of alfalfa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(2): 123-135. |
| 王彦华, 王成章, 李德锋, 等. 播种量和品种对紫花苜蓿植株动态变化、产量及品质的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(2): 123-135. | |
| 41 | Luo Z Z, Niu Y N, Li L L, et al. Soil moisture and alfalfa productivity response from different years of growth on the Loess Plateau of central Gansu. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(1): 31-38. |
| 罗珠珠, 牛伊宁, 李玲玲, 等. 陇中黄土高原不同种植年限苜蓿草地土壤水分及产量响应. 草业学报, 2015, 24(1): 31-38. | |
| 42 | Wang A X, Ma Y L, Qi G P, et al. Water and nitrogen regulation patterns for productivity improvement of Bromus inermis and alfalfa mixed grassland. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 36(2): 322-330. |
| 汪爱霞, 马彦麟, 齐广平, 等. 无芒雀麦与苜蓿混播草地生产力提升的水氮调控模式. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(2): 322-330. | |
| 43 | Han L N, Ding J, Han Q F, et al. Effects of alfalfa-grain (oil) crop plowing rotation on soil moisture and crop yield in Loess Plateau. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(24): 129-137. |
| 韩丽娜, 丁静, 韩清芳, 等. 黄土高原区草粮(油)翻耕轮作的土壤水分及作物产量效应. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(24): 129-137. |
| [1] | 苗阳阳, 张艳蕊, 宋标, 刘旭桐, 张安琪, 吕金泽, 张浩, 张小华, 欧阳佳慧, 李旺, 曲善民. 碱蓬根际和内生细菌菌株对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 107-117. |
| [2] | 赵俊威, 李生仪, 孙延亮, 刘选帅, 马春晖, 张前兵. 不同氮磷水平下不同土层中紫花苜蓿细根周转特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 118-128. |
| [3] | 陈卫东, 张玉霞, 张庆昕, 刘庭玉, 王显国, 王东儒. 末次刈割时间对苜蓿根颈抗氧化系统及抗寒性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 129-138. |
| [4] | 张耀, 黄小云, 陈鑫珠, 黄勤楼, 黄秀声, 韩海东. 海鲜菇菌糠发酵饲料对山羊屠宰性能及肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 195-205. |
| [5] | 付东青, 贾春英, 张力, 张凡凡, 马春晖. 南疆干旱灌溉区青贮玉米农艺性状和发酵品质动态分析及评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 111-125. |
| [6] | 李影正, 程榆林, 徐璐璐, 李万松, 严旭, 李晓锋, 何如钰, 周阳, 郑军军, 汪星宇, 张德龙, 程明军, 夏运红, 何建美, 唐祈林. 不同玉米品种(系)的全株、果穗与秸秆青贮特性比较[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 144-156. |
| [7] | 吴永杰, 丁浩, 邵涛, 赵杰, 董东, 代童童, 尹雪敬, 宗成, 李君风. 酶制剂对水稻秸秆青贮发酵品质及体外消化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 167-177. |
| [8] | 赵建涛, 岳亚飞, 张前兵, 马春晖. 不同秋眠级紫花苜蓿品种抗寒性对新疆北疆地区覆雪厚度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 24-34. |
| [9] | 田骄阳, 王秋霞, 郑淑文, 刘文献. 全基因组水平蒺藜苜蓿CPP基因家族的鉴定及表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 111-121. |
| [10] | 刘彩婷, 毛丽萍, 阿依谢木, 于应文, 沈禹颖. 紫花苜蓿与垂穗披碱草混播比例对其抗寒生长生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 133-143. |
| [11] | 王雪萌, 何欣, 张涵, 宋瑞, 毛培胜, 贾善刚. 基于多光谱成像技术快速无损检测紫花苜蓿人工老化种子[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 197-208. |
| [12] | 戈建珍, 傅文慧, 张露, 蔺宝珺, 赵帅, 白玛噶翁, 寇建村. 多菌灵在果园白三叶青贮中的降解及其对微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 64-75. |
| [13] | 李君风, 赵杰, 唐小月, 代童童, 董东, 宗成, 邵涛. 瘤胃纤维素降解菌系对灭菌水稻秸秆结构性碳水化合物降解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 85-95. |
| [14] | 张铎, 李岚涛, 林迪, 郑龙辉, 耿赛男, 石纹碹, 盛开, 苗玉红, 王宜伦. 施磷水平对菊芋块茎产量、品质、植株生理特性与磷利用率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 139-149. |
| [15] | 郭香, 吴硕, 郑明扬, 陈德奎, 邹璇, 陈晓阳, 周玮, 张庆. 添加黄梁木叶和壳寡糖对甘蔗梢青贮饲料发酵品质及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 202-210. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||