

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (8): 88-98.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024355
李文秀1( ), 姚拓1(
), 姚拓1( ), 李昌宁1, 贾倩民2, 何傲蕾1, 周杨3
), 李昌宁1, 贾倩民2, 何傲蕾1, 周杨3
收稿日期:2024-09-23
修回日期:2024-10-28
出版日期:2025-08-20
发布日期:2025-06-16
通讯作者:
姚拓
作者简介:E-mail: yaotuo@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Wen-xiu LI1( ), Tuo YAO1(
), Tuo YAO1( ), Chang-ning LI1, Qian-min JIA2, Ao-lei HE1, Yang ZHOU3
), Chang-ning LI1, Qian-min JIA2, Ao-lei HE1, Yang ZHOU3
Received:2024-09-23
Revised:2024-10-28
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-06-16
Contact:
Tuo YAO
摘要:
为了探究凹凸棒加有机基质作为菌肥载体的可行性以及制作菌肥时菌液的最佳添加量。本试验通过向有机基质中添加不同梯度凹凸棒(分别为5%、7.5%、10%)作为菌肥载体,然后向其中添加不同梯度菌液(分别为25%、27.5%、30%)制作成固体菌肥;通过测定菌肥货架期及紫花苜蓿盆栽试验验证菌肥促生效果,确定凹凸棒添加量以及菌液添加量。结果显示:菌肥保存180 d后,不同载体菌肥有效活菌数均大于2×108 cfu·g-1,杂菌数均小于3×106 cfu·g-1,其中5%凹凸棒加25%的菌液(F2+25%菌液)处理效果最好;7.5%凹凸棒加30%菌液(F3+30%菌液)处理下,紫花苜蓿结瘤数最多,为62.7个·盆-1,较对照提高了317.8%。5%凹凸棒加25%的菌液(F2+25%菌液)处理下,紫花苜蓿地上、地下生物量、叶绿素含量较对照分别提高了46.5%、86.2%和54.9%;总根长、总根表面积、根尖数和根分叉数较对照提高了87.7%、108.4%、96.2%和252.0%;通过隶属函数分析得出,5%凹凸棒加25%的菌液(F2+25%菌液)处理对紫花苜蓿促生效果最好。
李文秀, 姚拓, 李昌宁, 贾倩民, 何傲蕾, 周杨. “凹凸棒-有机基质”菌肥载体最佳配比的筛选及对紫花苜蓿的促生效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 88-98.
Wen-xiu LI, Tuo YAO, Chang-ning LI, Qian-min JIA, Ao-lei HE, Yang ZHOU. Screening of the best ratio of ‘attapulgite-organic matrix’ bacterial fertilizer carrier and its growth-promotion effect on alfalfa[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(8): 88-98.
| 编号Code | 菌株Strain | 寄主植物Host plant | 促生特性Growth promoting characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| LY | 蕈状芽孢杆菌Bacillus mycoides | 珠芽蓼Polygonum viviparum | 溶磷,分泌植物生长素Phosphorus dissolving, secreting auxin |
| LM3 | 猴假单胞菌Pseudomonas simiae | 毛稃羊茅Festuca kirilowii | 溶磷,固氮,分泌植物生长素Phosphorus dissolving, nitrogen fixation, secreting auxin |
| LM2 | 莫哈韦芽孢杆菌Bacillus mojavensis | 黑果枸杞Lycium ruthenicum | 固氮,分泌植物生长素Nitrogen fixation, secreting auxin |
表1 供试菌株
Table 1 Strains for test
| 编号Code | 菌株Strain | 寄主植物Host plant | 促生特性Growth promoting characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| LY | 蕈状芽孢杆菌Bacillus mycoides | 珠芽蓼Polygonum viviparum | 溶磷,分泌植物生长素Phosphorus dissolving, secreting auxin |
| LM3 | 猴假单胞菌Pseudomonas simiae | 毛稃羊茅Festuca kirilowii | 溶磷,固氮,分泌植物生长素Phosphorus dissolving, nitrogen fixation, secreting auxin |
| LM2 | 莫哈韦芽孢杆菌Bacillus mojavensis | 黑果枸杞Lycium ruthenicum | 固氮,分泌植物生长素Nitrogen fixation, secreting auxin |
处理 Treatment | 载体 Carrier |
|---|---|
| F1 | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer |
| F2 | 有机肥+5%凹凸棒 Organic fertilizer+5% attapulgite |
| F3 | 有机肥+7.5%凹凸棒 Organic fertilizer+7.5% attapulgite |
| F4 | 有机肥+10%凹凸棒 Organic fertilizer+10% attapulgite |
表2 菌肥载体配方
Table 2 Formulation of bactericide carrier
处理 Treatment | 载体 Carrier |
|---|---|
| F1 | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer |
| F2 | 有机肥+5%凹凸棒 Organic fertilizer+5% attapulgite |
| F3 | 有机肥+7.5%凹凸棒 Organic fertilizer+7.5% attapulgite |
| F4 | 有机肥+10%凹凸棒 Organic fertilizer+10% attapulgite |
处理 Treatment | 重复Repeat | 平均 Mean | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| F1 | 30 | 27 | 28 | 28a |
| F2 | 26 | 26 | 27 | 26a |
| F3 | 29 | 27 | 28 | 28a |
| F4 | 26 | 28 | 27 | 27a |
表3 载体吸水率
Table 3 Water absorbing capability of carriers (%)
处理 Treatment | 重复Repeat | 平均 Mean | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| F1 | 30 | 27 | 28 | 28a |
| F2 | 26 | 26 | 27 | 26a |
| F3 | 29 | 27 | 28 | 28a |
| F4 | 26 | 28 | 27 | 27a |
处理 Treatment | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 有效钾 Available potassium (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 3.28±0.26a | 2.69±0.17a | 446.48±0.55a | 1.18±0.01a | 1.76±0.09a |
| F2 | 2.91±0.13a | 2.64±0.02a | 411.80±41.95a | 1.21±0.02a | 1.88±0.01a |
| F3 | 2.99±0.33a | 3.05±0.02a | 388.88±34.55a | 1.19±0.01a | 1.82±0.01a |
| F4 | 2.75±0.03a | 3.15±0.36a | 433.99±15.01a | 1.15±0.03a | 1.84±0.01a |
表4 载体营养成分分析
Table 4 Analysis of nutrient composition of carriers
处理 Treatment | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 有效钾 Available potassium (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 3.28±0.26a | 2.69±0.17a | 446.48±0.55a | 1.18±0.01a | 1.76±0.09a |
| F2 | 2.91±0.13a | 2.64±0.02a | 411.80±41.95a | 1.21±0.02a | 1.88±0.01a |
| F3 | 2.99±0.33a | 3.05±0.02a | 388.88±34.55a | 1.19±0.01a | 1.82±0.01a |
| F4 | 2.75±0.03a | 3.15±0.36a | 433.99±15.01a | 1.15±0.03a | 1.84±0.01a |
| 简称Abbreviation | 处理 Treatment | 简称Abbreviation | 处理 Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1+0 | F1+0菌液F1+0 bacterial solution | F3+0 | F3+0菌液F3+0 bacterial solution |
| F1+25% | F1+25%菌液F1+25% bacterial solution | F3+25% | F3+25%菌液F3+25% bacterial solution |
| F1+27.5% | F1+27.5%菌液F1+27.5% bacterial solution | F3+27.5% | F3+27.5%菌液F3+27.5% bacterial solution |
| F1+30% | F1+30%菌液F1+30% bacterial solution | F3+30% | F3+30%菌液F3+30% bacterial solution |
| F2+0 | F2+0菌液F2+0 bacterial solution | F4+0 | F4+0菌液F4+0 bacterial solution |
| F2+25% | F2+25%菌液F2+25% bacterial solution | F4+25% | F4+25%菌液F4+25% bacterial solution |
| F2+27.5% | F2+27.5%菌液F2+27.5% bacterial solution | F4+27.5% | F4+27.5%菌液F4+27.5% bacterial solution |
| F2+30% | F2+30%菌液F2+30% bacterial solution | F4+30% | F4+30%菌液F4+30% bacterial solution |
表5 试验处理
Table 5 Experimental treatments
| 简称Abbreviation | 处理 Treatment | 简称Abbreviation | 处理 Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1+0 | F1+0菌液F1+0 bacterial solution | F3+0 | F3+0菌液F3+0 bacterial solution |
| F1+25% | F1+25%菌液F1+25% bacterial solution | F3+25% | F3+25%菌液F3+25% bacterial solution |
| F1+27.5% | F1+27.5%菌液F1+27.5% bacterial solution | F3+27.5% | F3+27.5%菌液F3+27.5% bacterial solution |
| F1+30% | F1+30%菌液F1+30% bacterial solution | F3+30% | F3+30%菌液F3+30% bacterial solution |
| F2+0 | F2+0菌液F2+0 bacterial solution | F4+0 | F4+0菌液F4+0 bacterial solution |
| F2+25% | F2+25%菌液F2+25% bacterial solution | F4+25% | F4+25%菌液F4+25% bacterial solution |
| F2+27.5% | F2+27.5%菌液F2+27.5% bacterial solution | F4+27.5% | F4+27.5%菌液F4+27.5% bacterial solution |
| F2+30% | F2+30%菌液F2+30% bacterial solution | F4+30% | F4+30%菌液F4+30% bacterial solution |
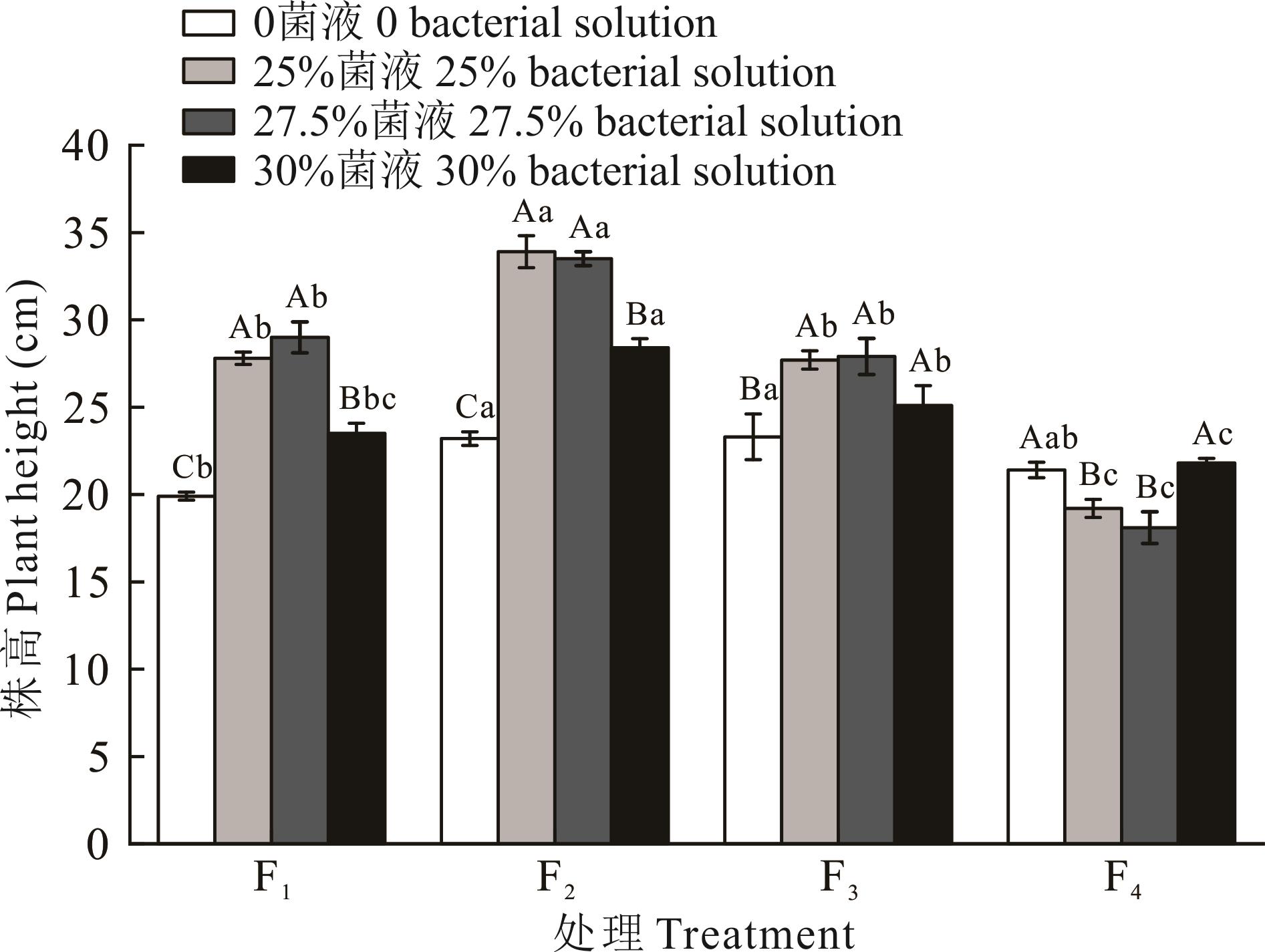
图3 不同处理菌肥对紫花苜蓿株高的影响不同大写字母表示在同一载体处理下不同菌液浓度处理之间差异显著(P<0.05),不同小写字母表示在同一菌液浓度处理下不同载体处理之间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。The capital letters represent the significant differences (P<0.05)among different bacterial solution concentrations treated with the same carrier, and the lowercase letters represent the significant differences (P<0.05) among different carrier treated with the same bacterial solution concentration, the same below.
Fig.3 Effect of different treatments on plant height of alfalfa
处理 Treatment | 总根长 Total root length (cm) | 总根表面积 Total root surface area (cm2) | 总根体积 Total root volume (cm3) | 根尖数 Root tip number | 根分叉数 Root bifurcation number | 根交叉数 Root crossing number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1+0 | 368.50±18.50bcd | 89.95±7.51c | 2.07±0.39cd | 430.00±30.99b | 356.33±23.38c | 42.00±4.04c |
| F1+25% | 252.86±26.99def | 36.97±3.61d | 0.38±0.02d | 241.33±11.10de | 522.00±19.01bc | 86.33±4.41abc |
| F1+27.5% | 256.94±19.61def | 34.20±2.39d | 0.36±0.02d | 365.67±11.35bc | 551.33±30.60bc | 100.67±13.69abc |
| F1+30% | 283.73±63.04cde | 39.66±8.61d | 0.44±0.09d | 228.67±14.66def | 578.67±164.66bc | 122.00±19.86ab |
| F2+0 | 474.50±43.47b | 122.68±17.03b | 2.73±0.37c | 399.00±23.86b | 416.33±17.52bc | 70.33±16.46bc |
| F2+25% | 691.52±80.19a | 187.42±10.63a | 5.66±0.47b | 843.67±23.55a | 1254.33±78.61a | 125.67±6.17ab |
| F2+27.5% | 386.25±6.37bc | 123.29±16.46b | 1.39±0.40cd | 448.00±47.90b | 751.33±69.87b | 152.67±12.67a |
| F2+30% | 206.67±51.73efg | 34.17±9.29d | 0.45±0.14d | 244.00±61.52de | 561.67±174.94bc | 93.67±34.92abc |
| F3+0 | 169.38±28.07efg | 25.03±4.35d | 7.97±1.38a | 213.00±25.70def | 385.00±77.53bc | 67.67±14.45bc |
| F3+25% | 340.30±44.85cd | 67.31±17.73c | 1.22±0.63cd | 299.00±37.40cd | 737.00±289.66b | 147.00±67.51a |
| F3+27.5% | 160.21±5.62fg | 23.63±1.06d | 0.28±0.02d | 175.33±11.33ef | 386.33±6.49bc | 81.67±3.28abc |
| F3+30% | 138.57±8.28fg | 21.00±1.43d | 0.25±0.02d | 163.67±25.31ef | 326.67±45.48c | 66.33±10.71bc |
| F4+0 | 208.29±33.02efg | 28.71±4.67d | 9.14±1.49a | 222.67±41.86def | 386.00±89.18bc | 66.67±22.02bc |
| F4+25% | 101.00±6.65g | 15.93±0.59d | 0.20±0.01d | 131.00±7.23f | 210.33±22.33c | 28.67±2.19c |
| F4+27.5% | 155.34±23.19fg | 24.41±4.76d | 0.31±0.08d | 190.33±27.02ef | 423.00±90.07bc | 71.33±11.67bc |
| F4+30% | 206.66±14.55efg | 28.96±2.48d | 0.32±0.04d | 243.33±26.08de | 461.33±82.49bc | 102.33±11.89abc |
表6 不同处理菌肥对紫花苜蓿根系形态的影响
Table 6 Effect of different treatments on root morphology of alfalfa
处理 Treatment | 总根长 Total root length (cm) | 总根表面积 Total root surface area (cm2) | 总根体积 Total root volume (cm3) | 根尖数 Root tip number | 根分叉数 Root bifurcation number | 根交叉数 Root crossing number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1+0 | 368.50±18.50bcd | 89.95±7.51c | 2.07±0.39cd | 430.00±30.99b | 356.33±23.38c | 42.00±4.04c |
| F1+25% | 252.86±26.99def | 36.97±3.61d | 0.38±0.02d | 241.33±11.10de | 522.00±19.01bc | 86.33±4.41abc |
| F1+27.5% | 256.94±19.61def | 34.20±2.39d | 0.36±0.02d | 365.67±11.35bc | 551.33±30.60bc | 100.67±13.69abc |
| F1+30% | 283.73±63.04cde | 39.66±8.61d | 0.44±0.09d | 228.67±14.66def | 578.67±164.66bc | 122.00±19.86ab |
| F2+0 | 474.50±43.47b | 122.68±17.03b | 2.73±0.37c | 399.00±23.86b | 416.33±17.52bc | 70.33±16.46bc |
| F2+25% | 691.52±80.19a | 187.42±10.63a | 5.66±0.47b | 843.67±23.55a | 1254.33±78.61a | 125.67±6.17ab |
| F2+27.5% | 386.25±6.37bc | 123.29±16.46b | 1.39±0.40cd | 448.00±47.90b | 751.33±69.87b | 152.67±12.67a |
| F2+30% | 206.67±51.73efg | 34.17±9.29d | 0.45±0.14d | 244.00±61.52de | 561.67±174.94bc | 93.67±34.92abc |
| F3+0 | 169.38±28.07efg | 25.03±4.35d | 7.97±1.38a | 213.00±25.70def | 385.00±77.53bc | 67.67±14.45bc |
| F3+25% | 340.30±44.85cd | 67.31±17.73c | 1.22±0.63cd | 299.00±37.40cd | 737.00±289.66b | 147.00±67.51a |
| F3+27.5% | 160.21±5.62fg | 23.63±1.06d | 0.28±0.02d | 175.33±11.33ef | 386.33±6.49bc | 81.67±3.28abc |
| F3+30% | 138.57±8.28fg | 21.00±1.43d | 0.25±0.02d | 163.67±25.31ef | 326.67±45.48c | 66.33±10.71bc |
| F4+0 | 208.29±33.02efg | 28.71±4.67d | 9.14±1.49a | 222.67±41.86def | 386.00±89.18bc | 66.67±22.02bc |
| F4+25% | 101.00±6.65g | 15.93±0.59d | 0.20±0.01d | 131.00±7.23f | 210.33±22.33c | 28.67±2.19c |
| F4+27.5% | 155.34±23.19fg | 24.41±4.76d | 0.31±0.08d | 190.33±27.02ef | 423.00±90.07bc | 71.33±11.67bc |
| F4+30% | 206.66±14.55efg | 28.96±2.48d | 0.32±0.04d | 243.33±26.08de | 461.33±82.49bc | 102.33±11.89abc |
| 处理Treatment | 隶属平均值Membership mean | 排序Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| F1+0 | 0.241 | 13 |
| F1+25% | 0.372 | 7 |
| F1+27.5% | 0.378 | 5 |
| F1+30% | 0.361 | 8 |
| F2+0 | 0.374 | 6 |
| F2+25% | 0.869 | 1 |
| F2+27.5% | 0.592 | 2 |
| F2+30% | 0.384 | 4 |
| F3+0 | 0.278 | 11 |
| F3+25% | 0.448 | 3 |
| F3+27.5% | 0.378 | 5 |
| F3+30% | 0.323 | 9 |
| F4+0 | 0.298 | 10 |
| F4+25% | 0.146 | 15 |
| F4+27.5% | 0.170 | 14 |
| F4+30% | 0.252 | 12 |
表7 不同处理菌肥的综合评价
Table 7 Comprehensive evaluation of different treatments of bacterial fertilizer
| 处理Treatment | 隶属平均值Membership mean | 排序Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| F1+0 | 0.241 | 13 |
| F1+25% | 0.372 | 7 |
| F1+27.5% | 0.378 | 5 |
| F1+30% | 0.361 | 8 |
| F2+0 | 0.374 | 6 |
| F2+25% | 0.869 | 1 |
| F2+27.5% | 0.592 | 2 |
| F2+30% | 0.384 | 4 |
| F3+0 | 0.278 | 11 |
| F3+25% | 0.448 | 3 |
| F3+27.5% | 0.378 | 5 |
| F3+30% | 0.323 | 9 |
| F4+0 | 0.298 | 10 |
| F4+25% | 0.146 | 15 |
| F4+27.5% | 0.170 | 14 |
| F4+30% | 0.252 | 12 |
| 1 | Liu F, Jing S X, Hu J, et al. Effects of cadmium and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation on the growth and nitrogen uptake of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(2): 69-77. |
| 刘芳, 景戍旋, 胡健, 等. 镉污染和接种丛枝菌根真菌对紫花苜蓿生长和氮吸收的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(2): 69-77. | |
| 2 | Ge X L, Yang H S, Liu J, et al. Effects of phosphorus level on growth and hay yield of alfalfa. Journal of Inner Mongolia Minzu University (Natural Sciences), 2009, 24(5): 509-513. |
| 葛选良, 杨恒山, 刘晶, 等. 施磷水平对紫花苜蓿生长及草产量的影响. 内蒙古民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 24(5): 509-513. | |
| 3 | Li Y B, Li Y L, Guan G H, et al. Screening, identification of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and its effect on reducing fertilization while increasing efficiency in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2020, 28(8): 1471-1476. |
| 李永斌, 李云龙, 关国华, 等. 植物根际促生菌的筛选、鉴定及其对小麦的减肥增产效果. 农业生物技术学报, 2020, 28(8): 1471-1476. | |
| 4 | Duan Q B, Yao T, Han H W, et al. Formulation of biofertilizer carrier using solid agricultural residues. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(1): 147-151. |
| 段淇斌, 姚拓, 韩华雯, 等. 利用几种固体农业废弃物配制生物肥料载体的研究. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(1): 147-151. | |
| 5 | Zhang S Y. Application of fly ash in absorbing silicate bacteria. Journal of the Hebei Academy of Sciences, 2006, 23(3): 30-33. |
| 章淑艳. 粉煤灰在硅酸盐菌剂中的应用. 河北省科学院学报, 2006, 23(3): 30-33. | |
| 6 | Stephens J H G, Rask H M. Inoculant production and formulation. Field Crops Research, 2000, 65(2/3): 249-258. |
| 7 | Wei Y F, Wang J T, Li W H, et al. Effects of attapulgite-biochar composites on nutrient slow-release in pakchoi field and the growth of pakchoi. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39(22): 121-132. |
| 魏彦凤, 王继涛, 李文慧, 等. 凹凸棒土-生物炭缓释材料对养分缓释及小白菜生长的影响. 农业工程学报, 2023, 39(22): 121-132. | |
| 8 | Sainao W Q, Zhang M D, Ma X J, et al. Physiological effects of cadmium stress on Astragalus membranaceus seedlings and alleviative effects of attapulgite clay on cadmium stress. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2018, 43(15): 3115-3126. |
| 赛闹汪青, 张牡丹, 马小俊, 等. 镉胁迫对黄芪幼苗的生理学影响及凹凸棒粘土对镉胁迫缓解作用的研究. 中国中药杂志, 2018, 43(15): 3115-3126. | |
| 9 | Tian Z H, Xue S P. Attapulgite modification and its research of repairing the soil of heavy metal contaminated. Applied Chemical Industry, 2019, 48(4): 883-887. |
| 田振华, 薛胜平. 凹凸棒石改性及其修复重金属污染土壤的研究. 应用化工, 2019, 48(4): 883-887. | |
| 10 | Wang A Q, Lu Y S, Kang Y R, et al. Research progress on the applications of attapulgite in animal healthy breeding. Feed Industry, 2024, 45(10): 1-9. |
| 王爱勤, 卢予沈, 康玉茹, 等. 凹凸棒石在动物健康养殖中应用研究进展. 饲料工业, 2024, 45(10): 1-9. | |
| 11 | Bao S D. Agrochemical analysis of soil. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2006: 39-114. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006: 39-114. | |
| 12 | Hu Z Q, Wang K H, Li C, et al. Cluster analysis of bacteriostatic effects of 50 heat-clearing Chinese medicine against Staphylococcus aureus. Chinese Journal of Medical Guide, 2023, 25(11): 1161-1166. |
| 胡子卿, 王珂慧, 李驰, 等. 50种清热类中药对金黄色葡萄球菌抑菌作用的聚类分析. 中国医药导刊, 2023, 25(11): 1161-1166. | |
| 13 | Li Q, Yao T, Yang X M, et al. Effects of different dosages of microbial fertilizers on growth and quality of oat in semi-arid area. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2020, 34(3): 159-165. |
| 李琦, 姚拓, 杨晓玫, 等. 半干旱地区不同剂型微生物菌肥替代部分化肥对燕麦生长和品质的影响. 干旱区资源与环境, 2020, 34(3): 159-165. | |
| 14 | Jin Y L, Yao T, Lan X J, et al. Inhibition characteristics of four strains of biocontrol bacteria against root rot pathogens of oats. Grassland and Turf, 2023, 43(6): 9-16. |
| 金艳丽, 姚拓, 兰晓君, 等. 4株生防细菌对燕麦根腐病原菌抑菌特性研究. 草原与草坪, 2023, 43(6): 9-16. | |
| 15 | Xie X, Yang J L, Liu X Y. Optimizing the determination conditions of total bacterial colonies in soil. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(11): 92-95. |
| 谢夏, 杨建兰, 刘新育. 土壤中细菌菌落总数的测定条件优化. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(11): 92-95. | |
| 16 | Lou X D, Zhang G L, Ye B C. Screening of high selenium-enriched yeast and enhancement of its selenium-enriched capacity. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2017, 33(12): 132-137. |
| 娄兴丹, 张根林, 叶邦策. 高富硒酵母的筛选及富硒强化研究. 生物技术通报, 2017, 33(12): 132-137. | |
| 17 | Wang L R, Wang W, Pu X J, et al. Comparison of feeding quality and production performance of different alfalfa (Medicago sativa L) varieties in the arid zone of eastern Qinghai Province. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(6): 1936-1943. |
| 王龙然, 王伟, 蒲小剑, 等. 青海东部干旱区不同紫花苜蓿品种饲用品质和生产性能比较. 草地学报, 2024, 32(6): 1936-1943. | |
| 18 | Han D R, Yao T, Li H Y, et al. Effect of reducing chemical fertilizer and substitution with microbial fertilizer on the growth of Elymus nutans. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(4): 53-61. |
| 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 等. 化肥减量配施微生物肥料对垂穗披碱草生长的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 53-61. | |
| 19 | Li X M, Yao T, Li C N, et al. Screening and identification of symbiotically efficient and stress-resistant rhizobia of wild Medicago lupulina in Gannan. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(3): 134-143. |
| 李雪梅, 姚拓, 李昌宁, 等. 甘南野生天蓝苜蓿高效共生、抗逆根瘤菌筛选鉴定. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 134-143. | |
| 20 | Li H S. Plant physiology biochemistry experiment principle and technology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000: 186-187. |
| 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000: 186-187. | |
| 21 | Dong W K, Ma X, Zhou X W, et al. Effects of exogenous glycine betaine on the physiological characteristics in Medicago sativa seedlings under low-temperature stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(1): 130-140. |
| 董文科, 马祥, 周学文, 等. 外源甜菜碱对低温胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗生理特性的影响. 草地学报, 2019, 27(1): 130-140. | |
| 22 | General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. Microbial inoculants in agriculture,GB20287-2006. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2006. |
| 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 农用微生物菌剂, GB20287-2006. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006. | |
| 23 | Andreeva O A, Kozhevin P A. Optimization of natural communities of soil microorganisms as a way to create microbial fertilizers. Moscow University Soil Science Bulletin, 2014, 69(4): 184-187. |
| 24 | Liu J J. Effects of microbial fertilizer on maize seedling and growth in black soil. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2023. |
| 刘京京. 微生物肥料对黑土农田玉米苗情及生长发育的影响研究. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2023. | |
| 25 | Wang Y X, E S Z, Yuan J H, et al. Effects of attapulgite addition on fermentation temperature and nutrient content of organic fertilizer. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(12): 2779-2787. |
| 王钰轩, 俄胜哲, 袁金华, 等. 凹凸棒添加对有机肥发酵温度及养分的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(12): 2779-2787. | |
| 26 | Lynch J P, Brown K M. New roots for agriculture: exploiting the root phenome. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 2012, 367(1595): 1598-1604. |
| 27 | Niu X L, Nan Z B. Review of minirhizotron applications for study of fine roots in grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(11): 205-215. |
| 牛学礼, 南志标. 运用微根管技术研究草地植物细根的进展. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 205-215. | |
| 28 | Li Z Y, Zhang R, Zhang J, et al. Effect of compound microbial fertilizer on the root growth of Trifolium pratense L.cv. Minshan by partly replacing chemical fertilizer. China Herbivore Science, 2018, 38(1): 38-42. |
| 李智燕, 张榕, 张洁, 等. 微生物专用菌肥与化肥配施对红三叶根系生长的影响. 中国草食动物科学, 2018, 38(1): 38-42. | |
| 29 | Yang J J, Cheng W D, Lin H M, et al. Effect of palygorskite adding NPK fertilizer on plant dry matter accumulation and polysaccharide content of Radix hedysari. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(9): 4536-4538, 4541. |
| 杨建军, 程卫东, 蔺海明, 等. 坡缕石与氮磷钾配施对红芪干物质积累及多糖含量的影响. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(9): 4536-4538, 4541. | |
| 30 | Kusi N Y O. Growth response of alfalfa to Azomite composite micronutrient fertilizer on four lime-amended Virginia soils. Grassland Science, 2021, 67(3): 225-233. |
| 31 | He S B, Yu C F, Pei H D, et al. Application effect of Xinqing attapulgite compound microbial fertilizer on red Earth grape. Agricultural Technology and Information, 2023(10): 132-136. |
| 贺生兵, 余彩芬, 裴海东, 等. 欣庆凹凸棒复合微生物肥料在红地球葡萄上的应用效果. 农业科技与信息, 2023(10): 132-136. | |
| 32 | Guan Y, Song C, Gan Y, et al. Increased maize yield using slow-release attapulgite-coated fertilizers. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2014, 34(3): 657-665. |
| 33 | Li C N, Li Z X, Cao Q X, et al. Effects of 5 plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on the growth and quality of Medicago sativa. Grassland and Turf, 2018, 38(3): 29-34. |
| 李昌宁, 李政璇, 曹全熙, 等. 5株植物根际促生菌对紫花苜蓿生长和品质的影响. 草原与草坪, 2018, 38(3): 29-34. | |
| 34 | Cheng Q D. Research on the effects of microbial fertilizer on growth and development of Lycium barba L. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2014. |
| 程乾斗. 微生物肥料对枸杞生长发育影响的研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2014. | |
| 35 | Zhu D. Study on growth promoting effect of compound microbial fertilizer on oat growth. Harbin: Harbin Normal University, 2022. |
| 祝丹. 复合微生物肥料对燕麦的促生效果研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨师范大学, 2022. |
| [1] | 蒋学乾, 杨青川, 康俊梅. 紫花苜蓿在干旱胁迫下的产量损失与抗旱性遗传研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 219-234. |
| [2] | 温小月, 赵颖, 王宝强, 王贤, 朱晓林, 王义真, 魏小红. 外源NO调控干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿AP2/ERFs基因的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 154-167. |
| [3] | 张英豪, 刘楚波, 周坤, 郭家存, 刘世鹏, 孙娈姿. 果草系统中枣树对不同方位紫花苜蓿和鸭茅生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 203-212. |
| [4] | 崔灿, 王梦琦, 赵琬璐, 刘新颖, 鉴晶晶, 严俊鑫. 胺鲜酯浸种对NaCl胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 46-58. |
| [5] | 曾燕霞, 陈志龙, 尚继红, 沙晓弟, 吴娟, 陈彩锦. 太空诱变对PEG-6000模拟干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿材料苗期生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 59-69. |
| [6] | 魏孔钦, 张盈盈, 回金峰, 马春晖, 张前兵. 菌磷配施对紫花苜蓿根系非结构碳水化合物及碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 40-50. |
| [7] | 周昕越, 王丽萍, 蒋庆雪, 马晓冉, 仪登霞, 王学敏. 紫花苜蓿低温诱导蛋白MsLTI65的分离及其对不同逆境的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 89-104. |
| [8] | 罗天蓉, 马健芝, 杜明阳, 多杰措, 熊辉岩, 段瑞君. 紫花苜蓿LACS基因家族成员鉴定及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 124-136. |
| [9] | 冯雅琪, 陈嘉慧, 张静妮, 隋超, 陈基伟, 刘志鹏, 周强, 刘文献. 基于重测序紫花苜蓿高蛋白、高产关联InDel分子标记开发[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 137-149. |
| [10] | 董拓轩, 陈训锋, 梅大海, 郭永莎, 魏旭红, 宋秋艳. 纳米铁与铜对苜蓿壳二孢及其引致春季黑茎病的抑制与防治作用[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 201-211. |
| [11] | 陈彩锦, 包明芳, 王文虎, 尚继红, 曾燕霞, 沙晓弟, 朱新忠, 王学敏, 刘文辉. 紫花苜蓿抗旱育种研究现状及展望[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 204-223. |
| [12] | 胡鹏飞, 叶雨浓, 王通锐, 王晶, 王星, 伏兵哲, 高雪芹. 紫花苜蓿半同胞家系农艺性状的遗传变异分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 85-96. |
| [13] | 马超, 孙熙婧, 冯雅岚, 周爽, 琚吉浩, 吴毅, 王添宁, 郭彬彬, 张均. 紫花苜蓿GLK基因家族鉴定及渗透胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 174-190. |
| [14] | 蔡文祺, 李淑霞, 王晓彤, 宋文学, 麻旭霞, 马小梅, 李小红, 代昕瑶. 外源褪黑素与乙烯交互对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 80-93. |
| [15] | 王晓彤, 李小红, 麻旭霞, 蔡文祺, 冯学丽, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿FBA基因家族成员的鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 81-93. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||