

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 206-222.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025066
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
柳家乐( ), 祁娟(
), 祁娟( ), 李文亮, 路欣, 袁琪, 李明洁, 张奥龙, 杜旺毅
), 李文亮, 路欣, 袁琪, 李明洁, 张奥龙, 杜旺毅
收稿日期:2025-03-04
修回日期:2025-04-28
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2025-11-13
通讯作者:
祁娟
作者简介:E-mail: qijuan@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Jia-le LIU( ), Juan QI(
), Juan QI( ), Wen-liang LI, Xin LU, Qi YUAN, Ming-jie LI, Ao-long ZHANG, Wang-yi DU
), Wen-liang LI, Xin LU, Qi YUAN, Ming-jie LI, Ao-long ZHANG, Wang-yi DU
Received:2025-03-04
Revised:2025-04-28
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2025-11-13
Contact:
Juan QI
摘要:
Jacalin类凝集素基因家族在植物中广泛存在,与植物的生长发育、逆境胁迫及病虫害防御密切相关。基于老芒麦基因组数据,利用生物信息学方法对EsJRL基因家族进行鉴定,并对其进行理化性质、染色体分布、系统进化、基因结构、保守结构域和启动子顺式作用元件分析。通过RNA-Seq数据及实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)对EsJRL基因在不同时期的旗叶及非生物胁迫(外源激素、干旱和低温)下的表达模式进行分析。结果显示,从老芒麦中共鉴定到84个EsJRL基因,在13条染色体两端不均匀分布,编码氨基酸序列长度为93~1574 bp。根据系统发育分析结果,将EsJRL家族成员分为8个组。保守基序分析发现大部分EsJRL基因包含Motif 1、Motif 3和Motif 7。种内共线性结果显示,在老芒麦基因组中共发现39个基因重复事件。非同义替代率与同义替代率的比值(Ka/Ks)分析显示,所有重复基因对均受到纯化选择。顺式作用元件预测表明,EsJRL基因启动子区域富含与光响应、胁迫响应、激素响应以及植物生长发育有关的功能元件。表达模式分析显示,仅有33个EsJRL基因在老芒麦不同时期旗叶中表达,其中19个EsJRL基因在两个种质中均表达。RT-qPCR结果表明,多数EsJRL基因在赤霉素(GA)、脱落酸(ABA)和水杨酸(SA)处理下显著上调(P<0.05),少数EsJRL基因响应干旱和低温胁迫后上调表达,其中,EsJRL28-2基因表达量在干旱胁迫和GA处理下显著下调(P<0.05),低温胁迫下仅EsJRL43基因表达量显著下调(P<0.05)。
柳家乐, 祁娟, 李文亮, 路欣, 袁琪, 李明洁, 张奥龙, 杜旺毅. 老芒麦EsJRL基因家族鉴定与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 206-222.
Jia-le LIU, Juan QI, Wen-liang LI, Xin LU, Qi YUAN, Ming-jie LI, Ao-long ZHANG, Wang-yi DU. Identification and expression analysis of EsJRL genes in Elymus sibiricus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(1): 206-222.
| 基因号Gene ID | 基因名称Gene name | 正向引物Forward primer (5′-3′) | 反向引物Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Es2StG00000039474.1 | EsJRL23 | ATAGGTCCTTGCGGTGGTAGTG | TGGTCTCATCATGGTTGACTTCG |
| Es7HG00000031260.1 | EsJRL74 | GCCGTTTGGGAAAGAGGATGG | CAGGACCGCCCGTGGAAG |
| Es3HG00000084164.1 | EsJRL32 | GGAGGAGCCGAAGCAGCAG | GCGGGAGCACGGTGGTC |
| Es3StG00000005761.1 | EsJRL37 | CGGCGTGGTGGTGGTGAG | CGGGAGGGTGAACGGCATG |
| Es3HG00000084157.2 | EsJRL31-2 | CCTCTGAGATCCGCCTGAGC | ACCACCACCACGCCCTTG |
| Es3HG00000084157.1 | EsJRL31-1 | CCTCTGAGATCCGCCTGAGC | ACCACCACCACGCCCTTG |
| Es3HG00000084155.1 | EsJRL29 | ACCGCCGTGAAGCAGCAG | CCGTGAGGACCGCAGAACC |
| Es1StG00000032567.1 | EsJRL14 | CTGTCAACCGGCTGCGTACTG | CCTCCACAACTGGCGTGTCTTC |
| Es1HG00000058078.1 | EsJRL8 | ACAAGGTGCATCATCTGGGG | TGATGCTGAACTCTCGCCTC |
| Es3HG00000088654.1 | EsJRL35 | AGCTCCGAATCCGTGCTATG | TCTTTTCCTCCATTCCCGCC |
| Es3StG00000010545.1 | EsJRL43 | ACTCAAGGCGAGCCAGACAGG | ATGAACGACGATGGAGCCAAACTC |
| Es2StG00000045601.2 | EsJRL28-2 | GCTTGCCTGCCCTTCGTTCTC | GCTATCGCATGACCACCAGTTCTC |
| Es1HG00000053830.1 | EsJRL6 | GCCGCTACAAACCCTTCCTACTAC | AGTGTGTTGGTTGGCGTTGGTAG |
表1 EsJRL基因的RT-qPCR特异性引物
Table 1 RT-qPCR specific primers for EsJRL gene
| 基因号Gene ID | 基因名称Gene name | 正向引物Forward primer (5′-3′) | 反向引物Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Es2StG00000039474.1 | EsJRL23 | ATAGGTCCTTGCGGTGGTAGTG | TGGTCTCATCATGGTTGACTTCG |
| Es7HG00000031260.1 | EsJRL74 | GCCGTTTGGGAAAGAGGATGG | CAGGACCGCCCGTGGAAG |
| Es3HG00000084164.1 | EsJRL32 | GGAGGAGCCGAAGCAGCAG | GCGGGAGCACGGTGGTC |
| Es3StG00000005761.1 | EsJRL37 | CGGCGTGGTGGTGGTGAG | CGGGAGGGTGAACGGCATG |
| Es3HG00000084157.2 | EsJRL31-2 | CCTCTGAGATCCGCCTGAGC | ACCACCACCACGCCCTTG |
| Es3HG00000084157.1 | EsJRL31-1 | CCTCTGAGATCCGCCTGAGC | ACCACCACCACGCCCTTG |
| Es3HG00000084155.1 | EsJRL29 | ACCGCCGTGAAGCAGCAG | CCGTGAGGACCGCAGAACC |
| Es1StG00000032567.1 | EsJRL14 | CTGTCAACCGGCTGCGTACTG | CCTCCACAACTGGCGTGTCTTC |
| Es1HG00000058078.1 | EsJRL8 | ACAAGGTGCATCATCTGGGG | TGATGCTGAACTCTCGCCTC |
| Es3HG00000088654.1 | EsJRL35 | AGCTCCGAATCCGTGCTATG | TCTTTTCCTCCATTCCCGCC |
| Es3StG00000010545.1 | EsJRL43 | ACTCAAGGCGAGCCAGACAGG | ATGAACGACGATGGAGCCAAACTC |
| Es2StG00000045601.2 | EsJRL28-2 | GCTTGCCTGCCCTTCGTTCTC | GCTATCGCATGACCACCAGTTCTC |
| Es1HG00000053830.1 | EsJRL6 | GCCGCTACAAACCCTTCCTACTAC | AGTGTGTTGGTTGGCGTTGGTAG |
基因ID Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 氨基酸数目Number of amino acid (aa) | 分子质量 Molecular weight (MW, Da) | 等电点 Isoelectric point (pI) | 不稳定系数 Instability index (II) | 脂溶性指数 Aliphatic index (AI) | 亲水性平均值 Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Es1HG00000053762.1 | EsJRL1 | 144 | 14897.71 | 8.93 | 10.79 | 75.07 | -0.199 |
| Es1HG00000053820.1 | EsJRL2 | 146 | 15568.32 | 4.19 | 18.04 | 78.70 | -0.128 |
| Es1HG00000053821.1 | EsJRL3 | 146 | 15554.30 | 4.19 | 17.46 | 78.01 | -0.125 |
| Es1HG00000053822.1 | EsJRL4 | 146 | 15568.32 | 4.19 | 18.04 | 78.70 | -0.128 |
| Es1HG00000053823.1 | EsJRL5 | 146 | 15554.30 | 4.19 | 17.46 | 78.01 | -0.125 |
| Es1HG00000053830.1 | EsJRL6 | 249 | 27090.86 | 8.79 | 32.09 | 74.10 | -0.160 |
| Es1HG00000057612.1 | EsJRL7 | 589 | 63979.22 | 7.09 | 41.32 | 64.67 | -0.447 |
| Es1HG00000058078.1 | EsJRL8 | 218 | 23602.69 | 8.89 | 46.10 | 67.94 | -0.454 |
| Es1HG00000059055.2 | EsJRL9-2 | 153 | 15994.03 | 5.84 | 27.08 | 77.12 | -0.137 |
| Es1HG00000059055.1 | EsJRL9-1 | 158 | 16481.60 | 5.84 | 30.54 | 75.32 | -0.128 |
| Es1HG00000059056.2 | EsJRL10-2 | 153 | 16057.13 | 6.06 | 32.45 | 77.78 | -0.133 |
| Es1HG00000059056.1 | EsJRL10-1 | 158 | 16544.70 | 6.06 | 35.73 | 75.95 | -0.125 |
| Es1HG00000059057.2 | EsJRL11-2 | 153 | 15969.06 | 6.71 | 27.02 | 77.78 | -0.110 |
| Es1HG00000059057.1 | EsJRL11-1 | 158 | 16456.64 | 6.71 | 30.48 | 75.95 | -0.103 |
| Es1HG00000059058.2 | EsJRL12-2 | 153 | 15969.06 | 6.71 | 27.02 | 77.78 | -0.110 |
| Es1HG00000059058.1 | EsJRL12-1 | 158 | 16456.64 | 6.71 | 30.48 | 75.95 | -0.103 |
| Es1HG00000059059.2 | EsJRL13-2 | 153 | 15957.01 | 6.06 | 27.99 | 77.12 | -0.090 |
| Es1HG00000059059.1 | EsJRL13-1 | 158 | 16471.65 | 6.71 | 30.94 | 75.32 | -0.103 |
| Es1StG00000032567.1 | EsJRL14 | 152 | 16247.31 | 5.40 | 35.76 | 94.14 | -0.003 |
| Es1StG00000032569.1 | EsJRL15 | 93 | 10391.95 | 9.51 | 29.75 | 86.88 | 0.000 |
| Es1StG00000036517.1 | EsJRL16 | 584 | 63221.47 | 7.38 | 37.84 | 65.58 | -0.395 |
| Es1StG00000037075.1 | EsJRL17 | 220 | 23694.74 | 9.27 | 46.56 | 64.27 | -0.502 |
| Es2HG00000060203.1 | EsJRL18 | 309 | 33637.74 | 4.87 | 41.26 | 77.28 | -0.224 |
| Es2HG00000065677.1 | EsJRL19 | 581 | 65180.76 | 6.56 | 45.25 | 93.80 | -0.100 |
| Es2HG00000065745.1 | EsJRL20 | 696 | 77761.06 | 7.31 | 42.89 | 71.14 | -0.422 |
| Es2StG00000039181.1 | EsJRL21 | 155 | 16561.74 | 9.06 | 25.62 | 76.71 | -0.101 |
| Es2StG00000039209.1 | EsJRL22 | 157 | 16896.14 | 9.01 | 18.57 | 76.43 | -0.152 |
| Es2StG00000039474.1 | EsJRL23 | 148 | 16611.77 | 5.93 | 31.73 | 72.36 | -0.511 |
| Es2StG00000039475.1 | EsJRL24 | 298 | 32302.38 | 6.31 | 14.65 | 72.62 | -0.278 |
| Es2StG00000039477.1 | EsJRL25 | 301 | 32804.94 | 5.92 | 21.33 | 71.26 | -0.274 |
| Es2StG00000039478.1 | EsJRL26 | 310 | 34429.84 | 8.92 | 17.46 | 70.06 | -0.327 |
| Es2StG00000039795.1 | EsJRL27 | 243 | 26449.77 | 7.01 | 38.77 | 75.84 | -0.272 |
| Es2StG00000045601.1 | EsJRL28-1 | 494 | 55341.59 | 6.22 | 44.25 | 96.68 | -0.030 |
| Es2StG00000045601.2 | EsJRL28-2 | 581 | 65047.63 | 6.35 | 45.09 | 94.96 | -0.071 |
| Es3HG00000084155.1 | EsJRL29 | 325 | 34920.95 | 7.53 | 38.87 | 75.23 | -0.129 |
| Es3HG00000084156.1 | EsJRL30 | 244 | 26216.12 | 7.54 | 44.28 | 79.84 | 0.032 |
| Es3HG00000084157.1 | EsJRL31-1 | 145 | 15447.50 | 6.83 | 38.05 | 73.17 | -0.194 |
| Es3HG00000084157.2 | EsJRL31-2 | 139 | 14811.70 | 6.28 | 37.12 | 76.33 | -0.188 |
| Es3HG00000084164.1 | EsJRL32 | 244 | 25959.49 | 8.48 | 40.17 | 74.30 | -0.431 |
| Es3HG00000084173.1 | EsJRL33 | 166 | 18209.30 | 5.53 | 42.25 | 70.30 | -0.452 |
| Es3HG00000087351.1 | EsJRL34 | 451 | 48576.97 | 9.23 | 24.63 | 71.33 | -0.276 |
| Es3HG00000088654.1 | EsJRL35 | 317 | 34442.01 | 6.66 | 19.20 | 82.11 | -0.150 |
| Es3StG00000005754.1 | EsJRL36 | 141 | 15118.15 | 6.06 | 39.42 | 75.96 | -0.274 |
| Es3StG00000005761.1 | EsJRL37 | 145 | 15697.80 | 6.97 | 43.98 | 70.48 | -0.220 |
| Es3StG00000005767.1 | EsJRL38 | 332 | 35598.66 | 7.07 | 41.03 | 78.34 | -0.105 |
| Es3StG00000006647.1 | EsJRL39 | 155 | 16763.02 | 9.34 | 28.10 | 74.84 | -0.153 |
| Es3StG00000006682.1 | EsJRL40 | 157 | 16960.14 | 7.90 | 20.70 | 75.22 | -0.196 |
| Es3StG00000007172.1 | EsJRL41 | 103 | 11180.64 | 5.29 | 27.97 | 74.76 | -0.333 |
| Es3StG00000009097.1 | EsJRL42 | 451 | 48623.73 | 9.06 | 22.92 | 69.58 | -0.345 |
| Es3StG00000010545.1 | EsJRL43 | 317 | 34353.81 | 7.07 | 21.78 | 80.85 | -0.183 |
| Es4HG00000066395.1 | EsJRL44 | 147 | 16121.96 | 5.75 | 45.11 | 68.30 | -0.441 |
| Es4HG00000066397.1 | EsJRL45 | 147 | 16121.96 | 5.75 | 45.11 | 68.30 | -0.441 |
| Es4HG00000066399.1 | EsJRL46 | 147 | 16121.96 | 5.75 | 45.11 | 68.30 | -0.441 |
| Es4HG00000066400.1 | EsJRL47 | 147 | 16182.00 | 5.75 | 40.81 | 68.30 | -0.467 |
| Es4HG00000066401.1 | EsJRL48 | 147 | 16121.96 | 5.75 | 45.11 | 68.30 | -0.441 |
| Es4HG00000066403.1 | EsJRL49 | 147 | 16121.96 | 5.75 | 45.11 | 68.30 | -0.441 |
| Es4HG00000066404.1 | EsJRL50 | 147 | 16182.00 | 5.75 | 40.81 | 68.30 | -0.467 |
| Es4HG00000066405.1 | EsJRL51 | 147 | 16121.96 | 5.75 | 45.11 | 68.30 | -0.441 |
| Es4HG00000066407.1 | EsJRL52 | 147 | 16145.98 | 5.50 | 43.69 | 70.27 | -0.458 |
| Es4HG00000067604.1 | EsJRL53 | 149 | 16142.07 | 5.07 | 35.89 | 77.79 | -0.303 |
| Es4HG00000071276.1 | EsJRL54-1 | 919 | 101893.84 | 5.99 | 40.98 | 85.55 | -0.210 |
| Es4HG00000071276.2 | EsJRL54-2 | 989 | 109609.44 | 6.20 | 39.14 | 83.83 | -0.230 |
| Es4StG00000000171.1 | EsJRL55 | 196 | 20629.91 | 7.78 | 29.02 | 59.13 | -0.433 |
| Es4StG00000000209.1 | EsJRL56 | 235 | 24515.95 | 4.76 | 32.34 | 63.87 | -0.177 |
| Es4StG00000000300.1 | EsJRL57 | 180 | 18897.27 | 5.42 | 30.39 | 80.22 | -0.051 |
| Es4StG00000000301.1 | EsJRL58 | 169 | 17764.90 | 4.75 | 32.38 | 83.08 | -0.039 |
| Es4StG00000004303.1 | EsJRL59 | 301 | 31898.48 | 6.30 | 29.27 | 68.87 | -0.225 |
| Es5HG00000074467.1 | EsJRL60 | 304 | 32991.16 | 5.16 | 29.49 | 78.88 | -0.129 |
| Es5HG00000077065.1 | EsJRL61 | 1010 | 109900.74 | 5.64 | 31.82 | 87.95 | -0.140 |
| Es5StG00000012697.1 | EsJRL62 | 504 | 57157.44 | 5.28 | 43.36 | 82.52 | -0.385 |
| Es5StG00000012895.1 | EsJRL63 | 148 | 15890.99 | 6.65 | 34.07 | 83.51 | -0.185 |
| Es5StG00000018974.1 | EsJRL64 | 341 | 37258.82 | 5.80 | 16.13 | 71.99 | -0.283 |
| Es5StG00000018980.1 | EsJRL65 | 341 | 37258.82 | 5.80 | 16.13 | 71.99 | -0.283 |
| Es5StG00000018983.1 | EsJRL66 | 341 | 37258.82 | 5.80 | 16.13 | 71.99 | -0.283 |
| Es6HG00000078673.1 | EsJRL67-1 | 183 | 19167.51 | 5.12 | 34.72 | 78.36 | -0.072 |
| Es6HG00000078673.2 | EsJRL67-2 | 207 | 21931.69 | 4.89 | 35.03 | 79.13 | -0.075 |
| Es6HG00000078921.1 | EsJRL68 | 319 | 34380.79 | 8.87 | 26.94 | 75.11 | -0.186 |
| Es6HG00000079987.1 | EsJRL69 | 321 | 34277.48 | 9.88 | 35.74 | 74.24 | -0.286 |
| Es7HG00000027580.1 | EsJRL70 | 155 | 16735.84 | 5.03 | 29.45 | 80.45 | -0.127 |
| Es7HG00000028732.1 | EsJRL71 | 155 | 16795.83 | 6.97 | 43.97 | 67.87 | -0.393 |
| Es7HG00000030707.1 | EsJRL72 | 328 | 35853.54 | 6.06 | 21.98 | 77.56 | -0.200 |
| Es7HG00000030708.1 | EsJRL73 | 346 | 37760.64 | 6.20 | 22.32 | 75.23 | -0.225 |
| Es7HG00000031260.1 | EsJRL74 | 168 | 18260.90 | 8.45 | 32.02 | 80.60 | -0.238 |
| Es7HG00000032129.1 | EsJRL75 | 310 | 33630.75 | 6.14 | 18.99 | 76.42 | -0.253 |
| Es7HG00000032133.1 | EsJRL76 | 311 | 34065.22 | 6.12 | 26.63 | 78.01 | -0.283 |
| Es7StG00000046382.1 | EsJRL77 | 1574 | 178373.74 | 7.92 | 44.52 | 88.70 | -0.348 |
| Es7StG00000046394.1 | EsJRL78 | 906 | 101125.34 | 5.71 | 39.59 | 76.05 | -0.298 |
| Es7StG00000048488.1 | EsJRL79 | 162 | 17437.63 | 5.07 | 31.44 | 80.00 | -0.168 |
| Es7StG00000049687.1 | EsJRL80-1 | 155 | 16781.84 | 6.50 | 44.16 | 69.74 | -0.370 |
| Es7StG00000049687.2 | EsJRL80-2 | 148 | 15999.87 | 6.18 | 43.69 | 68.45 | -0.386 |
| Es7StG00000052256.1 | EsJRL81 | 307 | 32583.53 | 6.10 | 21.36 | 79.09 | -0.144 |
| Es7StG00000052743.1 | EsJRL82 | 342 | 36912.21 | 6.79 | 30.06 | 80.96 | -0.018 |
| Es7StG00000053443.1 | EsJRL83 | 93 | 9714.84 | 5.38 | 21.86 | 66.13 | 0.006 |
| Es7StG00000053444.1 | EsJRL84 | 298 | 32035.85 | 5.80 | 30.58 | 66.41 | -0.343 |
表2 EsJRL基因家族成员理化性质分析
Table 2 Physicochemical properties analysis of EsJRL gene family members
基因ID Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 氨基酸数目Number of amino acid (aa) | 分子质量 Molecular weight (MW, Da) | 等电点 Isoelectric point (pI) | 不稳定系数 Instability index (II) | 脂溶性指数 Aliphatic index (AI) | 亲水性平均值 Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Es1HG00000053762.1 | EsJRL1 | 144 | 14897.71 | 8.93 | 10.79 | 75.07 | -0.199 |
| Es1HG00000053820.1 | EsJRL2 | 146 | 15568.32 | 4.19 | 18.04 | 78.70 | -0.128 |
| Es1HG00000053821.1 | EsJRL3 | 146 | 15554.30 | 4.19 | 17.46 | 78.01 | -0.125 |
| Es1HG00000053822.1 | EsJRL4 | 146 | 15568.32 | 4.19 | 18.04 | 78.70 | -0.128 |
| Es1HG00000053823.1 | EsJRL5 | 146 | 15554.30 | 4.19 | 17.46 | 78.01 | -0.125 |
| Es1HG00000053830.1 | EsJRL6 | 249 | 27090.86 | 8.79 | 32.09 | 74.10 | -0.160 |
| Es1HG00000057612.1 | EsJRL7 | 589 | 63979.22 | 7.09 | 41.32 | 64.67 | -0.447 |
| Es1HG00000058078.1 | EsJRL8 | 218 | 23602.69 | 8.89 | 46.10 | 67.94 | -0.454 |
| Es1HG00000059055.2 | EsJRL9-2 | 153 | 15994.03 | 5.84 | 27.08 | 77.12 | -0.137 |
| Es1HG00000059055.1 | EsJRL9-1 | 158 | 16481.60 | 5.84 | 30.54 | 75.32 | -0.128 |
| Es1HG00000059056.2 | EsJRL10-2 | 153 | 16057.13 | 6.06 | 32.45 | 77.78 | -0.133 |
| Es1HG00000059056.1 | EsJRL10-1 | 158 | 16544.70 | 6.06 | 35.73 | 75.95 | -0.125 |
| Es1HG00000059057.2 | EsJRL11-2 | 153 | 15969.06 | 6.71 | 27.02 | 77.78 | -0.110 |
| Es1HG00000059057.1 | EsJRL11-1 | 158 | 16456.64 | 6.71 | 30.48 | 75.95 | -0.103 |
| Es1HG00000059058.2 | EsJRL12-2 | 153 | 15969.06 | 6.71 | 27.02 | 77.78 | -0.110 |
| Es1HG00000059058.1 | EsJRL12-1 | 158 | 16456.64 | 6.71 | 30.48 | 75.95 | -0.103 |
| Es1HG00000059059.2 | EsJRL13-2 | 153 | 15957.01 | 6.06 | 27.99 | 77.12 | -0.090 |
| Es1HG00000059059.1 | EsJRL13-1 | 158 | 16471.65 | 6.71 | 30.94 | 75.32 | -0.103 |
| Es1StG00000032567.1 | EsJRL14 | 152 | 16247.31 | 5.40 | 35.76 | 94.14 | -0.003 |
| Es1StG00000032569.1 | EsJRL15 | 93 | 10391.95 | 9.51 | 29.75 | 86.88 | 0.000 |
| Es1StG00000036517.1 | EsJRL16 | 584 | 63221.47 | 7.38 | 37.84 | 65.58 | -0.395 |
| Es1StG00000037075.1 | EsJRL17 | 220 | 23694.74 | 9.27 | 46.56 | 64.27 | -0.502 |
| Es2HG00000060203.1 | EsJRL18 | 309 | 33637.74 | 4.87 | 41.26 | 77.28 | -0.224 |
| Es2HG00000065677.1 | EsJRL19 | 581 | 65180.76 | 6.56 | 45.25 | 93.80 | -0.100 |
| Es2HG00000065745.1 | EsJRL20 | 696 | 77761.06 | 7.31 | 42.89 | 71.14 | -0.422 |
| Es2StG00000039181.1 | EsJRL21 | 155 | 16561.74 | 9.06 | 25.62 | 76.71 | -0.101 |
| Es2StG00000039209.1 | EsJRL22 | 157 | 16896.14 | 9.01 | 18.57 | 76.43 | -0.152 |
| Es2StG00000039474.1 | EsJRL23 | 148 | 16611.77 | 5.93 | 31.73 | 72.36 | -0.511 |
| Es2StG00000039475.1 | EsJRL24 | 298 | 32302.38 | 6.31 | 14.65 | 72.62 | -0.278 |
| Es2StG00000039477.1 | EsJRL25 | 301 | 32804.94 | 5.92 | 21.33 | 71.26 | -0.274 |
| Es2StG00000039478.1 | EsJRL26 | 310 | 34429.84 | 8.92 | 17.46 | 70.06 | -0.327 |
| Es2StG00000039795.1 | EsJRL27 | 243 | 26449.77 | 7.01 | 38.77 | 75.84 | -0.272 |
| Es2StG00000045601.1 | EsJRL28-1 | 494 | 55341.59 | 6.22 | 44.25 | 96.68 | -0.030 |
| Es2StG00000045601.2 | EsJRL28-2 | 581 | 65047.63 | 6.35 | 45.09 | 94.96 | -0.071 |
| Es3HG00000084155.1 | EsJRL29 | 325 | 34920.95 | 7.53 | 38.87 | 75.23 | -0.129 |
| Es3HG00000084156.1 | EsJRL30 | 244 | 26216.12 | 7.54 | 44.28 | 79.84 | 0.032 |
| Es3HG00000084157.1 | EsJRL31-1 | 145 | 15447.50 | 6.83 | 38.05 | 73.17 | -0.194 |
| Es3HG00000084157.2 | EsJRL31-2 | 139 | 14811.70 | 6.28 | 37.12 | 76.33 | -0.188 |
| Es3HG00000084164.1 | EsJRL32 | 244 | 25959.49 | 8.48 | 40.17 | 74.30 | -0.431 |
| Es3HG00000084173.1 | EsJRL33 | 166 | 18209.30 | 5.53 | 42.25 | 70.30 | -0.452 |
| Es3HG00000087351.1 | EsJRL34 | 451 | 48576.97 | 9.23 | 24.63 | 71.33 | -0.276 |
| Es3HG00000088654.1 | EsJRL35 | 317 | 34442.01 | 6.66 | 19.20 | 82.11 | -0.150 |
| Es3StG00000005754.1 | EsJRL36 | 141 | 15118.15 | 6.06 | 39.42 | 75.96 | -0.274 |
| Es3StG00000005761.1 | EsJRL37 | 145 | 15697.80 | 6.97 | 43.98 | 70.48 | -0.220 |
| Es3StG00000005767.1 | EsJRL38 | 332 | 35598.66 | 7.07 | 41.03 | 78.34 | -0.105 |
| Es3StG00000006647.1 | EsJRL39 | 155 | 16763.02 | 9.34 | 28.10 | 74.84 | -0.153 |
| Es3StG00000006682.1 | EsJRL40 | 157 | 16960.14 | 7.90 | 20.70 | 75.22 | -0.196 |
| Es3StG00000007172.1 | EsJRL41 | 103 | 11180.64 | 5.29 | 27.97 | 74.76 | -0.333 |
| Es3StG00000009097.1 | EsJRL42 | 451 | 48623.73 | 9.06 | 22.92 | 69.58 | -0.345 |
| Es3StG00000010545.1 | EsJRL43 | 317 | 34353.81 | 7.07 | 21.78 | 80.85 | -0.183 |
| Es4HG00000066395.1 | EsJRL44 | 147 | 16121.96 | 5.75 | 45.11 | 68.30 | -0.441 |
| Es4HG00000066397.1 | EsJRL45 | 147 | 16121.96 | 5.75 | 45.11 | 68.30 | -0.441 |
| Es4HG00000066399.1 | EsJRL46 | 147 | 16121.96 | 5.75 | 45.11 | 68.30 | -0.441 |
| Es4HG00000066400.1 | EsJRL47 | 147 | 16182.00 | 5.75 | 40.81 | 68.30 | -0.467 |
| Es4HG00000066401.1 | EsJRL48 | 147 | 16121.96 | 5.75 | 45.11 | 68.30 | -0.441 |
| Es4HG00000066403.1 | EsJRL49 | 147 | 16121.96 | 5.75 | 45.11 | 68.30 | -0.441 |
| Es4HG00000066404.1 | EsJRL50 | 147 | 16182.00 | 5.75 | 40.81 | 68.30 | -0.467 |
| Es4HG00000066405.1 | EsJRL51 | 147 | 16121.96 | 5.75 | 45.11 | 68.30 | -0.441 |
| Es4HG00000066407.1 | EsJRL52 | 147 | 16145.98 | 5.50 | 43.69 | 70.27 | -0.458 |
| Es4HG00000067604.1 | EsJRL53 | 149 | 16142.07 | 5.07 | 35.89 | 77.79 | -0.303 |
| Es4HG00000071276.1 | EsJRL54-1 | 919 | 101893.84 | 5.99 | 40.98 | 85.55 | -0.210 |
| Es4HG00000071276.2 | EsJRL54-2 | 989 | 109609.44 | 6.20 | 39.14 | 83.83 | -0.230 |
| Es4StG00000000171.1 | EsJRL55 | 196 | 20629.91 | 7.78 | 29.02 | 59.13 | -0.433 |
| Es4StG00000000209.1 | EsJRL56 | 235 | 24515.95 | 4.76 | 32.34 | 63.87 | -0.177 |
| Es4StG00000000300.1 | EsJRL57 | 180 | 18897.27 | 5.42 | 30.39 | 80.22 | -0.051 |
| Es4StG00000000301.1 | EsJRL58 | 169 | 17764.90 | 4.75 | 32.38 | 83.08 | -0.039 |
| Es4StG00000004303.1 | EsJRL59 | 301 | 31898.48 | 6.30 | 29.27 | 68.87 | -0.225 |
| Es5HG00000074467.1 | EsJRL60 | 304 | 32991.16 | 5.16 | 29.49 | 78.88 | -0.129 |
| Es5HG00000077065.1 | EsJRL61 | 1010 | 109900.74 | 5.64 | 31.82 | 87.95 | -0.140 |
| Es5StG00000012697.1 | EsJRL62 | 504 | 57157.44 | 5.28 | 43.36 | 82.52 | -0.385 |
| Es5StG00000012895.1 | EsJRL63 | 148 | 15890.99 | 6.65 | 34.07 | 83.51 | -0.185 |
| Es5StG00000018974.1 | EsJRL64 | 341 | 37258.82 | 5.80 | 16.13 | 71.99 | -0.283 |
| Es5StG00000018980.1 | EsJRL65 | 341 | 37258.82 | 5.80 | 16.13 | 71.99 | -0.283 |
| Es5StG00000018983.1 | EsJRL66 | 341 | 37258.82 | 5.80 | 16.13 | 71.99 | -0.283 |
| Es6HG00000078673.1 | EsJRL67-1 | 183 | 19167.51 | 5.12 | 34.72 | 78.36 | -0.072 |
| Es6HG00000078673.2 | EsJRL67-2 | 207 | 21931.69 | 4.89 | 35.03 | 79.13 | -0.075 |
| Es6HG00000078921.1 | EsJRL68 | 319 | 34380.79 | 8.87 | 26.94 | 75.11 | -0.186 |
| Es6HG00000079987.1 | EsJRL69 | 321 | 34277.48 | 9.88 | 35.74 | 74.24 | -0.286 |
| Es7HG00000027580.1 | EsJRL70 | 155 | 16735.84 | 5.03 | 29.45 | 80.45 | -0.127 |
| Es7HG00000028732.1 | EsJRL71 | 155 | 16795.83 | 6.97 | 43.97 | 67.87 | -0.393 |
| Es7HG00000030707.1 | EsJRL72 | 328 | 35853.54 | 6.06 | 21.98 | 77.56 | -0.200 |
| Es7HG00000030708.1 | EsJRL73 | 346 | 37760.64 | 6.20 | 22.32 | 75.23 | -0.225 |
| Es7HG00000031260.1 | EsJRL74 | 168 | 18260.90 | 8.45 | 32.02 | 80.60 | -0.238 |
| Es7HG00000032129.1 | EsJRL75 | 310 | 33630.75 | 6.14 | 18.99 | 76.42 | -0.253 |
| Es7HG00000032133.1 | EsJRL76 | 311 | 34065.22 | 6.12 | 26.63 | 78.01 | -0.283 |
| Es7StG00000046382.1 | EsJRL77 | 1574 | 178373.74 | 7.92 | 44.52 | 88.70 | -0.348 |
| Es7StG00000046394.1 | EsJRL78 | 906 | 101125.34 | 5.71 | 39.59 | 76.05 | -0.298 |
| Es7StG00000048488.1 | EsJRL79 | 162 | 17437.63 | 5.07 | 31.44 | 80.00 | -0.168 |
| Es7StG00000049687.1 | EsJRL80-1 | 155 | 16781.84 | 6.50 | 44.16 | 69.74 | -0.370 |
| Es7StG00000049687.2 | EsJRL80-2 | 148 | 15999.87 | 6.18 | 43.69 | 68.45 | -0.386 |
| Es7StG00000052256.1 | EsJRL81 | 307 | 32583.53 | 6.10 | 21.36 | 79.09 | -0.144 |
| Es7StG00000052743.1 | EsJRL82 | 342 | 36912.21 | 6.79 | 30.06 | 80.96 | -0.018 |
| Es7StG00000053443.1 | EsJRL83 | 93 | 9714.84 | 5.38 | 21.86 | 66.13 | 0.006 |
| Es7StG00000053444.1 | EsJRL84 | 298 | 32035.85 | 5.80 | 30.58 | 66.41 | -0.343 |
同源基因 Homologous gene | 非同义替代率 Non-synonymous substitution (Ka) | 同义替代率 Synonymous substitution (Ks) | 非同义替代率/同义替代率Ka/Ks | 同源基因 Homologous gene | 非同义替代率 Non-synonymous substitution (Ka) | 同义替代率 Synonymous substitution (Ks) | 非同义替代率/同义替代率Ka/Ks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EsJRL8~EsJRL17 | 0.031309 | 0.125153 | 0.250166 | EsJRL34~EsJRL42 | 0.020869 | 0.160252 | 0.130227 |
| EsJRL7~EsJRL16 | 0.015508 | 0.139083 | 0.111505 | EsJRL35~EsJRL43 | 0.031225 | 0.063006 | 0.495590 |
| EsJRL1~EsJRL14 | 0.415929 | 0.577628 | 0.720063 | EsJRL33~EsJRL36 | 0.314220 | 0.878862 | 0.357530 |
| EsJRL7~EsJRL34 | 0.301874 | 0.666092 | 0.453202 | EsJRL33~EsJRL37 | 0.384634 | 1.148341 | 0.334947 |
| EsJRL7~EsJRL42 | 0.305636 | 0.674034 | 0.453443 | EsJRL29~EsJRL38 | 0.054512 | 0.129426 | 0.421181 |
| EsJRL16~EsJRL34 | 0.308583 | 0.719593 | 0.428830 | EsJRL29~EsJRL37 | 0.256467 | 0.638630 | 0.401589 |
| EsJRL16~EsJRL42 | 0.284311 | 0.709209 | 0.400884 | EsJRL55~EsJRL56 | 0.350654 | 0.538459 | 0.651218 |
| EsJRL18~EsJRL24 | 0.464964 | 1.109302 | 0.419150 | EsJRL57~EsJRL67 | 0.089606 | 0.146610 | 0.611185 |
| EsJRL19~EsJRL28 | 0.016781 | 0.034327 | 0.488853 | EsJRL70~EsJRL79 | 0.052291 | 0.106226 | 0.492263 |
| EsJRL21~EsJRL39 | 0.020150 | 0.104351 | 0.193097 | EsJRL71~EsJRL80 | 0.027931 | 0.084786 | 0.329428 |
| EsJRL22~EsJRL40 | 0.019738 | 0.085265 | 0.231489 |
表3 EsJRL基因家族片段重复基因对的Ka/Ks
Table 3 Ka/Ks of segmental duplicated gene pairs in the EsJRL gene family
同源基因 Homologous gene | 非同义替代率 Non-synonymous substitution (Ka) | 同义替代率 Synonymous substitution (Ks) | 非同义替代率/同义替代率Ka/Ks | 同源基因 Homologous gene | 非同义替代率 Non-synonymous substitution (Ka) | 同义替代率 Synonymous substitution (Ks) | 非同义替代率/同义替代率Ka/Ks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EsJRL8~EsJRL17 | 0.031309 | 0.125153 | 0.250166 | EsJRL34~EsJRL42 | 0.020869 | 0.160252 | 0.130227 |
| EsJRL7~EsJRL16 | 0.015508 | 0.139083 | 0.111505 | EsJRL35~EsJRL43 | 0.031225 | 0.063006 | 0.495590 |
| EsJRL1~EsJRL14 | 0.415929 | 0.577628 | 0.720063 | EsJRL33~EsJRL36 | 0.314220 | 0.878862 | 0.357530 |
| EsJRL7~EsJRL34 | 0.301874 | 0.666092 | 0.453202 | EsJRL33~EsJRL37 | 0.384634 | 1.148341 | 0.334947 |
| EsJRL7~EsJRL42 | 0.305636 | 0.674034 | 0.453443 | EsJRL29~EsJRL38 | 0.054512 | 0.129426 | 0.421181 |
| EsJRL16~EsJRL34 | 0.308583 | 0.719593 | 0.428830 | EsJRL29~EsJRL37 | 0.256467 | 0.638630 | 0.401589 |
| EsJRL16~EsJRL42 | 0.284311 | 0.709209 | 0.400884 | EsJRL55~EsJRL56 | 0.350654 | 0.538459 | 0.651218 |
| EsJRL18~EsJRL24 | 0.464964 | 1.109302 | 0.419150 | EsJRL57~EsJRL67 | 0.089606 | 0.146610 | 0.611185 |
| EsJRL19~EsJRL28 | 0.016781 | 0.034327 | 0.488853 | EsJRL70~EsJRL79 | 0.052291 | 0.106226 | 0.492263 |
| EsJRL21~EsJRL39 | 0.020150 | 0.104351 | 0.193097 | EsJRL71~EsJRL80 | 0.027931 | 0.084786 | 0.329428 |
| EsJRL22~EsJRL40 | 0.019738 | 0.085265 | 0.231489 |
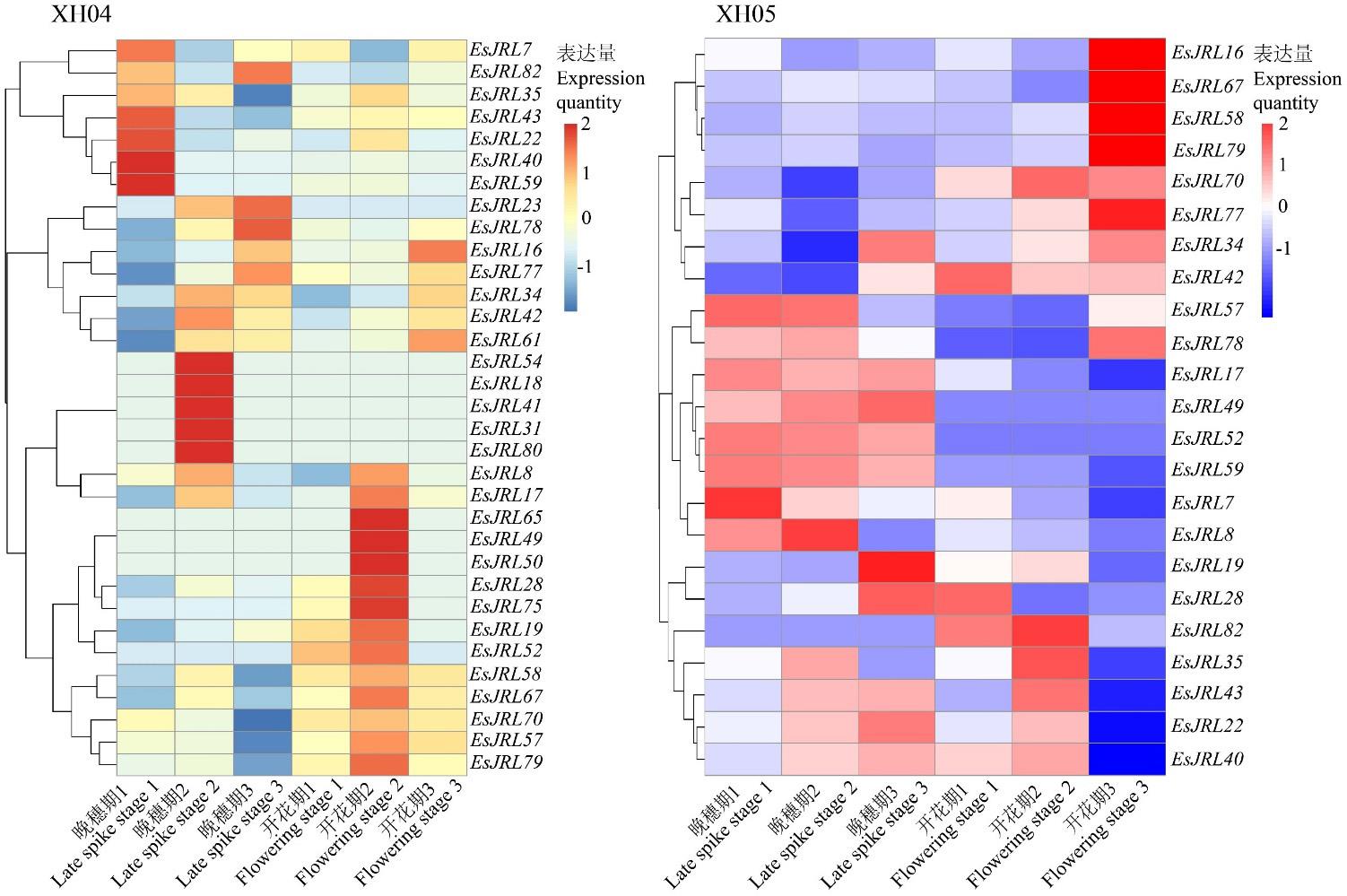
图6 EsJRL基因在不同种质老芒麦旗叶的表达分析1、2、3代表3个重复转录组测序。1, 2, and 3 represent three replicate transcriptome sequencing.
Fig.6 Expression analysis of EsJRL gene in different germplasm
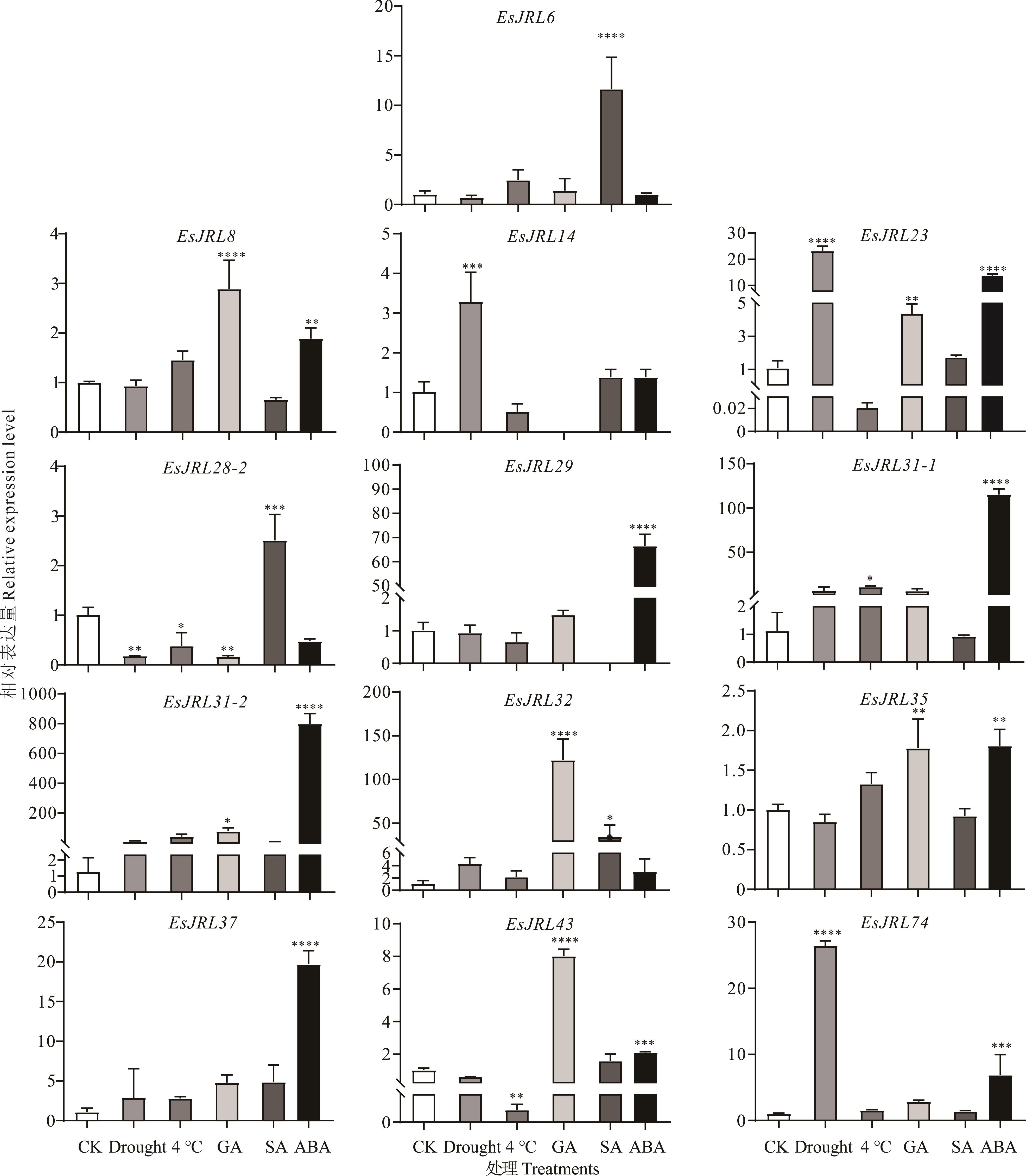
图7 EsJRL基因家族在外源GA、ABA、SA、干旱和低温胁迫下的表达模式分析CK: 空白对照Blank control; Drought: 20%的PEG 6000模拟干旱处理20% PEG 6000 mimicking drought treatment; 4 ℃: 低温处理Low temperature treatment; GA: 100 μmol·L-1 赤霉素Gibberellin; SA: 100 μmol·L-1水杨酸Salicylic acid; ABA: 100 μmol·L-1脱落酸Abscisic acid. *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001; ****: P<0.0001.
Fig.7 Expression pattern analysis of EsJRL gene family under exogenous GA, ABA, SA, drought and low temperature stresses
| [1] | Han Y J, Zhong Z H, Song L L, et al. Evolutionary analysis of plant jacalin-related lectins (JRLs) family and expression of rice JRLs in response to Magnaporthe oryzae. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2017, 17(6): 1252-1266. |
| [2] | Van Damme E J M, Lannoo N, Peumans W J. Plant lectins. Advances in Botanical Research, 2008, 48: 107-209. |
| [3] | Esch L, Schaffrath U. An update on jacalin-like lectins and their role in pant defense. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2017, 18: 1592-1602. |
| [4] | Bunn-Moreno M M, Campos-Neto A. Lectin(s) extracted from seeds of Artocarpus integrifolia (jackfruit): potent and selective stimulator(s) of distinct human T and B cell functions. Journal of Immunology, 1981, 127(2): 427-429. |
| [5] | Sankaranarayanan R, Sekar K, Banerjee R, et al. A novel mode of carbohydrate recognition in jacalin, a Moraceae plant lectin with a β-prism fold. Nature Structural Biology, 1996, 3(7): 596-603. |
| [6] | Williams C E, Collier C C, Nemacheck J A, et al. A lectin-like wheat gene responds systemically to attempted feeding by avirulent first-instar Hessian fly larvae. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 2002, 28: 1411-1428. |
| [7] | Azarkan M, Feller G, Vandenameele J, et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of a mannose binding jacalin-related lectin with two-sugar binding sites from pineapple (Ananas comosus) stem. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 11508. |
| [8] | Peumans J W, Hause B, Damme V J E. The galactose-binding and mannose-binding jacalin-related lectins are located in different sub-cellular compartments. FEBS Letters, 2000, 477(3): 186-192. |
| [9] | Pratap J V, Jeyaprakash A A, Rani P G, et al. Crystal structures of artocarpin, a Moraceae lectin with mannose specificity, and its complex with methyl-alpha-D-mannose: implications to the generation of carbohydrate specificity. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2002, 317(2): 237-247. |
| [10] | Weidenbach D, Esch L, Möller C, et al. Polarized defense against fungal pathogens is mediated by the jacalin-related lectin domain of modular Poaceae-specific proteins. Molecular Plant, 2016, 9(4): 514-527. |
| [11] | An Z X, Yang Z H, Zhou Y, et al. OsJRL negatively regulates rice cold tolerance via interfering phenylalanine metabolism and flavonoid biosynthesis. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2024, 47(11): 4071-4085. |
| [12] | Gao Q M, Yin X L, Wang F, et al. Jacalin-related lectin 45 (OsJRL45) isolated from ‘sea rice 86’ enhances rice salt tolerance at the seedling and reproductive stages. BMC Plant Biology, 2023, 23(1): 553. |
| [13] | Gao Q M, Yin X L, Wang F, et al. OsJRL40, a jacalin-related lectin gene, promotes salt stress tolerance in rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(8): 7441. |
| [14] | Yin X, Gao Q, Wang F, et al. Marker-assisted selection of jacalin-related lectin genes OsJRL45 and OsJRL40 derived from sea rice 86 enhances salt tolerance in rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024, 25(20): 10912. |
| [15] | Quan X Y, Chen M, Xie C J, et al. Genome-wide and transcriptome analysis of jacalin-related lectin genes in barley and the functional characterization of HvHorcH in low-nitrogen tolerance in Arabidopsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(23): 16641. |
| [16] | Zhang Z J, Huang B, Chen J L, et al. Genome-wide identification of JRL genes in moso bamboo and their expression profiles in response to multiple hormones and abiotic stresses. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 12: 809666. |
| [17] | Xing L J, Li J, Xu Y Y, et al. Phosphorylation modification of wheat lectin VER2 is associated with vernalization-induced O-GlcNAc signaling and intracellular motility. Public Library of Science ONE, 2017, 4(3): e4854. |
| [18] | Xiao J, Li C H, Xu S J, et al. Jacalin-lectin like1 regulates the nuclear accumulation of glycine-rich RNA-binding protein7, influencing the RNA processing of flowering locus c antisense transcripts and flowering time in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 2015, 169(3): 2102-2117. |
| [19] | Zhang H H, Liang W W, Zhang X Z, et al. Analysis on morphology and growth characteristics of wild Elymus sibiricus L. germplasm resources in Xinjiang. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(4): 701-708. |
| 张荟荟, 梁维维, 张学洲, 等. 新疆野生老芒麦种质资源形态及生长特性分析. 草地学报, 2021, 29(4): 701-708. | |
| [20] | Mitchell A L, Attwood T K, Babbitt P C, et al. InterPro in 2019: improving coverage, classification and access to protein sequence annotations. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(D1): 351-360. |
| [21] | Jiang S Y, Ma Z G, Ramachandran S. Evolutionary history and stress regulation of the lectin superfamily in higher plants. BMC Ecology and Evolution, 2010, 10(1): 79. |
| [22] | Song M, Xu W Q, Xiang Y, et al. Association of jacalin-related lectins with wheat responses to stresses revealed by transcriptional profiling. Plant Molecular Biology, 2014, 84: 95-110. |
| [23] | Nagano A J, Fukao Y, Fujiwara M, et al. Antagonistic jacalin-related lectins regulate the size of ER body-type β-glucosidase complexes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2008, 49(6): 969-980. |
| [24] | Jia Y W. Analysis of telomere variation patterns in Elymus sibiricus at different ages and mining of senescence candidate genes. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2023. |
| 贾燕伟. 不同株龄老芒麦端粒变化规律分析及衰老候选基因挖掘. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2023. | |
| [25] | Han Y J, Song L L, Peng C L, et al. A Magnaporthe chitinase interacts with a rice jacalin-related lectin to promote host colonization. Plant Physiology, 2019, 179(4): 1416-1430. |
| [26] | Weidenbach D, Esch L, Möller C, et al. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biology, 2004, 4(1): 10. |
| [27] | Zhu Y, Wu N N, Song W L, et al. Soybean (Glycine max) expansin gene superfamily origins: segmental and tandem duplication events followed by divergent selection among subfamilies. BMC Plant Biology, 2014, 14: 1-19. |
| [28] | Gong L P, Lu Y T, Wang Y J, et al. Comparative analysis of the JRL gene family in the whole-genome of five gramineous plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2024, 15: 15150197. |
| [29] | He X, Li L, Xu H, et al. A rice jacalin-related mannose-binding lectin gene, OsJRL, enhances Escherichia coli viability under high salinity stress and improves salinity tolerance of rice. Plant Biology, 2017, 19(2): 257-267. |
| [30] | Hu W Y. Functional analysis of rice lectin gene OsJRL in response to cadmium stress. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2020. |
| 胡婉茵. 水稻凝集素基因OsJRL响应镉胁迫的功能研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020. | |
| [31] | Damme E J M V, Peumans W J, Barre A, et al. Plant lectins: a composite of several distinct families of structurally and evolutionary related proteins with diverse biological roles. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 1998, 17(6): 575-692. |
| [32] | Xiang Y, Song M, Wei Z Y, et al. A jacalin-related lectin-like gene in wheat is a component of the plant defence system. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(15): 5471-5483. |
| [33] | Chen T R, Luo Y J, Zhao P T, et al. Overexpression of TaJRL53 enhances the Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2021, 47(1): 19-29. |
| 陈同睿, 罗艳君, 赵潘婷, 等. 过表达TaJRL53基因提高了小麦赤霉病抗性. 作物学报, 2021, 47(1): 19-29. | |
| [34] | Zhang H L. The role of Populus euphratica PeREMs and PeJRL in the mediation of salt tolerance in higher plants. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2019. |
| 张会龙. 胡杨PeREMs和PeJRL调控植物耐盐机制研究. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2019. |
| [1] | 王若非, 李昕哲, 李祺策, 张嘉仪, 王焙钧, 谢文刚. 不同浓度的硅处理对老芒麦苗期抗寒性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 130-139. |
| [2] | 邹苇鹏, 刘怡, 翟佳兴, 周思懿, 宫祉祎, 岑慧芳, 朱慧森, 许涛. 紫花苜蓿MsNAC053基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 121-133. |
| [3] | 鲜燃, 邓雨, 付秋月, 蒋晶霞, 陶佳丽, 许涛, 朱慧森, 岑慧芳. 紫花苜蓿MsMYB86基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 162-172. |
| [4] | 刘启林, 王小军, 王金兰, 刘文辉, 马巧玲, 李建辉, 张生原, 曹文侠, 李文. 氮磷配施对高寒区老芒麦饲草产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 193-202. |
| [5] | 左志芳, 李永龙, 魏雨佳, 周生辉, 李岩, 杨国锋. 结缕草DREB基因家族的鉴定及非生物胁迫下的表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 74-88. |
| [6] | 周昕越, 王丽萍, 蒋庆雪, 马晓冉, 仪登霞, 王学敏. 紫花苜蓿低温诱导蛋白MsLTI65的分离及其对不同逆境的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 89-104. |
| [7] | 罗天蓉, 马健芝, 杜明阳, 多杰措, 熊辉岩, 段瑞君. 紫花苜蓿LACS基因家族成员鉴定及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 124-136. |
| [8] | 王文虎, 梁国玲, 刘文辉, 王凤宇, 李文. 青藏高原区8份老芒麦资源农艺性状与生产性能综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 123-132. |
| [9] | 汪欣瑶, 彭亚萍, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 司二静, 张宏, 杨轲, 马小乐, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草HgS5基因的克隆与抗旱性鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 184-195. |
| [10] | 边林, 张岩, 霍晓伟, 代蕊, 郭娜, 伊风艳, 高翠萍, 张志强. 紫花苜蓿CKX基因家族鉴定及其对非生物胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(11): 125-135. |
| [11] | 秦晓芳, 何芷睿, 贾彤, 杨玉娇, 付薇, 李航, 彭燕. 白三叶几丁质酶基因家族鉴定及TrChit3功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 187-201. |
| [12] | 贺龙义, 谭萌萌, 车海涛, 张红鹰, 朱雨欣, 张彦妮. 细叶百合LpDREB9基因克隆及耐旱性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 161-173. |
| [13] | 马超, 孙熙婧, 冯雅岚, 周爽, 琚吉浩, 吴毅, 王添宁, 郭彬彬, 张均. 紫花苜蓿GLK基因家族鉴定及渗透胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 174-190. |
| [14] | 崔红丽, 孙明哲, 贾博为, 孙晓丽. 蒺藜苜蓿OSCA基因家族鉴定及低温逆境表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 111-125. |
| [15] | 王晓彤, 李小红, 麻旭霞, 蔡文祺, 冯学丽, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿FBA基因家族成员的鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 81-93. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||