

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (11): 125-135.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024517
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
边林1( ), 张岩1, 霍晓伟1, 代蕊1, 郭娜1, 伊风艳2, 高翠萍1, 张志强1,3(
), 张岩1, 霍晓伟1, 代蕊1, 郭娜1, 伊风艳2, 高翠萍1, 张志强1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-27
修回日期:2025-03-10
出版日期:2025-11-20
发布日期:2025-10-09
通讯作者:
张志强
作者简介:E-mail: zhangzq19890102@126.com基金资助:
Lin BIAN1( ), Yan ZHANG1, Xiao-wei HUO1, Rui DAI1, Na GUO1, Feng-yan YI2, Cui-ping GAO1, Zhi-qiang ZHANG1,3(
), Yan ZHANG1, Xiao-wei HUO1, Rui DAI1, Na GUO1, Feng-yan YI2, Cui-ping GAO1, Zhi-qiang ZHANG1,3( )
)
Received:2024-12-27
Revised:2025-03-10
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-10-09
Contact:
Zhi-qiang ZHANG
摘要:
紫花苜蓿是世界上种植最广泛的豆科牧草,具有产量高、抗逆性强以及适口性好等特点。低温和干旱是影响苜蓿产量、品质及大面积推广的重要非生物胁迫因子。细胞分裂素氧化酶/脱氢酶(cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase, CKX)能够不可逆地降解细胞分裂素,调节植物的生长发育,帮助植物应对环境胁迫。本研究采用生物信息学方法在全基因组水平对紫花苜蓿CKX基因家族进行鉴定和生物信息学分析。结果表明,紫花苜蓿基因组中鉴定出31个CKX基因,分布于1、2、3、4、7和8号染色体上。紫花苜蓿CKX基因家族成员编码氨基酸数为273~545个,除MsCKX30其余均为亲水性蛋白;CKX基因家族分为3个亚族,且具有较高的保守性;紫花苜蓿CKX基因家族与蒺藜苜蓿的同源性较高。qPT-PCR结果表明,MsCKX2、MsCKX3、MsCKX7、MsCKX8、MsCKX15、MsCKX16和MsCKX18的表达量受低温胁迫诱导;干旱胁迫诱导MsCKX2、MsCKX15的表达;低温和干旱胁迫均能诱导MsCKX15表达。研究结果为紫花苜蓿MsCKX基因功能鉴定提供了参考。
边林, 张岩, 霍晓伟, 代蕊, 郭娜, 伊风艳, 高翠萍, 张志强. 紫花苜蓿CKX基因家族鉴定及其对非生物胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(11): 125-135.
Lin BIAN, Yan ZHANG, Xiao-wei HUO, Rui DAI, Na GUO, Feng-yan YI, Cui-ping GAO, Zhi-qiang ZHANG. Identification of the CKX gene family in alfalfa and its responses to abiotic stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(11): 125-135.
| 引物名称Primers name | 引物序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) | 引物名称Primers name | 引物序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX2-F1 | GGAGGGCTTGGTCAATTTGG | qRT-PCR-MsCKX10-R2 | AGGCCATATTGTTCCACCCA |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX2-R1 | TTGGCTGGCTTTAAGAGGGT | qRT-PCR-MsCKX15-F1 | ATAGCAGCCAGAGGACAAGG |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX2-F2 | AGCACGTCAAGGACTAGTCA | qRT-PCR-MsCKX15-R1 | CAGGTGCAAGTCCATGTTCA |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX2-R2 | AAGAGTGCCTCCAACAGTGA | qRT-PCR-MsCKX15-F2 | CTACCACCAGAGCTAGCCAA |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX3-F1 | GCAACAAGTGGGCTGATAGG | qRT-PCR-MsCKX15-R2 | CCTTGTCCTCTGGCTGCTAT |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX3-R1 | AGTGCCAAAGTGTTCAACCC | qRT-PCR-MsCKX16-F1 | CACACGAGGACAAGCTATGG |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX7-F2 | AATTCCCAGCAGCAGTGTTC | qRT-PCR-MsCKX16-R1 | CAGTCCAAGAAACAGGTGCA |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX7-R2 | TCAACAACAACACCATCACGT | qRT-PCR-MsCKX16-F2 | TGGCAACCTCGTACATGAAT |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX8-F1 | GCTGGTGTAAGTGGACAAGC | qRT-PCR-MsCKX16-R2 | ATAGCTTGTCCTCGTGTGGA |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX8-R1 | TGGAAGGTGCTGGTTCAAGA | qRT-PCR-MsCKX18-F2 | AAGCCCCTGATATGGTGAGG |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX8-F2 | TGTTGCAGCAAGAGGACATG | qRT-PCR-MsCKX18-R2 | ATAGAGAACCGGTCCAGCTG |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX8-R2 | AGAGAGTGCCACCAACTGTT | qRT-PCR-β-actin-F | TTTGAGACTTTCAATGTGCCCGCC |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX10-F2 | TGAACCGAACAAAGTGGGATG | qRT-PCR-β-actin-R | TAGCATGTGGGAGTGCATAACCCT |
表1 qRT-PCR引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequence of qRT-PCR
| 引物名称Primers name | 引物序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) | 引物名称Primers name | 引物序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX2-F1 | GGAGGGCTTGGTCAATTTGG | qRT-PCR-MsCKX10-R2 | AGGCCATATTGTTCCACCCA |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX2-R1 | TTGGCTGGCTTTAAGAGGGT | qRT-PCR-MsCKX15-F1 | ATAGCAGCCAGAGGACAAGG |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX2-F2 | AGCACGTCAAGGACTAGTCA | qRT-PCR-MsCKX15-R1 | CAGGTGCAAGTCCATGTTCA |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX2-R2 | AAGAGTGCCTCCAACAGTGA | qRT-PCR-MsCKX15-F2 | CTACCACCAGAGCTAGCCAA |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX3-F1 | GCAACAAGTGGGCTGATAGG | qRT-PCR-MsCKX15-R2 | CCTTGTCCTCTGGCTGCTAT |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX3-R1 | AGTGCCAAAGTGTTCAACCC | qRT-PCR-MsCKX16-F1 | CACACGAGGACAAGCTATGG |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX7-F2 | AATTCCCAGCAGCAGTGTTC | qRT-PCR-MsCKX16-R1 | CAGTCCAAGAAACAGGTGCA |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX7-R2 | TCAACAACAACACCATCACGT | qRT-PCR-MsCKX16-F2 | TGGCAACCTCGTACATGAAT |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX8-F1 | GCTGGTGTAAGTGGACAAGC | qRT-PCR-MsCKX16-R2 | ATAGCTTGTCCTCGTGTGGA |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX8-R1 | TGGAAGGTGCTGGTTCAAGA | qRT-PCR-MsCKX18-F2 | AAGCCCCTGATATGGTGAGG |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX8-F2 | TGTTGCAGCAAGAGGACATG | qRT-PCR-MsCKX18-R2 | ATAGAGAACCGGTCCAGCTG |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX8-R2 | AGAGAGTGCCACCAACTGTT | qRT-PCR-β-actin-F | TTTGAGACTTTCAATGTGCCCGCC |
| qRT-PCR-MsCKX10-F2 | TGAACCGAACAAAGTGGGATG | qRT-PCR-β-actin-R | TAGCATGTGGGAGTGCATAACCCT |
基因登录号 Gene ID | 基因名Gene name | 染色体号 Chromosome number | 氨基酸数目Number of amino acids (aa) | 分子质量Molecular weight (MW, Da) | 等电点Isoeletric point (pI) | 总平均亲水性Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) | 不稳定系数Instability index (II) | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS.gene57642.t1 | MsCKX1 | Chr8.3 | 526 | 59752.51 | 8.37 | -0.193 | 35.42 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene025106.t1 | MsCKX2 | Chr2.3 | 518 | 58195.70 | 6.13 | -0.105 | 31.71 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene85633.t1 | MsCKX3 | Chr2.1 | 518 | 58155.64 | 6.13 | -0.098 | 30.53 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene21966.t1 | MsCKX4 | Chr2.4 | 518 | 57982.41 | 6.36 | -0.090 | 29.52 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene051863.t1 | MsCKX5 | Chr8.2 | 476 | 53638.81 | 5.11 | -0.192 | 38.56 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene57641.t1 | MsCKX6 | Chr8.3 | 537 | 61217.66 | 5.77 | -0.288 | 41.04 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene85629.t1 | MsCKX7 | Chr2.1 | 545 | 62258.97 | 8.15 | -0.293 | 37.19 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene026082.t1 | MsCKX8 | Chr2.2 | 545 | 62135.90 | 7.72 | -0.267 | 36.00 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene051862.t1 | MsCKX9 | Chr8.2 | 415 | 47459.29 | 7.24 | -0.267 | 37.40 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene069617.t1 | MsCKX10 | Chr3.4 | 454 | 51318.47 | 6.07 | -0.205 | 37.62 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene42561.t1 | MsCKX11 | Chr7.1 | 544 | 61440.09 | 6.33 | -0.144 | 36.79 | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| MS.gene014082.t1 | MsCKX12 | Chr7.2 | 544 | 61459.14 | 6.39 | -0.147 | 37.30 | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| MS.gene017841.t1 | MsCKX13 | Chr7.3 | 544 | 61426.02 | 6.26 | -0.144 | 36.95 | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| MS.gene85631.t1 | MsCKX14 | Chr2.1 | 463 | 51802.53 | 6.42 | -0.087 | 29.53 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene025468.t1 | MsCKX15 | Chr4.4 | 459 | 52111.26 | 6.88 | -0.260 | 41.46 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene71156.t1 | MsCKX16 | Chr4.1 | 459 | 52137.21 | 6.75 | -0.263 | 40.36 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene012275.t1 | MsCKX17 | Chr8.4 | 324 | 37503.00 | 8.87 | -0.399 | 45.53 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MS.gene016164.t1 | MsCKX18 | Chr1.2 | 509 | 56811.82 | 6.29 | -0.202 | 34.52 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene57615.t1 | MsCKX19 | Chr8.3 | 312 | 35813.91 | 8.27 | -0.357 | 42.27 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MS.gene63612.t1 | MsCKX20 | Chr3.2 | 406 | 45391.81 | 6.68 | -0.180 | 34.28 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene93997.t1 | MsCKX21 | Chr3.1 | 352 | 39525.18 | 6.12 | -0.109 | 35.72 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene070417.t1 | MsCKX22 | Chr3.3 | 352 | 39425.07 | 6.23 | -0.100 | 34.43 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene34593.t1 | MsCKX23 | Chr4.3 | 370 | 41484.16 | 6.49 | -0.221 | 39.43 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene025112.t1 | MsCKX24 | Chr2.4 | 297 | 35130.28 | 8.98 | -0.467 | 43.14 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene42306.t1 | MsCKX25 | Che3.2 | 422 | 46570.09 | 5.54 | -0.099 | 27.05 | 胞外Extracellular |
| MS.gene051560.t1 | MsCKX26 | Chr1.3 | 411 | 45309.57 | 5.47 | -0.123 | 32.81 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene52444.t1 | MsCKX27 | Chr1.4 | 405 | 44558.64 | 5.38 | -0.134 | 32.55 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene33043.t1 | MsCKX28 | Chr1.1 | 405 | 44544.57 | 5.29 | -0.133 | 32.55 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene35542.t1 | MsCKX29 | Chr4.2 | 301 | 33828.21 | 5.95 | -0.196 | 39.14 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene014478.t1 | MsCKX30 | Chr3.1 | 386 | 42018.91 | 5.48 | 0.042 | 30.42 | 细胞膜Plasma membrane |
| MS.gene064702.t1 | MsCKX31 | Chr3.4 | 273 | 29908.98 | 5.29 | -0.039 | 32.93 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
表2 MsCKX基因家族的基本信息分析
Table 2 Bioinformatic analysis of MsCKX gene family in alfalfa
基因登录号 Gene ID | 基因名Gene name | 染色体号 Chromosome number | 氨基酸数目Number of amino acids (aa) | 分子质量Molecular weight (MW, Da) | 等电点Isoeletric point (pI) | 总平均亲水性Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) | 不稳定系数Instability index (II) | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS.gene57642.t1 | MsCKX1 | Chr8.3 | 526 | 59752.51 | 8.37 | -0.193 | 35.42 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene025106.t1 | MsCKX2 | Chr2.3 | 518 | 58195.70 | 6.13 | -0.105 | 31.71 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene85633.t1 | MsCKX3 | Chr2.1 | 518 | 58155.64 | 6.13 | -0.098 | 30.53 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene21966.t1 | MsCKX4 | Chr2.4 | 518 | 57982.41 | 6.36 | -0.090 | 29.52 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene051863.t1 | MsCKX5 | Chr8.2 | 476 | 53638.81 | 5.11 | -0.192 | 38.56 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene57641.t1 | MsCKX6 | Chr8.3 | 537 | 61217.66 | 5.77 | -0.288 | 41.04 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene85629.t1 | MsCKX7 | Chr2.1 | 545 | 62258.97 | 8.15 | -0.293 | 37.19 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene026082.t1 | MsCKX8 | Chr2.2 | 545 | 62135.90 | 7.72 | -0.267 | 36.00 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene051862.t1 | MsCKX9 | Chr8.2 | 415 | 47459.29 | 7.24 | -0.267 | 37.40 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene069617.t1 | MsCKX10 | Chr3.4 | 454 | 51318.47 | 6.07 | -0.205 | 37.62 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene42561.t1 | MsCKX11 | Chr7.1 | 544 | 61440.09 | 6.33 | -0.144 | 36.79 | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| MS.gene014082.t1 | MsCKX12 | Chr7.2 | 544 | 61459.14 | 6.39 | -0.147 | 37.30 | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| MS.gene017841.t1 | MsCKX13 | Chr7.3 | 544 | 61426.02 | 6.26 | -0.144 | 36.95 | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| MS.gene85631.t1 | MsCKX14 | Chr2.1 | 463 | 51802.53 | 6.42 | -0.087 | 29.53 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene025468.t1 | MsCKX15 | Chr4.4 | 459 | 52111.26 | 6.88 | -0.260 | 41.46 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene71156.t1 | MsCKX16 | Chr4.1 | 459 | 52137.21 | 6.75 | -0.263 | 40.36 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene012275.t1 | MsCKX17 | Chr8.4 | 324 | 37503.00 | 8.87 | -0.399 | 45.53 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MS.gene016164.t1 | MsCKX18 | Chr1.2 | 509 | 56811.82 | 6.29 | -0.202 | 34.52 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene57615.t1 | MsCKX19 | Chr8.3 | 312 | 35813.91 | 8.27 | -0.357 | 42.27 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| MS.gene63612.t1 | MsCKX20 | Chr3.2 | 406 | 45391.81 | 6.68 | -0.180 | 34.28 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene93997.t1 | MsCKX21 | Chr3.1 | 352 | 39525.18 | 6.12 | -0.109 | 35.72 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene070417.t1 | MsCKX22 | Chr3.3 | 352 | 39425.07 | 6.23 | -0.100 | 34.43 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene34593.t1 | MsCKX23 | Chr4.3 | 370 | 41484.16 | 6.49 | -0.221 | 39.43 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene025112.t1 | MsCKX24 | Chr2.4 | 297 | 35130.28 | 8.98 | -0.467 | 43.14 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| MS.gene42306.t1 | MsCKX25 | Che3.2 | 422 | 46570.09 | 5.54 | -0.099 | 27.05 | 胞外Extracellular |
| MS.gene051560.t1 | MsCKX26 | Chr1.3 | 411 | 45309.57 | 5.47 | -0.123 | 32.81 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene52444.t1 | MsCKX27 | Chr1.4 | 405 | 44558.64 | 5.38 | -0.134 | 32.55 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene33043.t1 | MsCKX28 | Chr1.1 | 405 | 44544.57 | 5.29 | -0.133 | 32.55 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene35542.t1 | MsCKX29 | Chr4.2 | 301 | 33828.21 | 5.95 | -0.196 | 39.14 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| MS.gene014478.t1 | MsCKX30 | Chr3.1 | 386 | 42018.91 | 5.48 | 0.042 | 30.42 | 细胞膜Plasma membrane |
| MS.gene064702.t1 | MsCKX31 | Chr3.4 | 273 | 29908.98 | 5.29 | -0.039 | 32.93 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
基因登录号 Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 蛋白质 Protein | α-螺旋 Alpha helix | β-转角 Beta turn | 延伸链 Extended strand | 无规则卷曲 Random coil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS.gene57642.t1 | MsCKX1 | MsCKX1 | 33.46 | 5.70 | 18.63 | 42.21 |
| MS.gene025106.t1 | MsCKX2 | MsCKX2 | 35.71 | 5.41 | 19.69 | 39.19 |
| MS.gene85633.t1 | MsCKX3 | MsCKX3 | 33.98 | 5.79 | 20.08 | 40.15 |
| MS.gene21966.t1 | MsCKX4 | MsCKX4 | 34.94 | 6.18 | 20.46 | 38.42 |
| MS.gene051863.t1 | MsCKX5 | MsCKX5 | 32.35 | 6.72 | 19.75 | 41.18 |
| MS.gene57641.t1 | MsCKX6 | MsCKX6 | 37.43 | 5.59 | 16.95 | 40.04 |
| MS.gene85629.t1 | MsCKX7 | MsCKX7 | 31.93 | 6.24 | 17.43 | 44.40 |
| MS.gene026082.t1 | MsCKX8 | MsCKX8 | 33.39 | 5.69 | 17.98 | 42.94 |
| MS.gene051862.t1 | MsCKX9 | MsCKX9 | 32.53 | 7.71 | 20.00 | 39.76 |
| MS.gene069617.t1 | MsCKX10 | MsCKX10 | 33.26 | 6.17 | 19.82 | 40.75 |
| MS.gene42561.t1 | MsCKX11 | MsCKX11 | 31.07 | 5.51 | 19.30 | 44.12 |
| MS.gene014082.t1 | MsCKX12 | MsCKX12 | 29.04 | 6.99 | 20.77 | 43.20 |
| MS.gene017841.t1 | MsCKX13 | MsCKX13 | 31.07 | 6.07 | 19.85 | 43.01 |
| MS.gene85631.t1 | MsCKX14 | MsCKX14 | 33.05 | 5.62 | 20.52 | 40.82 |
| MS.gene025468.t1 | MsCKX15 | MsCKX15 | 32.24 | 6.54 | 19.61 | 41.61 |
| MS.gene71156.t1 | MsCKX16 | MsCKX16 | 32.24 | 6.10 | 20.70 | 40.96 |
| MS.gene012275.t1 | MsCKX17 | MsCKX17 | 37.35 | 5.86 | 17.59 | 39.20 |
| MS.gene016164.t1 | MsCKX18 | MsCKX18 | 31.83 | 6.29 | 20.04 | 41.85 |
| MS.gene57615.t1 | MsCKX19 | MsCKX19 | 38.46 | 5.45 | 17.63 | 38.46 |
| MS.gene63612.t1 | MsCKX20 | MsCKX20 | 36.70 | 5.91 | 19.95 | 37.44 |
| MS.gene93997.t1 | MsCKX21 | MsCKX21 | 31.53 | 5.40 | 20.74 | 42.33 |
| MS.gene070417.t1 | MsCKX22 | MsCKX22 | 31.82 | 6.25 | 20.45 | 41.48 |
| MS.gene34593.t1 | MsCKX23 | MsCKX23 | 30.81 | 5.68 | 19.46 | 44.05 |
| MS.gene025112.t1 | MsCKX24 | MsCKX24 | 39.39 | 5.39 | 16.50 | 38.72 |
| MS.gene42306.t1 | MsCKX25 | MsCKX25 | 37.44 | 5.45 | 17.06 | 40.05 |
| MS.gene051560.t1 | MsCKX26 | MsCKX26 | 30.90 | 5.60 | 19.46 | 44.04 |
| MS.gene52444.t1 | MsCKX27 | MsCKX27 | 31.60 | 7.16 | 18.52 | 42.72 |
| MS.gene33043.t1 | MsCKX28 | MsCKX28 | 33.09 | 6.91 | 19.51 | 40.49 |
| MS.gene35542.t1 | MsCKX29 | MsCKX29 | 32.89 | 7.31 | 22.59 | 37.21 |
| MS.gene014478.t1 | MsCKX30 | MsCKX30 | 36.27 | 7.25 | 20.98 | 35.49 |
| MS.gene064702.t1 | MsCKX31 | MsCKX31 | 34.07 | 6.59 | 20.51 | 38.83 |
表3 MsCKX蛋白质二级结构
Table 3 The secondary structure of MsCKX proteins in alfalfa (%)
基因登录号 Gene ID | 基因名 Gene name | 蛋白质 Protein | α-螺旋 Alpha helix | β-转角 Beta turn | 延伸链 Extended strand | 无规则卷曲 Random coil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS.gene57642.t1 | MsCKX1 | MsCKX1 | 33.46 | 5.70 | 18.63 | 42.21 |
| MS.gene025106.t1 | MsCKX2 | MsCKX2 | 35.71 | 5.41 | 19.69 | 39.19 |
| MS.gene85633.t1 | MsCKX3 | MsCKX3 | 33.98 | 5.79 | 20.08 | 40.15 |
| MS.gene21966.t1 | MsCKX4 | MsCKX4 | 34.94 | 6.18 | 20.46 | 38.42 |
| MS.gene051863.t1 | MsCKX5 | MsCKX5 | 32.35 | 6.72 | 19.75 | 41.18 |
| MS.gene57641.t1 | MsCKX6 | MsCKX6 | 37.43 | 5.59 | 16.95 | 40.04 |
| MS.gene85629.t1 | MsCKX7 | MsCKX7 | 31.93 | 6.24 | 17.43 | 44.40 |
| MS.gene026082.t1 | MsCKX8 | MsCKX8 | 33.39 | 5.69 | 17.98 | 42.94 |
| MS.gene051862.t1 | MsCKX9 | MsCKX9 | 32.53 | 7.71 | 20.00 | 39.76 |
| MS.gene069617.t1 | MsCKX10 | MsCKX10 | 33.26 | 6.17 | 19.82 | 40.75 |
| MS.gene42561.t1 | MsCKX11 | MsCKX11 | 31.07 | 5.51 | 19.30 | 44.12 |
| MS.gene014082.t1 | MsCKX12 | MsCKX12 | 29.04 | 6.99 | 20.77 | 43.20 |
| MS.gene017841.t1 | MsCKX13 | MsCKX13 | 31.07 | 6.07 | 19.85 | 43.01 |
| MS.gene85631.t1 | MsCKX14 | MsCKX14 | 33.05 | 5.62 | 20.52 | 40.82 |
| MS.gene025468.t1 | MsCKX15 | MsCKX15 | 32.24 | 6.54 | 19.61 | 41.61 |
| MS.gene71156.t1 | MsCKX16 | MsCKX16 | 32.24 | 6.10 | 20.70 | 40.96 |
| MS.gene012275.t1 | MsCKX17 | MsCKX17 | 37.35 | 5.86 | 17.59 | 39.20 |
| MS.gene016164.t1 | MsCKX18 | MsCKX18 | 31.83 | 6.29 | 20.04 | 41.85 |
| MS.gene57615.t1 | MsCKX19 | MsCKX19 | 38.46 | 5.45 | 17.63 | 38.46 |
| MS.gene63612.t1 | MsCKX20 | MsCKX20 | 36.70 | 5.91 | 19.95 | 37.44 |
| MS.gene93997.t1 | MsCKX21 | MsCKX21 | 31.53 | 5.40 | 20.74 | 42.33 |
| MS.gene070417.t1 | MsCKX22 | MsCKX22 | 31.82 | 6.25 | 20.45 | 41.48 |
| MS.gene34593.t1 | MsCKX23 | MsCKX23 | 30.81 | 5.68 | 19.46 | 44.05 |
| MS.gene025112.t1 | MsCKX24 | MsCKX24 | 39.39 | 5.39 | 16.50 | 38.72 |
| MS.gene42306.t1 | MsCKX25 | MsCKX25 | 37.44 | 5.45 | 17.06 | 40.05 |
| MS.gene051560.t1 | MsCKX26 | MsCKX26 | 30.90 | 5.60 | 19.46 | 44.04 |
| MS.gene52444.t1 | MsCKX27 | MsCKX27 | 31.60 | 7.16 | 18.52 | 42.72 |
| MS.gene33043.t1 | MsCKX28 | MsCKX28 | 33.09 | 6.91 | 19.51 | 40.49 |
| MS.gene35542.t1 | MsCKX29 | MsCKX29 | 32.89 | 7.31 | 22.59 | 37.21 |
| MS.gene014478.t1 | MsCKX30 | MsCKX30 | 36.27 | 7.25 | 20.98 | 35.49 |
| MS.gene064702.t1 | MsCKX31 | MsCKX31 | 34.07 | 6.59 | 20.51 | 38.83 |
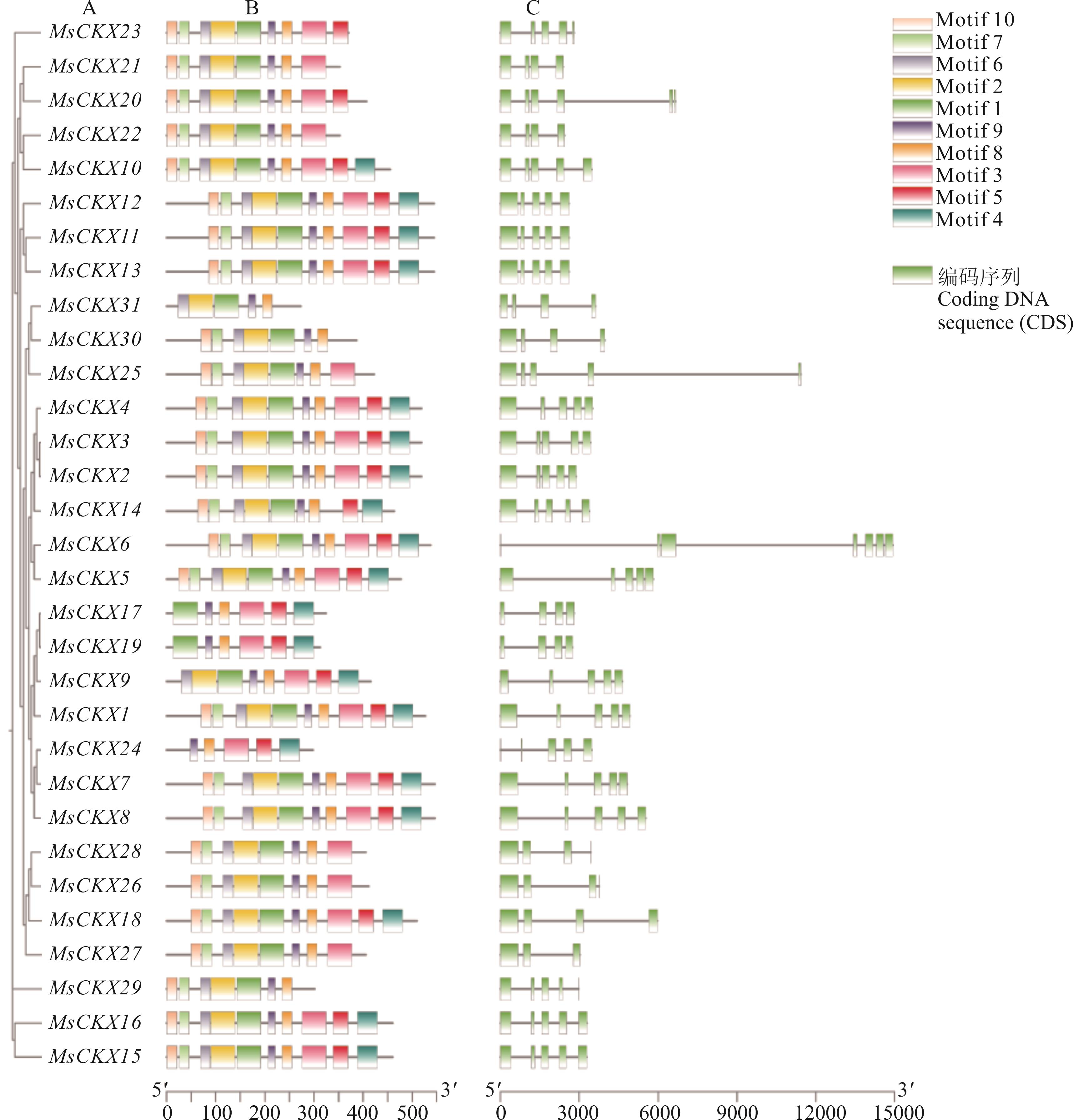
图 2 MsCKX基因家族系统进化关系(A)、保守基序(B)及基因结构(C)分析
Fig.2 Phylogenetic relationships (A), conserved motif (B) and gene structure (C) analyses of the MsCKX gene family

图4 紫花苜蓿和拟南芥、蒺藜苜蓿间CKX 基因的共线性分析Mt: 蒺藜苜蓿M. truncatula; 数字代表不同染色体The numbers represent different chromosomes.
Fig.4 Analysis of collinearity of CKX genes among M. sativa, A. thaliana and M. truncatula
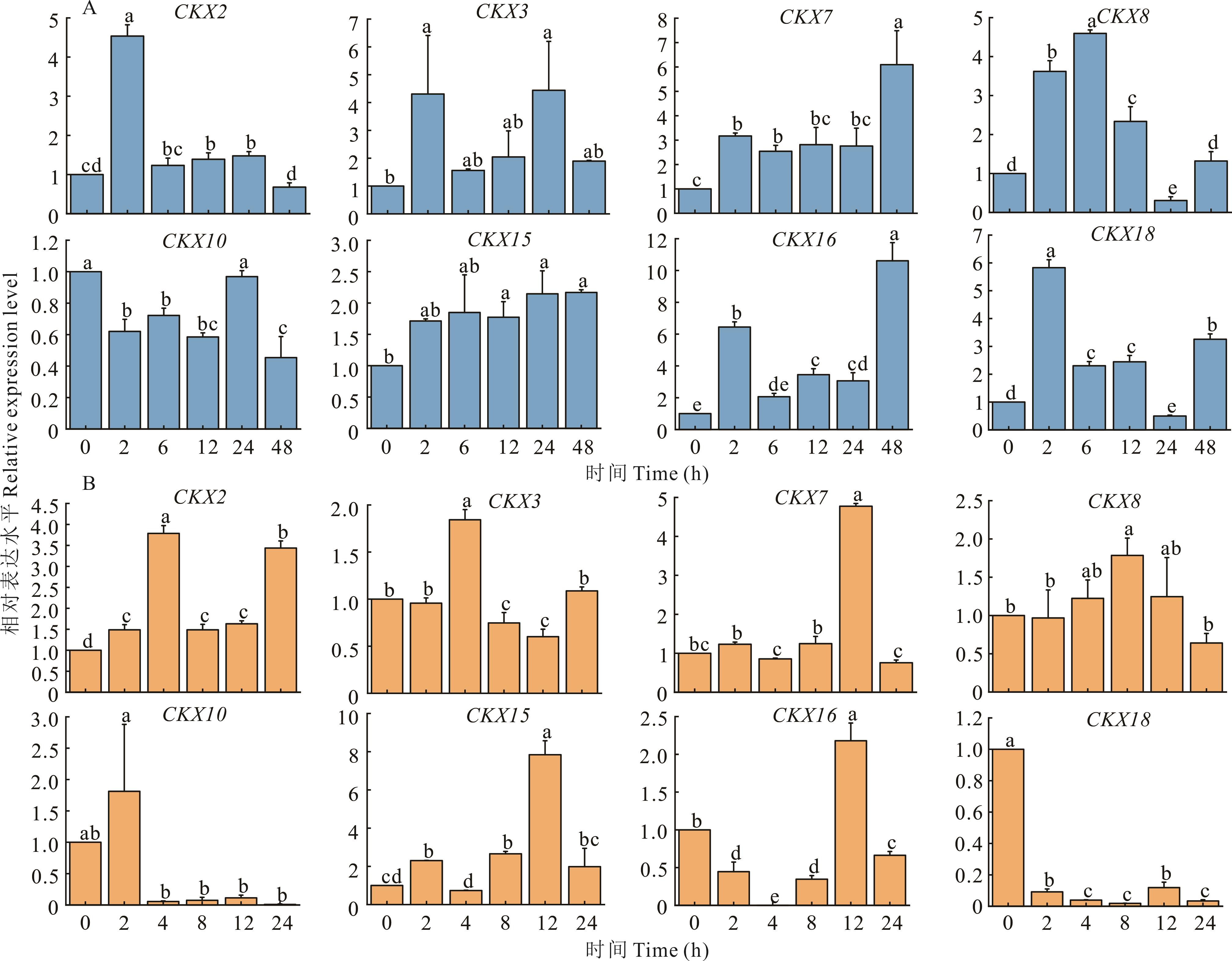
图 5 紫花苜蓿MsCKX基因在非生物胁迫下的qRT-PCR分析A: MsCKXs基因在低温胁迫下的表达量Expressions of MsCKXs under low temperature stress; B: MsCKXs基因在干旱胁迫下的表达量Expressions of MsCKXs under drought stress. 不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference (P<0.05).
Fig.5 qRT-PCR analysis of MsCKX gene under abiotic stresses in alfalfa
| [1] | Jan Š, Ioanna A, Jitka Š, et al. Plant hormonomics: Multiple phytohormone profiling by targeted metabolomics. Plant Physiology, 2018, 177(2): 476-489. |
| [2] | Tu T L. Coordinated cytokinin signaling and auxin biosynthesis mediates arsenate-induced root growth inhibition. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2021. |
| 涂田莉. 细胞分裂素信号传导和生长素生物合成协同调控砷酸盐诱导的根生长抑制.泰安: 山东农业大学, 2021. | |
| [3] | Wang H B. Mechanism analysis of phytohormone regulates seed abortion and fruit development of seedlesspear. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2021. |
| 王会滨. 激素调控无籽梨种子败育及果实发育的机理解析. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021. | |
| [4] | Miller C O, Skoog F, Okumura F S, et al. Isolation, structure and synthesis of kinetin, a substance promoting cell division 1, 2. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1956, 78(7): 1375-1380. |
| [5] | Dörte M, Ottoline L. Auxin, cytokinin and the control of shoot branching. Annals of Botany, 2011, 107(7): 1203-1212. |
| [6] | O’Brien J A, Benková E. Cytokinin cross-talking during biotic and abiotic stress responses. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2013, 4: 451. |
| [7] | Vyroubalová S, Václavíková K, Turecková V, et al. Characterization of new maize genes putatively involved in cytokinin metabolism and their expression during osmotic stress in relation to cytokinin levels. Plant Physiology, 2009, 151(1): 433-447. |
| [8] | Le D, Nishiyama R, Watanabe Y, et al. Identification and expression analysis of cytokinin metabolic genes in soybean under normal and drought conditions in relation to cytokinin levels. PLoS One, 2012, 7: e42411. |
| [9] | Tomás W, Václav M, Valérie L, et al. Cytokinin-deficient transgenic arabidopsis plants show multiple developmental alterations indicating opposite functions of cytokinins in the regulation of shoot and root meristem activity. The Plant Cell, 2003, 15(11): 2532-2550. |
| [10] | Ashikari M, Sakakibara H, Lin S, et al. Cytokinin oxidase regulates rice grain production. Science, 2005, 309(5735): 741-745. |
| [11] | Rong C Y, Liu Y X, Chang Z Y, et al. Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase family genes exhibit functional divergence and overlap in rice growth and development, especially in control of tillering. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2022, 73(11): 3552-3568. |
| [12] | Zalabák D, Galuszka P, Mrízová K, et al. Biochemical characterization of the maize cytokinin dehydrogenase family and cytokinin profiling in developing maize plantlets in relation to the expression of cytokinin dehydrogenase genes. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2014, 74: 283-293. |
| [13] | Du Y, Zhang Z, Gu Y, et al. Genome-wide identification of the soybean cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase gene family and its diverse roles in response to multiple abiotic stress. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1163219. |
| [14] | Mameaux S, Cockram J, Thiel T, et al. Molecular, phylogenetic and comparative genomic analysis of the cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase gene family in the Poaceae. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2012, 10(1): 67-82. |
| [15] | Evans T G, Song J, Jameson P E. Micro-scale chlorophyll analysis and developmental expression of a cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase gene during leaf development and senescence. Plant Growth Regulation, 2012, 66: 95-99. |
| [16] | Brugière N, Jiao S, Hantke S, et al. Cytokinin oxidase gene expression in maize is localized to the vasculature, and is induced by cytokinins, abscisic acid, and abiotic stress. Plant Physiology, 2003, 132(3): 1228-1240. |
| [17] | Li S S, Li H, Yang Z, et al. Research progress on evaluation indexes of alfalfa germplasm resources in China. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2019(3): 47-51. |
| 李莎莎, 李红, 杨曌, 等. 我国苜蓿种质资源评价指标研究进展. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2019(3): 47-51. | |
| [18] | Tang L L, Cai H, Zhai H, et al. Overexpression of Glycine soja WRKY20 enhances both drought and salt tolerance in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 2014, 118: 77-86. |
| [19] | Jin X, Yin X, Ndayambaza B, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of the ERF gene family in Medicago sativa L. under various abiotic stresses. DNA and Cell Biology, 2019, 38(10): 1056-1068. |
| [20] | Min X, Jin X, Zhang Z, et al. Genome-wide identification of NAC transcription factor family and functional analysis of the abiotic stress-responsive genes in Medicago sativa L. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2020, 39: 324-337. |
| [21] | Yang P, Zhang P, Li B, et al. Effect of nodules on dehydration response in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2013, 86: 29-34. |
| [22] | Chen H, Zeng Y, Yang Y, et al. Allele-aware chromosome-level genome assembly and efficient transgene-free genome editing for the autotetraploid cultivated alfalfa. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 2494. |
| [23] | Artimo P, Jonnalagedda M, Arnold K, et al. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 40(Web Server issue): W597-W603. |
| [24] | He F, Zhang L, Zhao G, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NAC gene family in alfalfa revealed its potential roles in response to multiple abiotic stresses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(17): 10015. |
| [25] | Wang Z H, Li W, Luo Y L, et al. Overview of PCR technology and calibration methods of PCR instrument. Industrial Metrology, 2024, 34(S1): 1-4. |
| 王智辉, 黎巍, 罗逸龙, 等. PCR技术及PCR仪校准方法概述. 工业计量, 2024, 34(S1): 1-4. | |
| [26] | Guo C Z. Identification and analysis of CKX gene family in apple. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2022, 20(4): 1104-1111. |
| 郭彩珍. 苹果CKX基因家族的鉴定及分析. 分子植物育种, 2022, 20(4): 1104-1111. | |
| [27] | Wang X Y, Zhang T, Li C S, et al. Identify CmCKXs gene family and its effect on fruit set in cucubit melon. Molecular Plant Breeding, (2024-11-29)[ 2024-12-27]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/46.1068.S.20241129.1148.015. |
| 王雪艳, 张婷, 李朝森, 等. 甜瓜CKX基因家族鉴定及对坐果的影响. 分子植物育种, (2024-11-29)[2024-12-27]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/46.1068.S.20241129.1148.015. | |
| [28] | Ahmad B, Zhang S, Yao J, et al. Genomic organization of the B3-domain transcription factor family in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) and expression during seed development in seedless and seeded cultivars. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(18): 4553. |
| [29] | Xu G, Guo C, Shan H, et al. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon-intron structure. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(4): 1187-1192. |
| [30] | Jeffares D C, Penkett C J, Bähler J. Rapidly regulated genes are intron poor. Trends in Genetics, 2008, 24(8): 375-378. |
| [31] | Shaul O. How introns enhance gene expression. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 2017, 91(Pt B): 145-155. |
| [32] | Li Y J, Chen D M, Luo S W, et al. Intron-mediated regulation of β-tubulin genes expression affects the sensitivity to carbendazim in Fusarium graminearum. Current Genetics, 2019, 65(4): 1057-1069. |
| [33] | Liu P, Zhang C, Ma J Q, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (CKX) genes reveal likely roles in pod development and stress responses in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Genes, 2018, 9(3): 168. |
| [34] | Zhu M Z, Wang Y, Lu S J, et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of cytokinin dehydrogenase/oxidase (CKX) family genes in Brassica oleracea L. reveals their involvement in response to Plasmodiophora brassicae infections. Horticultural Plant Journal, 2022, 8(1): 68-80. |
| [35] | Sun X, Zhu L, Hao Z, et al. Genome-wide identification and abiotic-stress-responsive expression of CKX gene family in Liriodendron chinense. Plants, 2023, 12(11): 2157. |
| [1] | 邹苇鹏, 刘怡, 翟佳兴, 周思懿, 宫祉祎, 岑慧芳, 朱慧森, 许涛. 紫花苜蓿MsNAC053基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 121-133. |
| [2] | 鲜燃, 邓雨, 付秋月, 蒋晶霞, 陶佳丽, 许涛, 朱慧森, 岑慧芳. 紫花苜蓿MsMYB86基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 162-172. |
| [3] | 刘沂欣, 隋晓青, 王鑫尧, 郎梦卿, 孙凌子寅, 吉尔尔格. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿的缓解作用[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 206-214. |
| [4] | 李文秀, 姚拓, 李昌宁, 贾倩民, 何傲蕾, 周杨. “凹凸棒-有机基质”菌肥载体最佳配比的筛选及对紫花苜蓿的促生效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 88-98. |
| [5] | 蒋学乾, 杨青川, 康俊梅. 紫花苜蓿在干旱胁迫下的产量损失与抗旱性遗传研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(7): 219-234. |
| [6] | 温小月, 赵颖, 王宝强, 王贤, 朱晓林, 王义真, 魏小红. 外源NO调控干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿AP2/ERFs基因的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 154-167. |
| [7] | 张英豪, 刘楚波, 周坤, 郭家存, 刘世鹏, 孙娈姿. 果草系统中枣树对不同方位紫花苜蓿和鸭茅生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 203-212. |
| [8] | 崔灿, 王梦琦, 赵琬璐, 刘新颖, 鉴晶晶, 严俊鑫. 胺鲜酯浸种对NaCl胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 46-58. |
| [9] | 曾燕霞, 陈志龙, 尚继红, 沙晓弟, 吴娟, 陈彩锦. 太空诱变对PEG-6000模拟干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿材料苗期生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 59-69. |
| [10] | 魏孔钦, 张盈盈, 回金峰, 马春晖, 张前兵. 菌磷配施对紫花苜蓿根系非结构碳水化合物及碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 40-50. |
| [11] | 周昕越, 王丽萍, 蒋庆雪, 马晓冉, 仪登霞, 王学敏. 紫花苜蓿低温诱导蛋白MsLTI65的分离及其对不同逆境的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 89-104. |
| [12] | 罗天蓉, 马健芝, 杜明阳, 多杰措, 熊辉岩, 段瑞君. 紫花苜蓿LACS基因家族成员鉴定及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 124-136. |
| [13] | 冯雅琪, 陈嘉慧, 张静妮, 隋超, 陈基伟, 刘志鹏, 周强, 刘文献. 基于重测序紫花苜蓿高蛋白、高产关联InDel分子标记开发[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 137-149. |
| [14] | 董拓轩, 陈训锋, 梅大海, 郭永莎, 魏旭红, 宋秋艳. 纳米铁与铜对苜蓿壳二孢及其引致春季黑茎病的抑制与防治作用[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 201-211. |
| [15] | 陈彩锦, 包明芳, 王文虎, 尚继红, 曾燕霞, 沙晓弟, 朱新忠, 王学敏, 刘文辉. 紫花苜蓿抗旱育种研究现状及展望[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 204-223. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||