

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 220-233.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021229
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2021-06-09
修回日期:2021-07-27
出版日期:2022-07-20
发布日期:2022-06-01
通讯作者:
赵丽丽
作者简介:E-mail: zhaolili_0508@163.com基金资助:
Wen-hui XIE( ), Li-juan HUANG, Li-li ZHAO(
), Li-juan HUANG, Li-li ZHAO( ), Lei-ting WANG, Wen-wu ZHAO
), Lei-ting WANG, Wen-wu ZHAO
Received:2021-06-09
Revised:2021-07-27
Online:2022-07-20
Published:2022-06-01
Contact:
Li-li ZHAO
摘要:
为探明葛藤对喀斯特山区土壤富钙环境的适应机制,以3份不同产地葛藤种质种子为试验材料,采用室内模拟试验,研究不同浓度(0、50、100、150和200 mmol·L-1 CaCl2)钙盐胁迫对3份葛藤种质种子萌发、幼苗生长、渗透调节物质、抗氧化酶系统及植物内源激素的影响。结果表明,随钙盐胁迫浓度升高,澳大利亚(AUS)和江苏(JS)种质种子发芽率、发芽势、发芽指数、活力指数均显著降低,种子萌发率、萌发速度及种苗生活力均受到显著抑制(P<0.05),湖南(HN)种质在胁迫浓度为100 mmol·L-1时,种子发芽率、发芽势、发芽指数升高;3份葛藤种质幼苗叶长、叶宽、株高和生物量显著降低;叶片丙二醛(MDA)含量和相对电导率均显著升高;叶片脯氨酸(Pro)、可溶性糖含量和超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性均先增后降;AUS和HN种质叶片过氧化物酶(POD)活性先增后降,JS种质表现为显著上升;HN和JS种质叶片抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX)活性显著升高,AUS种质则表现为先升后降;3份葛藤种质叶片脱落酸(ABA)、生长素(IAA)、赤霉素(GA3)、玉米素(ZT)(除JS种质)含量均先增后减。0~50 mmol·L-1 CaCl2胁迫对3份葛藤种质种子萌发及幼苗生长抑制不显著,150~200 mmol·L-1 钙盐胁迫显著抑制3种葛藤种子萌发及幼苗生长,HN种质种子依靠种子休眠抵御钙盐胁迫,说明葛藤幼苗对低钙盐胁迫具有一定的耐受性。中高钙盐浓度胁迫时,葛藤幼苗通过提高自身渗透物质含量、增强抗氧化酶活性、增加部分激素含量、改变地上地下生物量等方式积极调节自身生理代谢, 以适应高钙盐环境。结合隶属函数和主成分分析,除Pro含量和APX活性外,其余指标均可作为评价3份葛藤种质耐盐性的主要指标,3份种质的耐盐性大小顺序为JS>HN>AUS。
谢文辉, 黄莉娟, 赵丽丽, 王雷挺, 赵文武. 钙盐胁迫对3份葛藤种质种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 220-233.
Wen-hui XIE, Li-juan HUANG, Li-li ZHAO, Lei-ting WANG, Wen-wu ZHAO. Effects of calcium salt stress on seed germination and seedling physiological characteristics of three Pueraria lobata germplasm lines[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(7): 220-233.
| 种质材料代号Germplasm material code | 产地Place of origin | 来源Source |
|---|---|---|
| AUS | 澳大利亚Australia | 江苏冈仁波齐种业有限公司Jiangsu Gangrenboqi seed Co. , Ltd. |
| HN | 湖南 Hunan | 湖南种子市场Hunan seed market |
| JS | 江苏Jiangsu | 江苏种业科技有限公司Jiangsu seed technology Co., Ltd |
表1 3份葛藤种质的资源信息
Table 1 Resource information of the three P. lobata germplasms
| 种质材料代号Germplasm material code | 产地Place of origin | 来源Source |
|---|---|---|
| AUS | 澳大利亚Australia | 江苏冈仁波齐种业有限公司Jiangsu Gangrenboqi seed Co. , Ltd. |
| HN | 湖南 Hunan | 湖南种子市场Hunan seed market |
| JS | 江苏Jiangsu | 江苏种业科技有限公司Jiangsu seed technology Co., Ltd |
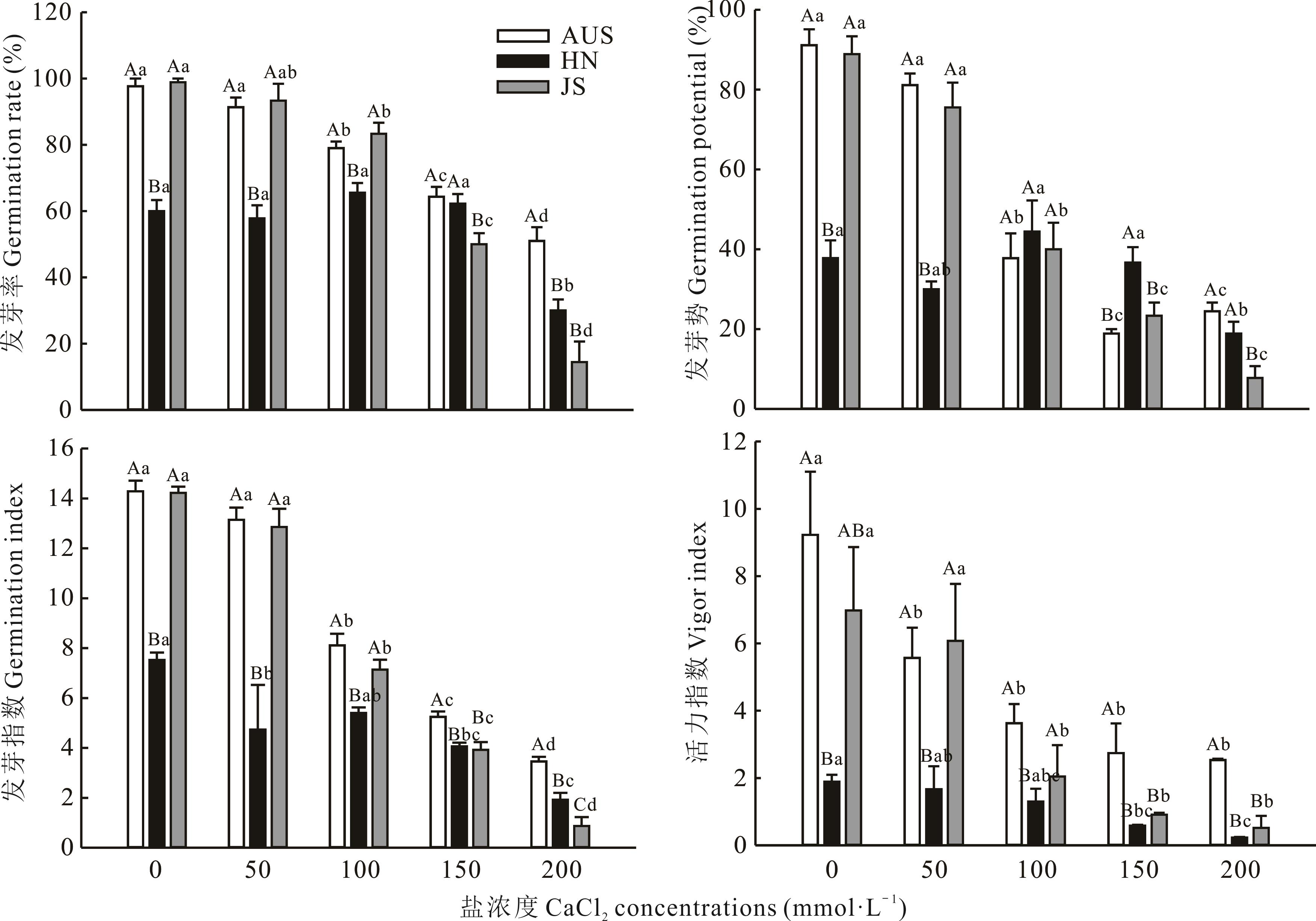
图1 钙盐胁迫对3份葛藤种质种子发芽指标的影响不同大写字母表示同一处理不同种质之间差异显著(P<0.05),不同小写字母表示同一种质不同处理之间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。The different capital letters indicate the significant differences among different varieties of the same treatment concentration (P<0.05), and the different small letters indicate the significant differences among different treatment concentrations of the same variety (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Effects of calcium salt stress on seed germination indexes of three P. lobata germplasms
材料 Materials | CaCl2浓度 Concentration of CaCl2 (mmol·L-1) | 叶长 Leaf length (cm) | 叶宽 Leaf width (cm) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 地上部干重 Aboveground dry weight (g·plant-1) | 地下部干重 Underground dry weight (g·plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUS | 0 (CK) | 6.33±0.24Aa | 5.18±0.20Aa | 16.23±0.59Aa | 0.50±0.0031Aa | 0.03±0.0033Aa |
| 50 | 5.61±0.66Aa | 4.74±0.24Aab | 14.72±1.12Aab | 0.47±0.0200Aa | 0.03±0.0031Aab | |
| 100 | 4.46±0.24Bb | 4.46±0.24Bab | 14.08±1.04Ab | 0.37±0.0201Ab | 0.02±0.0033Abc | |
| 150 | 3.97±0.04Cb | 4.10±0.15Bbc | 13.75±0.14Aab | 0.28±0.0057Ac | 0.02±0.0027Ac | |
| 200 | 3.68±0.05Cb | 3.18±0.12Bc | 8.50±0.31Ac | 0.27±0.0119Ac | 0.02±0.0020Ac | |
| HN | 0 (CK) | 6.55±0.30Aa | 5.54±0.05Aa | 15.72±0.64Aa | 0.45±0.0067Ba | 0.03±0.0032Aa |
| 50 | 6.35±0.28Aa | 5.27±0.17Aa | 14.17±0.45Ab | 0.40±0.0033Bab | 0.03±0.0033Aa | |
| 100 | 6.91±0.12Aa | 5.41±0.09Aa | 13.93±0.18Ab | 0.35±0.0125Abc | 0.02±0.0067Aa | |
| 150 | 6.96±0.13Aa | 4.82±0.07Ab | 11.67±0.09Bc | 0.31±0.0426Ac | 0.02±0.0034Aab | |
| 200 | 5.16±0.02Ab | 3.24±0.10Bb | 10.55±0.25Ac | 0.25±0.0239Ad | 0.01±0.0036Bb | |
| JS | 0 (CK) | 5.88±0.24Aa | 4.68±0.01Ba | 15.48±0.44Aa | 0.44±0.0100Ba | 0.03±0.0088Aab |
| 50 | 5.28±0.12Aab | 4.75±0.12Aa | 14.48±0.17Aa | 0.42±0.0067Ba | 0.03±0.0056Aa | |
| 100 | 5.08±0.34Bbc | 4.54±0.30Ba | 13.80±1.50Aa | 0.34±0.0227Ab | 0.03±0.0033Aab | |
| 150 | 4.51±0.20Bbc | 4.32±0.10Ba | 11.14±0.20Bb | 0.31±0.0337Ab | 0.02±0.0036Ab | |
| 200 | 4.46±0.21Bc | 3.95±0.09Ab | 10.83±0.33Ab | 0.28±0.0236Ab | 0.02±0.0033Ab |
表2 钙盐胁迫对3份葛藤种质幼苗生长指标的影响
Table 2 Effects of calcium salt stress on seedling growth indexes of three P. lobata germplasms
材料 Materials | CaCl2浓度 Concentration of CaCl2 (mmol·L-1) | 叶长 Leaf length (cm) | 叶宽 Leaf width (cm) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 地上部干重 Aboveground dry weight (g·plant-1) | 地下部干重 Underground dry weight (g·plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUS | 0 (CK) | 6.33±0.24Aa | 5.18±0.20Aa | 16.23±0.59Aa | 0.50±0.0031Aa | 0.03±0.0033Aa |
| 50 | 5.61±0.66Aa | 4.74±0.24Aab | 14.72±1.12Aab | 0.47±0.0200Aa | 0.03±0.0031Aab | |
| 100 | 4.46±0.24Bb | 4.46±0.24Bab | 14.08±1.04Ab | 0.37±0.0201Ab | 0.02±0.0033Abc | |
| 150 | 3.97±0.04Cb | 4.10±0.15Bbc | 13.75±0.14Aab | 0.28±0.0057Ac | 0.02±0.0027Ac | |
| 200 | 3.68±0.05Cb | 3.18±0.12Bc | 8.50±0.31Ac | 0.27±0.0119Ac | 0.02±0.0020Ac | |
| HN | 0 (CK) | 6.55±0.30Aa | 5.54±0.05Aa | 15.72±0.64Aa | 0.45±0.0067Ba | 0.03±0.0032Aa |
| 50 | 6.35±0.28Aa | 5.27±0.17Aa | 14.17±0.45Ab | 0.40±0.0033Bab | 0.03±0.0033Aa | |
| 100 | 6.91±0.12Aa | 5.41±0.09Aa | 13.93±0.18Ab | 0.35±0.0125Abc | 0.02±0.0067Aa | |
| 150 | 6.96±0.13Aa | 4.82±0.07Ab | 11.67±0.09Bc | 0.31±0.0426Ac | 0.02±0.0034Aab | |
| 200 | 5.16±0.02Ab | 3.24±0.10Bb | 10.55±0.25Ac | 0.25±0.0239Ad | 0.01±0.0036Bb | |
| JS | 0 (CK) | 5.88±0.24Aa | 4.68±0.01Ba | 15.48±0.44Aa | 0.44±0.0100Ba | 0.03±0.0088Aab |
| 50 | 5.28±0.12Aab | 4.75±0.12Aa | 14.48±0.17Aa | 0.42±0.0067Ba | 0.03±0.0056Aa | |
| 100 | 5.08±0.34Bbc | 4.54±0.30Ba | 13.80±1.50Aa | 0.34±0.0227Ab | 0.03±0.0033Aab | |
| 150 | 4.51±0.20Bbc | 4.32±0.10Ba | 11.14±0.20Bb | 0.31±0.0337Ab | 0.02±0.0036Ab | |
| 200 | 4.46±0.21Bc | 3.95±0.09Ab | 10.83±0.33Ab | 0.28±0.0236Ab | 0.02±0.0033Ab |
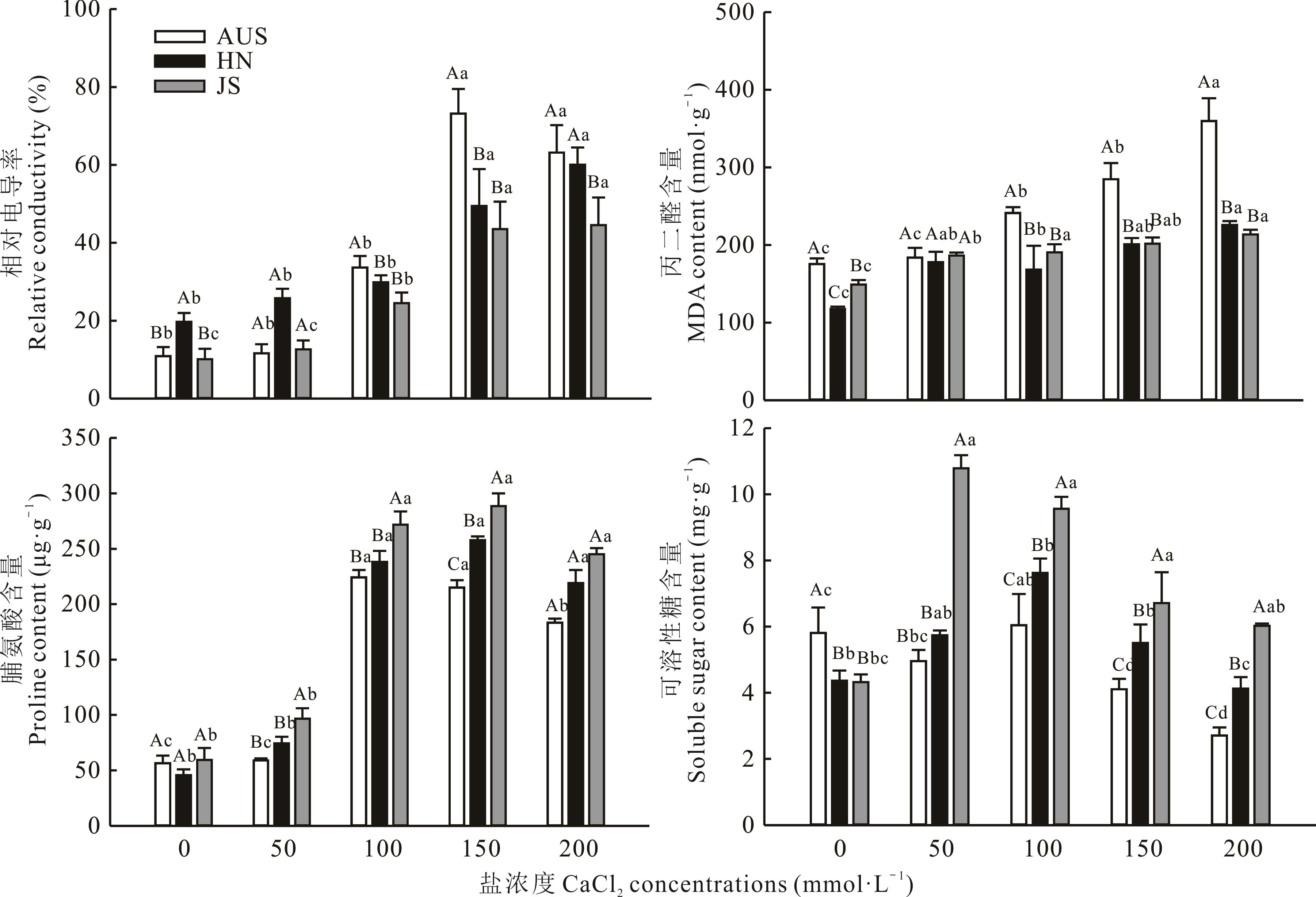
图2 钙盐胁迫对3份葛藤种质相对电导率、丙二醛和渗透调节物质含量的影响
Fig.2 Effects of calcium salt stress on relative conductivity, malondialdehyde and osmotic adjustment substance contents of three P. lobata germplasms

图3 钙盐胁迫对3份葛藤种质叶片过氧化物酶、过氧化氢酶、超氧化物歧化酶和抗坏血酸过氧化物酶活性的影响
Fig.3 Effect of calcium salt stress on the activities of peroxidase (POD), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and ascorbate peroxidase (APX) in leaves of three kinds of P. lobata germplasms
材料 Materials | CaCl2 浓度 Concentration of CaCl2 (mmol·L-1) | ABA含量 ABA content | IAA含量 IAA content | GA3含量 GA3 content | ZT含量 ZT content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUS | 0 (CK) | 55.84±13.11Ab | 73.76±4.09Aab | 7.51±0.18Ac | 17.70±0.80Bb |
| 50 | 103.67±10.91Aa | 76.94±4.63Aa | 9.24±0.11Aa | 18.44±0.53Ba | |
| 100 | 86.32±11.29Aab | 85.08±5.57Aa | 9.65±0.18Aa | 19.61±0.20Aa | |
| 150 | 76.88±0.76Aab | 62.07±1.89Bb | 8.09±0.24Ab | 17.10±0.14Ac | |
| 200 | 82.23±8.39Aab | 62.05±0.08Bb | 8.60±0.06Ab | 16.50±0.25Bb | |
| HN | 0 (CK) | 53.59±5.14Ac | 66.52±1.89Aab | 6.46±0.02Bc | 16.93±0.23Bb |
| 50 | 60.08±4.80Bbc | 66.91±4.52Bab | 7.88±0.10Bb | 17.59±0.42Ab | |
| 100 | 68.68±5.56Aabc | 73.77±6.25Aa | 7.99±0.00Bb | 19.48±0.28Aa | |
| 150 | 78.46±6.76Aa | 61.19±2.34Bab | 8.64±0.16Aa | 17.71±0.17Bb | |
| 200 | 72.03±2.41Aab | 58.51±3.57Bb | 7.71±0.10Ab | 16.69±0.32Bb | |
| JS | 0 (CK) | 61.78±6.11Ac | 77.33±4.34Aa | 7.53±0.07Ab | 18.54±0.20Aa |
| 50 | 61.85±2.41Bc | 80.88±0.43Aa | 7.98±0.28Bb | 17.18±0.44Aa | |
| 100 | 83.89±3.83Aa | 78.20±3.15Aa | 10.22±0.40Aa | 17.71±0.27Aa | |
| 150 | 79.98±0.48Abc | 73.34±4.43Aa | 8.08±0.07Ab | 16.42±0.06Ab | |
| 200 | 71.50±2.67Aab | 74.81±3.44Aa | 7.38±0.06Bb | 16.15±0.50Cb |
表3 钙盐胁迫下3份葛藤种质叶片内源激素含量的变化
Table 3 Changes of endogenous hormone contents in leaves of three P. lobata germplasms under calcium salt stress (ng·g-1)
材料 Materials | CaCl2 浓度 Concentration of CaCl2 (mmol·L-1) | ABA含量 ABA content | IAA含量 IAA content | GA3含量 GA3 content | ZT含量 ZT content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUS | 0 (CK) | 55.84±13.11Ab | 73.76±4.09Aab | 7.51±0.18Ac | 17.70±0.80Bb |
| 50 | 103.67±10.91Aa | 76.94±4.63Aa | 9.24±0.11Aa | 18.44±0.53Ba | |
| 100 | 86.32±11.29Aab | 85.08±5.57Aa | 9.65±0.18Aa | 19.61±0.20Aa | |
| 150 | 76.88±0.76Aab | 62.07±1.89Bb | 8.09±0.24Ab | 17.10±0.14Ac | |
| 200 | 82.23±8.39Aab | 62.05±0.08Bb | 8.60±0.06Ab | 16.50±0.25Bb | |
| HN | 0 (CK) | 53.59±5.14Ac | 66.52±1.89Aab | 6.46±0.02Bc | 16.93±0.23Bb |
| 50 | 60.08±4.80Bbc | 66.91±4.52Bab | 7.88±0.10Bb | 17.59±0.42Ab | |
| 100 | 68.68±5.56Aabc | 73.77±6.25Aa | 7.99±0.00Bb | 19.48±0.28Aa | |
| 150 | 78.46±6.76Aa | 61.19±2.34Bab | 8.64±0.16Aa | 17.71±0.17Bb | |
| 200 | 72.03±2.41Aab | 58.51±3.57Bb | 7.71±0.10Ab | 16.69±0.32Bb | |
| JS | 0 (CK) | 61.78±6.11Ac | 77.33±4.34Aa | 7.53±0.07Ab | 18.54±0.20Aa |
| 50 | 61.85±2.41Bc | 80.88±0.43Aa | 7.98±0.28Bb | 17.18±0.44Aa | |
| 100 | 83.89±3.83Aa | 78.20±3.15Aa | 10.22±0.40Aa | 17.71±0.27Aa | |
| 150 | 79.98±0.48Abc | 73.34±4.43Aa | 8.08±0.07Ab | 16.42±0.06Ab | |
| 200 | 71.50±2.67Aab | 74.81±3.44Aa | 7.38±0.06Bb | 16.15±0.50Cb |
材料 Materials | 主成分 Principal component | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 贡献率 Contribution(%) | 累积贡献率 Cumulative(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUS | Ⅰ | 15.008 | 71.468 | 71.468 |
| Ⅱ | 4.137 | 19.699 | 91.167 | |
| HN | Ⅰ | 12.585 | 59.931 | 59.931 |
| Ⅱ | 7.199 | 34.281 | 94.212 | |
| JS | Ⅰ | 14.192 | 67.583 | 67.583 |
| Ⅱ | 4.917 | 23.413 | 90.996 |
表4 3份葛藤种质耐盐性指标的特征值和贡献率
Table 4 Eigenvalue and contribution of salt tolerance index of three kinds of P. lobata germplasms
材料 Materials | 主成分 Principal component | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 贡献率 Contribution(%) | 累积贡献率 Cumulative(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUS | Ⅰ | 15.008 | 71.468 | 71.468 |
| Ⅱ | 4.137 | 19.699 | 91.167 | |
| HN | Ⅰ | 12.585 | 59.931 | 59.931 |
| Ⅱ | 7.199 | 34.281 | 94.212 | |
| JS | Ⅰ | 14.192 | 67.583 | 67.583 |
| Ⅱ | 4.917 | 23.413 | 90.996 |
材料 Materials | 主成分 Principal component | 耐盐性指标特征向量 Indicator eigenvector | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 | T8 | T9 | T10 | T11 | ||
| AUS | Ⅰ | 0.245 | 0.251 | 0.257 | 0.257 | 0.258 | 0.234 | 0.148 | 0.257 | 0.255 | -0.244 | -0.215 |
| Ⅱ | 0.032 | 0.002 | -0.001 | -0.009 | -0.025 | 0.011 | -0.281 | 0.048 | 0.075 | -0.158 | 0.060 | |
| HN | Ⅰ | 0.182 | 0.139 | 0.235 | 0.282 | 0.138 | 0.259 | 0.278 | 0.271 | 0.260 | -0.237 | -0.254 |
| Ⅱ | 0.282 | 0.278 | 0.188 | 0.005 | 0.322 | 0.113 | 0.027 | 0.065 | 0.139 | 0.202 | 0.037 | |
| JS | Ⅰ | 0.254 | 0.260 | 0.262 | 0.245 | 0.260 | 0.228 | 0.259 | 0.257 | 0.254 | -0.260 | -0.096 |
| Ⅱ | 0.111 | -0.080 | -0.050 | -0.170 | 0.036 | 0.126 | 0.055 | -0.100 | -0.110 | 0.024 | -0.410 | |
材料 Materials | 主成分 Principal component | 耐盐性指标特征向量 Indicator eigenvector | ||||||||||
| T12 | T13 | T14 | T15 | T16 | T17 | T18 | T19 | T20 | T21 | |||
| AUS | Ⅰ | -0.243 | 0.175 | 0.232 | 0.231 | -0.183 | 0.253 | 0.082 | 0.170 | 0.160 | -0.092 | |
| Ⅱ | -0.137 | 0.283 | -0.202 | -0.163 | 0.123 | 0.058 | 0.463 | -0.369 | 0.383 | 0.443 | ||
| HN | Ⅰ | -0.245 | 0.249 | -0.070 | -0.266 | -0.193 | -0.161 | -0.230 | -0.227 | -0.151 | 0.010 | |
| Ⅱ | 0.180 | -0.127 | -0.349 | 0.059 | 0.224 | 0.304 | 0.212 | 0.205 | -0.298 | -0.364 | ||
| JS | Ⅰ | -0.254 | 0.252 | -0.126 | -0.236 | -0.223 | 0.091 | -0.138 | 0.118 | 0.107 | 0.207 | |
| Ⅱ | -0.110 | 0.069 | 0.220 | -0.050 | 0.227 | 0.418 | 0.318 | -0.340 | 0.406 | 0.206 | ||
表5 3份葛藤种质耐盐性指标的主成分分析
Table 5 Principal component analysis of salt tolerance index of three kinds of P. lobata
材料 Materials | 主成分 Principal component | 耐盐性指标特征向量 Indicator eigenvector | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 | T8 | T9 | T10 | T11 | ||
| AUS | Ⅰ | 0.245 | 0.251 | 0.257 | 0.257 | 0.258 | 0.234 | 0.148 | 0.257 | 0.255 | -0.244 | -0.215 |
| Ⅱ | 0.032 | 0.002 | -0.001 | -0.009 | -0.025 | 0.011 | -0.281 | 0.048 | 0.075 | -0.158 | 0.060 | |
| HN | Ⅰ | 0.182 | 0.139 | 0.235 | 0.282 | 0.138 | 0.259 | 0.278 | 0.271 | 0.260 | -0.237 | -0.254 |
| Ⅱ | 0.282 | 0.278 | 0.188 | 0.005 | 0.322 | 0.113 | 0.027 | 0.065 | 0.139 | 0.202 | 0.037 | |
| JS | Ⅰ | 0.254 | 0.260 | 0.262 | 0.245 | 0.260 | 0.228 | 0.259 | 0.257 | 0.254 | -0.260 | -0.096 |
| Ⅱ | 0.111 | -0.080 | -0.050 | -0.170 | 0.036 | 0.126 | 0.055 | -0.100 | -0.110 | 0.024 | -0.410 | |
材料 Materials | 主成分 Principal component | 耐盐性指标特征向量 Indicator eigenvector | ||||||||||
| T12 | T13 | T14 | T15 | T16 | T17 | T18 | T19 | T20 | T21 | |||
| AUS | Ⅰ | -0.243 | 0.175 | 0.232 | 0.231 | -0.183 | 0.253 | 0.082 | 0.170 | 0.160 | -0.092 | |
| Ⅱ | -0.137 | 0.283 | -0.202 | -0.163 | 0.123 | 0.058 | 0.463 | -0.369 | 0.383 | 0.443 | ||
| HN | Ⅰ | -0.245 | 0.249 | -0.070 | -0.266 | -0.193 | -0.161 | -0.230 | -0.227 | -0.151 | 0.010 | |
| Ⅱ | 0.180 | -0.127 | -0.349 | 0.059 | 0.224 | 0.304 | 0.212 | 0.205 | -0.298 | -0.364 | ||
| JS | Ⅰ | -0.254 | 0.252 | -0.126 | -0.236 | -0.223 | 0.091 | -0.138 | 0.118 | 0.107 | 0.207 | |
| Ⅱ | -0.110 | 0.069 | 0.220 | -0.050 | 0.227 | 0.418 | 0.318 | -0.340 | 0.406 | 0.206 | ||
指标 Parameters | 种质名Germplasm name | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| AUS | HN | JS | |
| T1 | 0.443 | 0.410 | 0.430 |
| T2 | 0.517 | 0.476 | 0.608 |
| T3 | 0.497 | 0.486 | 0.480 |
| T4 | 0.470 | 0.395 | 0.416 |
| T5 | 0.463 | 0.526 | 0.514 |
| T6 | 0.488 | 0.478 | 0.461 |
| T7 | 0.476 | 0.474 | 0.460 |
| T8 | 0.485 | 0.529 | 0.582 |
| T9 | 0.421 | 0.458 | 0.501 |
| T10 | 0.533 | 0.565 | 0.443 |
| T11 | 0.344 | 0.498 | 0.488 |
| T12 | 0.496 | 0.498 | 0.535 |
| T13 | 0.478 | 0.526 | 0.461 |
| T14 | 0.421 | 0.458 | 0.501 |
| T15 | 0.512 | 0.525 | 0.496 |
| T16 | 0.468 | 0.426 | 0.472 |
| T17 | 0.474 | 0.504 | 0.519 |
| T18 | 0.499 | 0.549 | 0.533 |
| T19 | 0.542 | 0.464 | 0.501 |
| 平均值 Average | 0.475 | 0.487 | 0.495 |
| 耐受性顺序Order of resistant | 3 | 2 | 1 |
表6 3份葛藤种质对不同钙盐浓度的耐受性综合评价
Table 6 Comprehensive evaluation of tolerance of three P. lobata germplasms to different calcium concentrations
指标 Parameters | 种质名Germplasm name | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| AUS | HN | JS | |
| T1 | 0.443 | 0.410 | 0.430 |
| T2 | 0.517 | 0.476 | 0.608 |
| T3 | 0.497 | 0.486 | 0.480 |
| T4 | 0.470 | 0.395 | 0.416 |
| T5 | 0.463 | 0.526 | 0.514 |
| T6 | 0.488 | 0.478 | 0.461 |
| T7 | 0.476 | 0.474 | 0.460 |
| T8 | 0.485 | 0.529 | 0.582 |
| T9 | 0.421 | 0.458 | 0.501 |
| T10 | 0.533 | 0.565 | 0.443 |
| T11 | 0.344 | 0.498 | 0.488 |
| T12 | 0.496 | 0.498 | 0.535 |
| T13 | 0.478 | 0.526 | 0.461 |
| T14 | 0.421 | 0.458 | 0.501 |
| T15 | 0.512 | 0.525 | 0.496 |
| T16 | 0.468 | 0.426 | 0.472 |
| T17 | 0.474 | 0.504 | 0.519 |
| T18 | 0.499 | 0.549 | 0.533 |
| T19 | 0.542 | 0.464 | 0.501 |
| 平均值 Average | 0.475 | 0.487 | 0.495 |
| 耐受性顺序Order of resistant | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | Gu X H. Effects of calcium fertiiizer application on peanut physiological characteristics, yield and quality under drought stress. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2014. |
| 顾学花. 施钙对干旱胁迫下花生生理特性,产量和品质的影响. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2014. | |
| 2 | Wang J. Response of poa pratensis to exogenous calcium addition under salt stress. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2020. |
| 王婧. 盐胁迫下草地早熟禾对外源钙添加的响应. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2020. | |
| 3 | Yuan J W, Zhang J, Wang L, et al. Effects of exogenous calcium on physiological indexes of apple flower organs under low temperature stress. Northern Horticulture, 2021, 11(5): 28-33. |
| 袁嘉玮, 张健, 王璐, 等. 外源钙对低温胁迫下苹果花器官生理指标的影响. 北方园艺, 2021, 11(5): 28-33. | |
| 4 | Han Z P, Zhang H X, Li X, et al. Effects of Ca(NO3)2 stress on growth and physiological properties of cucumber seedlings. Northern Horticulture, 2019, 11(1): 22-29. |
| 韩志平, 张海霞, 李侠, 等. 硝酸钙胁迫对黄瓜幼苗生长和生理特性的影响. 北方园艺, 2019, 11(1): 22-29. | |
| 5 | Liao J, Ren H M, Liu C K, et al. Advances in plant physiology and molecular mechanism of calcium signaling pathway under saline-alkali stress.Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 25(1): 1-8. |
| 廖婕, 任慧敏, 柳参奎, 等. 盐碱胁迫下植物生理和钙信号通路分子机制的研究进展. 分子植物育种, 2020, 25(1): 1-8. | |
| 6 | Wang G, Yu L H, Wang Y G, et al. Effect of calcium nutrition on salt tolerance of sugar beet seedlings. Sugar Crops of China, 2021, 43(2): 40-46. |
| 王堽, 於丽华, 王宇光, 等. 钙营养对甜菜幼苗耐盐性的影响. 中国糖料, 2021, 43(2): 40-46. | |
| 7 | Shi H F, Lu J Y Z, Han Z R, et al. The effect of calcium on seed germination and seedling growth of Lolium multiflorum Lam. Seed, 2019, 38(9): 105-108. |
| 石慧芳, 陆锦优子, 韩卓锐, 等. 钙对多花黑麦草种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 种子, 2019, 38(9): 105-108. | |
| 8 | Chi Y K. Study on mode and technology of grassland establishment and ecological animal husbandry in the karst rocky desertification area. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University, 2019. |
| 池永宽. 喀斯特石漠化草地建植与生态畜牧业模式及技术研究. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2019. | |
| 9 | Liu J. Environmental impact by mining in karst rocky desertification areas and research on comprehensive treatment. Changsha: Central South University, 2010. |
| 刘霁. 喀斯特石漠化地区采矿环境影响及综合治理研究. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010. | |
| 10 | Du W P, Yan H M, Zhen L, et al. The experience and practice of desertification control in karst region of Southwest China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(16): 5798-5808. |
| 杜文鹏, 闫慧敏, 甄霖, 等. 西南岩溶地区石漠化综合治理研究. 生态学报, 2019, 39(16): 5798-5808. | |
| 11 | Li X F. Speciation of valcium in soil and plants’ leaves in karst ecosystem and its ecological significance. Guilin: Guangxi Normal University, 2006. |
| 李小方. 岩溶环境中土壤-植物系统钙元素形态分析及其生态意义. 桂林: 广西师范大学, 2006. | |
| 12 | Hu P, Liu S, Ye Y, et al. Soil carbon and nitrogen accumulation following agricultural abandonment in a subtropical karst region. Applied Soil Ecology, 2018, 13(2): 169-178. |
| 13 | Yu H J. Study on the effects of dispersible tab lets containing I sofiavones from Pueraria lobata on osteoporosis in rats and its mechanism. Jinan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicin, 2012. |
| 虞慧娟. 葛藤异黄酮分散片抗大鼠骨质疏松作用及机理的研究. 济南: 山东中医药大学, 2012. | |
| 14 | Yuan X F. Pueraria montana is covered in treasure. Health Preserving, 2020, 432(9): 44-46. |
| 袁秀芬. 葛藤一身都是宝. 养生月刊, 2020, 432(9): 44-46. | |
| 15 | Li A D, Li W J, Peng X, et al. Niche characteristics for dominant species of a wild Pueraria lobata community in the Guizhou Karst Region. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2012, 29(4): 491-497. |
| 李安定, 李苇洁, 彭熙, 等. 贵州喀斯特区野生葛藤群落主要种群生态位. 浙江农林大学学报, 2012, 29(4): 491-497. | |
| 16 | Li H S. Principles and techniques of plant physiological and biochemical experiments. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000. |
| 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. | |
| 17 | Nakano Y, Asada K. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant and Cell Physiology, 1980, 22(5): 867-880. |
| 18 | Wang J Y, Ao H, Zhang J. Experimental techniques and principles of plant physiology and biochemistry. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University Press, 2003. |
| 王晶英, 敖红, 张杰. 植物生理生化实验技术与原理. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学出版社, 2003. | |
| 19 | Zhang L, Jia Z G, Ma Q H, et al. Effects of saline-alkali stresses on the growth and endogenous hormone contents in leaves of hybrid hazelnut Liaozhen 3. Forest Research, 2015, 28(3): 394-401. |
| 张丽, 贾志国, 马庆华, 等. 盐碱胁迫对平欧杂种榛生长及叶片内源激素含量的影响. 林业科学研究, 2015, 28(3): 394-401. | |
| 20 | Yuan H, Wang J L, Yuan H. Quality evaluation of Xinjiang jujube based on principal component analysis and cluster analysis. The Food Industry, 2020, 41(9): 305-309. |
| 袁辉, 王建玲, 远辉. 基于主成分分析和聚类分析对新疆红枣的品质评价. 食品工业, 2020, 41(9): 305-309. | |
| 21 | Chen Y Q, Su K Q, Chen T X, et al. Effects of complex saline-alkali stress on seed germination and seedling physiological characteristics of Achnatherum inebrians. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 137-157. |
| 陈雅琦, 苏楷淇, 陈泰祥, 等. 混合盐碱胁迫对醉马草种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 137-157. | |
| 22 | Xu X, Fan R, Zheng R, et al. Proteomic analysis of seed germination under salt stress in soybeans. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science B (Biomedicine & Biotechnology), 2011, 12(7): 25-28. |
| 23 | Guo X L, Zhao P P, Yang J J. Drought-resistant evaluation of three kinds of herbage during seed germination in artificial drought conditions. Seed, 2020, 39(6): 19-23. |
| 郭小龙, 赵珮珮, 杨建军. 模拟干旱胁迫下3种牧草种子萌发期抗旱性评价. 种子, 2020, 39(6): 19-23. | |
| 24 | Kong D Z, Liu Y P, Su S W, et al. Effects of exogenous calcium on the physiological characteristics of lotus under salt stress. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2020, 20(4): 56-64. |
| 孔德政, 刘艺平, 苏少文, 等. 外源钙对盐胁迫下荷花生理特性的影响. 河南农业大学学报, 2020, 20(4): 56-64. | |
| 25 | Li Y M, Jiang Y T, Qu G N. Effects of salt stress on seed germination of Pogostemon cablin. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2019, 42(11): 2491-2496. |
| 李玉梅, 姜云天, 曲广男. 盐胁迫对东北藿香种子萌发的影响. 中药材, 2019, 42(11): 2491-2496. | |
| 26 | Dong L Y, Xu D, Fu R X. The environmental factors affecting seed germination of Carolina crane’s-bill Geranium carolinianum. Journal of Plant Protection, 2020, 47(5): 102-108. |
| 董立尧, 徐丹, 付瑞霞. 野老鹳草Geranium carolinianum种子的萌发条件. 植物保护学报, 2020, 47(5): 102-108. | |
| 27 | Jose A M, Maria O, Agustina B V, et al. Plant responses to salt stress: Adaptive mechanisms. Agronomy, 2017, 7(1): 18-22. |
| 28 | Satish B, Mansi G, Prachi J, et al. Signaling mechanisms and biochemical pathways regulating pollen-stigma interaction, seed development and seedling growth in sunflower under salt stress. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2021, 16(11): 98-110. |
| 29 | Mi Y W, Wang G X, Gong C W, et al. Effects of salt stress on growth and physiology of Isatis indigotica seedlings. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(6): 43-51. |
| 米永伟, 王国祥, 龚成文, 等. 盐胁迫对菘蓝幼苗生长和抗性生理的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(6): 43-51. | |
| 30 | Liu Y G, Peng B, Xu M Z, et al. Effects of calcium stress on growth and physiological index of Typha angustifolia L. in karst wetland. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2020, 49(4): 168-175. |
| 刘云根, 彭博, 徐鸣洲, 等. 钙胁迫对狭叶香蒲的生长及逆境生理指标的影响. 西部林业科学, 2020, 49(4): 168-175. | |
| 31 | Zhao L L, Wang P C, Chen C, et al. Influence of long-term persistent drought stress on growth, physiological and ecological characteristics of Fagopyrum dibotrys and comprehensive evaluation of their drought resistance. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2016, 24(4): 825-833. |
| 赵丽丽, 王普昶, 陈超, 等. 持续干旱对金荞麦生长、生理生态特性的影响及抗旱性评价. 草地学报, 2016, 24(4): 825-833. | |
| 32 | Qiu Q H, Deng S Y. Influence of salt stress on seeds germination and seedling growth of Brassica campestris. Northern Horticulture, 2013, 11(18): 27-29. |
| 邱清华, 邓绍云. 盐胁迫对七个品种紫菜薹种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 北方园艺, 2013, 11(18): 27-29. | |
| 33 | Shi R G, Zhao H Y, Qi M Y, et al. Effects of exogenous choline chloride and calcium chloride on germination and physiological characteristics of wheat under salt stress. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(14): 22-26. |
| 侍瑞高, 赵慧云, 戚名扬, 等. 外源氯化胆碱和氯化钙对盐胁迫下小麦种子萌发和幼苗生理特性的影响. 安徽农业科学, 2020, 48(14): 22-26. | |
| 34 | Jia X P, Deng Y M, Sun X B, et al. Impacts of salt stress on the growth and physiological characteristics of Paspalum vaginatum. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(12): 204-212. |
| 贾新平, 邓衍明, 孙晓波, 等. 盐胁迫对海滨雀稗生长和生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2015, 24(12): 204-212. | |
| 35 | Zhu Y P, Meng X H, Gai W L, et al. Effects of salt stress on antioxidant enzymes and osmotic adjustment substances of winter wheat. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2017, 19(19): 7-12. |
| 朱玉鹏, 孟祥浩, 盖伟玲, 等. 盐胁迫对冬小麦花后抗氧化酶, 渗透调节物质的影响. 中国农学通报, 2017, 19(19): 7-12. | |
| 36 | Marcelo F P, Pedro P B, Agnaldo R M C, et al. Physiological, metabolic, and stomatal adjustments in response to salt stress in Jatropha curcas. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 168(1): 56-70. |
| 37 | Yan J Q Z, Li G T, Wang Y L, et al. Effects of salt stress on seed germination and seedling physiological characteristics of Morus mongolica. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(1): 33-42. |
| 闫晶秋子, 李钢铁, 王月林, 等. 盐胁迫对蒙桑种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(1): 33-42. | |
| 38 | Guo Y Y, Yu H Y, Yang M M, et al. Effect of drought stress on lipid peroxidation, osmotic adjustment and antioxidant enzyme activity of leaves and roots of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. seedling. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 2018, 65(2): 65-68. |
| 39 | Bai X S. Adaptive responses of soybean leaves to osmotic retion under drought and salt stress. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 1(1): 5-6. |
| 柏新盛. 旱盐胁迫下大豆叶片渗透调节的适应性响应. 现代农业科技, 2019, 1(1): 5-6. | |
| 40 | Sun C C, Zhao H X, Zheng C X. Effects of NaCl stress on osmolyte and proline metabolism in Ginkgo biloba seedling. Plant Physiology Communications, 2017, 53(3): 470-476. |
| 孙聪聪, 赵海燕, 郑彩霞. NaCl胁迫对银杏幼树渗透调节物质及脯氨酸代谢的影响. 植物生理学报, 2017, 53(3): 470-476. | |
| 41 | Xu D, Wang W, Gao T, et al. Calcium alleviates decreases in photosynthesis under salt stress by enhancing antioxidant metabolism and adjusting solute accumulation in Calligonum mongolicum. Conservation Physiology, 2017, 12(1): 1-3. |
| 42 | Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, et al. Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends in Plant Science, 2004, 9(10): 25-26. |
| 43 | Yildiztugay E, Sekmen A H, Turkan I, et al. Elucidation of physiological and biochemical mechanisms of an endemic halophyte Centaurea tuzgoluensis under salt stress. Plant Physiology & Biochemistry, 2011, 49(8): 816-824. |
| 44 | Ma Y. Physiological responses of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica seedling under NaCl stress. Liaoning Forestry Science and Technology, 2020, 1(3): 47-49. |
| 马莹. NaCl胁迫下樟子松苗木的生理响应. 辽宁林业科技, 2020, 1(3): 47-49. | |
| 45 | Liu Y J, Zhang L, Tian X Y, et al. The effects of salt stress on endogenous hormones, NADKase and Ca2+-ATPase in leaves of Puccinellia chinampoensis seedlings. Pratacultural Science, 2008, 11(4): 51-54 |
| 刘延吉, 张蕾, 田晓艳, 等. 盐胁迫对碱茅幼苗叶片内源激素, NAD激酶及Ca2+-ATPase的效应. 草业科学, 2008, 11(4): 51-54. | |
| 46 | Yu Z, Duan X, Luo L, et al. How plant hormones mediate salt stress responses. Trends in Plant Science, 2020, 25(11): 33-36. |
| 47 | Luo Y J, Zou X, Peng Y, et al. Effects of salt stress on growth and endogenous hormones of two species of crabapple. Non-wood Forest Research, 2021, 39(1): 201-210. |
| 罗玉婕, 邹旭, 彭冶, 等. 盐胁迫对两种海棠生长和内源激素的影响. 经济林研究, 2021, 39(1): 201-210. | |
| 48 | Sun R Z, Jiang G B, Wu X Y, et al. Response of endogenous hormone in apoplast of two poplars to salt stress. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2013, 48(2): 62-66. |
| 孙若峥, 姜国斌, 吴祥云, 等. 2种杨树嫩茎质外体内源激素对盐胁迫的响应. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2013, 48(2): 62-66. | |
| 49 | Li H Y, Li A X, Wang C, et al. Effects of salt stress on endogenous hormone contents in sunflower seedlings. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2018, 36(6): 92-97. |
| 李海洋, 李爱学, 王成, 等. 盐胁迫对苗期向日葵内源激素含量的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2018, 36(6): 92-97. | |
| 50 | Yuan C X, Ding J. Effects of water stress on the content of IAA and the activities of IAA oxidase and peroxidase in cotton leaves. Acta Phytophysiologica Sinica, 1990, 16(2): 179-180. |
| 袁朝兴, 丁静. 水分胁迫对棉花叶片中IAA从含量、IAA氧化酶和过氧化物酶活性的影响. 植物生理学报, 1990, 16(2): 179-180. | |
| 51 | Chen D, Liu Y J, Wu K. Effect of salt stress on the content of endogenous hormones in the leaf of Puccinellia chinampoensis seedling. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 35(12): 3476-3477. |
| 陈丹, 刘延吉, 吴阔. 盐胁迫对碱茅幼苗叶片内源激素的影响. 安徽农业科学, 2007, 35(12): 3476-3477. |
| [1] | 刘彩婷, 毛丽萍, 阿依谢木, 于应文, 沈禹颖. 紫花苜蓿与垂穗披碱草混播比例对其抗寒生长生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 133-143. |
| [2] | 纪童, 蒋齐, 王占军, 季波. 7种禾本科牧草抗旱性研究与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 144-156. |
| [3] | 苏世平, 李毅, 刘小娥, 种培芳, 单立山, 后有丽. 外源脯氨酸对缓解红砂干旱胁迫的机理研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 127-138. |
| [4] | 张铎, 李岚涛, 林迪, 郑龙辉, 耿赛男, 石纹碹, 盛开, 苗玉红, 王宜伦. 施磷水平对菊芋块茎产量、品质、植株生理特性与磷利用率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 139-149. |
| [5] | 曲婷, 周立业. 入侵植物少花蒺藜草异型种子萌发策略及其幼苗生长特性[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 91-100. |
| [6] | 赵娟娟, 车大璐, 郭玮婷, 张伟涛, 刘连超, 赵俐辰, 高玉红, 孙新胜, 李雪梅, 王媛. 复方中药对热应激条件下杂交小尾寒羊生产性能、生理参数和血液理化指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 178-189. |
| [7] | 吴瑞, 刘文辉, 张永超, 刘敏洁. 老芒麦离区形态特征及生理特性差异研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 81-92. |
| [8] | 李玉洁, 沈启维, 张澳, 刘丹, 叶代桦, 李廷轩. 畜禽粪便处理下矿山生态型水蓼磷积累及去除能力研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 114-123. |
| [9] | 王志恒, 魏玉清, 赵延蓉, 王悦娟. 基于转录组学比较研究甜高粱幼苗响应干旱和盐胁迫的生理特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 71-84. |
| [10] | 赵利清, 郝志刚, 崔笑岩, 彭向永. 赤霉素及其抑制剂调控草地早熟禾生长及赤霉素相关基因表达的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 85-91. |
| [11] | 王循刚, 张晓玲, 徐田伟, 耿远月, 胡林勇, 赵娜, 刘宏金, 康生萍, 徐世晓. 饲粮蛋白质水平对藏系绵羊瘤胃真菌菌群结构及功能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 182-191. |
| [12] | 高鹏飞, 张静, 范卫芳, 高冰, 郝宏娟, 吴建慧. 干旱胁迫对光叉委陵菜根系特征、结构和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 203-212. |
| [13] | 郭文婷, 王国华, 缑倩倩, 刘婧. 河西走廊荒漠绿洲过渡带3种典型一年生藜科植物构件生长及生物量分配特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 25-38. |
| [14] | 张家驹, 于洁, 李明娜, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 龙瑞才. 蒺藜苜蓿lncRNA167及其剪切产物miR167c的鉴定和功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 164-180. |
| [15] | 汪精海, 李广, 银敏华, 齐广平, 康燕霞, 马彦麟. 调亏灌溉对高寒荒漠区人工混播草地土壤环境与牧草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 95-106. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||