

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 118-128.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021340
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
赵俊威( ), 李生仪, 孙延亮, 刘选帅, 马春晖, 张前兵(
), 李生仪, 孙延亮, 刘选帅, 马春晖, 张前兵( )
)
收稿日期:2021-09-13
修回日期:2021-11-29
出版日期:2022-09-20
发布日期:2022-08-12
通讯作者:
张前兵
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: qbz102@163.com基金资助:
Jun-wei ZHAO( ), Sheng-yi LI, Yan-liang SUN, Xuan-shuai LIU, Chun-hui MA, Qian-bing ZHANG(
), Sheng-yi LI, Yan-liang SUN, Xuan-shuai LIU, Chun-hui MA, Qian-bing ZHANG( )
)
Received:2021-09-13
Revised:2021-11-29
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-08-12
Contact:
Qian-bing ZHANG
摘要:
为探讨不同氮磷配施条件下紫花苜蓿细根周转及不同土层分布动态特征,分析苜蓿细根周转各指标之间的关系。采用双因素随机区组设计进行田间试验,设置4个施磷水平[0(P0)、50(P1)、100(P2)和150 kg·hm-2(P3)]和两个氮水平[0(N0)和120 kg·hm-2(N1)],共计8个处理,通过微根管根系监测0~60 cm的土层细根周转特征。结果表明:在相同施氮条件下,随着施磷量的增加,紫花苜蓿细根总现存量、细根表面积密度、细根生产量和死亡量呈先增加后降低的趋势,在P2条件下达到最大值,且P1、P2处理显著大于P0处理(P<0.05),在相同施磷条件下,N1处理显著大于N0处理。在不同土层中,在相同施氮条件下,随着施磷量的增加,苜蓿细根现存量在0~30 cm土层中呈先增加后降低的趋势,在0~15 cm土层中,P2处理苜蓿细根现存量显著高于其他处理(P<0.05)。不同处理下,苜蓿细根现存量主要集中在15~30 cm土层。在相同施氮条件下,随施磷量的增加,苜蓿细根周转率呈先降低后增加的趋势。细根周转率受细根现存量与细根死亡动态变化的影响较大。细根死亡量与周转率拟合的相关系数最大,拟合效果最好。综上所述,当施磷(P2O5)量为100 kg·hm-2、施氮(N)量为120 kg·hm-2时,能够显著增加苜蓿细根的现存量和根表面积密度,进而促进苜蓿根系周转和生长。
赵俊威, 李生仪, 孙延亮, 刘选帅, 马春晖, 张前兵. 不同氮磷水平下不同土层中紫花苜蓿细根周转特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 118-128.
Jun-wei ZHAO, Sheng-yi LI, Yan-liang SUN, Xuan-shuai LIU, Chun-hui MA, Qian-bing ZHANG. Fine root turnover of alfalfa in different soil horizons under different nitrogen and phosphorus levels[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 118-128.
处理 Treatment | TFRB (cm·cm-3) | RSAD (cm2·cm-2) | FRB (cm·cm-3) | FRP (cm·cm-3) | FRM (cm·cm-3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~15 cm | 15~30 cm | 30~45 cm | 45~60 cm | |||||
| 茬次Cut | ||||||||
| 第一茬First cut | 1.639 | 1.524 | 1.162 | 2.128 | 1.777 | 1.488 | - | - |
| 第二茬Second cut | 1.471 | 1.611 | 0.909 | 1.847 | 1.664 | 1.465 | 0.114 | 0.282 |
| 第三茬Third cut | 1.136 | 1.690 | 0.739 | 1.431 | 1.318 | 1.057 | 0.125 | 0.460 |
| 第四茬Fourth cut | 0.968 | 1.889 | 0.836 | 1.164 | 1.096 | 0.777 | 0.261 | 0.429 |
| SE | 0.135 | 0.265 | 0.157 | 0.371 | 0.271 | 0.297 | 0.067 | 0.078 |
| 氮Nitrogen (N) | ||||||||
| N0 | 1.180 | 1.479 | 0.737 | 1.748 | 1.467 | 0.767 | 0.140 | 0.388 |
| N1 | 1.428 | 1.877 | 1.086 | 1.537 | 1.460 | 1.627 | 0.193 | 0.392 |
| SE | 0.124 | 0.199 | 0.175 | 0.105 | 0.003 | 0.430 | 0.027 | 0.002 |
| 磷Phosphorus (P) | ||||||||
| P0 | 0.915 | 1.040 | 0.627 | 1.196 | 1.332 | 0.505 | 0.169 | 0.267 |
| P1 | 1.684 | 1.813 | 0.756 | 2.429 | 1.892 | 1.657 | 0.151 | 0.461 |
| P2 | 1.689 | 2.868 | 1.521 | 2.263 | 1.570 | 1.404 | 0.186 | 0.497 |
| P3 | 0.927 | 0.992 | 0.741 | 0.682 | 1.061 | 1.221 | 0.161 | 0.336 |
| SE | 0.383 | 0.760 | 0.356 | 0.729 | 0.306 | 0.428 | 0.013 | 0.093 |
| P值P value | ||||||||
| 茬次Cut | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 氮Nitrogen (N) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.339 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.037 |
| 磷Phosphorus (P) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 茬次×氮Cut×N | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 茬次×磷Cut×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 氮×磷N×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 茬次×氮×磷Cut×N×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
表1 紫花苜蓿细根生长相关分析和统计结果
Table 1 Correlation analysis and statistical results of fine root growth of alfalfa
处理 Treatment | TFRB (cm·cm-3) | RSAD (cm2·cm-2) | FRB (cm·cm-3) | FRP (cm·cm-3) | FRM (cm·cm-3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~15 cm | 15~30 cm | 30~45 cm | 45~60 cm | |||||
| 茬次Cut | ||||||||
| 第一茬First cut | 1.639 | 1.524 | 1.162 | 2.128 | 1.777 | 1.488 | - | - |
| 第二茬Second cut | 1.471 | 1.611 | 0.909 | 1.847 | 1.664 | 1.465 | 0.114 | 0.282 |
| 第三茬Third cut | 1.136 | 1.690 | 0.739 | 1.431 | 1.318 | 1.057 | 0.125 | 0.460 |
| 第四茬Fourth cut | 0.968 | 1.889 | 0.836 | 1.164 | 1.096 | 0.777 | 0.261 | 0.429 |
| SE | 0.135 | 0.265 | 0.157 | 0.371 | 0.271 | 0.297 | 0.067 | 0.078 |
| 氮Nitrogen (N) | ||||||||
| N0 | 1.180 | 1.479 | 0.737 | 1.748 | 1.467 | 0.767 | 0.140 | 0.388 |
| N1 | 1.428 | 1.877 | 1.086 | 1.537 | 1.460 | 1.627 | 0.193 | 0.392 |
| SE | 0.124 | 0.199 | 0.175 | 0.105 | 0.003 | 0.430 | 0.027 | 0.002 |
| 磷Phosphorus (P) | ||||||||
| P0 | 0.915 | 1.040 | 0.627 | 1.196 | 1.332 | 0.505 | 0.169 | 0.267 |
| P1 | 1.684 | 1.813 | 0.756 | 2.429 | 1.892 | 1.657 | 0.151 | 0.461 |
| P2 | 1.689 | 2.868 | 1.521 | 2.263 | 1.570 | 1.404 | 0.186 | 0.497 |
| P3 | 0.927 | 0.992 | 0.741 | 0.682 | 1.061 | 1.221 | 0.161 | 0.336 |
| SE | 0.383 | 0.760 | 0.356 | 0.729 | 0.306 | 0.428 | 0.013 | 0.093 |
| P值P value | ||||||||
| 茬次Cut | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 氮Nitrogen (N) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.339 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.037 |
| 磷Phosphorus (P) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 茬次×氮Cut×N | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 茬次×磷Cut×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 氮×磷N×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 茬次×氮×磷Cut×N×P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
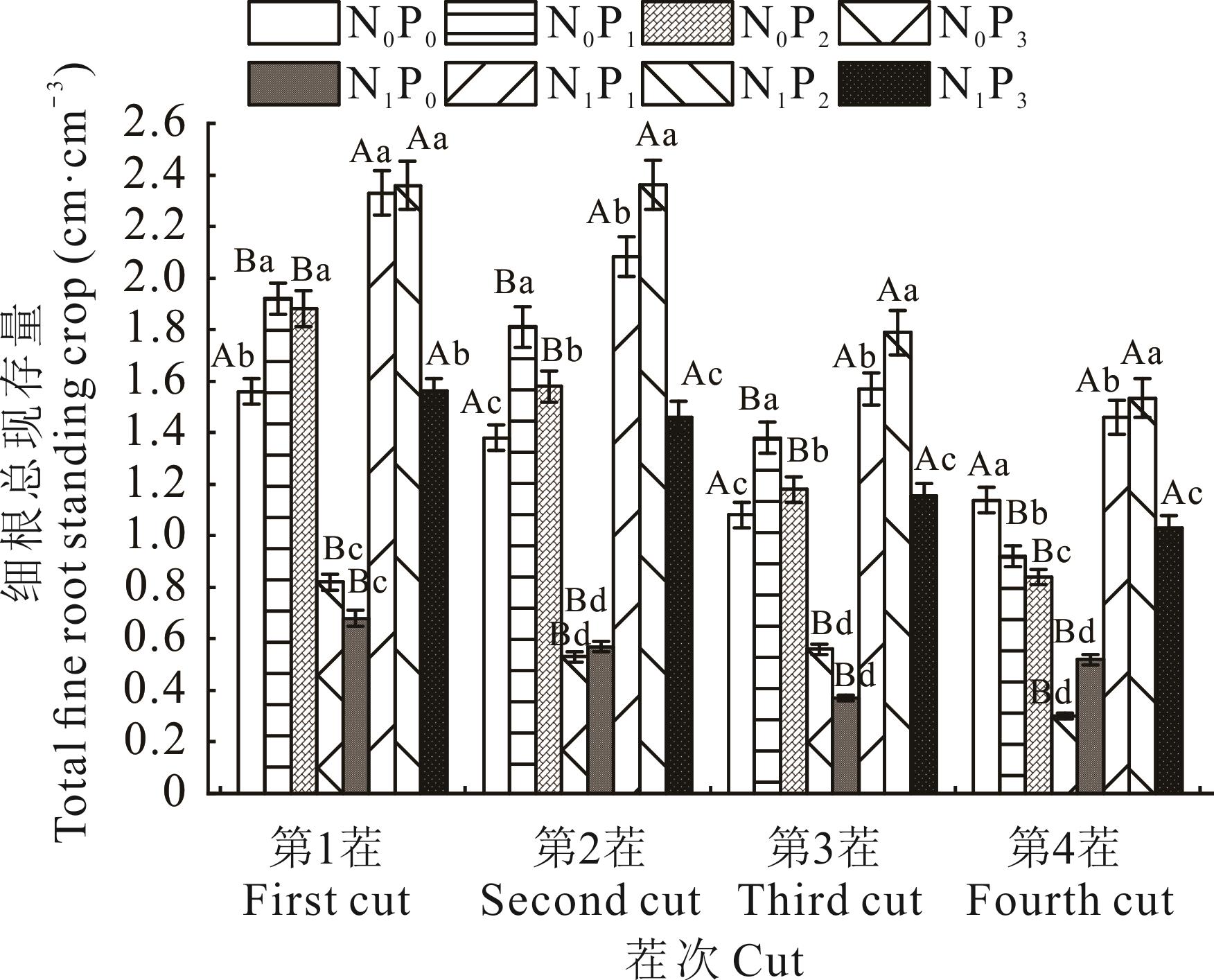
图1 苜蓿细根总现存量误差线表示标准偏差,不同小写字母表示相同施氮处理下,不同施磷处理间差异显著(P<0.05);不同大写字母表示相同施磷处理下,不同施氮处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。The error bar represents the standard deviation, different lowercase letters indicate that under the same nitrogen application, there are significant differences among different phosphorus application treatments (P<0.05). Different capital letters indicate that under the same phosphorus application treatment, there is significant difference among different nitrogen application treatments (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Total fine root standing crop of alfalfa
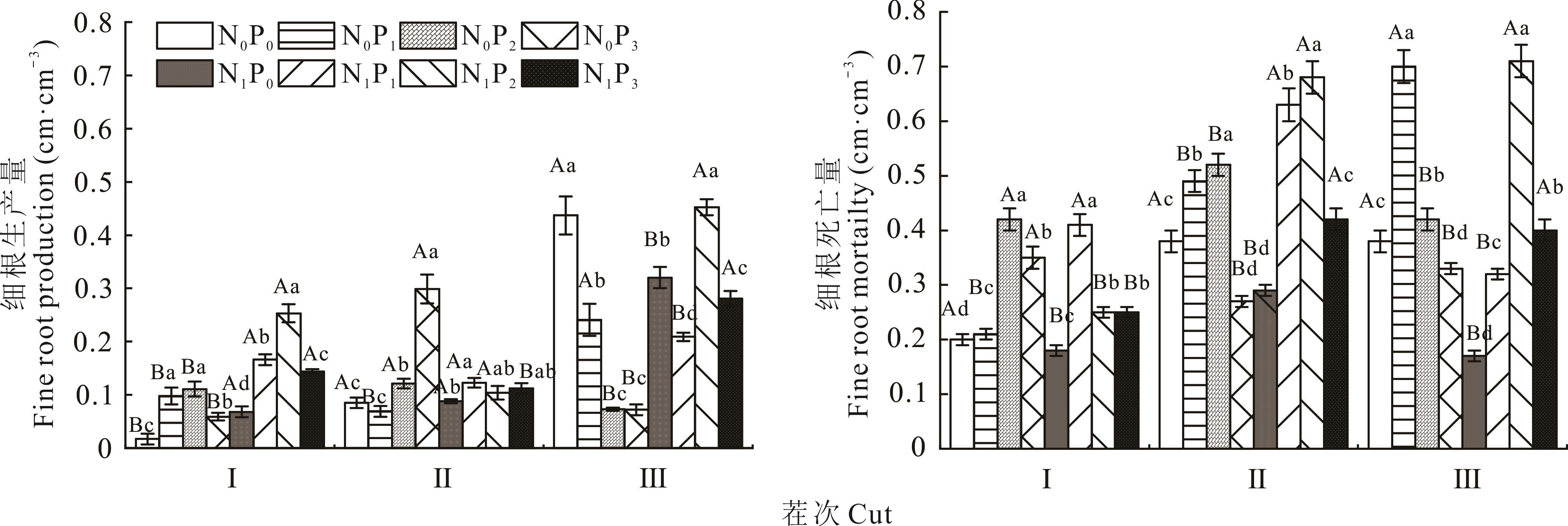
图4 不同施肥处理下苜蓿细根生产量和死亡量I: 第1茬~第2茬First cut-second cut; Ⅱ: 第2茬~第3茬Second cut-third cut; Ⅲ: 第3茬~第4茬Third cut-fourth cut.
Fig.4 Fine root production and mortality of alfalfa under different fertilization treatments
处理 Treatments | 年细根生产量 Annual production of fine root (cm·cm-3·a-1) | 年细根死亡量 Annual mortality of fine root (cm·cm-3·a-1) | 年细根最大现存量 Maximum annual standing crop of fine root (cm·cm-3) | 周转率 Turnover rate (a-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0P0 | 0.546±0.013B | 0.964±0.043E | 1.564±0.050D | 0.344±0.012C |
| N0P1 | 0.415±0.010F | 1.402±0.063B | 1.916±0.060B | 0.213±0.010D |
| N0P2 | 0.310±0.010G | 1.348±0.053C | 1.880±0.070C | 0.162±0.007E |
| N0P3 | 0.436±0.010E | 0.944±0.043E | 0.817±0.030E | 0.526±0.022B |
| N1P0 | 0.482±0.010D | 0.637±0.023F | 0.683±0.025F | 0.697±0.032A |
| N1P1 | 0.504±0.010C | 1.365±0.043C | 2.330±0.085A | 0.214±0.010D |
| N1P2 | 0.820±0.019A | 1.634±0.073A | 2.359±0.093A | 0.343±0.014C |
| N1P3 | 0.545±0.013B | 1.069±0.043D | 1.562±0.050D | 0.344±0.015C |
| N | ** | ns | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| N×P | ** | ** | ** | ** |
表2 苜蓿细根周转率
Table 2 Fine root turnover rate of alfalfa
处理 Treatments | 年细根生产量 Annual production of fine root (cm·cm-3·a-1) | 年细根死亡量 Annual mortality of fine root (cm·cm-3·a-1) | 年细根最大现存量 Maximum annual standing crop of fine root (cm·cm-3) | 周转率 Turnover rate (a-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0P0 | 0.546±0.013B | 0.964±0.043E | 1.564±0.050D | 0.344±0.012C |
| N0P1 | 0.415±0.010F | 1.402±0.063B | 1.916±0.060B | 0.213±0.010D |
| N0P2 | 0.310±0.010G | 1.348±0.053C | 1.880±0.070C | 0.162±0.007E |
| N0P3 | 0.436±0.010E | 0.944±0.043E | 0.817±0.030E | 0.526±0.022B |
| N1P0 | 0.482±0.010D | 0.637±0.023F | 0.683±0.025F | 0.697±0.032A |
| N1P1 | 0.504±0.010C | 1.365±0.043C | 2.330±0.085A | 0.214±0.010D |
| N1P2 | 0.820±0.019A | 1.634±0.073A | 2.359±0.093A | 0.343±0.014C |
| N1P3 | 0.545±0.013B | 1.069±0.043D | 1.562±0.050D | 0.344±0.015C |
| N | ** | ns | ** | ** |
| P | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| N×P | ** | ** | ** | ** |
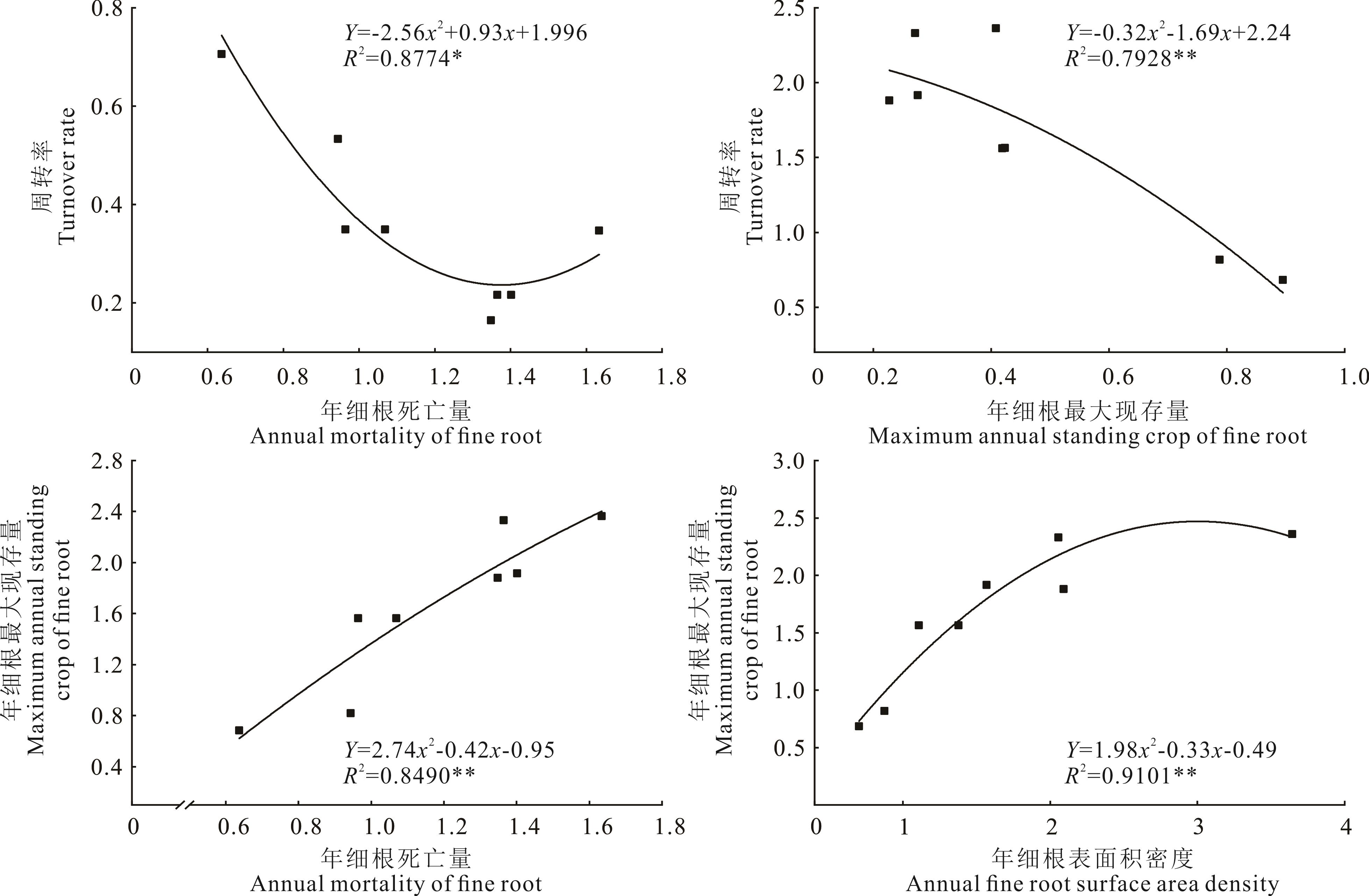
图5 苜蓿各指标的相关性分析*表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关,**表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关。* indicates significant correlation was found at the 0.05 level (bilateral), ** indicates significant correlation was found at the 0.01 level (bilateral).
Fig.5 Correlation coefficients between indexes of alfalfa
| 1 | Kumar A, Shahbaz M, Koirala M. Root trait plasticity and plant nutrient acquisition in phosphorus limited soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2019, 182(6): 1-8. |
| 2 | Yang W Z, Ma X, Yang W, et al. Seasonal dynamics of biomass, root turnover, and carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus storage in Zoige alpine marsh. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(5): 1285-1292. |
| 阳维宗, 马骁, 杨文, 等. 若尔盖草本沼泽生物量季节动态、根系周转及碳氮磷储量. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(5): 1285-1292. | |
| 3 | Ji J J, Zhang Q F, Yang Z J, et al. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on root biomass of subtropical Chinese fir saplings.Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(17): 6118-6125. |
| 纪娇娇, 张秋芳, 杨智杰, 等. 模拟氮沉降对中亚热带杉木幼树根系生物量的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(17): 6118-6125. | |
| 4 | Wang Y, Zhong Q L, Xu C B, et al. Effect of adding a combination of nitrogen and phosphorus on fine root morphology and soil microbes of Machilus pauhoi seedling. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(7): 2271-2278. |
| 王艳, 钟全林, 徐朝斌, 等. 短期氮磷配施对刨花楠细根形态及其土壤微生物的影响. 生态学报, 2018, 38(7): 2271-2278. | |
| 5 | Gao X M, Liu S R, Wang Y, et al. Effects of throughfall reduction and nitrogen addition on stoichiometry of leaf and fine root in Phyllostachys edulis forests. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(4): 1440-1450. |
| 高小敏, 刘世荣, 王一, 等. 穿透雨减少和氮添加对毛竹叶片和细根化学计量学的影响. 生态学报, 2021, 41(4): 1440-1450. | |
| 6 | Ding L Z, Xing Y J, Yan G Y, et al. Fine roots in northern forests: Response to atmospheric N deposition increase and temperature rise. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(11): 63-73. |
| 丁丽智, 邢亚娟, 闫国永, 等. 北方森林细根对大气N沉降增加和温度升高的响应. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(11): 63-73. | |
| 7 | Zhao J J, Lu G. Response of fine root carbohydrate content to soil nitrogen addition and its relationship with soil factors in a schrenk (Picea schrenkiana) forest. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2020, 40(3): 1-12. |
| 8 | Zhao J N, Liang Y, Liu Y, et al. Patterns and influence factors of fine root turnover in forest ecosystems. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(3): 308-317. |
| 赵佳宁, 梁韵, 柳莹, 等. 森林生态系统细根周转规律及影响因素. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 308-317. | |
| 9 | Ji W P, Wang J J, Zhao X C, et al. Fine root production and turnover of Alhagi sparsifolia community in arid area of Xinjiang, Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2013, 32(10): 2635-2640. |
| 冀卫萍, 王健健, 赵学春, 等. 干旱区骆驼刺群落细根生产与周转. 生态学杂志, 2013, 32(10): 2635-2640. | |
| 10 | Tang L T, Mao R, Wang C T, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on root characteristics of alpine meadow. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(9): 105-116. |
| 唐立涛, 毛睿, 王长庭, 等. 氮磷添加对高寒草甸植物群落根系特征的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 105-116. | |
| 11 | Peng Q, He H H, Zhang X C. Mechanisms of increasing alfalfa growth and phosphorus uptake by inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal under low phosphorus application level. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(2): 293-300. |
| 彭琪, 何红花, 张兴昌. 低磷环境下接种丛枝菌根真菌促进紫花苜蓿生长和磷素吸收的机理. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(2): 293-300. | |
| 12 | Zeng W F, Li Y S, Cui X N, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on the distribution of photosynthates in roots, stems, leaves and alfalfa resistance to thrips. Plant Protection, 2021, 47(2): 109-115. |
| 曾文芳, 李亚姝, 崔晓宁, 等. 施氮对苜蓿根茎叶光合产物分配及抗蓟马的影响. 植物保护, 2021, 47(2): 109-115. | |
| 13 | Li D Z, Zeng N B, Zhang Z F, et al. Effects of waterlogging stress on the root growth of alfalfa under different phosphorus level. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(6): 1563-1571. |
| 李丹竹, 曾宁波, 张志飞, 等. 渍水胁迫对不同磷水平下紫花苜蓿根系生长的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(6): 1563-1571. | |
| 14 | Liu J Y, Hui J F, Sun M Y, et al. Effects of phosphorus application and inoculation arbuscular mycorrhizae fungi (AMF) and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on dry matter yield and phosphorus use efficiency of alfalfa. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(19): 142-149. |
| 刘俊英, 回金峰, 孙梦瑶, 等. 施磷水平和接种AMF与解磷细菌对苜蓿产量及磷素利用效率的影响. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(19): 142-149. | |
| 15 | Kong D N, Kang G D, Li P, et al. Effects of combined application of organic fertilizer on the active components of organic carbon in upland purple soil under reducing chemical fertilizer application. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(4): 1073-1080. |
| 孔德宁, 康国栋, 李鹏, 等. 化肥减施条件下配施有机肥对旱地紫色土有机碳活性组分的影响. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(4): 1073-1080. | |
| 16 | Li W B, Jin C J, Guan D X, et al. The effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on plant root traits: A meta-analysis. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2015, 82(5): 112-118. |
| 17 | Guo D L, Fan P P. Four hypotheses about the effects of soil nitrogen availability on fine root production and turnover. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2007, 18(10): 2354-2360. |
| 郭大立, 范萍萍. 关于氮有效性影响细根生产量和周转率的四个假说. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(10): 2354-2360. | |
| 18 | Sun Y M, Miao X R, Liu J Y, et al. Fine root turnover and distribution characteristics in different soil layers of three alfalfa varieties under drip irrigation. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(10): 91-100. |
| 孙艳梅, 苗晓茸, 刘俊英, 等. 滴灌条件下3种紫花苜蓿细根周转及不同土层分布特征. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 91-100. | |
| 19 | Kerstin P, Christoph L, Jürgen H. Topography as a factor driving small-scale variation in tree fine root traits and root functional diversity in a species-rich tropical montane forest. New Phytologist, 2020, 230(1): 129-138. |
| 20 | Zhang J F, Geng Q L, Liang Z, et al. Effects of drip fertigation around root zone on yield and quality of red jujube and utilization of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in Xinjiang. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(12): 65-71. |
| 张计峰, 耿庆龙, 梁智, 等. 根区孔下滴灌施肥对新疆红枣产量品质和氮磷钾利用影响. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(12): 65-71. | |
| 21 | Li Q, Huang Y X, Zhou D W, et al. Mechanism of the trade-off between biological nitrogen fixation and phosphorus acquisition strategies of herbaceous legumes under nitrogen and phosphorus addition. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2021, 45(3): 286-297. |
| 李强, 黄迎新, 周道玮, 等. 土壤氮磷添加下豆科草本植物生物固氮与磷获取策略的权衡机制. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(3): 286-297. | |
| 22 | Gao Y, Tian Q Y, Shi F L, et al. Comparative studies on adaptive strategies of Medicago falcata and M. truncatula to phosphorus deficiency in soil. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2011, 35(6): 632-640. |
| 高艳, 田秋英, 石凤翎, 等. 黄花苜蓿与蒺藜苜蓿对土壤低磷胁迫适应策略的比较研究. 植物生态学报, 2011, 35(6): 632-640. | |
| 23 | Fan X Y, Yang H S, Gao J L, et al. Effects of phosphorus application on root characteristics of super-high-yield spring maize. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2012, 18(3): 562-570. |
| 范秀艳, 杨恒山, 高聚林, 等. 超高产栽培下磷肥运筹对春玉米根系特性的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(3): 562-570. | |
| 24 | Yu X F, Gao J L, Ye J, et al. Effects of deep loosening with nitrogen deep placement on root growth, grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of super high-yield spring maize. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2013, 21(1): 114-119. |
| 于晓芳, 高聚林, 叶君, 等. 深松及氮肥深施对超高产春玉米根系生长、产量及氮肥利用效率的影响. 玉米科学, 2013, 21(1): 114-119. | |
| 25 | Zhang F S, Shen J B, Jing J Y, et al. Rhizosphere processes and management for improving nutrient use efficiency and crop productivity. Advances in Agronomy, 2010, 107(5): 1-32. |
| 26 | Fernandes A M, Soratto R P, Gonsales J R. Root morphology and phosphorus uptake by potato cultivars grown under deficient and sufficient phosphorus supply. Scientia Horticulturae, 2014, 180(28): 190-198. |
| 27 | Wang W X, Sun M, Lin W, et al. Effects of phosphorus fertilizer on root characteristics, uptake and utilization of phosphorus and yield of dryland wheat with contrasting yearly rainfall pattern. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(3): 895-905. |
| 王文翔, 孙敏, 林文, 等. 不同降雨年型磷肥对旱地小麦根系特征、磷素吸收利用和产量的影响. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(3): 895-905. | |
| 28 | Niu Y F, Chai R S, Jin G L, et al. Responses of root architecture development to low phosphorus availability: A review. Annals of Botany, 2013, 112: 391-408. |
| 29 | Zou Y X, Zhong Q L, You Y L, et al. Short-term effects of nitrogen and water treatments on fine root order morphology of Machilus pauhoi seedlings. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(7): 2323-2329. |
| 邹宇星, 钟全林, 游雅玲, 等. 短期氮-水处理对刨花楠幼苗细根根序形态的影响. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(7): 2323-2329. | |
| 30 | Su Z T, Wu C Y, He T H, et al. Soil nutrient characteristics and plant response in meadow wetland in the Yinchuan plain. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(4): 816-823. |
| 苏芝屯, 吴春燕, 何彤慧, 等. 银川平原草甸湿地土壤养分特征与植物响应. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(4): 816-823. | |
| 31 | Yu L Z, Ding G Q, Zhu J J, et al. Effects of fertilization on nutrient concentrations of different root orders’ fine roots in Larix kaempferi plantation. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(4): 747-753. |
| 于立忠, 丁国泉, 朱教君, 等. 施肥对日本落叶松不同根序细根养分浓度的影响. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(4): 747-753. | |
| 32 | Chen L N, Liu X C, Sun Z X, et al. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on dry matter accumulation, distribution and yield of grape under alternate partial root-zone drip irrigation. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(5): 1807-1815. |
| 陈丽楠, 刘秀春, 孙占祥, 等. 交替根区滴灌下不同施氮量对葡萄干物质积累、分配和产量的影响. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(5): 1807-1815. | |
| 33 | Yu M, Cai J H, Xue L. Responses of fine root morphology of Cinnamomum camphora seedlings to nitrogen and phosphorus additions and planting density. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(20): 7641-7648. |
| 余明, 蔡金桓, 薛立. 樟树(Cinnamomum camphora)幼苗细根形态对氮磷添加和幼苗密度的响应. 生态学报, 2019, 39(20): 7641-7648. | |
| 34 | Li J, Pan P, Wang C T, et al. Root dynamics of artificial grassland for swards of differing ages in the “Three-River Source” region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 28-40. |
| 李洁, 潘攀, 王长庭, 等. 三江源区不同建植年限人工草地根系动态特征. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 28-40. | |
| 35 | Zhang X P, Yin Y, Yu L Z, et al. Influence of water and soil nutrients on biomass and productivity of fine tree roots: A review. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College, 2010, 27(4): 606-613. |
| 张小朋, 殷有, 于立忠, 等. 土壤水分与养分对树木细根生物量及生产力的影响. 浙江林学院学报, 2010, 27(4): 606-613. | |
| 36 | Zhang J Y, Wang W, Zeng H. Fine root productivity and turnover rate respond nonlinearly to increased nitrogen availability. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2018, 54(4): 828-838. |
| 张江勇, 王娓, 曾辉. 樟子松人工林细根生产、周转和碳归还对施氮的响应. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 54(4): 828-838. | |
| 37 | Zi H B, Chen Y, Hu L, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on root dynamics in an alpine meadow, Northwestern Sichuan. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2018, 42(1): 38-49. |
| 字洪标, 陈焱, 胡雷, 等. 氮肥添加对川西北高寒草甸植物群落根系动态的影响. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(1): 38-49. |
| [1] | 苗阳阳, 张艳蕊, 宋标, 刘旭桐, 张安琪, 吕金泽, 张浩, 张小华, 欧阳佳慧, 李旺, 曲善民. 碱蓬根际和内生细菌菌株对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 107-117. |
| [2] | 周大梁, 石薇, 蒋紫薇, 魏正业, 梁欢欢, 贾倩民. 沟垄集雨下密度和施氮对黄土高原青贮玉米叶片酶活性及水氮利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 126-143. |
| [3] | 刘晓婷, 姚拓. 高寒草地耐低温植物根际促生菌的筛选鉴定及特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 178-187. |
| [4] | 赵建涛, 岳亚飞, 张前兵, 马春晖. 不同秋眠级紫花苜蓿品种抗寒性对新疆北疆地区覆雪厚度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 24-34. |
| [5] | 牛伟玲, 陈辉, 侯慧新, 郭晨睿, 马娇林, 武建双. 10年禁牧未改变藏西北高寒荒漠植物水氮利用效率[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 35-48. |
| [6] | 田骄阳, 王秋霞, 郑淑文, 刘文献. 全基因组水平蒺藜苜蓿CPP基因家族的鉴定及表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 111-121. |
| [7] | 刘彩婷, 毛丽萍, 阿依谢木, 于应文, 沈禹颖. 紫花苜蓿与垂穗披碱草混播比例对其抗寒生长生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 133-143. |
| [8] | 蒋紫薇, 刘桂宇, 安昊云, 石薇, 常生华, 张程, 贾倩民, 侯扶江. 种植密度与施氮对玉米/秣食豆间作系统饲草产量、品质和氮肥利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 157-171. |
| [9] | 王雪萌, 何欣, 张涵, 宋瑞, 毛培胜, 贾善刚. 基于多光谱成像技术快速无损检测紫花苜蓿人工老化种子[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 197-208. |
| [10] | 张铎, 李岚涛, 林迪, 郑龙辉, 耿赛男, 石纹碹, 盛开, 苗玉红, 王宜伦. 施磷水平对菊芋块茎产量、品质、植株生理特性与磷利用率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 139-149. |
| [11] | 陆姣云, 张鹤山, 田宏, 熊军波, 刘洋. 氮沉降影响草地生态系统土壤氮循环过程的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 221-234. |
| [12] | 李洋, 王毅, 韩国栋, 孙建, 汪亚峰. 青藏高原高寒草地土壤微生物量碳氮含量特征及其控制要素[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 50-60. |
| [13] | 刘亚男, 于人杰, 高燕丽, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 武志海, 王珍. 蒺藜苜蓿膜联蛋白MtANN2基因的表达模式及盐胁迫下的功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 124-134. |
| [14] | 李满有, 李东宁, 王斌, 李小云, 沈笑天, 曹立娟, 倪旺, 王腾飞, 兰剑. 不同苜蓿品种混播和播种量对牧草产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 61-75. |
| [15] | 张欢, 牟怡晓, 张桂杰. 添加枸杞副产物对紫花苜蓿青贮发酵品质及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 136-144. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||