

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 40-52.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023006
李鸿1( ), 谌芸1(
), 谌芸1( ), 刘枭宏2, 刘有斌1, 都艺芝1
), 刘枭宏2, 刘有斌1, 都艺芝1
收稿日期:2023-01-05
修回日期:2023-03-27
出版日期:2023-11-20
发布日期:2023-09-27
通讯作者:
谌芸
作者简介:E-mail: sy22478@126.com基金资助:
Hong LI1( ), Yun CHEN1(
), Yun CHEN1( ), Xiao-hong LIU2, You-bin LIU1, Yi-zhi DU1
), Xiao-hong LIU2, You-bin LIU1, Yi-zhi DU1
Received:2023-01-05
Revised:2023-03-27
Online:2023-11-20
Published:2023-09-27
Contact:
Yun CHEN
摘要:
为探明紫色土坡耕地不同地埂草篱根系土壤抗蚀和抗冲性的差异,以拉巴豆和紫花苜蓿地埂草篱为研究对象,以未种植草篱地埂为对照(CK),系统性地研究了土壤抗蚀和抗冲性能对草篱种类的响应,阐明了二者与根系形态特征及土壤理化性质间的耦合关系。结果表明:1)拉巴豆整株根系长度、根表面积和土壤有机质含量显著高于紫花苜蓿,且土壤含水率、总孔隙度和非毛管孔隙度显著高于紫花苜蓿和CK(P<0.05);2)土壤水稳性团聚体平均质量直径、平均几何直径及微团聚体团聚度大小表现为拉巴豆>紫花苜蓿,水稳性团聚体结构破坏率和微团聚体分散系数大小表现为紫花苜蓿>拉巴豆; 3)拉巴豆土壤抗冲指数及抗冲指数变化值均大于紫花苜蓿,抗冲指数是冲刷时间的对数函数,抗冲指数变化值是冲刷时间的二次函数;4)冗余分析的结果表明整株分叉数、根尖数、土壤有机质及非毛管孔隙度对土壤抗蚀和抗冲性能的影响较大,逐步回归的结果表明>0.5 mm的水稳性团聚体结构破坏率是影响土壤抗冲指数的决定因子。综上,拉巴豆地埂草篱土壤抗蚀和抗冲性能优于紫花苜蓿。本研究可为紫色土坡耕地地埂草篱技术的推广应用提供理论依据。
李鸿, 谌芸, 刘枭宏, 刘有斌, 都艺芝. 紫色土坡耕地地埂草篱根系土壤抗蚀与抗冲性能特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 40-52.
Hong LI, Yun CHEN, Xiao-hong LIU, You-bin LIU, Yi-zhi DU. Factors affecting the soil erosion and scouring resistance of bank hedgerows in purple soil sloping cropland[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(11): 40-52.
图1 试验小区示意a为对照地埂未种植草篱小区,b为紫花苜蓿地埂草篱小区,c为拉巴豆地埂草篱小区。a is the control plots with no bank hedgerows, b is the plots with M. sativa bank hedgerows and c is the plots with D. lablab bank hedgerows.
Fig.1 Schematic of test plots
地埂草篱种类 Types of grasses hedgerows | 根系长度 Root length (cm) | 根系表面积 Root surface area (cm2) | 根系体积 Root volume (cm3) | 根尖数 Root tips | 根分枝数 Root forks | 根分叉数 Root crossings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拉巴豆 D. lablab | 299.73±44.75a | 40.84±10.20a | 0.45±0.17a | 1433.22±626.25a | 1965.78±1016.01a | 345.67±259.71a |
| 紫花苜蓿 M. sativa | 145.72±39.33b | 25.77±14.39b | 0.56±0.69a | 977.78±477.07a | 891.00±416.98a | 141.89±108.72a |
表1 不同地埂草篱根系形态特征
Table 1 Root parameters of different bank hedgerows
地埂草篱种类 Types of grasses hedgerows | 根系长度 Root length (cm) | 根系表面积 Root surface area (cm2) | 根系体积 Root volume (cm3) | 根尖数 Root tips | 根分枝数 Root forks | 根分叉数 Root crossings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拉巴豆 D. lablab | 299.73±44.75a | 40.84±10.20a | 0.45±0.17a | 1433.22±626.25a | 1965.78±1016.01a | 345.67±259.71a |
| 紫花苜蓿 M. sativa | 145.72±39.33b | 25.77±14.39b | 0.56±0.69a | 977.78±477.07a | 891.00±416.98a | 141.89±108.72a |
地埂草篱种类 Types of grasses hedgerows | 土壤含水率 Soil moisture (%) | 土壤容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 总孔隙度 Total porosity (%) | 毛管孔隙度 Capillary porosity (%) | 非毛管孔隙度 Noncapillary porosity (%) | 田间持水量 Field capacity (%) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拉巴豆D. lablab | 16.93±0.32a | 1.20±0.01c | 54.72±0.33a | 27.92±2.73a | 26.79±3.00a | 23.26±2.15ab | 38.69±10.00a |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 11.93±0.32c | 1.30±0.01b | 52.42±0.33b | 31.92±2.73a | 19.99±3.00b | 25.26±2.15a | 21.77±5.03b |
| 对照CK | 15.65±0.46b | 1.41±0.03a | 46.89±1.02c | 28.34±1.02a | 18.55±1.31b | 20.14±0.88b | 30.99±4.00ab |
表2 不同地埂草篱土壤理化性质
Table 2 Soil physicochemical properties of different bank hedgerows
地埂草篱种类 Types of grasses hedgerows | 土壤含水率 Soil moisture (%) | 土壤容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 总孔隙度 Total porosity (%) | 毛管孔隙度 Capillary porosity (%) | 非毛管孔隙度 Noncapillary porosity (%) | 田间持水量 Field capacity (%) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拉巴豆D. lablab | 16.93±0.32a | 1.20±0.01c | 54.72±0.33a | 27.92±2.73a | 26.79±3.00a | 23.26±2.15ab | 38.69±10.00a |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 11.93±0.32c | 1.30±0.01b | 52.42±0.33b | 31.92±2.73a | 19.99±3.00b | 25.26±2.15a | 21.77±5.03b |
| 对照CK | 15.65±0.46b | 1.41±0.03a | 46.89±1.02c | 28.34±1.02a | 18.55±1.31b | 20.14±0.88b | 30.99±4.00ab |
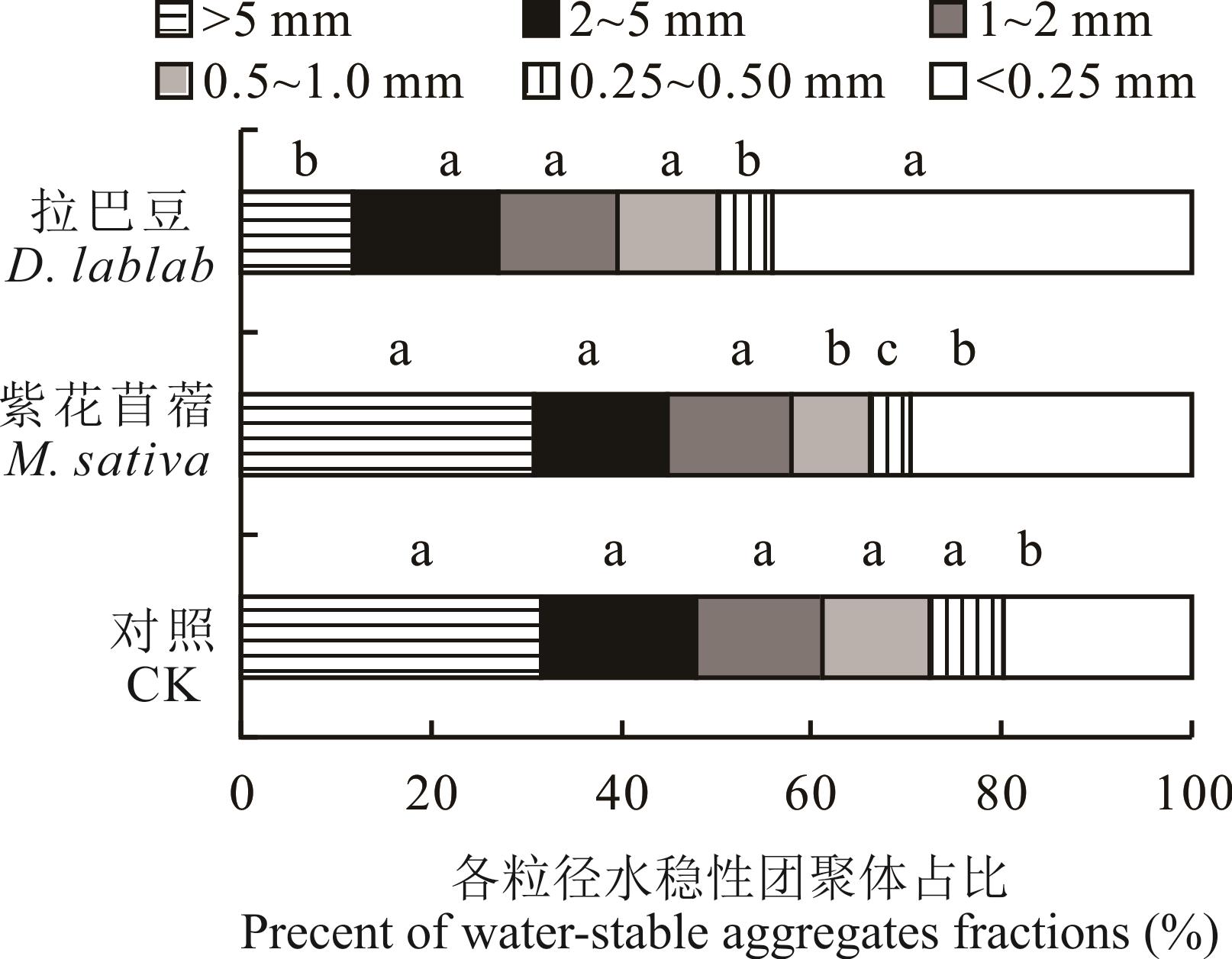
图2 地埂草篱土壤水稳性团聚体含量不同小写字母表示不同地埂草篱间存在显著差异(P<0.05),n=3,下同。Different small letters indicate that there is significant difference between different bank hedgerows (P<0.05), n=3, the same below.
Fig.2 Soil water-stable aggregates content of bank hedgerows
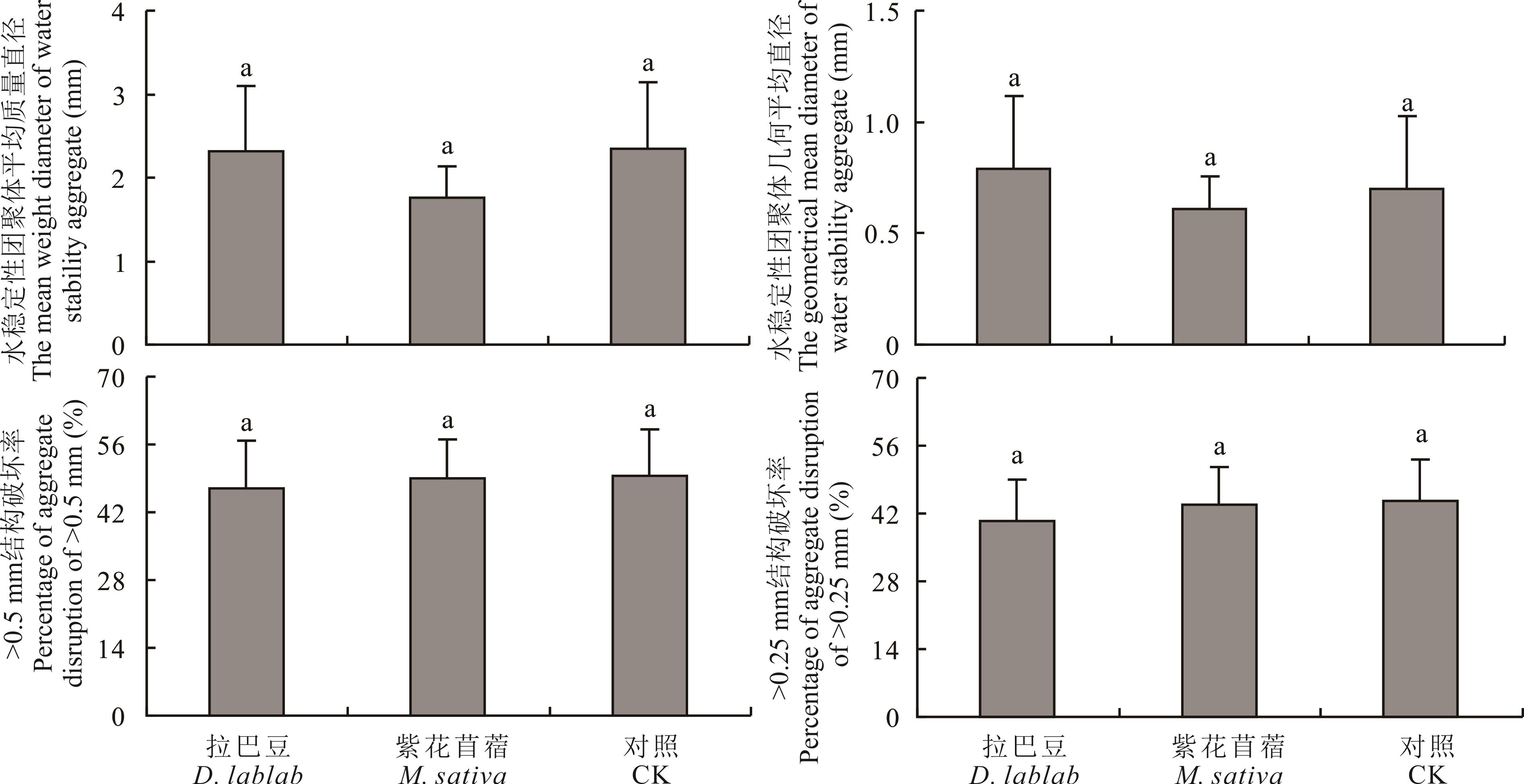
图3 地埂草篱土壤水稳性团聚体平均质量直径、几何平均直径、>0.5 mm结构破坏率、>0.25 mm结构破坏率
Fig.3 MWDb, GMDb,PAD0.25 and PAD0.5 of soil water-stable aggregates affected by bank hedgerows

图8 地埂草篱根系特性与土壤抗蚀、抗冲性的冗余分析L: 拉巴豆D. lablab; Z: 紫花苜蓿M. sativa.下同The same below.
Fig.8 Redundancy analysis among soil anti-erodibility and anti-scouribility of root parameters of bank hedgerows
变量 Variable | 非标准化模型 Nonstandardized coefficient model | 标准化模型 Standardized coefficient model | 显著性 P-level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非标准化回归系数Nonstandardized regression coefficient | 标准误Standard error | 标准化回归系数Standardized regression coefficient | T检验结果值Resulting value of t-test | ||
| 截距Intercept | -4.20 | 3.44 | -1.22 | 0.28 | |
| >0.5 mm结构破坏率Percentage of aggregate disruption of >0.5 mm | -0.21 | 0.07 | 0.073 | 2.86 | 0.04 |
表3 土壤抗冲指数与土壤抗蚀指标间的逐步多元回归模型参数
Table 3 Stepwise multiple regression models for ASI and soil anti-erodibility properties
变量 Variable | 非标准化模型 Nonstandardized coefficient model | 标准化模型 Standardized coefficient model | 显著性 P-level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非标准化回归系数Nonstandardized regression coefficient | 标准误Standard error | 标准化回归系数Standardized regression coefficient | T检验结果值Resulting value of t-test | ||
| 截距Intercept | -4.20 | 3.44 | -1.22 | 0.28 | |
| >0.5 mm结构破坏率Percentage of aggregate disruption of >0.5 mm | -0.21 | 0.07 | 0.073 | 2.86 | 0.04 |
| 1 | Cheng L, Guo Z L. Knowledge map of purple soil erosion study (1960~2018) -Quantitative analysis based on the CiteSpace. Subtropical Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 32(1): 1-10, 26. |
| 程谅, 郭忠录. 紫色土土壤侵蚀研究的知识图谱(1960~2018)——基于CiteSpace计量分析. 亚热带水土保持, 2020, 32(1): 1-10, 26. | |
| 2 | Zhang J L, Shi D M, Liu Y, et al. Effects of soil bulk density and water content on shear strength of cultivated-layer in purple soil sloping farmland. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(3): 162-167, 174. |
| 张健乐, 史东梅, 刘义, 等. 土壤容重和含水率对紫色土坡耕地耕层抗剪强度的影响. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(3): 162-167, 174. | |
| 3 | Bao Y H, Cong P J, Feng W, et al. Comprehensive management system of soil and water loss in purple soil area of southwestern China. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 38(3): 143-150. |
| 鲍玉海, 丛佩娟, 冯伟, 等. 西南紫色土区水土流失综合治理技术体系. 水土保持通报, 2018, 38(3): 143-150. | |
| 4 | Ren L H, Jia T H, Li X F, et al. Effects of ridge hedgerows on soil physical properties of sloping farmland in Liaodong mountain area. Technology of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018(2): 6-8. |
| 任丽华, 贾天会, 李欣峰, 等. 辽东山区坡耕地地埂植物篱对土壤物理性状的影响. 水土保持应用技术, 2018(2): 6-8. | |
| 5 | Qiang J J, Yan Z H, Chen Y, et al. Factors affecting the shear strength of root-soil complexes from three types of grass hedgerows in a karst area. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 27-37. |
| 强娇娇, 颜哲豪, 谌芸, 等. 喀斯特区3种草篱根-土复合体抗剪性能及其影响因素. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 27-37. | |
| 6 | Tang H, Chen Y, Liu X H, et al. Study on the mechanic features of root and root-soil matrix of Dolichos lablab L. hedgerows on the slopes of the karst area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(16): 6114-6125. |
| 唐菡, 谌芸, 刘枭宏, 等. 喀斯特坡地拉巴豆地埂篱根及根-土复合体力学特性. 生态学报, 2019, 39(16): 6114-6125. | |
| 7 | Ma X, Wang W W, Zheng J K, et al. Effects of hedgerows on runoff and sediment yield and microtopography on purple soil sloping farmland. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(6): 85-89, 188. |
| 马星, 王文武, 郑江坤, 等. 植物篱措施对紫色土坡耕地产流产沙及微地形的影响. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(6): 85-89, 188. | |
| 8 | Guo P C, Zhang Z Z, Yang K B. A study on soil anti-erodibility prediction and evaluation method in loess region. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 1992(3): 48-51, 58. |
| 郭培才, 张振中, 杨开宝. 黄土区土壤抗蚀性预报及评价方法研究. 水土保持学报, 1992(3): 48-51, 58. | |
| 9 | Bai X M, Han Y Z, Guo H Q. Study on soil anti-erodibility of different vegetation restoration types in Guandi Mountain. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 28(2): 79-84. |
| 白秀梅, 韩有志, 郭汉清. 关帝山不同植被恢复类型土壤抗蚀性研究. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(2): 79-84. | |
| 10 | Wang Z Z, Liu X H, Chen Y, et al. Study on soil anti-erodibility between sedimentation zone in front of hedgerows and ridge behind hedgerows in purple soil area. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(5): 61-67. |
| 王针针, 刘枭宏, 谌芸, 等. 紫色土区植物篱篱前淤积带与篱下土坎土壤抗蚀性研究. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(5): 61-67. | |
| 11 | Xie X J, Li Y F. Degree of coupling relationship between anti-erodibility and soil factors of purple soil in different Eucalyptus grandis plantations. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(1): 97-102. |
| 谢贤健, 李永飞. 不同巨桉林下紫色土壤抗蚀性与土壤因子的耦合关系分析. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(1): 97-102. | |
| 12 | Zhao J M, Xu C L, Ma R, et al. Study on soil anti-erodibility of different alpine shrub grassland in eastern Qilian Mountain. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2016, 30(5): 119-123. |
| 赵锦梅, 徐长林, 马瑞, 等. 东祁连山不同高寒灌丛草地土壤抗蚀性研究. 水土保持学报, 2016, 30(5): 119-123. | |
| 13 | Guo M M, Wang W L, Shi Q H, et al. Soil anti-scouribility of abandoned land and its relationship with influencing factors in Loess Plateau Gully region. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(10): 129-136. |
| 郭明明, 王文龙, 史倩华, 等. 黄土高塬沟壑区退耕地土壤抗冲性及其与影响因素的关系. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(10): 129-136. | |
| 14 | Li Y, Wu Q X, Zhu X M, et al. Studies on the intensification of soil anti-scourability by plant roots in the loess plateau——I. the increasing effect of soil anti-scourability by the roots of Chinese pine. Acta Conservation Soil et Aquae Sinica, 1990, 4(1): 1-5, 10. |
| 李勇, 吴钦孝, 朱显谟, 等. 黄土高原植物根系提高土壤抗冲性能的研究——Ⅰ.油松人工林根系对土壤抗冲性的增强效应. 水土保持学报, 1990, 4(1): 1-5, 10. | |
| 15 | Xiao J B, Sun B Y, Li Z B, et al. Variation characteristics of aeolian sandy soil anti-scourability under freezing and thawing conditions. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 2017(1): 37-40, 68. |
| 肖俊波, 孙宝洋, 李占斌, 等. 冻融条件下土壤抗冲性的变化特征. 中国水土保持, 2017(1): 37-40, 68. | |
| 16 | Osman N, Abdullah M N, Abdullah C H. Pull-out and tensile strength properties of two selected tropical trees. Sains Malaysiana, 2011, 40(6): 577-585. |
| 17 | Chen Y, He B H, Lian C X, et al. Root-soil system anti-scourability on steep slopes in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(16): 5173-5181. |
| 谌芸, 何丙辉, 练彩霞, 等. 三峡库区陡坡根-土复合体抗冲性能. 生态学报, 2016, 36(16): 5173-5181. | |
| 18 | Liu X H, Chen Y, Yan Z H, et al. The effects of grass hedgerow roots on shear strength and scouring resistance of root-soil complexes in the purple soil region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(11): 98-107. |
| 刘枭宏, 谌芸, 颜哲豪, 等. 紫色土区草篱根系对其根-土复合体抗剪和抗冲性能的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 98-107. | |
| 19 | Wang J C, Yang J Y, Shi C Q, et al. Analysis of soil anti-erodibility of different typical forests in Beichuan Area. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(1): 71-75. |
| 王俭成, 杨建英, 史常青, 等. 北川地区典型林分土壤抗蚀性分析. 水土保持学报, 2013, 27(1): 71-75. | |
| 20 | Fattet M, Fu Y, Ghestem M, et al. Effects of vegetation type on soil resistance to erosion: Relationship between aggregate stability and shear strength. Catena, 2011, 87(1): 60-69. |
| 21 | Sha X Y, Li K, Wang W L, et al. Characteristics of soil anti-scouribility in gully head wall of grass-covering on the gullied Loess Plateau, Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(1): 133-140. |
| 沙小燕, 李魁, 王文龙, 等. 黄土高塬沟壑区草地沟头立壁土壤抗冲性特征. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(1): 133-140. | |
| 22 | Liu Z, Yang R, Pei Y D. Soil erosion resistance characteristics of Zanthoxylum bungeanum and Lonicera japonica forest land in canyon areas of karst plateau. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2019, 56(2): 466-474. |
| 刘志, 杨瑞, 裴仪岱. 喀斯特高原峡谷区顶坛花椒与金银花林地土壤抗侵蚀特征. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(2): 466-474. | |
| 23 | Xu W X, Bao Y H, Wei J, et al. Impacts of the typical herbaceous plant roots on soil scour resistance in the reservoir riparian zone. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(4): 65-71, 109. |
| 徐文秀, 鲍玉海, 韦杰, 等. 水库消落带典型草本植物根系对土壤抗冲性能的影响. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(4): 65-71, 109. | |
| 24 | Nanjing Soil Institute of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Soil physical properties analysis. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1978. |
| 中国科学院南京土壤研究所土壤物理研究室. 土壤物理性质测定法. 上海: 上海科技出版社, 1978. | |
| 25 | Li T Y, He B H, Tian J L, et al. Soil physical and chemical properties and soil infiltration characteristics of five agroforestry intercropping types in Bishan, Chongqing. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(4): 103-108, 200. |
| 李天阳, 何丙辉, 田家乐, 等. 重庆璧山5种典型农林混作模式土壤理化性质及水分入渗特性. 水土保持学报, 2013, 27(4): 103-108, 200. | |
| 26 | Zhang C, Liu G B, Xue S, et al. Fractal features of rhizosphere soil microaggregate and particle-size distribution under different vegetation types in the hilly-gully region of Loess Plateau. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(3): 507-515. |
| 张超, 刘国彬, 薛萐, 等. 黄土丘陵区不同植被类型根际土壤微团聚体及颗粒分形特征. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(3): 507-515. | |
| 27 | Zhou G Y, Xiong X. Exploration history of soil organic carbon formation mechanisms. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 2019, 27(5): 481-490. |
| 周国逸, 熊鑫. 土壤有机碳形成机制的探索历程. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2019, 27(5): 481-490. | |
| 28 | Tong C H, Wang H, Tan S, et al. Effects of economic fruit forest planting on the stability of red soil aggregates in the subtropical hilly area. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(4): 1012-1020. |
| 童晨晖, 王辉, 谭帅, 等. 亚热带丘岗区经果林种植对红壤团聚体稳定性的影响. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(4): 1012-1020. | |
| 29 | Huang Z, Tian F P, Liu Y, et al. Effects of different grassland types on particle size distribution and stability of water stable aggregate on the Loess Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(11): 216-221. |
| 黄泽, 田福平, 刘玉, 等. 黄土高原不同草地类型对水稳性团聚体粒径分布及稳定性的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 216-221. | |
| 30 | Lu Q Q, Wang E H, Chen X W. Effect of mechanical compaction on soil micro-aggregate composition and stability of black soil. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(11): 54-59. |
| 卢倩倩, 王恩姮, 陈祥伟. 模拟机械压实对黑土微团聚体组成及稳定性的影响. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(11): 54-59. | |
| 31 | Gong W, Hu T X, Wang J Y, et al. Fractal features of soil microaggregates in soils under natural and regenerated evergreen broadleaved forests in south Sichuan Province. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2007(3): 571-575. |
| 龚伟, 胡庭兴, 王景燕, 等. 川南天然常绿阔叶林人工更新后土壤微团聚体分形特征研究. 土壤学报, 2007(3): 571-575. | |
| 32 | Wei W. Study on the chemical constitutions and allelopathy in rhizosphere soil extracts of the 1st and 2nd Pinus massoniana plantation. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2017. |
| 韦玮. 一二代马尾松人工林根际土壤浸提物的化学组成及其化感效应研究. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2017. | |
| 33 | Lv D, Yang Y H, Zhao W H, et al. Fine root biomass distribution and coupling to soil physicochemical properties under different restored vegetation types. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(11): 3979-3987. |
| 吕渡, 杨亚辉, 赵文慧, 等. 不同恢复类型植被细根分布及与土壤理化性质的耦合关系. 生态学报, 2018, 38(11): 3979-3987. | |
| 34 | Yan Z H, Chen Y, Liu X H, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of shear strength and anti-scourability of root-soil complex of two grass hedgerows in karst slope land. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(5): 1811-1820. |
| 颜哲豪, 谌芸, 刘枭宏, 等. 喀斯特坡地2种地埂篱根-土复合体抗剪和抗冲性能综合评价. 生态学报, 2022, 42(5): 1811-1820. | |
| 35 | Qu D X, Lv G, Zhai J X, et al. Effects of root system of different forest and grass measures on soil anti-scouring in southern margin of Horqin Sandy Land. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(1): 21-25. |
| 屈东旭, 吕刚, 翟景轩, 等. 科尔沁沙地南缘不同林草措施根系对土壤抗冲性的影响. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(1): 21-25. | |
| 36 | Zhang R, Dong H J, Zhou R H, et al. Effects of root characteristics of shrub community on soil anti-scourability in the Jiajin Mountains, Sichuan Province. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(11): 3558-3566. |
| 张荣, 董洪君, 周润惠, 等. 四川夹金山灌丛群落根系特征对土壤抗冲性的影响. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(11): 3558-3566. | |
| 37 | Wang T, Wang Q X, Li Y M, et al. Effect of maize and soybean intercropping on root system and soil aggregate stability. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2021, 36(3): 507-515. |
| 王婷, 王强学, 李永梅, 等. 玉米大豆间作对作物根系及土壤团聚体稳定性的影响. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学), 2021, 36(3): 507-515. | |
| 38 | Gao R, Zhao Y G, Liu X F, et al. Effects of stand age and slope position of Caragana korshinskii plantations on soil aggregate stability in the loess hilly region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(9): 2964-2974. |
| 高冉, 赵勇钢, 刘小芳, 等. 黄土丘陵区人工柠条种植年限和坡位对土壤团聚体稳定性的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(9): 2964-2974. | |
| 39 | Deng L, Kim D G, Peng C H, et al. Controls of soil and aggregate-associated organic carbon variations following natural vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau in China. Land Degradation & Development, 2018, 29(11): 3974-3984. |
| 40 | Li J Q, Zhang H J, Chen Q B, et al. Anti-scourability and anti-erodibility of soil under different hedgerow systems in upper reaches of Yangtze River. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2012, 21(7): 1223-1228. |
| 黎建强, 张洪江, 陈奇伯, 等. 长江上游不同植物篱系统土壤抗冲、抗蚀特征. 生态环境学报, 2012, 21(7): 1223-1228. | |
| 41 | Sun L L, Zha X, Huang S Y, et al. Experimental on soil anti-scouribility factors under different management modes in granite red soil region. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(5): 34-40, 49. |
| 孙丽丽, 査轩, 黄少燕, 等. 花岗岩红壤区不同治理模式土壤抗冲性因素试验. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(5): 34-40, 49. |
| [1] | 李林芝, 张德罡, 马源, 罗珠珠, 林栋, 海龙, 白兰鸽. 不同退化程度高寒草甸土壤团聚体养分及生态化学计量特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 48-60. |
| [2] | 魏艳, 刘有斌, 刘枭宏, 谌芸, 颜哲豪, 都艺芝. 紫色土区拉巴豆和紫花苜蓿根-土复合体抗剪性能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 82-90. |
| [3] | 杨瑞杰, 何淑勤, 周树峰, 杨晶月, 金钰宪, 郑子成. 杂交粱草生长期土壤抗冲性变化特征及其根系调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 149-159. |
| [4] | 郭鑫, 罗欢, 许雪梅, 马爱霞, 尚振艳, 韩天虎, 牛得草, 文海燕, 李旭东. 不同品质凋落物分解对黄土高原草地土壤有机碳及其稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 83-93. |
| [5] | 王茂鉴, 石薇, 常生华, 张程, 贾倩民, 侯扶江. 灌溉模式对河西灌区禾-豆间作系统饲草产量、品质和水分利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 13-29. |
| [6] | 王腾飞, 王斌, 邓建强, 李满有, 倪旺, 冯琴, 妥昀昀, 兰剑. 宁夏干旱区滴灌条件下拉巴豆不同播种量与甜高粱混播饲草生产性能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 30-40. |
| [7] | 张勇, 王海娣, 高玉红, 吴兵, 剡斌, 王一帆, 崔政军, 文泽东. 多元胡麻轮作模式对土壤团聚体特征及氮素含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 75-88. |
| [8] | 马文明, 刘超文, 周青平, 邓增卓玛, 唐思洪, 迪力亚尔·莫合塔尔null, 侯晨. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体生态化学计量学及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 57-68. |
| [9] | 刘枭宏, 谌芸, 颜哲豪, 唐菡, 强娇娇, 齐越, 都艺芝. 紫色土区草篱根系对其根-土复合体抗剪和抗冲性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 98-107. |
| [10] | 陈红, 马文明, 周青平, 杨智, 刘超文, 刘金秋, 杜中曼. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体稳定性及其铁铝氧化物分异的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 73-84. |
| [11] | 马晓静, 郭艳菊, 张嘉玉, 许爱云, 刘金龙, 许冬梅. 宁夏盐池县沙化草地土壤团聚体分异特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 27-37. |
| [12] | 李亚娇, 马培杰, 吴佳海, 牟琼, 覃涛英, 王晓强, 马宁, 张蓉, 李德芳, 朗永祥, 吴有松, 田应学, 韩永芬. 不同品种青贮玉米与拉巴豆套种对青贮玉米农艺性状及产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 209-216. |
| [13] | 周涛, 谌芸, 王润泽, 李铁, 唐菡, 翟婷婷, 刘枭宏. 种草和施用聚丙烯酰胺对荒坡紫色土抗剪和抗蚀性能的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 62-73. |
| [14] | 李明, 秦洁, 红雨, 杨殿林, 周广帆, 王宇, 王丽娟. 氮素添加对贝加尔针茅草原土壤团聚体碳、氮和磷生态化学计量学特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 29-40. |
| [15] | 王亚麒, 袁玲. 甜高粱、高丹草和拉巴豆对难溶性磷的活化与吸收[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 33-43. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||