

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 41-57.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023302
收稿日期:2023-08-29
修回日期:2023-10-17
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-02-03
通讯作者:
王国华
作者简介:E-mail: gimi123@126.com基金资助:
Lu-jing ZENG1( ), Guo-hua WANG1,2(
), Guo-hua WANG1,2( )
)
Received:2023-08-29
Revised:2023-10-17
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-02-03
Contact:
Guo-hua WANG
摘要:
一年生草本植物种群组成荒漠与绿洲生态系统的恒有性植物层片,在防风固沙和保护绿洲生态系统稳定方面具有重要的作用。本研究选取河西走廊荒漠绿洲过渡带人工林下典型5种一年生草本植物虎尾草、狗尾草、白茎盐生草、沙米和雾冰藜为研究对象,采用盆栽试验模拟干旱胁迫及复水,测定5种植物幼苗根系和叶片的生长(株高、根体积、根系平均直径、根系总表面积、根系总长和根系干重)与生理指标(根系活力、光合色素、丙二醛、渗透调节物质和抗氧化酶活性)的变化特征和规律,分析其对干旱环境的适应能力。研究结果表明,轻度干旱胁迫(土壤水分相对于CK减少2%)对5种一年生草本植物生长影响较小,甚至有一定的促进作用;中度(土壤水分相对于CK减少4%)和重度(土壤水分相对于CK减少6%)干旱胁迫下植物生长受到明显抑制。随着干旱胁迫程度的加剧,5种植物根系和叶片的丙二醛、过氧化物酶活性和渗透调节物质含量呈上升趋势;而根系活力呈下降趋势。禾本科一年生草本植物虎尾草和狗尾草根系酶活性(超氧化物歧化酶)随干旱胁迫程度的加剧呈持续增加的趋势;藜科一年生草本植物沙米和雾冰藜随干旱胁迫程度的加剧表现出先增加后下降的趋势。复水处理后,5种植物的生长和生理均得到不同程度的补偿,且根系的恢复能力高于叶片,浅根系植物的恢复能力优于深根系的。5种一年生草本植物的抗旱性具有显著差异,依次为狗尾草>白茎盐生草>雾冰藜>虎尾草>沙米。
曾露婧, 王国华. 干旱及复水对荒漠绿洲过渡带一年生草本植物生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 41-57.
Lu-jing ZENG, Guo-hua WANG. Effects of drought stress and rehydration on the growth and physiological characteristics of annual herbaceous plants from a desert-oasis ecotone[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 41-57.

图2 干旱胁迫及复水下5种一年生草本植物生长特性CK: 对照Control; LS: 轻度干旱胁迫Light drought stress; LS-CK: 轻度干旱胁迫-复水Light drought stress-rehydration; MS: 中度干旱胁迫Moderate drought stress; MS-CK: 中度干旱胁迫-复水Moderate drought stress-rehydration; SS: 重度干旱胁迫Severe drought stress; SS-CK: 重度干旱胁迫-复水Severe drought stress-rehydration. 1:虎尾草C. virgata; 2:狗尾草S. viridis; 3:白茎盐生草H. arachnoideus; 4:沙米A. squarrosum; 5:雾冰藜B. dasyphylla. 不同字母表示同一物种不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different letters indicate significant difference among different treatments of the same species. The same below.
Fig.2 Growth characteristics of five annual herbaceous plants under drought stress and rehydration
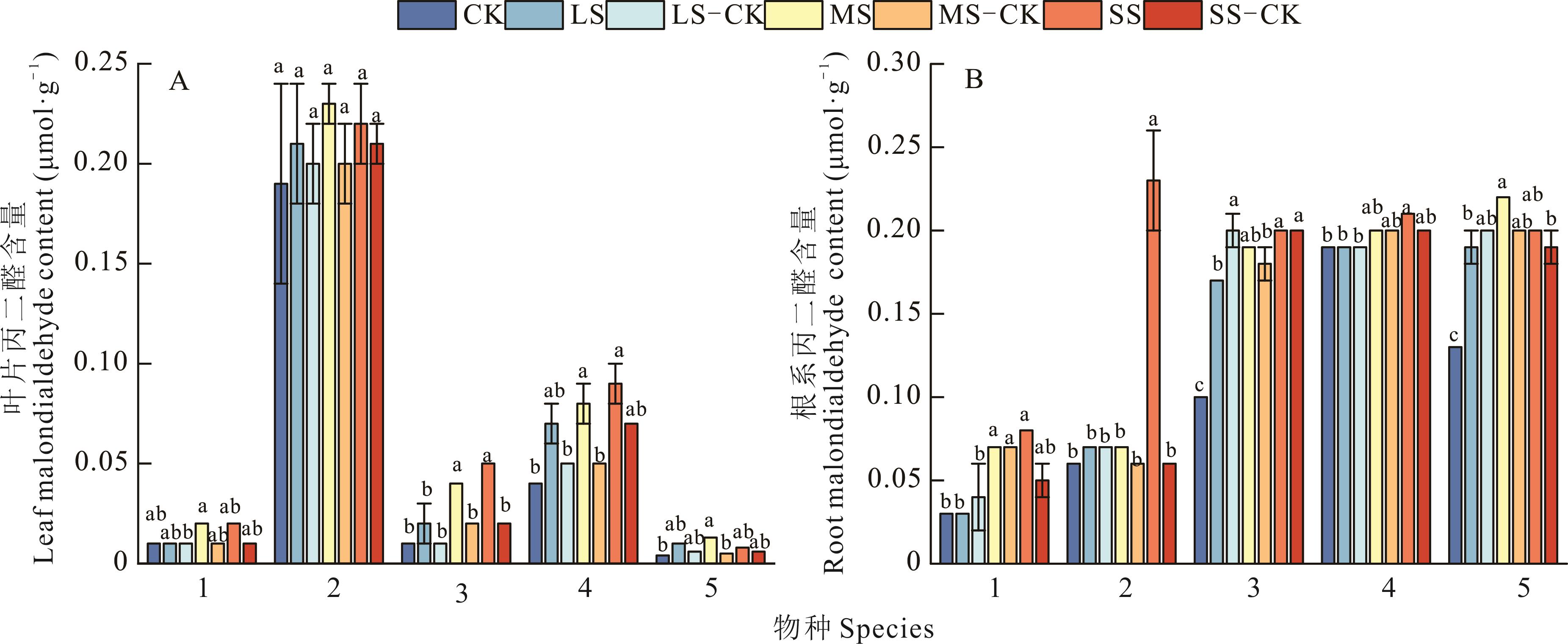
图5 干旱胁迫及复水下5种一年生草本植物生长早期细胞膜稳定性
Fig.5 Cell membrane stability of five annual herbaceous plants at early growth stage under drought stress and rehydration

图6 干旱胁迫及复水下5种一年生草本植物生长早期抗氧化酶(SOD,POD)活性
Fig.6 Antioxidant enzymes (SOD, POD) activity of five annual herbaceous plants at early growth stage under drought stress and rehydration

图7 干旱胁迫及复水下5种一年生草本植物生长早期渗透调节物质含量
Fig.7 The contents of osmoregulatory substances of five annual herbaceous plants at early growth stage under drought stress and rehydration

图8 干旱胁迫及复水下5种一年生草本植物早期生长与生理指标的相关性A: 地上部分Aboveground parts of plants; B: 地下部分Underground parts of plants. *: P<0.05.
Fig.8 Correlation of growth and physiological indicators of five annual herbaceous plants under drought stress and rehydration

图9 干旱胁迫下5种一年生草本植物生长早期路径A: 地上部分Aboveground parts of plants; B: 地下部分Underground parts of plants; C: 地上部分和地下部分的协同关系Linking aboveground and belowground interactions. *: P<0.05,**: P<0.01.
Fig.9 Early growth path of five annual herbaceous plants under drought stress
物种 Species | 指标Indexes | 平均值Average | 排序Order | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | X13 | X14 | X15 | X16 | X17 | X18 | X19 | X20 | X21 | X22 | |||
| 虎尾草C. virgata | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.36 | 0.32 | 0.48 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.42 | 0.57 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.51 | 0.64 | 0.38 | 0.60 | 0.51 | 0.404 | 4 |
| 狗尾草S. viridis | 0.31 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 0.39 | 0.52 | 0.17 | 0.57 | 0.49 | 0.19 | 0.51 | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.56 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.62 | 0.438 | 1 |
| 白茎盐生草H. arachnoideus | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.35 | 0.48 | 0.27 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.72 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.37 | 0.39 | 0.55 | 0.46 | 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.53 | 0.430 | 2 |
| 沙米A. squarrosum | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.52 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.49 | 0.33 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.35 | 0.390 | 5 |
| 雾冰藜B. dasyphylla | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.32 | 0.47 | 0.64 | 0.52 | 0.47 | 0.28 | 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.56 | 0.50 | 0.54 | 0.30 | 0.44 | 0.49 | 0.22 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.428 | 3 |
表1 5种一年生草本植物耐旱性指标隶属函数值及排序
Table 1 Affiliation function values and ranking of drought tolerance indicators for five annual herbaceous plants
物种 Species | 指标Indexes | 平均值Average | 排序Order | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | X13 | X14 | X15 | X16 | X17 | X18 | X19 | X20 | X21 | X22 | |||
| 虎尾草C. virgata | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.36 | 0.32 | 0.48 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.42 | 0.57 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.51 | 0.64 | 0.38 | 0.60 | 0.51 | 0.404 | 4 |
| 狗尾草S. viridis | 0.31 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 0.39 | 0.52 | 0.17 | 0.57 | 0.49 | 0.19 | 0.51 | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.56 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.62 | 0.438 | 1 |
| 白茎盐生草H. arachnoideus | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.35 | 0.48 | 0.27 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.72 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.37 | 0.39 | 0.55 | 0.46 | 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.53 | 0.430 | 2 |
| 沙米A. squarrosum | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.52 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.49 | 0.33 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.35 | 0.390 | 5 |
| 雾冰藜B. dasyphylla | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.32 | 0.47 | 0.64 | 0.52 | 0.47 | 0.28 | 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.56 | 0.50 | 0.54 | 0.30 | 0.44 | 0.49 | 0.22 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.428 | 3 |
| 1 | Zhang D K, Ma Q L, Liu Y J, et al. Composition and distribution characteristics of annual plant in desert area in Hexi Corridor. Pratacultural Science, 2009, 26(12): 37-41. |
| 张德魁, 马全林, 刘有军, 等. 河西走廊荒漠区一年生植物组成及其分布特征. 草业科学, 2009, 26(12): 37-41. | |
| 2 | Li X, Zhao W Z. Effects of salt-alkaline mixed stresses on seed germination and seedling growth of Bassia dasyphylla in desert region. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(2): 300-306. |
| 李辛, 赵文智. 雾冰藜(Bassia dasyphylla)种子萌发和幼苗生长对盐碱胁迫的响应. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(2): 300-306. | |
| 3 | Li X, Zhao W Z. Response of various salt-alkaline mixed stresses on the photosynthetic characteristics of Bassia dasyphylla in a desert region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(4): 1183-1193. |
| 李辛, 赵文智. 荒漠区植物雾冰藜光合特性对混合盐碱胁迫的响应. 生态学报, 2018, 38(4): 1183-1193. | |
| 4 | Li X H, Li X L, Jiang D M, et al. Annual plant species in arid and semi-arid desert regions: A review. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2006, 25(7): 851-856. |
| 5 | Feng Y Z, Zhao Y, Wang B P, et al. Effects of drought and rewatering on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence of Paulownia catalpifolia seedlings. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2020, 40(4): 1-8. |
| 冯延芝, 赵阳, 王保平, 等. 干旱复水对楸叶泡桐幼苗光合和叶绿素荧光的影响. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(4): 1-8. | |
| 6 | Yang Y, Zhou Y, Ban X W, et al. Effects of morphological and physiological characteristics of Coix lacryma-jobi L. seedlings under drought stress. Molecular Plant Breeding: 1-19. (2023-07-07)[2023-08-14]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20230706.1405.006.html. |
| 杨云, 周宇, 班秀文, 等. 干旱胁迫对薏苡幼苗形态和生理特征的影响. 分子植物种: 1-19. (2023-07-07)[2023-08-14]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20230706.1405.006.html. | |
| 7 | Wang F L, Chai C W, Zhao P, et al. Photosynthetic and chlorophyll fluorescence responses of three desert species to drought stress and evaluation of drought resistance. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2021, 41(10): 1755-1765. |
| 王方琳, 柴成武, 赵鹏, 等. 3种荒漠植物光合及叶绿素荧光对干旱胁迫的响应及抗旱性评价. 西北植物学报, 2021, 41(10): 1755-1765. | |
| 8 | Gong J R, Zhao A F, Zhang L X, et al. A comparative study on anti-oxidative ability of several desert plants under drought stress. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2004, 24(9): 1570-1577. |
| 龚吉蕊, 赵爱芬, 张立新, 等. 干旱胁迫下几种荒漠植物抗氧化能力的比较研究. 西北植物学报, 2004, 24(9): 1570-1577. | |
| 9 | Yu Y C. Effect of drought stress and rewatering on the photosynthetic physiological characteristics of leaves and bark of ‘84K’ poplar. Journal of Landscape Research, 2020, 12(4): 93-96, 102. |
| 10 | Chen A P, Sui X Q, Wang Y X, et al. Effects of drought and re-watering on growth and physiological characteristics of Seriphidium transiliense seedlings. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(5): 1216-1225. |
| 陈爱萍, 隋晓青, 王玉祥, 等. 干旱胁迫及复水对伊犁绢蒿幼苗生长及生理特性的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(5): 1216-1225. | |
| 11 | Bao X X, Lian Y, Mu Z J, et al. Comparative study on root and leaf photosynthesis of Allium polyrhizum from different sources under drought Stress. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2022, 37(4): 122-127. |
| 包秀霞, 廉勇, 慕宗杰, 等. 干旱胁迫下不同来源多根葱根系及叶片光合特性的比较. 华北农学报, 2022, 37(4): 122-127. | |
| 12 | Zhang J Y, Li Y, Zhao W Z, et al. Tracking analysis on changes of ecological patterns in Hexi Corridor Region. Water Resources Protection, 2015, 31(3): 5-10. |
| 张建永, 李扬, 赵文智, 等. 河西走廊生态格局演变跟踪分析. 水资源保护, 2015, 31(3): 5-10. | |
| 13 | Wang G H, Chen Y L, Gou Q Q. Responses of Haloxylon ammodendron with different plantation ages to changes of soil moisture in a desert-oasis ecotone. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(14): 5658-5668. |
| 王国华, 陈蕴琳, 缑倩倩. 荒漠绿洲过渡带不同年限雨养梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)对土壤水分变化的响应. 生态学报, 2021, 41(14): 5658-5668. | |
| 14 | Guo W T, Wang G H, Gou Q Q, et al. Module growth and biomass allocation of three typical Chenopodiaceae annuals in a typical desert-oasis ecotone of the Hexi Corridor in Gansu Province, China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(2): 25-38. |
| 郭文婷, 王国华, 缑倩倩, 等. 河西走廊荒漠绿洲过渡带3种典型一年生藜科植物构件生长及生物量分配特征. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 25-38. | |
| 15 | Zhang Z L, Qu W J. The experimental guide for plant physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1990. |
| 张志良, 瞿伟菁. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1990. | |
| 16 | Gao J F. Experimental guidance for plant physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. |
| 高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. | |
| 17 | Feng S L. Effects of drought stress and rewatering on growth and physiological characteristics of Platycladus orientalis and Amorpha fruticosa seedlings. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2020. |
| 冯树林. 干旱胁迫和复水对侧柏和紫穗槐幼苗生长和生理特征的影响研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2020. | |
| 18 | Li Y, Qiman Yunus, Zhu Y. Effects of water stress on photosynthetic characteristics and biomass partition of Elaeagnus moorcroftii. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2006, 26(12): 2493-2499. |
| 李阳, 齐曼·尤努斯, 祝燕. 水分胁迫对大果沙枣光合特性及生物量分配的影响. 西北植物学报, 2006, 26(12): 2493-2499. | |
| 19 | Zhuang Y, Ge J X, Wang X G, et al. Effect of rehydration after drought stress on the growth and physiological characteristics of flue-cured tobacco. Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 2022, 28(4): 48-58. |
| 庄晔, 葛嘉雪, 汪孝国, 等. 干旱胁迫后复水对烤烟生长及其生理特性的影响. 中国烟草学报, 2022, 28(4): 48-58. | |
| 20 | Ma T C, Yu R R, Chen R J, et al. Effect of drought stress simulated with PEG-6000 on root system in rice seedling. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2010, 18(6): 1206-1211. |
| 马廷臣, 余蓉蓉, 陈荣军, 等. PEG-6000模拟干旱对水稻幼苗期根系的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2010, 18(6): 1206-1211. | |
| 21 | Zheng M, Guo Y, Wang L M. Effect of drought stress on root morphology and physiological characteristics of Malus micromalus cv. ‘Ruby’. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 22(3): 24-30. |
| 郑淼, 郭毅, 王丽敏. 干旱胁迫对红宝石海棠根系形态及生理特性的影响. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(3): 24-30. | |
| 22 | Wang X X, Li Y, Zhang B, et al. Effects of drought stress and rehydration on root growth and physiological characteristics of oats. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(6): 1588-1596. |
| 王晓雪, 李越, 张斌, 等. 干旱胁迫及复水对燕麦根系生长及生理特性的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(6): 1588-1596. | |
| 23 | Bai L P, Sui F G, Sun Z H, et al. Effects of soil water stress on morphological development and yield of maize. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(7): 1556-1560. |
| 白莉萍, 隋方功, 孙朝晖, 等. 土壤水分胁迫对玉米形态发育及产量的影响. 生态学报, 2004, 24(7): 1556-1560. | |
| 24 | Zhang C M, Shi S L, Wu F. Effects of drought stress on root and physiological responses of different drought-tolerant alfalfa varieties. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(5): 868-882. |
| 张翠梅, 师尚礼, 吴芳. 干旱胁迫对不同抗旱性苜蓿品种根系生长及生理特性影响. 中国农业科学, 2018, 51(5): 868-882. | |
| 25 | Dai H J. Study of physiological mechanism on drought-wet change and compensative effect of crops. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 35(32): 10222-10224. |
| 代红军. 干湿变化与植物补偿效应的生理机制研究. 安徽农业科学, 2007, 35(32): 10222-10224. | |
| 26 | Zhao L Y, Deng X P, Shan L. A review on types and mechanisms of compensation effect of crops under water deficit. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2004, 15(3): 523-526. |
| 赵丽英, 邓西平, 山仑. 水分亏缺下作物补偿效应类型及机制研究概述. 应用生态学报, 2004, 15(3): 523-526. | |
| 27 | Liu Z P, Chu L L. Advances in research on compensation effects of crops under drought stress. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2016, 34(9): 804-808. |
| 刘展鹏, 褚琳琳. 作物干旱胁迫补偿效应研究进展. 排灌机械工程学报, 2016, 34(9): 804-808. | |
| 28 | Liu Y H, Xu J, Lei L, et al. Physiological and biochemical responses of seedling roots of Pinus massoniana to different phosphorus concentrations. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2023, 40(1): 126-134. |
| 刘娅惠, 徐瑾, 雷蕾, 等. 不同磷质量分数下马尾松幼苗根的生理生化特征. 浙江农林大学学报, 2023, 40(1): 126-134. | |
| 29 | Xu L M, Cao Y, Tang S W, et al. Effects of drought stress and rewatering on physiological characteristics of Arundo donax var. versicolor. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 18(3): 59-66. |
| 许令明, 曹昀, 汤思文, 等. 干旱胁迫及复水对花叶芦竹生理特性的影响. 中国水土保持科学, 2020, 18(3): 59-66. | |
| 30 | Zhou H H, Fu L C, Ma L, et al. Physiological characteristics of Osmanthus fragrans ‘Boyejingui’ with drought stress and rewatering. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2019, 36(4): 687-696. |
| 周欢欢, 傅卢成, 马玲, 等. 干旱胁迫及复水对‘波叶金桂’生理特性的影响. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(4): 687-696. | |
| 31 | Cai L P, Wu P F, Hou X L, et al. Effects of drought stress on photosynthetic characteristics of pioneer plant Neyraudia reynaudiana on soil and water conservation. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 25(6): 237-241, 259. |
| 蔡丽平, 吴鹏飞, 侯晓龙, 等. 干旱胁迫对水土保持先锋植物类芦光合特性的影响. 水土保持学报, 2011, 25(6): 237-241, 259. | |
| 32 | Ren L, Zhao X L, Xu J, et al. Varied morphological and physiological responses to drought stress among four tea Chrysanthemum cultivars. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(15): 5131-5139. |
| 任磊, 赵夏陆, 许靖, 等. 4种茶菊对干旱胁迫的形态和生理响应. 生态学报, 2015, 35(15): 5131-5139. | |
| 33 | Li T T. Relationship between growth characteristics of different artificial shrubs and soil moisture in desert steppe. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2019. |
| 李婷婷. 荒漠草原柠条沙柳灌木林生长特征与土壤水分关系. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2019. | |
| 34 | Pei B, Zhang G C, Zhang S Y, et al. Effects of soil drought stress on photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant enzyme activities in Hippophae rhamnoides Linn. seedings. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(5): 1386-1396. |
| 裴斌, 张光灿, 张淑勇, 等. 土壤干旱胁迫对沙棘叶片光合作用和抗氧化酶活性的影响. 生态学报, 2013, 33(5): 1386-1396. | |
| 35 | Wang N, Yuan M L, Chen H, et al. Effects of drought stress and rewatering on growth and physiological characteristics of invasive Aegilops tauschii seedlings. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(1): 70-78. |
| 王宁, 袁美丽, 陈浩, 等. 干旱胁迫及复水对入侵植物节节麦幼苗生长及生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 70-78. | |
| 36 | Cui T R, Yu H M, Li H B, et al. Effect of drought stress and rewatering on physiological characteristics of Pennisetum alopecuroides seedlings. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(4): 788-793. |
| 崔婷茹, 于慧敏, 李会彬, 等. 干旱胁迫及复水对狼尾草幼苗生理特性的影响. 草业科学, 2017, 34(4): 788-793. | |
| 37 | Jia X J, Dong L H, Ding C B, et al. Effects of drought stress on reactive oxygen species and their scavenging systems in Chlorophytum capense var. medio-pictum leaf. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(5): 248-255. |
| 贾学静, 董立花, 丁春邦, 等. 干旱胁迫对金心吊兰叶片活性氧及其清除系统的影响. 草业学报, 2013, 22(5): 248-255. | |
| 38 | Wang L J, Zhou Z B, Chang Q, et al. Growth, physiological and biochemical characteristics of Populus pruinosa seedlings under salt-drought stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(19): 7026-7033. |
| 王利界, 周智彬, 常青, 等. 盐旱交叉胁迫对灰胡杨(Populus pruinosa)幼苗生长和生理生化特性的影响. 生态学报, 2018, 38(19): 7026-7033. | |
| 39 | Liu Y Y, Xu Z, Luo Y M. Effect of drought stress on physiological characteristics of different tea varieties. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 23(2): 387-389. |
| 刘玉英, 徐泽, 罗云米. 干旱胁迫对不同茶树品种生理特性的影响. 西南农业学报, 2010, 23(2): 387-389. | |
| 40 | Liu Y, Cai G F, Chen G L. Effects of drought stress on active oxygen metabolism in Glycyrrhiza uralensis seedlings. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2012, 34(5): 93-98. |
| 刘艳, 蔡贵芳, 陈贵林. 干旱胁迫对甘草幼苗活性氧代谢的影响. 中国草地学报, 2012, 34(5): 93-98. | |
| 41 | Shan C J, Han R L, Liang Z S. Responses to drought stress of the biosynthetic and recycling metabolism of glutathione and ascorbate in Agropyron cristatum leaves on the Loess Plateau of China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2011, 35(6): 653-662. |
| 单长卷, 韩蕊莲, 梁宗锁. 黄土高原冰草叶片抗坏血酸和谷胱甘肽合成及循环代谢对干旱胁迫的生理响应. 植物生态学报, 2011, 35(6): 653-662. | |
| 42 | Li W R, Zhang S Q, Shan L. Physiological and biochemical responses of leaves and roots of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) to water stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2007, 15(4): 299-305. |
| 李文娆, 张岁岐, 山仑. 苜蓿叶片及根系对水分亏缺的生理生化响应. 草地学报, 2007, 15(4): 299-305. | |
| 43 | Liu J X, Wang X, Wang F Q. Effect of water stress on osmotic adjustment and activity of protective enzymes in alfalfa seedlings. Pratacultural Science, 2005, 22(3): 18-21. |
| 刘建新, 王鑫, 王凤琴. 水分胁迫对苜蓿幼苗渗透调节物质积累和保护酶活性的影响. 草业科学, 2005, 22(3): 18-21. | |
| 44 | Chen J F, Wu X, Yang J R, et al. Effects of drought and rewatering on above-ground plants and below-ground microorganisms under climate change: review and perspectives. Chinese Journal of Ecology. (2022-10-19)[2023-08-15]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20221018.1947.020.html. |
| 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 杨佳绒, 等. 全球气候变化下干旱及复水对地上植物和地下微生物的影响: 进展与展望. 生态学杂志. (2022-10-19)[2023-08-15]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20221018.1947.020.html. | |
| 45 | Li Y. Osmoregulation in plants in relation to other physiological processes and its application to crop improvement. Plant Physiology Communications, 1994, 30(5): 377-383. |
| 黎裕. 植物的渗透调节与其它生理过程的关系及其在作物改良中的应用. 植物生理学通讯, 1994, 30(5): 377-383. | |
| 46 | Wang M, Wang F, Wang J. Evaluation of potato drought resistance by subordinate function. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2014, 29(4): 476-481. |
| 王谧, 王芳, 王舰. 应用隶属函数法对马铃薯进行抗旱性综合评价. 云南农业大学学报 (自然科学版), 2014, 29(4): 476-481. | |
| 47 | Zhou R L, Zhao H L, Wang H O. Physiological mechanism of succession of the plants in Horqin Sandland, China. Arid Zone Research, 2001, 18(3): 13-19. |
| 周瑞莲, 赵哈林, 王海鸥. 科尔沁沙地植物演替的生理机制. 干旱区研究, 2001, 18(3): 13-19. | |
| 48 | Zhao G X, Xu T Y, Li W C, et al. Response of Halogeton arachnoideus seedling to drought stress. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2021, 35(4): 195-202. |
| 赵广兴, 徐天渊, 李王成, 等. 白茎盐生草幼苗对干旱胁迫的响应研究. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(4): 195-202. |
| [1] | 申迪, 曾子铭, 庞凯悦, 柴沙驼, 聂洪辛, 李毓敏, 廖扬, 王迅, 黄伟华, 刘书杰, 杨英魁, 王书祥. 低精料日粮和高精料日粮对牦牛生长性能和瘤胃菌群结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 155-165. |
| [2] | 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 李雯. 基于转录组测序的狗牙根抗旱根系关键代谢途径分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 186-198. |
| [3] | 李妍, 马富龙, 韩路, 王海珍. 美国‘WL’系列不同秋眠级苜蓿品种在南疆的生产性能与适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 139-149. |
| [4] | 张瑞, 安雪姣, 李建烨, 卢曾奎, 牛春娥, 徐振飞, 张金霞, 耿智广, 岳耀敬, 杨博辉. 湖羊及其不同杂交组合生长性能、产肉性能及肌肉品质比较分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 186-197. |
| [5] | 谭炯锐, 查同刚, 张泽宇, 张晓霞, 滕红梅, 王玲丽, 赵莉丽, 王奥, 王馨珧. 猪毛菜响应干旱胁迫的叶片结构、生理及转录组分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 75-88. |
| [6] | 姜瑛, 张辉红, 魏畅, 徐正阳, 赵颖, 刘芳, 李鸽子, 张雪海, 柳海涛. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下玉米幼苗根系发育及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 143-159. |
| [7] | 宫珂, 靳瑰丽, 刘文昊, 马建, 刘智彪, 李嘉欣, 李莹. 模拟增温对无芒雀麦生长特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 93-103. |
| [8] | 王宝强, 马文静, 王贤, 朱晓林, 赵颖, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗次生代谢产物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 141-151. |
| [9] | 史锋厚, 倪岳, 杨成参, 赵娅如, 付红祥. 粉砂性高速公路路基边坡植物护坡方案对比分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 71-81. |
| [10] | 张一龙, 李雯, 喻启坤, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 狗牙根叶与根氮代谢对不同干旱胁迫的响应机制[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 175-187. |
| [11] | 张浩, 胡海英, 李惠霞, 贺海明, 马霜, 马风华, 宋柯辰. 荒漠草原优势植物牛枝子对干旱胁迫的生理响应与转录组分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 188-205. |
| [12] | 梁佳, 胡朝阳, 谢志明, 马刘峰, 陈芸, 方志刚. 外源褪黑素缓解甜高粱幼苗干旱胁迫的生理效应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 206-215. |
| [13] | 马绍英, 陈桂平, 王娜, 马蕾, 连荣芳, 李胜, 张绪成. 豌豆土壤中潜在自毒物质的鉴定及自毒效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 134-145. |
| [14] | 崔婷, 王勇, 马晖玲. 外源IAA作用下草地早熟禾中调控Cd长距离运输的关键基因表达及其代谢通路分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 146-156. |
| [15] | 马婧, 郭方君, 邹枝慧, 孙琳, 陈芳. 腾格里沙漠南缘不同恢复阶段沙质草地植被的季节变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 203-210. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||