

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6): 76-88.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023353
收稿日期:2023-09-20
修回日期:2023-11-06
出版日期:2024-06-20
发布日期:2024-03-20
通讯作者:
包爱科
作者简介:E-mail: baoaik@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Min WANG1( ), Li LI2, Rong JIA3, Ai-ke BAO1(
), Li LI2, Rong JIA3, Ai-ke BAO1( )
)
Received:2023-09-20
Revised:2023-11-06
Online:2024-06-20
Published:2024-03-20
Contact:
Ai-ke BAO
摘要:
为了明确紫花苜蓿在低温胁迫下的生理特性并筛选出具有高耐寒能力的品种,选取了来自不同地区的10个紫花苜蓿品种作为试验材料,通过测定其幼苗在4 °C低温胁迫下的12项生理指标,结合相关性分析、主成分分析和隶属函数评价方法,对其耐寒能力进行了评价;同时,采用半致死温度(LT50)对评估出的耐寒能力进行验证。结果表明:1)在4 °C低温胁迫下,10个紫花苜蓿品种的叶片蒸腾速率(Tr)较对照组均有不同程度的下降,而相对电导率(REC)、脯氨酸(Pro)、可溶性糖(SS)、可溶性蛋白(SP)含量以及超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)和过氧化物酶(POD)活性均呈现出不同程度的增加趋势;2)隶属函数评价结果显示耐寒能力为龙牧801>肇东>Bara 520 YQ>公农1号>佰苜401>敖汉>挑战者>东农1号>骑士>新牧4号。各品种叶片的半致死温度(LT50)揭示,龙牧801和新牧4号分别是LT50值最低和最高的品种,与隶属函数的评价结果吻合;3)紫花苜蓿苗期耐寒性综合评价值(D)=0.138+0.178×SP+0.203×POD+0.170×Pro,表明SP、POD和Pro是评估紫花苜蓿幼苗耐寒性的关键生理指标。上述研究结果为深入了解紫花苜蓿幼苗的低温适应机制及耐寒紫花苜蓿品种的筛选奠定了基础。
王敏, 李莉, 贾蓉, 包爱科. 10种紫花苜蓿在低温胁迫下的生理特性及耐寒性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 76-88.
Min WANG, Li LI, Rong JIA, Ai-ke BAO. Evaluation of physiological characteristics and cold resistance of 10 alfalfa varieties under low temperature stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(6): 76-88.
编号 Number | 品种名称 Variety name | 品种来源 Variety source |
|---|---|---|
| BM | 佰苜401 Baimu 401 | 中国(北京) Beijing, China |
| BA | Bara 520 YQ | 美国 America |
| XM | 新牧4号 Xinmu 4 | 中国(新疆)Xinjiang, China |
| QS | 骑士 Knights | 美国 America |
| TZ | 挑战者 Challenger | 美国 America |
| GN | 公农1号 Gongnong 1 | 中国(吉林) Jilin, China |
| ZD | 肇东 Zhaodong | 中国(黑龙江) Heilongjiang, China |
| DN | 东农1号 Dongnong 1 | 中国(黑龙江) Heilongjiang, China |
| AH | 敖汉 Aohan | 中国(北京) Beijing, China |
| LM | 龙牧801 Longmu 801 | 中国(黑龙江) Heilongjiang, China |
表1 供试品种
Table 1 Test cultivars
编号 Number | 品种名称 Variety name | 品种来源 Variety source |
|---|---|---|
| BM | 佰苜401 Baimu 401 | 中国(北京) Beijing, China |
| BA | Bara 520 YQ | 美国 America |
| XM | 新牧4号 Xinmu 4 | 中国(新疆)Xinjiang, China |
| QS | 骑士 Knights | 美国 America |
| TZ | 挑战者 Challenger | 美国 America |
| GN | 公农1号 Gongnong 1 | 中国(吉林) Jilin, China |
| ZD | 肇东 Zhaodong | 中国(黑龙江) Heilongjiang, China |
| DN | 东农1号 Dongnong 1 | 中国(黑龙江) Heilongjiang, China |
| AH | 敖汉 Aohan | 中国(北京) Beijing, China |
| LM | 龙牧801 Longmu 801 | 中国(黑龙江) Heilongjiang, China |
化学成分 Chemical component | 浓度 Concentration (mmol·L-1) | 化学成分 Chemical component | 浓度 Concentration (μmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 硝酸钾KNO3 | 2.00 | 四水氯化锰MnCl2·4H2O | 10.00 |
| 磷酸二氢钾KH2PO4 | 0.50 | 七水硫酸锌ZnSO4·7H2O | 1.60 |
| 七水硫酸镁MgSO4·7H2O | 0.50 | 硫酸铜CuSO4 | 0.60 |
| 硝酸钙Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | 0.50 | 钼酸钠Na2MoO4·2H2O | 0.05 |
| 三水合柠檬酸铁Fe-citrate·3H2O | 0.06 | 硼酸H3BO3 | 50.00 |
表2 优化后的1/2 Hoagland 营养液配方
Table 2 Modified formula of 1/2 Hoagland nutrient solution
化学成分 Chemical component | 浓度 Concentration (mmol·L-1) | 化学成分 Chemical component | 浓度 Concentration (μmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 硝酸钾KNO3 | 2.00 | 四水氯化锰MnCl2·4H2O | 10.00 |
| 磷酸二氢钾KH2PO4 | 0.50 | 七水硫酸锌ZnSO4·7H2O | 1.60 |
| 七水硫酸镁MgSO4·7H2O | 0.50 | 硫酸铜CuSO4 | 0.60 |
| 硝酸钙Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | 0.50 | 钼酸钠Na2MoO4·2H2O | 0.05 |
| 三水合柠檬酸铁Fe-citrate·3H2O | 0.06 | 硼酸H3BO3 | 50.00 |
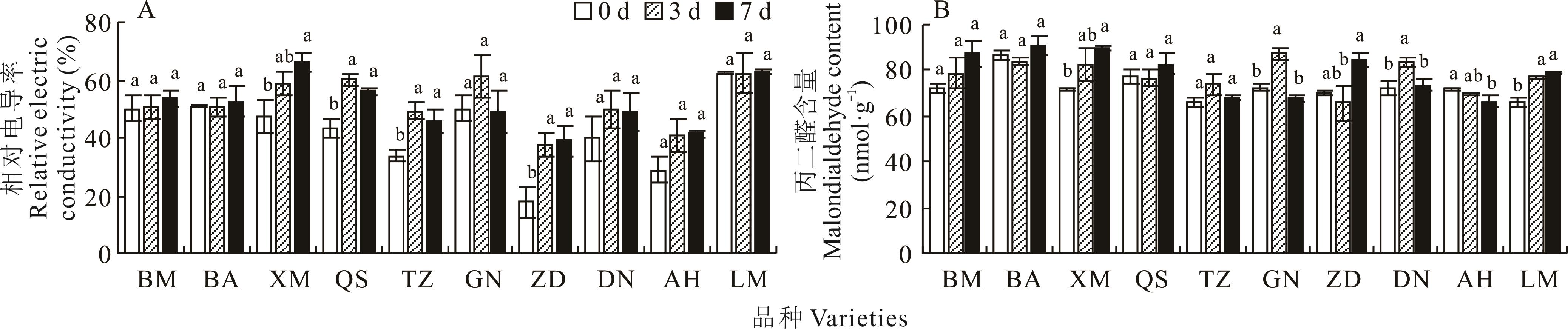
图1 低温胁迫对不同紫花苜蓿品种相对电导率和丙二醛含量的影响BM:佰苜401;BA:Bara 520 YQ;XM:新牧4号;QS:骑士;TZ:挑战者;GN:公农1号;ZD:肇东;DN:东农1号;AH:敖汉;LM:龙牧801。0、3 和7 d分别代表4 °C低温处理第0、3和7 d。所有数据均以平均值±标准误表示(n=5),不同小写字母表示不同处理时间下差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。BM represents Baimu 401; BA represents Bara 520 YQ; XM represents Xinmu 4; QS represents Knights; TZ represents Challenger; GN represents Gongnong 1; ZD represents Zhaodong; DN represents Dongnong 1; AH represents Aohan; LM represents Longmu 801. 0, 3, and 7 d represent 0, 3, and 7 days of 4 ℃ low-temperature treatment, respectively. All data are presented as mean±standard error (n=5), and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatment time (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of low temperature stress on relative electric conductivity and malondialdehyde content of different alfalfa varieties
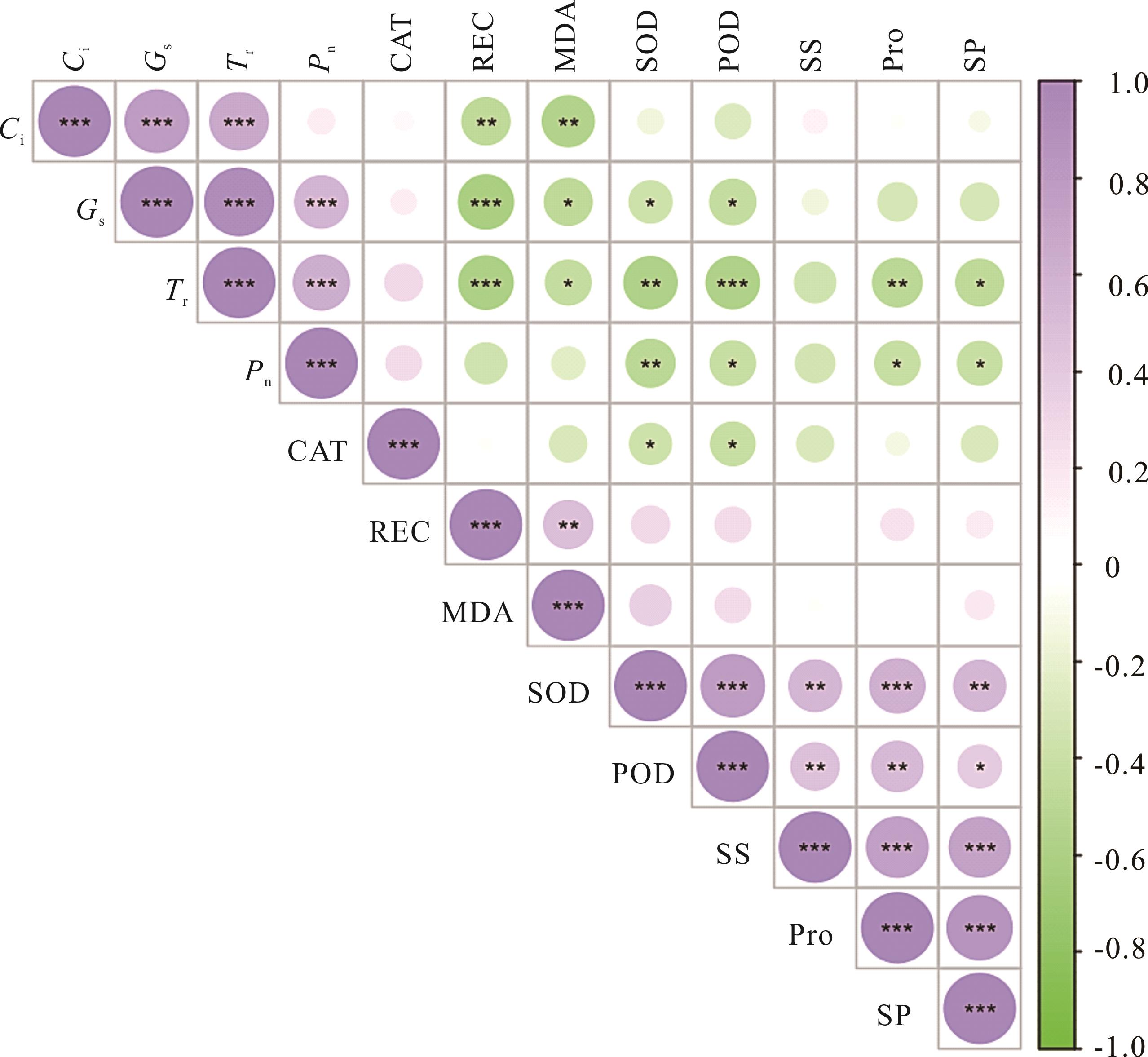
图5 不同品种紫花苜蓿幼苗响应低温主要生理生化指标相关性分析*表示0.05水平显著相关,**在0.01水平显著相关,***在0.001水平显著相关。Ci:胞间二氧化碳浓度;Gs:气孔导度;Tr:蒸腾速率;Pn:净光合速率;CAT:过氧化氢酶;REC:相对电导率;MDA:丙二醛;SOD:超氧化物歧化酶;POD:过氧化物酶;SS:可溶性糖;Pro:脯氨酸;SP:可溶性蛋白。下同。*, **, ** means significant correlation at 0.05, 0.01 and 0.001 level, respectively. Ci: Intercellular carbon dioxide concentration; Gs: Stomatal conductance; Tr: Transpiration rate; Pn: Net photosynthetic rate; CAT: Catalase; REC: Relative electric conductivity; MDA: Malondialdehyde; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; POD: Peroxidase; SS: Soluble sugar; Pro: Proline; SP: Soluble protein. The same below.
Fig.5 Correlation analysis of main physiological and biochemical indexes of alfalfa seedlings of different varieties in response to low temperature
项目 Item | 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 | 主成分3 Principal component 3 | 主成分4 Principal component 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 5.373 | 2.412 | 1.103 | 0.743 |
| 贡献率Rate of contribution (%) | 44.777 | 20.096 | 9.190 | 6.195 |
| 累计贡献率Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 44.777 | 64.873 | 74.063 | 80.258 |
| 特征向量 Eigenvector | ||||
| 相对电导率Relative electric conductivity | 0.569 | -0.474 | 0.193 | 0.050 |
| 丙二醛Malondialdehyde | 0.500 | -0.493 | -0.343 | 0.410 |
| 脯氨酸Proline | 0.708 | 0.529 | 0.327 | 0.160 |
| 可溶性糖Soluble sugars | 0.578 | 0.683 | 0.104 | 0.119 |
| 净光合速率Net photosynthetic rate | -0.679 | -0.017 | -0.060 | 0.579 |
| 过氧化氢酶Catalase | -0.413 | -0.135 | 0.767 | 0.036 |
| 可溶性蛋白Soluble protein | 0.691 | 0.489 | 0.186 | 0.314 |
| 过氧化物酶Peroxidase | 0.748 | 0.178 | -0.291 | -0.127 |
| 气孔导度Stomatal conductivity | -0.780 | 0.503 | -0.209 | 0.132 |
| 超氧化物歧化酶Superoxide dismutase | 0.785 | 0.278 | -0.230 | -0.027 |
| 蒸腾速率Transpiration rate | -0.896 | 0.283 | -0.126 | 0.129 |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度Intercellular CO2 concentration | -0.516 | 0.705 | -0.076 | -0.216 |
表3 主成分分析
Table 3 Principal component analysis
项目 Item | 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 | 主成分3 Principal component 3 | 主成分4 Principal component 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 5.373 | 2.412 | 1.103 | 0.743 |
| 贡献率Rate of contribution (%) | 44.777 | 20.096 | 9.190 | 6.195 |
| 累计贡献率Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 44.777 | 64.873 | 74.063 | 80.258 |
| 特征向量 Eigenvector | ||||
| 相对电导率Relative electric conductivity | 0.569 | -0.474 | 0.193 | 0.050 |
| 丙二醛Malondialdehyde | 0.500 | -0.493 | -0.343 | 0.410 |
| 脯氨酸Proline | 0.708 | 0.529 | 0.327 | 0.160 |
| 可溶性糖Soluble sugars | 0.578 | 0.683 | 0.104 | 0.119 |
| 净光合速率Net photosynthetic rate | -0.679 | -0.017 | -0.060 | 0.579 |
| 过氧化氢酶Catalase | -0.413 | -0.135 | 0.767 | 0.036 |
| 可溶性蛋白Soluble protein | 0.691 | 0.489 | 0.186 | 0.314 |
| 过氧化物酶Peroxidase | 0.748 | 0.178 | -0.291 | -0.127 |
| 气孔导度Stomatal conductivity | -0.780 | 0.503 | -0.209 | 0.132 |
| 超氧化物歧化酶Superoxide dismutase | 0.785 | 0.278 | -0.230 | -0.027 |
| 蒸腾速率Transpiration rate | -0.896 | 0.283 | -0.126 | 0.129 |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度Intercellular CO2 concentration | -0.516 | 0.705 | -0.076 | -0.216 |
品种 Variety | 脯氨酸得分 Proline score | 可溶性糖得分 Soluble sugars score | 可溶性蛋白得分 Soluble protein score | 超氧化物歧化酶得分 Superoxide dismutase score | 过氧化物酶得分 Peroxidase score | 综合评价值 Comprehensive evaluation value | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM | 0.199 | 0.195 | 0.498 | 0.367 | 0.377 | 0.327 | 5 |
| BA | 0.184 | 0.146 | 0.459 | 0.436 | 0.435 | 0.332 | 3 |
| XM | 0.144 | 0.112 | 0.276 | 0.518 | 0.362 | 0.282 | 10 |
| QS | 0.149 | 0.219 | 0.420 | 0.409 | 0.230 | 0.286 | 9 |
| TZ | 0.223 | 0.197 | 0.357 | 0.423 | 0.332 | 0.306 | 7 |
| GN | 0.187 | 0.276 | 0.403 | 0.354 | 0.421 | 0.328 | 4 |
| ZD | 0.207 | 0.238 | 0.512 | 0.454 | 0.383 | 0.359 | 2 |
| DN | 0.195 | 0.293 | 0.377 | 0.359 | 0.242 | 0.293 | 8 |
| AH | 0.302 | 0.236 | 0.548 | 0.311 | 0.212 | 0.322 | 6 |
| LM | 0.426 | 0.199 | 0.575 | 0.379 | 0.297 | 0.375 | 1 |
表4 基于隶属函数值的紫花苜蓿不同品种的耐寒性综合评价
Table 4 Comprehensive evaluation of cold tolerance among different alfalfa varieties based on the membership function values
品种 Variety | 脯氨酸得分 Proline score | 可溶性糖得分 Soluble sugars score | 可溶性蛋白得分 Soluble protein score | 超氧化物歧化酶得分 Superoxide dismutase score | 过氧化物酶得分 Peroxidase score | 综合评价值 Comprehensive evaluation value | 排序 Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM | 0.199 | 0.195 | 0.498 | 0.367 | 0.377 | 0.327 | 5 |
| BA | 0.184 | 0.146 | 0.459 | 0.436 | 0.435 | 0.332 | 3 |
| XM | 0.144 | 0.112 | 0.276 | 0.518 | 0.362 | 0.282 | 10 |
| QS | 0.149 | 0.219 | 0.420 | 0.409 | 0.230 | 0.286 | 9 |
| TZ | 0.223 | 0.197 | 0.357 | 0.423 | 0.332 | 0.306 | 7 |
| GN | 0.187 | 0.276 | 0.403 | 0.354 | 0.421 | 0.328 | 4 |
| ZD | 0.207 | 0.238 | 0.512 | 0.454 | 0.383 | 0.359 | 2 |
| DN | 0.195 | 0.293 | 0.377 | 0.359 | 0.242 | 0.293 | 8 |
| AH | 0.302 | 0.236 | 0.548 | 0.311 | 0.212 | 0.322 | 6 |
| LM | 0.426 | 0.199 | 0.575 | 0.379 | 0.297 | 0.375 | 1 |

图7 不同紫花苜蓿品种的半致死温度(LT50)不同小写字母表示不同品种间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different varieties (P<0.05).
Fig.7 Semi-lethal temperature (LT50) of different alfalfa varieties
项目 Item | 非标准化系数 Non-normalized coefficient | 标准化系数 Standardization coefficient | B/标 准误 (t) | P值 P-value | 多重共线性严重程度 (VIF) | 曲线回归的拟合程度 (R2) | 调整R2 The adjusted R2 | F检验 F-test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 系数Coefficient (B) | 标准误Standard error | Beta | |||||||
| 常数Constant | 0.138 | 0.022 | 0 | 6.348 | 0.001** | 0.935 | 0.903 | F=28.80, P=0.001** | |
| 可溶性蛋白Soluble protein | 0.178 | 0.048 | 0.546 | 3.674 | 0.010* | 2.044 | |||
| 过氧化物酶Peroxidase | 0.203 | 0.042 | 0.536 | 4.896 | 0.003** | 1.108 | |||
| 脯氨酸Proline | 0.170 | 0.056 | 0.469 | 3.044 | 0.023* | 2.195 | |||
表5 逐步线性回归分析
Table 5 The results of stepwise linear regression analysis (n=10)
项目 Item | 非标准化系数 Non-normalized coefficient | 标准化系数 Standardization coefficient | B/标 准误 (t) | P值 P-value | 多重共线性严重程度 (VIF) | 曲线回归的拟合程度 (R2) | 调整R2 The adjusted R2 | F检验 F-test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 系数Coefficient (B) | 标准误Standard error | Beta | |||||||
| 常数Constant | 0.138 | 0.022 | 0 | 6.348 | 0.001** | 0.935 | 0.903 | F=28.80, P=0.001** | |
| 可溶性蛋白Soluble protein | 0.178 | 0.048 | 0.546 | 3.674 | 0.010* | 2.044 | |||
| 过氧化物酶Peroxidase | 0.203 | 0.042 | 0.536 | 4.896 | 0.003** | 1.108 | |||
| 脯氨酸Proline | 0.170 | 0.056 | 0.469 | 3.044 | 0.023* | 2.195 | |||
品种 Variety | 可溶性蛋白评分 Soluble protein score | 过氧化物酶评分 Peroxidase score | 脯氨酸评分 Proline score | 综合评价值 Comprehensive evaluation value | 回归综合评价值 Return to comprehensive valuation value | 相对误差值 Relative error value | 估计精度 Estimation precision (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM | 0.498 | 0.377 | 0.199 | 0.327 | 0.337 | -0.030 | 97.13 |
| BA | 0.459 | 0.435 | 0.184 | 0.332 | 0.339 | -0.022 | 97.88 |
| XM | 0.276 | 0.362 | 0.144 | 0.282 | 0.285 | -0.010 | 99.05 |
| QS | 0.420 | 0.230 | 0.149 | 0.286 | 0.285 | 0.003 | 99.74 |
| TZ | 0.357 | 0.332 | 0.223 | 0.306 | 0.307 | -0.002 | 99.82 |
| GN | 0.403 | 0.421 | 0.187 | 0.328 | 0.327 | 0.004 | 99.61 |
| ZD | 0.512 | 0.383 | 0.207 | 0.359 | 0.342 | 0.047 | 95.32 |
| DN | 0.377 | 0.242 | 0.195 | 0.293 | 0.287 | 0.020 | 98.03 |
| AH | 0.548 | 0.212 | 0.302 | 0.322 | 0.330 | -0.025 | 97.53 |
| LM | 0.575 | 0.297 | 0.426 | 0.375 | 0.373 | 0.006 | 99.40 |
表6 回归方程的估计精度分析
Table 6 Estimation accuracy analysis of regression equation
品种 Variety | 可溶性蛋白评分 Soluble protein score | 过氧化物酶评分 Peroxidase score | 脯氨酸评分 Proline score | 综合评价值 Comprehensive evaluation value | 回归综合评价值 Return to comprehensive valuation value | 相对误差值 Relative error value | 估计精度 Estimation precision (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM | 0.498 | 0.377 | 0.199 | 0.327 | 0.337 | -0.030 | 97.13 |
| BA | 0.459 | 0.435 | 0.184 | 0.332 | 0.339 | -0.022 | 97.88 |
| XM | 0.276 | 0.362 | 0.144 | 0.282 | 0.285 | -0.010 | 99.05 |
| QS | 0.420 | 0.230 | 0.149 | 0.286 | 0.285 | 0.003 | 99.74 |
| TZ | 0.357 | 0.332 | 0.223 | 0.306 | 0.307 | -0.002 | 99.82 |
| GN | 0.403 | 0.421 | 0.187 | 0.328 | 0.327 | 0.004 | 99.61 |
| ZD | 0.512 | 0.383 | 0.207 | 0.359 | 0.342 | 0.047 | 95.32 |
| DN | 0.377 | 0.242 | 0.195 | 0.293 | 0.287 | 0.020 | 98.03 |
| AH | 0.548 | 0.212 | 0.302 | 0.322 | 0.330 | -0.025 | 97.53 |
| LM | 0.575 | 0.297 | 0.426 | 0.375 | 0.373 | 0.006 | 99.40 |
| 1 | Soualiou S, Duan F, Li X, et al. Crop production under cold stress: an understanding of plant responses, acclimation processes, and management strategies. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2022, 190: 47-61. |
| 2 | Hasegawa T, Sakurai G, Fujimori S, et al. Extreme climate events increase risk of global food insecurity and adaptation needs. Nature Food, 2021, 2(8): 587-595. |
| 3 | Ministry of Emergency Management. The ministry of emergency management released the basic situation of natural disasters in China in 2022. Overview of Disaster Prevention, 2023(1): 26-27. |
| 应急管理部. 应急管理部发布2022年全国自然灾害基本情况. 防灾博览, 2023(1): 26-27. | |
| 4 | Yan X D, Zhuang N S. A review on the research of plant-cold-resistant breeding. Tropical Agricultural Science & Technology, 2006, 29(2): 18-22, 27. |
| 严学东, 庄南生. 植物抗寒育种研究进展简述. 热带农业科技, 2006, 29(2): 18-22, 27. | |
| 5 | Le Y, Hannoufa A, Yu P. The use of gene modification and advanced molecular structure analyses towards improving alfalfa forage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2017, 18(2): 298. |
| 6 | Wang X, Kang W, Wu F, et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals new insight of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cultivars in response to abrupt freezing stress. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 798118. |
| 7 | Yu S. Analysis of market supply and demand and industry operation status of China’s alfalfa industry in 2022. 08-24. [2023-11-26]. https://www.chyxx.com/industry/1123206.html. |
| 余思. 2022年中国苜蓿草行业市场供需及产业运行现状分析. 08-24. [2023-11-26]. https://www.chyxx.com/industry/1123206.html. | |
| 8 | Wang X L. Identification of cold tolerance and screening of cold tolerant germplasm of alfalfa. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2021. |
| 王晓龙. 苜蓿抗寒性鉴定及耐寒种质筛选. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2021. | |
| 9 | Yu R G, Wang X J, Wang G L, et al. Analysis of salinity-tolerance and screening evaluation indicators to salinity-tolerance in Medicago sativa seedlings. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(7): 1781-1789. |
| 余如刚, 王雪茄, 王国良, 等. 紫花苜蓿品种苗期耐盐性分析及评价指标筛选. 草地学报, 2022, 30(7): 1781-1789. | |
| 10 | Yang Y W, Wang L, Lu J F, et al. Evaluation of membership function on heat tolerance of 10 alfalfa varieties. Grassland and Turf, 2021, 41(4): 81-88. |
| 杨雨薇, 王琳, 卢俊峰, 等. 应用隶属函数法评价10个紫花苜蓿品种的耐热性. 草原与草坪, 2021, 41(4): 81-88. | |
| 11 | Wang F, Wang Q, Zhang X Y. Research progress of phenotype and physiological response mechanism of plants under low temperature stress. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(15): 5144-5153. |
| 王芳, 王淇, 赵曦阳. 低温胁迫下植物的表型及生理响应机制研究进展. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(15): 5144-5153. | |
| 12 | Jia X, Duo J G S, Zhao A M, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of cold resistance of 4 species of gramineae at seedling stage. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(5): 1372-1378. |
| 贾祥, 多吉格桑, 赵爱民, 等. 4种禾本科牧草苗期抗寒性综合评价. 草地学报, 2020, 28(5): 1372-1378. | |
| 13 | He H P, Nan L L, Ma B, et al. Screening and evaluation of seedling stage cold tolerance in different sainfoin varieties. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(5): 41-49. |
| 何海鹏, 南丽丽, 马彪, 等. 红豆草种质苗期耐寒性筛选及评价. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(5): 41-49. | |
| 14 | Zhao M L, Guo Y T, Sun S Y, et al. Evaluation of cold resistance of four Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus) under low temperature stress. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020, 56(7): 1419-1431. |
| 赵孟良, 郭怡婷, 孙世英, 等. 低温胁迫下4种菊芋的耐寒性评价. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(7): 1419-1431. | |
| 15 | He Y T, Hu Y, Duan H R, et al. Advance of evaluation indexes on stress resistance of Elymus plants in China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(8): 96-108. |
| 何永涛, 胡宇, 段慧荣, 等. 我国披碱草属植物抗逆性评价指标研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(8): 96-108. | |
| 16 | Liu L B, Sun W C, Liu Z G, et al. Genetic analysis of traits related to cold resistance in winter rapeseed (Brassica rapa L.). Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(21): 4085-4095. |
| 刘林波, 孙万仓, 刘自刚, 等. 白菜型冬油菜抗寒相关性状的遗传分析. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(21): 4085-4095. | |
| 17 | Hao J J, Kang Z L, Yu Y. Experimental techniques in plant physiology. Beijing: Beijing Chemical Industry Press, 2007: 98-112. |
| 郝建军, 康宗利, 于洋. 植物生理学实验技术. 北京: 北京化学工业出版社, 2007: 98-112. | |
| 18 | Ma L Y. Study on responses and memory effects of Arabidopsis thaliana to low temperature stress. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2022. |
| 马丽亚. 拟南芥对低温胁迫的响应与记忆效应研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2022. | |
| 19 | Lai M, Chen J, Zhang J, et al. Research progress in plant response mechanism to low temperature stress and lmprovement of cold resistance. Molecular Plant Breeding, 1-11. [2023-11-26]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46. |
| 赖铭, 陈佳, 张军, 等. 植物低温胁迫响应机制及提高抗冷性研究进展. 分子植物育种, 1-11. [2023-11-26]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46. | |
| 20 | Yamori W, Hikosaka K, Danielle A W, et al. Temperature response of photosynthesis in C3, C4, and CAM plants: temperature acclimation and temperature adaptation. Photosynthesis Research, 2014, 119(1/2): 101-117. |
| 21 | Smallwood M, Bowles D J. Plants in a cold climate. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B-Biological Sciences, 2002, 357(1423): 831-847. |
| 22 | Das K, Roychoudhury A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2014, 2(53): 1-13. |
| 23 | Anjum N A, Sharma P, Gill S S, et al. Catalase and ascorbate peroxidase-representative H2O2-detoxifying heme enzymes in plants. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(19): 19002-19029. |
| 24 | Deng X K, Qiao D R, Li L, et al. The effect of chilling stress on physiological characters of Medicago sativa. Journal of Sichuan University (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 42(1): 190-194. |
| 邓雪柯, 乔代蓉, 李良, 等. 低温胁迫对紫花苜蓿生理特性影响的研究. 四川大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 42(1): 190-194. | |
| 25 | Quan W, Xue W T, Zhao T Y, et al. A review on the response mechanism of plant to low temperature stress. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2023, 28(2): 14-22. |
| 权威, 薛文通, 赵天瑶, 等. 植物对低温胁迫的响应机制研究进展. 中国农业大学学报, 2023, 28(2): 14-22. | |
| 26 | Li J Q, Liu X J, Yun X K, et al. Response of alfalfa to low temperatures at different growth stages and its cold resistance. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(11): 2505-2512. |
| 李佳奇, 刘晓静, 运向凯, 等. 不同生长时期的紫花苜蓿对低温的响应及其抗寒性研究. 草地学报, 2021, 29(11): 2505-2512. | |
| 27 | Luo X Y, Feng C J, Li H, et al. Study on changes of SOD and proline activity during low temperature stress on Medicago sativa L. cv. Zhaodong. Grassland of China, 2004, 26(4): 79-81. |
| 罗新义, 冯昌军, 李红, 等. 低温胁迫下肇东苜蓿SOD、脯氨酸活性变化初报. 中国草地, 2004, 26(4): 79-81. | |
| 28 | Chen W D, Zhang Y X, Cong B M, et al. Effects of cold stress on different alfalfa varieties’ physiological characteristics. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(7): 115-120. |
| 陈卫东, 张玉霞, 丛百明, 等. 低温胁迫对不同苜蓿品种生理特性的影响. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(7): 115-120. | |
| 29 | Wu H, Hou L L, Zhou Y F, et al. Analysis of chilling-tolerance and determination of chilling-tolerance evaluation indicators in cotton of different genotypes. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(9): 1703-1713. |
| 武辉, 侯丽丽, 周艳飞, 等. 不同棉花基因型幼苗耐寒性分析及其鉴定指标筛选. 中国农业科学, 2012, 45(9): 1703-1713. | |
| 30 | Xu Y, Chen Y, Chen F D, et al. Analysis of cold-tolerance and determination of cold-tolerance evaluation indicators in chrysanthemum. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2009, 42(3): 974-981. |
| 许瑛, 陈煜, 陈发棣, 等. 菊花耐寒特性分析及其评价指标的确定. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(3): 974-981. | |
| 31 | Yang Y. Evaluation and analysis of weighting method in multi-index comprehensive evaluation. Statistics & Decision, 2006(13): 17-19. |
| 杨宇. 多指标综合评价中赋权方法评析. 统计与决策, 2006(13): 17-19. | |
| 32 | Zhao Y H, Meng L D, Zhang X M, et al. Evaluation of physiological response and cold resistance of four alfalfa cultivars to low temperature stress. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(4): 683-692. |
| 赵一航, 孟令东, 张晓萌, 等. 4个紫花苜蓿品种对低温胁迫的生理响应及抗寒性评价. 草业科学, 2021, 38 (4): 683-692. | |
| 33 | Wang Y Y, Liu W D, He L, et al. Evaluation of low temperature freezing injury in winter wheat and difference analysis of water effect based on multivariate statistical analysis. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(7): 1301-1318. |
| 王洋洋, 刘万代, 贺利, 等. 基于多元统计分析的小麦低温冻害评价及水分效应差异研究. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(7): 1301-1318. |
| [1] | 高金柱, 赵东豪, 高乐, 苏喜浩, 何学青. 硝酸铈与脱落酸处理对紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 175-186. |
| [2] | 谭英, 尹豪. 盐胁迫下根施AMF和褪黑素对紫花苜蓿生长、光合特征以及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. |
| [3] | 孔海明, 宋家兴, 杨静, 李倩, 杨培志, 曹玉曼. 紫花苜蓿CAMTA基因家族鉴定及其在非生物胁迫下的表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 143-154. |
| [4] | 何升然, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 汪雪, 王静. 紫花苜蓿/甜高粱间作对根际土壤特性及微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 92-105. |
| [5] | 刘昊, 李显炀, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 紫花苜蓿SAUR基因家族的鉴定及其在非生物胁迫中的表达模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 135-153. |
| [6] | 李显炀, 刘昊, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿WRKY转录因子家族鉴定与表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 154-170. |
| [7] | 李妍, 马富龙, 韩路, 王海珍. 美国‘WL’系列不同秋眠级苜蓿品种在南疆的生产性能与适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 139-149. |
| [8] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 王静, 吴勇, 童长春. 连续间作下的紫花苜蓿/燕麦根系与碳氮代谢特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 85-96. |
| [9] | 唐璎, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 董霖. 甘肃不同区域青贮紫花苜蓿乳酸菌群落特征及其驱动因子研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 112-124. |
| [10] | 罗颖, 李聪, 王沛, 田莉华, 汪辉, 周青平, 雷映霞. 低氮胁迫下不同皮燕麦品种早期的响应研究及耐低氮性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 164-184. |
| [11] | 张永亮, 滕泽, 郝凤, 于铁峰, 张玉霞. 苜蓿混播方式及比例对混播草地生产力和稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 185-197. |
| [12] | 白旭琴, 贾春云, 李文栓, 李亚敏, 刘长风, 韩秀云, 褚美函, 巩宗强, 李晓军. 叶面喷施硒肥对紫花苜蓿富硒降镉效果的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 50-60. |
| [13] | 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 马春晖, 张前兵. 菌磷耦合下紫花苜蓿的干物质产量及磷素空间分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 104-115. |
| [14] | 康燕霞, 姜渊博, 齐广平, 银敏华, 马彦麟, 汪精海, 贾琼, 唐仲霞, 汪爱霞. 红豆草与无芒雀麦混播草地生产力提升的水分调控模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 115-128. |
| [15] | 徐蕊, 王峥, 王仪明, 苏连泰, 高鲤, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿对轮作水稻产量和蔗糖代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 129-140. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||