

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (7): 192-204.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023289
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-08-10
修回日期:2023-10-09
出版日期:2024-07-20
发布日期:2024-04-08
作者简介:徐寿霞(1976-),女,山东济南人,馆员,硕士。E-mail: xushoux@126.com
基金资助:Received:2023-08-10
Revised:2023-10-09
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-04-08
摘要:
小麦是人类种植的最为重要的作物之一,对保障粮食安全有着极其重要的作用,因此,小麦的高产、稳产、优质一直是研究的热点科学问题;而丛枝菌根(arbuscular mycorrhizae,AM)是存在于植物根系的最广泛共生体,能够改善植物营养、提高植物产量和提升植物品质。为了系统、全面地评估AM在小麦生产方面的功能,筛选有利于小麦生产的高效AM真菌,本研究采用meta分析方法,基于171篇相关研究文献建立了数据库,整体评价了AM对小麦产量和品质的影响,并探讨了不同AM真菌的效应差异。结果表明,AM能通过提高17.1%的穗粒数和15.7%的千粒重,而实现小麦增产24.2%;同时,AM改善了小麦的品质,使籽粒蛋白质含量提高15.7%,P和Zn含量分别增加15.2%和21.5%;AM对小麦产量和品质的改善可能是基于改善了小麦植物营养状况和叶片叶绿素含量,其提高小麦植株地上部N含量8.4%、P 16.2%、Ca 91.2% 和Zn 11.3% ,并提高叶绿素含量27.5%。不同属或种的AM真菌对小麦产量和品质的影响存在明显差异,其中,斗管囊霉属真菌的效应更显著和稳定。本研究全面评价了AM对小麦产量和品质的影响,探讨了其作用机制,分析了不同AM真菌的效应差异,以期为丛枝菌根应用于小麦生产,以及选择高效的AM真菌提供理论和实践依据。
徐寿霞. 基于meta分析的丛枝菌根对小麦产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 192-204.
Shou-xia XU. Meta-analysis of the effects of arbuscular mycorrhizae on the yield and quality of wheat[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(7): 192-204.

图2 不同丛枝菌根真菌对小麦籽粒产量的影响F.m.:摩西斗管囊霉F. mosseae; R.f.:聚生根孢囊霉R. fasciculatus;R.i.: 根内根孢囊霉R. intraradices; MA: 混合的丛枝菌根真菌Mixture of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi; C.e.:幼套近明球囊霉C. etunicatum;S.d.:沙荒隔球囊霉S. deserticola. 下同The same below.
Fig.2 The effect of different species of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on grains yields of wheat
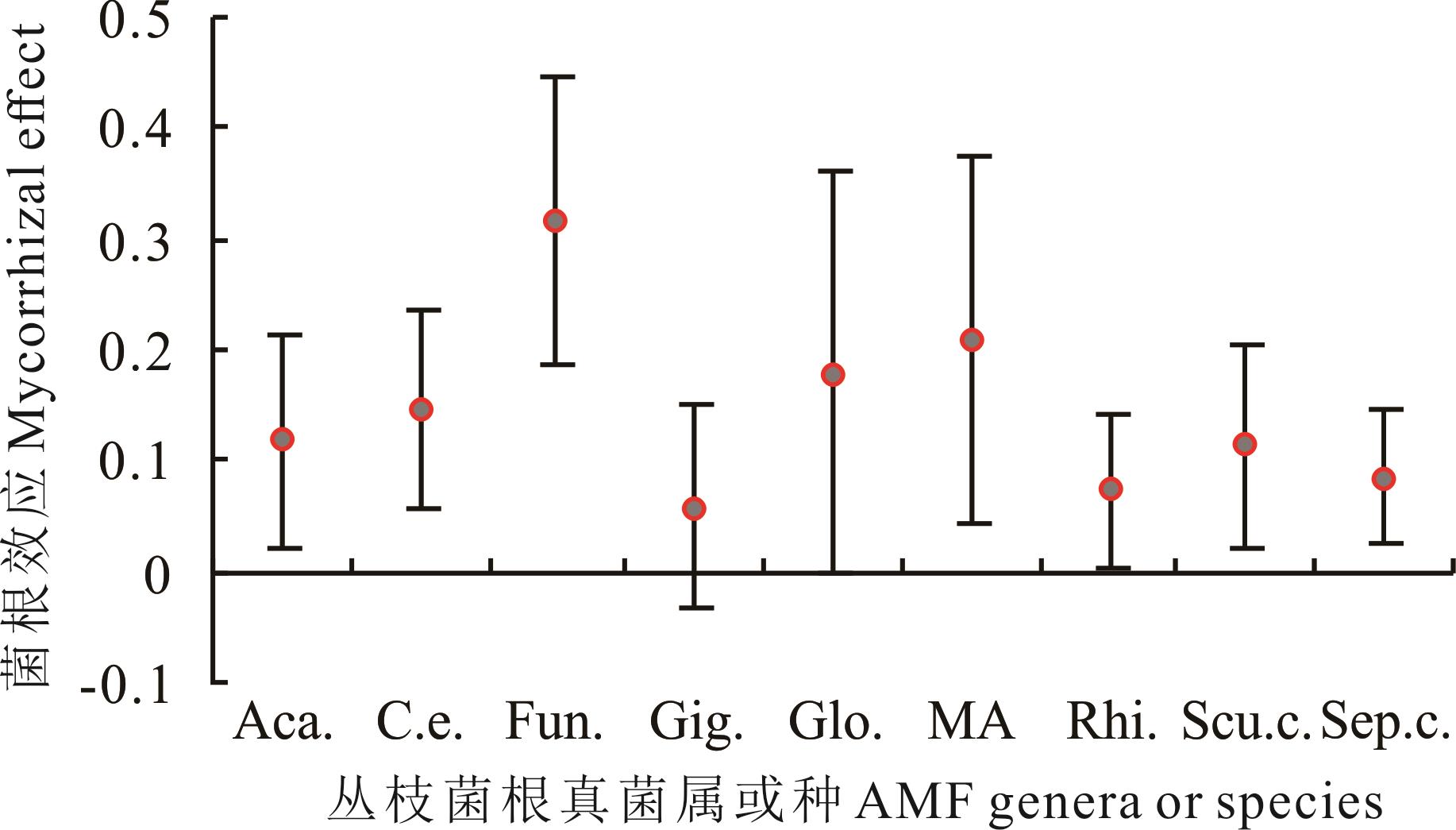
图8 不同丛枝菌根真菌属或种对小麦地上部植株P含量的影响Aca.: 无梗囊霉属Acaulospora; Fun.: 斗管囊霉属Funneliformis; Gig.: 巨孢囊霉属Gigaspora; Glo.: 球囊霉属Glomus; Rhi.: 根孢囊霉属Rhizophagus; Scu.c.: 美丽盾巨孢囊霉S. calospora; Sep.c.: 缩隔球囊霉S. constrictum.
Fig.8 The effect of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal genera or species on P content in shoot of wheat

图9 丛枝菌根对小麦地上部植株微量营养元素和叶片叶绿素、N与P含量的影响
Fig.9 The effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on content of trace elements in shoots and leaf chlorophyll, N and P of wheat
| 1 | Schiefer J, Lair G J, Blum W E H. Potential and limits of land and soil for sustainable intensification of European agriculture. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2016, 230: 283-293. |
| 2 | Bene C, Bakker D, Chavarro M J, et al. Global assessment of the impacts of COVID19 on food security. Global Food Security Agriculture Policy Economics and Environment, 2021, 31: 100575. |
| 3 | Anonymous. War in Ukraine and the challenge to global food security. Nature, 2022, 604(7905): 217-218. |
| 4 | Wu K, Wang S S, Song W Z, et al. Enhanced sustainable green revolution yield via nitrogen-responsive chromatin modulation in rice. Science, 2020, 367(6478): 641. |
| 5 | Foley J A, Ramankutty N, Brauman K A, et al. Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature, 2011, 478(7369): 337-342. |
| 6 | Finger R. Food security: Close crop yield gap. Nature, 2011, 480(7375): 39. |
| 7 | Kuila D, Ghosh S. Aspects, problems and utilization of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) application as biofertilizer in sustainable agriculture. Current Research in Microbial Sciences, 2022, 3: 100107. |
| 8 | Youssef M A, Farag M I H. Coapplication of organic manure and biofertilizer to improve soil fertility and production of quinoa and proceeding Jew’s mallow crops. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2021, 21(3): 2472-2488. |
| 9 | Chen Q L, Hu H W, He Z Y, et al. Potential of indigenous crop microbiomes for sustainable agriculture. Nature Food, 2021, 2(4): 233-240. |
| 10 | Smith S E, Read D J. Mycorrhizal symbiosis (The Third Edition). London, United Kingdom: Academic Press, 2008. |
| 11 | Jia Y Y, Zhang T, Walder F, et al. Can mycorrhizal fungi alleviate plant community instability caused by increased precipitation in arid ecosystems?Plant and Soil, 2022, 478(1/2): 559-577. |
| 12 | Lin G, McCormack M L, Guo D. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal effects on plant competition and community structure. Journal of Ecology, 2015, 103(5): 1224-1232. |
| 13 | Urcelay C, Diaz S. The mycorrhizal dependence of subordinates determines the effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on plant diversity. Ecology Letters, 2003, 6(5): 388-391. |
| 14 | Liang Y, Guo L D, Ma K P. The role of mycorrhizal fungi in ecosystems. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 2002, 26(6): 739-745. |
| 梁宇, 郭良栋, 马克平. 菌根真菌在生态系统中的作用. 植物生态学报, 2002, 26(6): 739-745. | |
| 15 | Wu S, Shi Z, Chen X, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi increase crop yields by improving biomass under rainfed condition: A meta-analysis. PeerJ, 2022, 10: 12861. |
| 16 | Rillig M C, Aguilar-Trigueros C A, Camenzind T, et al. Why farmers should manage the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. New Phytologist, 2019, 222(3): 1171-1175. |
| 17 | Bona E, Cantamessa S, Massa N, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant growth-promoting pseudomonads improve yield, quality and nutritional value of tomato: A field study. Mycorrhiza, 2017, 27(1): 1-11. |
| 18 | An X X, Zhang Y Y, Ma C H, et al. Effects of phosphorus application and inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on alfalfa yield and phosphorus use efficiency. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(6): 71-84. |
| 安晓霞, 张盈盈, 马春晖, 等. 施磷与接种丛枝菌根真菌对苜蓿产量和磷素利用效率的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 71-84. | |
| 19 | Zhang C X, Tian M H, Yang S, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculant diversity on yield, phosphorus and potassium uptake of maize in acidic soil. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(15): 2899-2910. |
| 张晨曦, 田明慧, 杨硕, 等. 酸性土壤中丛枝菌根真菌菌剂多样性对玉米产量及其磷钾吸收的影响. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(15): 2899-2910. | |
| 20 | Zhang S, Lehmann A, Zheng W, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi increase grain yields: A meta analysis. New Phytologist, 2019, 222(1): 543-555. |
| 21 | Yan M J, Bu C L, Huang G Q, et al. Positive effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) on the aboveground part of Morus alba. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020, 56(12): 2647-2654. |
| 晏梅静, 补春兰, 黄盖群, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌对桑树(Morus alba)地上部分的促进作用. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(12): 2647-2654. | |
| 22 | Qu M H, Yu Y C, Wang J, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on biomass distribution and root architecture characters of Zenia insignis seedlings in karst soil. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(3): 766-776. |
| 屈明华, 俞元春, 王佳, 等. 喀斯特土壤条件下丛枝菌根真菌侵染对任豆幼苗生物量分配和根系结构特征的影响. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(3): 766-776. | |
| 23 | Luo M, Shi Z, Yang S, et al. Mycorrhizal types regulated the responses of biomass in different plant organs to N addition. Agronomy, 2022, 12: 2357. |
| 24 | Smith S E, Smith F A, Jakobsen I. Mycorrhizal fungi can dominate phosphate supply to plants irrespective of growth responses. Plant Physiology, 2003, 133(1): 16-20. |
| 25 | Tedersoo L, Bahram M, Zobel M. How mycorrhizal associations drive plant population and community biology? Science, 2020, 367(6480): 867. |
| 26 | Kapulnik Y, Kushnir U. Growth dependency of wild, primitive and modern cultivated wheat lines on vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi. Euphytica, 1991, 56: 27-36. |
| 27 | Lehnert H, Serfling A, Enders M, et al. Genetics of mycorrhizal symbiosis in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum). New Phytologist, 2017, 215(2): 779-791. |
| 28 | De Vita P, Avio L, Sbrana C, et al. Genetic markers associated to arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization in durum wheat.Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 1-12. |
| 29 | Zhang H, Zhong X, Li S Z, et al. Responses of genes involved in mycorrhizal symbiosis to arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization in different wheat cultivars. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022(11): 199-211. |
| 张慧, 钟雄, 李素珍, 等. 菌根共生参与基因对不同品种小麦菌根侵染的响应. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(11): 199-211. | |
| 30 | Mathur S, Tomar R S, Jajoo A. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) protects photosynthetic apparatus of wheat under drought stress. Photosynthesis Research, 2019, 139: 227-238. |
| 31 | Gupta S, Thokchom S D, Kapoor R. Arbuscular mycorrhiza improves photosynthesis and restores alteration in sugar metabolism in Triticum aestivum L. grown in arsenic contaminated soil. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 640379. |
| 32 | Hoeksema J D, Chaudhary V B, Gehring C A, et al. A meta analysis of context dependency in plant response to inoculation with mycorrhizal fungi. Ecology Letters, 2010, 13(3): 394-407. |
| 33 | Van Houwelingen H C, Arends L R, Stijnen T. Advanced methods in meta-analysis: Multivariate approach and meta-regression. Statistics in Medicine, 2002, 21(4): 589-624. |
| 34 | Viechtbauer W. Conducting Meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. Journal of Statistical Software, 2010, 36(3): 1-48. |
| 35 | Wu F Y, Luo W Q, Xing W J, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on accumulation and translocation of selenium in winter wheat. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2022, 102(14): 6481-6490. |
| 36 | Hijri M. Analysis of a large dataset of mycorrhiza inoculation field trials on potato shows highly significant increases in yield. Mycorrhiza, 2016, 26(3): 209-214. |
| 37 | Renaut S, Daoud R, Masse J, et al. Inoculation with Rhizophagus irregularis does not alter arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community structure within the roots of corn, wheat, and soybean crops. Microorganisms, 2020, 8(1): 83. |
| 38 | Zhang X L, Li X L, He T Q, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on grain yield and nitrogen uptake in maize. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2021, 47(8): 1603-1615. |
| 张学林, 李晓立, 何堂庆, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌对玉米籽粒产量和氮素吸收的影响. 作物学报, 2021, 47(8): 1603-1615. | |
| 39 | Zhang S J, Wang L, Ma F, et al. Application of arbuscular mycorrhiza on promoting the growth of rice and reducing the usage of chemical fertilizer. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010, 42(6): 958-962. |
| 张淑娟, 王立, 马放, 等. 丛枝菌根(AM)对水稻生长促进及化肥减量研究. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2010, 42(6): 958-962. | |
| 40 | Chen Z C, Shi Z Y, Tian C Y, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculation on growth and nutrient uptake of two ephemeral plants. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2008, 32(3): 648-653. |
| 陈志超, 石兆勇, 田长彦, 等. 接种AM真菌对短命植物生长发育及矿质养分吸收的影响. 植物生态学报, 2008, 32(3): 648-653. | |
| 41 | Tan Q Y, Wu C B, He Y J, et al. Competition regulating strategy of nutrient allocation by arbuscular mycorrhizae affecting Eupatorium adenophorum and Artemisia annua seedlings on the aboveground and the belowground. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(14): 5804-5813. |
| 谭淇毓, 吴长榜, 何跃军, 等. 丛枝菌根对紫茎泽兰和黄花蒿地上地下养分分配的竞争调控策略. 生态学报, 2021, 41(14): 5804-5813. | |
| 42 | Wei Y, Wang X Y, Li Y D, et al. Stress tolerance signal transfer by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in a whiteclover-perennial ryegrass mixture. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(4): 138-146. |
| 魏勇, 王晓瑜, 李应德, 等. AM真菌在白三叶-黑麦草体系中对抗逆信号的传导作用. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 138-146. | |
| 43 | Shi J, Zhao B, Zheng S, et al. A phosphate starvation responsecentered network regulates mycorrhizal symbiosis. Cell, 2021, 184(22): 5527-5540. |
| 44 | Ding G L, Sun Y Y, Wang X Y, et al. Effects of different cultivation media and nitrogen on the growth and quality of mycorrhizal sweet corn. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2023(2): 138-145. |
| 丁国丽, 孙颖盈, 王欣雨, 等. 不同栽培介质及氮素对菌根化甜玉米生长及品质的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2023(2): 138-145. | |
| 45 | Shi Z Y, Mickan B, Feng G, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improved plant growth and nutrient acquisition of desert ephemeral Plantago minuta under variable soil water conditions. Journal of Arid Land, 2014, 7(3): 414-420. |
| 46 | Wu S, Shi Z, Huang M, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on leaf N∶P∶K stoichiometry in agroecosystem. Agronomy, 2023, 13: 358. |
| 47 | Wei W J, Shi Z Y, Zhang M G, et al. Response to fertilization of leaf functional traits of grassland plants with different mycorrhizal status. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(10): 104-114. |
| 韦文敬, 石兆勇, 张梦歌, 等. 基于数据库的菌根与施肥对草地植物叶片性状影响的分析. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 104-114. | |
| 48 | An X X, Li X, Cao G H, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphorus fertilizer interaction on the aboveground biomass and nutritional quality of alfalfa. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(4): 90-99. |
| 安晓霞, 李想, 曹冠华, 等. 菌磷互作对紫花苜蓿地上生物量及营养品质的影响. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(4): 90-99. | |
| 49 | Xie W, Hao Z P, Zhang X, et al. Research progress and prospect of signal transfer among plants mediated by arbuscular mycorrhizal networks. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2022, 46(5): 493-515. |
| 谢伟, 郝志鹏, 张莘, 等. 丛枝菌根网络介导的植物间信号交流研究进展及展望. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(5): 493-515. |
| [1] | 谭英, 尹豪. 盐胁迫下根施AMF和褪黑素对紫花苜蓿生长、光合特征以及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. |
| [2] | 张俊豪, 柴雪茹, 马嵩科, 张冬霞, 张静, 乔唱唱, 李爽, 黄明, 王贺正. 秸秆还田配施磷肥对豫西旱地小麦碳同化物积累的影响及其生理机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 89-104. |
| [3] | 段海霞, 师茜, 康生萍, 苟海青, 罗崇亮, 熊友才. 丛枝菌根真菌和根瘤菌与植物共生研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 166-182. |
| [4] | 李鸿飞, 周帮伟, 张淼, 施树楠, 李志坚. 不同燕麦品种在呼伦贝尔地区的引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 60-72. |
| [5] | 马路平, 石兆勇, 韦文敬, 杨爽. 基于Meta分析菌根菌对植物叶片生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 99-109. |
| [6] | 张瑞, 安雪姣, 李建烨, 卢曾奎, 牛春娥, 徐振飞, 张金霞, 耿智广, 岳耀敬, 杨博辉. 湖羊及其不同杂交组合生长性能、产肉性能及肌肉品质比较分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 186-197. |
| [7] | 张峰硕, 季秋蓉, 何婷莉, 苏曲杨昂毛, 王志有, 侯生珍, 桂林生. 低蛋白日粮中不同比例氨基酸对藏羊背腰最长肌肉品质、氨基酸和脂肪酸组成以及维生素和矿物质含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 198-208. |
| [8] | 张永亮, 滕泽, 郝凤, 于铁峰, 张玉霞. 苜蓿混播方式及比例对混播草地生产力和稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 185-197. |
| [9] | 张睿, 韩重阳, 蔡家邦, 汪阳, 黄琳凯, 张新全, 聂刚. 6个苇状羊茅(型)品种在成都平原区的生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 138-148. |
| [10] | 张珈敏, 关皓, 李海萍, 贾志锋, 马祥, 刘文辉, 陈有军, 陈仕勇, 蒋永梅, 甘丽, 周青平, 杨丽雪. 混播比例及乳酸菌剂对燕麦-饲用豌豆发酵TMR品质及瘤胃降解特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 169-181. |
| [11] | 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 马春晖, 张前兵. 菌磷耦合下紫花苜蓿的干物质产量及磷素空间分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 104-115. |
| [12] | 石永红, 高鹏, 方志红, 赵祥, 韩伟, 魏江铭, 刘琳, 李锦臻. 15个进口饲用燕麦品种炭疽病的抗病性评价及损失分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 130-142. |
| [13] | 康燕霞, 姜渊博, 齐广平, 银敏华, 马彦麟, 汪精海, 贾琼, 唐仲霞, 汪爱霞. 红豆草与无芒雀麦混播草地生产力提升的水分调控模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 115-128. |
| [14] | 赵杰, 尹雪敬, 王思然, 董志浩, 李君风, 贾玉山, 邵涛. 贮藏时间对甜高粱青贮发酵品质、微生物群落组成和功能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 164-175. |
| [15] | 凌文卿, 张磊, 李珏, 冯启贤, 李妍, 周燚, 刘一佳, 阳伏林, 周晶. 布氏乳杆菌和不同糖类联用对紫花苜蓿青贮营养成分、发酵品质、瘤胃降解率及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 122-134. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
